Decomposition and Variation in Carbon and Nitrogen of Leaf Litter Mixtures in a Subtropical Mangrove Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
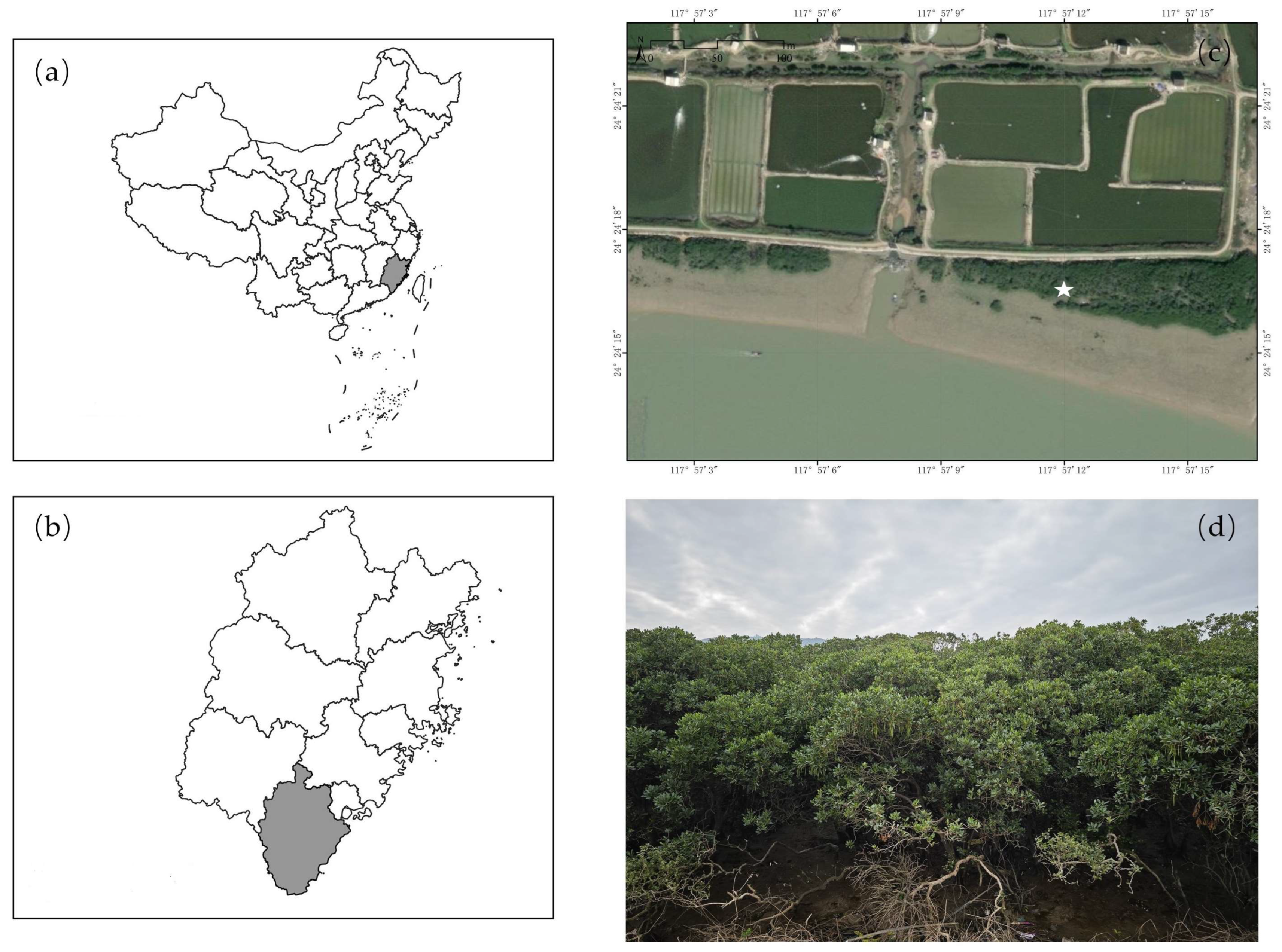
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Physiological and Biochemical Features of Kandelia obovata and Avicennia marina Leaves
2.4. Parameters’ Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
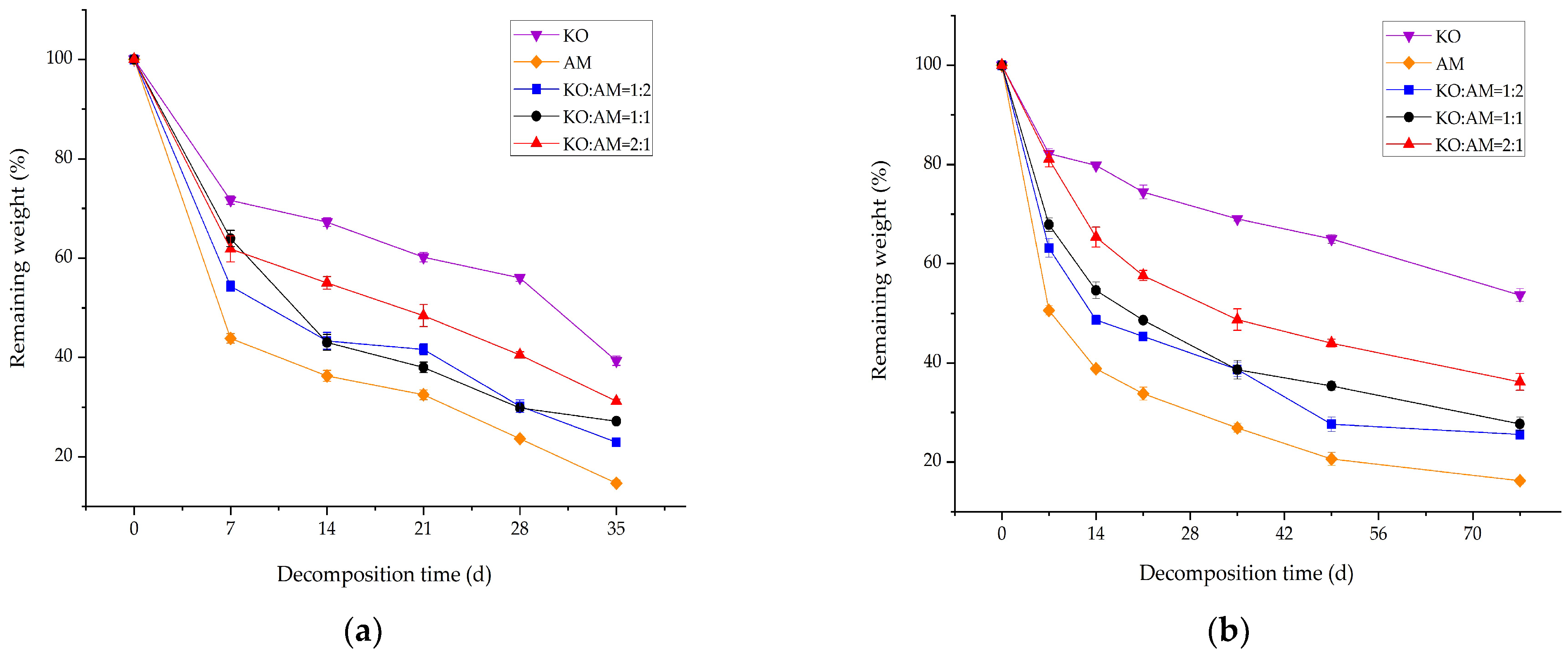
3.1. Remaining Weight of Mixed Litter Decomposition
3.2. Mathematical Model Fitting
3.3. Dynamic Changes in C and N from Mixed-Litter Decomposition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellison, A.M.; Farnsworth, E.J.; Merkt, R.E. Origins of mangrove ecosystems and the mangrove biodiversity anomaly. Golb. Ecol. Biogeogr. 1999, 8, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton-Grier, A.E.; Sandifer, P.A. Conservation of wetlands and other coastal ecosystems: A commentary on their value to protect biodiversity, reduce disaster impacts, and promote human health and well-being. Wetlands 2019, 39, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkur, R.; Kantamaneni, K.; Bokhoree, C.; Ravan, S. Mangroves’ role in supporting ecosystem-based techniques to reduce disaster risk and adapt to climate change: A review. J. Sea. Res. 2023, 196, 102449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Dong, K.; Tang, Y.; Huang, H.; Peng, G.; Wang, D. Research progress on the decomposition process of plant litter in wetlands: A review. Water 2023, 15, 3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayambaje, P.; Zhang, T.; Wei, L.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, C. Decomposition and nutrient release into water from litter mixtures of coastal wetland species. Wetlands 2022, 42, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.B.; Rizzo, A.E.; Couto, E.D.C.G. Assessing decomposition rates of Rhizophora mangle and Laguncularia racemosa leaves in a tropical mangrove. Estuar. Coast. 2013, 36, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidala, H.P.; Ganguly, D.; Purvaja, R.; Singh, G.; Das, S.; Rao, M.N.; Ramesh, R. Interspecific variations in leaf litter decomposition and nutrient release from tropical mangroves. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 116902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Cruz, Y.; García-Franco, J.G.; Zotz, G. Litter-trapping tank bromeliads in five different forests: Carbon and nutrient pools and fluxes. Biotropica 2022, 54, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyaningsih, A.P.; Deanova, A.K.; Pristiawati, C.M. Causes and impacts of anthropogenic activities on mangrove deforestation and degradation in Indonesia. Int. J. Bonorowo Wetl. 2022, 12, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Liang, G.; Yang, W.; Zhu, J.; Han, T.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M. Patterns and driving factors of litter decomposition across Chinese terrestrial ecosystems. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.P.; Mohan, M. Litter decomposition in forest ecosystems: A review. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2017, 2, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Bruelheide, H.; Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Zhang, N.; Ma, K. What drives leaf litter decomposition and the decomposer community in subtropical forests–the richness of the above-ground tree community or that of the leaf litter? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giweta, M. Role of litter production and its decomposition, and factors affecting the processes in a tropical forest ecosystem: A review. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, R.; Peng, X.; Hou, C.; Ma, J.; Guo, J. Contributions of plant litter decomposition to soil nutrients in ecological tea gardens. Agriculture 2022, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purahong, W.; Kapturska, D.; Pecyna, M.J.; Schulz, E.; Schloter, M.; Buscot, F. Influence of different forest system management practices on leaves litter decomposition rates, nutrient dynamics and the activity of ligninolytic enzymes: A case study from Central European forests. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria-Naranjo, M.; Sibaja-Cordero, J.A.; Cortés, J. Mangrove leaf litter decomposition in a seasonal tropical environment. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadio, H.K.; Koné, A.W.; Touré, G.P.T.; Konan, L.N.; Yapo, G.R.; Abobi, H.D. Litter decomposition in the mixed Chromolaena odorata (Asteraceae, herbaceous)-Cajanus cajan (Fabaceae, ligneous) fallow: Synergistic or antagonistic mixing effect? Agrofor. Syst. 2023, 97, 1525–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.G.; Colpo, K.D. Leaf-litter decomposition of the mangrove species Avicennia schaueriana, Laguncularia racemosa and Rhizophora mangle. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2014, 94, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchewaboripont, V.; Poungparn, S.; Patanaponpaiboon, P. Zonal variation in leaf-litter decomposition in a secondary mangrove forest. Tropics 2011, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajun, X.; Yonghong, X.; Xinsheng, C.; Feng, L.; Zhiyong, H.; Xu, L. Non-additive effects of water availability and litter quality on decomposition of litter mixtures. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2016, 31, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M.; Pfitzner, J.; Trott, L.A.; Tirendi, F.; Dixon, P.; Klumpp, D.W. Rapid sediment accumulation and microbial mineralization in forests of the mangrove Kandelia obovata in the Jiulongjiang Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. S. 2005, 63, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.P. The Geochemical Characteristics of Nutrient Elements in River Water in Jiulongjiang Basin; China University of Geosciences Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Guo, R.; Zhang, N.; Yang, S.; Cao, W. Soil organic carbon storages and bacterial communities along a restored mangrove soil chronosequence in the Jiulong River Estuary: From tidal flats to mangrove afforestation. Fundam. Res. 2023, 3, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, Z.; Du, B.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y. Bacterial communities in sediments of the shallow Lake Dongping in China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheue, C.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Yong, J.W. Kandelia obovata (Rhizophoraceae), a new mangrove species from Eastern Asia. Taxonomy 2003, 52, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Q.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. Phenolic metabolism and related heavy metal tolerance mechanism in Kandelia Obovata under Cd and Zn stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe. 2019, 169, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, T.L.; Peakall, R.; Saenger, P. Comparative analysis of genetic diversity in the mangrove species Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh.(Avicenniaceae) detected by AFLPs and SSRs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, S.; Palit, P.K. Anatomical and physiological adaptations of mangroves. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.S. Energy storage and the balance of producers and decomposers in ecological systems. Ecology 1963, 44, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OriginPro. OriginLab Corporation; OriginPro: Northampton, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- IBM SPSS Statistics, Version 24; IBM Corporation: Armonk, NY, USA, 2019.
- Rezende, R.D.S.; Pinto, M.D.O.; Gonçalves, J.F., Jr.; Petrucio, M.M. The effects of abiotic variables on detritus decomposition in Brazilian subtropical mangroves. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2013, 25, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastias, E.; Sponseller, R.A.; Bundschuh, M.; Jonsson, M. Seasonal variation in the coupling of microbial activity and leaf litter decomposition in a boreal stream network. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 812–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, G.; Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z. Non-additive effects of leaf litter mixtures from Robinia pseudoacacia and ten tree species on soil properties. J. Sustain. Forest. 