Identification and Expression Analysis of the FAD Gene Family in Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Based on Genome-Wide Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Analysis of the AglaFAD Gene Family
2.1.1. Identification of FAD Genes in the A. glabripennis Genome
2.1.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.1.3. Structural Characterization of AglaFADs
2.1.4. Chromosomal Locations of AglaFADs
2.2. Tissue Expression of AglaFADs
2.2.1. Insect Collection and Processing
2.2.2. RNA Extraction and qPCR Analysis of AglaFADs
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of AglaFADs
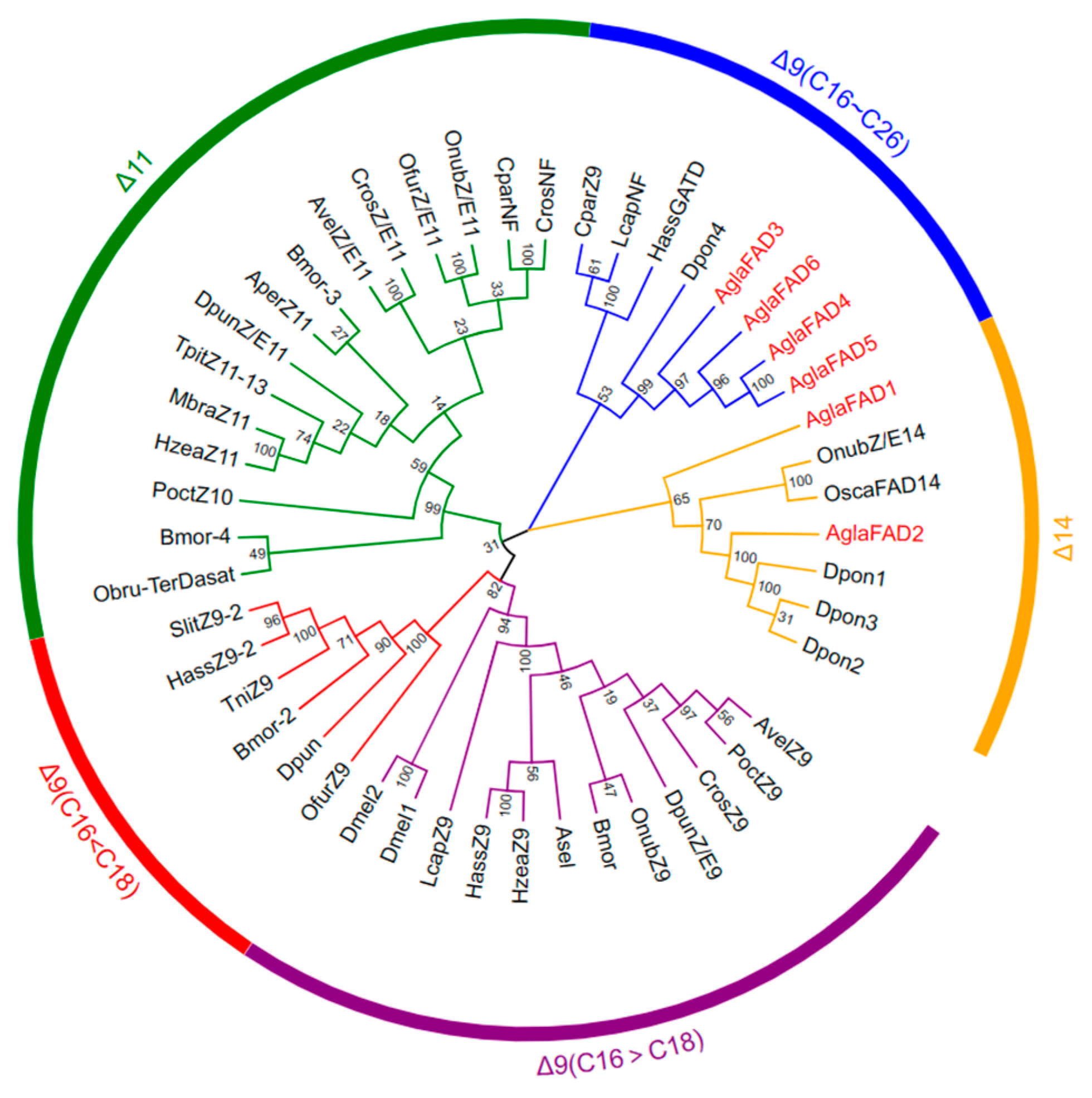
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Multiple Sequence Alignment of AglaFADs
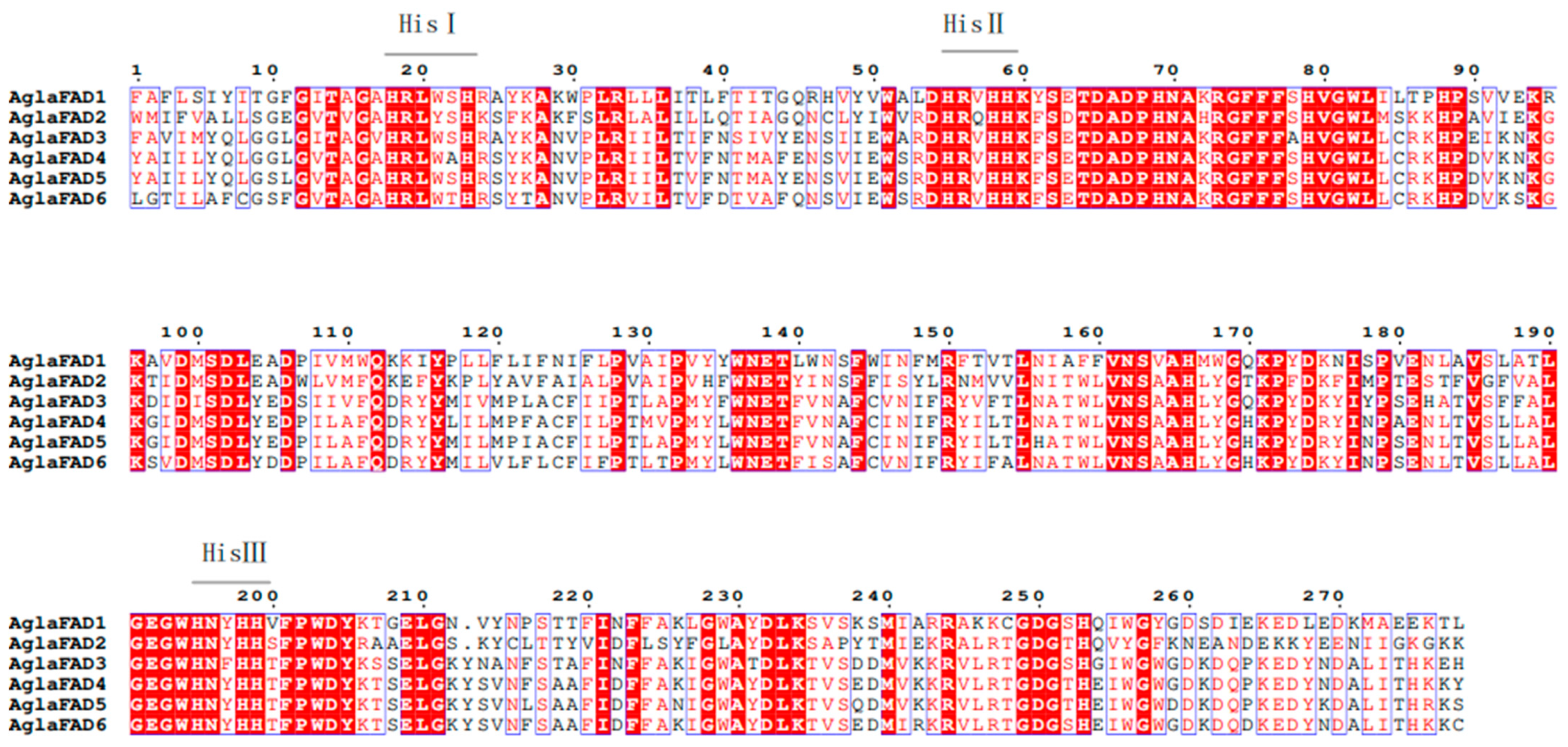
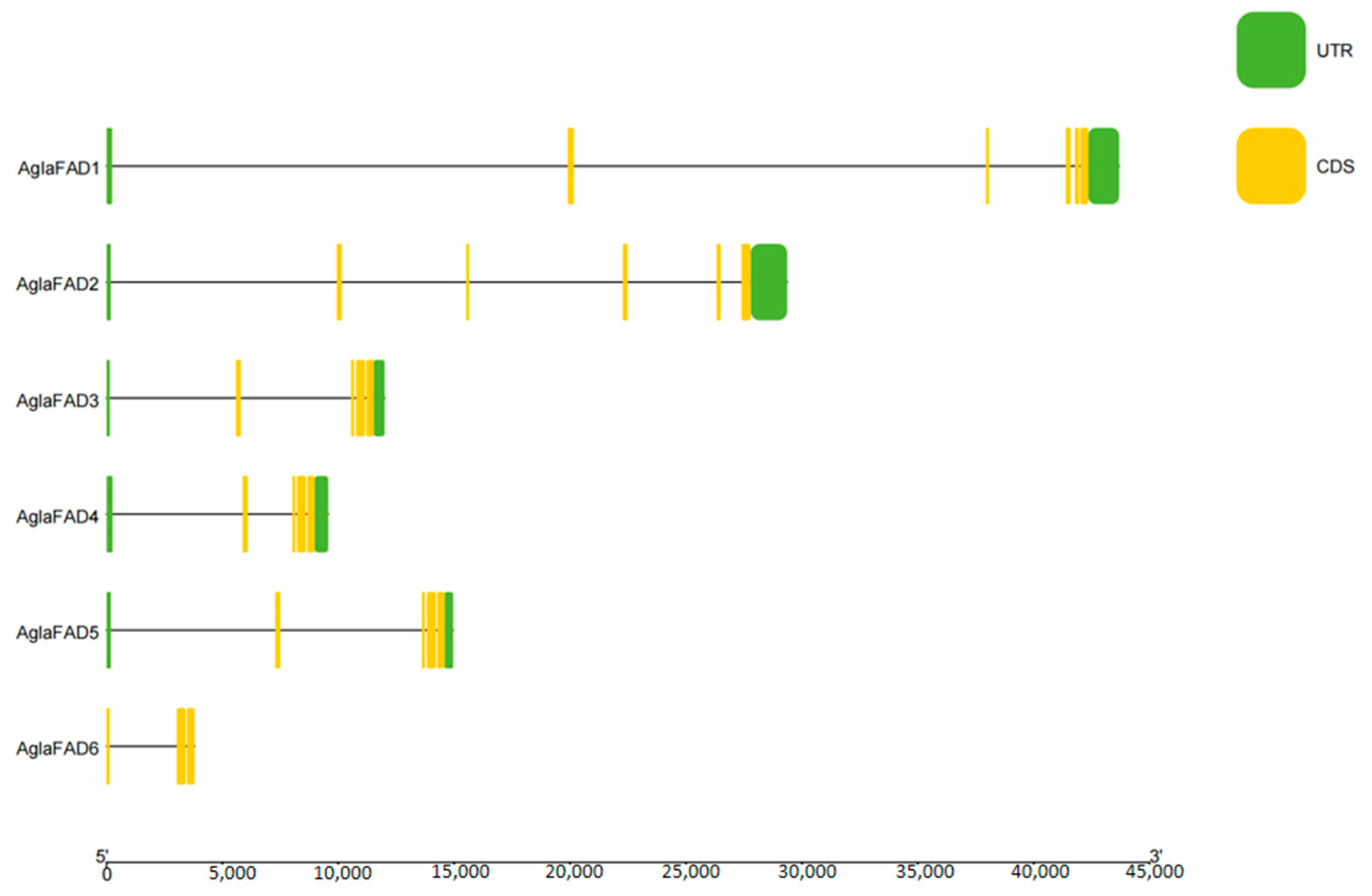
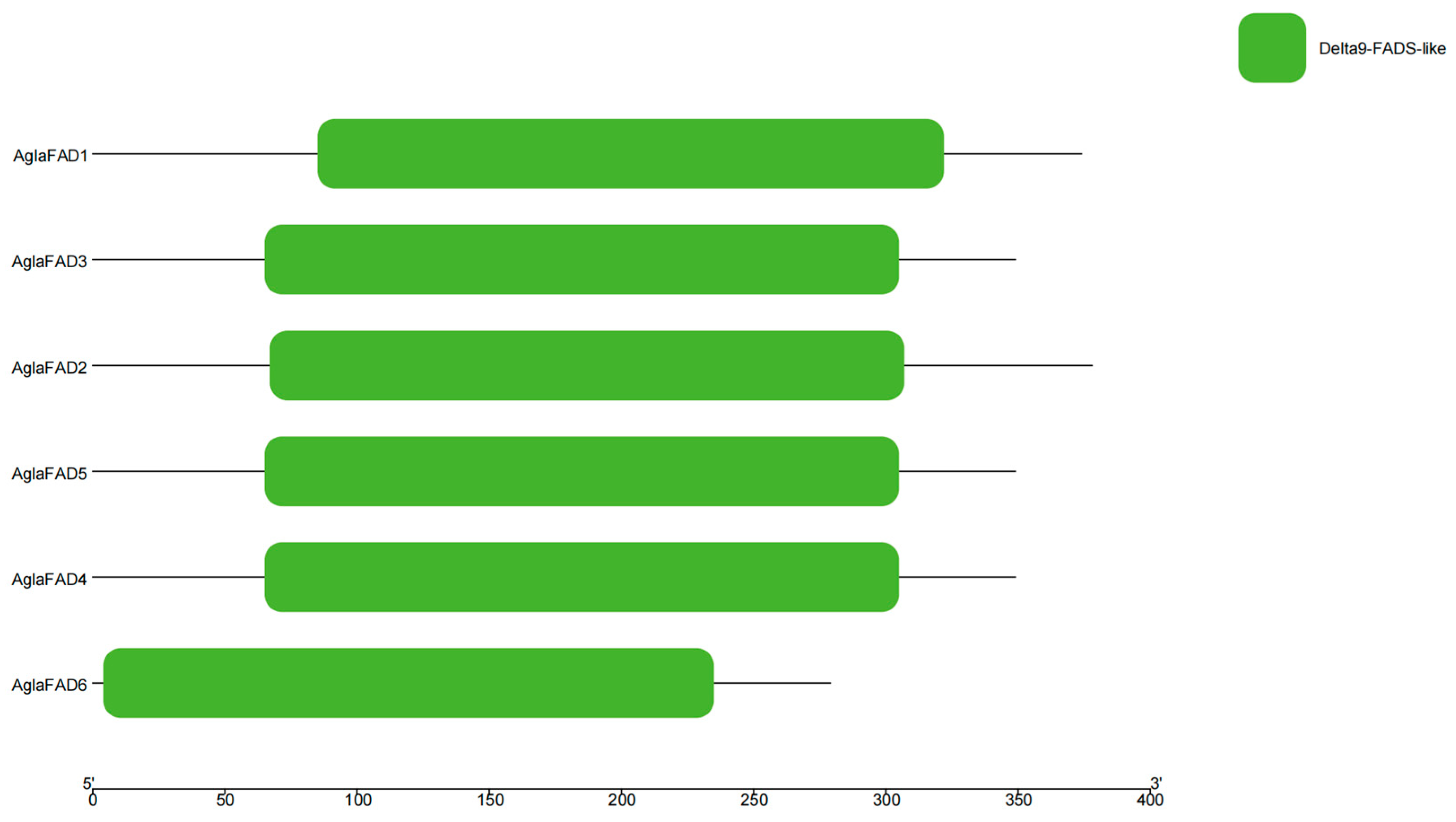
3.3. Structural Analysis of AglaFADs
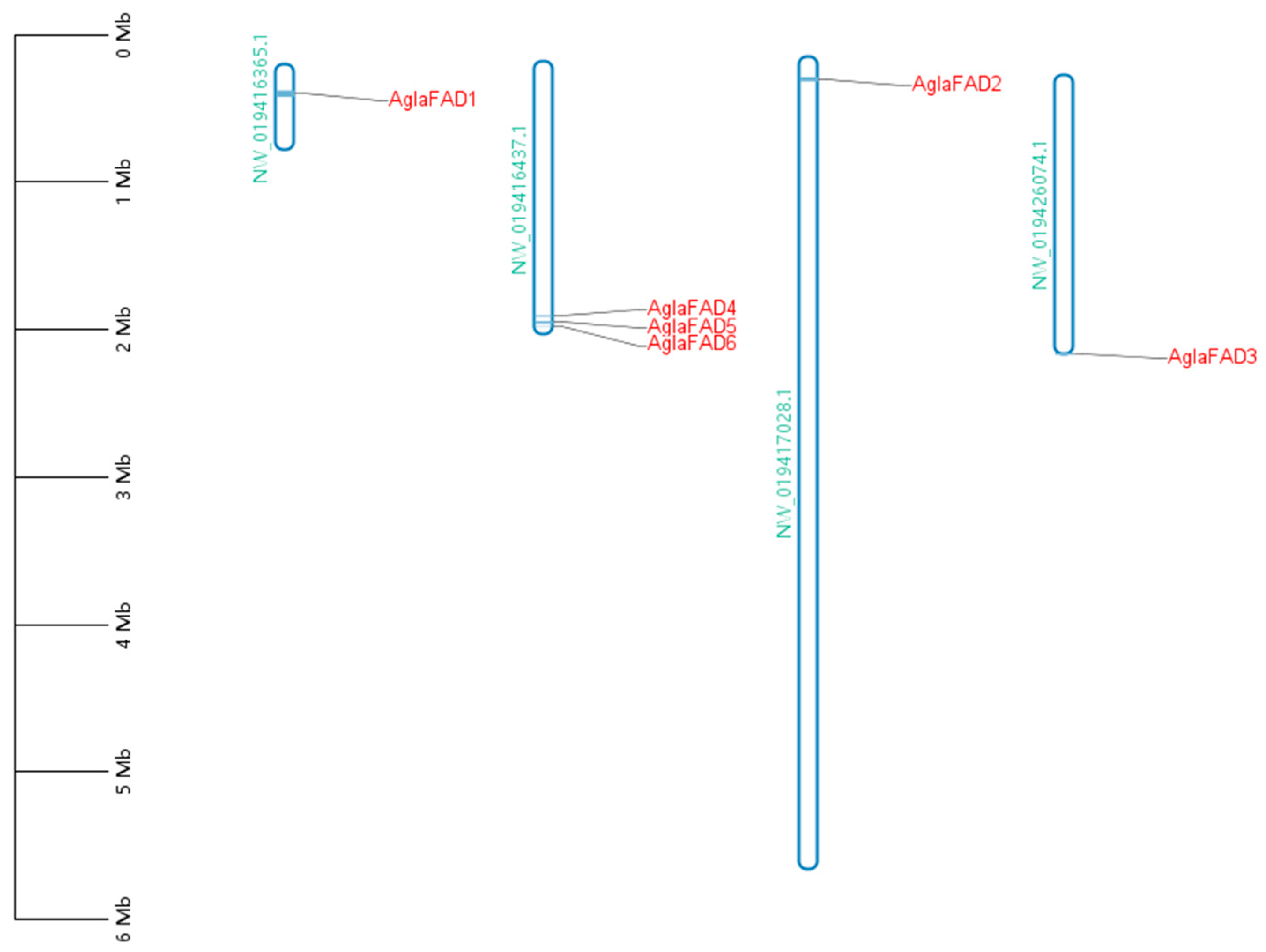
3.4. Analysis of Chromosomal Locations of AglaFADs
3.5. Expression Analysis of AglaFADs
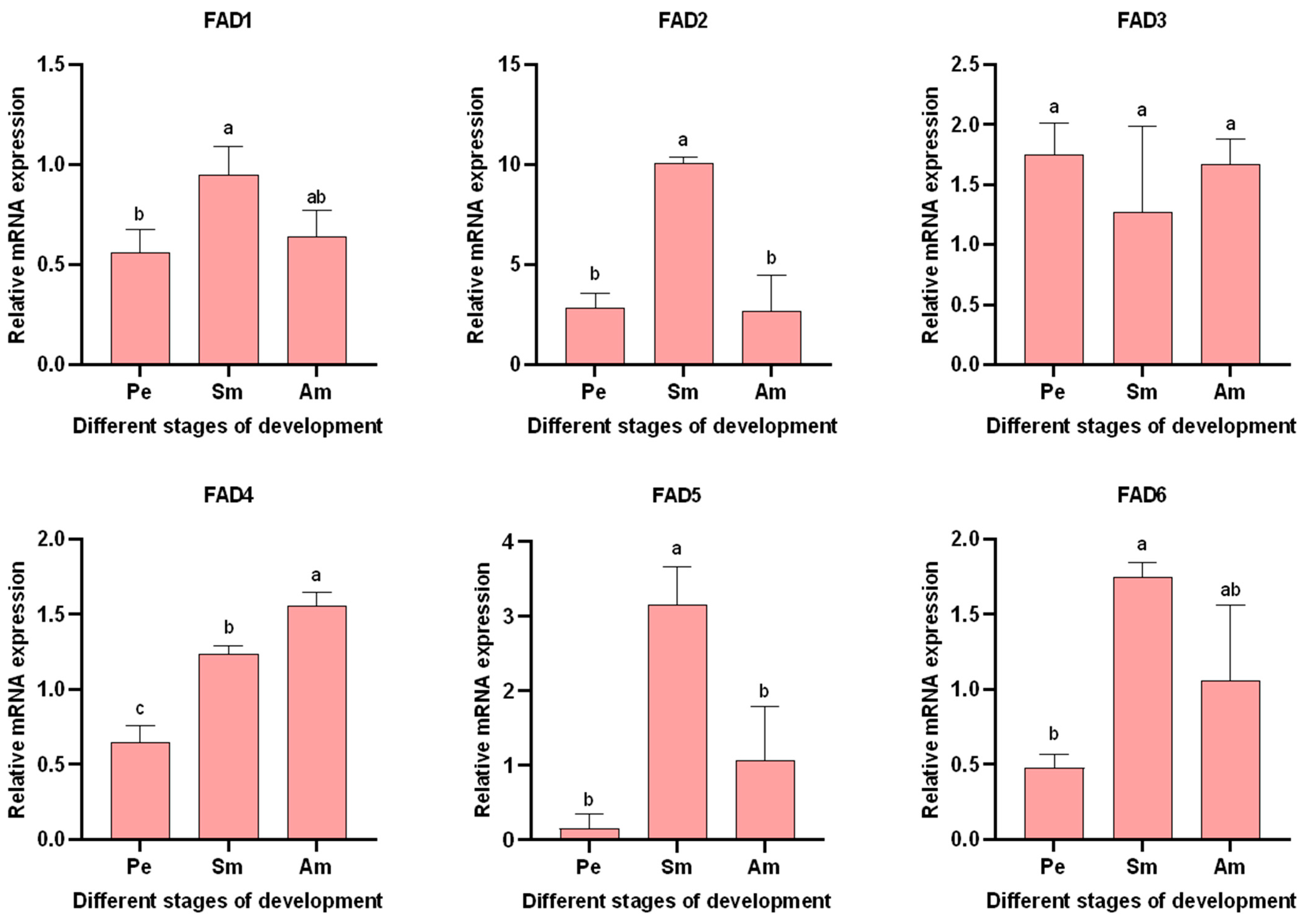
3.5.1. Expression of AglaFADs in Males and Females at Sexual Maturity
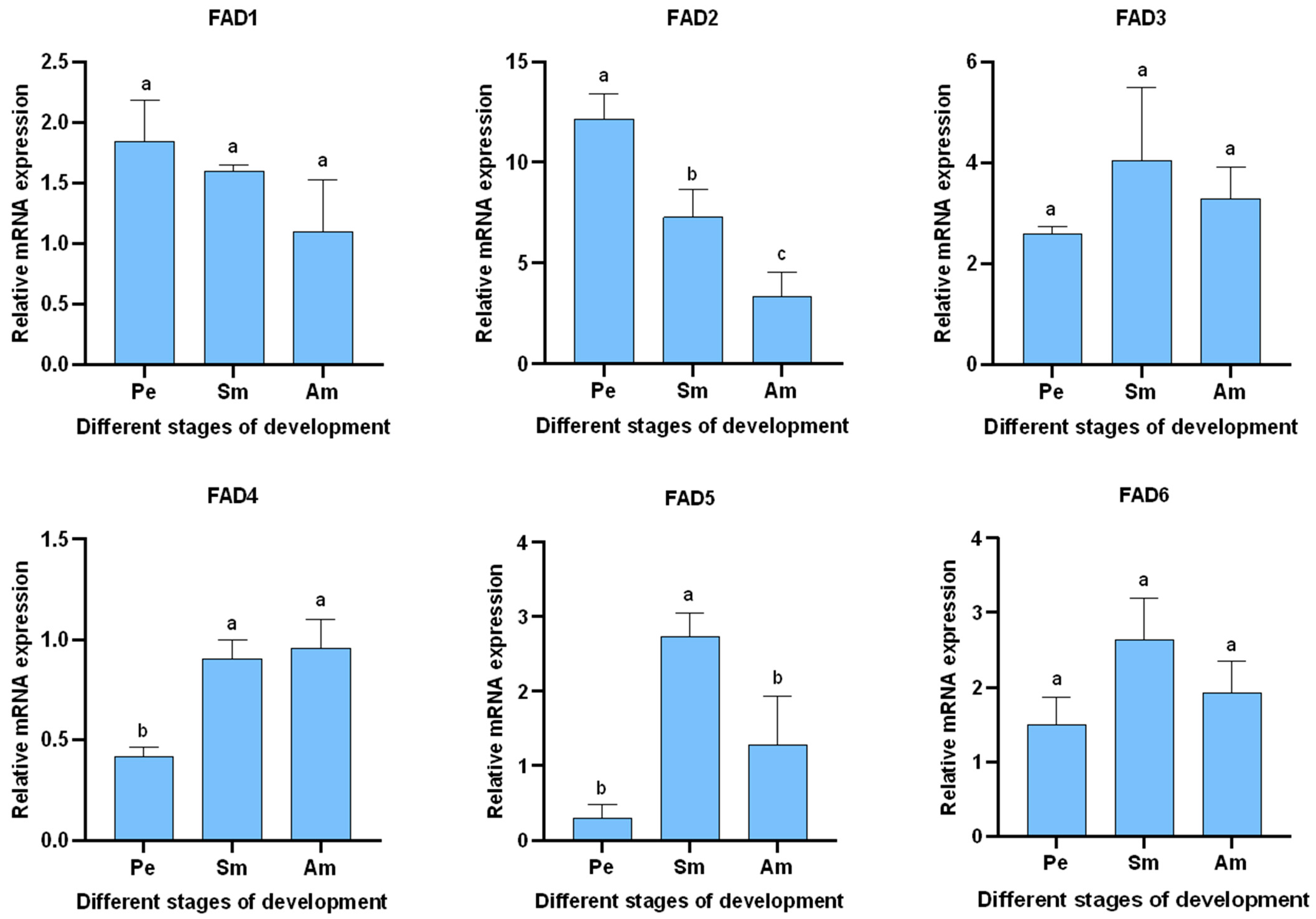
3.5.2. Expression of AglaFADs at Different Developmental Stages in the Wings and Gonads of Females
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helmkampf, M.; Cash, E.; Gadau, J. Evolution of the insect desaturase gene family with an emphasis on social Hymenoptera. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.D.; Li, X.; Bin, Z.; Du, M.F.; Yin, X.M.; An, S.H. Molecular identification of a pancreatic lipase-like gene involved in sex pheromone biosynthesis of Bombyx mori. Insect Sci. 2014, 21, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipple, D.C.; Rpsenfield, C.L.; Nielsen, R.; You, K.M.; Jeong, S.E. Evolution of the integral membrane desaturase gene family in moths and flies. Genetics 2002, 162, 1737–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, W.L.; Rooney, A.P. Molecular genetics and evolution of pheromone biosynthesis in