Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Causing Tea-Oil Camellia (Camellia oleifera C.Abel) Anthracnose in Hainan, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Survey, Sample Collection and Fungal Isolation
2.2. Cultural and Morphological Characterization
2.3. Pathogenicity Assay
2.4. Fungal DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and DNA Sequencing
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Disease Symptom Characteristics
3.2. Fungal Isolation
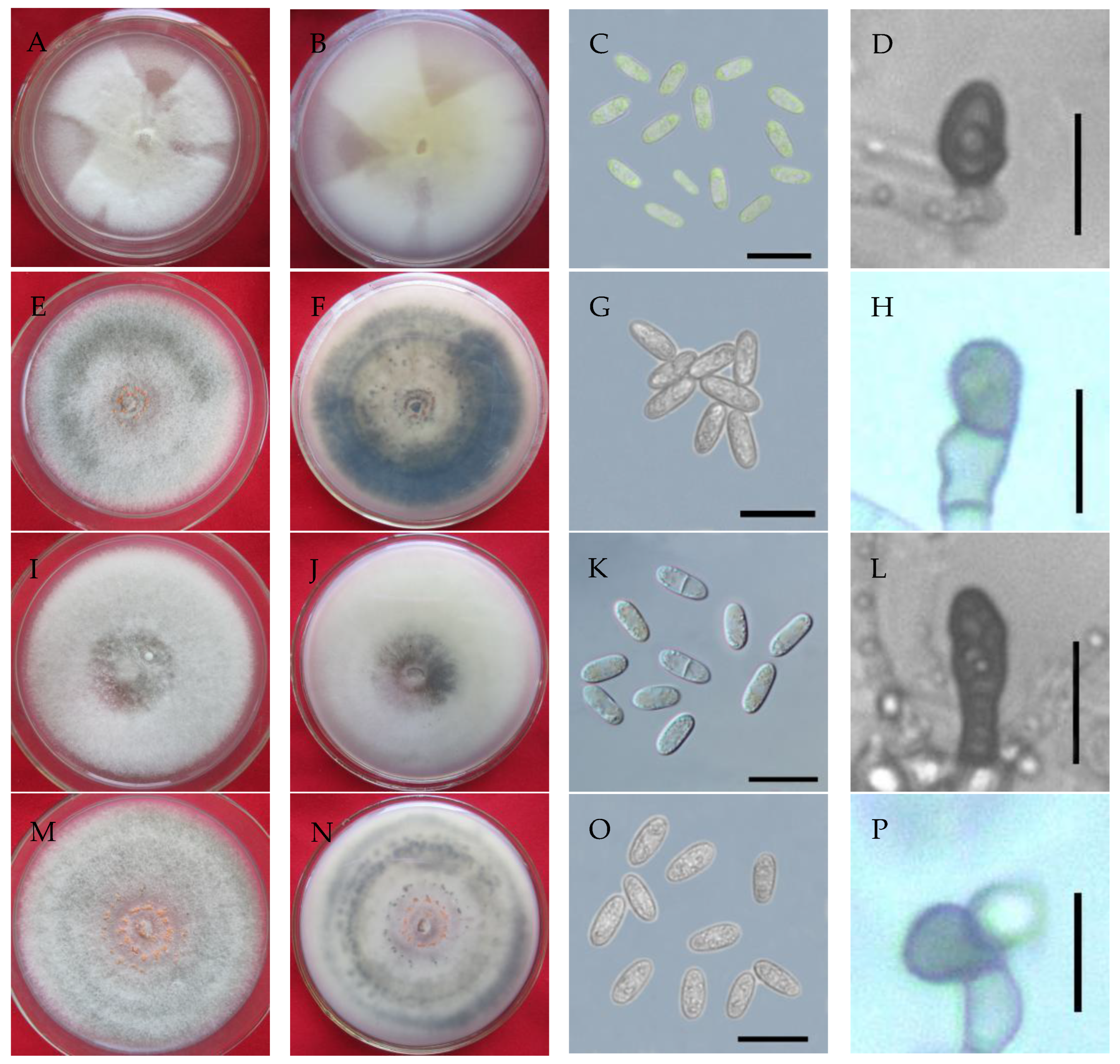
3.3. Cultural and Morphological Characteristics
3.4. Pathogenicity Test
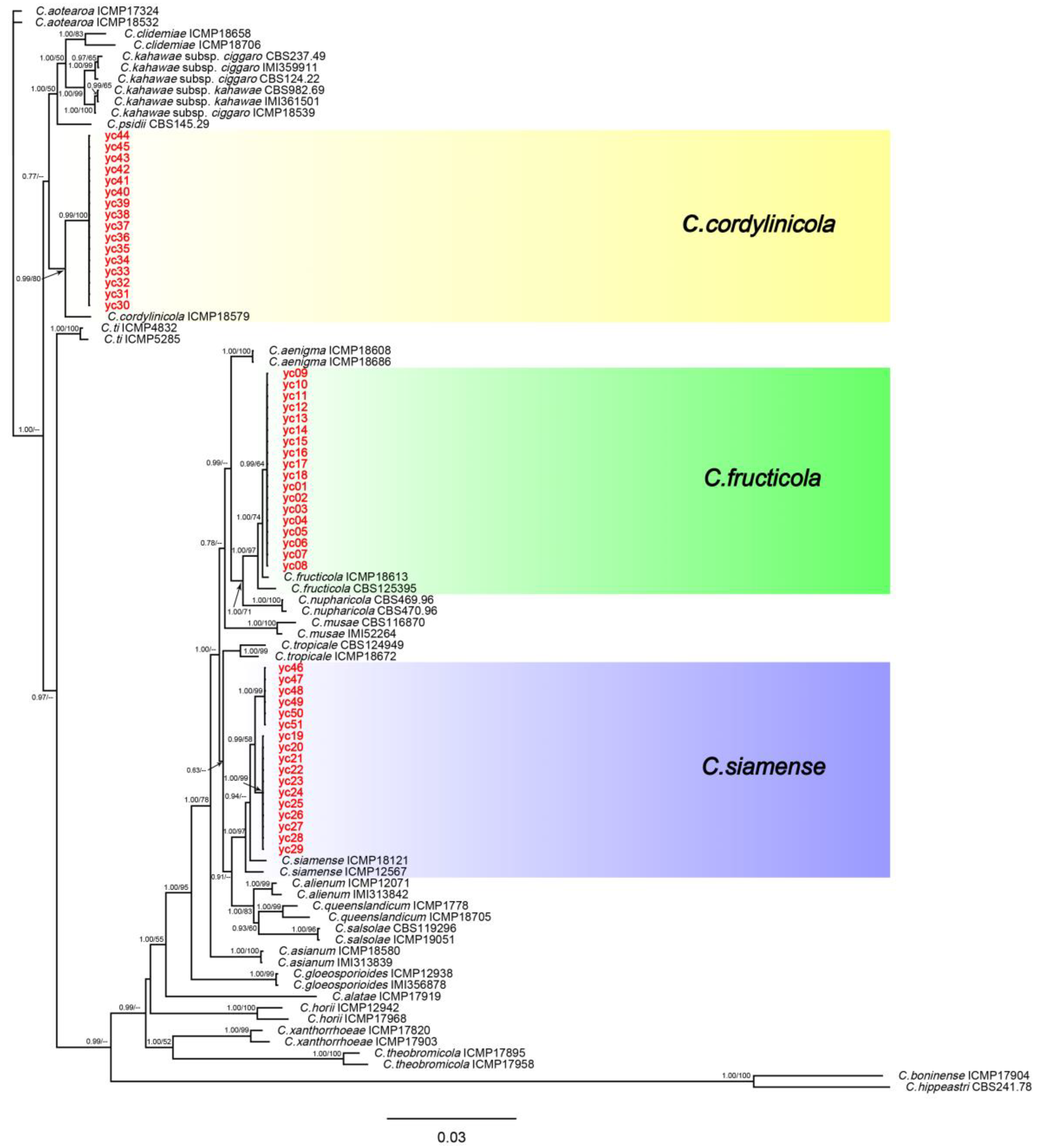
3.5. Multilocus Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, X.L.; Xie, G.S. Development of Refining Squeezing Tea Oil. Chem. Bioeng. 2008, 25, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, R.L. Tea Oil Camellia of China; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, S.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; et al. A new view on the development of oil tea camellia industry. J. Nanjing For. Univ. Nat. Sci. Edit 2020, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.J.; Chen, C.G.; Cheng, J. The medicine’s active role of Tea oil in health care. China Food Nutr. 2007, 9, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.Y. The total output value of Tea-oil camellia Industry in China reached 116 billion yuan. China Food 2020, 23, 159. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wu, L.C.; Chen, D.; Yu, Z.G.; Wei, C.J. Development of a soil quality index for Camellia oleifera forestland yield under three different parent materials in Southern China. Soil. Till. Res. 2018, 176, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, R.L.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.F. Research Progress on Camellia oleifera Diseases and Control. Biol. Disaster Sci. 2012, 35, 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Z.; Ran, F.; Long, Y.H.; Mo, F.X.; Shu, R.; Yin, X.H. Evidences of Colletotrichum fructicola Causing Anthracnose on Passiflora edulis Sims in China. Pathogens 2022, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, J.Z.; Li, X.G.; Zhong, J. Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum fructicola and Colletotrichum siamense Causing Anthracnose on Luffa Sponge Gourd in China. Plants 2022, 11, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Li, J.; Fang, L.L.; Li, J.Y.; Yu, Z.F. Morphology, Phylogeny and Pathogenicity of Colletotrichum menglaense sp. nov., Isolated from Air in China. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.X.; Li, H.; Zhou, G.Y. Progress, problem and prospect of oil camellia anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) research. For. Pest Dis. 2009, 28, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.J. Economic Forest Pathology; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, K.D.; Cai, L.; Cannon, P.F.; Crouch, J.A.; Crous, P.W.; Damm, U.; Goodwin, P.H.; Chen, H.; Johnston, P.R.; Jones, E.B.G.; et al. Colletotrichum—Names in current use. Fungal Divers. 2009, 39, 147–182. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, S.; Minz, D.; Jurkevitch, E.; Maymon, M.; Shabi, E. Molecular analyses of Colletotrichum species from almond and other fruits. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, M.; Garcia-Martinez, S.; Giner, M.J.; Alonso, A.; Ruiz, J.J. Benomyl sensitivity assays and species-specific PCR reactions highlight association of two Colletotrichum gloeosporioides types and C. acutatum with rumple disease on Primofiori lemons. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 127, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.A.; Jeger, M.J. Colletotrichum: Biology, Pathology and Control; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Hyde, K.D.; Taylor, P.W.J.; Weir, B.S.; Waller, J.M.; Abang, M.M.; Zhang, J.Z.; Yang, Y.L.; Phoulivong, S.; Liu, Z.Y.; et al. A polyphasic approach for studying Colletotrichum. Fungal Divers. 2009, 39, 183–204. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, P.F.; Damm, U.; Johnston, P.R.; Weir, B.S. Colletotrichum—Current status and future directions. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 73, 181–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, U.; Woudenberg, J.H.C.; Cannon, P.F.; Crous, P.W. Colletotrichum species with curved conidia from herbaceous hosts. Fungal Divers. 2009, 39, 45–87. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, B.S.; Johnston, P.R.; Damm, U. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 73, 115–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, M.; Carla, V.; Teresa, C.; António, B.D.; Doroteia, C.; Fernando, R.; Maria, R.F. Diversity of Colletotrichum Species Associated with Olive Anthracnose and New Perspectives on Controlling the Disease in Portugal. Agronomy 2018, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnaccia, V.; Martino, I.; Gilardi, G.; Garibaldi, A.; Gullino, M.L. Colletotrichum spp. causing anthracnose on ornamental plants in northern Italy. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 103, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Silva, D.D.; Moslemi, A.; Edwards, J.; Ades, P.K.; Crous, P.W.; Taylor, P.W.J. Colletotrichum Species Causing Anthracnose of Citrus in Australia. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Schnabel, G.; Chaisiri, C.; Yin, L.F.; Yin, W.X.; Luo, C.X. Colletotrichum Species Associated with Peaches in China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, R.