Evaluation of Spatial Structure and Homogeneity of Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
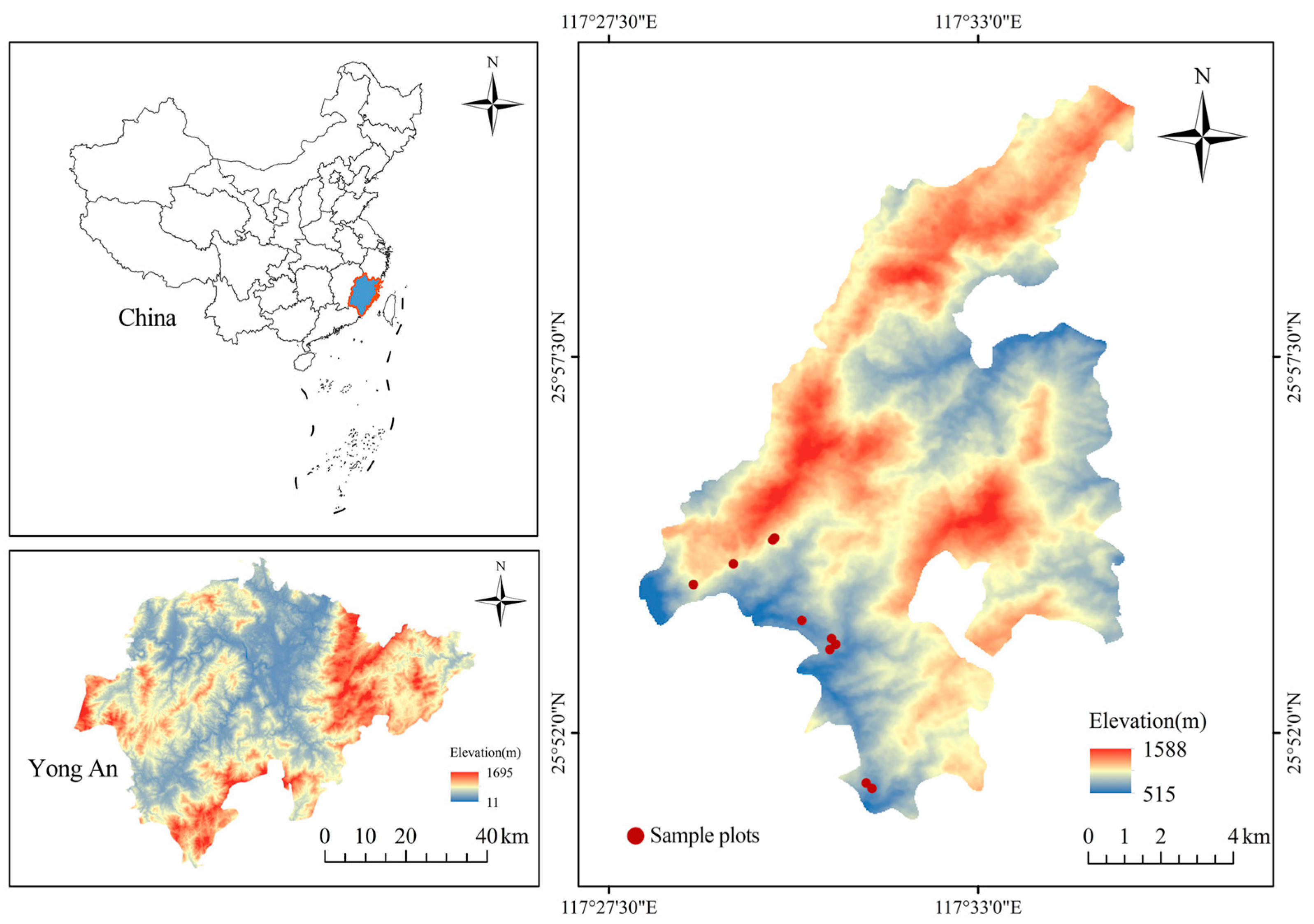
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Survey Method
2.3. Research Methodology
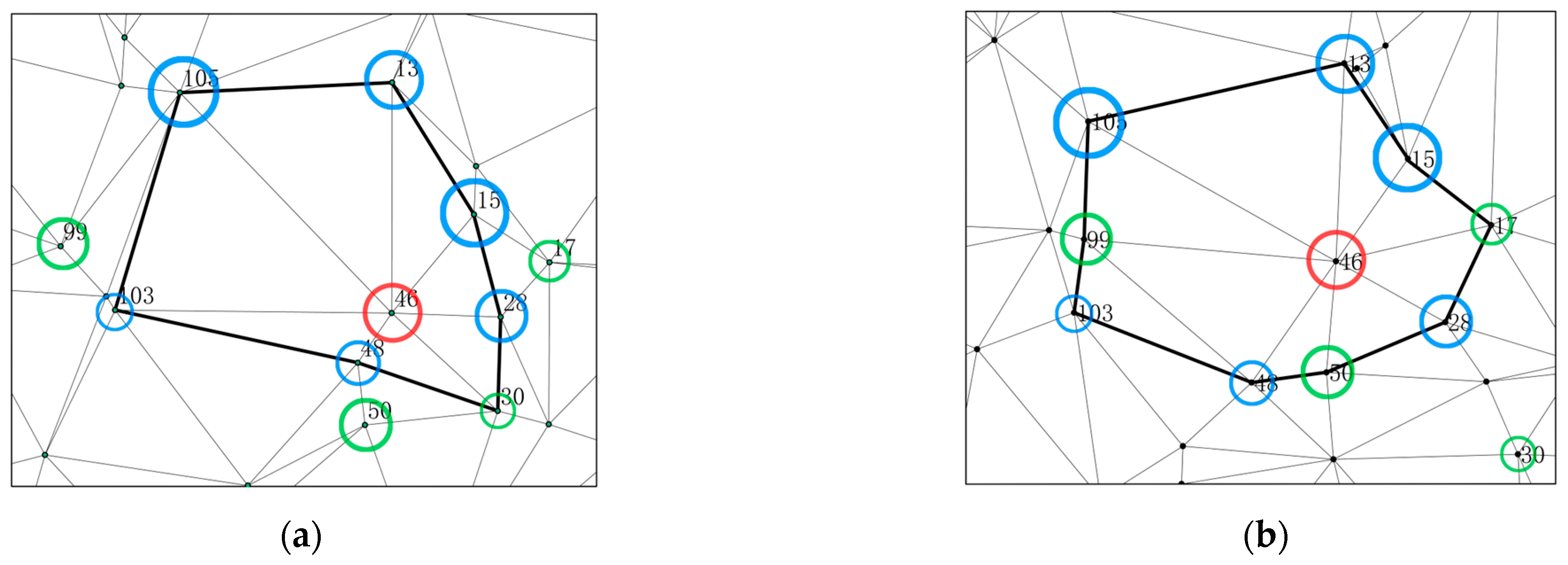
2.3.1. Determination of Stand Structure Units for Weighted Delaunay Triangular-Mesh Forest Stands
2.3.2. Edge Correction
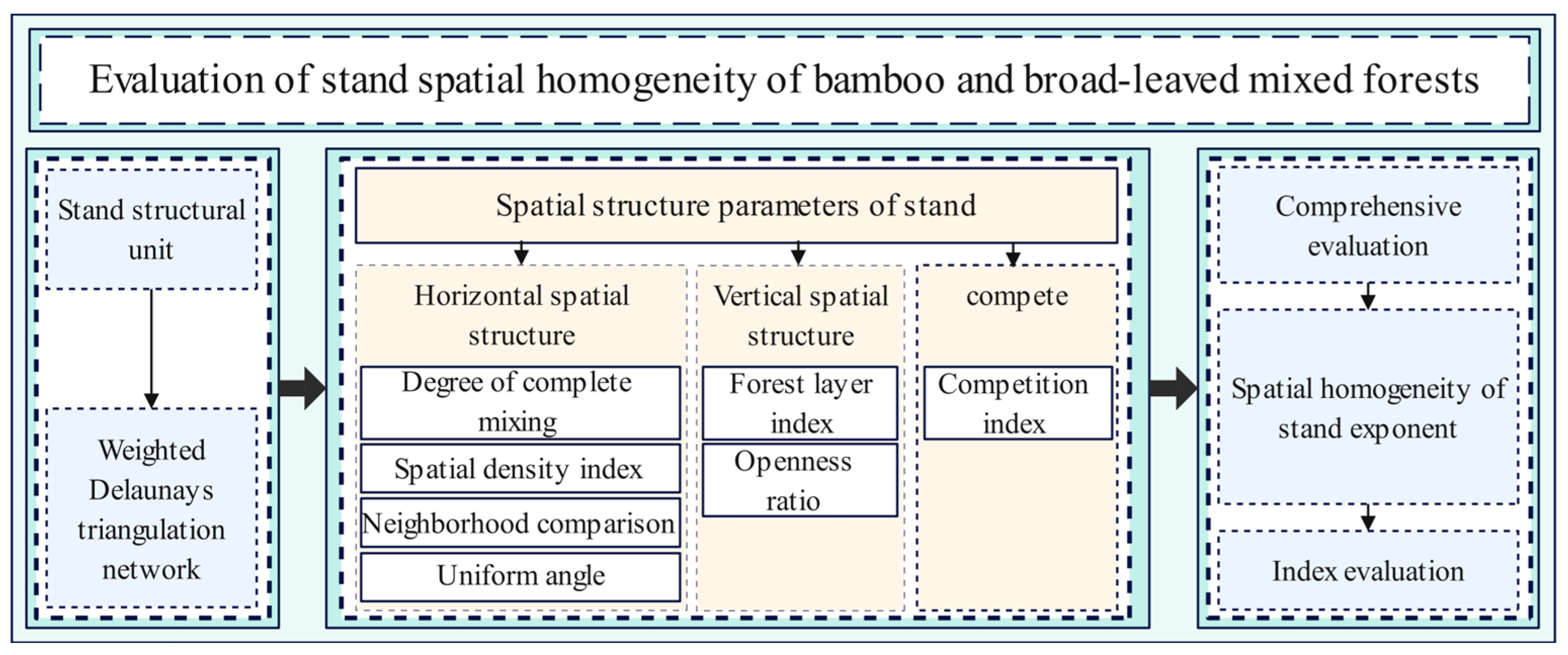
2.3.3. Parameter Selection for the Spatial Homogeneity Index of Stands
- Neighborhood comparison
- Complete mixing degree
- Uniform angle
- Competition index
- Forest layer index
- Openness ratio
- Spatial density index
2.3.4. Calculation and Evaluation of Spatial Homogeneity Index of Forest Stands
Spatial Homogeneity Index of Stands
Evaluation Criteria
2.3.5. Calculation of Moso Bamboo Biomass
3. Results
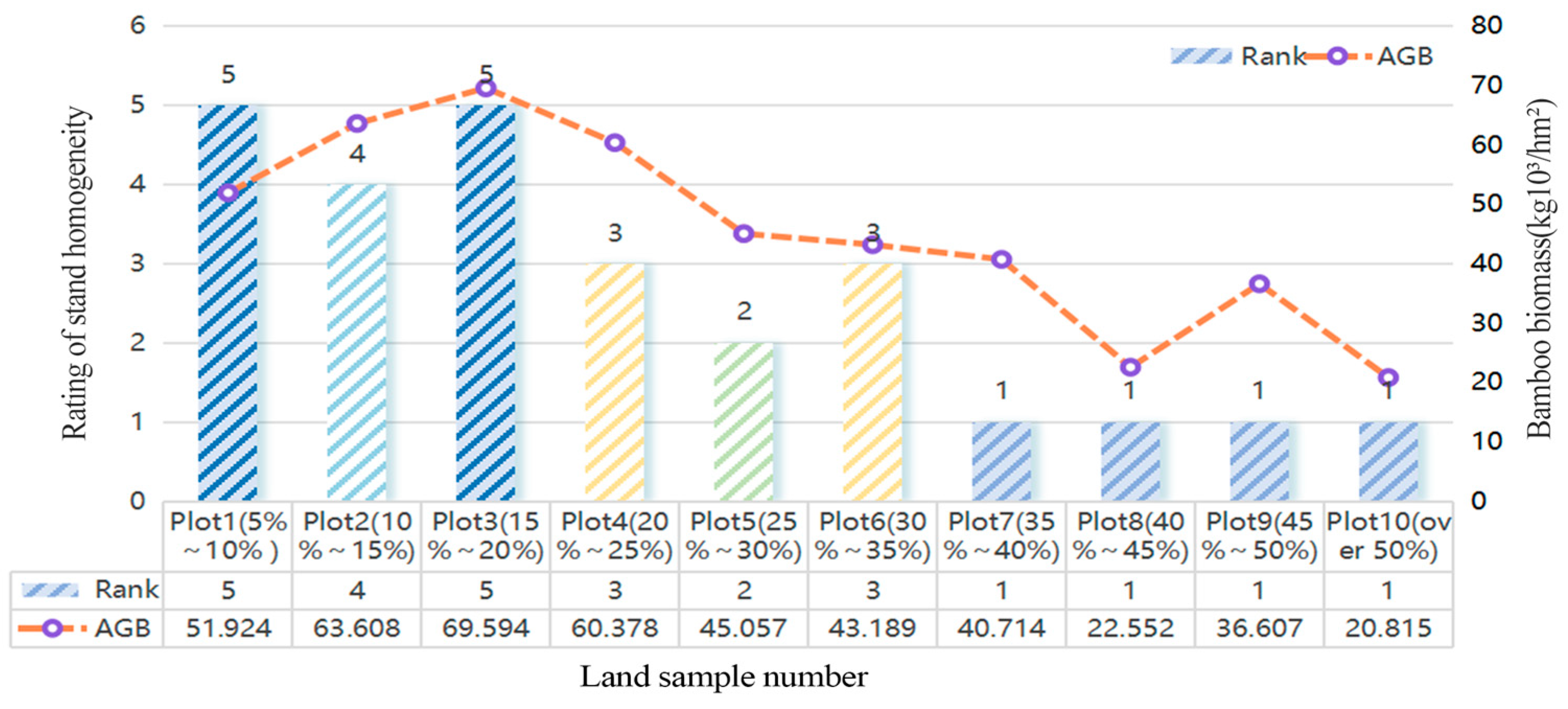
3.1. Evaluation of the Spatial Homogeneity in Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed-Forest Stands
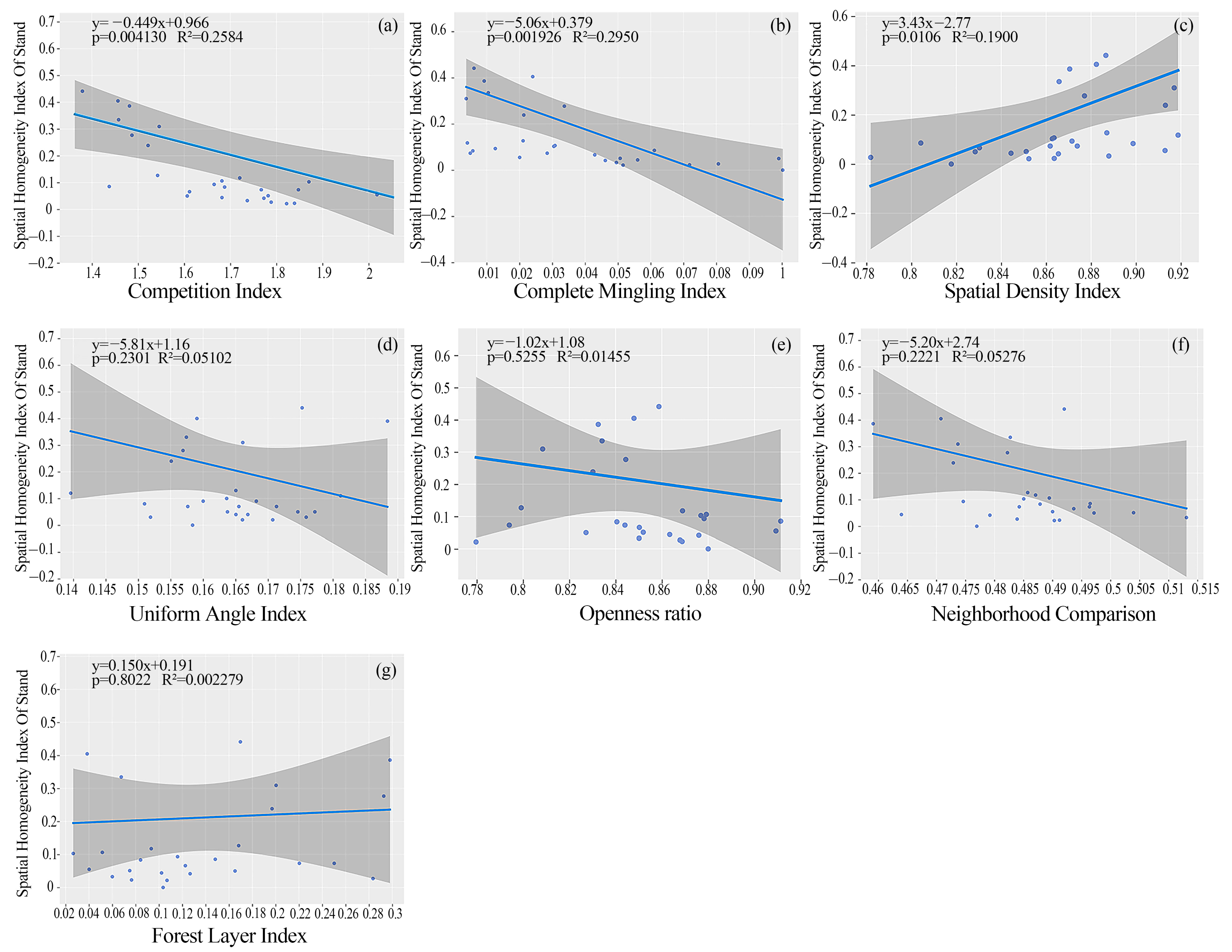
3.2. Coupling of Stand Spatial-Structure Parameters with the Spatial Homogeneity Index of the Stand
3.3. Effects of Spatial Structure of Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forests and Moso Bamboo Biomass
4. Discussion
4.1. Appropriate Mixing Ratios of Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forests from Different Research Perspectives
4.2. Effects of Different Mixing Ratios on the Spatial Structure of Forest Stands
4.3. Effects of Forest Stand Spatial Structure on the Productivity of Moso Bamboo at Various Mixing Ratios
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Hong, W.; Lin, S.; Liu, J.F. Comparison of forest resources in Asian countries based on the Global Forest Resources Assessment Programme. For. Sci. Technol. Newsl. 2023, 5, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.F.; Li, Y.M. Report on bamboo resources in China in 2021. World Bamboo Ratt. Newsl. 2023, 21, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Oshige, C.; Nakabayashi, M.; Okuda, T.; Zaw, M.A.; Hlaing, E.E. Spatial association of bamboos with trees in a commercial tree plantation forest in Myanmar. J. Trop. Ecol. 2023, 39, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.J.; Xia, M.P.; Fan, S.H.; Zhan, M.C.; Guan, F.Y. Detecting the Competition between Moso Bamboos and Broad-Leaved Trees in Mixed Forests Using a Terrestrial Laser Scanner. Forests 2018, 9, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Mei, T.; Zhou, G. Growing in Mixed Stands Increased Leaf Photosynthesis and Physiological Stress Resistance in Moso Bamboo and Mature Chinese Fir Plantations. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 649204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.L.; Chen, S.L.; Yu, M.Z.; Zheng, D.M.; Zhang, L.X. Comparison of the morphological quality of bamboo timber between pure stands of moso bamboo and mixed stands of bamboo and cedar. Zhejiang For. Sci. Technol. 2007, 27, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Dong, J.; Guan, F.Y.; Fan, S.H. Progress and prospect of broad mixed forest research. For. Resour. Manag. 2016, 3, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Ding, S.; OuYang, X.Z. Analysis of the spatial structure of typical evergreen broad-leaved forest stands in Jinggangshan National Nature Reserve. J. Northwest Agric. For. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2016, 44, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.H.; Lai, R.W.; Hu, R.J.; Ye, W. Analysis of spatial structure parameters and correlation study of planted cedar forest stands. Ecol. Sci. 2021, 6, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.M.; Meng, C.F.; Jiang, P.K.; Xu, Q.F. Review of carbon fixation in bamboo forests in China. Bot. Rev. 2011, 77, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, Y.; Misumi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Nanko, K. Characteristics of soil erosion in a moso-bambooforest of western Japan: Comparison with a broadleaved forest and a coniferous forest. Catena 2019, 172, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.Y.; Cao, W.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Ma, G.Y.; Wang, X.N.; Zhao, K.; Li, F. Discussion on rowan-bamboo composite hybrid model and forestry technology. Agric. Technol. 2024, 44, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.Q. Research on the productivity and management efficiency of moso bamboo in bamboo-width mixed forest. Bamboo Res. Repos. 2000, 4, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.A.; Zhong, J.H.; Meng, Y. Effects of bamboo forest structure on the yield of new bamboo in roughly managed moso bamboo forest. Hunan For. Sci. Technol. 2018, 6, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.T. Research on the productivity survey of bamboo-width mixed forest stands with different management types. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 10, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, S.P.; Huang, L.H. Effects of shallow rice straw mulching on asparagus in moso bamboo forest. Anhui Agric. Bull. 2023, 10, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Song, X.Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, B.L.; Lin, X.Y. Structural characteristics of stands at different expansion stages of moso bamboo. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2021, 11, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.Y.; Hu, Y.B. Research on the expression of spatial segregation degree of mixed forest species. For. Sci. Res. 2001, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommerening, A. Evaluating structural indices by reversing forest structural analysis. