Temporal Variations in Methane Emissions from a Restored Mangrove Ecosystem in Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
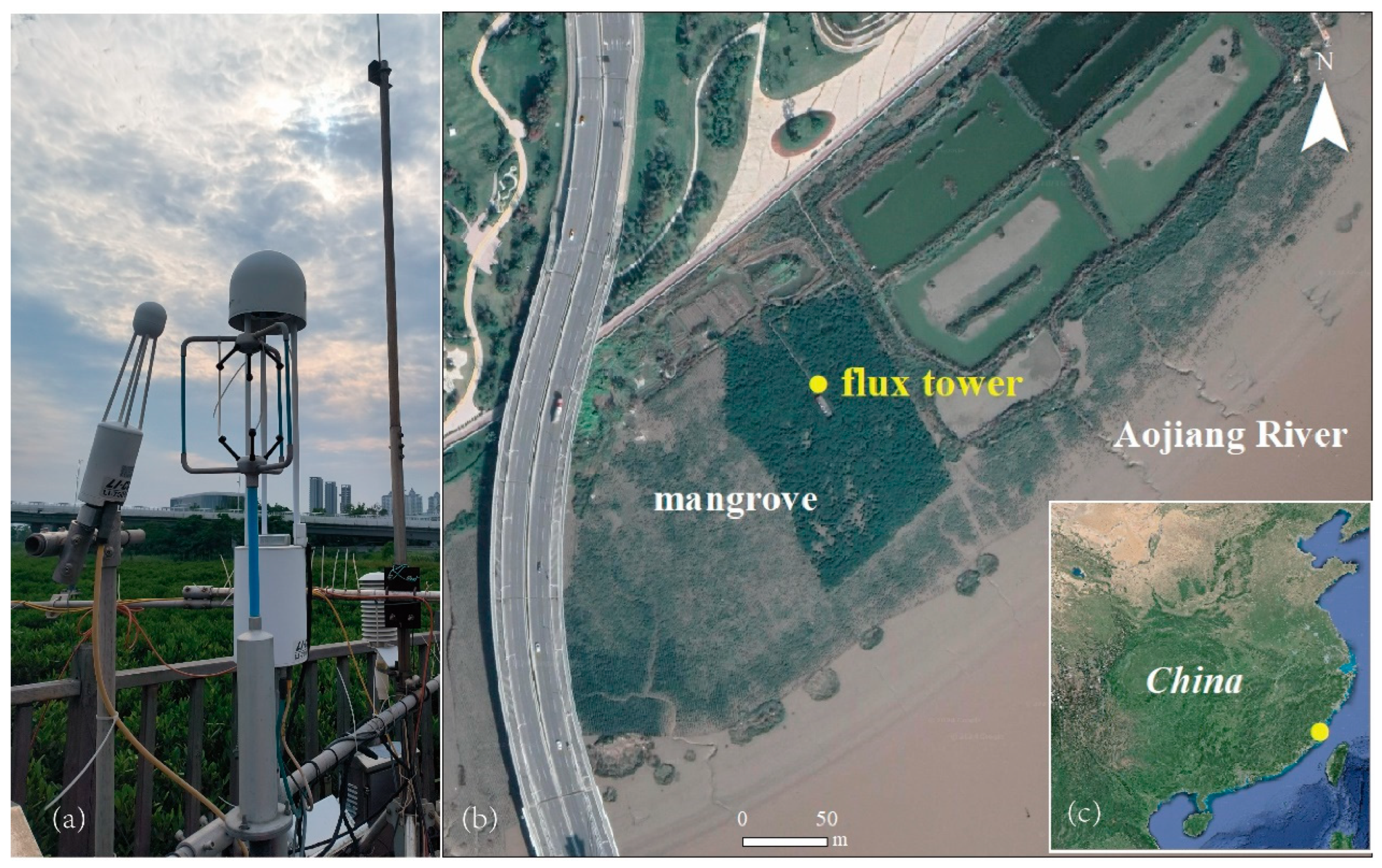
2.1. Study Site
2.2. EC Flux and Meteorological Measurements
2.3. Processing of Flux Data and Gap-Filling
2.4. Random Forest Models
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
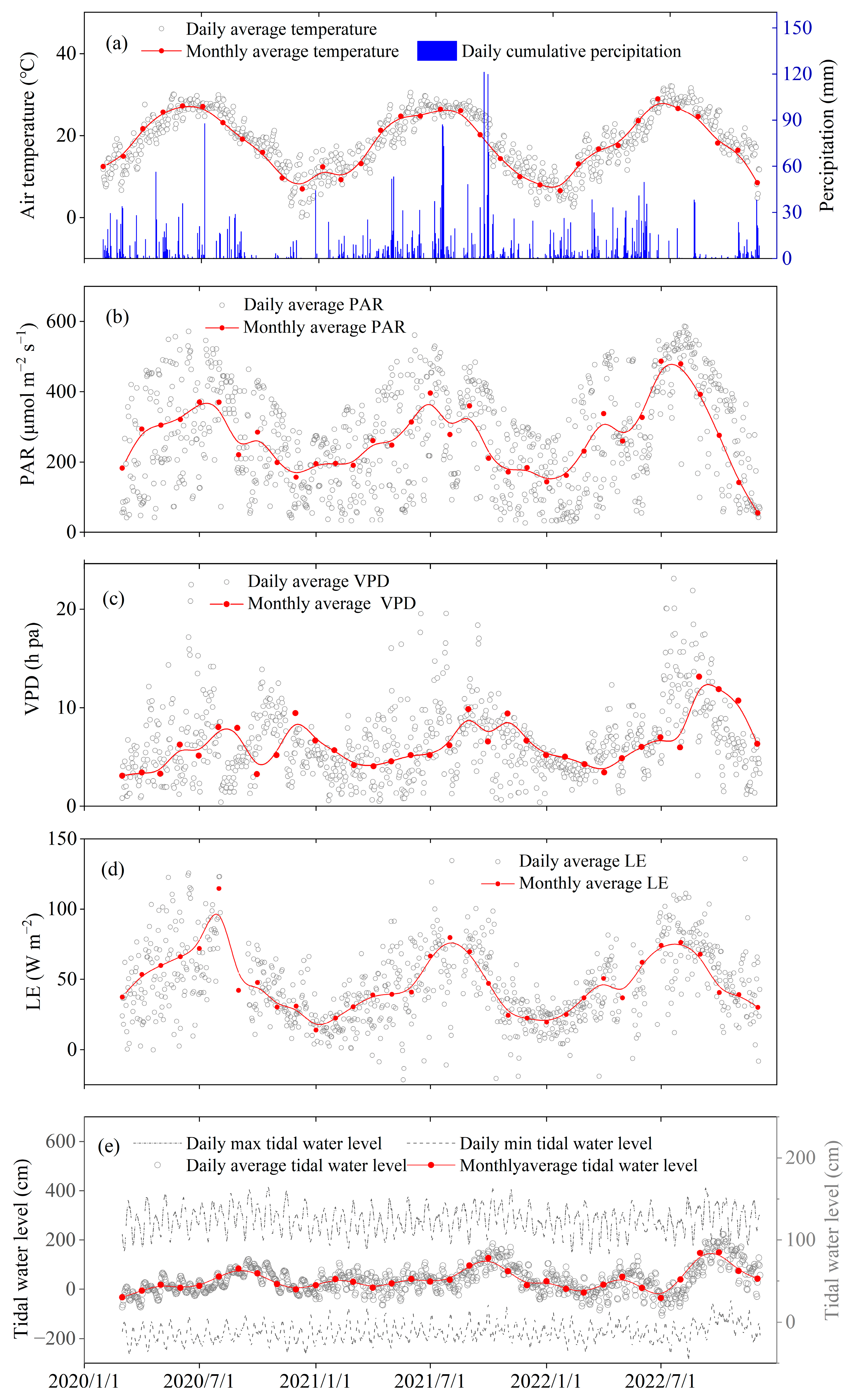
3.1. Environmental Conditions in the Restored Mangrove Ecosystem during 2020–2022
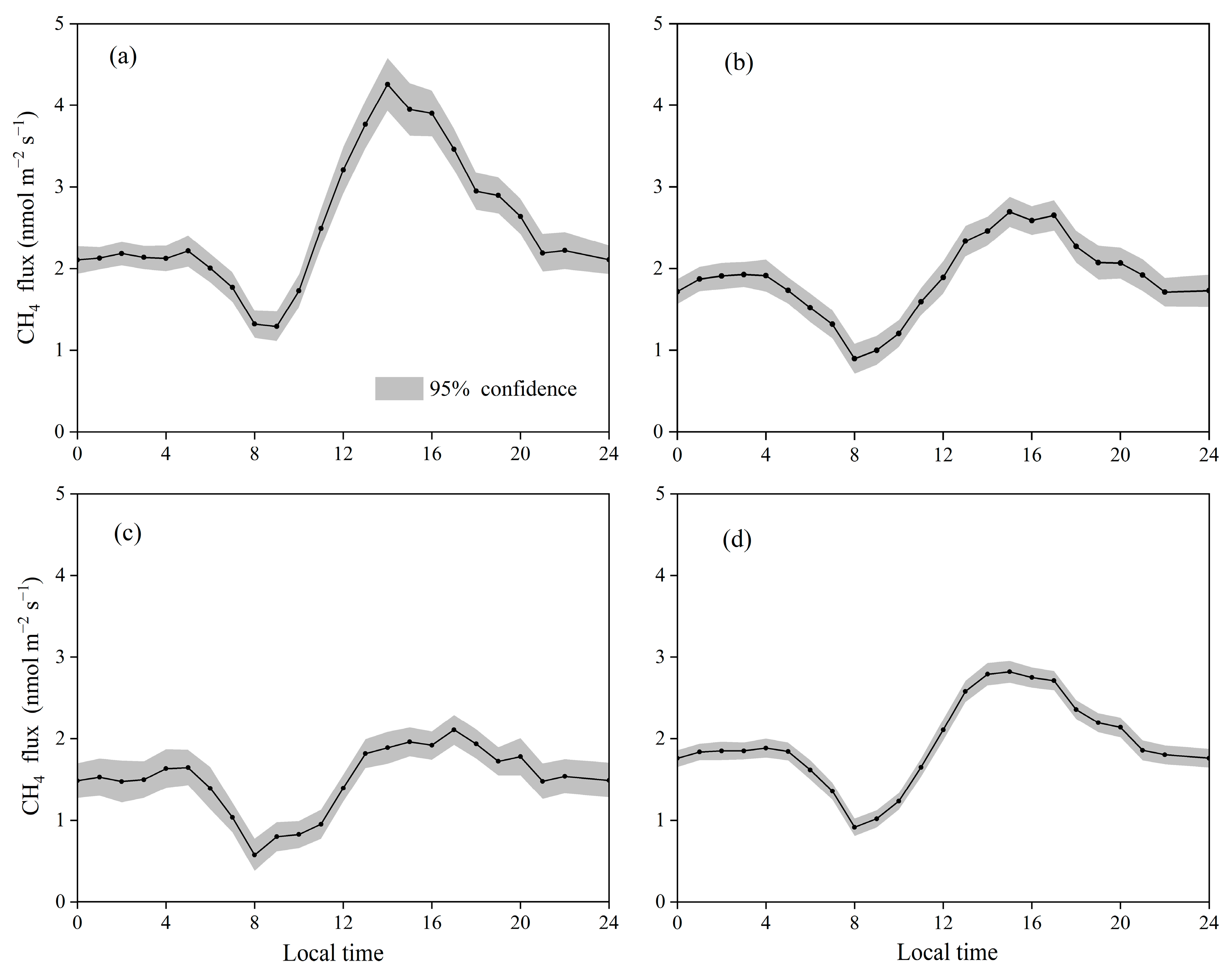
3.2. Temporal Variations in CH4 Fluxes in the Restored Mangrove
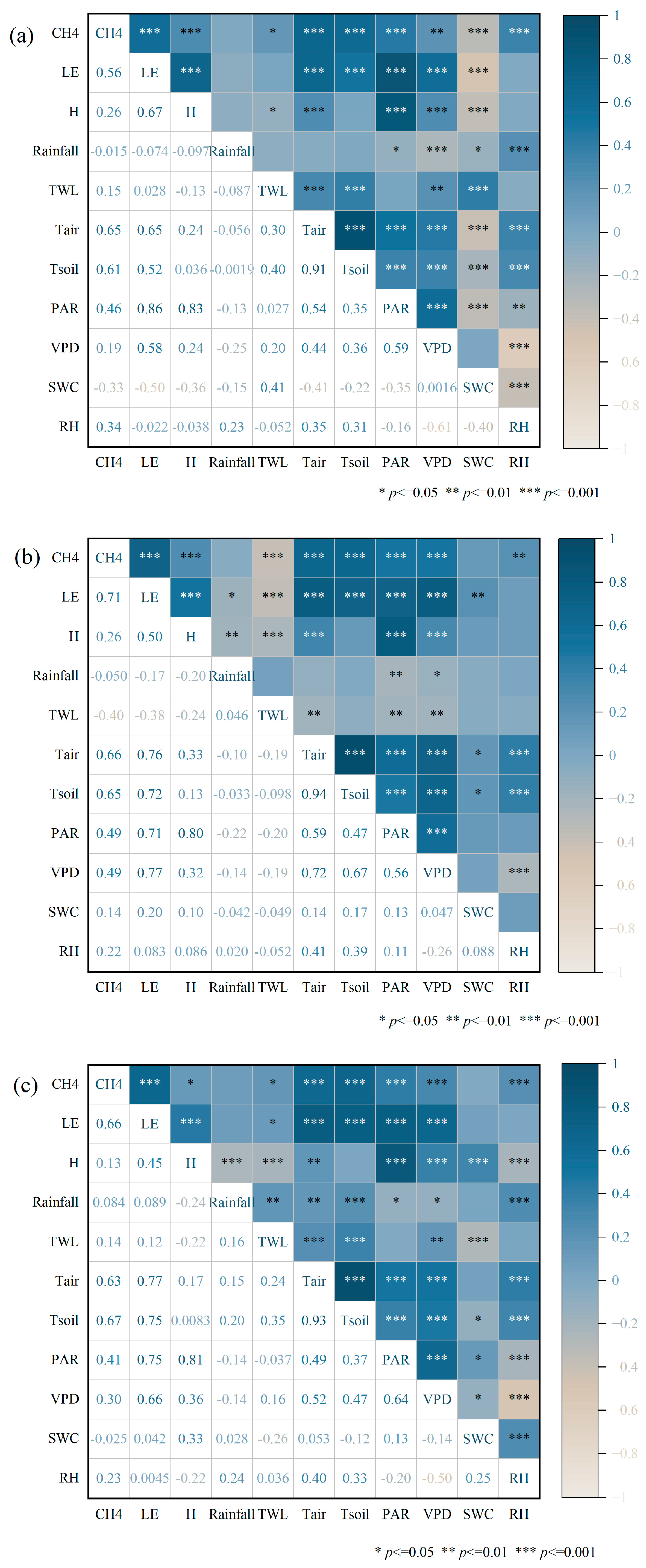
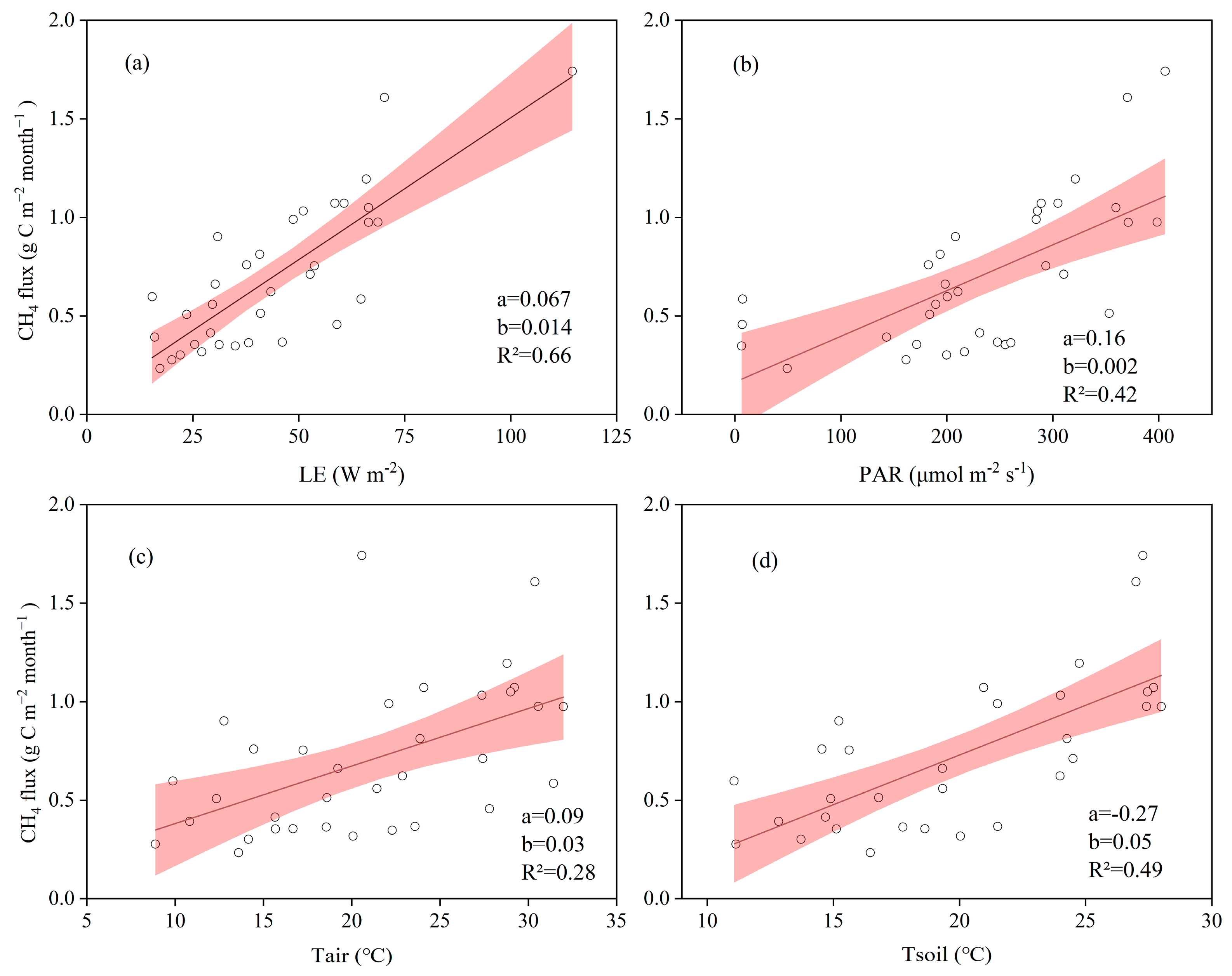
3.3. Biophysical Drivers of CH4 Fluxes in the Restored Mangrove
4. Discussion
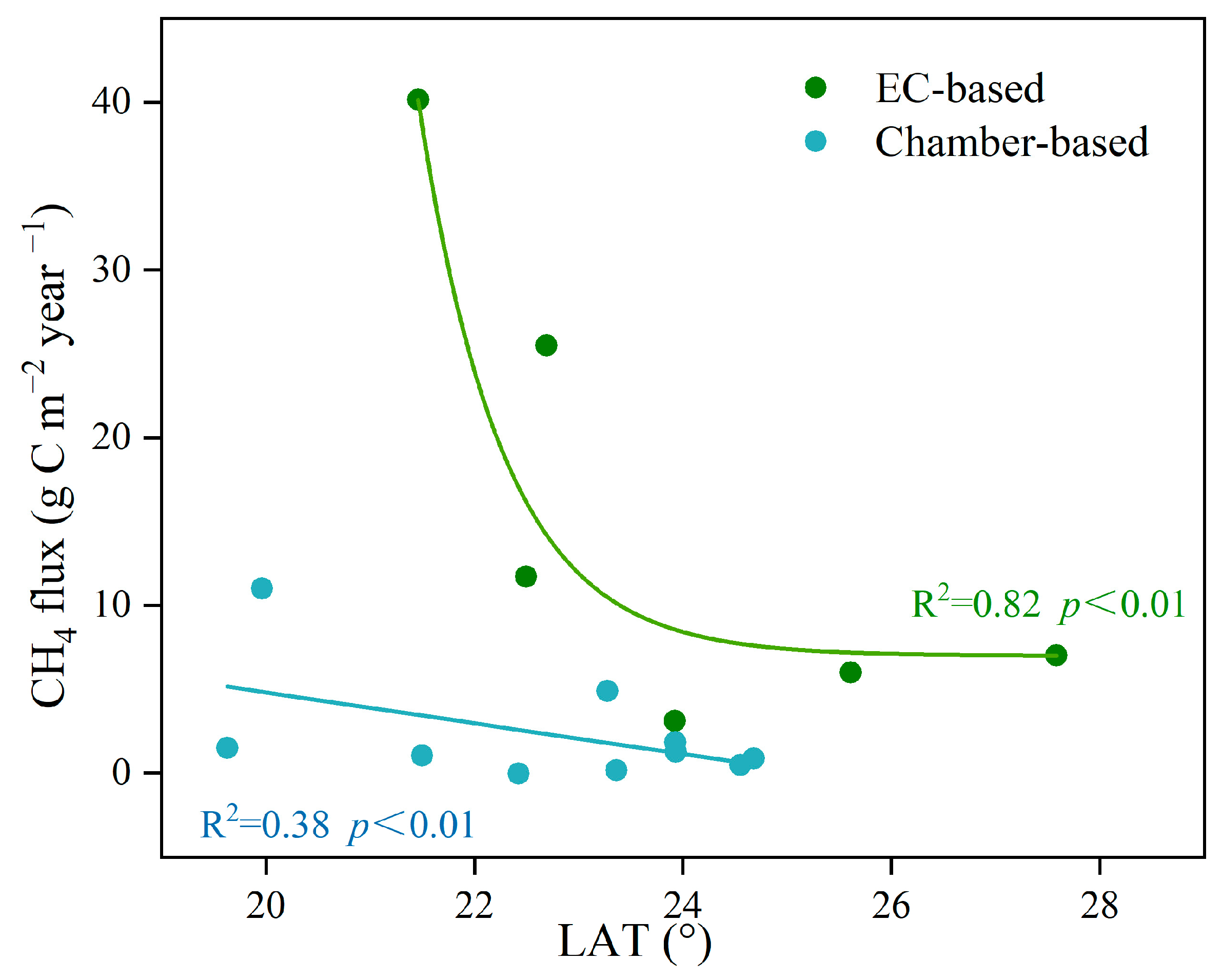
4.1. CH4 Emissions from Natural and Restored Mangrove Ecosystems
| Site | Location | Method | Annual CH4 Flux | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g C m−2 Year−1) | ||||
| Sundarbans, IND | 21.46° S, 81.43° E | Eddy Covariance | 40.15 | [32] |
| Guangdong, China | 22.60° N, 113.64° E | Eddy Covariance | 25.50 | [8] |
| Hong Kang, China | 22.49° N, 114.02° E | Eddy Covariance | 11.70 | [15] |
| Zhejiang, China | 27.58° N, 120.57° E | Eddy Covariance | 7.44 | This study |
| Pichavaram, IND | 25.61° S, 79.79° E | Eddy Covariance | 6.00 | [31] |
| Fujian, China | 23.92° N, 117.41° E | Eddy Covariance | 3.10 | [33] |
| Hainan, China | 19.96° N, 110.58° E | Chamber | 11.00 | [61] |
| Guangdong, China | 23.27° N, 116.52° E | Chamber | 4.90 | [62] |
| Hainan, China | 19.96°S, 110.54° E | Chamber | 3.63 | [63] |
| Fujian, China | 23.92° N, 117.41° E | Chamber | 1.83 | [64] |
| Hainan, China | 19.63° N, 110.77° E | Chamber | 1.49 | [55] |
| Fujian, China | 23.92° N, 117.41° E | Chamber | 1.26 | [54] |
| Guangxi, China | 21.50° N, 109.20° E | Chamber | 1.05 | [65] |
| Taiwan, China | 24.68° N, 120.84° E | Chamber | 0.88 | [56] |
| Fujian, China | 24.55° N, 118.03° E | Chamber | 0.47 | [66] |
| Taiwan, China | 23.36° N, 120.13° E | Chamber | 0.15 | [56] |
| Guangdong, China | 22.45° N, 113.63° E | Chamber | -0.03 | [67] |
4.2. Complex Effects of Environmental Factors on CH4 Fluxes in the Restored Mangrove Ecosystem
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duarte, C.M.; Losada, I.J.; Hendriks, I.E.; Mazarrasa, I.; Marbà, N. The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Nielsen, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Atwood, T.B.; Seymour, J.R.; Petrou, K.; Connolly, R.M.; Thomson, A.C.G.; Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Ralph, P.J. Can we manage coastal ecosystems to sequester more blue carbon? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellemann, C.; Corcoran, E.; Duarte, C.M. Blue Carbon: The Role of Healthy Oceans in Binding Carbon—A Rapid Response Assessment. U. N. Environ. Programme GRID 2009, 32, 589–598. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Sun, C.; Qin, Z. Drought-Induced Salinity Enhancement Weakens Mangrove Greenhouse Gas Cycling. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2021JG006416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Lee, S. Improved estimates on global carbon stock and carbon pools in tidal wetlands. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friess, D.A.; Krauss, K.W.; Taillardat, P.; Adame, M.F.; Yando, E.S.; Cameron, C.; Sasmito, S.D.; Sillanpää, M. Mangrove Blue Carbon in the Face of Deforestation, Climate Change, and Restoration. Annu. Plant Rev. 2020, 3, 427–456. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, R.; Buchmann, N.; Chi, J.; Luo, Y.; Mo, L.; Shekhar, A.; Feigenwinter, I.; Hörtnagl, L.; Lu, W.; Cui, X. Temporal variations of carbon and water fluxes in a subtropical mangrove forest: Insights from a decade-long eddy covariance measurement. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 343, 109764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zou, X.; Shen, C.; et al. Net CO2 and CH4 emissions from restored mangrove wetland: New insights based on a case study in estuary of the Pearl River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasmito, S.D.; Taillardat, P.; Clendenning, J.N.; Cameron, C.; Friess, D.A.; Murdiyarso, D.; Hutley, L.B. Effect of land-use and land-cover change on mangrove blue carbon: A systematic review. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 4291–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Li, T.; Qin, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhao, X. Asynchronous methane and carbon dioxide fluxes drive temporal variability of mangrove blue carbon sequestration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Costa, M.D.; Atwood, T.B.; Friess, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Kennedy, H.; Lovelock, C.E.; Serrano, O.; Duarte, C.M. Blue carbon as a natural climate solution. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haj, A.N.; Fulweiler, R.W. A synthesis of methane emissions from shallow vegetated coastal ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2988–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunois, M.; Stavert, A.R.; Poulter, B.; Bousquet, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Raymond, P.A.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Houweling, S.; Patra, P.K. The global methane budget 2000–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1561–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemes, K.S.; Chamberlain, S.D.; Eichelmann, E.; Knox, S.H.; Baldocchi, D.D. A biogeochemical compromise: The high methane cost of sequestering carbon in restored wetlands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6081–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Valach, A.; Shortt, R.; Kasak, K.; Rey-Sanchez, C.; Hemes, K.S.; Baldocchi, D.; Lai, D.Y.F. Methane emissions reduce the radiative cooling effect of a subtropical estuarine mangrove wetland by half. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 4998–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, G.O.; Perez, B.C.; McWhorter, D.E.; Krauss, K.W.; Johnson, D.J.; Raynie, R.C.; Killebrew, C.J. Ecosystem Level Methane Fluxes from Tidal Freshwater and Brackish Marshes of the Mississippi River Delta: Implications for Coastal Wetland Carbon Projects. Wetlands 2016, 36, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, S.H.; Jackson, R.B.; Poulter, B.; McNicol, G.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Zhang, Z.; Hugelius, G.; Bousquet, P.; Canadell, J.G.; Saunois, M. FLUXNET-CH4 synthesis activity: Objectives, observations, and future directions. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 2607–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, S.C.; Megonigal, J.P. Moving beyond global warming potentials to quantify the climatic role of ecosystems. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: Summary for Policymakers; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rosentreter, J.A.; Al-Haj, A.N.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Williamson, P. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions complicate coastal blue carbon assessments. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2021, 35, e2020GB006858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Takeuchi, W. Estimating mangrove forest gross primary production by quantifying environmental stressors in the coastal area. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liao, G.; D’Souza, M.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, T. Temporal and spatial variations of greenhouse gas fluxes from a tidal mangrove wetland in Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, S.R.; Thumaty, K.C.; Praveen, M.S.S.; Jha, C.S.; Dadhwal, V.K. Multi-year eddy covariance measurements of net ecosystem exchange in tropical dry deciduous forest of India. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 301–302, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, K.; Juang, J.-Y.; Deventer, M.J.; Klemm, O. Methane emissions from a subtropical grass marshland, northern Taiwan. Wetlands 2017, 37, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobrega, G.N.; Ferreira, T.O.; Siqueira Neto, M.; Queiroz, H.M.; Artur, A.G.; Mendonca Ede, S.; Silva Ede, O.; Otero, X.L. Edaphic factors controlling summer (rainy season) greenhouse gas emissions (CO2 and CH4) from semiarid mangrove soils (NE-Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Bai, J.; Gou, R.; Cui, X.; Feng, J.; Dai, Z.; Diao, X.; Zhu, X.; Lin, G. Relationships between above- and below-ground carbon stocks in mangrove forests facilitate better estimation of total mangrove blue carbon. Carbon Balance Manag. 