Lepidoptera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9179–9184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Ting, C.T.; Lee, C.R.; Chu, K.H.; Wang, C.C.; Tsaur, S.C. Molecular evolution and functional diversification of fatty acid desaturases after recurrent gene duplication in Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.Y.; Rooney, A.P.; Kajikawa, M.; Okada, N.; Roelofs, W.L. Novel sex pheromone desaturases in the genomes of corn borers generated through gene duplication and retroposon fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4467–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Okuda, S.; Kuma, K.; Goto, S.; Kanehisa, M. The repertoire of desaturases and elongases reveals fatty acid variations in 56 eukaryotic genomes. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keays, M.C.; Barker, D.; Wicker-Thomas, C.; Ritchie, M.G. Signatures of selection and sex-specific expression variation of a novel duplicate during the evolution of the Drosophila desaturase gene family. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 3617–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcillac, F.; Grosjean, Y.; Ferveur, J.F. A single mutation alters production and discrimination of Drosophila sex pheromones. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirangi, T.R.; Dufour, H.D.; Williams, T.M.; Carroll, S.B. Rapid evolution of sex pheromone-producing enzyme expression in Drosophila. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.H.; Shankar, S.; Shikichi, Y.; Akasaka, K.; Moro, K.; Yew, J.Y. Pheromone evolution and sexual behavior in Drosophila are shaped by male sensory exploitation of other males. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3056–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagstrom, A.K.; Albre, J.; Tooman, L.K.; Thirmawithana, A.H.; Corcoran, J.; Löfstedt, C.; Newcomb, R.D. A novel fatty acyl desaturase from the pheromone glands of Ctenopseustis obliquana and C. herana with specific Z5-desatu-rase activity on myristic acid. J. Chem. Ecol. 2014, 40, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, X.D.; Du, Y.J. Biosynthesis and endocrine regulation of sex pheromones in moth. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 3235–3250. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.T.; Bancroft, J.; Li, G.; Gao, R.; Teale, S. Dispersal of Anoplophora glabripennis (Cerambycidae). Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.W.; Lee, H.P.; Kim, I.K. Distribution and abundance of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in natural Acer stands in South Korea. Environ. Entomol. 2004, 33, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérard, F.; Ciampitti, M.; Maspero, M.; Krehan, H.; Benker, U.; Boegel, C.; Schrage, R.; Bouhot-Delduc, L.; Bialooki, P. Anoplophora species in Europe: Infestations and management processes 1. EPPO Bull. 2006, 36, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.; Smith, M.; Harrison, R. Genetic analyses of the Asian longhorned beetle (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Anoplophora glabripennis), in North America, Europe and Asia. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1165–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straw, N.A.; Fielding, N.J.; Tilbury, C.; Williams, D.T.; Cull, T. History and development of an isolated outbreak of Asian longhorn beetle Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in southern England. Agric. For. Entomol. 2016, 18, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J. Research on distribution of basicosta whitespotted longicorn in east China. J. North-East. For. Coll. China 1985, 13, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.G. Study on the Occurrence Dynamics of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) and Its Control Measures; Northeast Forestry University: Harbin, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, J. Major achievements, problems and prospects of poplar longicorn beetles research in China. Insect Knowl. 