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 3, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.P.; Zhou, G.M.; Chen, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.S.; He, Y.B. Mixing degree of evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tianmu Mountain based on Voronoi diagram. For. Sci. 2009, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, R.H.; Zheng, X.Y.; Yan, F. Evaluation of spatial structure of oil pine plantation forest using Voronoi diagram. J. Zhejiang Agric. For. Univ. 2018, 5, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.H.; Dang, J.X. A method for analysing spatial distribution patterns of forest trees. J. Ecol. 2007, 11, 4717–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.Y. Angular scale a structural parameter describing the distribution pattern of individual forest trees. For. Sci. 1999, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; He, F.H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, C.D. Methods for studying spatial patterns of forest stands. Ecol. Sci. 2003, 1, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.P.; Lou, M.H.; Chen, Y.G.; Xu, W.B.; Zhao, M.S. Comparative analysis of different hybridisation indices. For. Sci. 2012, 8, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, C.X.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Li, Y.X. Characteristics of the spatial structure of two major natural secondary forest stands in Daxing’anling. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2020, 6, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Fang, Y.; Bai, Z.Q.; Ye, G.; Han, Y.L. Characteristics of the spatial structure of natural coniferous forest stands in the Altai Mountains of Xinjiang. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2014, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, X.; Meng, Y.; Gao, T.; Mao, L.L.; Gao, R. A novel model to evaluate spatial structure in thinned conifer-broadleaved mixed natural forests. J. For. Res. 2023, 6, 1881–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Bettinger, P.; Liu, Z. Optimizing neighbourhood-based stand spatial structure: Four cases of boreal forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 506, 119965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Zhang, H.; Lei, K.; Hu, X.T.; Yang, T.D.; Jiang, X. A New Tree-Level Multi-Objective Forest Harvest Model (MO-PSO): Integrating Neighborhood Indices and PSO Algorithm to Improve the Optimization Effect of Spatial Structure. Forests 2023, 3, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.L. Research on the stability of different forest communities based on spatial structure index. J. Plant Sci. 2016, 5, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.Q.; Zhao, Z.H.; Hui, G.Y.