The Responses of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Microbial Nutrients to the Interaction between Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions and Apoplastic Litter in Broad-Leaved Korean Pine Forests in Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Processing and Analysis of Nutrients
2.3.1. Analysis of Soil Properties
2.3.2. Analysis of Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activity
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
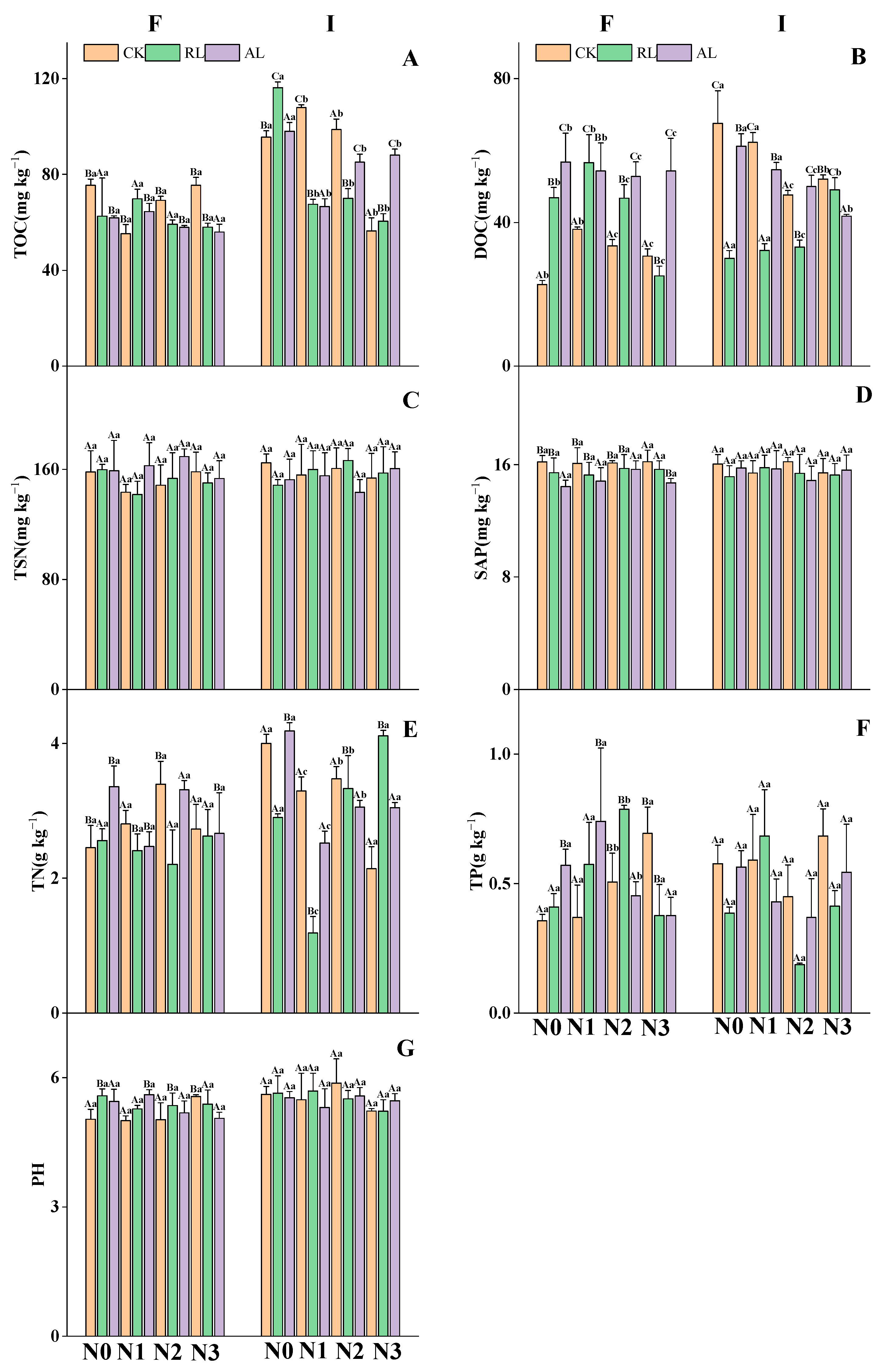
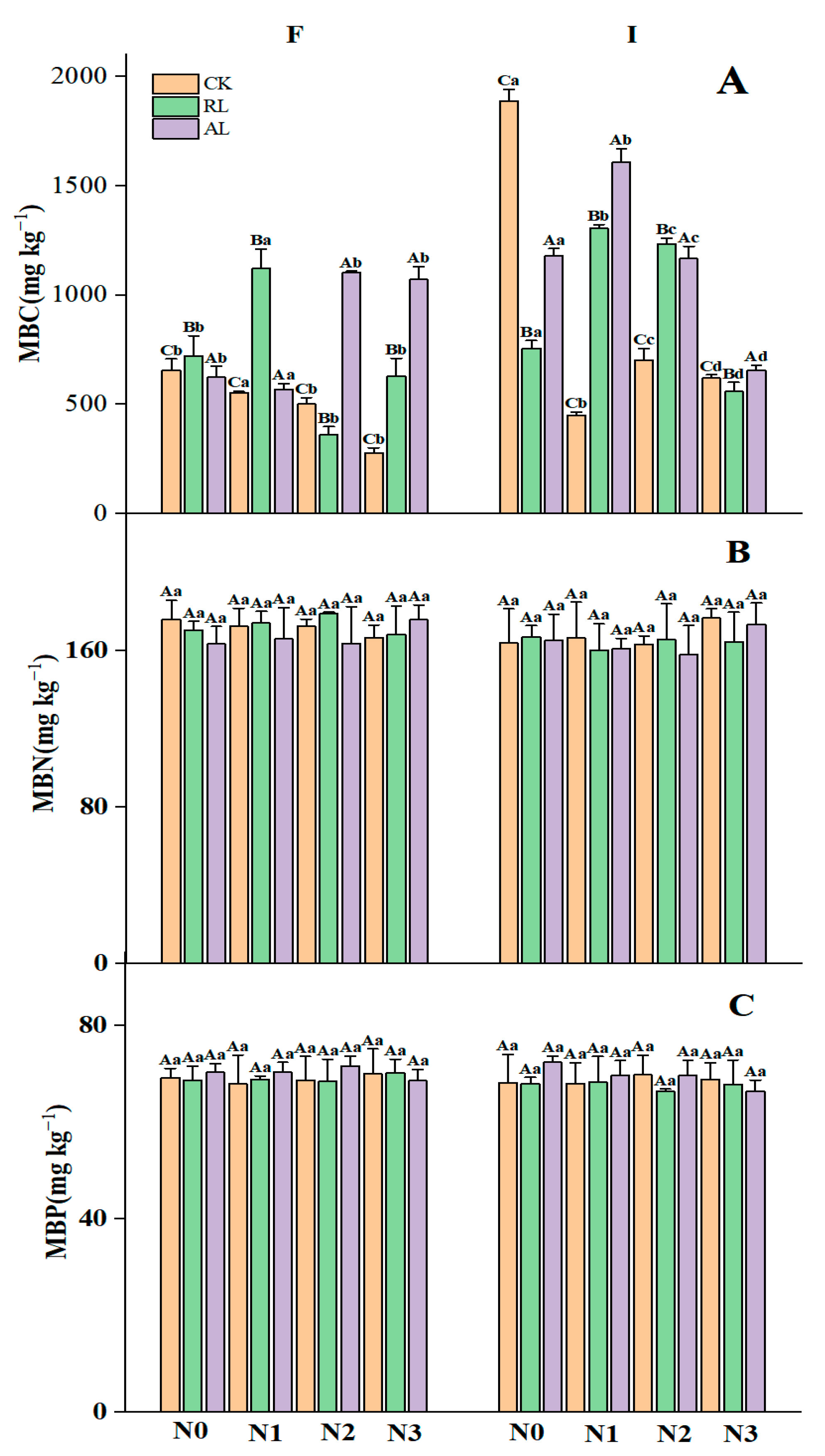
3.1. The Litter Treatment Regulates Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions to Soil Nutrients and Microbial Activities
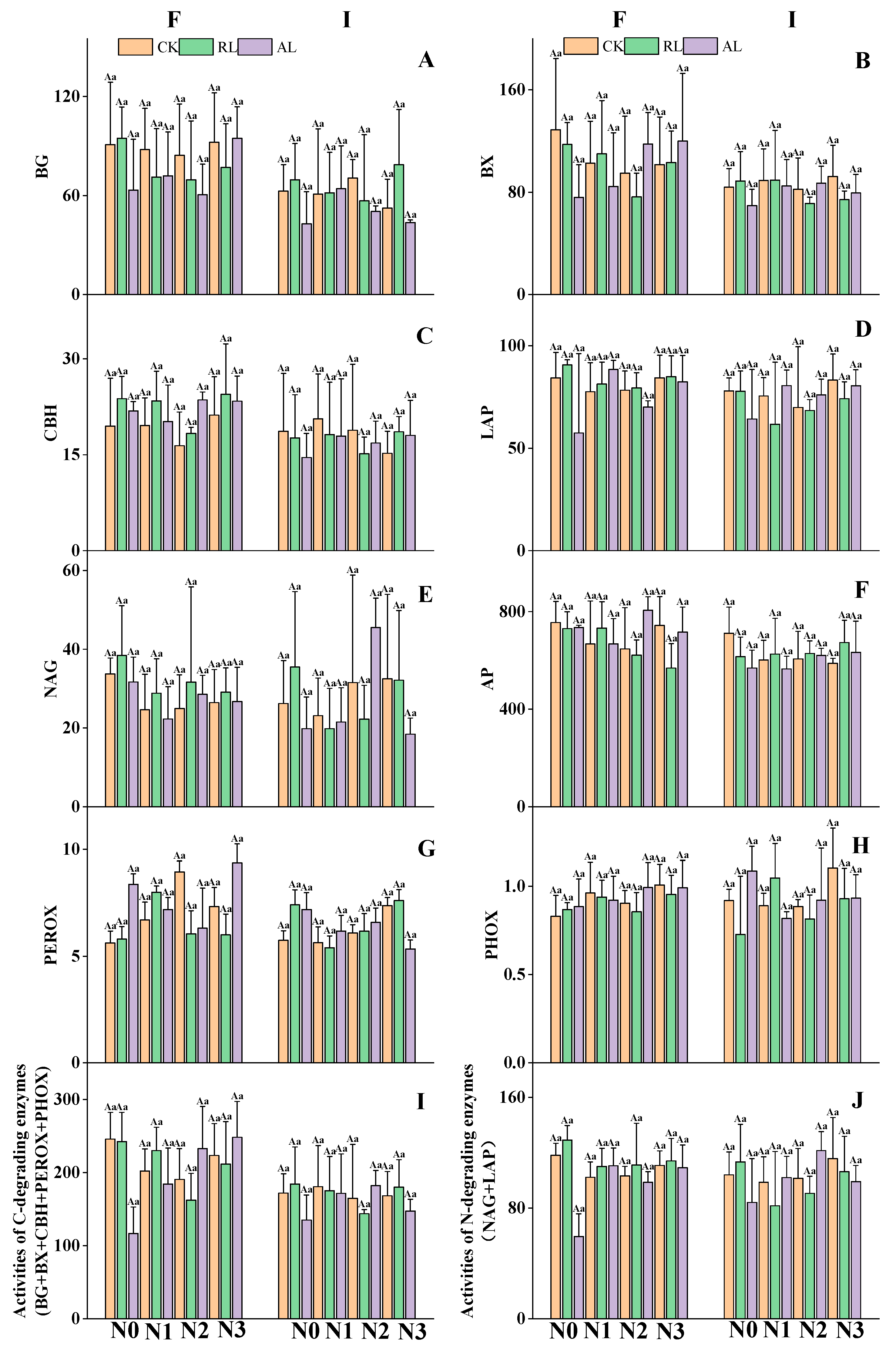
3.2. The Litter Treatment Regulates Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions to Soil Hydrolase Activities
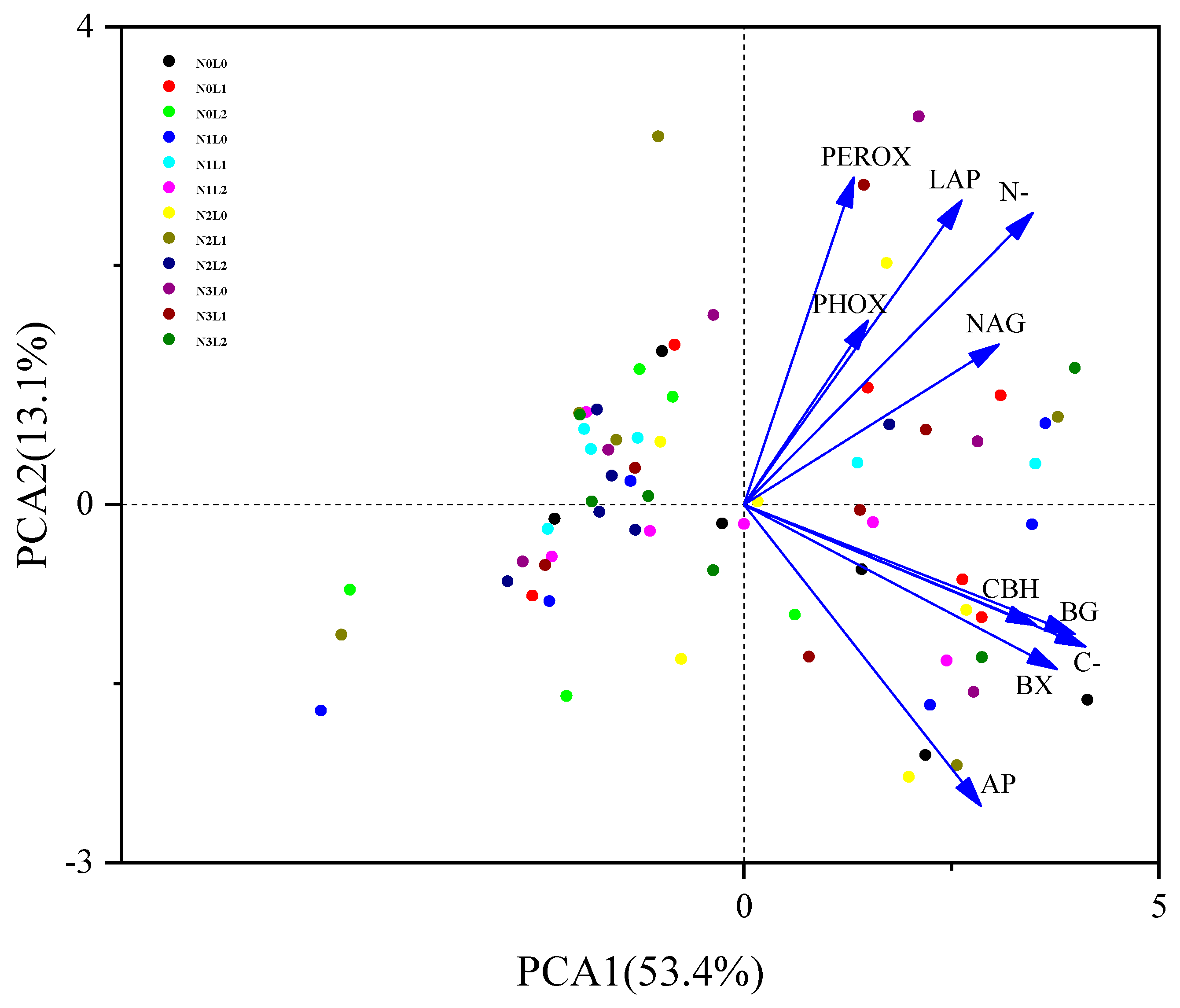
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activities Correlated with Chemical Indices and Microbial Biomass Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Responses of Soil Chemical Properties and Soil Microbial Biomass to N and P Addition and Litter Treatments
4.2. Responses of C-, N-, and P-Degrading Enzymes to N P Addition and Litter Treatments
4.3. Major Factors Affecting Soil EEAs and Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, R.F.; Rasmussen, L. Introduction to the Nitrex and Exman. For. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 101, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ma, H.; Gao, R.; Yin, Y.; Shi-dong, C.; Liu-ming, Y. Effects of nitrogen deposition on soluble organic carbon: A simulation study in subtropical forest soils. J. Subtrop. Resour. Environ. 2013, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, K.; Templer, P. Interacting effects of urbanization and climate on atmospheric deposition of phosphorus around the globe: A meta-analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 309, 119940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Xing, F.; Sun, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, X.; Chen, C.; Li, Z. Responses of soil extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community properties to interaction between nitrogen addition and increased precipitation in a semi-arid grassland ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 703, 134691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.; DeForest, J.