2000, 37, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Hajek, A.E.; Huang, B.; Dubois, T.; Smith, M.T.; Li, Z. Field studies of control of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera:Cerambycidae) using fiber bands containing the entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria brongniartii. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2006, 16, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.; Mei, W.; Liu, X. Research on the control technology of the Asian longhorned beetle. For. Sci. Technol. 2016, 41, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wu, L.P.; Hu, Q.; Fan, J.T. Attractiveness of aggregation pheromones and host plant volatiles to Anoplophora glabripennis and A. chinensis (Coleoptera:Cerambycidae). J. Entomol. 2017, 60, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Teale, S.A. Chemical ecology of the Asian longhorn beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 47, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginzel, M.D.; Hanks, L.M. Contact Pheromones as Mate Recognition Cues of Four Species of Longhorned Beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Insect Behav. 2003, 16, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Xu, Z.C.; Teale, S.A. Evidence for a female-produced, long range pheromone of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Insect Sci. 2012, 19, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Tokoro, M.; Nacashima, T. Mechanism of mating action of Anoplophora glabripennis (Motsch.). J. Beijing For. Univ. 1999, 21, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.J.; Oliver, J.E.; Chauhan, K.; Zhao, B.; Xia, L.; Xu, Z. Evidence for contact sex recognition pheromone of the Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Naturwissenschaften 2003, 90, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomquist, G.J.; Dillwith, J.W.; Adams, T.S. Biosynthesis and endocrine regulation of sex pheromone production in Diptera. In Pheromone Biochemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 217–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latli, B.; Prestwich, G.D. Metabolically blocked analogs of housefly sex pheromone: I. Synthesis of alternative