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Z.B.; Chen, R.S.; Liu, X.H. Evaluation method of urgency of natural forest stand management and its application. For. Sci. Res. 2009, 3, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, G.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Zhao, Z.H.; Hu, Y.B.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, S.Z.; Bai, C. The π-value law for optimal stand state of natural mixed forest. For. Sci. 2016, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Hui, G.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Z. A Novel Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Forest State Based on Unit Circle. Forests 2018, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Cheng, J.H.; Li, M.F.; Wang, Y. Characterisation of stand spatial structure of cedar-width mixed forests with different tree species configurations in Jiuhuashan Forest Farm, Hubei Province. J. Ecol. 2019, 6, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Li, J.P.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Y.J.; Zhang, C.C.; Fang, X.N.; Deng, C. Analysis and evaluation of the spatial structure of fir ecological public welfare forest stands. For. Sci. 2015, 7, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Zhu, K.W.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.M. Introducing tree neighbouring relationship factors in forest pattern spatial analysis: Weighted Delaunay triangulation method. J. For. Res. 2021, 5, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Li, J.P.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y.J. Intraspecific and interspecific competition based on weighted Voronoi diagrams in fir ecological public welfare forests. J. Ecol. 2016, 9, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hui, G.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ye, S. Spatial structural characteristics of three hardwood species in Korean pine broad-leaved forest- Validating the bivariate distribution of structural parameters from the point of tree population. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 314, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.Z.; Sun, C.L.; Wang, D.X.