Environmental Drivers of Gross Primary Production and Evapotranspiration at a Robinia pseudoacacia L. Restoration Plantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Meteorological and Eddy Covariance Measurements
2.3. Assessment of Seasonal Phenological Fluctuation
2.4. Ecophysiological and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Studied Black Locust Plantation Is Characterized by High GPP and ET
4.2. Physiological and Environmental Controls That Contribute to Elevated GPP and ET
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldocchi, D.D. Assessing the Eddy Covariance Technique for Evaluating Carbon Dioxide Exchange Rates of Ecosystems: Past, Present and Future: Carbon Balance and Eddy Covariance. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 9, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.P.; Noone, D.; Bowen, G. Hydrologic Connectivity Constrains Partitioning of Global Terrestrial Water Fluxes. Science 2015, 349, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bales, R.C.; Molotch, N.P.; Painter, T.H.; Dettinger, M.D.; Rice, R.; Dozier, J. Mountain Hydrology of the Western United States: Mountain Hydrology of the Western US. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, w08432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yan, X.; Dong, W.; Chou, J. Gross Primary Production of Global Forest Ecosystems Has Been Overestimated. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldocchi, D.; Falge, E.; Gu, L.; Olson, R.; Hollinger, D.; Running, S.; Anthoni, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Davis, K.; Evans, R.; et al. FLUXNET: A New Tool to Study the Temporal and Spatial Variability of Ecosystem–Scale Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor, and Energy Flux Densities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 82, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Buttlar, J.; Zscheischler, J.; Rammig, A.; Sippel, S.; Reichstein, M.; Knohl, A.; Jung, M.; Menzer, O.; Arain, M.A.; Buchmann, N.; et al. Impacts of Droughts and Extreme-Temperature Events on Gross Primary Production and Ecosystem Respiration: A Systematic Assessment across Ecosystems and Climate Zones. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 1293–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Tian, H.; Dangal, S.R.S.; Yang, Q.; Yang, J.; Lu, C.; Tao, B.; Ren, W.; Ouyang, Z. Responses of Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration to Climate Change and Increasing Atmospheric CO 2 in the 21st Century. Earth’s Future 2015, 3, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Lu, N.; Sun, G.; Ward, E.J.; Fu, B. Biophysical Controls on Canopy Transpiration in a Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) Plantation on the Semi-Arid Loess Plateau, China: Biophysical Controls on Transpiration in a Black Locust Plantation. Ecohydrol. 