substrates for the cuticular monooxygenases. J. Chem. Ecol. 1991, 17, 1745–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y. Identification of the Sex Pheromone Synthesis Genes of Spodoptera litura and Functional Study of Its Important Genes; Shanxi University: Taiyuan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Zhu, X.Y.; Fang, L.P.; He, P.; Wang, Z.Q.; Chen, G.; Sun, L.; Ye, Z.F.; Deng, D.G.; Li, J.B. Identification and expression profiles of sex pheromone biosynthesis and transport related genes in Spodoptera litura. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayanova, O.; Shewry, P.R.; Napier, J.A. Histidine-41 of the cytochrome b5 domain of the borage delta6 fatty acid desaturase is essential for enzyme activity. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libisch, B.; Michaelson, L.V.; Lewis, M.J.; Shewry, P.R.; Napier, J.A. Chimeras of Δ6 Fatty Acid and Δ8 Sphingolipid Desaturases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigenheer, A.L.; Young, S.; Blomquist, G.J.; Borgeson, C.E.; Tillman, J.A.; Tittiger, C. Isolation and molecular characterization of Musca domestica delta-9 desaturase sequences. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, S.; Hao, G.; Liu, W.; Piña, B.; Rooney, A.P.; Camps, F.; Roelofs, W.L.; Fabriàs, G. Expression and evolution of Δ9 and Δ11 desaturase genes in the moth Spodoptera littoralis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritzen, L.; Hansen, H.S.; Jørgensen, M.H.; Michaelsen, K.F. The Essentiality of Long Chain N-3 Fatty Acids in Relation to Development and Function of the Brain and Retina. Prog. Lipid Res. 2001, 40, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, W.C.; Miyazaki, M.; Chu, K.; Ntambi, J.M. Membrane topology of mouse stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.R. Bioinformatics Analysis of the SCD Protein in Pig. Anim. Feed. Sci. 2014, 35, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, G.R. cDNA cloning and prokaryotic expression of acyl-CoA delta 9 desaturase from Chrysomya megacephala (Fabricius). J. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 40, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.G.; Ma, G.H.; He, P.P.; Xiong, R.C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Han, X.; Yang, M.L. Gene Sequences and Expression Analysis of Fatty Acid Δ9 Desaturase of Euzophera pyriella during Different Stages. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2020, 57, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukey, J.E.; McDonough, V.M.; Martin, C.E. The OLE1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes the delta 9 fatty acid desaturase and can be functionally replaced by the rat stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 20144–20149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Lv, L.M.; Dong, S.L.; Cui, J.J. Transcriptome comparison of the sex pheromone glands from two sibling Helicoverpa species with opposite sex pheromone components. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, R.; Fukuzawa, M.; Nakano, R.; Tatsuki, S.; Ishikawa, Y. Alternative suppression of transcription from two desaturase genes is the key for species-specific sex pheromone biosynthesis in two Ostrinia moths. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.F. Characterization of the Biological Functions of Desaturase Nldesat10 and Salivary Protein NISEF1 of Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]


| Species | FAD Name | Protein Accession |
|---|---|---|
| Ostrinia nubilalis | OnubZ/E14 | AAL35330 |
| Ostrinia scapulalis | OscaFAD14 | BAE97679 |
| Choristoneura parallela | CparZ9 | AAQ12887 |
| Lampronia capitella | LcapZ9 | ABX71627 |
| Helicoverpa assulta | HassGATD | AAM28480 |
| Lampronia capitella | LcapNF | ABX71629 |
| Helicoverpa assulta | HassZ9 | AAM28481 |
| Ascotis selenaria cretacea | Asel | BAF97042 |
| Planotortrix octo | PoctZ9 | AAF73073 |
| Argyrotaenia velutinana | AvelZ9 | AAF44709 |
| Choristoneura rosaceana | CrosZ9 | AAN39697 |
| Ostrinia nubilalis | OnubZ9 | AAF44710 |
| Dendrolimus punctatus | DpunZ/E9 | ABX71810 |
| Bombyx mori | Bmor | NP_001036971 |
| Helicoverpa zea | HzeaZ11 | AAF81787 |
| Trichoplusia ni | TniZ9 | AAB92583 |
| Spodoptera littoralis | SlitZ9-2 | AAQ74257 |
| Helicoverpa assulta | HassZ9-2 | AAM28484 |
| Dendrolimus punctatus | Dpun | ABX71813 |
| Ostrinia furnacalis | OfurZ9 | AAL27034 |
| Bombyx mori | Bmor-2 | NP_001037018 |
| Argyrotaenia velutinana | AvelZ/E11 | AAL16642 |
| Dendrolimus punctatus | DpunZ/E11 | ABX71809 |
| Mamestra brassicae | MbraZ11 | ABX90049 |
| Thaumetopoea pityocampa | TpitZ11-13 | ABO43722 |
| Ostrinia furnacalis | OfurZ/E11 | AAL32060 |
| Ostrinia nubilalis | OnubZ/E11 | AAL35331 |
| Choristoneura rosaceana | CrosNF | AAN39698 |
| Bombyx mori | Bmor-3 | NP_001036914 |
| Choristoneura parallela | CparNF | AAN39693 |
| Choristoneura rosaceana | CrosZ/E11 | AAN41250 |
| Helicoverpa zea | HzeaZ9 | AAF81788 |
| Bombyx mori | Bmor-4 | NP_001040141 |
| Ostrinia brumata | Obru-TerDesat | AEH95845 |
| Planotortrix octo | PoctZ10 | AAG54077 |
| Antheraea pernyi | AperZ11 | ADO85596 |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Dmel1 | AAB17283 |
| Drosophila melanogaster | Dmel2 | CAB52474 |
| Dendroctonus ponderosae | Dpon1 | XP019762450 |
| Dendroctonus ponderosae | Dpon2 | XP019762452 |
| Dendroctonus ponderosae | Dpon3 | XP019762451 |
| Dendroctonus ponderosae | Dpon4 | XP019755346 |
| Anoplophora glabripennis | AglaFAD1 | XP_018565922.1 |
| Anoplophora glabripennis | AglaFAD2 | XP_018576960.1 |
| Anoplophora glabripennis | AglaFAD3 | XP_023313032.1 |
| Anoplophora glabripennis | AglaFAD4 | XP_018579075.1 |
| Anoplophora glabripennis | AglaFAD5 | XP_018579055.1 |
| Anoplophora glabripennis | AglaFAD6 | XP_023310323.1 |
| Gene Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| AglaFAD1 | 5′-TTCGTGCCGAGGATACGATG-3′ | 5′-AAGCCCTATGTGACCACAGC-3′ |
| AglaFAD2 | 5′-TCACACCGCTACGATGCTTT-3′ | 5′-ATGTTGCCTGTGATCTCGCA-3′ |
| AglaFAD3 | 5′-CTCTGGTCTCATCGTGCTT-3′ | 5′-TTCGCTGAATTTATGGTGG-3′ |
| AglaFAD4 | 5′-TGGTGGATTGGGTGTCACTG-3′ | 5′-GAATCCGCGTTTGGCATTGT-3′ |
| AglaFAD5 | 5′-AGAGGTGGTTGCAAAAGCCA-3′ | 5′-TGCCTTGTAGGAACGATGGG-3′ |
| AglaFAD6 | 5′-TGCTTTAAATGCCACATGGTTAGT-3′ | 5′-TGCAGCAGAGAAGTTTACACTG-3′ |