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, C.S. Spatial structure and dynamics of predominant populations in a virgin old-growth oak forest in the Qinling Mountains, China. Scand. J. For. Res. 2017, 32, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.R.; Kuang, Z.F.; Wang, C.L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X.P. Evaluation of spatial structure homogeneity of forest ecosystems in Dongting Lake. J. Ecol. 2013, 12, 3732–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.V.; Pham, M.P.; Meng, L.; Bui, H.M.; Pham, H.T.; Nguyen, H.V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kang, Y.X. Spatial Structure of the Dominant Tree Species in an Evergreen Broadleaved Forest Stand in South Vietnam. Biol. Bull. 2022, 49, S69–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommerening, A.; Durrheim, G.; Behrend, A.M. Rare spatio-temporal interactions between conspecific species mingling and size inequality in a diverse Afromontane forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 558, 121787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Li, J.P.; LI, J.J. Study on the spatial structure homogeneity of mangrove stands in different tidal zones. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Li, J.P.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, H.W.; Feng, X.L. Homogeneity index of mangrove spatial structure. For. Sci. 2010, 6, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lu, Y.C.; Knut, S.; Ning, J.K.; Lei, X.D. Research and application of near-naturalness evaluation method for forest management in Beijing forest area. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2009, 5, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, J. Spatial Structure Evaluation of Natural Secondary Forest around Dongting Lake Based on Entropy Weight—Cloud Model. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 103, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zang, H.; Wan, X.J.; Deng, Z.C.; Li, J.J. A study on the forest layer structure of mixed forests with blue species based on the forest layer index. For. Resour. Manag. 2012, 3, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.C.; Wang, W.F.; Men, X.L.; Sun, Y.S.; Li, G.C.; Liu, D.D. Spatial structure optimal of Larix gmelinii plantation. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2021, 4, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Li, J.P. Research on classification of decision-making factors for forest stand management based on rough set. Fujian For. Sci. Technol. 2008, 3, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, J.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Zhao, C.Y.; Cao, X.Y. Quantitative analysis of spatial structure of cedar ecological public welfare forest based on weighted Voronoi diagram. J. Cent. South For. Univ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.T.; Zhang, H.Q.; Yang, G.B.; Qiu, H.Q.; Lei, K.X.; Yang, T.D.