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Damm, U.; Cai, L.; Liu, M.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, W.S.; Yan, J.Y. Notes on currently accepted species of Colletotrichum. Mycosphere 2016, 7, 1192–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, D.X.; Xu, J.P.; Zhou, G.Y.; Hu, M.; Tian, F. Population genetic structure of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides causing anthracnose of Camellia oleifera in China. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2014, 44, 620–628. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.L.; Zhou, G.Y.; Li, H.; Zhong, W.B.; Gong, H.E.; Wang, L.Y. Identification of a New Anthracnose of Camellia Based on Multiple-gene Phylogeny. Chin. J. Trop. Crop. 2015, 36, 972–977. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Rao, X.; Lv, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Chen, Z.J. Anthracnose resistance of 149 Camellia oleifera varieties (lines) and their causal pathogens in Guangdong Province. J. Plant Prot. 2021, 48, 652–661. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.Q.; Liu, J.A.; Zhou, G.Y. Pathogen of Oil-Tea Trees Anthracnose Caused by Colletotrichum spp. in Hunan Province. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2017, 53, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Liao, W.J.; Zou, D.X.; Wu, Y.J.; Deng, Y. Identification and biological characteristics of the pathogen from Camellia oleifera anthracnose in Guangxi. J. Plant Prot. 2015, 42, 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.X.; Wang, Z.R.; Shi, L.; Ruan, J.F.; Zheng, S.Z.; Liu, W. Pathogen isolation and identification of Camellia oleifera anthracnose. Subtrop. Agric. Res. 2021, 17, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.Q.; Li, H. First report of leaf anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum karstii on tea-oil trees (Camellia oleifera) in China. Plant. Dis. 2018, 102, 674–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Li, H. First Report of Colletotrichum nymphaeae Causing Anthracnose on Camellia oleifera in China. Plant. Dis. 2020, 104, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Xu, X.W.; Cheng, J.Y.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J.B.; Li, D.W. Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Associated with Anthracnose Disease of Camellia oleifera in China. Plant. Dis. 2020, 104, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Hyde, K.D.; Ho, W. Single spore isolation of fungi. Fungal Divers. 