| β-Actin | 5′-ACATCAAGGAGAAACTCTGCTACG-3′ | 5′-CTTCATGATGGAGTTGTAGGTGGT-3′ |
| AglaFAD Member | Protein ID | AA | MW (Da) | pI | II | Transmembrane Domain | Subcellular Localization | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AglaFAD1 | XP_018565922.1 | 374 | 43,133.42 | 6.76 | 39.26 | 5 | Endoplasmic reticulum. | −0.192 |
| AglaFAD2 | XP_018576960.1 | 378 | 43,106.85 | 8.66 | 32.29 | 5 | Endoplasmic reticulum. | −0.032 |
| AglaFAD3 | XP_023313032.1 | 349 | 40,383.17 | 6.40 | 30.63 | 4 | Endoplasmic reticulum. | −0.131 |
| AglaFAD4 | XP_018579075.1 | 349 | 40,339.53 | 8.23 | 40.83 | 4 | Endoplasmic reticulum. | −0.113 |
| AglaFAD5 | XP_018579055.1 | 349 | 40,323.44 | 8.19 | 42.89 | 4 | Endoplasmic reticulum. | −0.134 |
| AglaFAD6 | XP_023310323.1 | 279 | 32,373.85 | 7.01 | 36.06 | 2 | Endoplasmic reticulum. | −0.190 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Xing, Y.; Tao, J.; Han, F. Identification and Expression Analysis of the FAD Gene Family in Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Based on Genome-Wide Data. Forests 2024, 15, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040690
Song X, Xu Y, Zhang S, Li M, Xing Y, Tao J, Han F. Identification and Expression Analysis of the FAD Gene Family in Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Based on Genome-Wide Data. Forests. 2024; 15(4):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040690
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xue, Yabei Xu, Sainan Zhang, Meng Li, Yu Xing, Jing Tao, and Fengying Han. 2024. "Identification and Expression Analysis of the FAD Gene Family in Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Based on Genome-Wide Data" Forests 15, no. 4: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040690
APA StyleSong, X., Xu, Y., Zhang, S., Li, M., Xing, Y., Tao, J., & Han, F. (2024). Identification and Expression Analysis of the FAD Gene Family in Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Based on Genome-Wide Data. Forests, 15(4), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040690