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, Y.Q.; Wang, J.S.; Cui, Z.Y. Visual simulation research on growth polymorphism of Chinese fir stand based on different comprehensive grade models of spatial structure parameters. Forests 2023, 14, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.L.; Fan, S.H.; Qi, L.H.; Guan, F.Y.; Du, M.Y.; Zhang, H. Soil respiration and net ecosystem production in relation to intensive management in Moso bamboo forests. Catena Interdiscip. J. Soil Sci. Hydrol.-Geomorphol. Focus. Geoecol. Landsc. Evol. 2016, 137, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, G.M.; Shi, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.F.; Xu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Fan, Y.Q.; Shen, Z.M. Effects of old bamboo level and management measures on the developmental quality of new bamboo in moso bamboo forest. J. Ecol. 2016, 8, 2243–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Q.; Cheng, X.F.; Huang, W.L.; Wang, F.S. Effects of mixed management of upper broad and lower bamboo on productivity of moso bamboo. Bamboo Res. Repos. 2015, 3, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Fu, M.Y.; Xie, J.Z.; Li, R.G.; Xiao, J.H. Ground conservation of moso bamboo and bamboo-width mixed forest communities. J. Bamboo Res. 2003, 1, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cai, T.J.; Ju, C.Y.; Zou, H.F. Evaluating spatial structure of a mixed broad-leaved/Korean pine forest based on neighbourhood relationships in Mudanfeng National Nature Reserve, China. For. Res. Engl. Ed. 2019, 30, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Yang, H.; Ma, S.Y.; Ren, M.M. Spatial structure diversity of semi-natural and plantation stands of larix gmelini in Changbai Mountains, northeastern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2015, 12, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J. Research on Forest Stand Structure Characteristics and Its Optimisation Model of Bamboo-Tree Mixed Forest in Northwest Fujian; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, A.G.; Liu, S.R.; Li, H.; Zeng, J.; Sun, D.J.; Lei, L.Q.; Meng, M.J.; Tao, Y.; Ming, C.D. Effects of near-naturalisation modification on biomass and its allocation of horsetail pine and fir plantation forests. J. Ecol. 2017, 23, 7833–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Hui, G.Y.; Hu, Y.B.; Zhang, G.Q.; Zhang, G.G.; Liu, R.H.; Yang, Y.M.; Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, H.B. Effects of structured forest management on forest quality of broad-leaved red pine forest in Northeast China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2019, 5, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Su, L.L.; Cao, L.Q. Effects of different types of natural mixed forests of moso bamboo on bamboo shoots and bamboo formation. World Bamboo Ratt. Newsl. 2018, 1, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.F.; Shi, P.J.; Hui, C.; Wang, F.S.; Liu, G.H.; Li, B.L. An optimal proportion of mixing broad-leaved forest for enhancing the effective productivity of moso bamboo. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.F.; JiaCheng, X.Z.; Yang, L.H.; Huang, X.B.; Lang, X.D.; Liu, W.D.; Su, J.R. Effects of stand density on the spatial distribution of root biomass in Simao pine plantation forest. Northwest J. Bot. 2017, 11, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.W.; Tang, M.P. Gravitational model-based competitive analysis of trees. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 10, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.L.; Wang, J.F.; Xu, H.; Ou, G.L. Relationship between spatial structure and aboveground biomass allocation of individual trees in Simao pine natural forest. J. Yunnan Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 2, 364–373. [Google Scholar]


| Sample Plot | Mixing Ratio | Gradient | Aspect | Slope | Altitude | Average DBH (cm) | Average Tree Height (m) | Density Bamboo (Plant/hm2) | Bamboo Biomass (kg103/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5%–10% | 34 | sunny | middle | 713 | 10.67 | 12.40 | 3206 | 51.924 |
| 2 | 10%–15% | 35 | sunny | middle | 788 | 11.43 | 12.95 | 3313 | 63.608 |
| 3 | 15%–20% | 21 | sunny | down | 774 | 10.71 | 12.43 | 4125 | 69.594 |
| 4 | 20%–25% | 28 | shady | middle | 810 | 10.84 | 12.52 | 3481 | 60.378 |
| 5 | 25%–30% | 30 | sunny | middle | 795 | 11.01 | 12.68 | 2794 | 45.057 |
| 6 | 30%–35% | 29 | sunny | middle | 712 | 10.38 | 12.17 | 3006 | 43.189 |
| 7 | 35%–40% | 24 | sunny | middle | 871 | 10.91 | 12.60 | 2581 | 40.714 |
| 8 | 40%–45% | 20 | sunny | up | 839 | 10.42 | 12.20 | 1569 | 22.552 |
| 9 | 45%–50% | 35 | shady | up | 631 | 11.38 | 12.96 | 2175 | 36.607 |
| 10 | More than 50% | 33 | sunny | middle | 872 | 10.90 | 12.57 | 1563 | 20.815 |
| Heterogeneity Evaluation Index | The Description of Stand Heterogeneity of State Feature | The Grade Value of Heterogeneity Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | Broad-leaved trees are dominant, the isolation degree of trees is low, the inter-specific competition intensity of stands is high, the stand closure is high, the stand light transmission is poor, the forest layer structure is relatively simple, and most of them are single-layer forests. | 1 |
| 0.2–0.4 | There are more broad-leaved trees, less bamboo, lower isolation degree, moderate inter-specific competition intensity, higher canopy density, poor light transmission of stand, relatively simple structure of forest layer, and less multilayer forest. | 2 |
| 0.4–0.6 | The proportion of bamboo increases, the expansion effect is obvious, the interspecific competition intensity is low, the spatial distribution is uniform, the stand closure is general, and the stand light transmission is reasonable. | 3 |