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.; Stromberger, M.; Wallenstein, M.; Weintraub, M.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, R.W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Shelton, S.K.; Jin, Z.; Walker, L.M. Costimulation of soil glycosidase activity and soil respiration by nitrogen addition. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Zhu, B. A meta-analysis of soil extracellular enzyme activities in response to global change. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Zhang, T.; Guo, R.; Cao, H.; Shi, L.; Guo, J.; Sun, W. Response of soil enzyme activity to warming and nitrogen addition in a meadow steppe. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Yang, X.; Ren, F.; Zhou, H.K.; Zhu, B.; He, J. Neutral effect of nitrogen addition and negative effect of phosphorus addition on topsoil extracellular enzymatic activities in an alpine grassland ecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Thornton, P.; Post, W. A global analysis of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Yang, L.M.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.Q.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zheng, X.Z.; Chu, H.; Yang, Y. Patterns of ecoenzymatic stoichiometry on types of forest soils form different parent materials in subtropical areas. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 5828–5836. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.L.; Wang, G.X.; Yang, Y. Response of soil surface enzyme activities to short-term warming and litter decomposition in a mountain forest. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 7071–7079. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, C.; Carrillo, Y.; Boot, C.M.; Rocca, J.D.; Pendall, E.; Wallenstein, M.D. Rhizosphere stoichiometry: Are C : N : P ratios of plants, soils, and enzymes conserved at the plant species-level? New Phytol 2014, 201, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Z. Effects of Simulated Nitrogen Deposition on Litter Decomposition and Soil Microbial Activities in Pinus massoniana Plantations. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lili, L.; Liu, E.; Gu, X.; Sun, J. Effects of litter manipulation and nitrogen addition on soil ecoenzymatic stoichiometry in a mixed pine and oak forest. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 9220–9233. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y. Effects of elevated nitrogen deposition on soil organic carbon mineralization and soil enzyme activities in a Chinese fir plantation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z. Effects of Nitrogen Addition and Litter on Soil Microorganism and Enzyme Activities. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Vance, E.; Brookes, P.; Jenkinson, D. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H. Modification of fumigation extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass carbon. Chin. J. Ecol. 1999, 2, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, C.W.; Fricks, B.E.; Rocca, J.D.; Steinweg, J.M.; McMahon, S.K.; Wallenstein, M.D. High-throughput fluorometric measurement of potential soil extracellular enzyme activities. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 81, e50961. [Google Scholar]
- Saiya-Cork, K.; Sinsabaugh, R.; Zak, D.R. The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, X.; Shao, M.; Wei, X.; Li, T. Changes in soil C-N-P stoichiometry after 20 years of typical artificial vegetation restoration in semiarid continental climate zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Wu, R.; Liu, B.; An, H.; Gao, R.; Ma, K.; Ndzana, G.; Du, L.; Kamran, M. Nutrient supplementation changes chemical composition of soil organic matter density fractions in desert steppe soil in northern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 241, 106107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fan, H.; Liu, W.; Huang, R.-Z.; Shen, F.F.; Hu, F.; Li, H.X. Effects of Simulated Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Enzyme Activities and Microbial Community Functional Diversities in a Chinese Fir Plantation. Soils 2013, 45, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.C.; Hu, Y.L.; Mao, R.; Zhao, Q.; Zeng, D.H. Effects of Nitrogen Addition on Litter Decomposition and CO2 Release: Considering Changes in Litter Quantity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, X.; Wei, F.; Xu, X. Decomposing litter and associated microbial activity responses to nitrogen deposition in two subtropical forests containing nitrogen-fixing or non-nitrogen-fixing tree species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, E.; Craig, B.L.H.; Henry, H. Short-term vs. long-term effects of warming and nitrogen addition on soil extracellular enzyme activity and litter decomposition in a grass-dominated system. Plant Soil 2022, 481, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Tao, Y.; Fang, N.; Yang, G.; Cai, J.; Jiang, Y.; Han, X.; Yu, F.