Effect of Gastrodia elata Bl Cultivation under Forest Stands on Runoff, Erosion, and Nutrient Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. An Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Design of Runoff Plots
2.2.2. Observation of Rainfall Indicators
2.2.3. Runoff Sediment Collection
2.2.4. Nutrient Loss Measurement Experiment
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Runoff Sands on Forested Land during Gastrodia elata Bl Cultivation
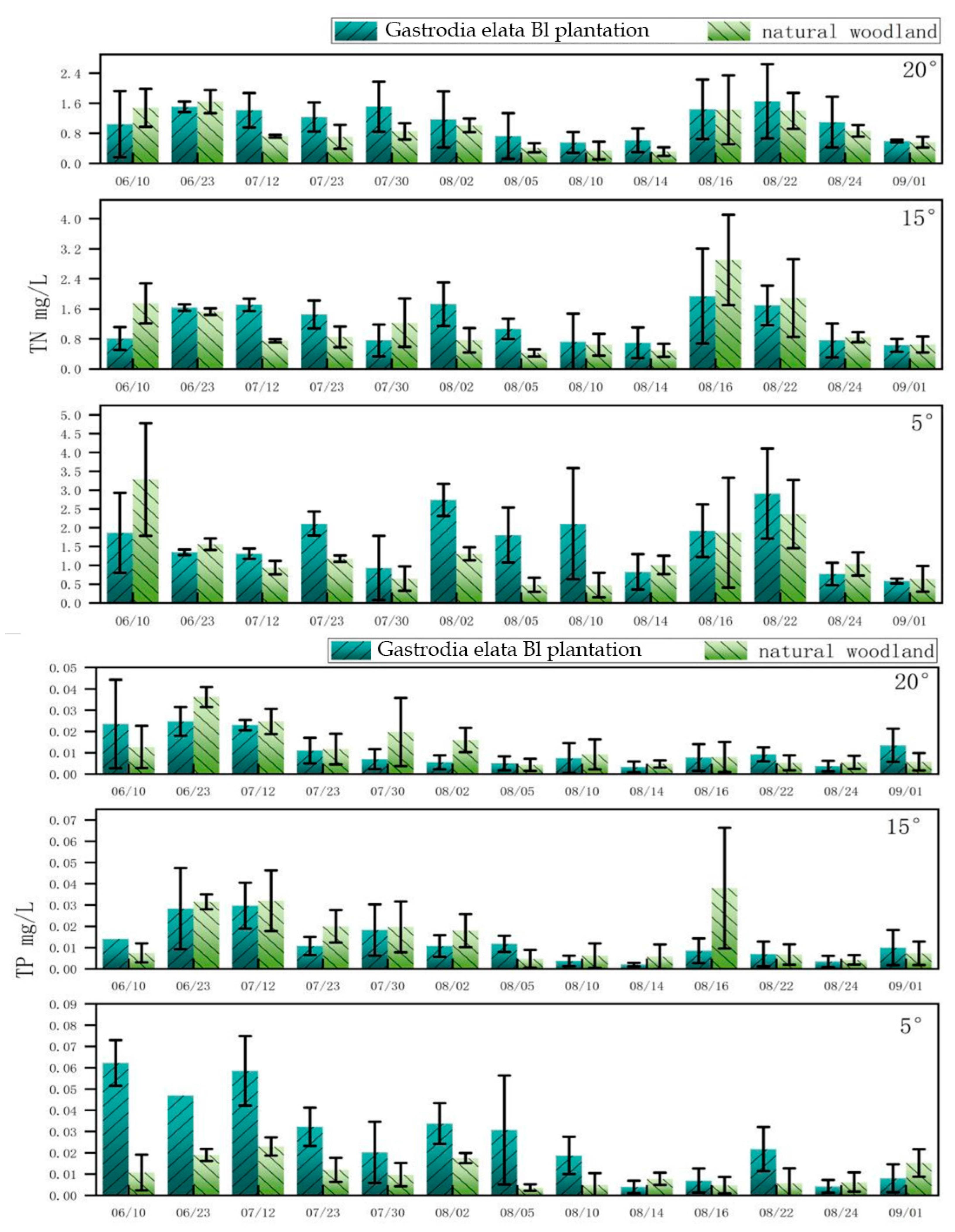
3.2. Effect of Different Slopes on Runoff Nutrient Loss of Gastrodia elata Bl Planted under Forest Canopy
3.3. Effect of Different Slopes on Sediment Nutrient Loss of Gastrodia elata Bl in Forest Plantations
3.4. Relationship between Runoff and Nutrient Loss from Sediments in Gastrodia elata Bl Plantation Stands
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Forest Gastrodia elata Bl Planting on Soil and Water and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutrient Losses
4.2. Effects of Rainfall Characteristics and Slopes on Soil, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus Nutrient Losses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Jiang, V.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Pan, C. Discussion on the ecological model of wild-imitation cultivation under the forest of Gastrodia elata Bl. China Mod. Chin. Med. 2018, 20, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Gui, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, Q.; Jin, J.; Zhu, G. Status quo and development countermeasures of Gastrodia elata Bl production in Guizhou. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. Research on Key Technology of Wild-Imitation Cultivation of Gastrodia elata Bl. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Lu, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, D. Standardized management of wild-like cultivation technology of Yunnan Zhaotong Gastrodia elata Bl. China Mod. Chin. Med. 2017, 19, 408–414. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Cao, L.; Ye, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, J.; He, D. Research on forest economy model and its industrial development countermeasures. Shanghai Agric. J. 2008, 3, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G.; Tan, Z.; Shen, A. Analysis of the main modes and advantages and disadvantages of understory economy. Hunan For. Sci. Technol. 2013, 40, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M. Research on Soil Nutrients and Plant Diversity in Forest Window of Forest Planted Gastrodia elata Bl. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, C.; Fan, H.; Lin, Y.; Wu, C. Effects of apoptosis removal/retention on soil respiration in the forest window and within the forest of a cedar plantation. J. Ecol. 2017, 37, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Gao, L.; Li, J. Effects of understory Panax Pseudoginseng planting on soil and water and carbon and nitrogen loss on slopes. J. Northwest Agric. For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yunnan Forestry and Grassland Bureau. Yunnan Province “14th Five-Year Plan” Forest Chinese Herbal Medicine Industry Plan; Yunnan Forestry and Grassland Bureau: Kunming, China, 2022.
- Zhang, Y.; Lei, J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Farooq, T.H.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Impact of Intercropping on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutrient Loss in Camellia oleifera Forests on Entisol Soil. Forests 2024, 15, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhuo, B.; Huang, X.; Nie, X.; Li, D. Relationships of nitrogen losses, phosphorus losses, and sediment under simulated rainfall conditions. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H. Effect of thaw depth on nitrogen and phosphorus loss in runoff of loess slope. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Cao, W.; Fang, J.; Cai, L. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses from agricultural systems in China: A meta-analysis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hou, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate and planting structure changes on watershed runoff and nitrogen and phosphorus loss. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 134489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Zhang, G.L.; Shi, X.Z.; Wang, H.; Cao, Z. Dynamic changes of nitrogen and phosphorus losses in ephemeral runoff processes by typical storm events in Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qiao, S.; Peng, M.; Ma, X. Coupling loss characteristics of runoff-sediment-adsorbed and dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus on bare loess slope. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14018–14031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, M.E.; Bøe, F. Soil tillage and crop growth effects on surface and subsurface runoff, loss of soil, phosphorus and nitrogen in a cold climate. Land 2021, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Huang, Y.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Tian, C.; Han, Y. The effects of the depth of fertilization on losses of nitrogen and phosphorus and soil fertility in the red paddy soil of China. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, S.; Ruan, Q.; Tian, C. Synergetic impact of climate and vegetation cover on runoff, sediment, and nitrogen and phosphorus losses in the Jialing River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 361, 132141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lai, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J. Characteristics of runoff and sand production in Panax Pseudoginseng plantations under natural rainfall conditions. China Soil Water Conserv. Sci. 2024, 1–10, (In Chinese and English). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Y. Soil Science Experiment Guide Tutorial; China Forestry Press Education Branch: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y. Experimental Methods in Soil Science; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Ma, F.; Wang, J.; Qiu, P.; Zhang, N.; Guo, W.; Xu, J.; Dai, T. Study on the Mechanism of Rainfall-Runoff Induced Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Hilly Slopes of Black Soil Area, China. Water 2023, 15, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Shen, J.; Bergström, L.; Zhang, F. Past, present, and future use of phosphorus in Chinese agriculture and its influence on phosphorus losses. Ambio 2015, 44, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, J.; Cui, L. Effects of vegetation patterns on soil nitrogen and phosphorus losses on the slope-gully system of the Loess Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- SL 190-2007; Soil Erosion Classification and Grading Standards. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. China Water Resources and Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Wang, G.; Wu, B.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Xu, Z. Role of soil erodibility in affecting available nitrogen and phosphorus losses under simulated rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2014, 514, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, P.; Shen, Z. Runoff