Effect of Heat Treatment on Hygroscopicity of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata [Lamb.] Hook.) Wood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dynamic Vapor Sorption (DVS) Experiments
- Moisture absorption and desorption:
- Hysteresis ratio:
- GAB model:
- The internal specific surface area (SGAB):
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Vapor Sorption Behavior of the Samples
3.2. Moisture Adsorption and Desorption Rate
3.3. Effect of Heat Treatment on Sorption Hysteresis
3.4. Fitting the GAB Model to the Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaziri, M.; Karlsson, O.; Abrahamsson, L.; Lin, C.-F.; Sandberg, D. Wettability of welded wood-joints investigated by the Wilhelmy method: Part 1. Determination of apparent contact angles, swelling, and water sorption. Holzforschung 2021, 75, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, M.; Sandberg, D. Welding of Thermally Modified Wood and Thermal Modification of the Welded Wood: Effects on the Shear Strength under Climatic Conditions. BioResources 2021, 16, 3224–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, M.; Dreimol, C.; Abrahamsson, L.; Niemz, P.; Sandberg, D. Water-vapour sorption of welded bond-line of European beech and Scots pine. Holzforschung 2023, 77, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.S. Wood Modification: Chemical, Thermal and Other Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 99–127. [Google Scholar]
- Thygesen, L.G.; Elder, T. Moisture in untreated, acetylated, and furfurylated norway spruce monitored during drying below fiber saturation using time domain NMR. Wood Fiber Sci. 2009, 41, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H. Effects of chemical modification on the mechanical properties of wood. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2013, 71, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Builes, J.F.; Sepúlveda-Villarroel, V.; Osorio, J.A.; Salvo-Sepúlveda, L.; Ananías, R.A. Effect of Thermal Modification Treatment on Some Physical and Mechanical Properties of Pinus oocarpa Wood. Forests 2021, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Lyu, J. Water Absorption Properties in Transverse Direction of Heat-Treated Chinese Fir Wood Determined Using TD-NMR. Forests 2021, 12, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Altgen, M.; Rautkari, L. Thermal modification of wood—A review: Chemical changes and hygroscopicity. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 6581–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ding, T.; Shi, J.; Du, J. Effect of heating rate on microstructure and selected physical and mechanical properties of heat-treated Mongolian oak wood. J. For. Eng. 2023, 8, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tjeerdsma, B.F.; Militz, H. Chemical changes in hydrothermal treated wood: FTIR analysis of combined hydrothermal and dry heat-treated wood. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2005, 63, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altgen, M.; Hofmann, T.; Militz, H. Wood moisture content during the thermal modification process affects the improvement in hygroscopicity of Scots pine sapwood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windeisen, E.; Strobel, C.; Wegener, G. Chemical changes during the production of thermo-treated beech wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Iruela, A.; Esteban, L.G.; Fernández, F.G.; Palacios, P.D.; Eugenio, M.E. Changes in cell wall components and hygroscopic properties of Pinus radiata caused by heat treatment. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2021, 79, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altgen, M.; Altgen, D.; Klueppel, A.; Rautkari, L. Effect of curing conditions on the water vapor sorption behavior of melamine formaldehyde resin and resin-modified wood. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 11253–11266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humar, M.; Repi, R.; Krinik, D.; Lesar, B.; Rep, G. Quality Control of Thermally Modified Timber Using Dynamic Vapor Sorption (DVS) Analysis. Forests 2020, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaludin, Z.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xie, Y.; Samsi, H.W.; Husain, H.; Awang, K.; Curling, S.F. Analysis of the water vapour sorption isotherms of thermally modified acacia and sesendok. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 5, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.S.; Ramsay, J.; Laine, K.; Rautkari, L.; Hughes, M. Water vapour sorption behaviour of thermally modified wood. J. Inst. Wood Sci. 2013, 4, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.F.; Calonego, F.W.; Bond, B.H.; Severo, E.T.D. Color Changes, EMC and Biological Resistance of Thermally Modified Yellow Poplar. Wood Fiber Sci. 2018, 50, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytner, O.; Laskowska, A.; Drodek, M.; Kozakiewicz, P.; Zawadzki, J. Evaluation of the Dimensional Stability of Black Poplar Wood Modified Thermally in Nitrogen Atmosphere. Materials 2021, 14, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautkari, L.; Curling, S.; Jalaludin, Z.; Ormondroyd, G. What is the role of the accessibility of wood hydroxyl groups in controlling moisture content? J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 6352–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.S.; Keating, B.; Laine, K.; Rautkari, L.; Hughes, M.; Constant, B. The water vapour sorption properties of thermally modified and densified wood. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 3191–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, K.; Obataya, E.; Zeniya, N.; Matsuo, M. Effects of heating humidity on the physical properties of hydrothermally treated spruce wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, J.; Jiang, J. Increased dimensional stability of Chinese fir through steam-heat treatment. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2011, 70, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratasz, Ł.; Kozłowska, A.; Kozłowski, R. Analysis of water adsorption by wood using the Guggenheim-Anderson-de Boer equation. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2012, 70, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.; Everett, D.; Haul, R.; Moscou, L.; Pierotte, R.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity Pure and Applied Chemistry. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, L.G.; Engelund, E.T.; Hoffmeyer, P. Water sorption in wood and modified wood at high values of relative humidity. Part I: Results for untreated, acetylated, and furfurylated Norway spruce. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olek, W.; Majka, J.; Czajkowski, Ł. Sorption isotherms of thermally modified wood. Holzforschung 2013, 67, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, L.X.; Takayama, M.; Shida, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Aoyagi, T. Determination of the accessible hydroxyl groups in