| 0.6–0.8 | The proportion of bamboo is relatively large, the proportion of broad-leaved trees is relatively small, the degree of forest isolation is high, the intensity of interspecific competition is weak, the stand light transmission condition is better, the structure of the forest layer is more complex, and the single-layer forest is less. | 4 |
| 0.8–1 | Phyllostachys bamboo is dominant, with weak interspecific competition, high isolation degree, low stand closure, good light transmission conditions, complex forest structure and multi-layered forest. | 5 |
| Samsam Plot | Mixing Ratio | OP | W | U | CI | M | S | D | L | Evaluate Exponent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (5%–10%) | 0.714 | 0.158 | 0.476 | 1.521 | 0.009 | 0.070 | 0.874 | 163,428.973 | 1.000 |
| 2 | (10%–15%) | 0.682 | 0.150 | 0.490 | 1.590 | 0.005 | 0.075 | 0.903 | 110,506.915 | 0.645 |
| 3 | (15%–20%) | 0.629 | 0.159 | 0.483 | 1.508 | 0.017 | 0.213 | 0.906 | 146,973.928 | 0.890 |
| 4 | (20%–25%) | 0.634 | 0.171 | 0.483 | 1.591 | 0.005 | 0.197 | 0.893 | 95,105.383 | 0.541 |
| 5 | (25%–30%) | 0.741 | 0.163 | 0.491 | 1.737 | 0.031 | 0.046 | 0.894 | 57,655.477 | 0.290 |
| 6 | (30%–35%) | 0.675 | 0.170 | 0.479 | 1.578 | 0.024 | 0.280 | 0.870 | 85,172.572 | 0.475 |
| 7 | (35%–40%) | 0.751 | 0.166 | 0.485 | 1.827 | 0.066 | 0.077 | 0.864 | 14,452.621 | 0.0000067 |
| 8 | (40%–45%) | 0.715 | 0.160 | 0.478 | 2.097 | 0.049 | 0.109 | 0.831 | 20,907.609 | 0.043 |
| 9 | (45%–50%) | 0.668 | 0.172 | 0.495 | 1.762 | 0.044 | 0.078 | 0.856 | 22,207.689 | 0.052 |
| 10 | (More than 50%) | 0.732 | 0.170 | 0.493 | 1.611 | 0.080 | 0.199 | 0.805 | 20,344.818 | 0.040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Fan, S.; Guan, F.; Yao, H.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of Spatial Structure and Homogeneity of Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest. Forests 2025, 16, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16010100
Zhou Y, Li S, Fan S, Guan F, Yao H, Zhang L. Evaluation of Spatial Structure and Homogeneity of Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest. Forests. 2025; 16(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yaqi, Shangsi Li, Shaohui Fan, Fengying Guan, Haifei Yao, and Luhai Zhang. 2025. "Evaluation of Spatial Structure and Homogeneity of Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest" Forests 16, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16010100
APA StyleZhou, Y., Li, S., Fan, S., Guan, F., Yao, H., & Zhang, L. (2025). Evaluation of Spatial Structure and Homogeneity of Bamboo and Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest. Forests, 16(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16010100