2016, 9, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markos, N.; Radoglou, K. Estimation of Ecosystem Evapotranspiration in a Robinia pseudoacacia L. Plantation with the Use of the Eddy Covariance Technique and Modeling Approaches. Water Supply 2021, 21, 2553–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, M.; Brenning, A.; Gans, F.; Reichstein, M.; Sippel, S.; Mahecha, M.D. Vegetation Modulates the Impact of Climate Extremes on Gross Primary Production. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, C.P.; Lubczynski, M.W.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Chavarro-Rincón, D. Transpiration and Canopy Conductance of Two Contrasting Forest Types in the Lesser Himalaya of Central Nepal. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 197, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Hu, S. Variability, Tendencies, and Climate Controls of Terrestrial Evapotranspiration and Gross Primary Productivity in the Recent Decade over China. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of Mean Annual Evapotranspiration to Vegetation Changes at Catchment Scale. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, P.A.; Law, B.E.; Williams, M.; Irvine, J.; Kurpius, M.; Moore, D. Climatic versus Biotic Constraints on Carbon and Water Fluxes in Seasonally Drought-Affected Ponderosa Pine Ecosystems: Carbon and Water Fluxes in Ponderosa Pine Ecosystems. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, GB4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Hu, Y. How Multiple Factors Control Evapotranspiration in North America Evergreen Needleleaf Forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Camarero, J.J.; Zabalza, J.; Sangüesa-Barreda, G.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Tague, C.L. Evapotranspiration Deficit Controls Net Primary Production and Growth of Silver Fir: Implications for Circum-Mediterranean Forests under Forecasted Warmer and Drier Conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 206, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, A.; Reichstein, M.; Bréda, N.; Janssens, I.A.; Falge, E.; Ciais, P.; Grünwald, T.; Aubinet, M.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; et al. Evidence for Soil Water Control on Carbon and Water Dynamics in European Forests during the Extremely Dry Year: 2003. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 143, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kume, T.; Takizawa, H.; Yoshifuji, N.; Tanaka, K.; Tantasirin, C.; Tanaka, N.; Suzuki, M. Impact of Soil Drought on Sap Flow and Water Status of Evergreen Trees in a Tropical Monsoon Forest in Northern Thailand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 238, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.P.; O’Gorman, P.A. Land–Ocean Warming Contrast over a Wide Range of Climates: Convective Quasi-Equilibrium Theory and Idealized Simulations. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 4000–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficklin, D.L.; Novick, K.A. Historic and Projected Changes in Vapor Pressure Deficit Suggest a Continental-scale Drying of the United States Atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2061–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zheng, Y.