1999, 3, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, D.; Wang, W.; Gleason, M.L.; Zhang, R.; Liang, X.; Sun, G. Diversity of Colletotrichum Species Causing Apple Bitter Rot and Glomerella Leaf Spot in China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; Ahmad, K.; Vadamalai, G.; Siddiqui, Y.; Saad, N.; Ahmed, O.H.; Hata, E.M.; Adzmi, F.; Rashed, O.; Rahman, M.Z.; et al. Phylogenetic Analysis and Genetic Diversity of Colletotrichum falcatum Isolates Causing Sugarcane Red Rot Disease in Bangladesh. Biology 2021, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, I.; Linda, M.K. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, N.A.; MacKenzie, S.J.; Peever, T.L. Postbloom fruit drop of citrus and key lime anthracnose are caused by distinct phylogenetic lineages of Colletotrichum acutatum. Phytopathology 2008, 98, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, J.; Tsukiboshi, T. Colletotrichum echinochloae, a new species on Japanese barnyard millet (Echinochloa utilis). Mycoscience 2009, 50, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 24, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Bio. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhaxybayeva, O.; Gogarten, J.P. Bootstrap, Bayesian probability and maximum likelihood mapping: Exploring new tools for comparative genome analyses. Genomics 2002, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Mark, P.V.D.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.D.M. TREEVIEW: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Math. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciola, S.O.; Gilardi, G.; Faedda, R.; Schena, L.; Pane, A.; Garibaldi, A.; Gullino, M.L. Characterization of Colletotrichum ocimi Population Associated with Black Spot of Sweet Basil (Ocimum basilicum) in Northern Italy. Plants 2020, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.C.; Haudenshield, J.S.; Hartman, G.L. Colletotrichum incanum sp. nov., a curved-conidial species causing soybean anthracnose in USA. Mycologia 2014, 106, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnaccia, V.; Gilardi, G.; Martino, I.; Garibaldi, A.; Gullino, M.L. Species Diversity in Colletotrichum Causing Anthracnose of Aromatic and Ornamental Lamiaceae in Italy. Agronomy 2019, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Damm, U.; Cai, L.; Crous, P.W. Species of the Colletotrichum gloeosporioides complex associated with anthracnose disease of Proteaceae. Fungal Divers. 2013, 61, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, X.J.; Khaskheli, M.I.; Sun, X.F.; Chang, X.L.; Gong, G.S. Identification of Colletotrichum Species Associated with Blueberry Anthracnose in Sichuan, China. Pathogens 2020, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Jiang, L.Y.; Bao, A.H.; Liu, C.L.; Liu, J.A.; Zhou, G.Y. Molecular Characterization, Pathogenicity and Biological Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Associated with Anthracnose of Camellia yuhsienensis Hu in China. Forests 2021, 12, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoulivong, S.; Cai, L.; Parinn, N.; Chen, H.