heat-treated Styrax tonkinensis (Pierre) Craib ex Hartwich wood by hydrogen-deuterium exchange and 2H NMR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 2007, 61, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Study on Properties and Mechanism of Larch Wood Modified by Vacuum Heat Treatment; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Simón, C.; Fernández, F.G.; Esteban, L.G.; Palacios, P.D.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Mai, C. Comparison of the saturated salt and dynamic vapor sorption methods in obtaining the sorption properties of Pinus pinea L. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2017, 75, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.S.; Norton, A.J.; Newman, G. The water vapour sorption properties of Sitka spruce determined using a dynamic vapour sorption apparatus. Wood Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Wang, C.; Peng, W. A theoretical study of moisture sorption behavior of heat-treated pine wood using Raman spectroscopic analysis. J. For. Eng. 2016, 1, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Engelund, E.T.; Thygesen, L.G.; Hoffmeyer, P. Water sorption in wood and modified wood at high values of relative humidity. Part 2: Appendix. Theoretical assessment of the amount of capillary water in wood microvoids. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelund, E.T.; Thygesen, L.G.; Svensson, S.; Hill, C.A.S. A critical discussion of the physics of wood–water interactions. Wood Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpourpia, R.; Adamopoulos, S.; Holstein, N.; Mai, C. Dynamic vapour sorption and water-related properties of thermally modified Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) wood pre-treated with proton acid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 138, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, L.G.; Simón, C.; Fernández, F.G.; Palacios, P.D.; Martín-Sampedro, R.; Eugenio, M.E.; Hosseinpourpia, R. Juvenile and mature wood of Abies pinsapo Boissier: Sorption and thermodynamic properties. Wood Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskan, M.; Göǧüş, F. The fitting of various models to water sorption isotherms of pistachio nut paste. J. Food Eng. 1997, 33, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
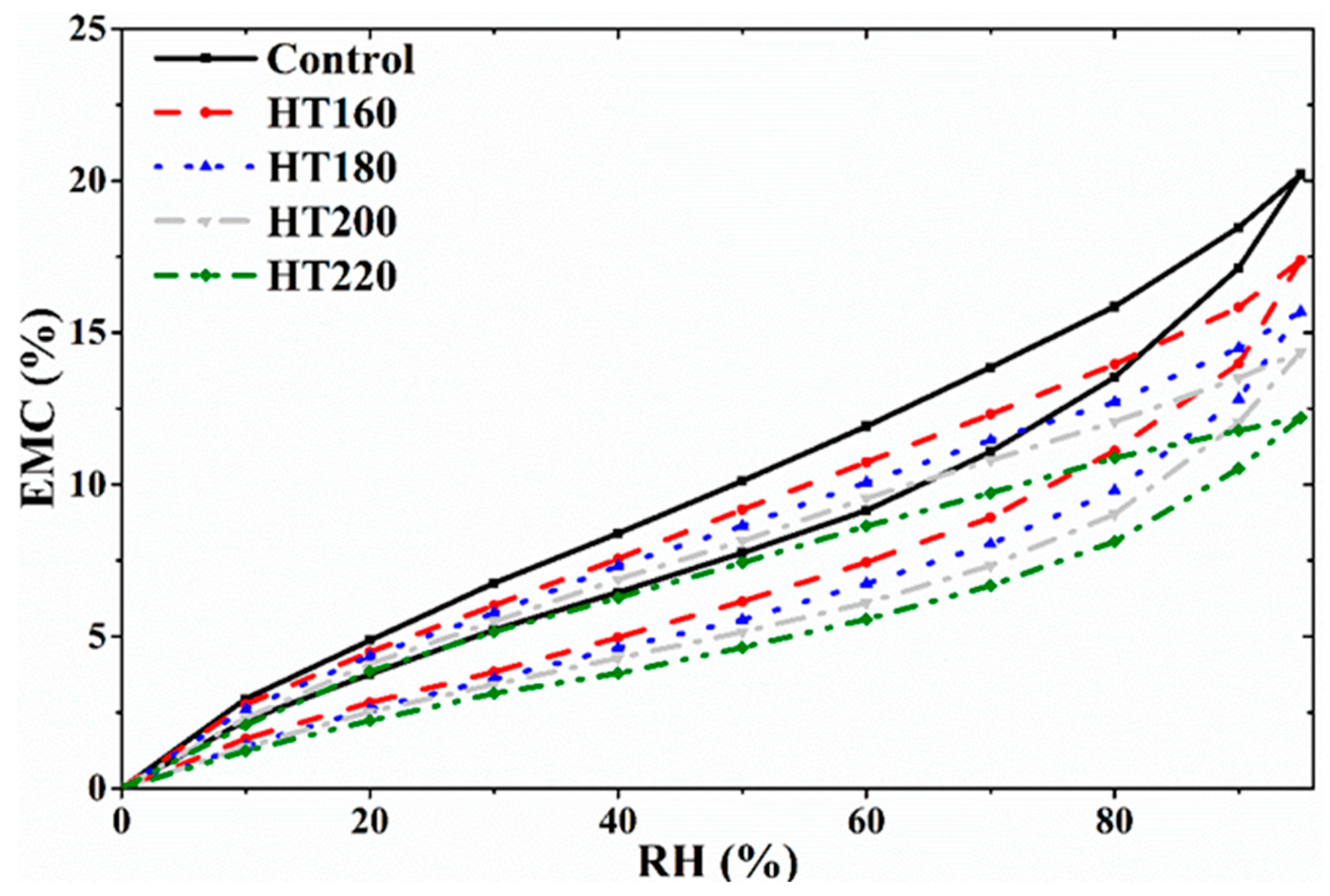
