Coupling UAV Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data for Mangrove Classification Using XGBoost in China’s Pinglu Canal Estuary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
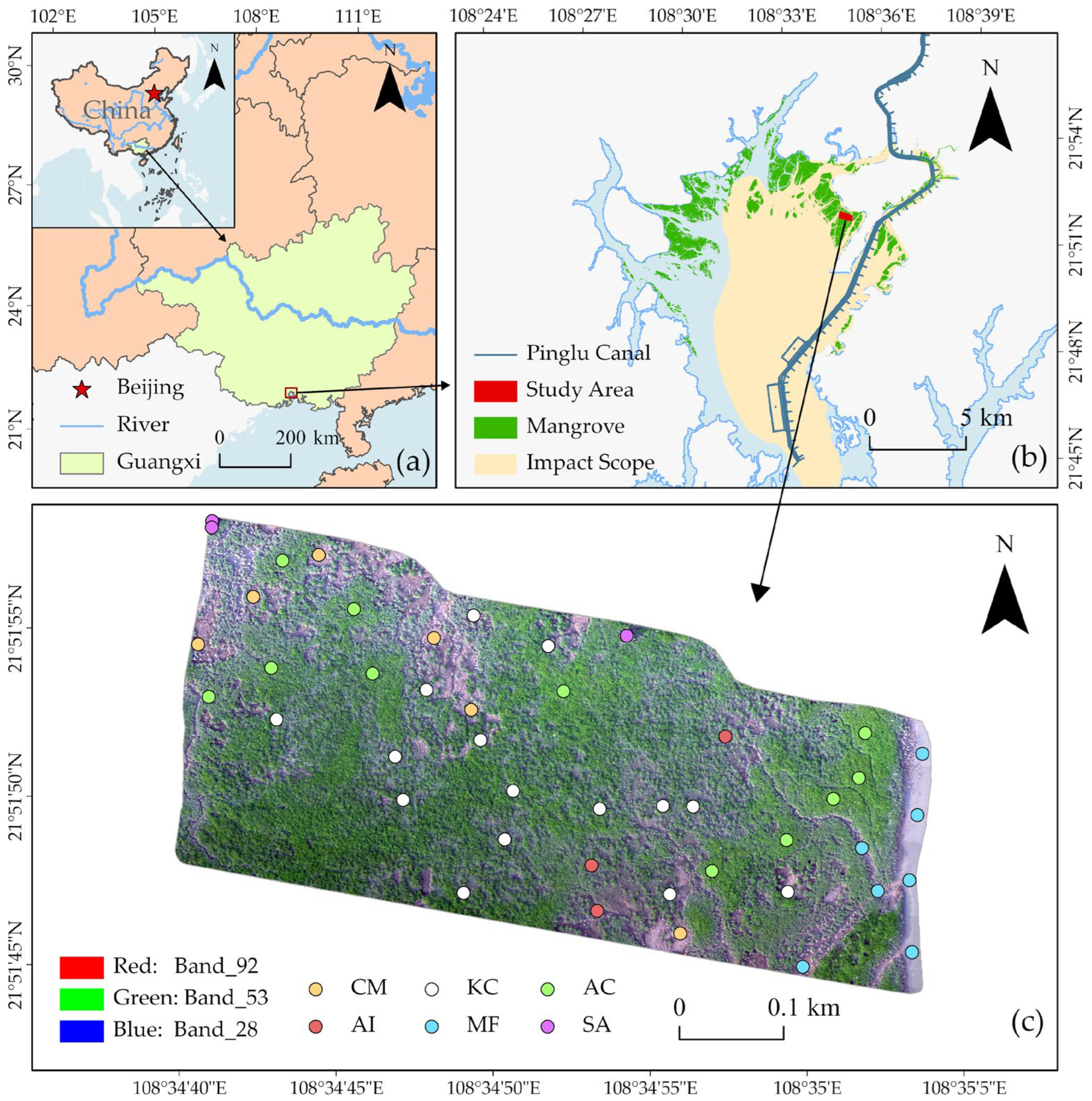
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
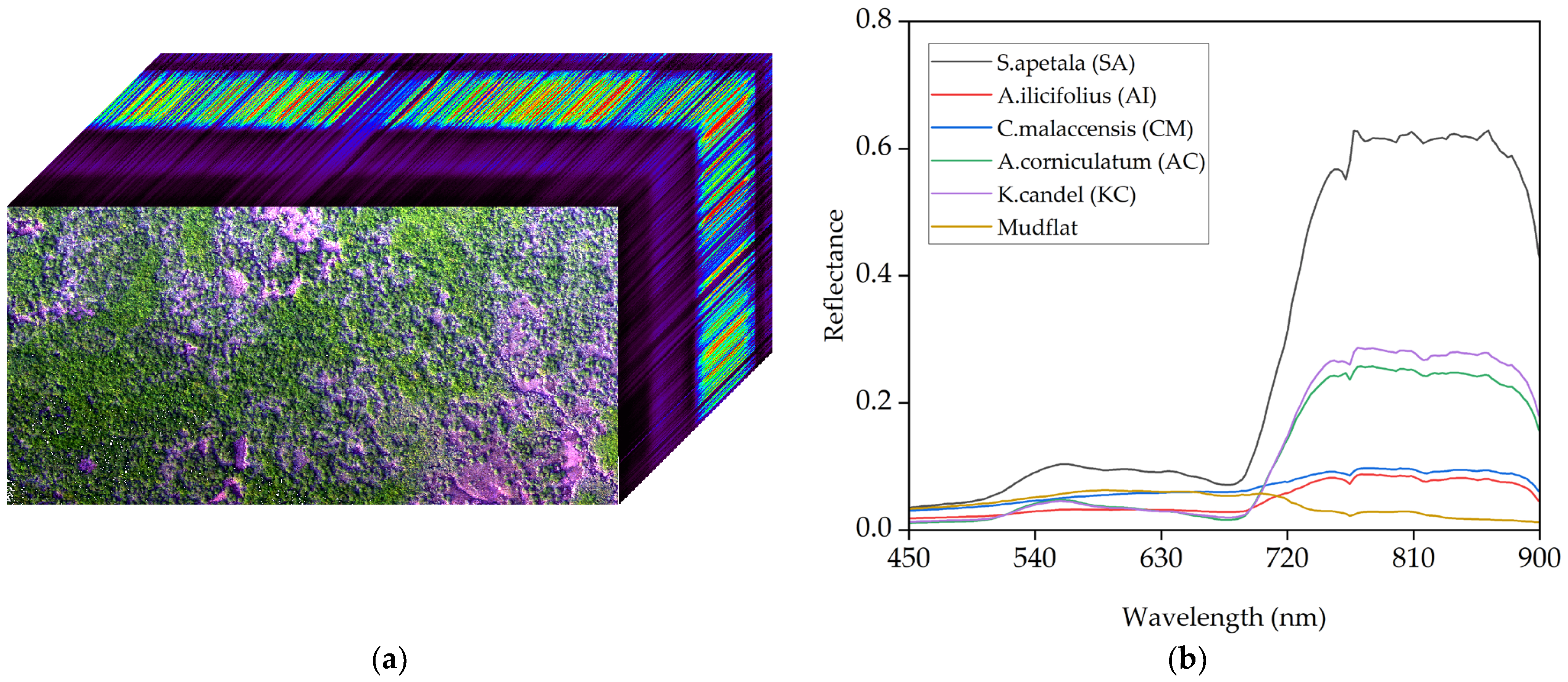
2.2.1. Hyperspectral Data Acquisition
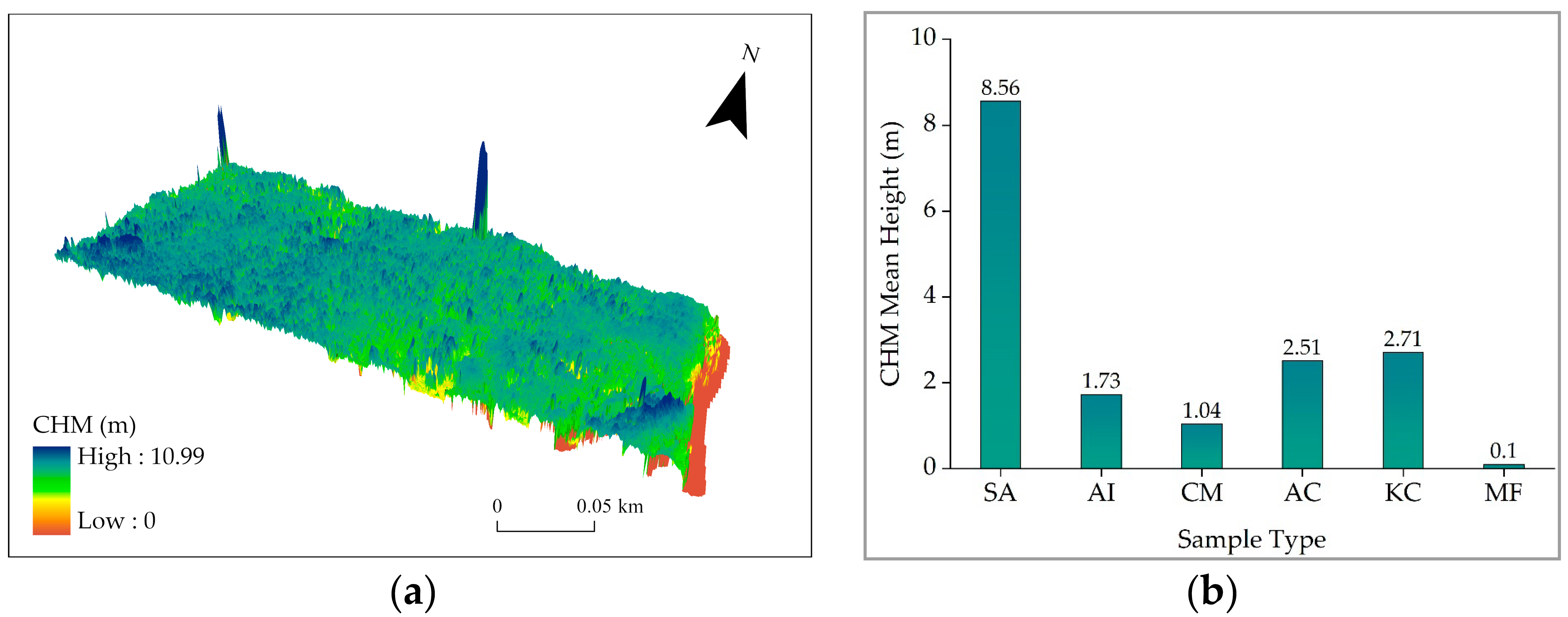
2.2.2. UAV-LiDAR Data Acquisition
2.2.3. Mangrove Species Sample Data Acquisition
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. UAV-Hyperspectral Feature Extraction
2.3.2. UAV-LiDAR Height Feature Extraction
2.3.3. XGBoost Machine Learning Algorithm
2.3.4. Feature Variable Scenario Selection
2.3.5. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
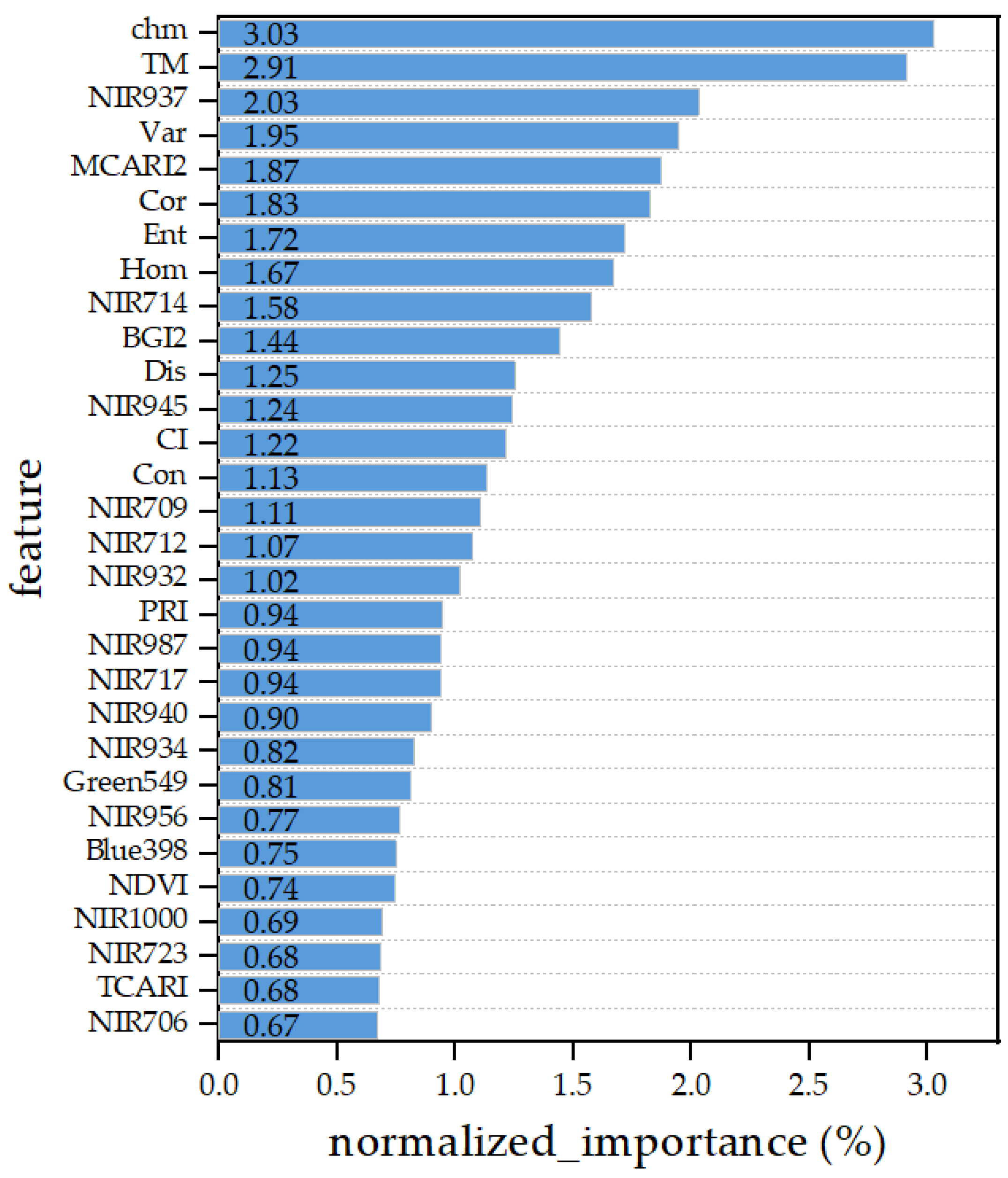
3.1. Variable Importance Analysis
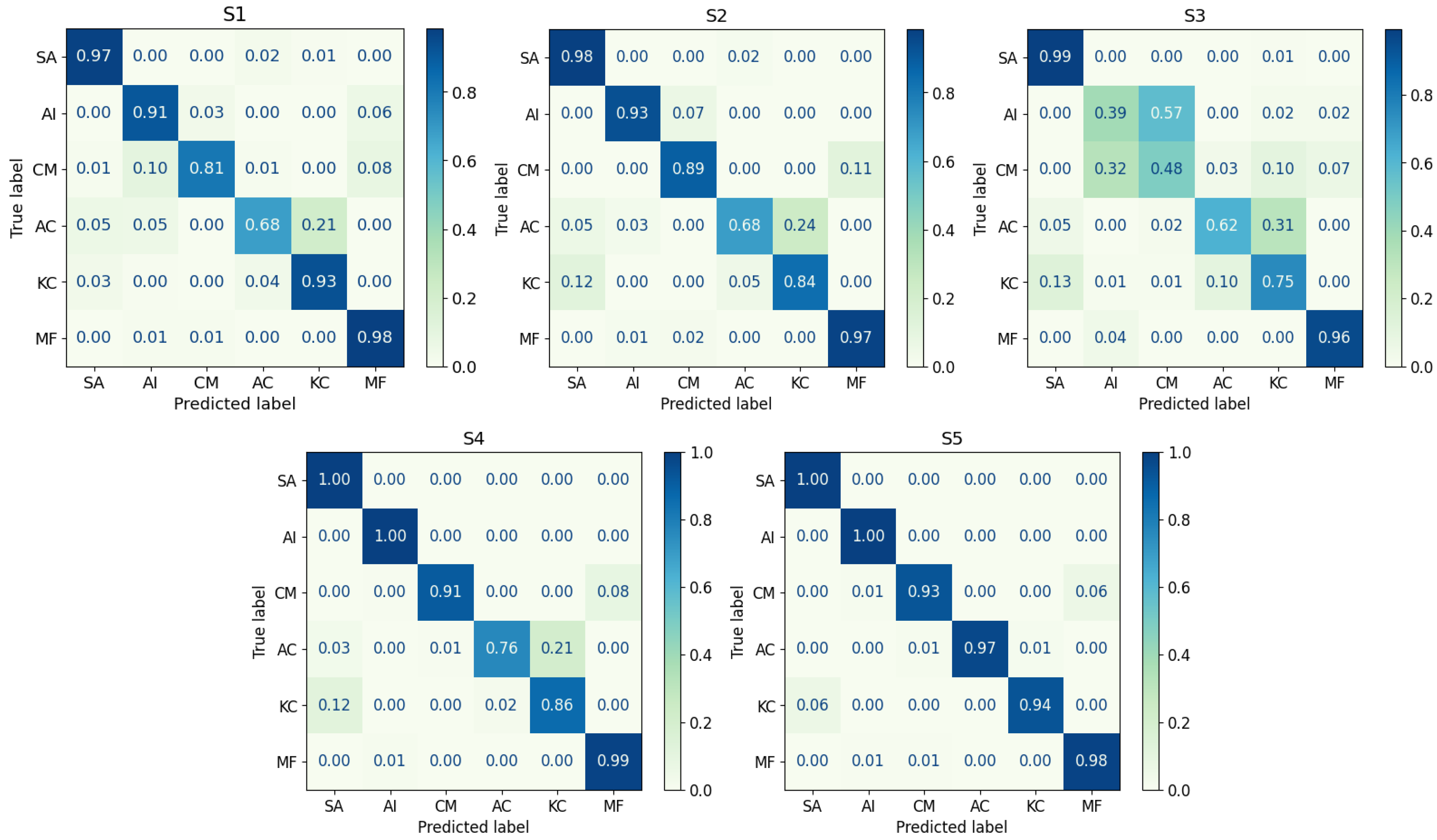
3.2. Comparison of Mangrove Classification Accuracy
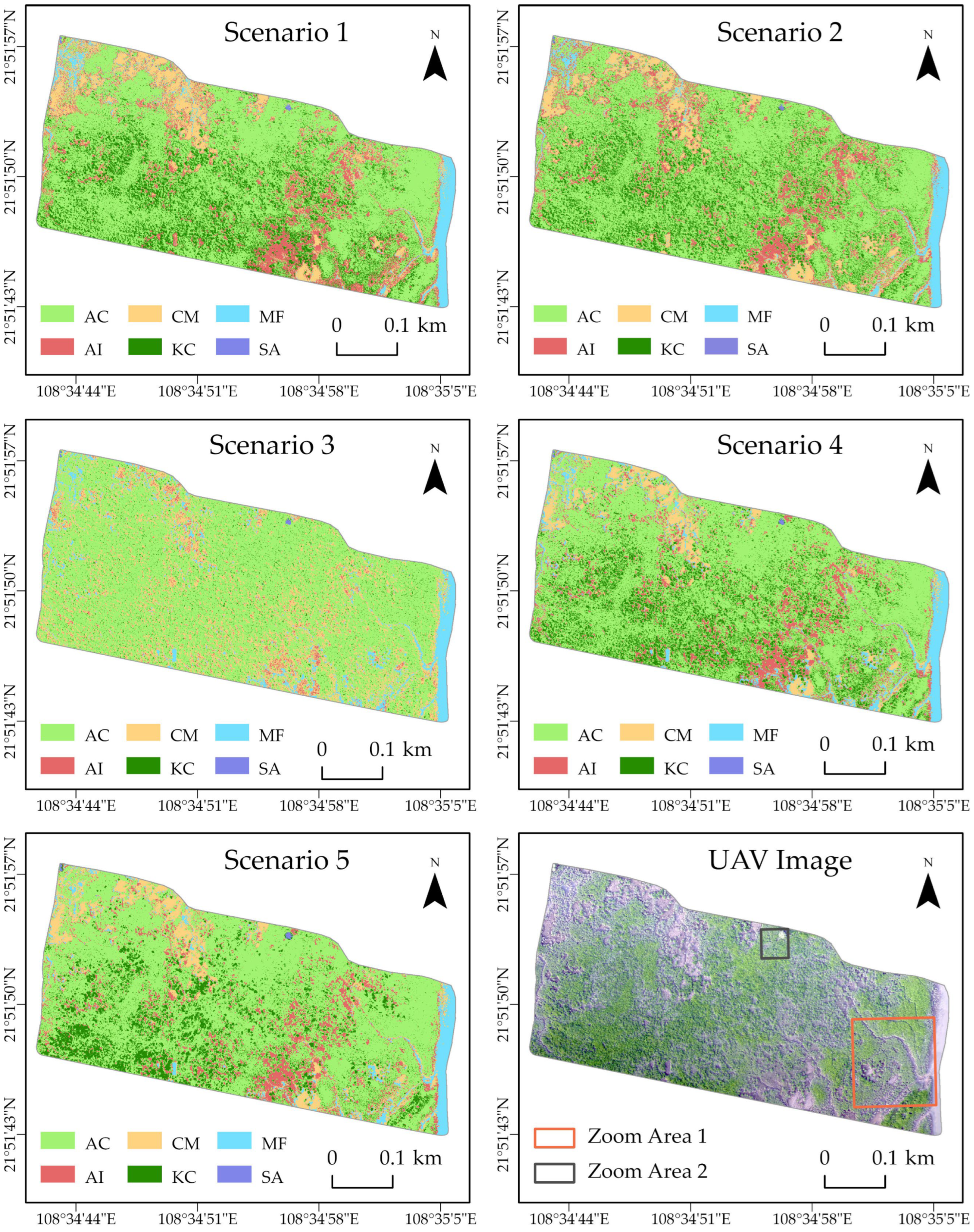
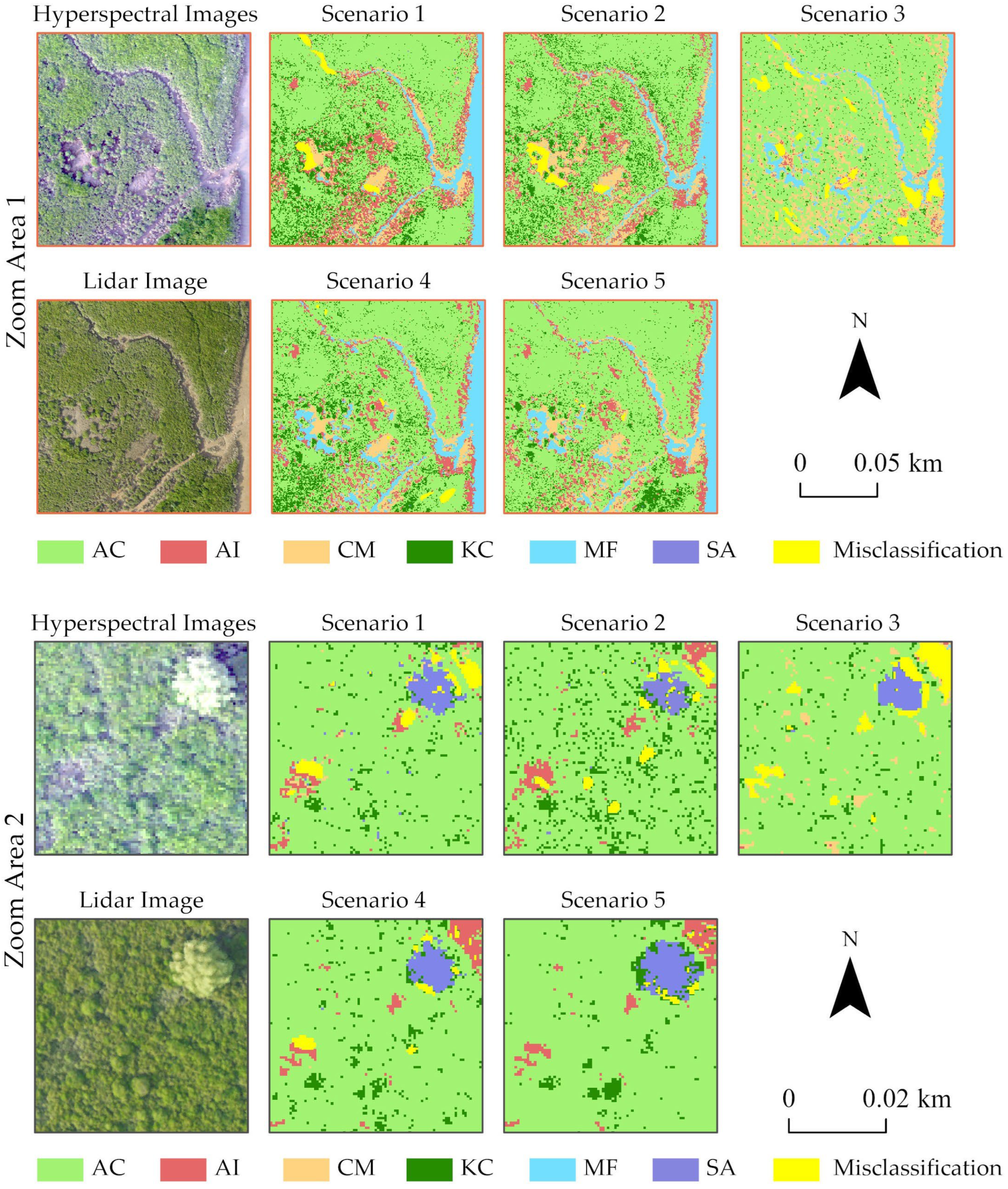
3.3. Mapping Mangrove Forests
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Individual and Fused Feature Scenarios on Classification
4.2. Contribution of LiDAR Data in Classification
4.3. Performance of XGBoost Algorithm Applied to Mangrove Classification
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The integration of UAV-based hyperspectral data with LiDAR-derived CHM data has significant positive implications for the classification performance. The inclusion of CHM data effectively mitigates the risk of misclassifying mangrove species with similar spectral attributes. This study achieves the highest precision of 96.78% and a commendable kappa coefficient of 95.96%.
- (2)
- The incorporation of texture measures leads to a reduction in the accuracy of mangrove species classification owing to the presence of redundant information. Enhancing the accuracy of mangrove species classification can be achieved by supplementing textural measures with data features derived from individual bands and vegetation indices.
- (3)
- The XGBoost algorithm adeptly assesses the importance of features, producing highly accurate classification outcomes, while maintaining a stable operational framework. Its performance is exceptional, showing significant potential for widespread application in the field of mangrove classification.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, T. Carbon Sequestration in Mangroves. In Blue Carbon in Shallow Coastal Ecosystems: Carbon Dynamics, Policy, and Implementation; Kuwae, T., Hori, M., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 73–99. ISBN 9789811312953. [Google Scholar]