characteristics and nutrient loss mechanism from plain farmland under simulated rainfall conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Lv, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Xie, Z. Runoff and soil and nutrient losses from gravel mulching: A field experiment with natural rainfall on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 76, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zheng, F.; Römkens, M.J.M.; Li, G.; Yang, Q.; Wen, L.; Wang, B. The role of soil surface water regimes and raindrop impact on hill slope soil erosion and nutrient losses. Nat. Hazards 2013, 67, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z.; Otsuki, K. A rainfall simulation study of soil erodibility and available nutrient losses from two contrasting soils in China. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2015, 60, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Yin, C. Direct and indirect effects of rainfall and vegetation coverage on runoff, soil loss, and nutrient loss in a semi-humid climate. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e13985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Wei, C.C.; Han, Y.; Qu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B. Soil erosion and nutrient loss due to changes in rainfall intensity under different wind directions. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Han, W.; Liu, D.; Gan, X. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses by runoff erosion: Field data monitored under natural rainfall in Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 2016, 147, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Yuan, S. Effects of rainfall intensities on sediment loss and phosphorus enrichment ratio from typical land use type in Taihu Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12866–12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Ren, M. An approximate semi-analytical model of sediment and nutrient transport on slopes under rainfall conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1247–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.-T.; Hu, W.; Chau, H.W.; Lei, B.-K.; Di, H.-J.; Chen, A.-Q.; Hou, M.-T.; Whitley, S. Combined cultivation pattern reduces soil erosion and nutrient loss from sloping farmland on red soil in Southwestern China. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
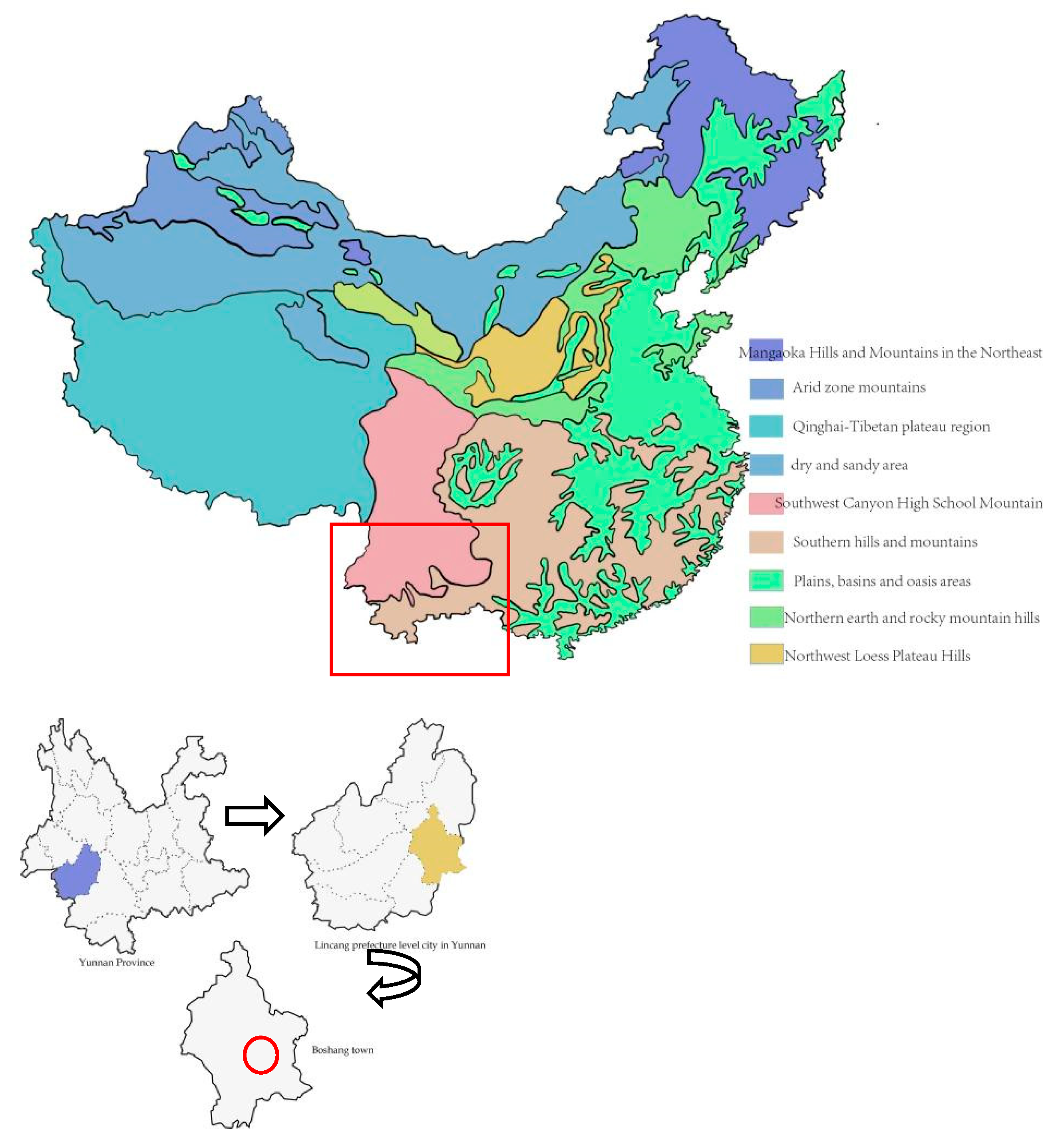

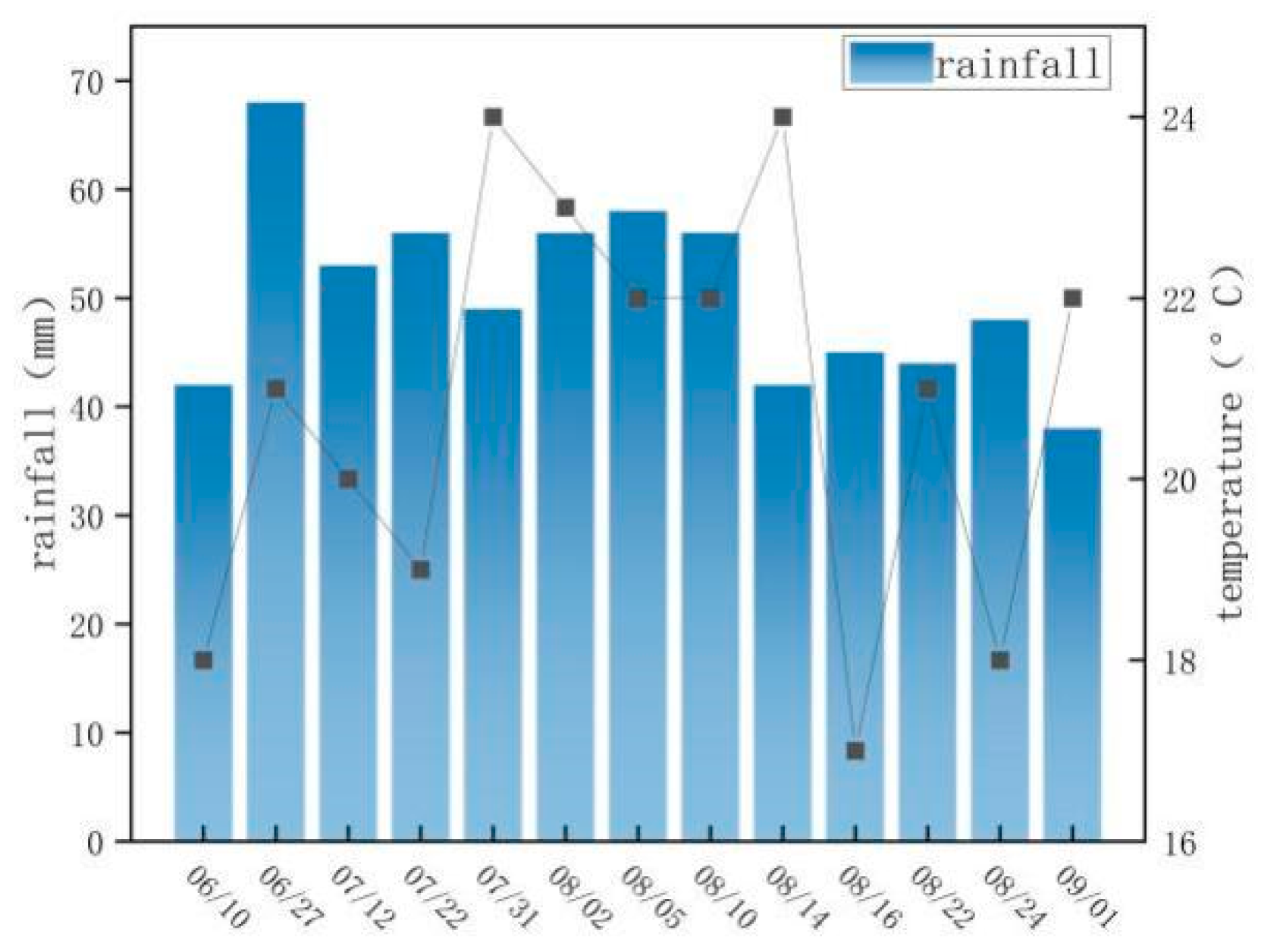
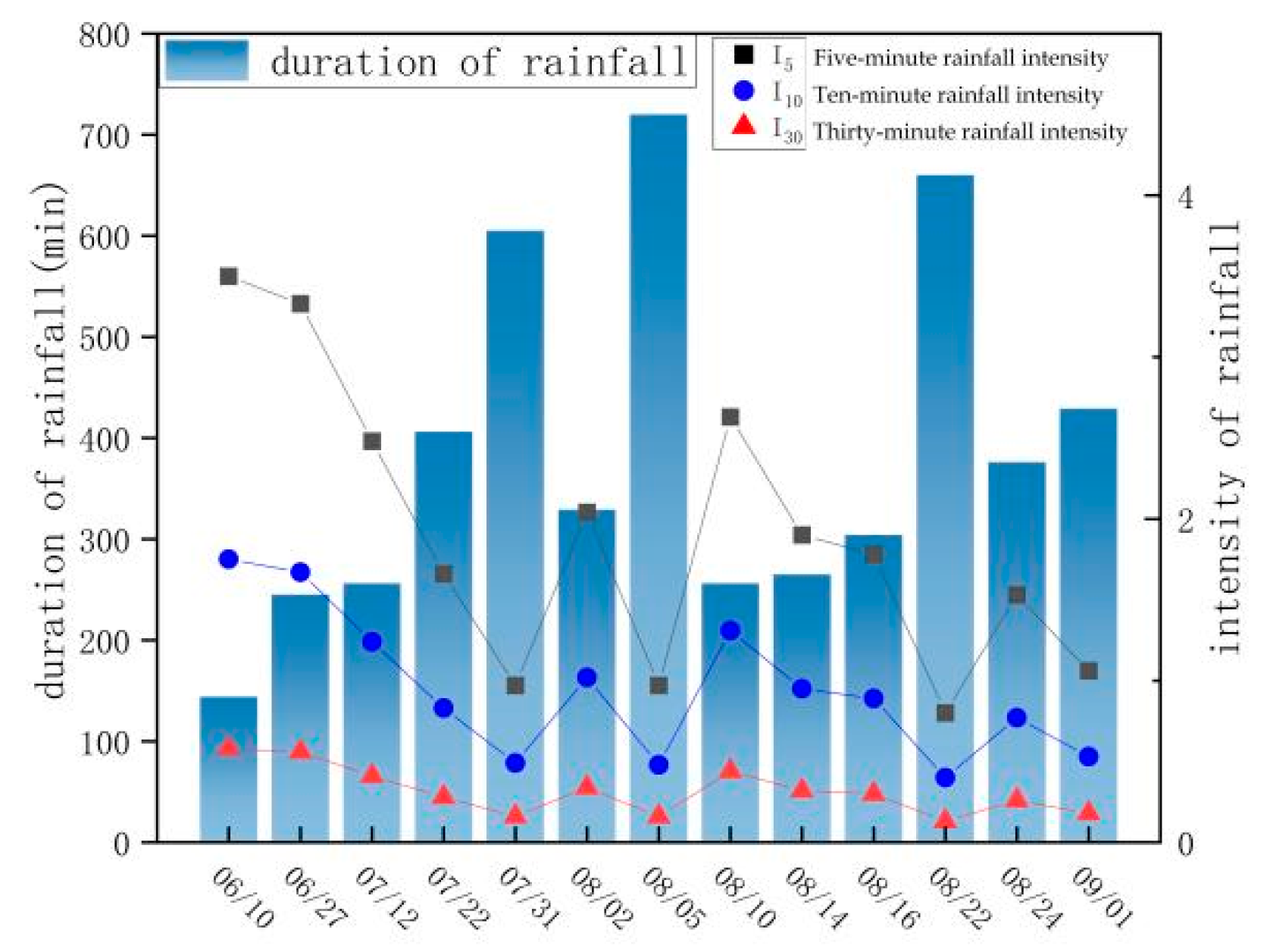
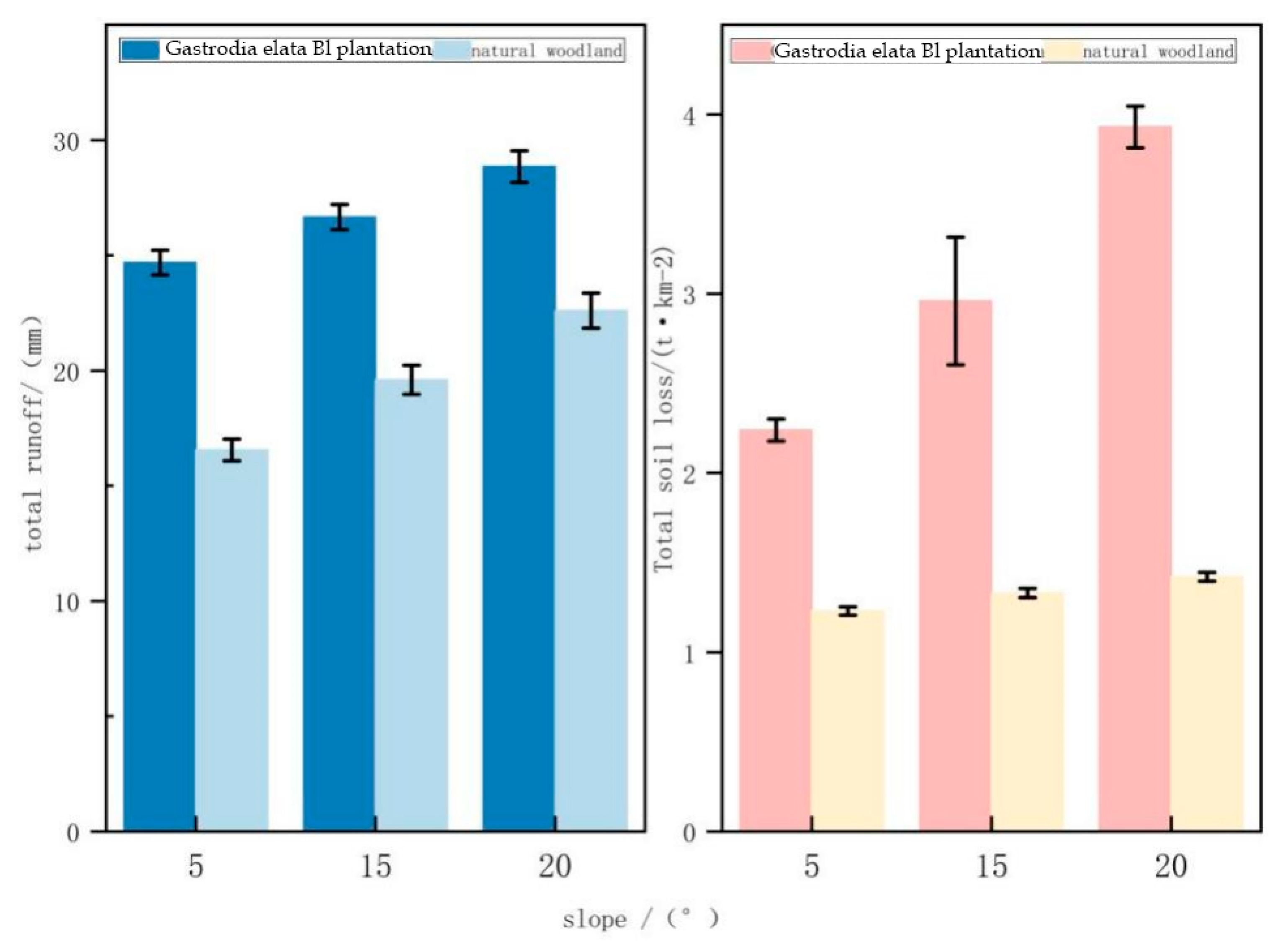



| Sample Plot Number | Slope | Slope Direction | Typical Tree Species | Physical Characteristics | Diameter at Breast Height/cm | Tree Height/m | Shading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—1 | 13° | South by west | Pinus yunnanensis | Forests that are nearly mature | 23.92 ± 4.49 | 15.12 ± 1.5 | 70% |
| 1—2 | 10° | South by west | Pinus yunnanensis | Forests that are nearly mature | 23.85 ± 5.27 | 15.03 ± 1.77 | 70% |
| 1—3 | 14° | South by west | Pinus yunnanensis | Forests that are nearly mature | 25.45 ± 5.77 | 15.76 ± 1.68 | 65% |
| Treatment | Runoff/mm | Soil Loss/(t·km2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | |
| S5° | 2.10 | 0.25 | 0.94 ± 0.54 a | 0.27 | 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.06 b |
| C5° | 1.7 | 0.20 | 0.75 ± 0.47 a | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.23 b |
| S15° | 2.50 | 0.30 | 1.02 ± 0.55 a | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.27 ± 0.35 a |
| C15° | 2.0 | 0.30 | 1.06 ± 0.63 a | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.25 b |