-H.; Li, M.-H. Beneficial effects of nitrogen deposition on carbon and nitrogen accumulation in grasses over other species in Inner Mongolian grasslands. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 26, e01507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Dech, J.P.; Yao, H.; Zhao, P.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, M. The effects of nitrogen addition on dissolved carbon in boreal forest soils of northeastern China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.J.; Li, X.S.; Chen, Z.J.; Zhou, J.B. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on carbon dioxide emissions from soils with different inorganic carbon contents. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 2493–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, W.; Du, X.; Hua, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, C.; Lu, H.; Shi, Y.; Yao, J. Determining the soil odor control area: A case study of an abandoned organophosphorus pesticide factory in China. Sci Total Env. 2024, 906, 167436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, W.; Bai, Y. Nitrogen enrichment alters plant N: P stoichiometry and intensifies phosphorus limitation in a steppe ecosystem. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 134, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bossio, D.A.; Smithson, P.C.; Frossard, E.; Oberson, A. Microbial community composition and substrate use in a highly weathered soil as affected by crop rotation and P fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gundersen, P.; Zhang, T.; Mo, J. Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in three forest types in tropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedorn, F.; Spinnler, D.; Siegwolf, R. Increased N deposition retards mineralization of old soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, D.; Yu, X. Soil microbial communities and enzyme activities in sea-buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) plantation at different ages. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; He, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhao, N.