- Kathiresan, K. Importance of Mangrove Ecosystem. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 2, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, W.; Jiang, C.; Yan, Y.; Guan, Q. Potential Ecosystem Service Values of Mangrove Forests in Southeastern China Using High-Resolution Satellite Data. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 209, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-de-Santiago, F.; Kovacs, J.M.; Wang, J.; Flores-Verdugo, F.; Zhang, C.; González-Farías, F. Examining the Influence of Seasonality, Condition, and Species Composition on Mangrove Leaf Pigment Contents and Laboratory Based Spectroscopy Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, I.A.L.; de Carvalho Júnior, O.A.; de Carvalho, O.L.F.; de Albuquerque, A.O.; Hermuche, P.M.; Merino, É.R.; Gomes, R.A.T.; Guimarães, R.F. Comparing Machine and Deep Learning Methods for the Phenology-Based Classification of Land Cover Types in the Amazon Biome Using Sentinel-1 Time Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Zhen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, X.; Shen, Z.; Gao, C.; Wu, G. Mapping Seasonal Leaf Nutrients of Mangrove with Sentinel-2 Images and XGBoost Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Yokoya, N.; Bui, D.T.; Yoshino, K.; Friess, D.A. Remote Sensing Approaches for Monitoring Mangrove Species, Structure, and Biomass: Opportunities and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, X.; Ou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J.; Lin, J. Mangrove Biodiversity Assessment Using UAV Lidar and Hyperspectral Data in China’s Pinglu Canal Estuary. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, P.; Rosenqvist, A.; Hilarides, L.; Lucas, R.M.; Thomas, N.; Tadono, T.; Worthington, T.A.; Spalding, M.; Murray, N.J.; Rebelo, L.-M. Global Mangrove Extent Change 1996–2020: Global Mangrove Watch Version 3.0. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damastuti, E.; de Groot, R.; Debrot, A.O.; Silvius, M.J. Effectiveness of Community-Based Mangrove Management for Biodiversity Conservation: A Case Study from Central Java, Indonesia. Trees For. People 2022, 7, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Bluemel, A.; Gebhardt, S.; Quoc, T.V.; Dech, S. Remote Sensing of Mangrove Ecosystems: A Review. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 878–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.; Boon, P.I.; Branigan, S.; Duke, N.C.; Field, C.D.; Fitzsimons, J.A.; Kirkman, H.; Mackenzie, J.R.; Saintilan, N. The State of Legislation and Policy Protecting Australia’s Mangrove and Salt Marsh and Their Ecosystem Services. Mar. Policy 2016, 72, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidik, F.; Supriyanto, B.; Krisnawati, H.; Muttaqin, M.Z. Mangrove Conservation for Climate Change Mitigation in Indonesia. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, e529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission and Ministry of Natural Resources, PRC. National Master Plan for Major Ecosystem Protection and Restoration Projects (2020–2025). 2020. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-08/29/content_5538354.htm (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Tian, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J. Aboveground Mangrove Biomass Estimation in Beibu Gulf Using Machine Learning and UAV Remote Sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, J.; Chen, D. Remote Sensing Technology for Mapping and Monitoring Land-Cover and Land-Use Change. Prog. Plan. 2004, 61, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Nayyar, Z.A. Extraction of Mangrove Forest through Landsat 8 Mangrove Index (L8MI). Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sousa, W.P.; Gong, P.; Biging, G.S. Comparison of IKONOS and QuickBird Images for Mapping Mangrove Species on the Caribbean Coast of Panama. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimizadeh, N.; Babaie Kafaky, S.; Sahebi, M.R.; Mataji, A. Forest Structure Parameter Extraction Using SPOT-7 Satellite Data by Object- and Pixel-Based Classification Methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 192, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Raychaudhuri, B. Mapping Distribution of Sundarban Mangroves Using Sentinel-2 Data and New Spectral Metric for Detecting Their Health Condition. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Evaluation of Morphological Texture Features for Mangrove Forest Mapping and Species Discrimination Using Multispectral IKONOS Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama-Landeros, L.; Flores-de-Santiago, F.; Kovacs, J.M.; Flores-Verdugo, F. An Assessment of Commonly Employed Satellite-Based Remote Sensors for Mapping Mangrove Species in Mexico Using an NDVI-Based Classification Scheme. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, D.; Bharti, R. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing and Geological Applications. Curr. Sci. 2015, 108, 879–891. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Ren, C. Mapping the Distribution of Mangrove Species in the Core Zone of Mai Po Marshes Nature Reserve, Hong Kong, Using Hyperspectral Data and High-Resolution Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. Mangrove Forest Species Classification Based on the UAV Hyperspectral Images. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2022, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Hati, J.; Samanta, S.; Rani Chaube, N.; Misra, A.; Giri, S.; Pramanick, N.; Gupta, K.; Datta Majumdar, S.; Chanda, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; et al. Mangrove Classification Using Airborne Hyperspectral AVIRIS-NG and Comparing with Other Spaceborne Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Treitz, P.M.; Chen, D.; Quan, C.; Shi, L.; Li, X. Mapping Mangrove Forests Using Multi-Tidal Remotely-Sensed Data and a Decision-Tree-Based Procedure. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 62, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakti, A.D.; Fauzi, A.I.; Wilwatikta, F.N.; Rajagukguk, Y.S.; Sudhana, S.A.; Yayusman, L.F.; Syahid, L.N.; Sritarapipat, T.; Principe, J.A.; Trang, N.T.Q. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Product Analysis: Investigating Anthropogenic and Naturogenic Impacts on Mangroves in Southeast Asia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Huang, B.; Xu, B. Multi-Source Remotely Sensed Data Fusion for Improving Land Cover Classification. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Fusion: Status and Trends. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2010, 1, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, M.; Qi, J.; Fu, T.; Fan, S.; Chen, B. High-Resolution Mangrove Forests Classification with Machine Learning Using Worldview and UAV Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Leng, W.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; He, Z.; Zhu, Y. Object-Based Mangrove Species Classification Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Images and Digital Surface Models. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, A.; Dubovyk, O.; Abou El-Magd, I.; Menz, G. Mapping Mangroves Extents on the Red Sea Coastline in Egypt Using Polarimetric SAR and High Resolution Optical Remote Sensing Data. Sustainability 2018, 10, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, C.; Pan, F.; Xi, X.; Li, G.; Nie, S.; Xia, S. Estimation of Wetland Vegetation Height and Leaf Area Index Using Airborne Laser Scanning Data. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lin, J. Aboveground Biomass of Typical Invasive Mangroves and Its Distribution Patterns Using UAV-LiDAR Data in a Subtropical Estuary: Maoling River Estuary, Guangxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannasiri, W.; Nagai, M.; Honda, K.; Santitamnont, P.; Miphokasap, P. Extraction of Mangrove Biophysical Parameters Using Airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1787–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Wang, L. Individual Mangrove Tree Measurement Using UAV-Based LiDAR Data: Possibilities and Challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wong, F.K.K.; Fung, T. Classification of Mangrove Species Using Combined WordView-3 and LiDAR Data in Mai Po Nature Reserve, Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wan, B.; Qiu, P.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Q. Mapping Mangrove Species Using Combined UAV-LiDAR and Sentinel-2 Data: Feature Selection and Point Density Effects. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, Z. Urban Tree Species Mapping Using Airborne LiDAR and Hyperspectral Data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, L.; Cho, M.A.; Mathieu, R.; Asner, G. Classification of Savanna Tree Species, in the Greater Kruger National Park Region, by Integrating Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data in a Random Forest Data Mining Environment. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 69, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, K.; Zhuo, L.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, L. Combining UAV-Based Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data for Mangrove Species Classification Using the Rotation Forest Algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, M.; Yin, D.; Tian, J. A Review of Remote Sensing for Mangrove Forests: 1956–2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tan, L.; Fan, J. Performance Evaluation of Mangrove Species Classification Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data Using Extremely Randomized Trees in Fucheng Town, Leizhou City, Guangdong Province. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwanto, A.D.; Asriningrum, W. Identification of mangrove forests using multispectral satellite imageries. Int. J. Remote Sens. Earth Sci. 2019, 16, 63–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.D.; Barnwal, S.; Paramanik, S.; Das, P.; Bhattyacharya, B.K.; Jagadish, B.; Roy, P.S.; Ghosh, S.M.; Behera, S.K. Species-Level Classification and Mapping of a Mangrove Forest Using Random Forest—Utilisation of AVIRIS-NG and Sentinel Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhen, J.N.; Jiang, X.P.; Wang, J.J. Mangrove Species Classification with UAV-Based Remote Sensing Data and XGBoost. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; He, X.; Yao, H.; Liang, Y.; Deng, T.; He, H.; Fan, D.; Lan, G.; He, W. Comparison of RFE-DL and Stacking Ensemble Learning Algorithms for Classifying Mangrove Species on UAV Multispectral Images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Wu, D.; Fang, L.; Zheng, X. Tree Species Identification Using XGBoost Based on GF-2 Images. For. Resour. Wanagement 2019, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, N.; Pádua, L.; Sousa, J.J.; Bento, A.; Couto, P. Almond Cultivar Identification Using Machine Learning Classifiers Applied to UAV-Based Multispectral Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 1533–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Kwan, K.; Zhang, Q. Dynamics of mangrove change: Insights from 30-year observations of Maowei Sea. J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 40, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Han, Z. Study on the Influence and Countermeasures of the Canal Projects on Aquatic Ecological Environment of Rivers along the Line. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 393, 01038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z. Analysis on the Relationship between Mangrove and Aquaculture in Maowei Sea Based on Object-Oriented Method. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 165, 03022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Phinn, S.; Johansen, K. Characterizing the Spatial Structure of Mangrove Features for Optimizing Image-Based Mangrove Mapping. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 984–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, T.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ting, K.C. A Review of Remote Sensing Methods for Biomass Feedstock Production. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2455–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; He, Z. Identifying Mangrove Species Using Field Close-Range Snapshot Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine-Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Lin, H. GF-5 Hyperspectral Data for Species Mapping of Mangrove in Mai Po, Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Berjón, A.; López-Lozano, R.; Miller, J.R.; Martín, P.; Cachorro, V.; González, M.R.; de Frutos, A. Assessing Vineyard Condition with Hyperspectral Indices: Leaf and Canopy Reflectance Simulation in a Row-Structured Discontinuous Canopy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 99, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, K.; Liu, Y.; Kovacs, J.M.; Flores-Verdugo, F.; Santiago, F.J.F. de Spectral Response to Varying Levels of Leaf Pigments Collected from a Degraded Mangrove Forest. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rivard, B.; Sánchez-Azofeifa, A.; Castro-Esau, K. Intra- and Inter-Class Spectral Variability of Tropical Tree Species at La Selva, Costa Rica: Implications for Species Identification Using HYDICE Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Ray, S.S.; Singh, J.P.; Panigrahy, S. Use of Hyperspectral Data to Assess the Effects of Different Nitrogen Applications on a Potato Crop. Precis. Agric. 2007, 8, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H. Canopy Clumping Index (CI): A Review of Methods, Characteristics, and Applications. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 303, 108374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xia, W.; Xu, B.; Bai, L. Multi-Feature Classification Approach for High Spatial Resolution Hyperspectral Images. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Guo, P.; Lu, H. Texture Feature Extraction of Multiband Remote Sensing Image Based on Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix. Comput. Sci. 2004, 31, 162–163. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Chen, G.; Tian, L.; Qin, K.; Qian, S.-E. Minimum Noise Fraction versus Principal Component Analysis as a Preprocessing Step for Hyperspectral Imagery Denoising. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 42, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.; Treitz, P.; Wulder, M.; St-Onge, B.; Flood, M. LiDAR Remote Sensing of Forest Structure. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2003, 27, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastaranta, M.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Pekkarinen, A.; Tuominen, S.; Ginzler, C.; Kankare, V.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, J.; Hyyppä, H. Airborne Laser Scanning and Digital Stereo Imagery Measures of Forest Structure: Comparative Results and Implications to Forest Mapping and Inventory Update. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 39, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Knapp, N.; Bohn, F.; Shugart, H.H.; Huth, A. The Relevance of Forest Structure for Biomass and Productivity in Temperate Forests: New Perspectives for Remote Sensing. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 709–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Mao, X. Multilevel Extraction of Vegetation Type Based on Airborne LiDAR Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 46, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zięba-Kulawik, K.; Hawrylo, P.; Wężyk, P.; Matczak, P.; Przewoźna, P.; Inglot, A.; Mączka, K. Improving Methods to Calculate the Loss of Ecosystem Services Provided by Urban Trees Using LiDAR and Aerial Orthophotos. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 63, 127195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortezza, R.; Giannico, V. Combining High-Resolution Images and LiDAR Data to Model Ecosystem Services Perception in Compact Urban Systems. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Fu, J.; Jiang, R.; Li, G.; Yang, Q. Lithological Classification by Hyperspectral Images Based on a Two-Layer XGBoost Model, Combined with a Greedy Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-429-05272-9. [Google Scholar]