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Lombardozzi, D.; Wang, Y.; Ryu, Y.; Chen, G.; Dong, W.; Hu, Z.; et al. Increased Atmospheric Vapor Pressure Deficit Reduces Global Vegetation Growth. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossiord, C.; Buckley, T.N.; Cernusak, L.A.; Novick, K.A.; Poulter, B.; Siegwolf, R.T.W.; Sperry, J.S.; McDowell, N.G. Plant Responses to Rising Vapor Pressure Deficit. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 1550–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peabody, F.J. A 350-Year-Old American Legume in Paris. Castanea 1982, 47, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolescu, V.-N.; Rédei, K.; Mason, W.L.; Vor, T.; Pöetzelsberger, E.; Bastien, J.-C.; Brus, R.; Benčať, T.; Đodan, M.; Cvjetkovic, B.; et al. Ecology, Growth and Management of Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.), a Non-Native Species Integrated into European Forests. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1081–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisz, M.; Puchałka, R.; Netsvetov, M.; Prokopuk, Y.; Vítková, M.; Sádlo, J.; Matisons, R.; Mionskowski, M.; Chakraborty, D.; Olszewski, P.; et al. Variability in Climate-Growth Reaction of Robinia pseudoacacia in Eastern Europe Indicates Potential for Acclimatisation to Future Climate. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 492, 119194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítková, M.; Müllerová, J.; Sádlo, J.; Pergl, J.; Pyšek, P. Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) Beloved and Despised: A Story of an Invasive Tree in Central Europe. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 384, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierjacks, A.; Kowarik, I.; Joshi, J.; Hempel, S.; Ristow, M.; von der Lippe, M.; Weber, E. Biological Flora of the British Isles: Robinia pseudoacacia. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, B.; Bell, T.L.; Flemetakis, E.; Rennenberg, H. Significance of Mycorrhizal Associations for the Performance of N2-Fixing Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 145, 107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Yin, X. Effects of Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) on Soil Properties in the Loessial Gully Region of the Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil 2010, 332, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinkenstein, A.; Böhm, C.; da Silva Matos, E.; Freese, D.; Hüttl, R.F. Assessing the Carbon Sequestration in Short Rotation Coppices of Robinia pseudoacacia L. on Marginal Sites in Northeast Germany. In Carbon Sequestration Potential of Agroforestry Systems; Kumar, B.M., Nair, P.K.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 8, pp. 201–216. ISBN 978-94-007-1629-2. [Google Scholar]