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in forest ecosystems along the North-South Transect in eastern China (NSTEC). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, M.; Andre, F.; Ponette, Q. Tree species mediated effects on leaf litter dynamics in pure and mixed stands of oak and beech. Can. J. For. Res. 2008, 38, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Responses of soil microbial biomass C:N:P stoichiometry to increased precipitation and nitrogen deposition in temperate shrublands. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2023, 119, 103553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X. Responses of soil microbial carbon use efficiency to elevated nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems. Adv. Earth Sci. 2023, 38, 999–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; You, Y.M.; Sun, J.X. Effects of forest floor litter and nitrogen addition on soil microbial biomass C and N and microbial activity in a mixed Pinus tabulaeformis and Quercus liaotungensis forest stand in Shanxi Province of China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, G.; Li, S.; Peng, T.; Qiu, X.; Luo, J.; Yang, S.; Hu, T.; Hu, H.; et al. Soil biochemical responses to nitrogen addition in a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.L.; Chen, J.Z.; Wang, D.; Deng, M.M.; Wu, M.-Y.; Tong, B.-L.; Liu, J.-M. Simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition inhibited the leaf litter decomposition of Cinnamomum migao H. W. Li in Southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Xing, Y.; Luo, W.; Yan, G.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Effects of Long-Term Nitrogen Addition and Throughfall Reduction on Extracellular Enzyme Activity and Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry in a Temperate Forest. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 1534–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, X.; Gong, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Response of litter decomposition and the soil environment to one-year nitrogen addition in a Schrenk spruce forest in the Tianshan Mountains, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Tian, D.; Niu, S. Different responses of soil respiration and its components to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in a subtropical secondary forest. For. Ecosyst. 2021, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.L.; Hättenschwiler, S.; Yang, J.J.; Sistla, S.; Wei, H.W.; Zhang, Z.W.