- Torabzadeh, H.; Leiterer, R.; Hueni, A.; Schaepman, M.E.; Morsdorf, F. Tree Species Classification in a Temperate Mixed Forest Using a Combination of Imaging Spectroscopy and Airborne Laser Scanning. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 279, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Su, B. Significant Remote Sensing Vegetation Indices: A Review of Developments and Applications. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, e1353691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Zhan, Y.; Tao, B.; Xu, K. Effects of Spatial Resolution and Texture Features on Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing Classification. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.-Y.; Shih, C.-N.; Tsai, T.-T. Sensitivity to Chilling Temperatures and Distribution Differ in the Mangrove Species Kandelia Candel and Avicennia Marina. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhtadi, A.; Yulianda, F.; Boer, M.; Krisanti, M. Spatial Distribution of Mangroves in Tidal Lake Ecosystem. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 454, 012131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.P.Y.; Fung, T.; Wong, F.K.K. Estimating Above-Ground Biomass of Subtropical Forest Using Airborne LiDAR in Hong Kong. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Shaker, A.; Silva, C.; Klauberg, C.; Pinagé, E. Remote Sensing of Leaf Area Index from LiDAR Height Percentile Metrics and Comparison with MODIS Product in a Selectively Logged Tropical Forest Area in Eastern Amazonia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wong, F.K.K.; Fung, T.; Brown, L.A.; Dash, J. Assessment of Active LiDAR Data and Passive Optical Imagery for Double-Layered Mangrove Leaf Area Index Estimation: A Case Study in Mai Po, Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Dikshit, O.; Gupta, A.; Singh, M.K. Feature Extraction for Hyperspectral Image Classification: A Review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 6248–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ren, G.; Wu, P.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. Mangrove Species Classification in the Hainan Bamen Bay Based on GF Optics and Fully Polarimetric SAR. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, X.P.; Zhen, J.N.; Wang, J.; Guo, G. Mangrove Species Classification with Combination of WorldView-2 and Zhuhai-1 Satellite Images. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Capture Date | 15 December 2022 |
| Flight Altitude | 150 m |
| Spectral Range | 400–1000 nm |
| Spatial Resolution | 0.1 m × 0.1 m |
| Bands | 220 |
| Flight Speed | 8 m/s |
| Sample Type | SA | AI | CM | AC | KC | MF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of stations | 3 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 20 | 8 |
