The Relationships between Root Traits and the Soil Erodibility of Farmland Shelterbelts in the Bashang Region of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Root Trait Measurements
2.3. Soil Trait Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Differences of Root Functional Traits across Species
3.2. Differences in the Soil Erodibility of Four Land Types
3.3. The Correlations among Soil Characteristics
3.4. The Correlations between Root Traits and Soil Erodibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. Wind erosion in arid and semiarid China: An overview. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 55, 439–444. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lang, L.; Yan, P.; Wang, G.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Hua, T. Aeolian processes and their effect on sandy desertification of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: A wind tunnel experiment. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 158, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Zhang, H.; Mao, N. Study on the changing laws of wind-blown mass affected by wind speed. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2004, 22, 149–153, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Wind initiation threshold of the moistened sand. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryrear, D.W. Soil ridges-clods and wind erosion. Trans. ASABE 1984, 27, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobeck, T.M. Soil properties affecting wind erosion. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Knapen, A.; Poesen, J.; Govers, G.; Gyssels, G.; Nachtergaele, J. Resistance of soils to concentrated flow erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2007, 80, 75–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tang, K.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X. Temporal variability in rill erodibility for two types of grasslands. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobeck, T.M.; Popham, T.W.; Skidmore, E.L.; Lamb, J.A.; Merril, S.D.; Lindstrom, M.J.; Mokma, D.L.; Yoder, R.E. Aggregate-mean diameter and wind-erodible soil predictions using dry aggregate-size distributions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, G.G.; Mendez, M.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Tillage affects soil aggregation parameters linked with wind erosion. Geoderma 2007, 140, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colazo, J.C.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Soil dry aggregate stability and wind erodible fraction in a semiarid environment of Argentina. Geoderma 2010, 159, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, C.; Zou, X.; Li, H.; Kang, L.; Liu, B.; Li, J. Wind erosion rate for vegetated soil cover: A prediction model based on surface shear strength. Catena 2020, 187, 104398. [Google Scholar]
- Chamizo, S.; Rodríguez-Caballero, E.; Cantón, Y.; Asensio, C.; Domingo, F. Penetration resistance of biological soil crusts and its dynamics after crust removal: Relationships with runoff and soil detachment. Catena 2015, 126, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, Z.E.; Al-Madhhachi, A.T.; Alzubaidi, L.A. Behavior of soil erodibility parameters due to biological soil crusts using jet erosion tests. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 153, 105903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryrear, D.W.; Krammes, C.A.; Williamson, D.L.; Zobeck, T.M. Computing the wind erodible fraction of soils. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1994, 49, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Chang, C.; Wang, R.; Li, J. Comparison of different methods to determine wind-erodible fraction of soil with rock fragments under different tillage/management. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 168, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobeck, T.M.; Sterk, G.; Funk, R.; Rajot, J.L.; Van Pelt, R.S. Measurement and data analysis methods for field-scale wind erosion studies and model validation. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2003, 28, 1163–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, N.P.; McGowan, H.A. Approaches to modeling land erodibility by wind. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2009, 33, 587–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, A.; Yu, D.; Zhou, J. Spatial wind speed and surface wind erosion characteristics of farm-shelter forest network in arid sandy area. Trans. CSAE 2018, 34, 135–141, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Jia, G.; Liu, Z. Determination of optimum vegetation type and layout for soil wind erosion control in desertified land in North China. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 171, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Askar, A.; Wang, H. Shelter Efficiency of Various Shelterbelt Configurations: A Wind Tunnel Study. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Jetten, V.; Baffaut, C.; Cerdan, O.; Couturier, A.; Hernandez, M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Nichols, M.H.; Nunes, J.P.; Renschler, C.S.; et al. Modeling response of soil erosion and runoff to changes in precipitation and cover. Catena 2005, 61, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Tuo, D.; Bai, R.; Qiao, F. Relative contribution of root physical enlacing and biochemistrical exudates to soil erosion resistance in the Loess soil. Catena 2017, 153, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, J. Response of soil detachment capacity to plant root and soil properties in typical grasslands on the Loess Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 266, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shit, P.K.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Bhunia, G.S. Role of Plant Roots to Control Rill-Gully Erosion: Hydraulic Flume Experiment. In Gully Erosion Studies from India and Surrounding Regions; Springer: Cham, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Su, X. Effects of root density on soil detachment capacity by overland flow during one growing season. J. Soil Sediment 2022, 22, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Huang, X. Particle interaction forces induce soil particle transport during rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xu, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; He, X. Particles interaction forces and their effects on soil aggregates breakdown. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 147, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, F. The role of roots traits of climax community species to shear strength in the Loess Hilly Region, China. Soil Till. Res. 2022, 221, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, H.; He, B.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X.; Qiang, J. Root tensile strength of terrace hedgerow plants in the karst trough valleys of SW China: Relation with root morphology and fiber content. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, I.J.; Quinton, J.N.; Weigelt, A.; de Deyn, G.; Bardgett, R.D. Plant diversity and root traits benefit physical properties key to soil function in grasslands. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Damour, G.; Gary, C.; Follain, S.; Bissonnais, Y.L.; Metay, A. Trait-based approach for agroecology: Contribution of service crop root traits to explain soil aggregate stability in vineyards. Plant Soil 2019, 435, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dorodnikov, M.; Splettstößer, T.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Pausch, J. Effects of maize roots on aggregate stability and enzyme activities in soil. Geoderma 2017, 306, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yao, K.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Chang, E.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T. Increased soil aggregate stability is strongly correlated with root and soil properties along a gradient of secondary succession on the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 143, 105671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Qin, J.; Sun, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J. Erosion-reducing effects of plant roots during concentrated flow under contrasting textured soils. Catena 2021, 203, 105378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z. Quantifying effects of root systems of planted and natural vegetation on rill detachment and erodibility of a loessial soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erktan, A.; Cecillon, L.; Graf, F.; Roumet, C.; Legout, C.; Rey, F. Increase in soil aggregate stability along a Mediterranean successional gradient in severely eroded gully bed ecosystems: Combined effects of soil, root traits and plant community characteristics. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, V.; Roumet, C.; Munson, A.D. The root of the matter: Linking root traits and soil organic matter stabilization processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, N.; Dong, Z.; Van Pelt, R.S.; Zobeck, T.M. Wind erosion induced soil degradation in Northern China: Status, measures and perspective. Sustainability 2014, 6, 8951–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, A.; Zou, C.; Xu, W.; Shimizu, H.; Wang, K. An overview of the “Three-North” Shelterbelt project in China. For. Stud. China 2012, 14, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Guo, D.; Yang, H.; Gao, W.; Li, S. Growth, morphological traits and mycorrhizal colonization of fine roots respond differently to nitrogen addition in a slash pine plantation in subtropical China. Plant Soil 2015, 391, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Kou, L.; Wang, H.; Fu, X.; Dai, X.; Li, S. Contrasting root foraging strategies of two subtropical coniferous forests under an increased diversity of understory species. Plant Soil 2019, 436, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, J.; Feng, Z.; Yang, M.; Chang, C.; Guo, Z.; Wang, R. Changes in shear strength of ploughed farmland soil during wind erosion. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 112–120, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Pregitzer, K.S.; DeForest, J.L.; Burton, A.J.; Allen, M.F.; Ruess, R.W.; Hendrick, R.L. Fine root architecture of nine North American trees. Ecol. Monogr. 2002, 72, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Freschet, G.T.; Wang, H.; Hogan, J.A.; Li, S.; Valverde-Barrantes, O.J.; Fu, X.; Wang, R.; Dai, X.; Jiang, L.; et al. Mycorrhizal symbiosis pathway and edaphic fertility frame root economics space among tree species. New Phytol. 2022, 234, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, P.; Ballabio, C.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L. Wind erosion susceptibility of European soils. Geoderma 2014, 232, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Tian, X.; Guo, Z.; Chang, C.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Wang, R.; Li, Q.; et al. Effect of Dry Soil aggregate size on microplastic distribution and its implications for microplastic emissions induced by wind erosion. Environ. Sci. Technol. Let. 2022, 9, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zobeck, T.M.; Zhang, K.; Li, F. Estimating potential wind erosion of agricultural lands in northern China using the Revised Wind Erosion Equation and geographic information systems. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Weynants, M.; Montanarella, L. Towards a pan-European assessment of land susceptibility to wind erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Xia, M.; Wei, X.; Chang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Anatomical traits associated with absorption and mycorrhizal colonization are linked to root branch order in twenty-three Chinese temperate tree species. New Phytol. 2008, 180, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Estrada, L.R.; Vivianette, V.C.; Ruth, L.E.; Eissenstat, D.M. Root anatomy, morphology, and longevity among root orders in Vaccinium Corymbosum (Ericaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2008, 95, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Xu, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Root diameter variations explained by anatomy and phylogeny of 50 tropical and temperate tree species. Tree Physiol. 2014, 34, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Chen, W.; Adams, T.S.; Wei, X.; Li, L.; McCormack, M.L.; DeForest, J.L.; Koide, R.T.; Eissenstat, D.M. Mycorrhizal fungi and roots are complementary in foraging within nutrient patches. Ecology 2016, 97, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Ma, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Which root traits determine nitrogen uptake by alpine plant species on the Tibetan Plateau? Plant Soil 2018, 424, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, B. Analysis of soil anti-erodibility of five different plantation lands in Zhongyang, Shanxi. J. Northwest A F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 40, 113–119, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, X.; Zhou, W. Soil anti-erodibility of different vegetation in karst area in central part of Guizhou. Res. Agric. Mod. 2007, 28, 633–636, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Cui, M.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhou, J. Effects of vegetation restoration on the aggregate stability and distribution of aggregate-associated organic carbon in a typical karst gorge region. Soild Earth 2017, 7, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, S.H.; Hamilton, H. Experimental effects of antecedent moisture and soil strength on rainwash erosion of two Ontario luvisols. Geoderma 1986, 37, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.; Vieira, C.; Lopes, M.D.L. Direct shear behaviour of residual soil-geosynthetic interfaces-influence of soil moisture content, soil density and geosynthetic type. Geosynth. Int. 2015, 22, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zydroń, T.; Zaleski, T.; Janik, D. Influence of moisture content and shearing rate on shear strength of silty soils from the neighborhood of Kotlina Sądecka. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Cir. 2016, 15, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Kang, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y. Estimation of surface shear strength of undisturbed soils in the eastern part of northern china’s wind erosion area. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 178, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuwa, S.I.; Olaiya, O.C. Evaluation of shear strength and cone penetration resistance behavior of tropical silt loam soil under uni-axial compression. Open J. Soil Sci. 2012, 2, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Su, C. Role of roots in the shear strength of root-reinforced soils with high moisture content. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 33, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yu, W.; Sun, H. Soil Erosion Resistance-enlarging Potential by Plant Roots as Determined in a Simulated Flume Experiment. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2022, 55, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Cheng, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, Z. Plant community characteristics and functional traits as drivers of soil erodibility mitigation along a land degradation gradient. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Campo, J.; Montserrat-Marti, G. Comparison of floristic changes on vegetation affected by different levels of soil erosion in Miocene clays and Eocene marls from Northeast Spain. Plant Ecol. 2004, 173, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, H.; Zhu, B.; Koide, R.T.; Eissenstat, D.M.; Guo, D. Complementarity in nutrient foraging strategies of absorptive fine roots and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi across 14 coexisting subtropical tree species. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Cai, C.; Yang, W.; Ma, R.; Zhang, G. Predicting physical equations of soil detachment by simulated concentrated flow in Ultisols (subtropical China). Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2012, 37, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burylo, M.; Rey, F.; Mathys, N.; Dutoit, T. Plant root traits affecting the resistance of soils to concentrated flow erosion. Earth. Surf. Proc. Land. 2012, 37, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Tang, K.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, X. Impact of grass root mass density on soil detachment capacity by concentrated flow on steep slopes. Trans. ASAE 2013, 56, 927–934. [Google Scholar]
- De Baets, S.; Torri, D.; Poesen, J.; Salvador, M.P.; Meersmans, J. Modelling increased soil cohesion due to roots with EUROSEM. Earth Surf. Proc. Land 2008, 33, 1948–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickovski, S.B.; Stokes, A.; van Beek, R.; Ghestem, M.; Fourcaud, T. Simulation of direct shear tests on rooted and non-rooted soil using finite element analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.; Cheng, D. Effects of vegetation on runoff generation, sediment yield and soil shear strength on road-side slopes under a simulation rainfall test in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 485, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Su, Z.; Yi, T.; Shi, Y. Effects of near soil surface characteristics on soil detachment by overland flow in a natural succession grassland. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, A.F.; Pedersen, M.J.; Merry, B.; Marcus, S.E.; Blacker, J.; Benning, L.G.; Field, K.J.; Knox, J.P. Xyloglucan is released by plants and promotes soil particle aggregation. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, G. Quantifying the binding and bonding effects of plant roots on soil detachment by overland flow in 10 typical grasslands on the Loess Plateau. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Xia, Z.; Gao, F.; Islam, M.S.; Xiao, H.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W. Evaluating the contribution of the physical and biochemical effects of root on detachment for the Coarse-Textured soil from the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar]
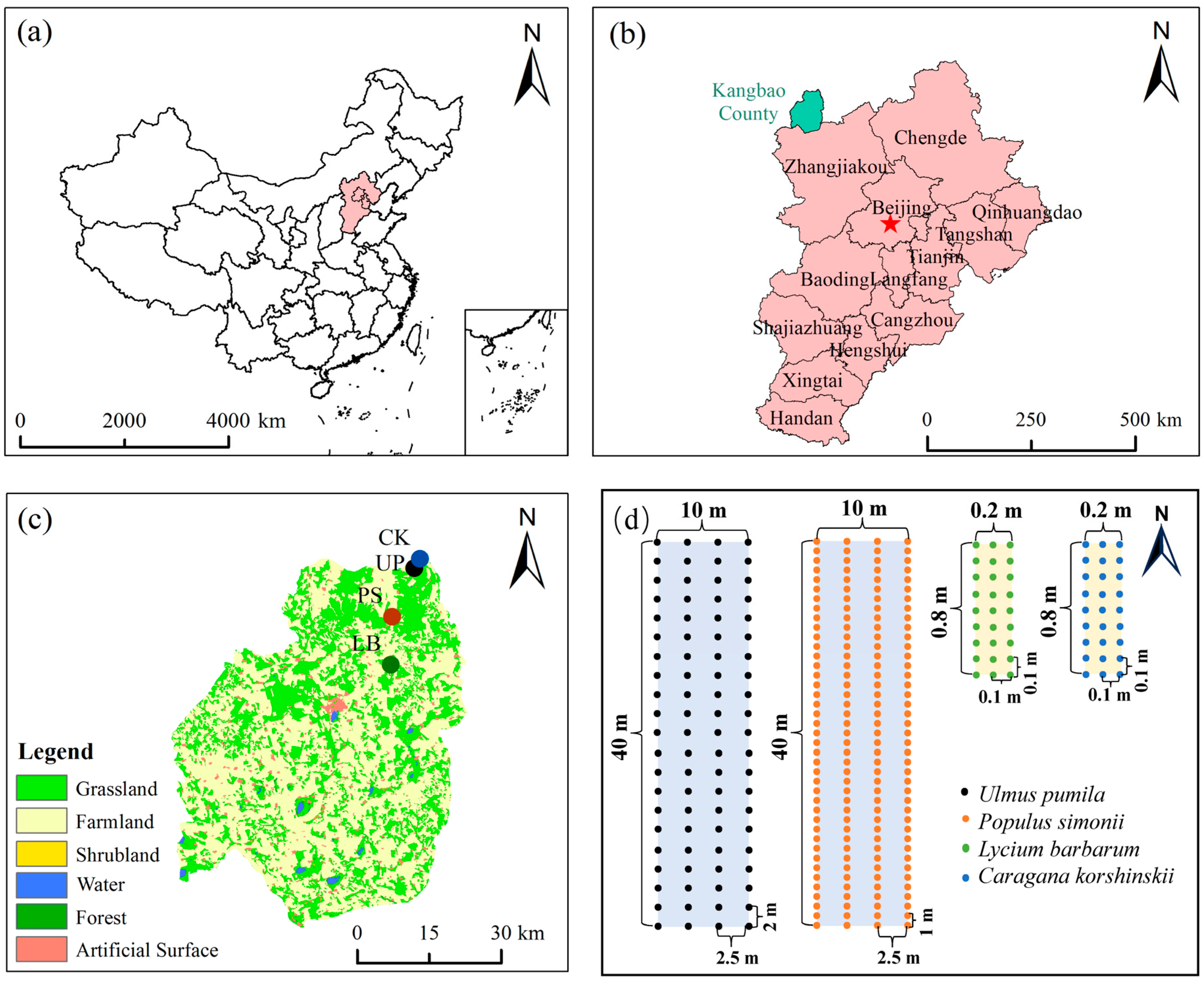





