Leaf–Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry and Homeostasis Characteristics of Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Plot Setting
2.3. Samples Collection and Determination
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
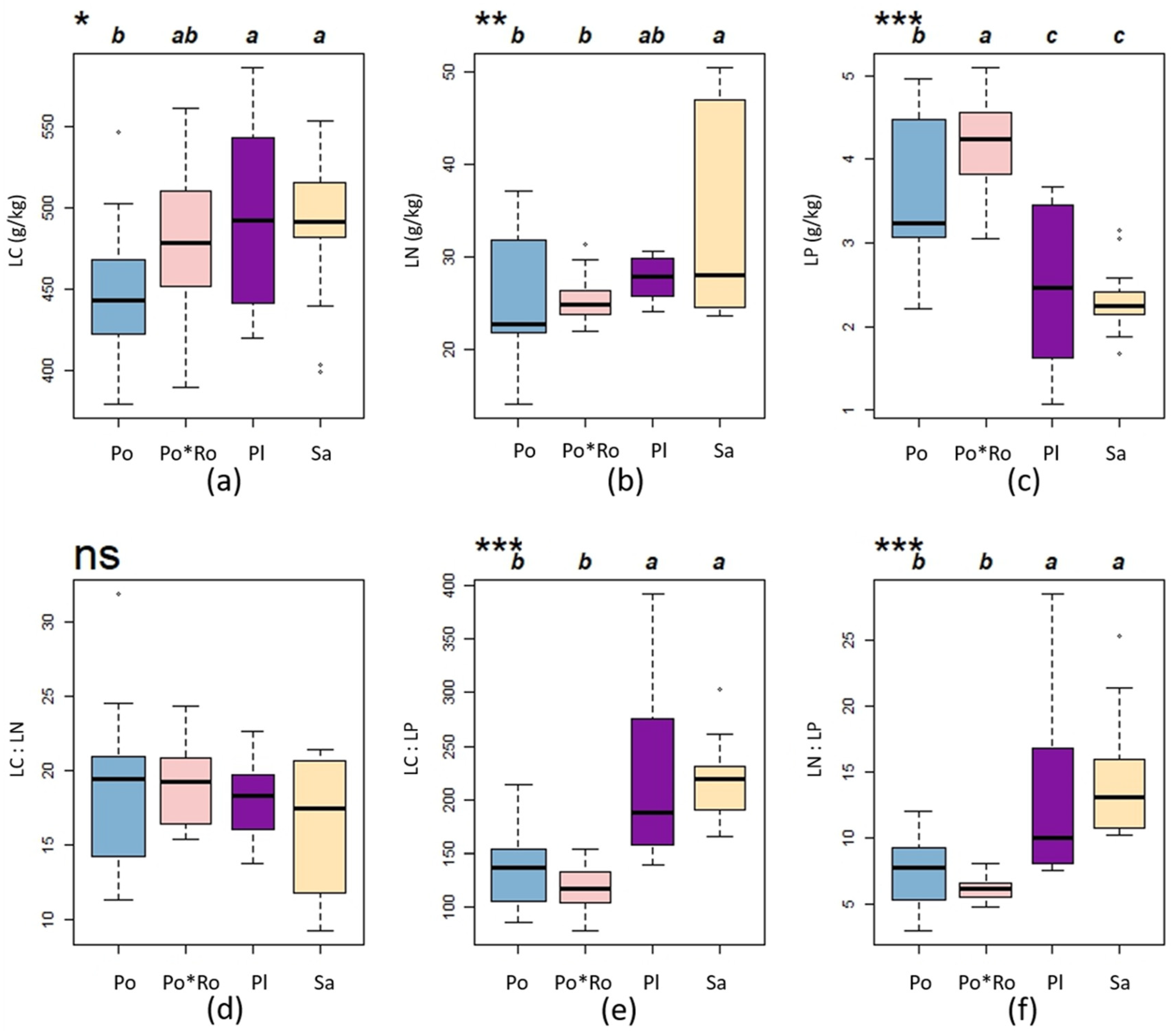
3.1. C, N, P, and C:N:P Ratios in Leaves
3.2. C, N, P, and C:N:P Ratios in Soil
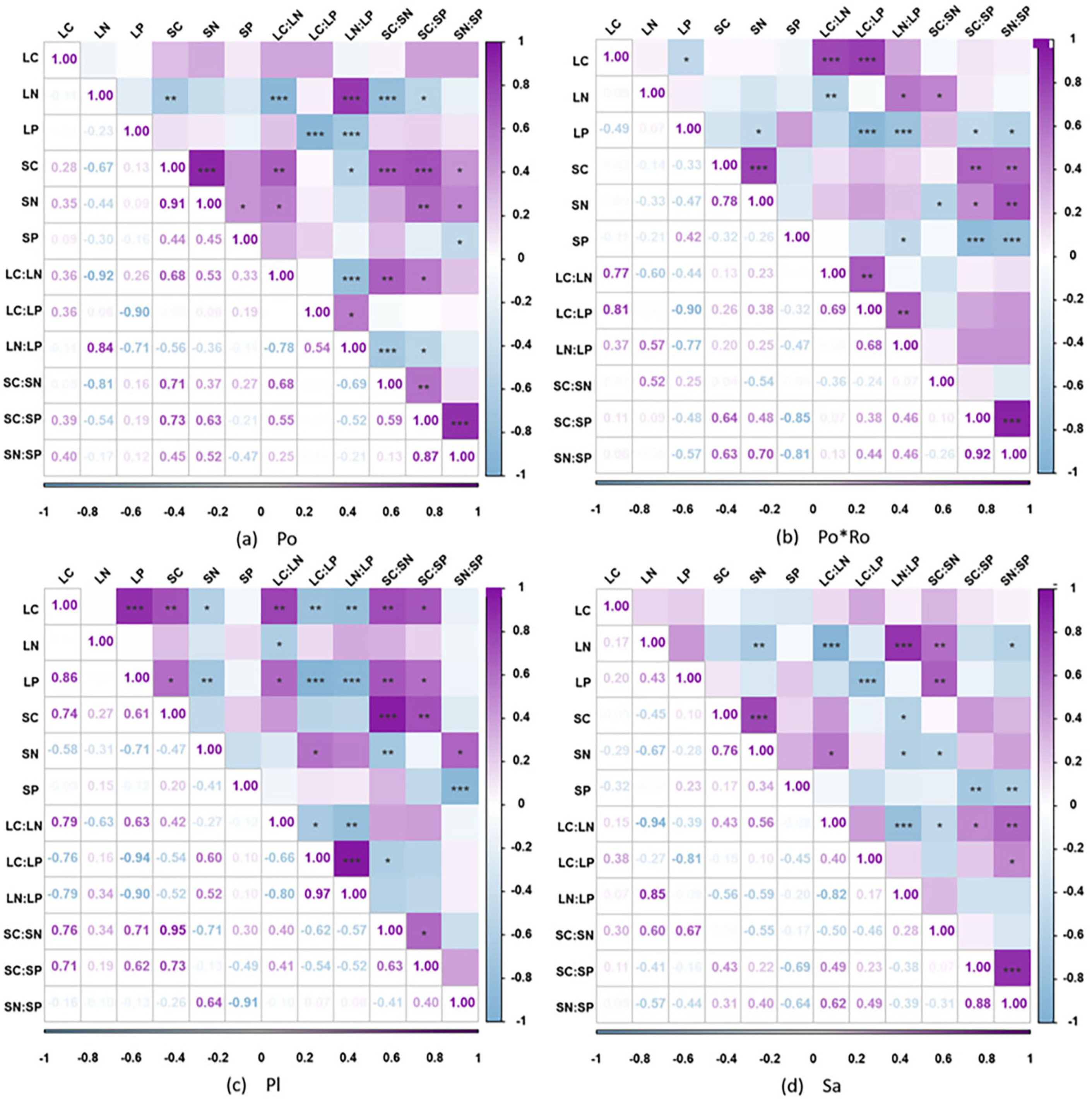
3.3. Stoichiometric Relationships within the Leaf–Soil Continuum
3.4. Homeostasis Analysis of leaf N, P, and N:P Ratios
4. Discussion
4.1. C, N, P, and C:N:P Ratios of Leaf and Soil among Different Forest Stand Types
4.2. Correlation Analysis of C, N, P, and C:N:P Ratios in Leaf–Soil of Four Forest Stand Types
4.3. Evaluation of Plant Homeostasis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elser, J.; Hamilton, A. Stoichiometry and the New Biology: The Future Is Now. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fang, J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Janssens, I.A.; Ciais, P.; Obersteiner, M.; Peñuelas, J. Recent advances and future research in ecological stoichiometry. Perspect. Plant Ecol. 2021, 50, 125611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, J.D.; Kyle, M.; Hobbie, S.E.; Fagan, W.F.; Elser, J.J. Stoichiometric tracking of soil nutrients by a desert insect herbivore. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, F.; Zeng, Z.; Du, H.; Zhang, L.; Su, L.; Lu, M.; Zhang, H. Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Stoichiometry and Its Influencing Factors in Karst Primary Forest. Forests 2022, 13, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Tjoelker, M.G.; Machado, J.-L.; Oleksyn, J. Universal scaling of respiratory metabolism, size and nitrogen in plants. Nature 2006, 439, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B. Global biogeography of plant chemistry: Filling in the blanks. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, J.T.; Raynal, D.J. Use of Nitrogen to Phosphorus Ratios in Plant Tissue as an Indicator of Nutrient Limitation and Nitrogen Saturation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Sheng, M.; Bai, Y.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil. 2022, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, J. Leaf-soil stoichiometry and homeostasis characteristics of desert-related plants. Arid. Zone Res. 2024, 41, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; Van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bowman, W.D.; Kaufmann, R.; Schmidt, S.K. A temporal approach to linking aboveground and belowground ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreeg, L.A.; Santiago, L.S.; Wright, S.J.; Turner, B.L. Stem, root, and older leaf N:P ratios are more responsive indicators of soil nutrient availability than new foliage. Ecology 2014, 95, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessen, D.O.; Gren, G.R.I.; Anderson, T.R.; Elser, J.J.; De Ruiter, P.C. Carbon sequestration in ecosystems: The role of stoichiometry. Ecology 2004, 85, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minden, V.; Kleyer, M. Internal and external regulation of plant organ stoichiometry. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Hu, T.; Tang, D.D.; Chen, Q. Characteristics of plant ecological stoichiometry homeostasis. Guihaia 2019, 39, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Fu, Z. Study on ecological stoichiometry homeostasis characteristics of different halophytes in the Yellow River Delta. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Xiong, K.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. Ecological stoichiometry and homeostasis characteristics of plant-litter-soil system with vegetation restoration of the karst desertification control. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1224691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, I.; Grau, O.; Sardans, J.; Ninot, J.M.; Peñuelas, J. Encroachment of shrubs into subalpine grasslands in the Pyrenees changes the plant-soil stoichiometry spectrum. Plant Soil. 2020, 448, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gou, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F. Seasonal patterns in the leaf C:N:P stoichiometry of four conifers on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 47, e2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Arif, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, C. Patterns and drivers of plant carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry in a novel riparian ecosystem. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1354222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, J.; Fink, P.; Goto, A.; Hood, J.M.; Jonas, J.; Kato, S. To be or not to be what you eat: Regulation of stoichiometric homeostasis among autotrophs and heterotrophs. Oikos 2010, 119, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Chang, M.; Jin, S.; Li, X.; Xie, H. Periodic Flooding Decoupled the Relations of Soil C, N, P, and K Ecological Stoichiometry in a Coastal Shelterbelt Forest of Eastern China. Forests 2023, 14, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, J.M.; Sterner, R.W. Diet mixing: Do animals integrate growth or resources across temporal heterogeneity? Am. Nat. 2010, 176, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Viliam, S. R Package ‘corrplot’: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix, (Version 0.92). 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- The RDevelopment Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, v. 4.2.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022.
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; Mccauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, W.; Xiong, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus concentration and the empirical regulations in dominant woody plants of shrublands across southern China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, S. Comparison of ecological stoichiometric characteristics of leaf-litter-soil in four types of Fraxinus mandshurica plantations. J. Nanjing For. Uni. 2019, 43, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, O.; Gulimia, I.; Duan, J.; Jia, L.; Xi, B. Chemical stoichiometry characteristics of various organs of trees in high-density Populus tomentosa pulp forests under water-nitrogen coupling. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2023, 45, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N.; Xi, B.; Jeremiah, R.P.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Jia, L. Root biomass distribution of triploid Populus tomentosa under wide- and narrow-row spacing planting schemes and its responses to soil nutrients. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 37, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Geng, Z.; Hu, F.; Xu, C. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Soil Organic Carbon and the Influencing Factors in Shanxi Province in Recent 30 Years. Environ. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Casa, J.; Sardans, J.; Galindo, M.; Peñuelas, J. Stoichiometry of litter decomposition under the effects of climate change and nutrient enrichment: A meta-analysis. Plant Soil. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazza, L.; Fontana, M.; Guillaume, T.; Scow, K.M.; Sinaj, S. Nutrient stoichiometry of a plant-microbe-soil system in response to cover crop species and soil type. Plant Soil. 2021, 461, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, F., IV; Menge, D.N.L.; Ostling, A.; Hosseini, P. Nutrient recycling affects autotroph and ecosystem stoichiometry. Am. Nat. 2008, 171, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Cha, X.; Sun, L.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q. Study on the Characteristics of Soil Ecological Stoichiometry and Non-Structural Carbon in Different Forest Ages of Fraxinus malacophylla. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2024, 38, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, C.; Zhao, J.; Lei, G. Characterization of the soil and leaf C, N, and P stoichiometry of poplar plantations of three different stand ages in Dongting Lake wetland, China. Perspect. Plant Ecol. 2018, 38, 6530–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M. Element cycling as driven by stoichiometric homeostasis of soil microorganisms. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2016, 17, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Stand Characteristics | Po | Po*Ro | Pl | Sa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lat and Lon | 36°47′ N; 116°3′~116°4′ E | 36°47′ N; 116°4′ E | 36°24′~36°47′ N; 116°16′~116°4′ E | 36°13′~36°24′ N; 116°15′~116°28′ E |
| H (m) | 20.85 ± 7.54 | 20.37 ± 10.18 | 15.8 ± 10.18 | 18.22 ± 3.24 |
| DBH (cm) | 23.71 ± 11.22 | 24.48 ± 13.62 | 15.78 ± 1.42 | 19.22 ± 30.6 |
| BD (g/cm3) | 1.19 ± 0.082 | 1.12 ± 0.05 | 1.17 ± 0.06 | 1.19 ± 0.08 |
| SWC (%) | 0.11 ± 0.021 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.04 |
| pH | 7.71 ± 0.14 | 7.73 ± 0.09 | 7.91 ± 0.08 | 7.99 ± 0.08 |
| EC (μs/cm) | 286.5 ± 49.84 | 270.28 ± 27.87 | 363.5 ± 11.02 | 300.64 ± 61.8 |
| MAT (°C) | 15.02 ± 0.14 | 15.04 ± 0.12 | 15.13 ± 0.18 | 15.39 ± 0.16 |
| MAP (mm) | 602.92 ± 0.62 | 602.94 ± 0.31 | 618.51 ± 16.08 | 637.05 ± 0.16 |
| HC (%) | 46.8 ± 19.77 | 45.44 ± 27.72 | 17.08 ± 15.77 | 65.78 ± 26.63 |
| Main species of the herb layer | Rubia cordifolia Setaria viridis Humulus scandens Commelina communis | Erigeron canadensis Humulus scandens Chenopodium album Bidenspilosa | Humulus scandens Chenopodium album Setaria viridis Salsola collina | Setaria viridis Cynodon dactylon Humulus scandens Rehmannia glutinosa |
| Forest Stand Types | SC (g/kg) | SN (g/kg) | SP (g/kg) | SC:SN | SC:SP | SN:SP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Po | 4.68 ± 3.50 a | 0.93 ± 0.45 ab | 0.50 ± 0.28 b | 4.67 ± 2.15 ab | 10.17 ± 7.52 a | 2.12 ± 1.05 a |
| Po*Ro | 5.28 ± 1.33 a | 1.03 ± 0.35 ab | 0.48 ± 0.24 b | 5.29 ± 0.87 a | 14.61 ± 0.87 a | 2.84 ± 1.82 a |
| Pl | 1.78 ± 0.78 b | 0.58 ± 0.08 b | 1.04 ± 0.35 a | 3.21 ± 1.59 b | 1.86 ± 0.97 b | 0.62 ± 0.24 b |
| Sa | 6.58 ± 2.70 a | 1.29 ± 0.65 a | 0.85 ± 0.39 a | 5.56 ± 1.76 a | 10.00 ± 7.39 a | 1.94 ± 1.49 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Lu, X. Leaf–Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry and Homeostasis Characteristics of Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China. Forests 2024, 15, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081433
Liu H, Lu X. Leaf–Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry and Homeostasis Characteristics of Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China. Forests. 2024; 15(8):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081433
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huiran, and Xinghui Lu. 2024. "Leaf–Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry and Homeostasis Characteristics of Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China" Forests 15, no. 8: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081433
APA StyleLiu, H., & Lu, X. (2024). Leaf–Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry and Homeostasis Characteristics of Plantations in the Yellow River Floodplain in Western Shandong, China. Forests, 15(8), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081433