| pixel point | 39 | 179 | 349 | 1683 | 322 | 621 |
| UAV aerial photography |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| UAV hyperspectral imagery |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Vegetation Index | Formula | References |
|---|---|---|
| Blue Green Pigment Index 2 (BGI2) | [59] | |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | [32] | |
| Reformed Difference Vegetation Index (RDVI) | [59] | |
| Transformed Chlorophyll Absorption in Reflectance Index (TCARI) | [60] | |
| Optimized Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index (OSAVI) | [46] | |
| Modified Chlorophyll Absorption Ratio Index 1 (MCARI1) | [57] | |
| Modified Chlorophyll Absorption Ratio Index 2 (MCARI2) | [57] | |
| Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI) | [61] | |
| Simple Ratio Index (SR) | [62] | |
| Clumping Index (CI) | [63] |
| Texture Features | Formula | References |
|---|---|---|
| Textural Mean (TM) | [15] | |
| Homogeneity (HOM) | ||
| Dissimilarity (Dis) | ||
| Correlation (Cor) | ||
| Variance (Var) | ||
| Entropy (Ent) | ||
| Contrast (Con) |
| Scenarios | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | UA (%) |
| SA | 74.75 | 97.37 | 65.66 | 98.48 | 71.21 | 99.3 | 74.75 | 100 | 88.38 | 100 |
| AI | 53.25 | 91.11 | 83.77 | 93.48 | 24.03 | 38.54 | 94.81 | 100 | 94.16 | 100 |
| CM | 96.23 | 80.00 | 91.98 | 88.64 | 66.04 | 48.28 | 97.64 | 91.19 | 94.81 | 93.06 |
| AC | 97.53 | 67.81 | 97.53 | 68.26 | 96.02 | 62.09 | 99.05 | 75.87 | 99.81 | 97.23 |
| KC | 56.30 | 92.92 | 52.01 | 83.62 | 24.13 | 75.00 | 61.93 | 86.19 | 98.12 | 93.61 |
| MF | 95.23 | 98.42 | 95.23 | 97.27 | 95.99 | 95.81 | 96.37 | 98.83 | 97.52 | 98.27 |
| OA (%) | 83.35 | 83.55 | 71.28 | 88.48 | 96.78 | |||||
| Kappa (%) | 78.81 | 79.07 | 63.36 | 85.42 | 95.96 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ou, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, J.; Lin, J. Coupling UAV Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data for Mangrove Classification Using XGBoost in China’s Pinglu Canal Estuary. Forests 2023, 14, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091838
Ou J, Tian Y, Zhang Q, Xie X, Zhang Y, Tao J, Lin J. Coupling UAV Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data for Mangrove Classification Using XGBoost in China’s Pinglu Canal Estuary. Forests. 2023; 14(9):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091838
Chicago/Turabian StyleOu, Jinhai, Yichao Tian, Qiang Zhang, Xiaokui Xie, Yali Zhang, Jin Tao, and Junliang Lin. 2023. "Coupling UAV Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data for Mangrove Classification Using XGBoost in China’s Pinglu Canal Estuary" Forests 14, no. 9: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091838
APA StyleOu, J., Tian, Y., Zhang, Q., Xie, X., Zhang, Y., Tao, J., & Lin, J. (2023). Coupling UAV Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data for Mangrove Classification Using XGBoost in China’s Pinglu Canal Estuary. Forests, 14(9), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091838