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D. A new species of Colletotrichum from Cordyline fruticosa and Eugenia javanica causing anthracnose disease. Mycotaxon 2010, 114, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Bu, J.Y.; Shu, J.; Yu, Z.H.; Tang, L.H.; Huang, S.P.; Guo, T.X.; Mo, J.Y.; Luo, S.M.; Solangi, G.S.; et al. Colletotrichum species associated with mango in southern China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Wei, W.; Wu, B.; Su, M.S.; Wang, D.X.; Jiang, Z.P. Isolation and Primary Identification of the Pathogen of Anthracnose in Camellia oleifera. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2014, 36, 314–318. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnaccia, V.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Polizzi, G.; Crous, P.W. High Species Diversity in Colletotrichum Associated with Citrus Diseases in Europe. Persoonia 2017, 39, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Pedraza, J.M.; Mora-Aguilera, J.A.; Nava-Díaz, C.; Lima, N.B.; Michereff, S.J.; Sandoval-Islas, J.S.; Câmara, M.P.S.; Téliz-Ortiz, D.; Leyva-Mir, S.G. Distribution and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum species associated with mango anthracnose in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Isolate Code | Location | Year | Isolate Code | Location | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| yc01 | Wenchang | 2018 | yc27 | Qiongzhong | 2021 |
| yc02 | Qiongzhong | 2019 | yc28 | Qiongzhong | 2020 |
| yc03 | Wenchang | 2017 | yc29 | Qiongzhong | 2020 |
| yc04 | Wenchang | 2020 | yc30 | Wenchang | 2017 |
| yc05 | Qiongzhong | 2018 | yc31 | Wenchang | 2020 |
| yc06 | Qiongzhong | 2021 | yc32 | Wenchang | 2021 |
| yc07 | Wuzhishan | 2021 | yc33 | Wenchang | 2020 |
| yc08 | Wuzhishan | 2020 | yc34 | Wenchang | 2018 |
| yc09 | Wuzhishan | 2019 | yc35 | Wenchang | 2021 |
| yc10 | Wenchang | 2021 | yc36 | Wenchang | 2021 |
| yc11 | Wenchang | 2021 | yc37 | Wenchang | 2019 |
| yc12 | Wuzhishan | 2018 | yc38 | Wenchang | 2021 |
| yc13 | Wuzhishan | 2021 | yc39 | Wenchang | 2020 |
| yc14 | Wuzhishan | 2021 | yc40 | Wenchang | 2018 |
| yc15 | Wuzhishan | 2021 | yc41 | Wenchang | 2021 |
| yc16 | Qiongzhong | 2019 | yc42 | Wenchang | 2020 |
| yc17 | Qiongzhong | 2019 | yc43 | Wenchang | 2021 |
| yc18 | Qiongzhong | 2021 | yc44 | Wenchang | 2019 |
| yc19 | Qiongzhong | 2017 | yc45 | Wenchang | 2021 |
| yc20 | Qiongzhong | 2020 | yc46 | Wuzhishan | 2021 |
