Production of Bamboo Source Microbial Fertilizer and Evaluate Its Effect on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions in Moso Bamboo Plantations in South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of PGPB
2.2. Wastewater Collection and BBPW-Fertilizer Preparation
2.3. Optimization of Various Growth Parameters
2.4. Field Experiment and Soil Sample Preparation
2.5. Soil Fractions and Soil Sample Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
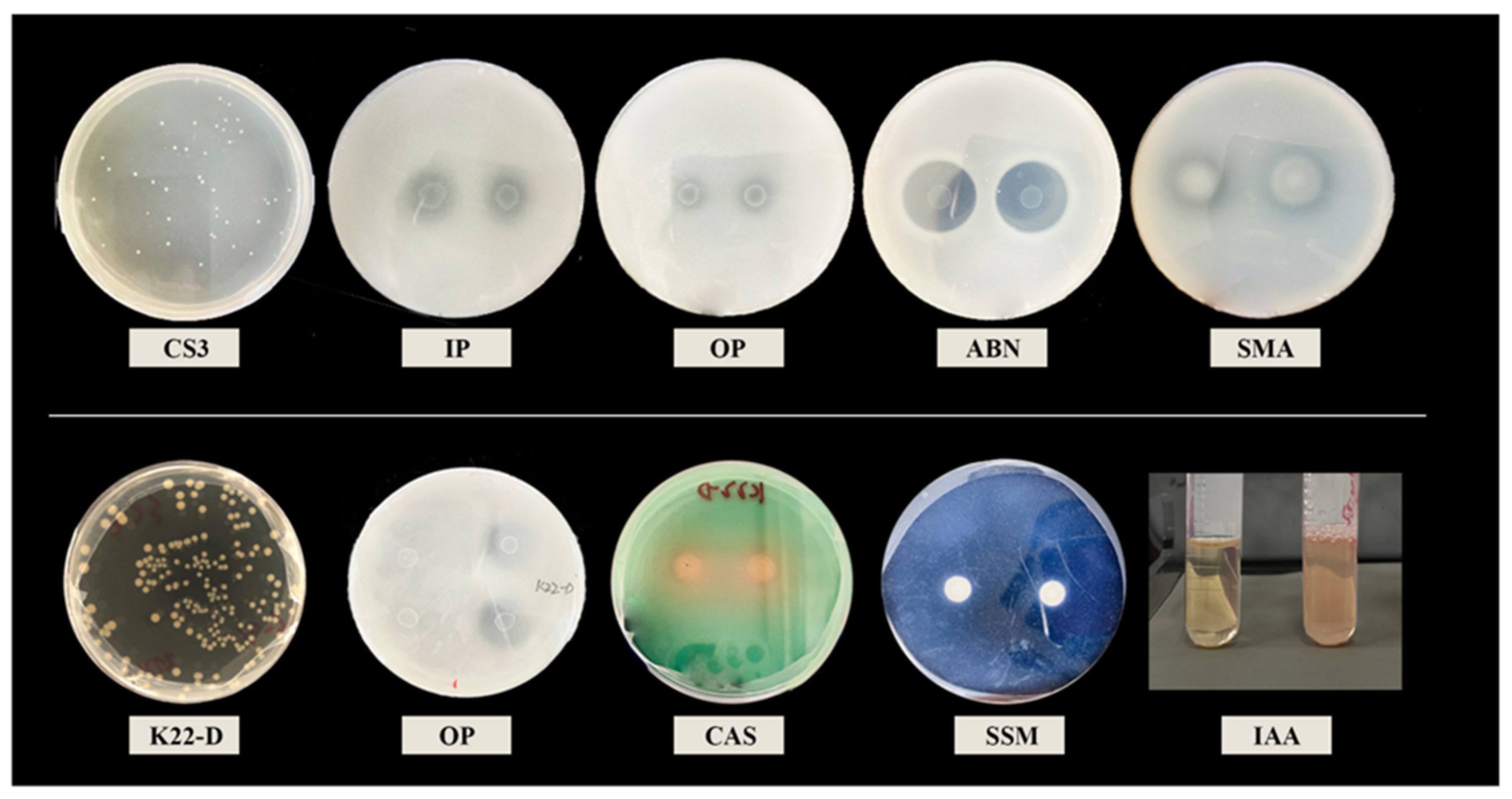
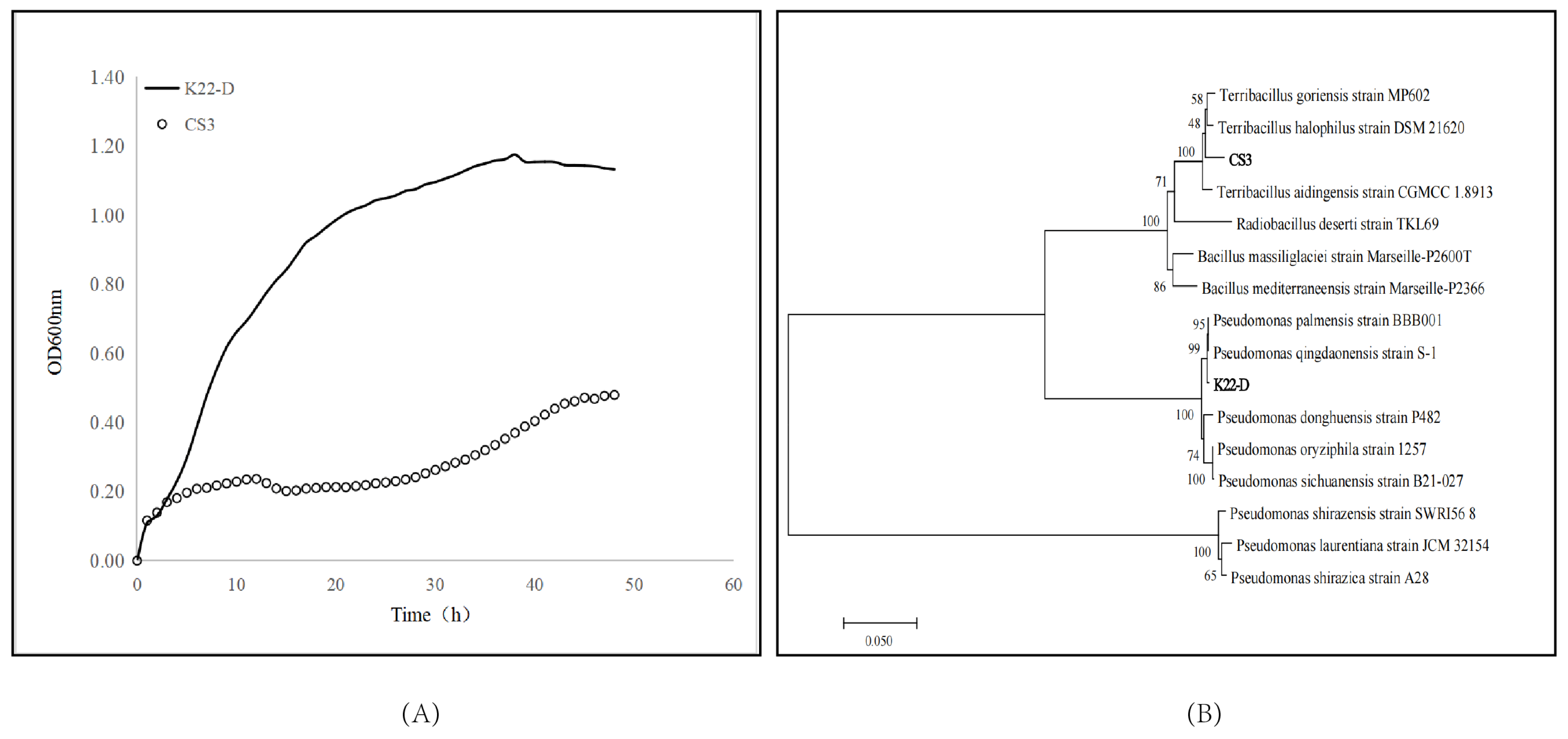
3.1. Isolation and Screening of PGPB
3.2. Optimization of CS3 and K22-D Culture Conditions
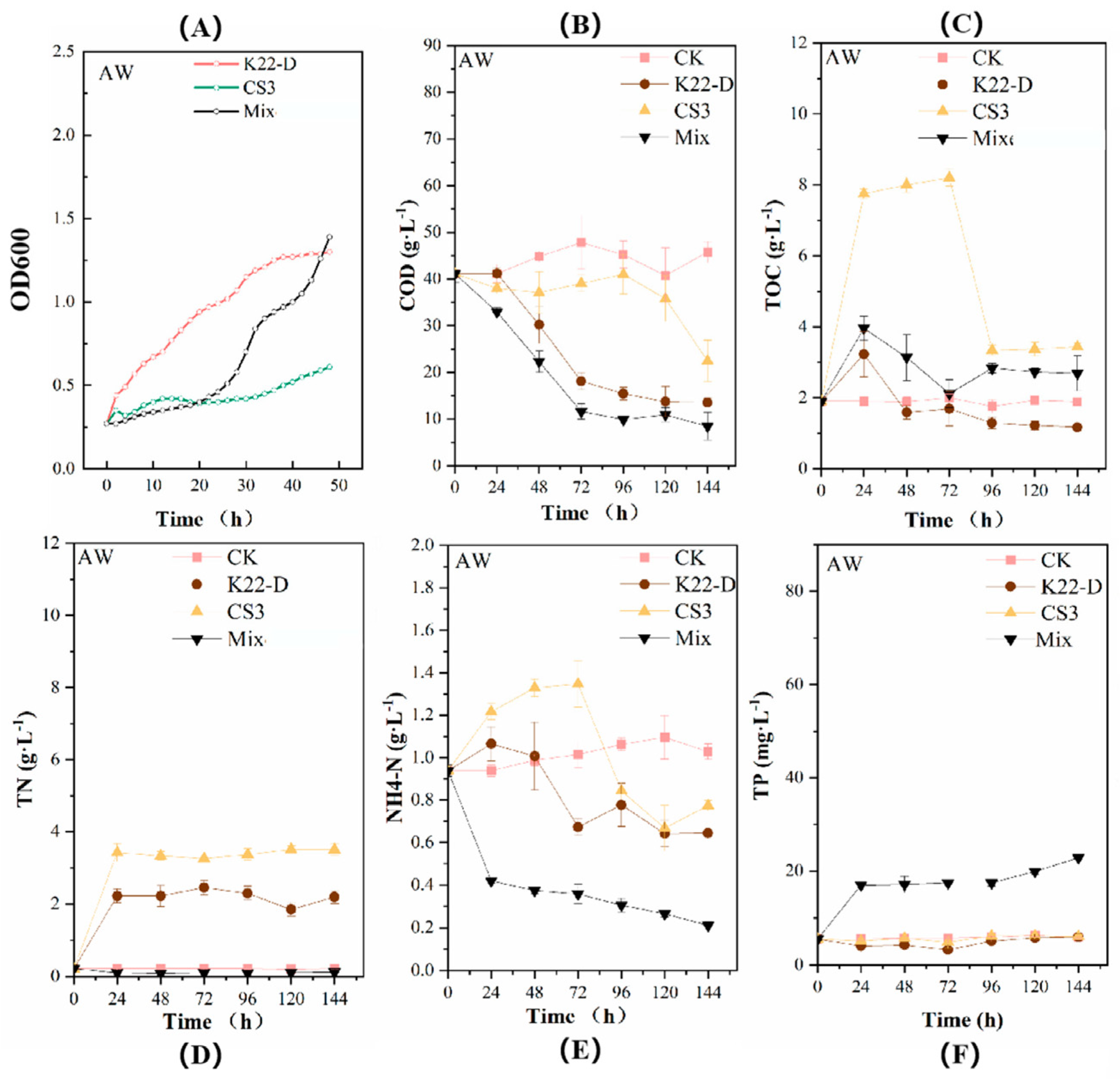
3.3. Biological Treatment of the Bamboo Shoot Wastewater
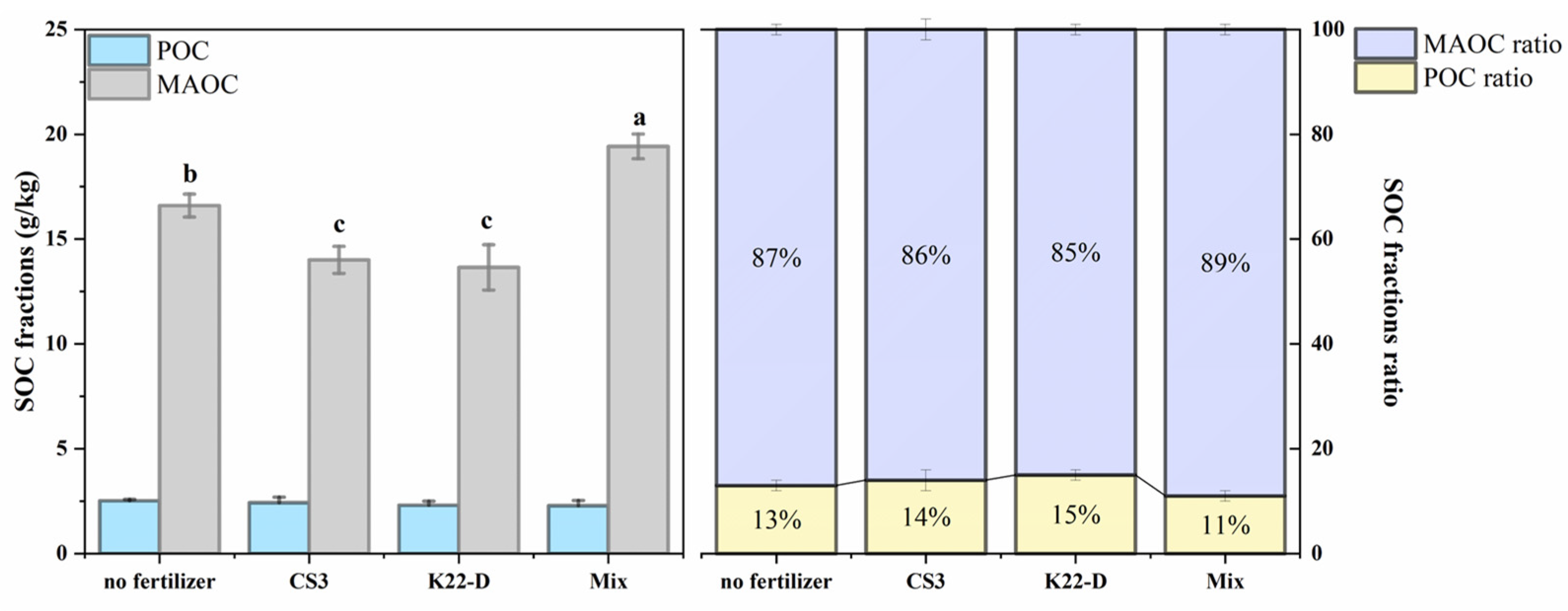
3.4. Effect of Different Microbial Fertilizers on Soil Properties and Carbon Fractions
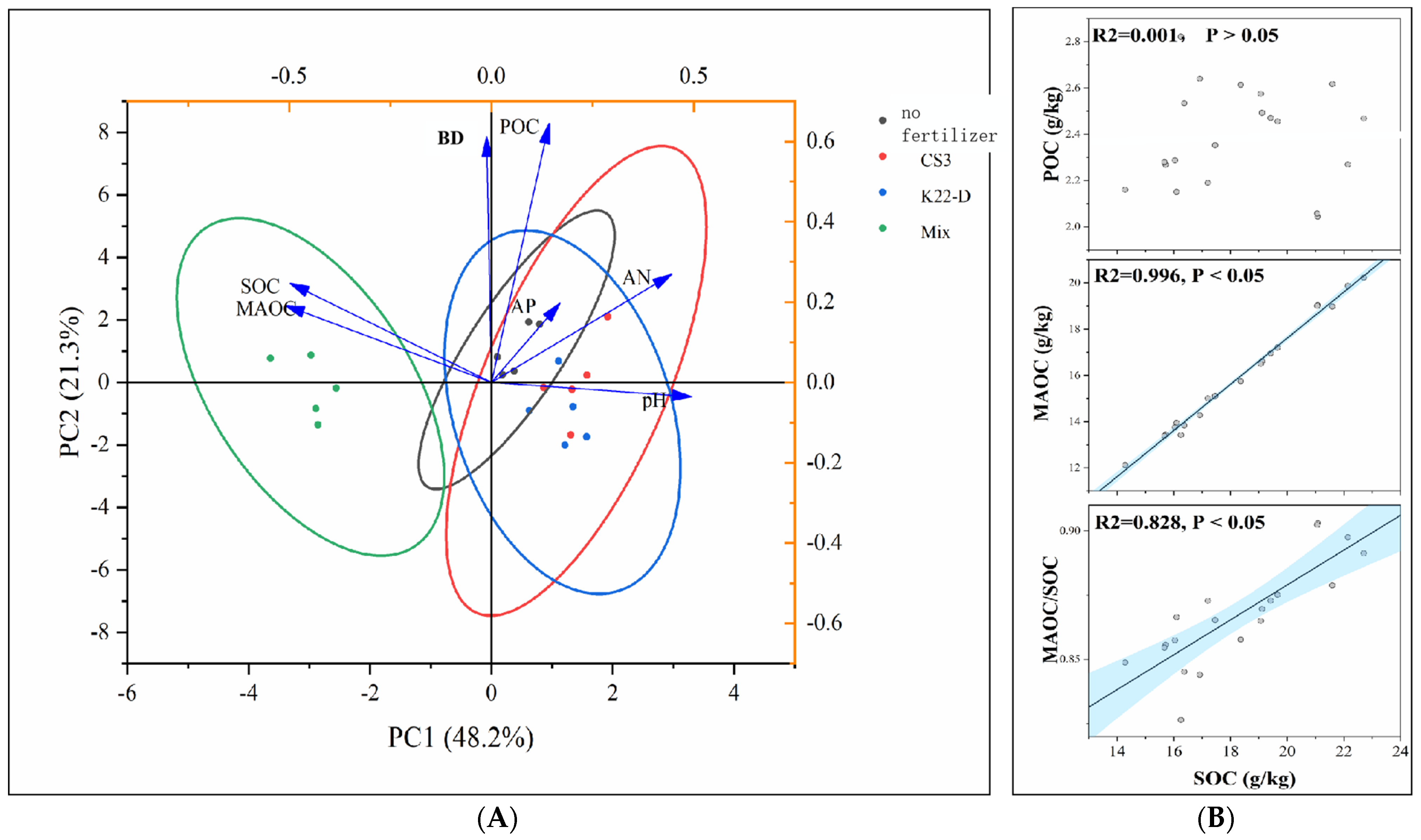
3.5. Effects of Soil Properties on Soil Carbon Fractions
4. Discussion
4.1. Isolation and Screening of Functions Bacteria
4.2. Biological Treatment of the Bamboo Shoot Wastewater
4.3. Effect of Different Microbial Fertilizers on Soil Properties
4.4. Effect of Different Microbial Fertilizers on Carbon Fractions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, S.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J. A Deep Learning-Based System for Monitoring the Number and Height Growth Rates of Moso Bamboo Shoots. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Zhu, B.; He, Z.R. Research progress of the use of bamboo shoots processing tail materials. Food Nutr. 2012, 18, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Brooks, M.S.L. Potential for Value-Added Utilization of Bamboo Shoot Processing Waste—Recommendations for a Biorefinery Approach. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2018, 11, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015 International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.F. Research on the Utilization of Fibers from Bamboo Shoot Processing and Recycling Industrial Chain Design; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Yu, Q.; Wei, X.; Ding, Y.; Kan, J. New insight into bamboo shoot (Chimonobambusa quadrangularis) polysaccharides: Impact of extraction processes on its prebiotic activity. Food Hydrocolloids 2019, 95, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.R.A.; Kiperstok, A.; Martin, J.; Morato, J.; Cohim, E. Decision support system for management of reactive nitrogen flows in wastewater system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8644–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulidzi, A.R. Winery wastewater treatment by constructed wetlands and the use of treated wastewater for cash crop production. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.; Yang, L. Combinations of waste seaweed liquid fertilizer and biochar on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) seedling growth in an acid-affected soil of Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 260, 115075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yan, X.; Gao, S.; Man, T.; Yang, Z.; Ren, L.; Wang, P. Preparation of liquid bacteria fertilizer with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria cultured by food wastewater and the promotion on the soil fertility and plants biomass. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 370, 133328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Su, M.; Li, J.; Man, T.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Gao, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; et al. Isolation of potassium solubilizing bacteria in soil and preparation of liquid bacteria fertilizer from food wastewater. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 181, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.R.; Zou, H.; Wang, B.S.; Yuan, F. Progress and Applications of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria in Salt Tolerance of Crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Y.L.; Huang, Y.L.; Zhang, H.; He, W.L.; Sheng, H.M.; An, L.Z. Screening of plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) from rhizosphere and bulk soil of Caragana microphylla in different habitats and their effects on the growth of Arabidopsis seedlings. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Tan, J.; Liu, F.; Wu, J. The mechanism of promoting rhizosphere nutrient turnover for arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi attributes to recruited functional bacterial assembly. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 32, 2335–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.B.; Govindan, R.; Muthuchamy, M.; Cheng, S.; Li, X.; Ye, L.; Wang, L.Y.; Guo, S.X.; Li, W.J.; Alharbi, N.S.; et al. Halophilic archaea and their extracellular polymeric compounds in the treatment of high salt wastewater containing phenol. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharaja, P.; Boopathy, R.; Anushree, V.V.; Mahesh, M.; Swarnalatha, S.; Ravindran, B.; Chang, S.W.; Sekaran, G. Bio removal of proteins, lipids and mucopolysaccharides in tannery hyper saline wastewater using halophilic bacteria. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Xie, X. Application of a Spiral Symmetric Stream Anaerobic Bioreactor for treating saline heparin sodium pharmaceutical wastewater: Reactor operating characteristics, organics degradation pathway and salt tolerance mechanism. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsipa, A.; Papalli, M.; Christou, A.; Pissaridou, P.; Vasquez, M.I. Ex-situ biological treatment of industrial saline seafood wastewater by salt-tolerant mixed cultures and phytotoxicity evaluation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Shang, H.; Li, Q.; Zhou, W. Dynamic characteristics