2020, 39, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ye, Y. Dynamics of decomposition and nutrient release of leaf litter in Kandelia obovata mangrove forests with different ages in Jiulongjiang Estuary, China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Wang, Y.S.; Su, B.Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Chang, L.F.; Ma, X.Y.; Li, X.M. Ecophysiological responses of five mangrove species (Bruguiera gymnorrhiza, Rhizophora stylosa, Aegiceras corniculatum, Avicennia marina, and Kandelia obovata) to chilling stress. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 846566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, M.U.F. Will changes in soil organic carbon act as a positive or negative feedback on global warming? Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Chen, Z.; Lin, G. Significant but short time assimilation of organic matter from decomposed exotic Spartina alterniflora leaf litter by mangrove polychaetes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 259, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.C.; Kang, H.X.; Wei, J.; Gao, C.J.; Hussain, M.; Fu, Y.J.; Lang, T. Microcosm study on fate and dynamics of mangrove tannins during leaf litter leaching. Ecol. Process. 2023, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, B.; Sietiö, O.M.; Straková, P. Plant roots increase both decomposition and stable organic matter formation in boreal forest soil. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Grootemaat, S.; Verheijen, L.M. Are litter decomposition and fire linked through plant species traits? New Phytol. 2017, 216, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraglia, A.; Cacciatori, C.; Chelli, S. Litter decomposition: Effects of temperature driven by soil moisture and vegetation type. Plant Soil. 2019, 435, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, D.; Chen, Z. Substrates quality and soil environmental conditions predict litter decomposition and drive soil nutrient dynamics following afforestation on the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2018, 325, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Beiyuan, J. Multifunctional applications of biochar beyond carbon storage. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 150–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, C.A.; Trumbore, S.E.; Davidson, E.A. Sensitivity of decomposition rates of soil organic matter with respect to simultaneous changes in temperature and moisture. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Niu, J.; Fang, H.; Feng, Y.; Bai, T.; Zhang, L. Moso bamboo expansion reduced soil N2O emissions while accelerated fine root litter decomposition: Contrasting non-additive effects. Plant Soil. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaou, D.; Gros, R.; Baldy, V.; Adotévi, A.; Gaboriau, M.; Estevez, Y.; Bousquet-Mélou, A. Comparison of leaf litter decomposition and microbial decomposer communities in fringe and riverine mangroves in French Guiana. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2022, 22, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment Group | Abbreviation | Weight of Samples (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-species treatments | Kandelia obovata | KO | KO = 36 | |