| yc21 | Qiongzhong | 2020 | yc47 | Wuzhishan | 2021 |
| yc22 | Qiongzhong | 2018 | yc48 | Wuzhishan | 2020 |
| yc23 | Qiongzhong | 2018 | yc49 | Wuzhishan | 2019 |
| yc24 | Qiongzhong | 2021 | yc50 | Wuzhishan | 2021 |
| yc25 | Qiongzhong | 2019 | yc51 | Wuzhishan | 2017 |
| yc26 | Qiongzhong | 2021 | --- | --- | --- |
| Number | Target Fragment | Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Internally transcribed space of ribosomal DNA (ITS) | ITS1-1F | CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA | Gardes et al. [39] |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC | |||
| 2 | β-tubulin (TUB) | T1 | AACATGCGTGAGATTGTAAGT | O’Donnell et al. [40] |
| T2 | TAGTGACCCTTGGCCCAGTTG | |||
| 3 | Chitinsynthase (CHS-1) | CHS-79F | TGGGGCAAGGATGCTTGGAAGAAG | Carbone et al. [41] |
| CHS-345R | TGGAAGAACCATCTGTGAGAGTTG | |||
| 4 | Actin (ACT) | ACT512F | ATGTGCAAGGCCGGTTTCGC | Carbone et al. [41] |
| ACT783R | TACGAGTCCTTCTGGCCCAT | |||
| 5 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) | GDF | GCCGTCAACGACCCCTTCATTGA | Peres et al. [42] |
| GDR | GGGTGGAGTCGTACTTGAGCATGT | |||
| 6 | Manganese-superoxide (SOD2) | SODglo2-F | CAGATCATGGAGCTGCACCA | Moriwaki et al. [43] |
| SODglo2-R | TAGTACGCGTGCTCGGACAT |
| Species Name | Culture | Country | Host | Accession Number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | TUB | CHS-1 | ACT | GAPDH | SOD2 | ||||
| C.aenigma | ICMP 18608 * | Israel | Persea americana | JX010244 | JX010389 | JX009774 | JX009443 | JX010044 | JX010311 |
| ICMP 18686 | Japan | Pyrus pyrifolia | JX010243 | JX010390 | JX009789 | JX009519 | JX009913 | JX010312 | |
| C. boninense | ICMP17904 *, CBS 123755 | Japan | Crinum asiaticum | JX010292 | JQ005588 | JX009827 | JX009583 | JX009905 | --- |
| C. alatae | CBS 304.67 *, ICMP 17919 | India | Dioscorea alata | JX010190 | JX010383 | JX009837 | JX009471 | JX009990 | JX010305 |
| C. alienum | IMI 313842, ICMP 18691 | Australia | Persea americana | JX010217 | JX010385 | JX009754 | JX009580 | JX010018 | JX010307 |
| ICMP 12071 * | New Zealand | Malus domestica | JX010251 | JX010411 | JX009882 | JX009572 | JX010028 | JX010333 | |
| C. aotearoa | ICMP 18532 | New Zealand | Vitex lucens | JX010220 | JX010421 | JX009764 | JX009544 | JX009906 | JX010338 |
| ICMP 17324 | New Zealand | Kunzea ericoides | JX010198 | JX010418 | JX009770 | JX009538 | JX009991 | JX010344 | |
| C. asianum | IMI 313839, ICMP18696 | Australia | Mangifera indica | JX010192 | JX010384 | JX009753 | JX009576 | JX009915 | JX010306 |
| ICMP18580 *, CBS 130418 | Thailand | Coffea arabica | JX010196 | JX010406 | JX009867 | JX009584 | JX010053 | JX010328 | |
| C. cordylinicola | MFLUCC090551 *, ICMP18579 | Thailand | Cordyline fruticosa | JX010226 | JX010440 | JX009864 | JX009586 | JX009975 | JX010361 |
