Root Distribution and Water Uptake Applied by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes for Lianas in Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.2.1. Root Distribution Experiment
2.2.2. Stable Isotope Experiment
2.2.3. Meteorological and Hydrological Factors Observation
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Meteorological and Hydrological Factors
3.2. Root Distribution
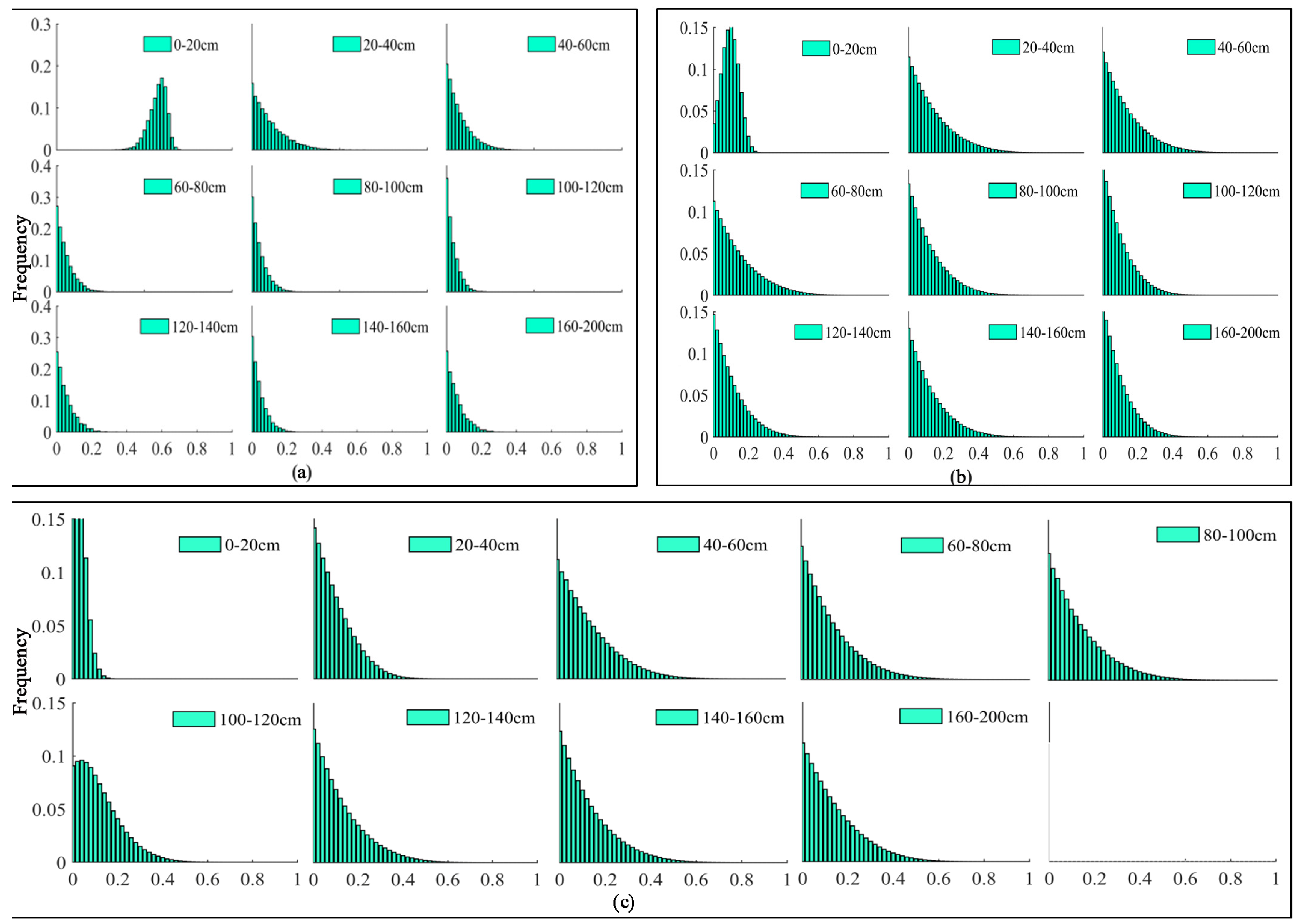
3.2.1. Vertical Root Distribution
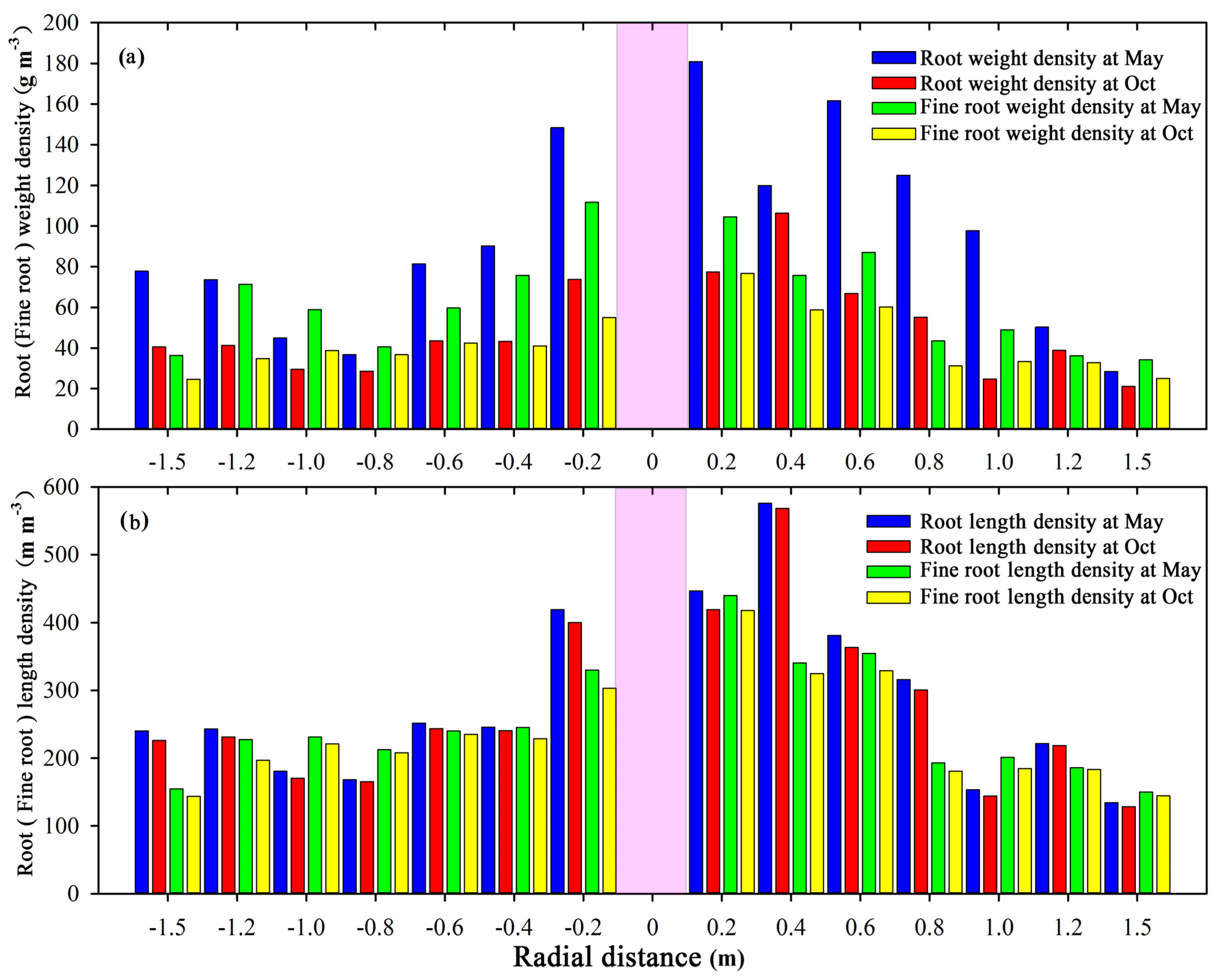
3.2.2. Horizontal Root Distribution
3.3. Water Uptake of Grapevines
3.3.1. Soil Water Content
3.3.2. Isotopes in Different Soil Depths and Xylem Water
3.3.3. Proportional Contributions of Soil Water
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodge, A. The plastic plant: Root responses to heterogeneous supplies of nutrients. New Phytol. 2004, 162, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, H.J. Vertical vegetation structure below ground: Scaling from root to globe. Prog. Bot. 2005, 66, 341–373. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, J.M.; Hanson, P.J.; Iversen, C.M.; Kumar, J.; Walker, A.P.; Wullschleger, S.D. Root structural and functional dynamics in terrestrial biosphere models—Evaluation and recommendations. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porporato, A.; Daly, E.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Fagan, W.F. Soil water balance and ecosystem response to climate change. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Tang, X.; Zhao, P.; Tang, J. Dynamics of water uptake by maize on sloping farmland in a shallow entisol in southwest china. Catena 2016, 147, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Xi, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, A. Hydraulic redistribution of soil water by roots of two desert riparian phreatophytes in northwest china’s extremely arid region. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.H.; Wu, P.T.; Wang, X. Root distribution chrono sequence of a dense dwarfed jujube plantation in the semiarid hilly region of the chinese loess plateau. J. For. Res. 2014, 19, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.T.; Kirchner, J.W.; Braun, S.; Siegwolf, R.; Goldsmith, G.R. Seasonal origins of soil water used by trees. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019, 23, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Canadell, J.G.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Mooney, H.A.; Schulze, E.D. A global analysis of root distributions for terrestrial biomes. Oecologia 1996, 108, 389–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teste, F.P.; Marchesini, V.A.; Veneklaas, E.J.; Dixon, K.W.; Lambers, H. Root dynamics and survival in a nutrient-poor and species-rich woodland under a drying climate. Plant Soil 2018, 424, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R. Some results on oxygen isotope stratigraphy in the deep drilling at king baudouin station, antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galewsky, J.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Field, R.D.; Worden, J.; Risi, C.; Schneider, M. Stable isotopes in atmospheric water vapor and applications to the hydrologic cycle. Rev. Geoph. 2016, 54, 809–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Song, X. Using stable isotopes to determine seasonal variations in water uptake of summer maize under different fertilization treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Nan, L.; Li, Z. Seasonal variation in water uptake patterns of three plant species based on stable isotopes in the semi-arid loess plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, P.; Liang, C.; Li, T.; Zhou, B. Understanding the rapidity of subsurface storm flow response from a fracture-oriented shallow vadose through a new perspective. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E.; Ehleringer, J.R. Streamside trees that do not use stream water. Nature 1991, 350, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, J.P.; Walker, G.R.; Dighton, J.C.; Monteny, B. Use of stable isotopes of water to determine the origin of water used by the vegetation and to partition evapotranspiration. a case study from hapex-sahel. J. Hydrol. 1997, 188, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.E.; Mambelli, S.; Plamboeck, A.H.; Templer, P.H.; Tu, K.P. Stable isotopes in plant ecology. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 507–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, L.; Barbante, C.; Barnes, P.R.; Barnola, J.M.; Bigler, M.; Castellano, E.; Cattani, O.; Chappellaz, J.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Delmonte, B.; et al. Eight glacial cycles from an antarctic ice core. Nature 2004, 429, 623–628. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Y.; Edmunds, W.M.; Ding, Z.; He, J. The composition and distribution of chemicals and isotopes in precipitation in the shiyang river system, northwestern china. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436–437, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.G.; Mosley-Thompson, E.; Davis, M.E.; Zagorodnov, V.S.; Howat, I.M.; Mikhalenko, V.N.; Lin, P.N. Annually resolved ice core records of tropical climate variability over the past ~1800 years. Science 2013, 340, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S. Preliminary research on hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope characteristics of different water bodies in the qilian mountains, northwestern tibetan plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Lu, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Water use characteristics of native and exotic shrub species in the semi-arid loess plateau using an isotope technique. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 276, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; HChen Zou, Q.; Nie, Y. Divergent root water uptake depth and coordinated hydraulic traits among typical karst plantations of subtropical China: Implication for plant water adaptation under precipitation changes. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 249, 106798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. Insights into the isotopic mismatch between bulk soil water and salix matsudana koidz trunk water from root water stable isotope measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3975–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.R.; Barnard, H.R.; Coulombe, R.; Mcdonnell, J.J. Ecohydrologic separation of water between trees and streams in a mediterranean climate. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Duan, W.; Li, H. Dry season water uptake by two dominant canopy tree species in a tropical seasonal rainforest of Xishuangbanna, SW China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Song, X.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. A study of root water uptake of crops indicated by hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes: A case in Shanxi Province, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, T.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Ding, R.; Tong, L. Quantification of maize water uptake from different layers and root zones under alternate furrow irrigation using stable oxygen isotope. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 168, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; He, B.