2021, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Johnson, M.S.; Knox, S.H.; Black, T.A.; Dalmagro, H.J.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.; Baldocchi, D. Gap-filling approaches for eddy covariance methane fluxes: A comparison of three machine learning algorithms and a traditional method with principal component analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 1499–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, J.G.; Engel, V.; Fuentes, J.D.; Zieman, J.C.; O’Halloran, T.L.; Smith, T.J.; Anderson, G.H. Controls on mangrove forest-atmosphere carbon dioxide exchanges in western Everglades National Park. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2010, 115, G02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, A.; Marchand, C.; Renchon, A.; Deborde, J.; Quiniou, T.; Allenbach, M. Net ecosystem CO2 exchange in the “Coeur de Voh” mangrove, New Caledonia: Effects of water stress on mangrove productivity in a semi-arid climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, S.; Thumaty, K.; Jha, C.; Dadhwal, V. Seasonal Variations of Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor and Energy Fluxes in Tropical Indian Mangroves. Forests 2016, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamoorthy, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Nagarajan, R.; Ramasubramanian, R.; Selvam, V.; Burman, P.K.D.; Sarathy, P.P.; Zeeshan, M.; Song, Q.; Zhang, Y. Seasonal variation of methane fluxes in a mangrove ecosystem in south India: An eddy covariance-based approach. Estuaries Coasts 2022, 45, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, C.S.; Rodda, S.R.; Thumaty, K.C.; Raha, A.; Dadhwal, V. Eddy covariance based methane flux in Sundarbans mangroves, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 123, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Qin, Z.; Song, L. How Land-Sea Interaction of Tidal and Sea Breeze Activity Affect Mangrove Net Ecosystem Exchange? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Cai, H.; Chen, W.; Ni, X.; Wu, E.; Zeng, G. Soil organic carbon stocks increased across the tide-induced salinity transect in restored mangrove region. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellví, F.; Perez, P.J.; Villar, J.M.; Rosell, J.I. Analysis of methods for estimating vapor pressure deficits and relative humidity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1996, 82, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Oncley, S.P.; Stage, S.A. Sonic anemometer tilt correction algorithms. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2001, 99, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.M.; Wofsy, S.C.; Bakwin, P.S.; Jacob, D.J.; Fitzjarrald, D.R. Atmosphere-Biosphere Exchange of CO2 and O3 in the Central-Amazon-Forest. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1990, 95, 16851–16864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, J.B.; Massheder, J.M.; de Bruin, H.; Elbers, J.; Friborg, T.; Heusinkveld, B.; Kabat, P.; Scott, S.; Soegaard, H.; Verhoef, A. A system to measure surface fluxes of momentum, sensible heat, water vapour and carbon dioxide. J. Hydrol. 1997, 188, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of Flux Measurements for Density Effects Due to Heat and Water-Vapor Transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauder, M.; Foken, T. Documentation and Instruction Manual of the Eddy Covariance Software Package TK2; Universität Bayreuth: Bayreuth, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Papale, D.; Reichstein, M.; Aubinet, M.; Canfora, E.; Bernhofer, C.; Kutsch, W.; Longdoz, B.; Rambal, S.; Valentini, R.; Vesala, T.; et al. Towards a standardized processing of Net Ecosystem Exchange measured with eddy covariance technique: Algorithms and uncertainty estimation. Biogeosciences 2006, 3, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Lai, D.Y.F. Subtropical mangrove wetland is a stronger carbon dioxide sink in the dry than wet seasons. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 278, 107644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Biophysical Models and Applications in Ecosystem Analysis; Michigan State University Press: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, K.J.; Kimes, R.V. Empirical characterization of random forest variable importance measures. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 52, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Helman, D.; Osem, Y.; Yakir, D.; Lensky, I.M. Relationships between climate, topography, water use and productivity in two key Mediterranean forest types with different water-use strategies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ping, X.Y.; Jia, Q.Y.; Li, R.P. Ten-year variability and environmental controls of ecosystem water use efficiency in a rainfed maize cropland in Northeast China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 226, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S. piecewiseSEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling in r for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Nat, F.-F.W.; Middelburg, J.J.; Van Meteren, D.; Wielemakers, A. Diel methane emission patterns from Scirpus lacustris and Phragmites australis. Biogeochemistry 1998, 41, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgham, S.D.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Keller, J.K.; Zhuang, Q. Methane emissions from wetlands: Biogeochemical, microbial, and modeling perspectives from local to global scales. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1325–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, P.H.; Welte, C.U.; Koehorst, J.J.; Plugge, C.M.; Jetten, M.S.; Stams, A.J. Reverse methanogenesis and respiration in methanotrophic archaea. Archaea 2017, 2017, 1654237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmagro, H.J.; Zanella de Arruda, P.H.; Vourlitis, G.L.; Lathuilliere, M.J.; de S. Nogueira, J.; Couto, E.G.; Johnson, M.S. Radiative forcing of methane fluxes offsets net carbon dioxide uptake for a tropical flooded forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1967–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukoski, J.J.; Dronova, I.; Potts, M.D. Net loss statistics underestimate carbon emissions from mangrove land use and land cover change. Ecography 2022, 2022, e05982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.-H.; Zhang, S.; Ding, Q.-S.; Wei, M.-Y.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Wen, C.; Gao, G.-F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.-J. Source or sink? A study on the methane flux from mangroves stems in Zhangjiang estuary, southeast coast of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Guo, J.; Song, W.; Feng, J.; Lin, G. Methane emission from mangrove wetland soils is marginal but can be stimulated significantly by anthropogenic activities. Forests 2018, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Kao, Y.-C.; Chou, M.-C.; Wu, H.-H.; Ho, C.-W.; Lin, H.-J. Methane emissions from subtropical and tropical mangrove ecosystems in Taiwan. Forests 2020, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, K.W.; Holm, G.O.; Perez, B.C.; McWhorter, D.E.; Cormier, N.; Moss, R.F.; Johnson, D.J.; Neubauer, S.C.; Raynie, R.C. Component greenhouse gas fluxes and radiative balance from two deltaic marshes in Louisiana: Pairing chamber techniques and eddy covariance. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1503–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, A.M.R.; Lohila, A.; Tuovinen, J.-P.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Desai, A.R.; Roulet, N.T.; Vesala, T.; Dolman, A.J.; Oechel, W.C.; Marcolla, B. The uncertain climate footprint of wetlands under human pressure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4594–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.C.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Ye, Y. Summer fluxes of atmospheric greenhouse gases N2O, CH4 and CO2 from mangrove soil in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, S.D.; Hemes, K.S.; Eichelmann, E.; Szutu, D.J.; Verfaillie, J.G.; Baldocchi, D.D. Effect of drought-induced salinization on wetland methane emissions, gross ecosystem productivity, and their interactions. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guan, W.; Xue, D.; Liu, L.; Peng, C.; Liao, B.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, G. Comparison of methane emissions among invasive and native mangrove species in Dongzhaigang, Hainan Island. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 133945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Yang, T.; Xiao, F.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, K.; Shu, L.; He, Q. Sonneratia apetala introduction alters methane cycling microbial communities and increases methane emissions in mangrove ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 144, 107775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, N.; Wu, F.; Liao, B.; Xin, K. Methane and carbon dioxide emissions from cultivated and native mangrove species in Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 168, 106285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, M.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Tan, F.; Huang, J. Massive methane emission from tree stems and pneumatophores in a subtropical mangrove wetland. Plant Soil 2022, 473, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, L.; Ye, W.; Wen, J.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Fluxes of dissolved methane and nitrous oxide in the tidal cycle in a mangrove in South China. Environ. Chem. 2021, 18, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, S.; Gao, M.; Chen, G.; Zhu, H.; Ye, Y. Potential effects of sea level rise on the soil-atmosphere greenhouse gas emissions in Kandelia obovata mangrove forests. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liao, B.; Jiang, Z.; Xin, K.; Xiong, Y.; Guan, W. Emission of greenhouse gases (CH4 and CO2) into the atmosphere from restored mangrove soil in South China. J. Coast. Res. 2021, 37, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covey, K.R.; Megonigal, J.P. Methane production and emissions in trees and forests. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, T.H. Advances in the eddy covariance approach to CH4 monitoring over two and a half decades. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, L.C.; Maher, D.T.; Santos, I.R.; Call, M.; Reading, M.J.; Holloway, C.; Tait, D.R. The spatial and temporal drivers of pCO2, pCH4 and gas transfer velocity within a subtropical estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 208, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D. The contribution of mangrove ecosystems to global carbon cycling and greenhouse gas emissions. In Greenhouse Gas and Carbon Balances in Mangrove Coastal Ecosystems; Maruzen Publishing: Tokyo, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Peltola, O.; Vesala, T.; Gao, Y.; Räty, O.; Alekseychik, P.; Aurela, M.; Chojnicki, B.; Desai, A.R.; Dolman, A.J.; Euskirchen, E.S. Monthly gridded data product of northern wetland methane emissions based on upscaling eddy covariance observations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1263–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pei, J.; Fang, C.; Li, B.; Nie, M. Opposing seasonal temperature dependencies of CO2 and CH4 emissions from wetlands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 29, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Carbon Cycling and Storage in Mangrove Forests. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2014, 6, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poffenbarger, H.J.; Needelman, B.A.; Megonigal, J.P. Salinity influence on methane emissions from tidal marshes. Wetlands 2011, 31, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, C.; Fan, X.; Shen, C.; Sun, M.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Q. Variations in CO2 and CH4 Exchange in Response to Multiple Biophysical Factors from a Mangrove Wetland Park in Southeastern China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Tian, P.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zou, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M. Global warming potentials of CO2 uptake, CH4 emissions, and albedo changes in a restored mangrove ecosystem. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2024, 129, e2023JG007924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Environmental Drivers | Stepwise Linear Regression | Random Forest Algorithm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | Feature Importance | SD | |
| LE | 0.09 | 0.157 | 0.012 |
| Tsoil | 0.18 | 0.044 | 0.037 |
| rainfall | 0.19 | 0.117 | 0.017 |
| Tide | 0.19 a | 0.086 | 0.014 |
| VPD | 0.19 a | 0.061 | 0.018 |
| H | 0.19 a | 0.046 | 0.011 |
| PAR | 0.19 a | 0.044 | 0.014 |
| SWC | 0.19 a | 0.043 | 0.002 |
| TA | 0.19 a | 0.034 | 0.020 |
| RH | 0.19 a | 0.031 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, P.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Cai, H.; Xu, M.; et al. Temporal Variations in Methane Emissions from a Restored Mangrove Ecosystem in Southern China. Forests 2024, 15, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091487
Tian P, Li X, Xu Z, Wu L, Huang Y, Zhang Z, Chen M, Zhang S, Cai H, Xu M, et al. Temporal Variations in Methane Emissions from a Restored Mangrove Ecosystem in Southern China. Forests. 2024; 15(9):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091487
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Pengpeng, Xianglan Li, Zhe Xu, Liangxu Wu, Yuting Huang, Zhao Zhang, Mengna Chen, Shumin Zhang, Houcai Cai, Minghai Xu, and et al. 2024. "Temporal Variations in Methane Emissions from a Restored Mangrove Ecosystem in Southern China" Forests 15, no. 9: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091487
APA StyleTian, P., Li, X., Xu, Z., Wu, L., Huang, Y., Zhang, Z., Chen, M., Zhang, S., Cai, H., Xu, M., & Chen, W. (2024). Temporal Variations in Methane Emissions from a Restored Mangrove Ecosystem in Southern China. Forests, 15(9), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091487





