14-3-3 Proteins Participate in Regulation of Natural Rubber Biosynthesis in Hevea brasiliensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. The Construction of a Y2H Library
2.3. Targeted Y2H Analysis
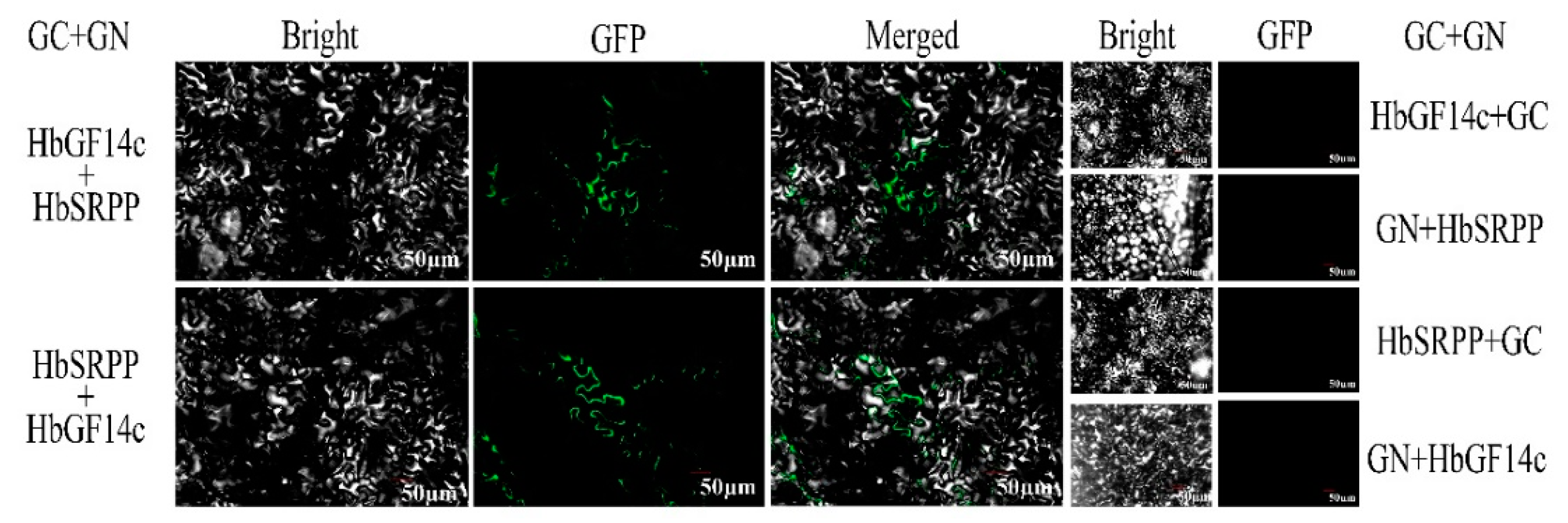
2.4. BIFC Assays
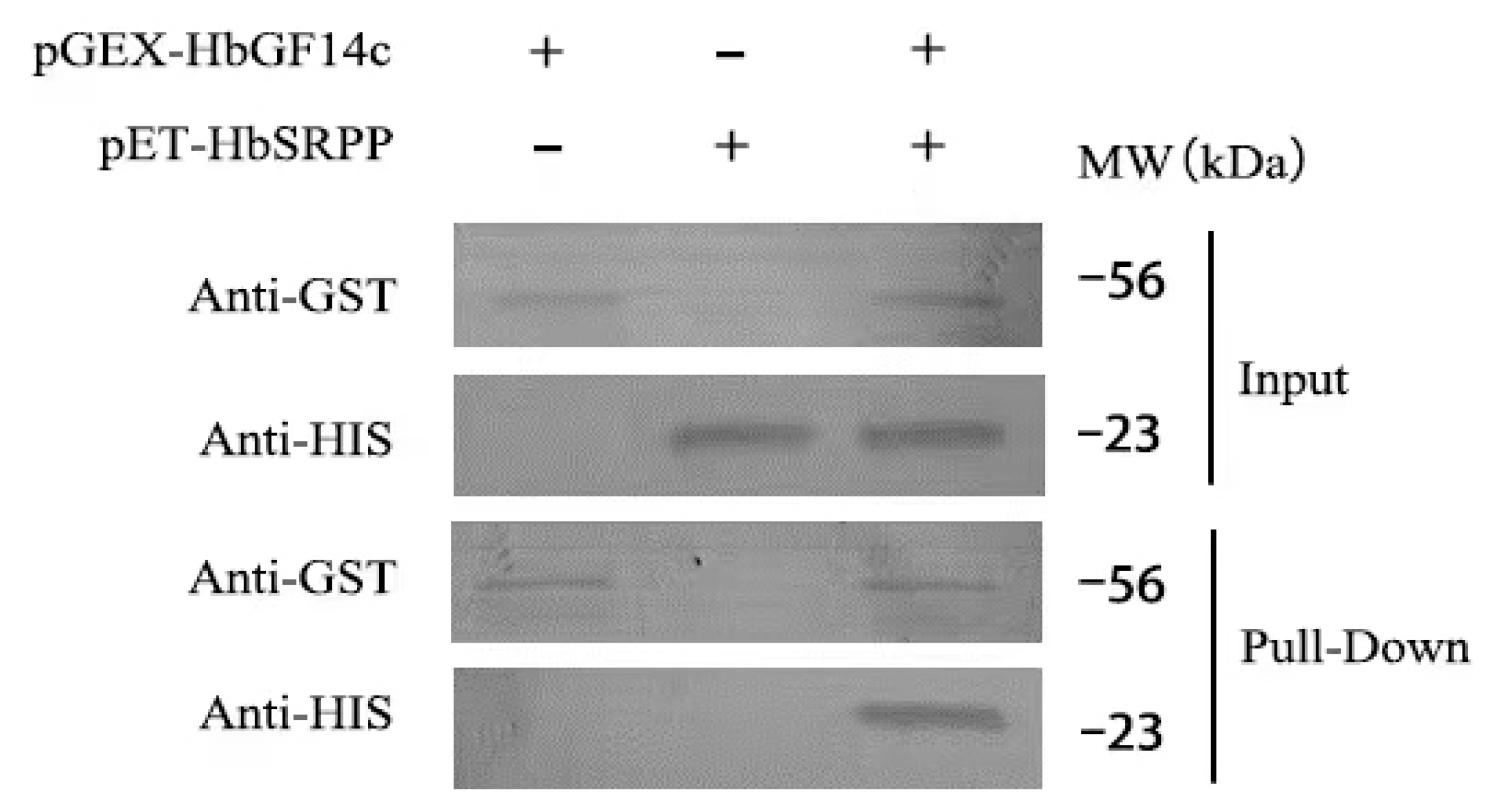
2.5. In Vitro Pull-Down Analysis
3. Results
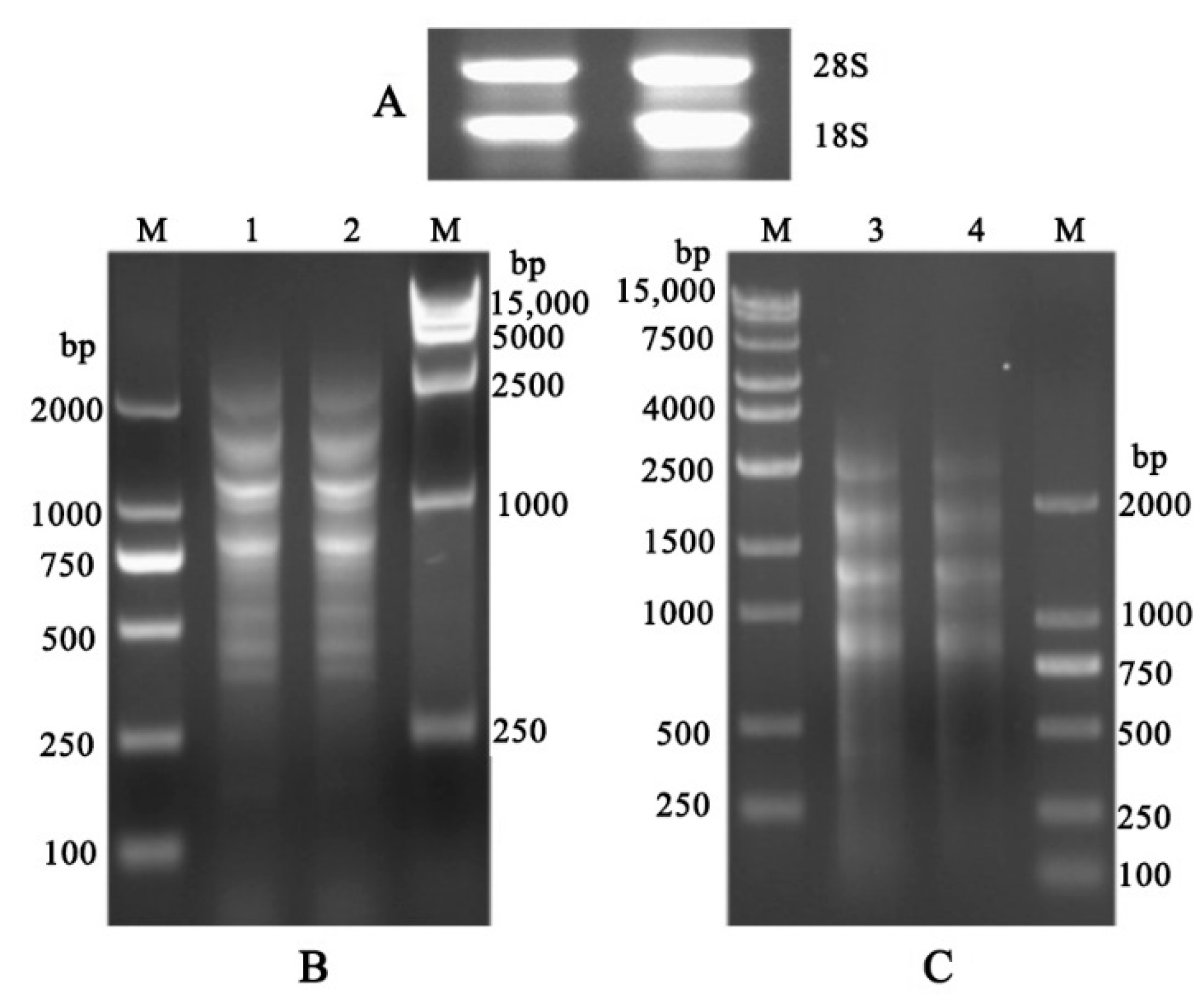
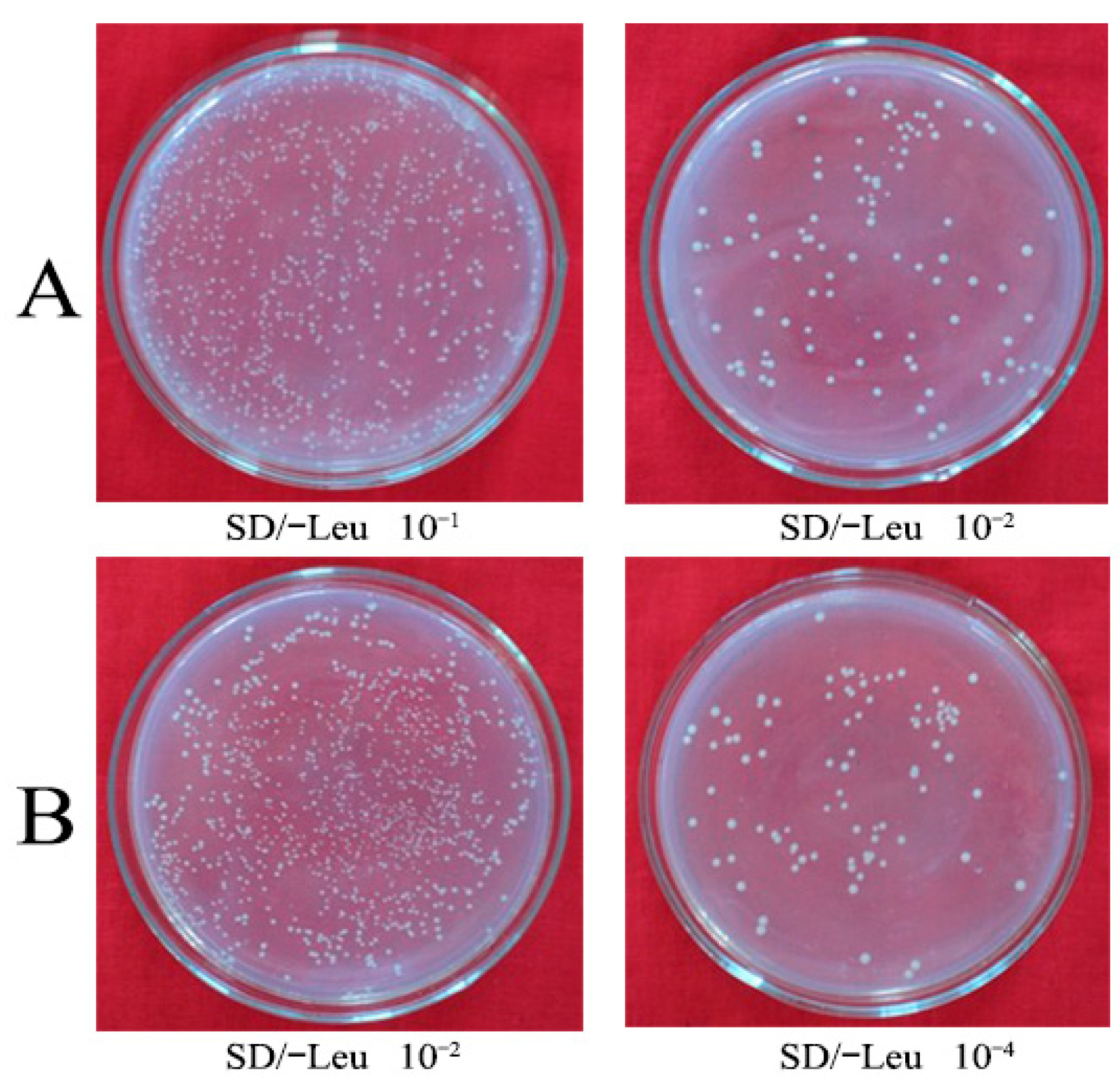
3.1. Construction of cDNA Library
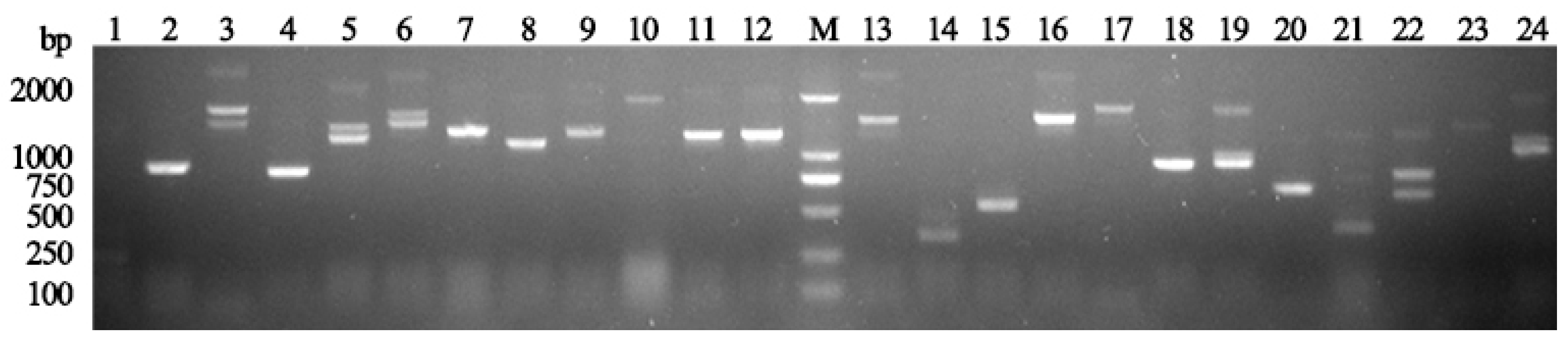
3.2. Construction of a Y2H Library and Screening of Proteins Interacting with HbGF14s
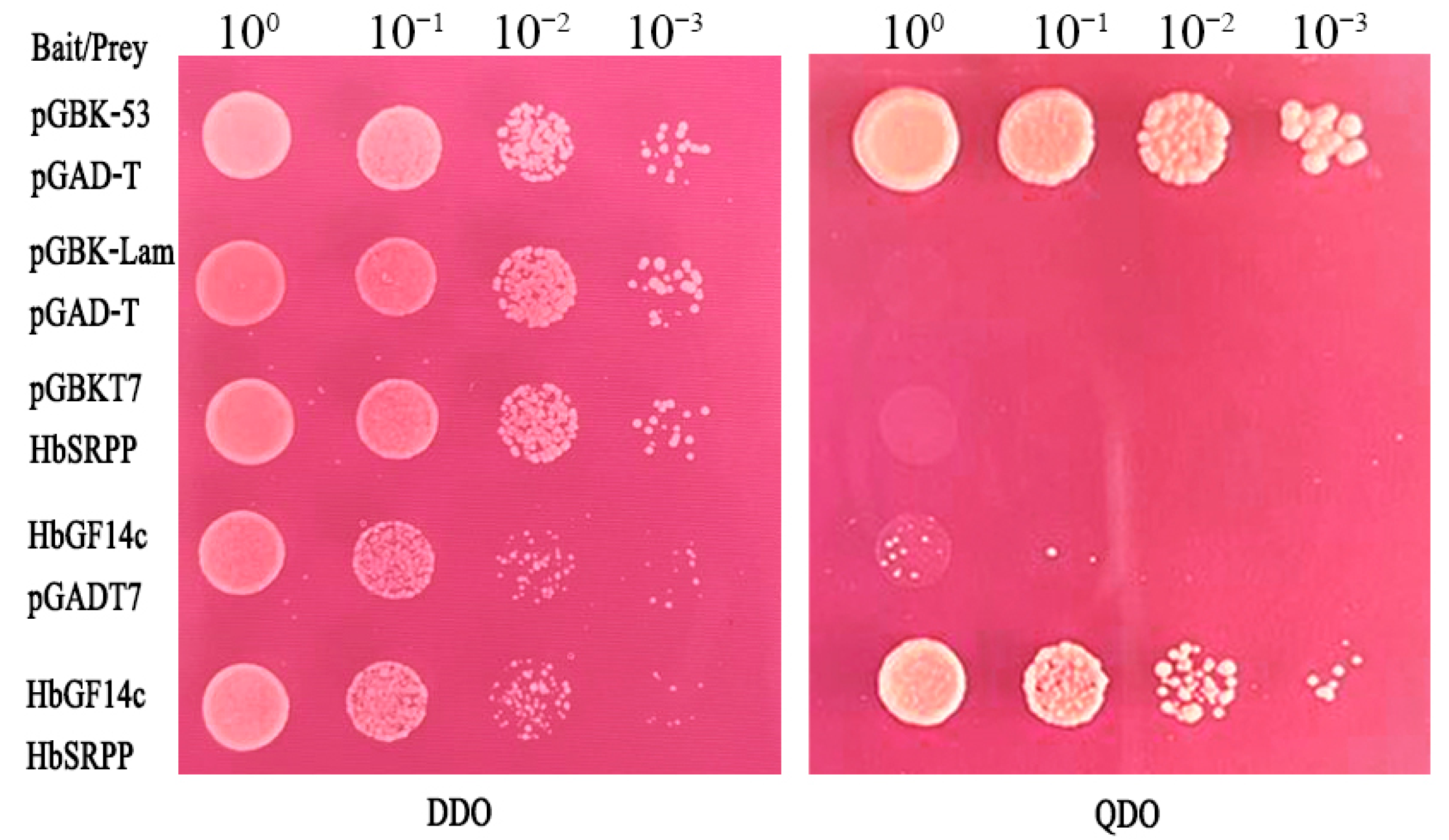
3.3. Analysis of the Interaction between HbGF14c and HbSRPP
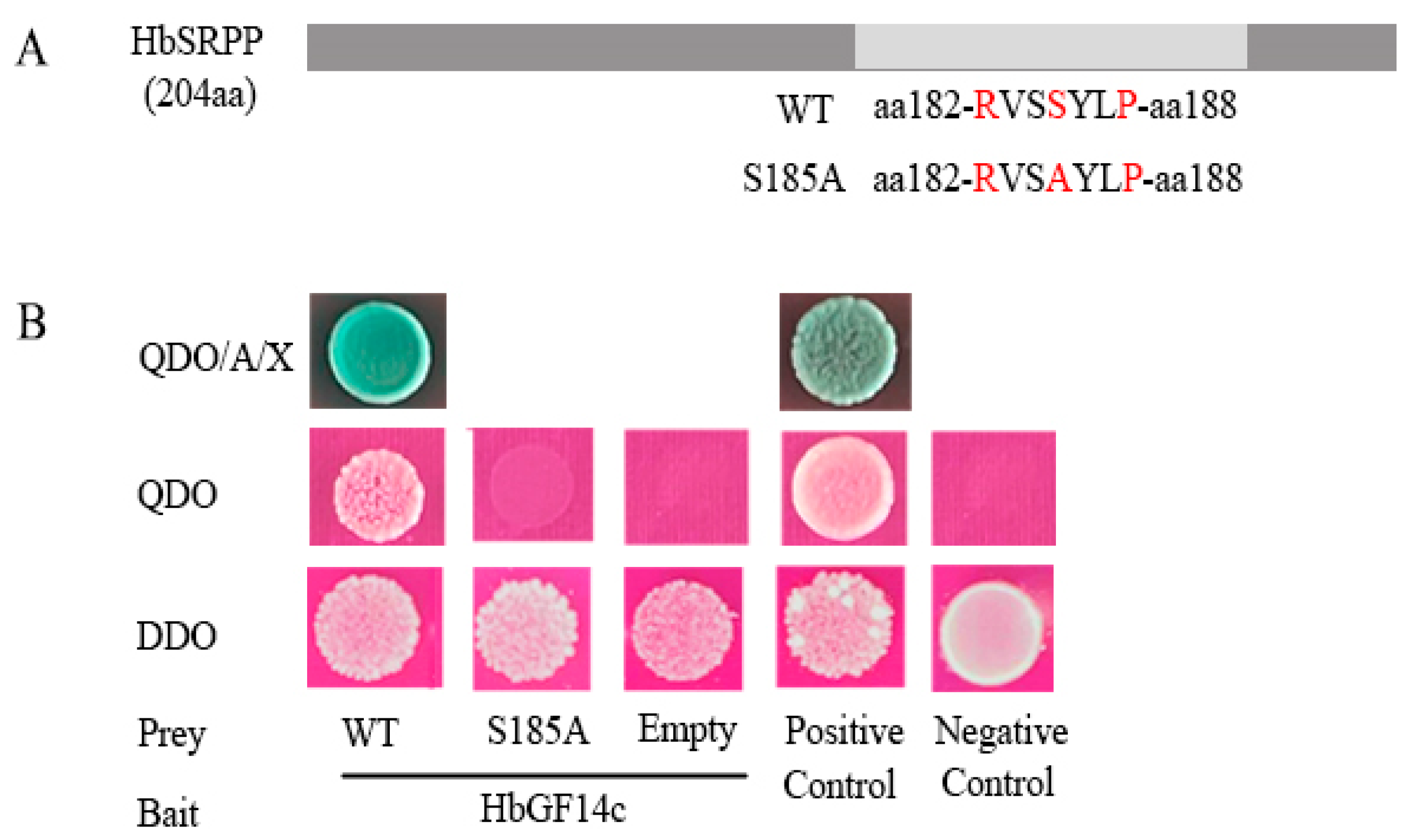
3.4. HbSRPP Binds to HbGF14c through the RVSSYLP Motif
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gökirmak, T.; Paul, A.L.; Ferl, R.J. Plant phosphopeptide-binding proteins as signalling mediators. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashvardhini, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Sengupta, D.N. Molecular characterization of the 14-3-3 gene family in rice and its expression studies under abiotic stress. Planta 2018, 247, 229–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, A.Q.; Jain, A.; Baldwin, J.C.; Raghothama, K.G. Phosphate differentially regulates 14-3-3 family members and GRF9 plays a role in Pi-starvation induced responses. Planta 2007, 226, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, D.; Morris, E.R.; Walker, J.C. 14-3-3 and FHA domains mediate phosphoprotein interactions. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.F.; Jia, L.G.; Shi, W.M.; Baluska, F.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Liang, J.S.; Zhang, J.H. The Tomato 14-3-3 protein TFT4 modulates H+ efflux, basipetal auxin transport, and the PKS5-J3 pathway in the root growth response to alkaline stress. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.F.; Shi, W.M. Expression profiling of the 14-3-3 gene family in response to salt stress and potassium and iron deficiencies in young tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) roots: Analysis by realtime RT-PCR. Ann. Bot. 2016, 98, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Sun, L.X.; He, Z.H. The rice 14-3-3 gene family and its involvement in responses to biotic and abiotic stress. DNA Res. 2006, 13, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konagaya, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Kasahara, M.; Nyunoya, H. Members of 14-3-3 protein isoforms interacting with the resistance gene product N and the elicitor of Tobacco mosaic virus. J. Gen. Plant Pahtology 2004, 70, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwak, G.; Lim, Y.P.; Oh, M.H. 14-3-3 proteins contribute to leaf and root development via brassinosteroid insensitive 1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.L.; Xie, F.L.; Zhang, B.H. Transcriptome-wide identification and stress properties of the 14-3-3 gene family in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2011, 11, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Li, H.L.; Guo, D.; Tang, X.; Peng, S.Q. Identification and characterization of the 14-3-3 gene family in Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, F.C.; Paul, A.L.; Zupanska, A.K.; Ferl, R.J. 14-3-3 proteins in plant physiology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Jia, Y.X.; Ding, Y.L.; Shi, Y.T.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Z.Z.; Yang, S.H. Plasma membrane CRPK1-mediated phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins induces their nuclear import to fine-tune CBF signaling during cold response. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.M.; Li, R.H.; Xia, S.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Jin, D.H.; Xie, X.; Dhaubhadel, S.; Zhai, L.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Li, X.Y. Soybean CCA1-like MYB transcription factor GmMYB133 modulates iso-flavonoid biosynthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Ho, T.H.D.; Liu, L.H.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Lin, S.Y.; Lu, C.A.; Yu, S.M. Sugar starvation-regulated MYBS2 and 14-3-3 protein interactions enhance plant growth, stress tolerance, and grain weight in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21925–21935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, N.; Liu, H.; Ma, B.; Huang, X.Z.; Zhuo, L.; Sun, Y.Q. Roles of the 14-3-3 gene family in cotton flowering. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, A.H.; van Kleeff, P.J.M.; Gao, J. Plant 14-3-3 proteins as spiders in a web of phosphorylation. Protoplasma 2013, 250, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.L.; Denison, F.C.; Schultz, E.R.; Zupanska, A.K.; Ferl, R.J. 14-3-3 phosphoprotein interaction networks—Does isoform diversity present functional interaction specification? Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, A. Functional specificity in 14-3-3 isoform interactions through dimer formation and phosphorylation. Chromosome location of mammalian isoforms and variants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 50, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsil, T.; Obsilova, V. Structural basis of 14-3-3 protein functions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, R.; Jez, J.M.; Basra, A.; Zhang, B.; Schachtman, D.P. 14-3-3 proteins fine-tune plant nutrient metabolism. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, T.; Wu, Z.; Feng, H.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B. Arbuscular mycorrhiza enhances drought tolerance of tomato plants by regulating the 14-3-3 genes in the ABA signaling pathway. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Ma, W. WRINKLED1 as a novel 14-3-3 client: Function of 14-3-3 proteins in plant lipid metabolism. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1482176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backhaus, R.A. Rubber formation in plants—A mini-review. Isr. J. Bot. 1985, 34, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, K.S.; Wan, K.L.; Isa, M.N.; Bahari, A.; Tan, S.H.; Harikrishna, K.; Yeang, H.Y. Insights into rubber biosynthesis from transcriptome analysis of Hevea brasiliensis latex. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M.S.; Light, D.R. Rubber elongation factor from Hevea brasiliensis. Identification, characterization and role in rubber biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 18608–18617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chye, M.L.; Tan, C.T.; Chuan, H. Three genes encode 3-hydroxy-3-methy lglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in Hevea brasiliensis: hmg1 and hmg3 are differentially expressed. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 19, 19473–19484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiwilaga, K.; Kush, A. Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding farnesyl diphosphate synthase from rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 30, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.K.; Kang, H.; Shin, D.H.; Yang, J.; Chow, K.S.; Yeang, H.Y.; Wagner, B.; Breiteneder, H.; Han, K.H. Isolation, characterization, and functional analysis of a novel cDNA clone encoding a small rubber particle protein from Hevea brasiliensis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17132–17138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Waki, T.; Aoki, Y.; Mizuno, M.; Yanbe, F.; Ishii, T.; Funaki, A.; Tozawa, Y.; Miyagi-Inoue, Y.; et al. Identification and reconstitution of the rubber biosynthetic machinery on rubber particles from Hevea brasiliensis. Elife 2016, 5, e19022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Feeney, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Lonoce, C.; Sajari, R.; Di-Cola, A.; Frigerio, L. Subcellular localization and interactions among rubber particle proteins from Hevea brasiliensis. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5045–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Yang, Z.P.; Li, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Peng, S.Q. The 14-3-3 protein HbGF14a interacts with a RING zinc finger protein to regulate expression of the rubber transferase gene in Hevea brasiliensis. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.R.; Qi, J.Y.; Li, H.P.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Y.K. A convenient and efficient protocol for isolating high-quality RNA from latex of Hevea brasiliensis (para rubber tree). J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Fu, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhao, P.J.; Liu, Z.X.; Wu, K.X.; Zhang, X.C. Turnip crinkle virus-encoded suppressor of RNA silencing interacts with Arabidopsis SGS3 to enhance virus infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparkes, I.A.; Runions, J.; Kearns, A.; Hawes, C. Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Crowther, S.; Stafford, M.J.; Campbell, D.G.; Toth, R.; MacKintosh, C. Bioinformatic and experimental survey of 14-3-3-binding sites. Biochem. J. 2010, 427, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Kong, Q.; Mantyla, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Ohlrogge, J.B.; Benning, C. 14-3-3 protein mediates plant seed oil biosynthesis through interaction with AtWRI1. Plant J. 2016, 88, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukayama, H.; Miyagawa, F.; Shibatani, N.; Koudou, A.; Sasayama, D.; Hatanaka, T.; Azuma, T.; Yamauchi, Y.; Matsuoka, D.; Morita, R. CO2-responsive CCT protein interacts with 14-3-3 proteins and controls the expression of starch synthesis-related genes. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 2480–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, A. 14-3-3 proteins: A historic overview. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Bonthala, V.S.; Roy, R.; Prasad, M. Unraveling 14-3-3 proteins in C4 panicoids with emphasis on model plant Setaria italica reveals phosphorylation dependent subcellular localization of RS splicing factor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camoni, L.; Visconti, S.; Aducci, P.; Marra, M. 14-3-3 proteins in plant hormone signaling: Doing several things at once. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, K.; Lecomte, S.; Estevez, Y.; Peruch, F. Hevea brasiliensis REF (Hevb 1) and SRPP (Hevb 3): An overview on rubber particle proteins. Biochimie 2014, 106, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.S.; Mat-Isa, M.N.; Bahari, A.; Ghazali, A.K.; Alias, H.; Mohd-Zainuddin, Z.; Hoh, C.C.; Wan, K.L. Metabolic routes affecting rubber biosynthesis in Hevea brasiliensis latex. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.Q.; Xu, J.; Li, H.L.; Tian, W.M. Cloning and molecular characterization of HbCOI1 from Hevea brasiliensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.M.; Huang, W.F.; Zhao, Y. Cloning and characterization of HbJAZ1 from the laticifer cells in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Müll. Arg.). Trees 2010, 24, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrecht, B.; Xue, G.P.; Sprague, S.J.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Ross, J.J.; Reid, J.B.; Fitt, G.P.; Sewelam, N.; Schenk, P.M.; Manner, J.M.; et al. MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2225–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, S.G.; Tian, W.M. MYC genes with differential responses to tapping, mechanical wounding, ethrel and methyl jasmonate in laticifers of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Müll. Arg.). J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.M.; Guo, D.; Yang, S.G.; Shi, M.J.; Chao, J.Q.; Li, H.L.; Peng, S.Q.; Tian, W.M. Jasmonate signalling in the regulation of rubber biosynthesis in laticifer cells of rubber tree, Hevea brasiliensis. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 3559–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qian, Z.; Yupei, J.; Chuanwei, Y.; Qianyue, W.; Lin, L. Shade-induced nuclear localization of PIF7 is regulated by phosphorylation and 14-3-3 proteins in Arabidopsis. Elife 2018, 7, e31636. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L.; Qu, L.; Guo, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Peng, S.Q. Histone deacetylase interacts with a WRKY transcription factor to regulate the expression of the small rubber particle protein gene from Hevea brasiliensis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 111989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Li, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Peng, S.Q. A myelocytomatosis transcription factor from Hevea brasiliensis positively regulates the expression of the small rubber particle protein gene. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 133, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, D.F.; Li, H.L.; Guo, D.; Zhu, J.H.; Peng, S.Q. Transcriptome-wide identification and characterization of MYB transcription factor genes in the laticifer cells of Hevea brasiliensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.L.; Wei, L.R.; Guo, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Chen, X.T.; Peng, S.Q. HbMADS4, a MADS-box transcription factor from Hevea brasiliensis, negatively regulates HbSRPP. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, D.; Li, H.L.; Peng, S.Q. Characterization of HbWRKY1, a WRKY transcription factor from Hevea brasiliensis that negatively regulates HbSRPP. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 71, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | Bait | Homologous Proteins | Function | Score | E-Value | Homology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HbGF14a | HEV2.1 | NRB | 140 | 6.00 × 10−53 | Id. 97%; Po. 97% |
| 2 | HbGF14a | HEV2.2 | NRB | 140 | 6.00 × 10−53 | Id. 97%; Po. 97% |
| 3 | HbGF14b | HEV2.2 | NRB | 407 | 3.00 × 10−162 | Id. 95%; Po. 99% |
| 4 | HbGF14c | Rubber elongation factor(REF) | NRB | 508 | 4.00 × 10−141 | Id. 99%; Po. 99% |
| 5 | HbGF14c | Small rubber particle protein (SRPP) | NRB | 674 | 8.00 × 10−69 | Id. 94%; Po. 94% |
| 6 | HbGF14e | glutaredoxin | NRB | 217 | 6.00 × 10−54 | Id. 96%; Po. 98% |
| 7 | HbGF14f | rubber elongation factor | NRB | 469 | 3.00 × 10−129 | Id. 99%; Po. 99% |
| 8 | HbGF14c | Hevein (HEV1) precursor | NRB, S | 774 | 3.00 × 10−80 | Id. 97%; Po. 98% |
| 9 | HbGF14c | Latex abundant protein 1 | NRB, S | 387 | 9.00 × 10−36 | Id. 99%; Po. 99% |
| 10 | HbGF14a | C3HC4-type RING zinc finger protein | S | 444 | 2.00 × 10−121 | Id. 97%; Po. 97% |
| 11 | HbGF14a | elicitor-responsive protein | S | 377 | 1.00 × 10−101 | Id. 97%; Po. 98% |
| 12 | HbGF14f | MYC2 | S | 282 | 3.00 × 10−130 | Id. 98%; Po. 99% |
| 13 | HbGF14b | DnaJ protein | D | 379 | 3.00 × 10−102 | Id. 100%; Po. 100% |
| 14 | HbGF14a | translation elongation factor 1-alpha | PT | 536 | 0 | Id. 97%; Po. 98% |
| 15 | HbGF14a | translation elongation factor 1B gamma | PT | 329 | 3.00 × 10−87 | Id. 92%; Po. 96% |
| 16 | HbGF14c | Chaperone protein dnaJ | PT | 388 | 7.00 × 10−36 | Id. 77%; Po. 80% |
| 17 | HbGF14g | 18S ribosomal | T | 378 | 8.00 × 10−102 | Id.100%; Po.100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Guo, D.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y. 14-3-3 Proteins Participate in Regulation of Natural Rubber Biosynthesis in Hevea brasiliensis. Forests 2023, 14, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050911
Zhang M, Yang Z, Guo D, Li H, Zhu J, Peng S, Wang Y. 14-3-3 Proteins Participate in Regulation of Natural Rubber Biosynthesis in Hevea brasiliensis. Forests. 2023; 14(5):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050911
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Miao, Ziping Yang, Dong Guo, Huiliang Li, Jiahong Zhu, Shiqing Peng, and Ying Wang. 2023. "14-3-3 Proteins Participate in Regulation of Natural Rubber Biosynthesis in Hevea brasiliensis" Forests 14, no. 5: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050911
APA StyleZhang, M., Yang, Z., Guo, D., Li, H., Zhu, J., Peng, S., & Wang, Y. (2023). 14-3-3 Proteins Participate in Regulation of Natural Rubber Biosynthesis in Hevea brasiliensis. Forests, 14(5), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050911