| Shelterbelt Types | Abbreviation | Latitude and Longitude | Altitude (m) | Age (Year) | Height (m) | Diameter (cm) | Length of Shelterbelt (m) | Width of Shelterbelt (m) | Line Number | Spacing of Line (m) | Spacing of Trees/Shrubs (m) | Farmland |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lycium barbarum | LB | 114°44′13″ E, 41° 55′51″ N | 1448 | 15 | 2.24 ± 0.16 | 4.17 ± 0.93 | 500 | 3 | 3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | Hulless oat and Oilseed rape |
| Caragana korshinskii | CK | 114°48′11″ E, 42°8′5″ N | 1283 | 17 | 0.89 ± 0.13 | 1.30 ± 0.15 | 5000 | 8 | 3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | Hulless oat |
| Populus simonii | PS | 114°44′12″ E, 42°1′21″ N | 1445 | 29 | 8.10 ± 0.41 | 25.29 ± 2.16 | 1000 | 10 | 4 | 2.5 | 1.0 | Hulless oat and Oilseed rape |
| Ulmus pumila | UP | 114°47′22″ E, 42°7′1″ N | 1312 | 36 | 6.94 ± 0.53 | 21.16 ± 1.96 | 1800 | 25 | 10 | 2.5 | 2.0 | Hulless oat |
| Parameters | Abbreviation | Units | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil characteristics | Soil water content | SWC | % | Soil water content |
| Soil total nitrogen | STN | g kg−1 | Soil total nitrogen | |
| Soil total organic carbon | STC | g kg−1 | Soil total organic carbon | |
| Mean weight diameter of dry aggregates | MWDd | mm | Mean weight diameter of soil dry aggregates using the dry sieving method | |
| Geometric mean diameter of dry aggregates | GMDd | mm | Geometric mean diameter of soil dry aggregates using the dry sieving method | |
| Erodible fraction of dry aggregates | EFd | % | Erodible fraction of the dry aggregates using the dry sieving method | |
| The dry aggregate stability | DAS | % | The dry aggregate stability using the dry sieving method | |
| The erodible fraction | EFw | % | The erodible fraction of soils using regression equations | |
| Geometric mean diameter | GMDw | mm | The geometric mean diameter of soils using regression equations | |
| Shear strength with 0.5 kg | SR0.5 | J | Shear strength of the surface soil when mass weight was 0.5 kg | |
| Shear strength with 2.0 kg | SR2 | J | Shear strength of the surface soil when mass weight was 2.0 kg | |
| Root morphological traits | Average root diameter | RD | mm | Average root diameter |
| Specific root length | SRL | m g−1 | The ratio of root cluster length to root dry mass | |
| Specific surface area | SSA | cm2 g−1 | The ratio of root surface area to root dry mass | |
| Root tissue density | RTD | g cm−3 | The ratio of root dry mass to root volume | |
| Root architectural traits | Branching ratio | BR | none | The ratio of 1st order root number to 2nd order root number |
| Branching intensity | BI | cm−1 | The ratio of 1st order root number to 2nd order root length |
| Shelterbelt | pH | Water Content (%) | Soil Organic Carbon (g kg−1) | Soil Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | Soil Particle Volume Content Percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay (<0.002 mm) | Silt (0.002–0.05 mm) | Sand (0.05–2 mm) | |||||
| Lycium barbarum | 8.07 ± 0.11 b | 21.02 ± 0.93 a | 18.06 ± 1.27 a | 2.23 ± 0.18 a | 3.78 ± 0.38 a | 30.33 ± 0.93 a | 65.89 ± 0.87 b |
| Caragana korshinskii | 8.49 ± 0.01 a | 16.98 ± 0.62 b | 11.55 ± 0.50 b | 1.61 ± 0.12 b | 3.14 ± 0.15 ab | 28.63 ± 1.84 a | 68.22 ± 1.84 b |
| Populus simonii | 8.31 ± 0.04 a | 14.18 ± 0.93 b | 13.19 ± 2.14 b | 1.81 ± 0.24 ab | 2.82 ± 0.27 b | 30.00 ± 1.22 a | 67.18 ± 1.44 b |
| Ulmus pumila | 8.41 ± 0.09 a | 16.72 ± 2.03 b | 14.46 ± 0.87 ab | 1.50 ± 0.13 b | 2.75 ± 0.16 b | 21.98 ± 0.93 b | 75.27 ± 0.94 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Chang, C.; Wang, H. The Relationships between Root Traits and the Soil Erodibility of Farmland Shelterbelts in the Bashang Region of China. Forests 2023, 14, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091827
Liu Q, Li J, Guo Z, Chang C, Wang H. The Relationships between Root Traits and the Soil Erodibility of Farmland Shelterbelts in the Bashang Region of China. Forests. 2023; 14(9):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091827
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qianyuan, Jifeng Li, Zhongling Guo, Chunping Chang, and Huimin Wang. 2023. "The Relationships between Root Traits and the Soil Erodibility of Farmland Shelterbelts in the Bashang Region of China" Forests 14, no. 9: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091827
APA StyleLiu, Q., Li, J., Guo, Z., Chang, C., & Wang, H. (2023). The Relationships between Root Traits and the Soil Erodibility of Farmland Shelterbelts in the Bashang Region of China. Forests, 14(9), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14091827