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wang, R.Z.; Cui, S.Y.; Lü, X.T.; et al. Increasing rates of long-term nitrogen deposition consistently increased litter decomposition in a semi-arid grassland. New Phytol 2021, 229, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Nitrogen Addition Alleviates Microbial Nitrogen Limitations and Promotes Soil Respiration in a Subalpine Coniferous Forest. Forests 2019, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, J.; Buckeridge, K. Decoupled above- and belowground responses to multi-decadal nitrogen and phosphorus amendments in two tundra ecosystems. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xiang, W. Inconsistent Responses of Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure and Extracellular Enzyme Activity to Short-Term Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Plantations. Forests 2023, 14, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-C.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X.-F.; Fang, X.-M.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.-S. Divergent responses of soil microbial community to long-term nitrogen and phosphorus additions in a subtropical Chinese fir plantation. CATENA 2024, 242, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivlin, S.N.; Treseder, K.K. Soil extracellular enzyme activities correspond with abiotic factors more than fungal community composition. Biogeochemistry 2013, 117, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, K.J.; Fuchslueger, L.; Quesada, C.A.; Hofhansl, F.; Valverde-Barrantes, O.; Camargo, P.B.; Hoosbeek, M.R. Seasonal fluctuations of extracellular enzyme activities are related to the biogeochemical cycling of C, N and P in a tropical terra-firme forest. Biogeochemistry 2023, 163, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Forest Types | Sample Plot | Topographical Factors | Forest Stand Survey Factors | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope Aspect | Slope Position | Slope (°) | Elevation /m | Age (a) | Average DBH/cm | Average Tree Height/m | Stand Density (Plant/hm2) | Species Composition | Canopy Closure | ||
| F | F1 | semi-shady slope | downhill | 8° | 415 | 65 | 19.91 | 17.71 | 983 | 10Pk+Am | 0.70 |
| F2 | semi-shady slope | midslope | 9° | 435 | 65 | 22.91 | 19.55 | 950 | 10Pk | 0.80 | |