| S20° | 2.9 | 0.10 | 0.8 ± 0.68 a | 1.24 | 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.11 b |
| C20° | 2.42 | 0.20 | 1.11 ± 0.76 a | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.24 b |
| Treatment | TN/(mg/L) TN in Runoff | TP/(mg/L) TP in Runoff | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | |
| S5° | 4.29 | 0.23 | 1.67 ± 0.98 a | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.02 a |
| C5° | 4.73 | 0.18 | 1.29 ± 1.01 b | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 b |
| S15° | 3.26 | 0.10 | 1.21 ± 0.67 bc | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.011 b |
| C15° | 4.39 | 0.27 | 1.13 ± 0.85 bc | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 b |
| S20° | 2.96 | 0.16 | 1.15 ± 0.65 bc | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.011 ± 0.01 b |
| C20° | 2.10 | 0.12 | 0.89 ± 0.51 c | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.013 ± 0.01 b |
| Treatment | NO3−-N mg/L in Runoff | NH4+-N mg/L in Runoff | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | |
| S5° | 2.56 | 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.66 a | 1.27 | 0.06 | 0.35 ± 0.24 a |
| C5° | 1.55 | 0.06 | 0.3 ± 0.26 bc | 1.11 | 0.06 | 0.34 ± 0.21 a |
| S15° | 1.16 | 0.06 | 0.35 ± 0.29 b | 1.35 | 0.06 | 0.36 ± 0.27 a |
| C15° | 2.02 | 0.05 | 0.24 ± 0.27 cd | 1.38 | 0.06 | 0.34 ± 0.23 a |
| S20° | 1.49 | 0.07 | 0.41 ± 0.32 bc | 1.41 | 0.06 | 0.37 ± 0.27 a |
| C20° | 0.5 | 0.06 | 0.17 ± 0.09 d | 1.29 | 0.06 | 0.35 ± 0.26 a |
| Treatment | TN/(mg·L−1) TN in Sediment | TP/(mg·L−1) TP in Sediment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | |
| S5° | 13.41 | 2.69 | 7.89 ± 2.62 c | 2.76 | 0.56 | 1.57 ± 0.51 b |
| C5° | 21.06 | 4.58 | 14.79 ± 4.78 a | 2.85 | 0.58 | 2.07 ± 0.71 a |
| S15° | 14.66 | 3.19 | 7.69 ± 2.38 c | 3.08 | 0.76 | 1.55 ± 0.46 b |