- Spyroglou, G.; Fotelli, M.; Nanos, N.; Radoglou, K. Assessing Black Locust Biomass Accumulation in Restoration Plantations. Forests 2021, 12, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Fei, L.; Gui, S.; Liu, Q.; Liu, G. Remote Sensing for Monitoring on the Health of Artificial Robinia pseudoacacia Forests in the Yellow River Delta. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2009 17th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Fairfax, VA, USA, 12–14 August 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa, Y.; Du, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Yamanaka, N.; Kumagai, T. Gas Exchange by the Mesic-Origin, Arid Land Plantation Species Robinia pseudoacacia under Annual Summer Reduction in Plant Hydraulic Conductance. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 1166–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detto, M.; Montaldo, N.; Albertson, J.D.; Mancini, M.; Katul, G. Soil Moisture and Vegetation Controls on Evapotranspiration in a Heterogeneous Mediterranean Ecosystem on Sardinia, Italy: Evapotranspiration in Mediterranean Ecosystem. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, W.; Kolb, T.E.; Springer, A.E.; Dore, S.; O’Donnell, F.C.; Martinez Morales, R.; Masek Lopez, S.; Koch, G.W. Evapotranspiration Comparisons between Eddy Covariance Measurements and Meteorological and Remote-Sensing-Based Models in Disturbed Ponderosa Pine Forests: Evapotranspiration Comparisons in Ponderosa Pine Forests. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 1335–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, L.; Moriondo, M.; Chiesi, M.; Bindi, M.; Maselli, F. Impacts of Climate Change on the Gross Primary Production of Italian Forests. Ann. For. Sci. 2019, 76, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazeides, C.I.; Christopoulou, A.; Fyllas, N.M. Coupling Photosynthetic Measurements with Biometric Data to Estimate Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) in Mediterranean Pine Forests of Different Post-Fire Age. Forests 2021, 12, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, H.; Di Prima, S.; Sirca, C.; Giadrossich, F.; Marras, S.; Spano, D.; Pirastru, M. Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation in a Mediterranean Ecosystem from Landsat Observations Using SEBAL Approach. Forests 2021, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; Meinshausen, M.; Arora, V.K.; Jones, C.D.; Anav, A.; Liddicoat, S.K.; Knutti, R. Uncertainties in CMIP5 Climate Projections Due to Carbon Cycle Feedbacks. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, C.; Gekaa, C.; Pavloudakis, F.; Roumpos, C.; Andreadou, S. Evaluation of the Soil Quality on the Reclaimed Lignite Mine Land in West Macedonia, Greece. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 15, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavloudakis, F.; Roumpos, C.; Karlopoulos, E.; Koukouzas, N. Sustainable Rehabilitation of Surface Coal Mining Areas: The Case of Greek Lignite Mines. Energies 2020, 13, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Hu, C.X.; Bai, J.; Gong, C.M. Carbon Sequestration of Mature Black Locust Stands on the Loess Plateau, China. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Pang, Y.; Cao, B.; Fan, Z.; Mao, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, P. Robinia pseudoacacia Decline and Fine Root Dynamics in a Plantation Chronosequence in the Yellow River Delta, China. For. Sci. 2022, 68, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolopoulos, D.; Vasileioris, K.; Milios, E.; Kitikidou, K.; Spyroglou, G.; Radoglou, K. Allometric Models for Estimating the Height of Robinia pseudoacacia L. in Restoration Plantations. Land 2022, 11, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.S.; Norman, J.M. An Introduction to Environmental Biophysics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-387-94937-6. [Google Scholar]
- Papale, D.; Reichstein, M.; Aubinet, M.; Canfora, E.; Bernhofer, C.; Kutsch, W.; Longdoz, B.; Rambal, S.; Valentini, R.; Vesala, T.; et al. Towards a Standardized Processing of Net Ecosystem Exchange Measured with Eddy Covariance Technique: Algorithms and Uncertainty Estimation. Biogeosciences 2006, 3, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Papale, D.; Aubinet, M.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Buchmann, N.; Gilmanov, T.; Granier, A.; et al. On the Separation of Net Ecosystem Exchange into Assimilation and Ecosystem Respiration: Review and Improved Algorithm. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1424–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutzler, T.; Lucas-Moffat, A.; Migliavacca, M.; Knauer, J.; Sickel, K.; Šigut, L.; Menzer, O.; Reichstein, M. Basic and Extensible Post-Processing of Eddy Covariance Flux Data with Reddy. Proc. Biogeosci. 2018, 15, 5015–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, H.; Amraoui, M.; Malheiro, A.C.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Eiras-Dias, J.; Silvestre, J.; Santos, J.A. Examining the Relationship between the Enhanced Vegetation Index and Grapevine Phenology. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 47, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blundo, C.; Gasparri, N.I.; Malizia, A.; Clark, M.; Gatti, G.; Campanello, P.I.; Grau, H.R.; Paolini, L.; Malizia, L.R.; Chediack, S.E.; et al. Relationships among Phenology, Climate and Biomass across Subtropical Forests in Argentina. J. Trop. Ecol. 2018, 34, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-37027-9. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, F.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J. The Links between Canopy Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Gross Primary Production Responses to Meteorological Factors in the Growing Season in Deciduous Broadleaf Forest. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita, G.; Gielen, B.; Zona, D.; Rodrigues, A.; Rambal, S.; Janssens, I.A.; Ceulemans, R. Carbon and Water Vapor Fluxes over Four Forests in Two Contrasting Climatic Zones. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 180, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cescatti, A.