| F3 | semi-shady slope | uphill | 7° | 415 | 65 | 20.95 | 18.53 | 867 | 10Pk+Bc | 0.75 | |
| I | I1 | semi-shady slope | uphill | 15° | 485 | 230 | 18.26 | 10.48 | 783 | 7Pk+2An+1Bc+Ta-Am | 0.71 |
| I2 | semi-shady slope | midslope | 15° | 499 | 230 | 13.57 | 8.22 | 750 | 8Pk+1An+1Ta-Am | 0.65 | |
| I3 | semi-shady slope | downhill | 15° | 471 | 230 | 16.05 | 9.98 | 550 | 10Pk+Ta+Bp-Bc | 0.50 | |
| Site (S) | Treatment (T) | Litter (L) | S × T | S × L | T × L | S × T × L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 10.637 ** | 0.277 | 1.794 | 0.444 | 0.524 | 0.573 | 0.469 |
| BX | 7.909 ** | 0.185 | 1.682 | 0.291 | 0.815 | 0.195 | 0.422 |
| CBH | 7.446 ** | 0.414 | 0.115 | 0.397 | 0.463 | 0.13 | 0.582 |
| NAG | 0.265 | 1.38 | 1.228 | 0.743 | 0.599 | 1.029 | 0.494 |
| LAP | 2.866 | 1.011 | 1.557 | 0.159 | 1.371 | 0.447 | 0.537 |
| PEROX | 2.086 | 0.292 | 0.187 | 0.477 | 0.698 | 0.63 | 1.288 |
| PHOX | 0.003 | 0.812 | 1.164 | 0.155 | 0.488 | 0.54 | 0.377 |
| AP | 11.182 ** | 0.579 | 2.741 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 1.085 | 1.255 |
| C-degrading enzymes | 7.980 ** | 0.292 | 2.268 | 0.281 | 1.05 | 0.406 | 0.472 |
| N-degrading enzymes | 0.712 | 0.437 | 2.892 | 0.281 | 1.579 | 0.104 | 0.999 |
| TOC | DOC | TSN | SAP | TN | TP | PH | MBC | MBN | MBP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | −0.242 ** | −0.236 ** | −0.100 | 0.104 | −0.093 | −0.088 | −0.056 | −0.216 | 0.198 | 0.042 |
| BX | −0.211 | −0.243 ** | −0.022 | 0.095 | −0.222 | −0.003 | −0.045 | −0.209 | 0.172 | −0.085 |
| CBH | −0.262 ** | −0.190 | −0.078 | 0.022 | −0.057 | −0.099 | −0.239 ** | −0.083 | −0.003 | 0.136 |
| NAG | −0.021 | −0.167 | 0.080 | −0.050 | 0.073 | −0.191 | −0.032 | −0.112 | 0.136 | 0.012 |
| LAP | −0.245 ** | −0.113 | 0.090 | 0.092 | −0.297 ** | 0.007 | −0.166 | −0.032 | 0.308 ** | −0.118 |
| PEROX | −0.191 | 0.067 | −0.009 | −0.236 ** | −0.100 | −0.028 | −0.129 | −0.141 | 0.175 | 0.017 |
| PHOX | −0.060 | 0.090 | 0.045 | −0.083 | 0.060 | 0.141 | −0.138 | −0.089 | −0.008 | −0.010 |
| AP | −0.159 | −0.124 | −0.019 | 0.211 | 0.102 | 0.083 | −0.066 | −0.187 | −0.008 | −0.127 |
| C- | −0.203 | −0.268 ** | −0.125 | 0.114 | −0.174 | −0.048 | −0.036 | −0.181 | 0.152 | 0.001 |
| N- | −0.105 | −0.200 | −0.005 | 0.073 | −0.161 | −0.089 | −0.059 | −0.038 | 0.212 | −0.047 |
| Site (S) | Treatment (T) | Litter (L) | S × T | S × L | T × L | S × T × L | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC | 381.173 *** | 58.550 *** | 26.202 *** | 38.751 *** | 5.160 ** | 14.763 *** | 48.320 *** |