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, X.Y. Determining root water uptake of two alpine crops in a rainfed cropland in the Qinghai Lake watershed: First assessment using stable isotopes analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 215, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, F.; Ai, Z.; Li, J.; Gu, C. Stable isotope evidences for identifying crop water uptake in a typical winter wheat–summer maize rotation field in the north China plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehemy, M.F.; Benettin, P.; Asadollahi, M.; Pratt, D.; Mcdonnell, J. How plant water status drives tree source water partitioning. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mennekes, D.; Rinderer, M.; Seeger, S.; Orlowski, N. Ecohydrological travel times derived from in situ stable water isotope measurements in trees during a semi-controlled pot experiment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 4513–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Tetzlaff, D.; Landgraf, J.; Dubbert, M.; Soulsby, C. Modelling temporal variability of in-situ soil water and vegetation isotopes reveals ecohydrological couplings in a willow plot. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 2465–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.L.; Gregg, J.W. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too many sources. Oecologia 2003, 136, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Zheng, X.J.; Tang, L.S.; Li, Y. Stable oxygen isotopes reveal distinct water use patterns of two haloxylon species in the gurbantonggut desert. Plant Soil 2015, 389, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youri, R.; Mathieu, J. Reviews and syntheses: Isotopic approaches to quantify root water uptake: A review and comparison of methods. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2199–2224. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Friedman, J.M.; Hati, J.H.A.; Fang, G. Use of 2H and 18O stable isotopes to investigate water sources for different ages of Populus euphratica, along the lower Heihe River. Ecol. Res. 2015, 30, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeta, A.; Peñuelas, J. Relative contribution of groundwater to plant transpiration estimated with stable isotopes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W.; Semmens, B.X. Incorporating uncertainty and prior information into stable isotope mixing models. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Phillips, D.L.; Bearhop, S.; Semmens, B.X.; Ward, E.J.; Moore, J.W.; Jackson, A.L.; Grey, J.; Kelly, D.J.; Inger, R. Bayesian stable isotope mixing models. Environmetrics 2013, 24, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Seasonal variations in depth of water uptake for a subtropical coniferous plantation subjected to drought in an East Asian monsoon region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 201, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyberg, J.V.; Allen, S.T.; Grossiord, C.; Dawson, T.E. Plant and root-zone water isotopes are difficult to measure, explain, and predict: Some practical recommendations for determining plant water sources. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1352–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, K.; Tucker, C.; Cable, J.M. Beyond simple linear mixing models: Process-based isotope partitioning of ecological processes. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, M.L.A.; de Jong van Lier, Q. Revisiting the Feddes reduction function for modeling root water uptake and crop transpiration. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, A.; Chaali, N.; Dragonetti, G.; Lamaddalena, N.; Comegna, A. Root uptake under non-uniform root-zone salinity. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 1363–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Difonzo, F.V.; Masciopinto, C.; Vurro, M.; Berardi, M. Shooting the Numerical Solution of Moisture Flow Equation with Root Water Uptake Models: A Python Tool. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Kodešová, R.; Šimůnek, J. Modeling the Translocation and Transformation of Chemicals in the Soil-Plant Continuum: A Dynamic Plant Uptake Module for the HYDRUS Model. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 8967–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Zuecco, G.; Geris, J.; Schwendenmann, L.; Penna, D. Depth distribution of soil water sourced by plants at the global scale: A new direct inference approach. Ecohydrology 2020, 13, e2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, D.; Buttle, J.; Carey, S.K.; Kohn, M.J.; Laudon, H.; Mcnamara, J.P.; Smith, A.; Sprenger, M.; Soulsby, C. Stable isotopes of water reveal differences in plant–soil water relationships across northern environments. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Irrigation depth far exceeds water uptake depth in an oasis cropland in the middle reaches of Heihe River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; He, J.; Qi, S.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, W.; Edmunds, W.M.; Zhao, Y. Groundwater recharge and evolution in the Dunhuang Basin, northwestern China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 28, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xia, D.; Ma, J.; Han, T.; Zhu, G. The characteristics of evapotranspiration and crop coefficients of an irrigated vineyard in arid Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.G.; Patrickson, S.J.; Ehleringer, J.R. Water extraction times for plant and soil materials used in stable isotope analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, H.; Iijima, M. Stable isotope analysis of water extraction from subsoil in upland rice (Oryza sativa L.) as affected by drought and soil compaction. Plant Soil 2007, 270, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, P.; Diels, J.; Vanderborght, J.; Elsen, F.; Elsen, A.; Deckers, T.; Vandendriessche, H. Numerical calculation of soil water potential in an irrigated ‘conference’ pear orchard. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, C. How do plants share water sources in a rubber-tea agroforestry system during the pronounced dry season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, P.D.; Chorover, J.; Fan, Y.; Godsey, S.E.; Maxwell, R.M.; Mcnamara, J.P.; Tague, C. Hydrological partitioning in the critical zone: Recent advances and opportunities for developing transferable understanding of water cycle dynamics. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 6973–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhu, G.; Bai, W.; Yuan, R.; Zhang, Y. Root Distribution and Water Uptake Applied by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes for Lianas in Northwest China. Forests 2024, 15, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040626
Wang S, Zhu G, Bai W, Yuan R, Zhang Y. Root Distribution and Water Uptake Applied by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes for Lianas in Northwest China. Forests. 2024; 15(4):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040626
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shangtao, Gaofeng Zhu, Wenwen Bai, Riping Yuan, and Yang Zhang. 2024. "Root Distribution and Water Uptake Applied by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes for Lianas in Northwest China" Forests 15, no. 4: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040626
APA StyleWang, S., Zhu, G., Bai, W., Yuan, R., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Root Distribution and Water Uptake Applied by Hydrogen and Oxygen Stable Isotopes for Lianas in Northwest China. Forests, 15(4), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040626