| Avicennia marina | AM | AM = 36 | ||
| Mixed-species treatments | Kandelia obovata:Avicennia marina =1:2 | KO:AM = 1:2 | KO = 12 | AM = 24 |
| Kandelia obovata:Avicennia marina =1:1 | KO:AM = 1:1 | KO = 18 | AM = 18 | |
| Kandelia obovata:Avicennia marina =2:1 | KO:AM = 2:1 | KO = 24 | AM = 12 | |
| Season | Treatment Group | Olson Model (Coefficient, Day−1) | Correlation Coefficient (R) | R2 | Observed Rates (k) | Calculated Rates (k’) | T50 (Day) | T95 (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | KO | ㏑R = −0.0645–0.0225t | 0.9593 | 0.9202 ** | 0.0225 d | - | 27.9 | 130.3 |
| AM | ㏑R = −0.2287–0.0471t | 0.9604 | 0.9223 ** | 0.0471 a | - | 9.9 | 58.8 | |
| KO:AM = 1:2 | ㏑R = −0.1773–0.0374t | 0.9655 | 0.9322 ** | 0.0374 b | 0.0353 | 13.8 | 75.4 | |
| KO:AM = 1:1 | ㏑R = −0.1574–0.0364t | 0.9680 | 0.9370 ** | 0.0364 b | 0.0321 | 14.7 | 78.0 | |
| KO:AM = 2:1 | ㏑R = −0.1293–0.0295t | 0.9718 | 0.9444 ** | 0.0295 c | 0.0289 | 20.1 | 104.8 | |
| Winter | KO | ㏑R = −0.1015–0.0070t | 0.9643 | 0.9299 ** | 0.0070 d | - | 84.5 | 413.5 |
| AM | ㏑R = −0.4684–0.0204t | 0.9104 | 0.8288 ** | 0.0204 a | - | 11.0 | 123.9 | |
| KO:AM = 1:2 | ㏑R = −0.3320–0.0160t | 0.9122 | 0.8322 ** | 0.0160 b | 0.0159 | 22.6 | 166.5 | |
| KO:AM = 1:1 | ㏑R = −0.2813–0.0149t | 0.9292 | 0.8635 ** | 0.0149 bc | 0.0137 | 27.6 | 182.2 | |
| KO:AM = 2:1 | ㏑R = −0.1741–0.0124t | 0.9460 | 0.8950 ** | 0.0124 c | 0.0115 | 41.9 | 227.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, Z.; Ma, L. Decomposition and Variation in Carbon and Nitrogen of Leaf Litter Mixtures in a Subtropical Mangrove Forest. Forests 2024, 15, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040672
Wang Y, Li D, Lu Z, Ma L. Decomposition and Variation in Carbon and Nitrogen of Leaf Litter Mixtures in a Subtropical Mangrove Forest. Forests. 2024; 15(4):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040672
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi, Danyang Li, Zhiqiang Lu, and Li Ma. 2024. "Decomposition and Variation in Carbon and Nitrogen of Leaf Litter Mixtures in a Subtropical Mangrove Forest" Forests 15, no. 4: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040672
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, D., Lu, Z., & Ma, L. (2024). Decomposition and Variation in Carbon and Nitrogen of Leaf Litter Mixtures in a Subtropical Mangrove Forest. Forests, 15(4), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040672