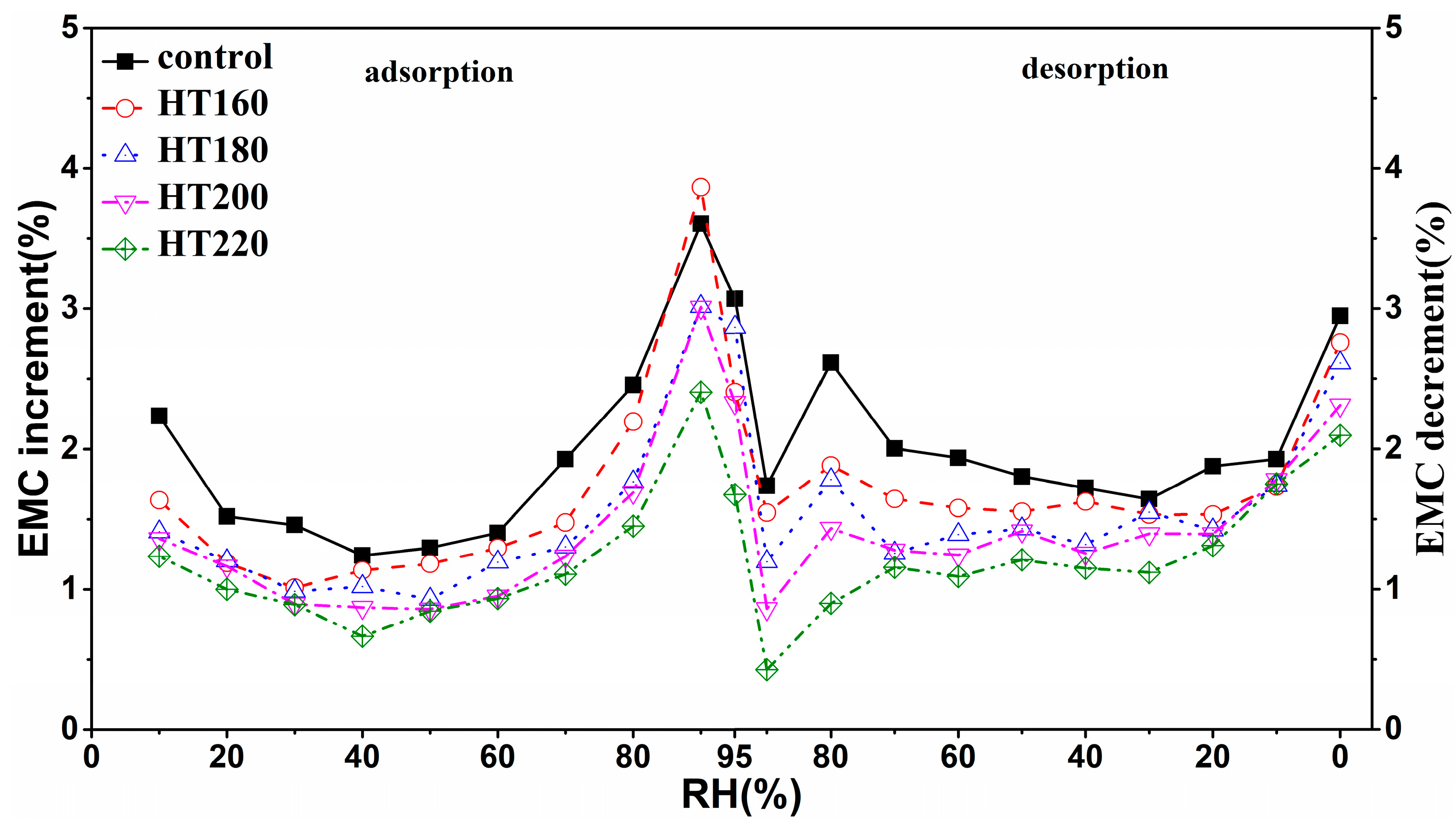
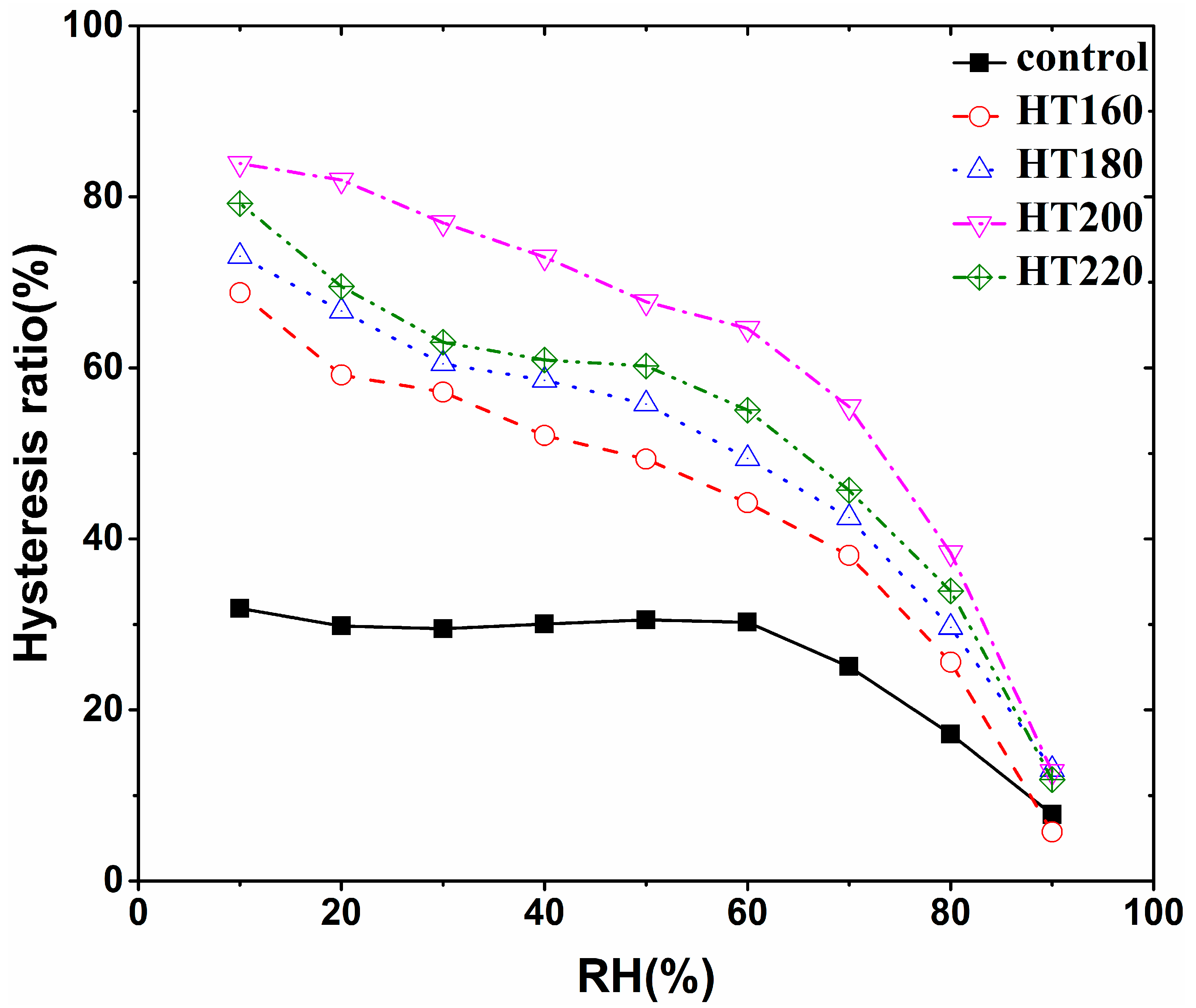
| Relative Humidity/% | Source | DF | SS | MS | F Value | Sign. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | Inter-group | 4 | 7.362 | 1.840 | 42.531 | * |
| Intra-group | 10 | 0.433 | 0.043 | |||
| Total | 14 | 7.795 | ||||
| 60 | Inter-group | 4 | 23.250 | 5.812 | 211.933 | * |
| Intra-group | 10 | 0.274 | 0.027 | |||
| Total | 14 | 23.524 | ||||
| 95 | Inter-group | 4 | 110.381 | 27.595 | 572.804 | * |
| Intra-group | 10 | 0.482 | 0.048 | |||
| Total | 14 | 110.863 |
| Temperature/°C | 30% RH | 60% RH | 95% RH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMC/% | Duncan Grouping | EMC/% | Duncan Grouping | EMC/% | Duncan Grouping | |
| Control | 5.21 | A | 9.15 | A | 20.21 | A |
| 160 | 3.83 | A | 7.44 | B | 17.38 | B |
| 180 | 3.60 | AB | 6.74 | C | 15.69 | C |
| 200 | 3.42 | B | 6.10 | D | 14.36 | D |
| 220 | 3.26 | C | 5.57 | E | 12.20 | E |
| Treated-Temperature/°C | Mm (%) | K | C | R2 | SGAB (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 5.73 | 0.7651 | 7.38665 | 0.999 | 219 |
| 160 | 4.47 | 0.78991 | 6.46471 | 0.997 | 171 |
| 180 | 3.96 | 0.79440 | 7.04448 | 0.998 | 152 |
| 200 | 3.58 | 0.79874 | 7.86002 | 0.998 | 137 |
| 220 | 3.51 | 0.76497 | 6.67798 | 0.999 | 134 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Lyu, J. Effect of Heat Treatment on Hygroscopicity of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata [Lamb.] Hook.) Wood. Forests 2024, 15, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040630
Gao Y, Li Z, Zhao L, Lyu J. Effect of Heat Treatment on Hygroscopicity of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata [Lamb.] Hook.) Wood. Forests. 2024; 15(4):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040630
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yulei, Zhu Li, Liyuan Zhao, and Jianxiong Lyu. 2024. "Effect of Heat Treatment on Hygroscopicity of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata [Lamb.] Hook.) Wood" Forests 15, no. 4: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040630
APA StyleGao, Y., Li, Z., Zhao, L., & Lyu, J. (2024). Effect of Heat Treatment on Hygroscopicity of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata [Lamb.] Hook.) Wood. Forests, 15(4), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040630