of microbial community and soluble microbial products in partial nitrification biofilm system developed from marine sediments treating high salinity wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohda, J.; Nakano, Y.; Kugimiya, A.; Takano, Y.; Yano, T. Recycling of biodiesel fuel wastewater for use as a liquid fertilizer for hydroponics. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latt, Z.K.; Yu, S.S.; Kyaw, E.P.; Kyaw, E.P.; Lynn, T.M.; Nwe, M.T.; Mon, W.W.; Aye, K.N. Using Cellulolytic Nitrogen Fixing Bacterium, Azomonas agilis for Effective Degradation of Agricultural Residues. Open Microbiol. J. 2018, 12, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.D.; Guan, H.C.; Zheng, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, P.; Dong, S.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, J. Novel liquid organic fertilizer: A potential way to effectively recycle spent mushroom substrate. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 376, 134368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Ranalli, M.G.; Haddix, M.L.; Six, J.; Lugato, E. Soil carbon storage informed by particulate and mineral-associated organic matter. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.T.; Li, L.; Gu, X.M.; Owusu, A.M.; Li, S.Y.; Han, S.; Cao, G.X.; Zhu, T.H.; Li, S.J. Seasonal variations in the composition and diversity of rhizosphere soil microbiome of bamboo plants as infected by soil-borne pathogen and screening of associated antagonistic strains. Ind. Crop Prod. 2023, 197, 116641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, H.; Ying, Y. Screening and activity assessing of phosphorus availability improving microorganisms associated with bamboo rhizosphere in subtropical China. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6074–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.; Zheng, H.; He, Z.; Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, G.; Ma, N.L.; Sun, Y. The combined action of biochar and nitrogen-fixing bacteria on microbial and enzymatic activities of soil N cycling. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadouli, I.; Mosbah, A.; Ferjani, R.; Ouzari, H.I. The Impact of the Inoculation of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria Pantoeaagglomerans on Phosphorus Availability and Bacterial Community Dynamics of a Semi-Arid Soil. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.J.; Silva, H.; Cunha, A. Siderophore-Producing Rhizobacteria as a Promising Tool for Empowering Plants to Cope with Iron Limitation in Saline Soils: A Review. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif Sahandi, M.; Mehrafarin, A.; Naghdi Badi, H.; Khalighi-Sigaroodi, F.; Sharifi, M. Improving growth, phytochemical, and antioxidant characteristics of peppermint by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria along with reducing phosphorus fertilizer use. Ind. Crop Prod. 2019, 141, 111777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rediers, H.; Vanderleyden, J.; De Mot, R. Nitrate respiration in Pseudomonas stutzeri A15 and its involvement in rice and wheat root colonization. Microbiol. Res. 2009, 164, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.H.; Nie, Y.F.; Liu, J.G.; Jin, Y.Y.; Sun, L. Impact of hydrothermal process on the nutrient ingredients of restaurant garbage. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.L.; Wang, X.C.C.; Hu, Y.S.; Pu, Y.H.; Huang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Zeng, Y.G.; Li, Y.Y. Nutrients removal performance and sludge properties using anaerobic fermentation slurry from food waste as an external carbon source for wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceretta, M.B.; Irazoqui, J.M.; Persico, M.M.; Nercessian, D.; Wolski, E.A. Population dynamics of microbial native consortia efficient for textile wastewater degradation. Environ. Sci. Water Res. 2022, 8, 1036–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Song, Z.; Zhou, S.; Guo, H.; Geng, B.; Peng, X.; Zhao, G.; Xie, Y. Insights into functional microbial succession during nitrogen transformation in an ectopic fermentation system. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.J.; Sun, L.F.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Qiao, J.J. Conversion of spent mushroom substrate to biofertilizer using a stress-tolerant phosphate-solubilizing Pichia farinose FL7. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 111, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scervino, J.M.; Papinutti, V.L.; Godoy, M.S.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Della Monica, I.; Recchi, M.; Pettinari, M.J.; Godeas, A.M. Medium pH, carbon and nitrogen concentrations modulate the phosphate solubilization efficiency of Penicillium purpurogenum through organic acid production. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, D.; Aldas, C.; Lopez, G.; Kaparaju, P. Municipal solid waste as a valuable renewable energy resource: A worldwide opportunity of energy recovery by using Waste-To-Energy Technologies. Engery Procedia 2017, 134, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohi, M.; Riaz, M.; Arif, M.S.; Shahzad, S.M.; Yasmeen, T.; Riaz, M.A.; Tahir, S.; Mahmood, K. Varied effects of untreated textile wastewater onto soil carbon mineralization and associated biochemical properties of a dryland agricultural soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 183, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mbarek, H.; Gargouri, K.; Mbadra, C.; Ben Mahmoud, I.; Chaker, R.; Maktouf, S.; Abbas, O.; Baeten, V.; Rigane, H. Effects of combination of tillage with olive mill wastewater on soil organic carbon groups in arid soils. Arab J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojid, M.A.; Hossain, A.B.M.Z.; Wyseure, G.C.L. Impacts of Municipal Wastewater on Basic Soil Properties as Evaluated by Soil Column Leaching Experiment in Laboratory. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Nisha, R.; Jagjeeta, K. Impact of long and short term irrigation of a sodic soil with distillery effluent in combination with bioamendments. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Perdomo, F.; Abril, J.; Camelo, M.; Moreno-Galvan, A.; Pastrana, I.; Rojas-Tapias, D.; Bonilla, R. Azotobacter chroococcum as a potentially useful bacterial biofertilizer for cotton (Gossypium hirsutum): Effect in reducing N fertilization. Rev. Argent Microbiol. 2017, 49, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plunkett, M.H.; Knutson, C.M.; Barney, B.M. Key factors affecting ammonium production by an Azotobacter vinelandii strain deregulated for biological nitrogen fixation. Microbial Cell Factories 2020, 19, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, M.-E.; Chantigny, M.H.; Vanasse, A.; Menasseri-Aubry, S.; Angers, D.A. Coarse mineral-associated organic matter is a pivotal fraction for SOM formation and is sensitive to the quality of organic inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, X.; Gao, G.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, B. Microbial pathways driving stable soil organic carbon change in abandoned Moso bamboo forests in southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| CODCr (mg/L) | pH | EC μs/cm | TN (mg/L) | NH4-N (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | Turbidity (mg/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater | 43,486 | 4.13 | 4630 | 95.96 | 207.65 | 87 | 14.70 |
| Characteristics | CS3 | K22-D |
|---|---|---|
| V-P | + | − |
| Citrate | + | + |
| Propionate | + | − |
| Nitrate reduction | − | − |
| D-xylose | − | + |
| L-arabinose | + | + |
| D-Mannitol | + | − |
| Lactose | − | − |
| Glucose | + | + |
| Sucrose | − | − |
| Gelatine | − | + |
| NaCl > 7% | − | + |
| Gram | + | − |
| Treatment | No-Fertiliter | K22-D | CS3 | Mix |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD | 1.27 ± 0.23 a | 1.06 ± 0.28 a | 1.37 ± 0.24 a | 1.37 ± 0.12 a |
| pH | 4.89 ± 0.01 a | 4.98 + 0.02 a | 4.87 ± 0.02 a | 4.5 ± 0.11 b |
| SOC (g·kg−1) | 19.12 ± 1.45 b | 15.96 ± 1.16 c | 16.44 ± 0.86 c | 21.71 ± 0.71 a |
| AN (mg·kg−1) | 168 ± 18.91 a | 127.4 ± 7.98 c | 147 ± 10.61 b | 59.78 ± 8.86 d |
| AP (mg·kg−1) | 2.36 ± 0.52 b | 0.70 ± 0.04 d | 4.49 ± 0.81 a | 1.63 ± 0.28 c |
| AK (mg·kg−1) | 94.54 ± 4.31 a | 85.56 ± 4.68 bc | 87.68 ± 9.45 ab | 77.88 ± 14.93 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Bian, F.; Zhang, X. Production of Bamboo Source Microbial Fertilizer and Evaluate Its Effect on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions in Moso Bamboo Plantations in South China. Forests 2024, 15, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030455
Li Q, Huang Z, Zhong Z, Bian F, Zhang X. Production of Bamboo Source Microbial Fertilizer and Evaluate Its Effect on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions in Moso Bamboo Plantations in South China. Forests. 2024; 15(3):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030455
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiaoling, Zhiyuan Huang, Zheke Zhong, Fangyuan Bian, and Xiaoping Zhang. 2024. "Production of Bamboo Source Microbial Fertilizer and Evaluate Its Effect on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions in Moso Bamboo Plantations in South China" Forests 15, no. 3: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030455
APA StyleLi, Q., Huang, Z., Zhong, Z., Bian, F., & Zhang, X. (2024). Production of Bamboo Source Microbial Fertilizer and Evaluate Its Effect on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions in Moso Bamboo Plantations in South China. Forests, 15(3), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15030455