| C15° | 21.73 | 2.46 | 11.61 ± 5.08 b | 2.68 | 0.35 | 1.62 ± 0.62 b |
| S20° | 13.79 | 1.60 | 7.38 ± 2.45 c | 2.33 | 0.06 | 1.45 ± 0.54 b |
| C20° | 15.06 | 3.35 | 8.10 ± 3.36 c | 1.65 | 0.62 | 1.08 ± 0.31 c |
| Runoff Volume | Soil Loss | TN Loss in Runoff | TP Loss in Runoff | TN Loss from Sediment | TP Loss in Sediment | NO3−-N Loss in Runoff | NH4+-N Loss in Runoff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runoff volume | 1 | |||||||
| Soil loss | −0.084 | 1 | ||||||
| TN loss in runoff | −0.012 | −0.06 | 1 | |||||
| TP loss in runoff | 0.172 * | −0.06 | 0.339 ** | 1 | ||||
| TN loss from sediment | −0.239 ** | −0.074 | −0.088 | −0.11 | 1 | |||
| TP loss in sediment | −0.340 ** | 0.067 | 0.015 | −0.13 | 0.813 ** | 1 | ||
| NO3−-N loss in runoff | −0.067 | 0.169 * | 0.248 ** | 0.002 | 0.015 | 0.173 * | 1 | |
| NH4+-N loss in runoff | 0.129 | −0.084 | 0.263 ** | 0.214 ** | −0.184 * | −0.187 * | −0.026 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Li, J. Effect of Gastrodia elata Bl Cultivation under Forest Stands on Runoff, Erosion, and Nutrient Loss. Forests 2024, 15, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071127
Yang S, Li J. Effect of Gastrodia elata Bl Cultivation under Forest Stands on Runoff, Erosion, and Nutrient Loss. Forests. 2024; 15(7):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071127
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuyuan, and Jianqiang Li. 2024. "Effect of Gastrodia elata Bl Cultivation under Forest Stands on Runoff, Erosion, and Nutrient Loss" Forests 15, no. 7: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071127
APA StyleYang, S., & Li, J. (2024). Effect of Gastrodia elata Bl Cultivation under Forest Stands on Runoff, Erosion, and Nutrient Loss. Forests, 15(7), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15071127