| DOC | 25.496 *** | 10.727 *** | 56.203 *** | 9.697 *** | 102.910 *** | 2.538 ** | 21.764 *** |
| TSN | 0.291 | 0.309 | 0.178 | 0.565 | 2.293 | 0.467 | 1.322 |
| SAP | 0.008 | 0.183 | 4.979 ** | 0.568 | 2.035 | 0.183 | 1.020 |
| TN | 27.143 *** | 26.597 *** | 14.665 *** | 11.645 *** | 0.649 | 18.862 *** | 16.246 *** |
| TP | 0.993 | 2.740 ** | 1.110 | 6.931 ** | 5.038 ** | 5.015 *** | 5.293 *** |
| PH | 10.087 ** | 0.874 | 0.751 | 2.148 | 1.575 | 0.764 | 2.625 ** |
| MBC | 863.943 *** | 181.412 *** | 227.335 *** | 150.589 *** | 18.362 *** | 224.040 *** | 227.640 *** |
| MBN | 3.647 | 0.485 | 0.772 | 0.748 | 0.378 | 0.773 | 0.402 |
| MBP | 0.916 | 0.165 | 1.199 | 0.249 | 0.168 | 0.796 | 0.207 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Duan, W. The Responses of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Microbial Nutrients to the Interaction between Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions and Apoplastic Litter in Broad-Leaved Korean Pine Forests in Northeast China. Forests 2024, 15, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101764
Chen L, Chen L, Chen M, Wang Y, Duan W. The Responses of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Microbial Nutrients to the Interaction between Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions and Apoplastic Litter in Broad-Leaved Korean Pine Forests in Northeast China. Forests. 2024; 15(10):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101764
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Liming, Lixin Chen, Meixuan Chen, Yafei Wang, and Wenbiao Duan. 2024. "The Responses of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Microbial Nutrients to the Interaction between Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions and Apoplastic Litter in Broad-Leaved Korean Pine Forests in Northeast China" Forests 15, no. 10: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101764
APA StyleChen, L., Chen, L., Chen, M., Wang, Y., & Duan, W. (2024). The Responses of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Microbial Nutrients to the Interaction between Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions and Apoplastic Litter in Broad-Leaved Korean Pine Forests in Northeast China. Forests, 15(10), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101764






