Contrasting Altitudinal Patterns and Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities along Stand Types in Larix principis-rupprechtii Forests in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
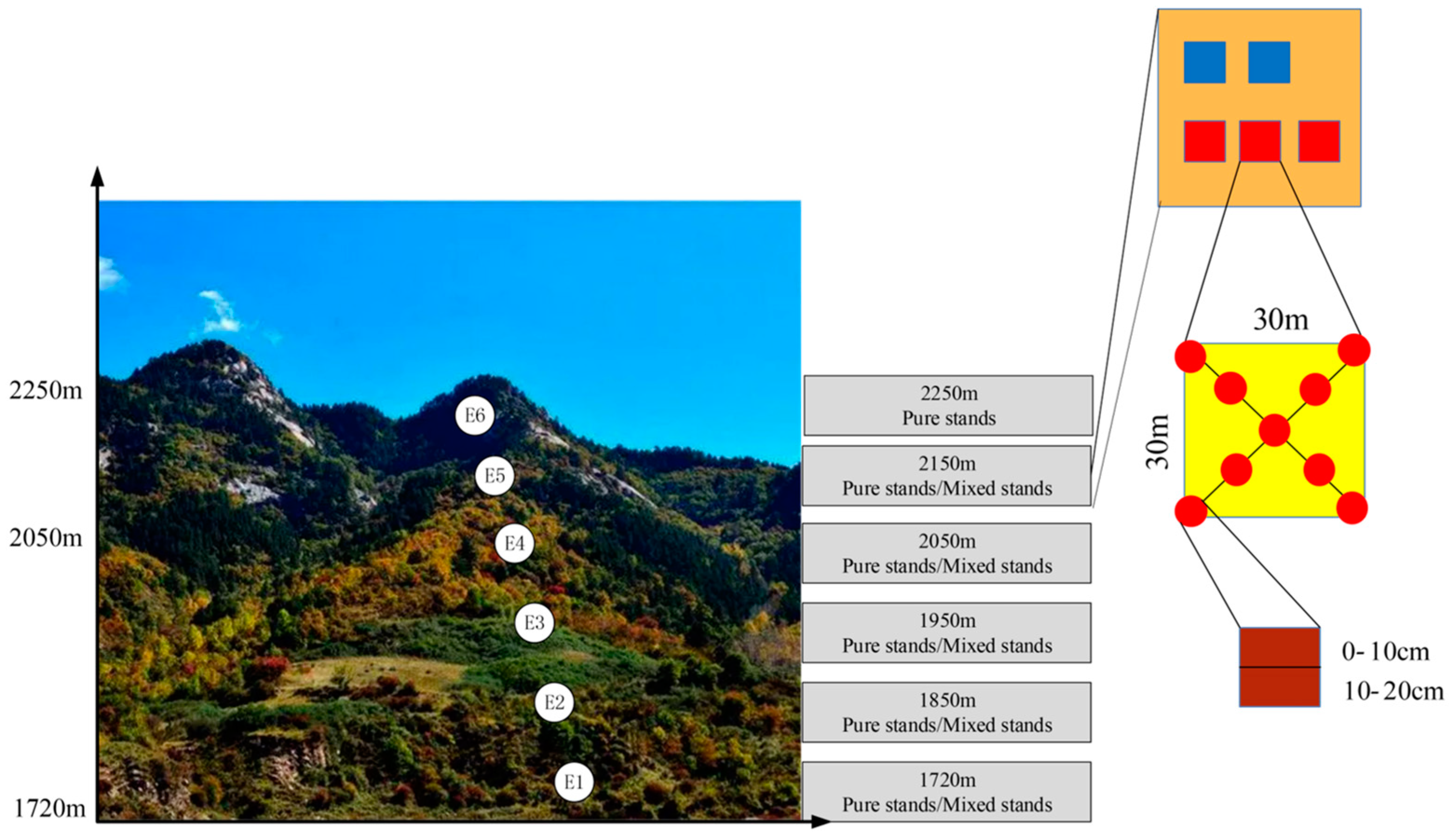
2.1. Site Description and Soil Sampling
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Illumina NovaSeq Sequencing and Processing of the Sequencing Data
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties along Altitudinal Gradients
3.2. Soil Bacterial Sequencing Summary and Community Composition
3.3. Soil Bacterial Community Diversity
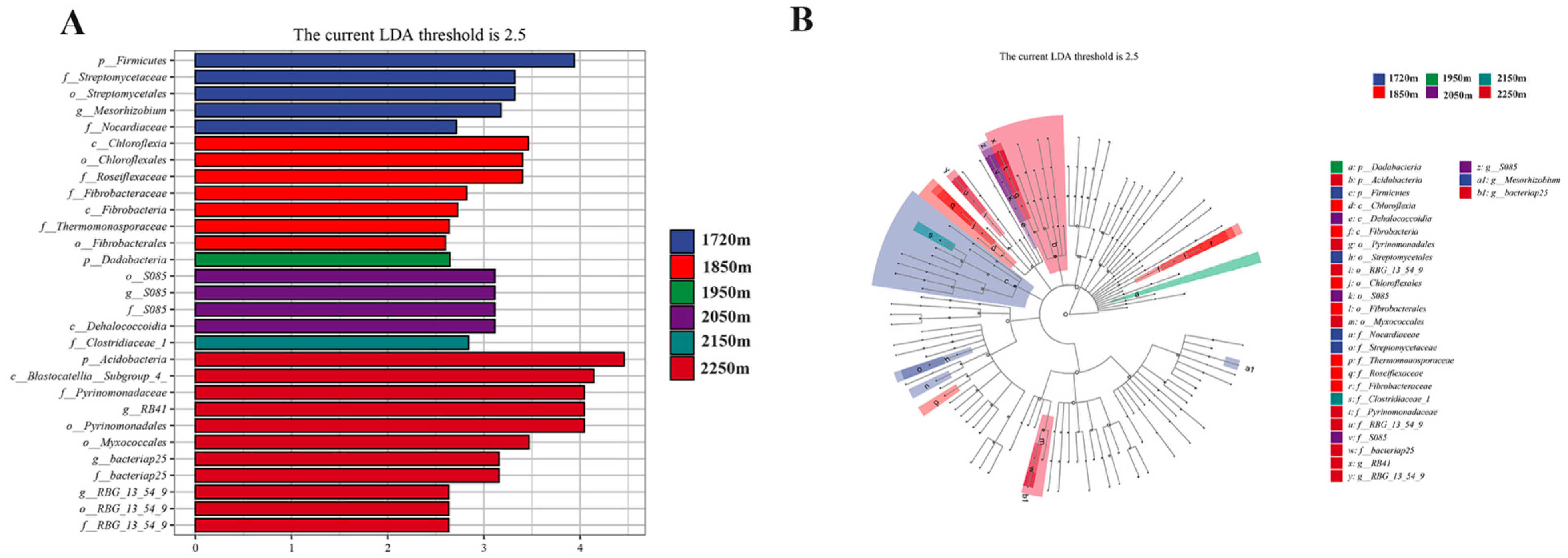
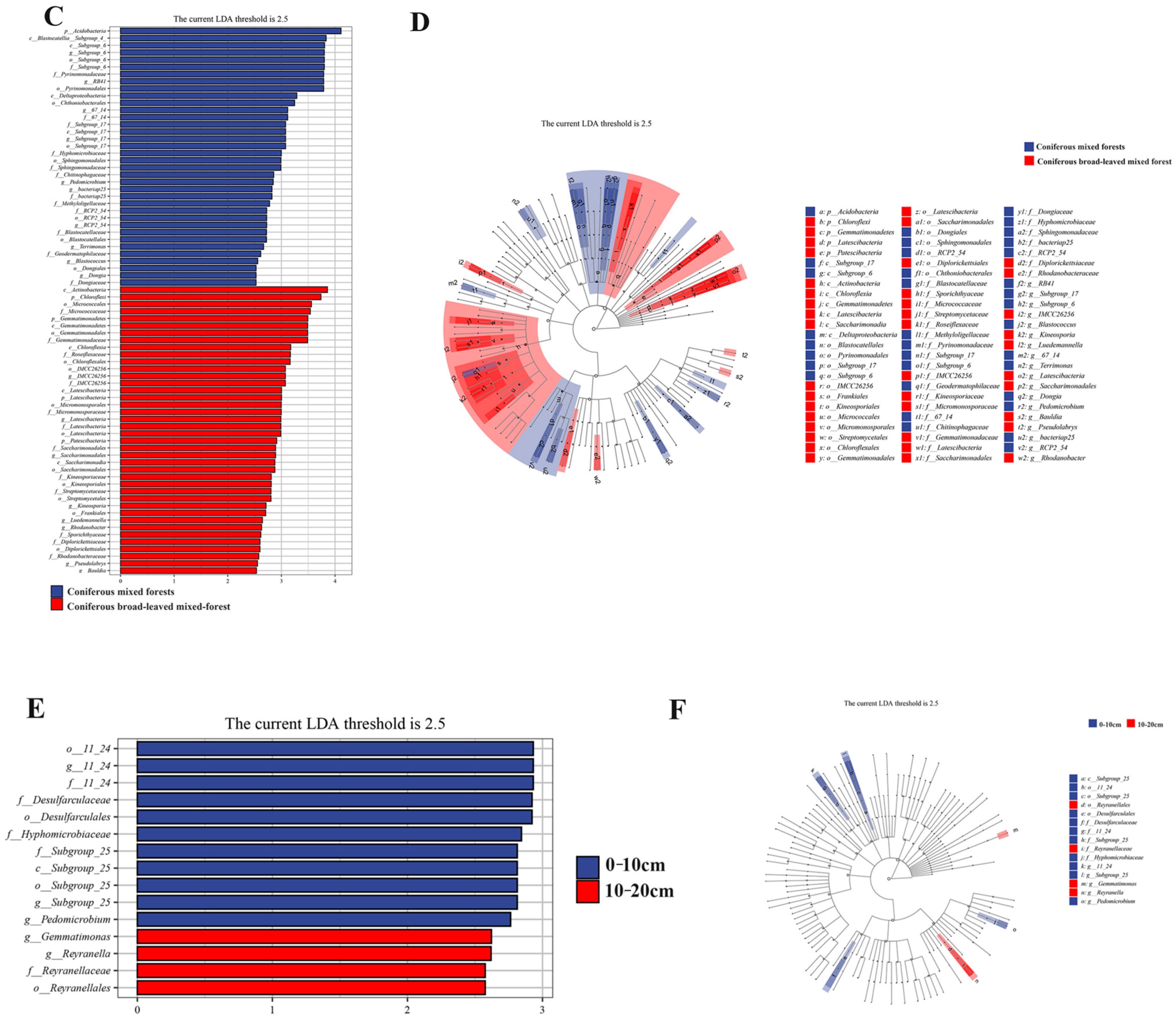
3.4. LEfSe Analysis
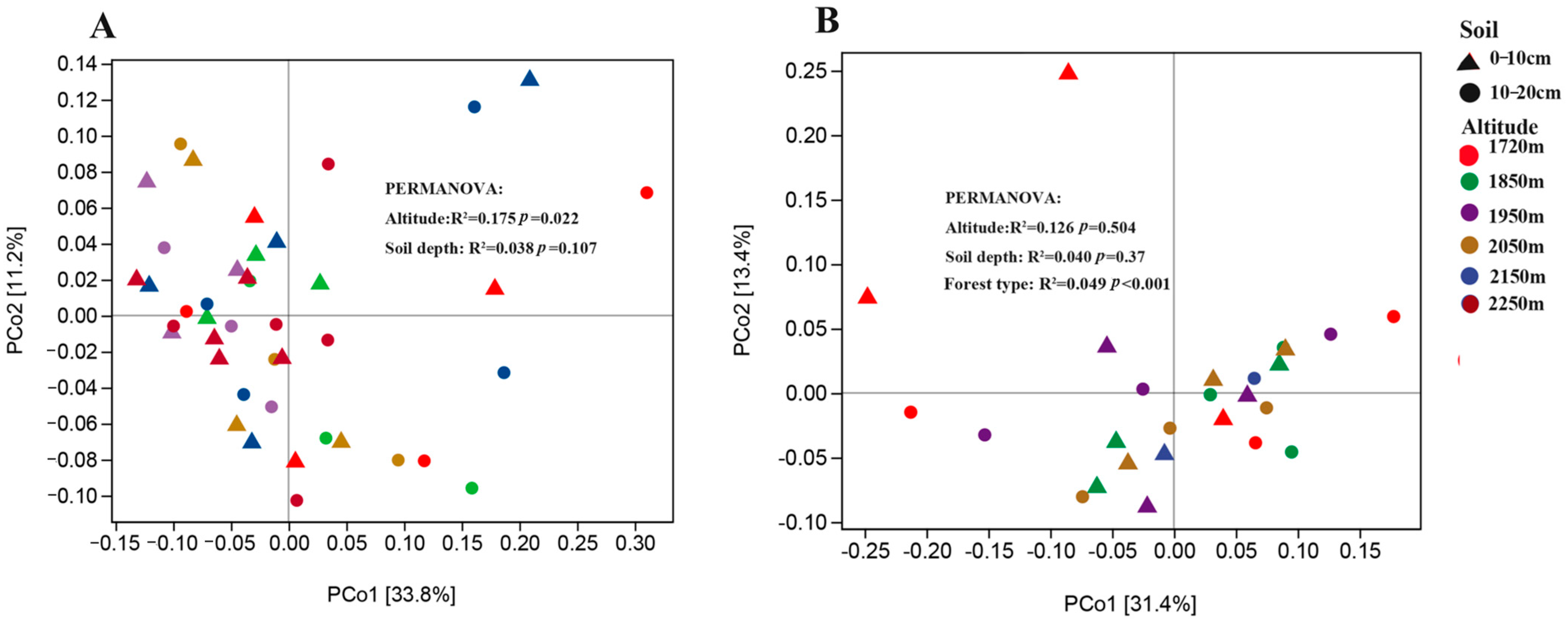
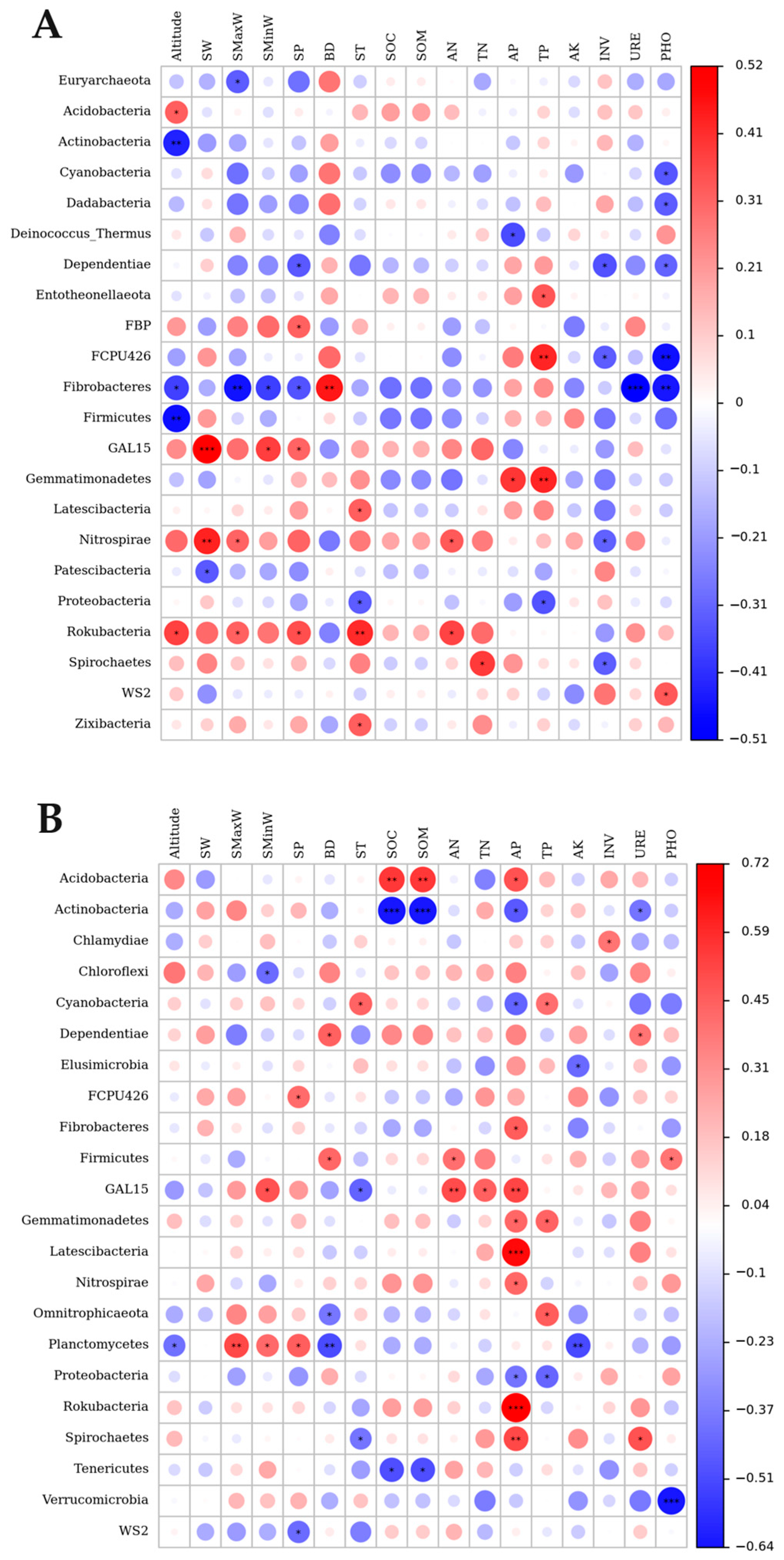
3.5. Relationship between the Soil Bacterial Community and Soil Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Divergent Factors Controlling Bacterial Diversities and Community Compositions along an Altitudinal Gradient
4.2. Variation in Vegetation Composition May Have Contributed to the Variability in Soil Bacterial Community
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bardgett, R.D.; Van Der Putten, W.H. Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nature 2014, 515, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, M.M.; Carlos, A.C.; Kristin, A.; Hammer, L. Microfluidic chips provide visual access to in situsoil ecology. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 889. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, X.; Kang, S.; Yang, S.; Mu, Q. Spatial patterns of dominant bacterial community components and their influential factors in the southern Qinling Mountains, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1024236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Liang, W.; Chu, H. Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cong, J.; Lu, H.; Li, G.; Xue, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, D. Soil bacterial diversity patterns and drivers along an elevational gradient on Shennongjia Mountain, China. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchenko, K.; Sushko, S.; Selezneva, A.; Ananyeva, N.; Zhuravleva, A.; Kudeyarov, V.; Makarov, M.; Blagodatsky, S. Soil microbial activity along an altitudinal gradient: Vegetation as a main driver beyond topographic and edaphic factors. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2021, 168, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Purahong, W.; Yang, L. Contrasting altitudinal patterns and co-occurrence networks of soil bacterial and fungal communities along soil depths in the cold-temperate mountain forests of China. Catena 2022, 209, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; You, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X. Elevational is the main factor controlling the soil microbial community structure in alpine tundra of the Changbai Mountain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, T.M.D.; Zeng, J.Y.; Man, X.L. Soil fungal and bacterial communities in southern boreal forests of the Greater Khingan Mountains and their relationship with soil properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Freedman, Z.; Fu, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Yao, M.; et al. Local community assembly mechanisms shape soil bacterial β diversity patterns along a latitudinal gradient. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liang, W.; Han, Y.; Wei, X. Characteristics and factors influencing the natural regeneration of Larix principis-rupprechtii seedlings in northern China. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Wei, X. Factors promoting the natural regeneration of Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in the Lvliang Mountains of central China. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Andersson, S.G.E.; Battin, T.J.; Prosser, J.I.; Schimel, J.P.; Whitman, W.B.; Hallin, S. The ecological coherence of high bacterial taxonomic ranks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L. Seasonal variations in soil fungal communities and co-occurrence networks along an altitudinal gradient in the cold temperate zone of China: A case study on Oakley Mountain. Catena 2021, 204, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Z.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass, diversity, and compositions to altitudinal gradients depend on plant and soil characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Ye, J.; Wang, X.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Feng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H. Microbial taxa distribution is associated with ecological trophic cascades along an elevation gradient. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Kong, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, X.; Xia, P. Diversity and distribution of autotrophic microbial community along environmental gradients in grassland soils on the Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8765–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Liu, F. Soil pH and organic carbon properties drive soil bacterial communities in surface and deep layers along an elevational gradient. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 646124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, B.F.T.; Prescott, C.E.; Grayston, S.J. Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven bio-geoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, C.S.; Beasley, W.H.; Elshahed, M.S.; Zhou, X.; Luo, Y.; Krumholz, L.R. Effect of warming and drought on grassland microbial communities. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Bardgett, R.D.; Smith, P.; Reay, D.S. Microorganisms and climate change: Terrestrial feedbacks and mitigation options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, G.; Ma, X.; Mu, C.; Zhao, L. Bacterial communities in the upper soil layers in the permafrost regions on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 120, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Escalas, A.; Feng, K.; He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, X.; et al. Steeper spatial scaling patterns of subsoil microbiota are shaped by deterministic assembly process. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.B.L.; Lallias, D.; Creer, S.; Seaton, F.M.; Kenny, J.G.; Eccles, R.M.; Griffiths, R.I.; Lebron, I.; Emmett, B.A.; Robinson, D.A.; et al. Divergent national-scale trends of microbial and animal biodiversity revealed across diverse temperate soil ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Oliverio, A.M.; Brewer, T.E.; Benavent-González, A.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K.; Fierer, N. A global atlas of the dominant bacteria found in soil. Science 2018, 359, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Staver, A.C. Enhanced activity of soil nutrient-releasing enzymes after plant invasion: A meta-analysis. Ecology 2019, 100, e02830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolen, M.J.; van de Giessen, J.; Zhu, E.Y.; Wuchter, C. Bioavailability of soil organic matter and microbial community dynamics upon permafrost thaw. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2299–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xue, K.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, M.; Yin, H.; He, Z.; Wu, L.; Schuur, E.A.G.; et al. Shifts of tundra bacterial and archaeal communities along a permafrost thaw gradient in A laska. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Qiu, J.; Liang, Y.; Lan, G. Soil bacterial community changes along elevation gradients in karst graben basin of Yunnan-Kweichow Plateau. Fron. Microbial. 2022, 13, 1054667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavridou, E.; Webster, R.J.; Robson, P.R.H. Novel Miscanthus genotypes selected for different drought tolerance phenotypes show enhanced tolerance across combinations of salinity and drought treatments. Ann. Bot. 2019, 124, 653–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlek, P.L.G.; Stumpe, J.M.; Byrnes, B.H. Urease activity and inhibition in flooded soil systems. Fertil. Res. 1980, 1, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z. Soil Enzyme and Its Research Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazutaka, K.; Misakwa, K.; Kei-ichi, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing Large Minimum Evolution Trees with Profiles instead of a Distance Matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peay, K.G.; von Sperber, C.; Cardarelli, E.; Toju, H.; Francis, C.A.; Chadwick, O.A.; Vitousek, P.M. Convergence and contrast in the community structure of Bacteria, Fungi and Archaea along a tropical elevation–climate gradient. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liang, W.; Shi, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Xie, G.; Chain, P.; Grogan, P.; Chu, H. Contrasting elevational diversity patterns between eukaryotic soil microbes and plants. Ecology 2014, 95, 3190–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Gunina, A.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Hemp, A.; Classen, A.T.; Ge, Y. Contrasting patterns and drivers of soil bacterial and fungal diversity across a mountain gradient. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgason, B.; Konschuh, H.; Bedard-Haughn, A.; VandenBygaart, A. Microbial distribution in an eroded landscape: Buried A horizons support abundant and unique communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 196, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.C.; Nemergut, D.R.; Grandy, A.S.; Leff, J.W.; Graham, E.B.; Hood, E.; Schmidt, S.K.; Wickings, K.; Cleveland, C.C. Biogeochemical drivers of microbial community convergence across actively retreating glaciers. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 101, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Liang, C.; Rubert-Nason, K.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Bao, X. Secondary successional forests undergo tightly coupled changes in soil microbial community structure and soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, S.A.; Högberg, M.N. Soil bacteria and archaea change rapidly in the first century of Fennoscandian boreal forest development. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lladó, S.; López-Mondéjar, R.; Baldrian, P. Forest soil bacteria: Diversity, involvement in ecosystem processes, and response to global change. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00063-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimek, B.; Chodak, M.; Jaźwa, M.; Solak, A.; Tarasek, A.; Niklińska, M. The relationship between soil bacteria substrate utilisation patterns and the vegetation structure in temperate forests. Eur. J. Res. 2016, 135, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Lanoue, A.; Strecker, T.; Scheu, S.; Steinauer, K.; Thakur, M.P.; Mommer, L. Root biomass and exudates link plant diversity with soil bacterial and fungal biomass. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Jin, C.; Hu, S.; Qian, S.; Lin, D.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y. Short-term decline of Castanopsis fargesii adult trees promotes conspecific seedling regeneration: The complete process from seed production to seedling establishment. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 10657–10671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeglin, L.H.; Wang, B.; Waythomas, C.; Rainey, F.; Talbot, S.L. Organic matter quantity and source affects microbial community structure and function following volcanic eruption on K asatochi I sland, A laska. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Xia, B.; Treves, D.S.; Wu, L.Y.; Marsh, T.L.; O’Neill, R.V.; Palumbo, A.V.; Tiedje, J.M. Spatial and resource factors influencing high microbial diversity in soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, S.; Wen, J.; Chen, D. Effect mechanism of land consolidation on soil bacterial community: A case study in Eastern China. Int. J. Environ. 2022, 19, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, K.; Lamprecht, A.; Pauli, H.; Illmer, P. Distribution of prokaryotic abundance and microbial nutrient cycling across a high-alpine altitudinal gradient in the Austrian Central Alps is affected by vegetation, temperature, and soil nutrients. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.H.; Chen, T.H.; Tian, G.; Chiu, C.Y. The effect of altitudinal gradient on soil microbial community activity and structure in moso bamboo plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Yang, W.; Chang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Tan, B. Differential seasonal changes in soil enzyme activity along an altitudinal gradient in an alpine-gorge region. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Tedersoo, L.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E.; Gilbert, J.A.; Sun, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Phylogenetic imprint of woody plants on the soil mycobiome in natural mountain forests of eastern China. ISME J. 2019, 13, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J. Positive effects of plant diversity on soil microbial biomass and activity are associated with more root biomass production. J. Plant Interact 2017, 12, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagodatskaya, E.; Blagodatsky, S.; Khomyakov, N.; Myachina, O.; Kuzyakov, Y. Temperature sensitivity and enzymatic mechanisms of soil organic matter decomposition along an altitudinal gradient on Mount Kilimanjaro. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Yu, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Su, W.; Xia, F.; Chang, S.X.; Brookes, P.C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; et al. Elevated temperature shifts soil N cycling from microbial immobilization to enhanced mineralization, nitrification and denitrification across global terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 5267–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuthia, L.W.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Debryun, J.; Schaeffer, S.; Tyler, D.; Odoi, E.; Mpheshea, M.; Walker, F.; Eash, N. Long term tillage, cover crop, and fertilization effects on microbial community structure, activity: Implications for soil quality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 89, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Factors | SW (%) | ST (°C) | SMaxW (g) | SMinW (g) | SP (%) | BD (g/cm3) | SOC (g/kg) | SOM (g/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | TN (g/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | TP (g/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | INV (mg) | URE (mg) | PHO (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANOVA | ||||||||||||||||
| A | 1.249 ns | 1.876 ns | 4.403 *** | 3.704 ** | 2.116 ns | 11.16 *** | 7.801 *** | 7.802 *** | 0.944 ns | 1.718 ns | 0.427 ns | 1.891 ns | 1.538 ns | 5.621 *** | 6.291 *** | 12.926 *** |
| F | 1.025 ns | 11.10 *** | 2.613 ns | 0.401 ns | 2.162 ns | 2.700 ns | 1.499 ns | 1.497 ns | 12.236 *** | 0.286 ns | 0.974 ns | 1.843 ns | 0.035 ns | 0.848 ns | 2.162 ns | 4.551 * |
| S | 0.339 ns | 5.542 * | 0.114 ns | 1.127 ns | 2.628 ns | 0.235 ns | 6.251 * | 6.259 * | 0.485 ns | 0.337 ns | 0.137 ns | 0.284 ns | 9.757 ** | 0.941 ns | 2.466 ns | 3.387 ns |
| A × F | 4.081 ** | 1.914 ns | 1.471 ns | 4.075 ** | 1.203 ns | 4.364 ** | 4.743 *** | 4.744 *** | 2.027 ns | 1.980 ns | 0.435 ns | 2.640 * | 2.013 ns | 4.943 *** | 8.643 *** | 5.986 *** |
| F × S | 0.106 ns | 0.070 ns | 0.020 ns | 0.826 ns | 0.063 ns | 0.009 ns | 5.494 * | 5.493 * | 0.368 ns | 1.087 ns | 0.181 ns | 0.157 ns | 0.958 ns | 1.325 ns | 0.193 ns | 0.168 ns |
| A × S | 0.283 ns | 0.007 ns | 0.479 ns | 1.059 ns | 0.615 ns | 0.945 ns | 6.224 *** | 6.226 *** | 1.338 ns | 1.079 ns | 0.261 ns | 0.254 ns | 0.399 ns | 0.349 ns | 0.220 ns | 1.514 ns |
| A × F × S | 0.287 ns | 0.024 ns | 0.182 ns | 0.746 ns | 0.266 ns | 0.567 ns | 2.675 * | 2.675 * | 0.417 ns | 2.075 ns | 0.197 ns | 0.134 ns | 0.577 ns | 0.317 ns | 0.106 ns | 0.255 ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Han, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Contrasting Altitudinal Patterns and Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities along Stand Types in Larix principis-rupprechtii Forests in Northern China. Forests 2024, 15, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020392
Niu Y, Li X, Wang C, Han Y, Wang Z, Yang J. Contrasting Altitudinal Patterns and Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities along Stand Types in Larix principis-rupprechtii Forests in Northern China. Forests. 2024; 15(2):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020392
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Yajie, Xin Li, Chuanxu Wang, Youzhi Han, Zhuo Wang, and Jing Yang. 2024. "Contrasting Altitudinal Patterns and Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities along Stand Types in Larix principis-rupprechtii Forests in Northern China" Forests 15, no. 2: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020392
APA StyleNiu, Y., Li, X., Wang, C., Han, Y., Wang, Z., & Yang, J. (2024). Contrasting Altitudinal Patterns and Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities along Stand Types in Larix principis-rupprechtii Forests in Northern China. Forests, 15(2), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15020392