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Buchmann, N.; Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Moyano, F.; Pumpanen, J.; Hirano, T.; et al. Effect of Climate Warming on the Annual Terrestrial Net Ecosystem CO2 Exchange Globally in the Boreal and Temperate Regions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, Y. Effects of Various Driving Factors on Potential Evapotranspiration Trends over the Main Grain-Production Area of China While Accounting for Vegetation Dynamics. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Rattan, P.; Mor, S.; Aggarwal, A.N. Generalized Additive Models: Building Evidence of Air Pollution, Climate Change and Human Health. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teubner, I.E.; Forkel, M.; Wild, B.; Mösinger, L.; Dorigo, W. Impact of Temperature and Water Availability on Microwave-Derived Gross Primary Production. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 3285–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorello, G.; Trotta, C.; Canfora, E.; Chu, H.; Christianson, D.; Cheah, Y.-W.; Poindexter, C.; Chen, J.; Elbashandy, A.; Humphrey, M.; et al. Author Correction: The FLUXNET2015 Dataset and the ONEFlux Processing Pipeline for Eddy Covariance Data. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Rambal, S.; Mouillot, F. Soil Drought Anomalies in MODIS GPP of a Mediterranean Broadleaved Evergreen Forest. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1154–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Wagle, P.; Ma, S.; Baldocchi, D.; Carrara, A.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y. Canopy and Climate Controls of Gross Primary Production of Mediterranean-Type Deciduous and Evergreen Oak Savannas. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 226–227, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.E.; Beringer, J.; Evans, B.; Hutley, L.B.; Tapper, N.J. Tree–Grass Phenology Information Improves Light Use Efficiency Modelling of Gross Primary Productivity for an Australian Tropical Savanna. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungee, J.; Bales, R.; Goulden, M. Evapotranspiration Response to Multiyear Dry Periods in the Semiarid Western United States. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, P.; Gimeno, C.; Carrara, A.; Lopez-Sangil, L.; Sanz, M.J. Soil CO2 Efflux and Extractable Organic Carbon Fractions under Simulated Precipitation Events in a Mediterranean Dehesa. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Ciais, P.; Papale, D.; Valentini, R.; Running, S.; Viovy, N.; Cramer, W.; Granier, A.; Ogée, J.; Allard, V.; et al. Reduction of Ecosystem Productivity and Respiration during the European Summer 2003 Climate Anomaly: A Joint Flux Tower, Remote Sensing and Modelling Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helman, D.; Givati, A.; Lensky, I.M. Annual Evapotranspiration Retrieved from Satellite Vegetation Indices for the Eastern Mediterranean at 250 m Spatial Resolution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12567–12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Li, H. Study on Vegetation Water Requirements of Robinia pseudoacacia and Its Mixed Plantation in Loess Gully Region. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 643, 012122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehleringer, J.; Forseth, I. Solar Tracking by Plants. Science 1980, 210, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, C.; Vitale, L.; De Santo, A.V. Paraheliotropism in Robinia pseudoacacia Plants: An Efficient Means to Cope with Photoinhibition. In Photosynthesis. Energy from the Sun; Allen, J.F., Gantt, E., Golbeck, J.H., Osmond, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1403–1406. ISBN 978-1-4020-6707-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ficklin, D.L.; Manzoni, S.; Wang, L.; Way, D.; Phillips, R.P.; Novick, K.A. Response of Ecosystem Intrinsic Water Use Efficiency and Gross Primary Productivity to Rising Vapor Pressure Deficit. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.; Way, D.A.; Sadok, W. Systemic Effects of Rising Atmospheric Vapor Pressure Deficit on Plant Physiology and Productivity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 1704–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massmann, A.; Gentine, P.; Lin, C. When Does Vapor Pressure Deficit Drive or Reduce evapotranspiration. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 11, 3305–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, D.; Veste, M.; Freese, D. Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) Ecophysiological and Morphological Adaptations to Drought and Their Consequence on Biomass Production and Water-Use Efficiency. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2014, 44, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



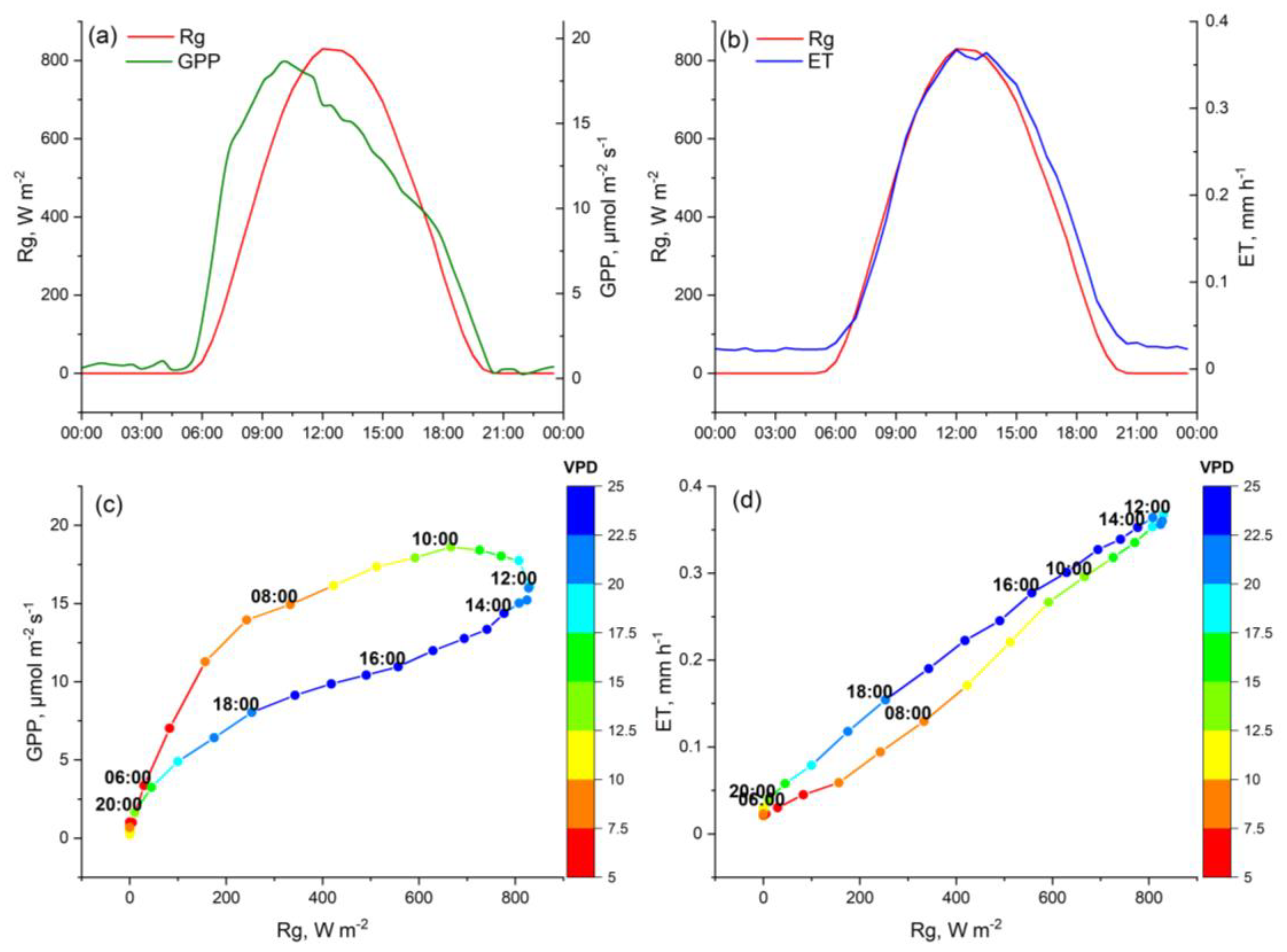

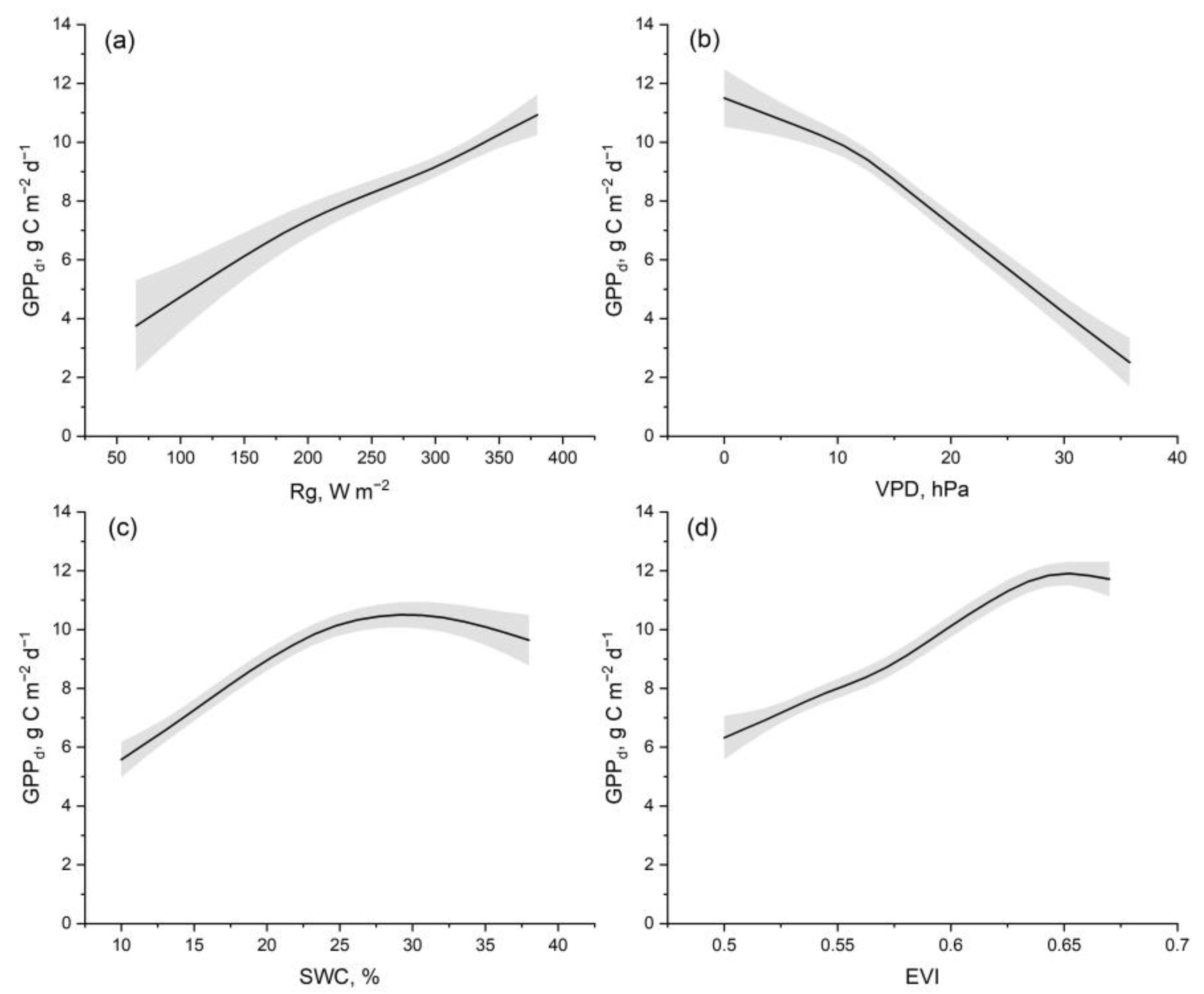
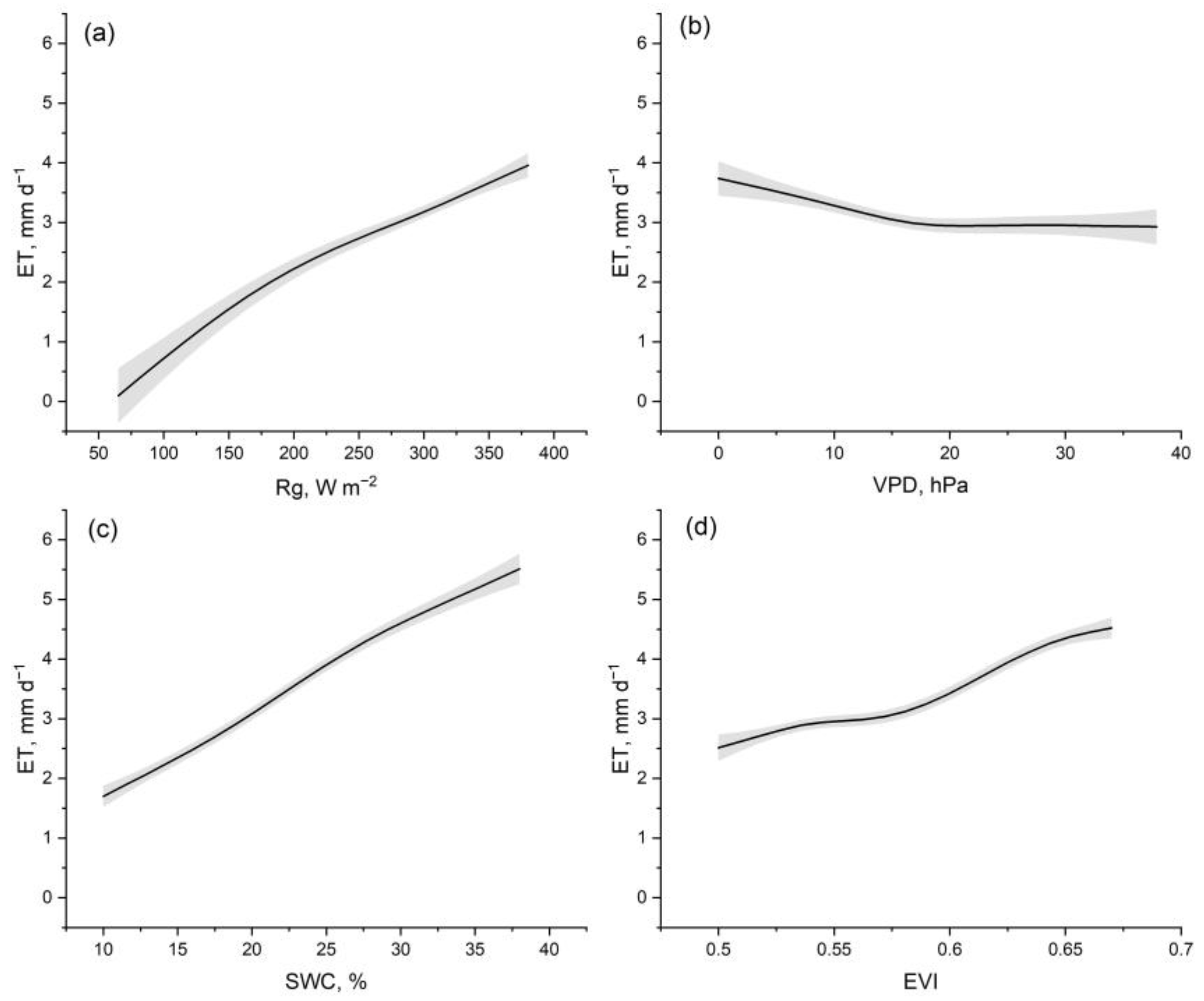
| GPP | ET | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | F | p-Value | F | p-Value |
| Rg | 8.726 | <0.001 | 26.27 | <0.001 |
| VPD | 35.744 | <0.001 | 3.51 | 0.016 |
| SWC | 28.561 | <0.001 | 109.11 | <0.001 |
| EVI | 30.053 | <0.001 | 38.71 | <0.001 |
| Regression coefficient | R2 = 0.79 | R2 = 0.84 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markos, N.; Radoglou, K.; Fotelli, M.N. Environmental Drivers of Gross Primary Production and Evapotranspiration at a Robinia pseudoacacia L. Restoration Plantation. Forests 2023, 14, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050916
Markos N, Radoglou K, Fotelli MN. Environmental Drivers of Gross Primary Production and Evapotranspiration at a Robinia pseudoacacia L. Restoration Plantation. Forests. 2023; 14(5):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050916
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkos, Nikos, Kalliopi Radoglou, and Mariangela N. Fotelli. 2023. "Environmental Drivers of Gross Primary Production and Evapotranspiration at a Robinia pseudoacacia L. Restoration Plantation" Forests 14, no. 5: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050916
APA StyleMarkos, N., Radoglou, K., & Fotelli, M. N. (2023). Environmental Drivers of Gross Primary Production and Evapotranspiration at a Robinia pseudoacacia L. Restoration Plantation. Forests, 14(5), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050916