| C. clidemiae | ICMP 18706 | USA | Vitis sp. | JX010274 | JX010439 | JX009777 | JX009476 | JX009909 | JX010353 |
| ICMP18658 * | USA, Hawaii | Clidemia hirta | JX010265 | JX010438 | JX009877 | JX009537 | JX009989 | JX010356 | |
| C. fructicola | ICMP18613 | Israel | Limonium sinuatum | JX010167 | JX010388 | JX009772 | JX009491 | JX009998 | JX010310 |
| CBS 125395, ICMP18645 | Panama | Theobroma cacao | JX010172 | JX010408 | JX009873 | JX009543 | JX009992 | JX010330 | |
| C. gloeosporioides | IMI356878 *, ICMP17821, CBS112999 | Italy | Citrus sinensis | JX010152 | JX010445 | JX009818 | JX009531 | JX010056 | JX010365 |
| ICMP12938 | New Zealand | Citrus sinensis | JX010147 | --- | JX009746 | JX009560 | JX009935 | --- | |
| C. hippeastri | CBS 241.78, ICMP17920 | Netherlands | Hippeastrum sp. | JX010293 | --- | JX009838 | JX009485 | JX009932 | --- |
| C. horii | ICMP12942 | New Zealand | Diospyros kaki | GQ329687 | JX010375 | JX009748 | JX009533 | GQ329685 | JX010296 |
| ICMP17968 | China | Diospyros kaki | JX010212 | JX010378 | JX009811 | JX009547 | GQ329682 | JX010300 | |
| C. kahawae subsp. ciggaro | ICMP18539 * | Australia | Olea europaea | JX010230 | JX010434 | JX009800 | JX009523 | JX009966 | JX010346 |
| IMI 359911, ICMP17931,CBS12988 | Switzerland | Dryas octopetala | JX010236 | JX010428 | JX009832 | JX009475 | JX009965 | JX010354 | |
| C. kahawae subsp. ciggaro | CBS 237.49 *, ICMP17922 | Germany | Hypericum perforatum | JX010238 | JX010432 | JX009840 | JX009450 | JX010042 | JX010355 |
| CBS 124.22 *, ICMP19122 | USA | Vaccinium sp. | JX010228 | JX010433 | JX009902 | JX009536 | JX009950 | JX010367 | |
| C. kahawae subsp. kahawae | CBS982.69, ICMP17915 | Angola | Coffea arabica | JX010234 | JX010435 | JX009829 | JX009474 | JX010040 | JX010352 |
| IMI 361501, ICMP17905 | Cameroon | Coffea arabica | JX010232 | JX010431 | JX009816 | JX009561 | JX010046 | JX010349 | |
| C. musae | CBS116870 *, ICMP19119 | USA | Musa sp. | JX010146 | HQ596280 | JX009896 | JX009433 | JX010050 | JX010335 |
| IMI 52264, ICMP17817 | Kenya | Musa sapientum | JX010142 | JX010395 | JX009815 | JX009432 | JX010015 | JX010317 | |
| C. nupharicola | CBS 469.96, ICMP17938 | USA | Nupharlutea subsp. polysepala | JX010189 | JX010397 | JX009834 | JX009486 | JX009936 | JX010319 |
| CBS 470.96 *, ICMP18187 | USA | Nupharlutea subsp. polysepala | JX010187 | JX010398 | JX009835 | JX009437 | JX009972 | JX010320 | |
| C. psidii | CBS 145.29 *, ICMP19120 | Italy | Psidium sp. | JX010219 | JX010443 | JX009901 | JX009515 | JX009967 | JX010366 |
| C. queenslandicum | ICMP1778 * | Australia | Carica papaya | JX010276 | JX010414 | JX009899 | JX009447 | JX009934 | JX010336 |
| ICMP18705 | