Source–Sink Structural Coupling Within Forest-Clustered Landscapes Drives Headstream Quality Dynamics in Mountainous Sub-Watersheds: A Case Study in Chongqing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Site
2.2. Division of the Sub-Watersheds
2.3. Headstream Sample Collection and Headstream Quality Evaluation
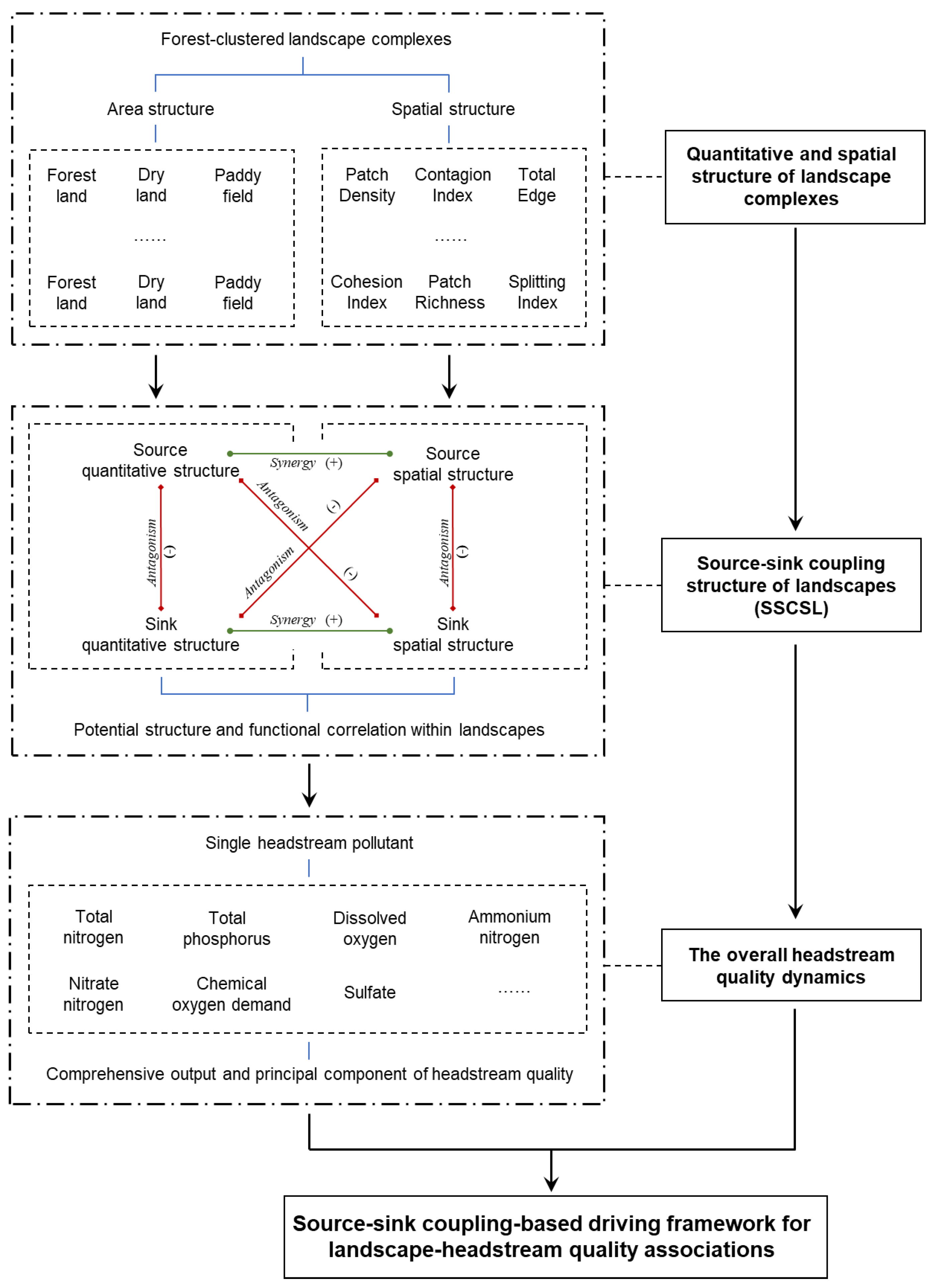
2.4. Landscape Element Classification and Landscape Structure Extraction
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
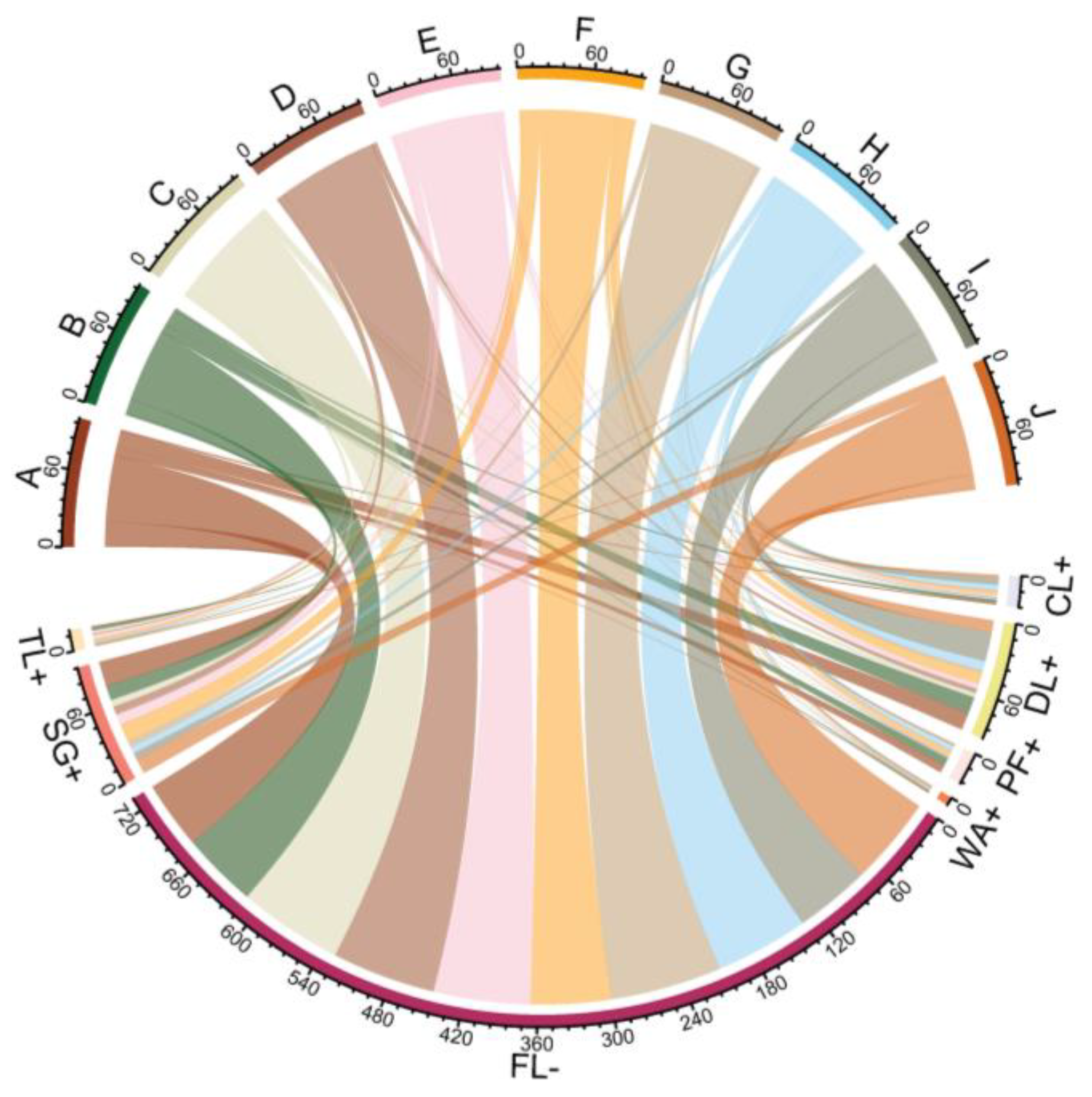
3.1. Headstream Quality Dynamics and the Underlying Source and Sink Structures of Landscapes
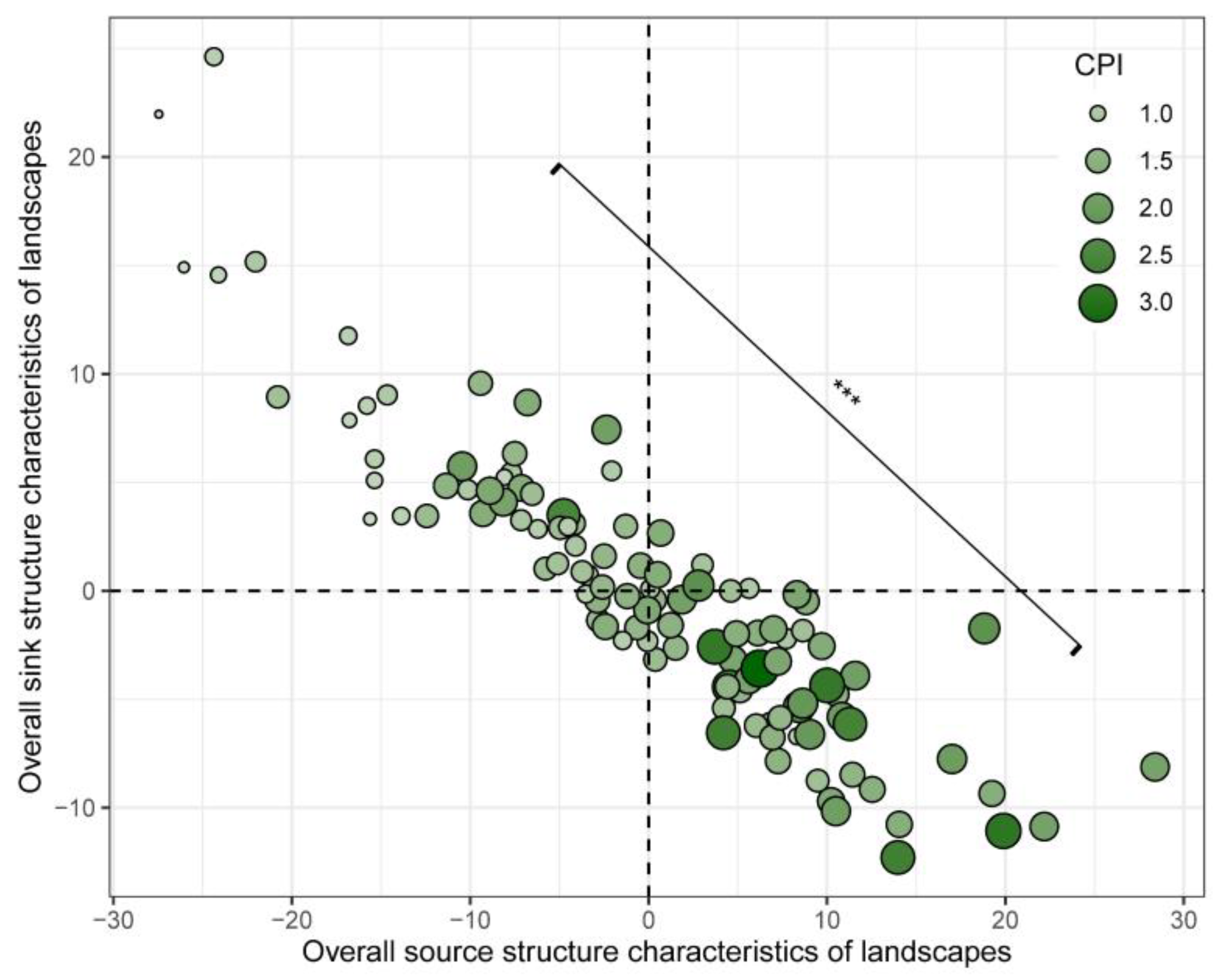
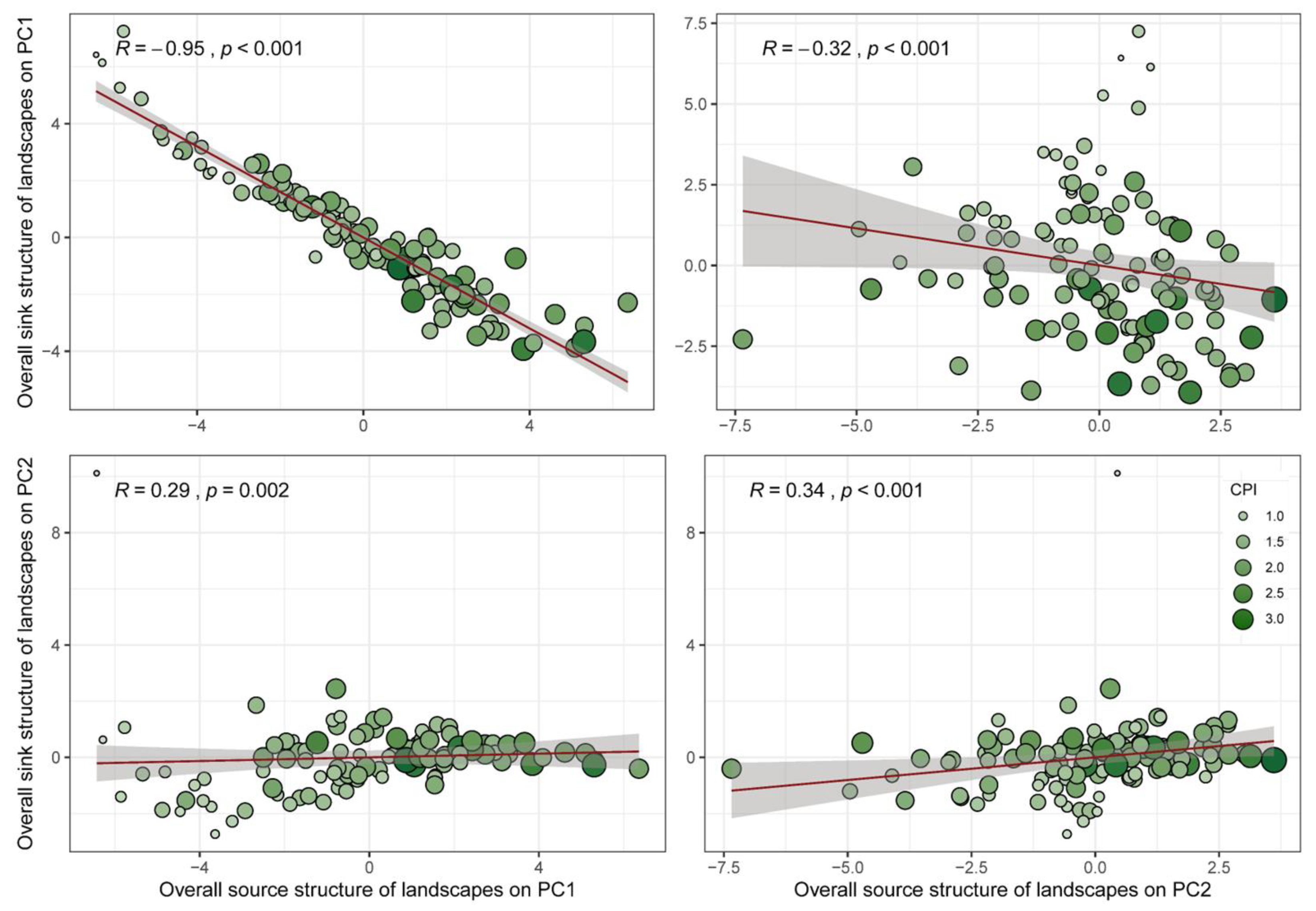
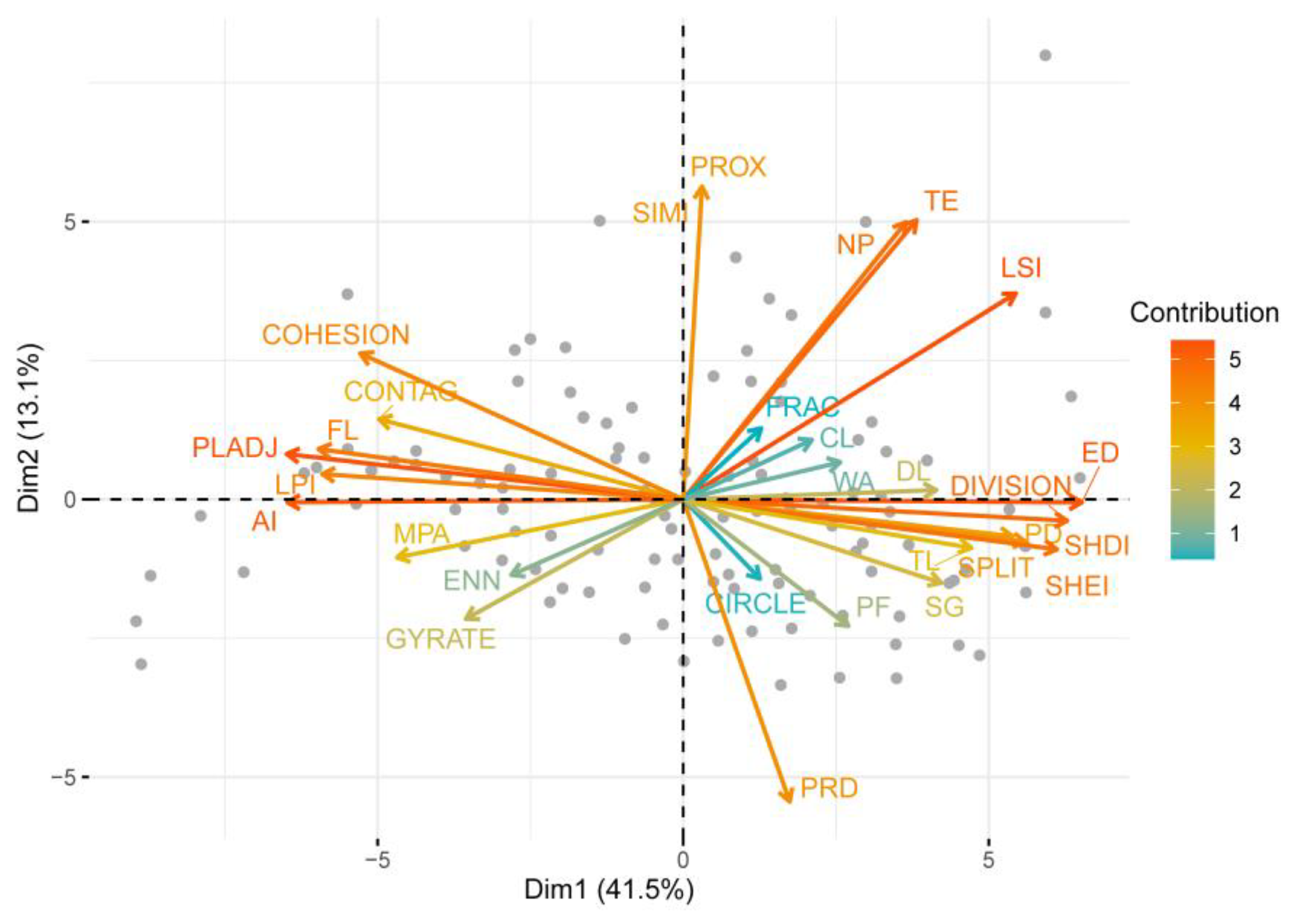
3.2. Headstream Quality-Based SSCSL That Reflect Source–Sink Function Trade-Offs
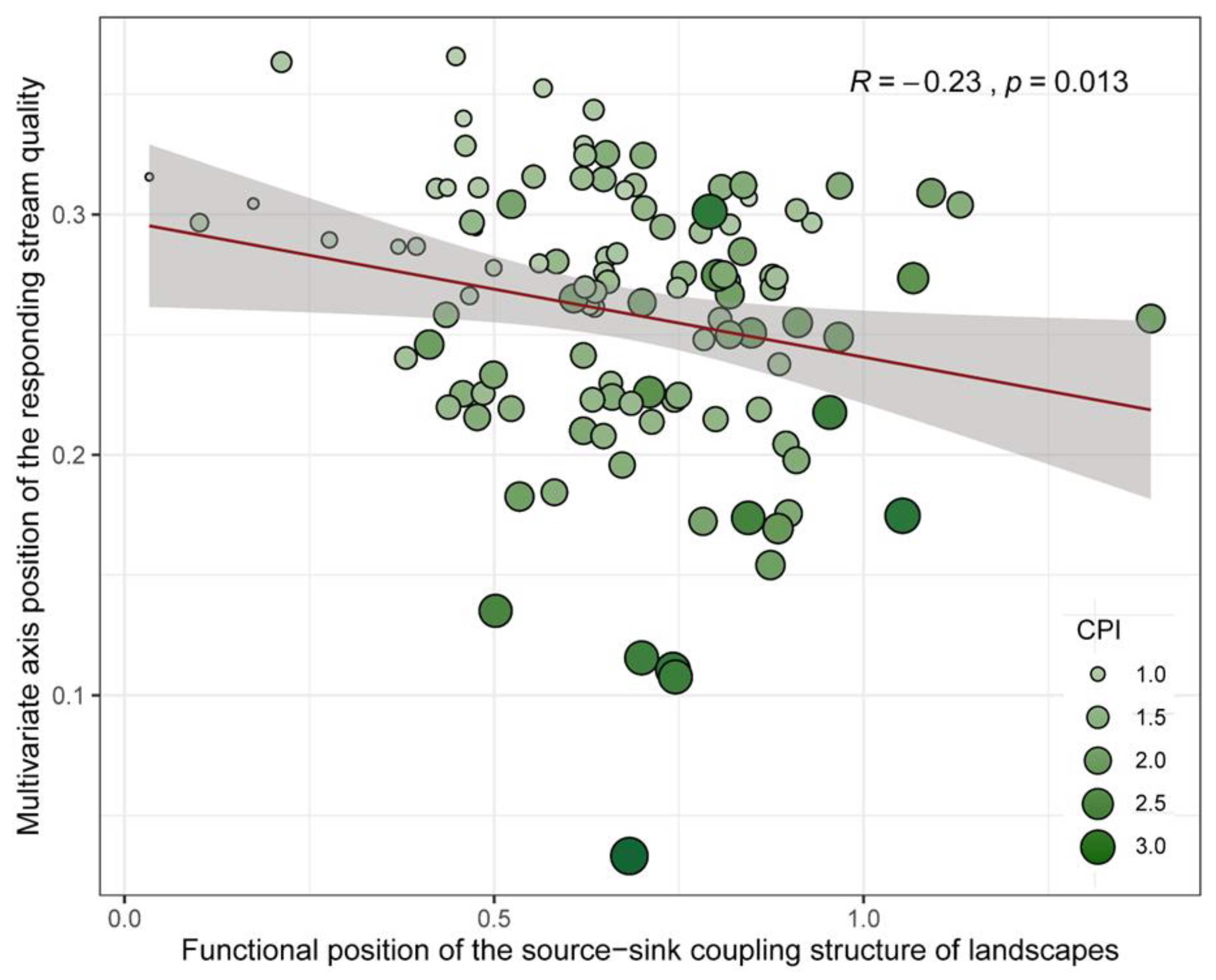
3.3. Response Pattern of Headstream Quality Dynamics to the SSCSL
3.4. Headstream Quality Feedback on Coupling Structure Differences Along the SSCSL Gradient
4. Discussion
4.1. Source and Sink Structures of the Forest-Clustered Landscapes
4.2. Coupling and Trade-Off Pattern of the Source–Sink Structures of Landscapes
4.3. Driving Force of the SSCSL Behind Headstream Quality Dynamics
4.4. Enlightenment for Future Landscape Sustainable Management in the Agroforestry Watersheds
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keeler, B.L.; Polasky, S.; Brauman, K.A.; Johnson, K.A.; Finlay, J.C.; O’Neill, A.; Kovacs, K.; Dalzell, B. Linking water quality and well-being for improved assessment and valuation of ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18619–18624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encalada, A.C.; Flecker, A.S.; Poff, N.L.; Suarez, E.; Herrera-R, G.A.; Rios-Touma, B.; Jumani, S.; Larson, E.I.; Anderson, E.P. A global perspective on tropical montane rivers. Science 2019, 365, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, G.; Gessner, M.O.; Giller, P.S.; Gulis, V.; Hladyz, S.; Lecerf, A.; Malmqvist, B.; McKie, B.G.; Tiegs, S.D.; Cariss, H.; et al. Continental-scale effects of nutrient pollution on stream ecosystem functioning. Science 2012, 336, 1438–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Wright, J.S.; Hall, J.W.; Gong, P.; Ni, S.; Qiao, S.; Huang, G.; et al. Managing nitrogen to restore water quality in China. Nature 2019, 567, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zuo, D. Effect of land use types on stream water quality under seasonal variation and topographic characteristics in the Wei River basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mi, W.; Ji, L.; He, Q.; Yang, P.; Xie, S.; Bi, Y. Urbanization and agriculture intensification jointly enlarge the spatial inequality of river water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. A source-sink landscape approach to mitigation of agricultural non-point source pollution: Validation and application. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Xu, R.; Wang, J. Effects of source-sink landscape proximity on the spatial-temporal water quality from the perspective of cost distance in an agricultural watershed. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, D.; Guichard, F.; Loreau, M.; Mouquet, N. Source and sink dynamics in meta-ecosystems. Ecology 2010, 91, 2172–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, Q.; Lang, K.; Wu, J. Linking potential heat source and sink to urban heat island: Heterogeneous effects of landscape pattern on land surface temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Xie, W.; Chen, L. A landscape connectivity model to quantify contributions of heat sources and sinks in urban regions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 178, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Lai, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H. Integrating landscape planning and stream quality management in mountainous watersheds: A targeted ecological planning approach for the characteristic landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.J.; Creed, I.F.; Alexander, L.; Basu, N.B.; Calhoun, A.J.K.; Craft, C.; D’Amico, E.; DeKeyser, E.; Fowler, L.; Golden, H.E.; et al. Do geographically isolated wetlands influence landscape functions? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubert, F.; Fischer, R.; Groeneveld, J.; Lehmann, S.; Mueller, M.S.; Roedig, E.; Wiegand, T.; Huth, A. Global patterns of tropical forest fragmentation. Nature 2018, 554, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhai, R. Influence of land use change on the ecosystem service trade-offs in the ecological restoration area: Dynamics and scenarios in the Yanhe watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, J.; Gimmi, U.; Houet, T.; Bolliger, J. Current practices and challenges for modelling past and future land use and land cover changes in mountainous regions. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Bryan, B.A. Finding pathways to national-scale land-sector sustainability. Nature 2017, 544, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.L.; Strayer, D.L.; Wallace, J.B.; Eggert, S.L.; Helfman, G.S.; Leonard, N.E. The contribution of headwater streams to biodiversity in river networks. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E. The significance of small streams. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Sidle, R.C.; Richardson, J.S. Understanding processes and downstream linkages of headwater systems. Bioscience 2002, 52, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.; Estrany, J.; Ranzini, M.; de Cicco, V.; Tarjuelo Martin-Benito, J.M.; Hedo, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Effects of land use and seasonality on stream water quality in a small tropical catchment: The headwater of Corrego Agua Limpa, Sao Paulo (Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.Y.; Van Meter, K.J.; Byrnes, D.K.; Basu, N.B. Maximizing US nitrate removal through wetland protection and restoration. Nature 2020, 588, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooley, S.W.; Ryan, J.C.; Smith, L.C. Human alteration of global surface water storage variability. Nature 2021, 591, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibon, A.; Sheeren, D.; Monteil, C.; Ladet, S.; Balent, G. Modelling and simulating change in reforesting mountain landscapes using a social-ecological framework. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.K.; Hemp, A.; Appelhans, T.; Becker, J.N.; Behler, C.; Classen, A.; Detsch, F.; Ensslin, A.; Ferger, S.W.; Frederiksen, S.B.; et al. Climate-land-use interactions shape tropical mountain biodiversity and ecosystem functions. Nature 2019, 568, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 21010-2017; Current Land Use Classification. National Technical Committee for Standardization of Natural Resources and Territory Spatial Planning of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Mottet, A.; Ladet, S.; Coque, N.; Gibon, A. Agricultural land-use change and its drivers in mountain landscapes: A case study in the Pyrenees. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkama, R.; Cescatti, A. Biophysical climate impacts of recent changes in global forest cover. Science 2016, 351, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; Gao, L.; Ye, Y.; Sun, X.; Connor, J.D.; Crossman, N.D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Wu, J.; He, C.; Yu, D.; et al. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 2018, 559, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, B.S.; O’Sullivan, A.D.; Faulkner, S.; Sherratt, M.; Clucas, R. Agricultural diffuse nutrient pollution transport in a mountain wetland complex. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q. Influences of the land use pattern on water quality in low-order streams of the Dongjiang River basin, China: A multi-scale analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, Z.; Teixeira, H.; Marques, J.C. Systematic processes of land use/land cover change to identify relevant driving forces: Implications on water quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 1320–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Yan, W.; Chen, C. Effects of landscape development intensity on river water quality in urbanized areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wear, D.N.; Turner, M.G.; Naiman, R.J. Land cover along an urban-rural gradient: Implications for water quality. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Coomes, D.A.; Gibson, L.; Hu, G.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, C.; Yu, M. Forest fragmentation in China and its effect on biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, J. Global forest fragmentation change from 2000 to 2020. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, W.; Huang, X. Spatial and seasonal patterns in stream water contamination across mountainous watersheds: Linkage with landscape characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Guo, S.F.; Zhai, L.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Yin, Y.H.; Liu, H.B. Guiding the landscape patterns evolution is the key to mitigating river water quality degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaijengo, G.N.; Msigwa, A.; Njau, K.N.; Brendonck, L.; Vanschoenwinkel, B. Where does land use matter most? Contrasting land use effects on river quality at different spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 134825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, F.; Ruiz, J.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Blais, D.; Campeau, S. Landscape diversity and forest edge density regulate stream water quality in agricultural catchments. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yi, Y.; Blagodatsky, S.; Cadisch, G. Impact of forest cover and conservation agriculture on sediment export: A case study in a montane reserve, south-western China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, F.A.; Scudder, B.C.; Lenz, B.N.; Sullivan, D.J. Effects of multi-scale environmental characteristics on agricultural stream biota in eastern Wisconsin. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1489–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Z.; Lyons, J.; Kanehl, P.; Gatti, R. Influences of watershed land use on habitat quality and biotic integrity in Wisconsin streams. Fisheries 1997, 22, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, M.A.; Madden, M.; Bosch, D. Land use/land cover and soil type covariation in a heterogeneous landscape for soil moisture studies using point data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2009, 46, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCary, M.A.; Minor, E.; Wise, D.H. Covariation between local and landscape factors influences the structure of ground-active arthropod communities in fragmented metropolitan woodlands. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkkinen, M.J.; Heino, J.; Ahonen, S.H.K.; Lehosmaa, K.; Mykra, H. Streams and riparian forests depend on each other: A review with a special focus on microbes. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 462, 117962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Toribio, M.; Zermeno-Hernandez, I.; Ibarra-Manriquez, G. Effect of land use on the structure and diversity of riparian vegetation in the Duero river watershed in Michoacan, Mexico. Plant Ecol. 2014, 215, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, P.V.; Martin, K.L.; Vose, J.M.; Baker, J.S.; Warziniack, T.W.; Costanza, J.K.; Frey, G.E.; Nehra, A.; Mihiar, C.M. Forested watersheds provide the highest water quality among all land cover types, but the benefit of this ecosystem service depends on landscape context. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.K.; McGlynn, B.L. Seasonality in spatial variability and influence of land use/land cover and watershed characteristics on stream water nitrate concentrations in a developing watershed in the Rocky Mountain West. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W08411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruelheide, H.; Dengler, J.; Purschke, O.; Lenoir, J.; Jimenez-Alfaro, B.; Hennekens, S.M.; Botta-Dukat, Z.; Chytry, M.; Field, R.; Jansen, F.; et al. Global trait-environment relationships of plant communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Song, Y.-B.; Li, Y.; Goudzwaard, L.; van Logtestijn, R.S.P.; Chang, C.; Broekman, R.; van Hal, J.; Zuo, J.; Sterck, F.J.; et al. Considering inner and outer bark as distinctive tissues helps to disentangle the effects of bark traits on decomposition. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 2359–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liao, Q.; Shen, S.; Wang, W.; Xiao, P.; Liao, J. Effects of landscape conservation on the ecohydrological and water quality functions and services and their driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymek, D.; Zglobicki, W.; Baran-Zglobicka, B. The impact of mosaic land use and land cover on the quality of river waters (Case study: Lubelskie Province, E Poland). Land 2021, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Chu, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Jiang, M. Is there any correlation between landscape characteristics and total nitrogen in wetlands receiving agricultural drainages? Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z. Spatial regression and prediction of water quality in a watershed with complex pollution sources. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Zhu, Q.; Qian, R.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J. Coupling mountain and lowland watershed models to characterize nutrient loading: An eight-year investigation in Lake Chaohu Basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J. Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.O.; Quinn, J.M. The effect of forestry management activities on stream water quality within a headwater plantation Pinus radiata forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 439, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Fu, B. The impact of land use structure on non-point source pollution. China Environ. Sci. 2000, 20, 506–510. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, L.; Qin, K.; Yan, C.; Ren, W.; Zhu, H.; Shu, C.; Lai, X.; Li, F.; Liao, L.; Lan, S.; et al. Source–Sink Structural Coupling Within Forest-Clustered Landscapes Drives Headstream Quality Dynamics in Mountainous Sub-Watersheds: A Case Study in Chongqing, China. Forests 2024, 15, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111979
Lin L, Qin K, Yan C, Ren W, Zhu H, Shu C, Lai X, Li F, Liao L, Lan S, et al. Source–Sink Structural Coupling Within Forest-Clustered Landscapes Drives Headstream Quality Dynamics in Mountainous Sub-Watersheds: A Case Study in Chongqing, China. Forests. 2024; 15(11):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111979
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Li, Kunrong Qin, Chen Yan, Wei Ren, Haoxiang Zhu, Chengji Shu, Xiaohong Lai, Fangying Li, Lingyun Liao, Siren Lan, and et al. 2024. "Source–Sink Structural Coupling Within Forest-Clustered Landscapes Drives Headstream Quality Dynamics in Mountainous Sub-Watersheds: A Case Study in Chongqing, China" Forests 15, no. 11: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111979
APA StyleLin, L., Qin, K., Yan, C., Ren, W., Zhu, H., Shu, C., Lai, X., Li, F., Liao, L., Lan, S., Li, M., & Wang, H. (2024). Source–Sink Structural Coupling Within Forest-Clustered Landscapes Drives Headstream Quality Dynamics in Mountainous Sub-Watersheds: A Case Study in Chongqing, China. Forests, 15(11), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15111979






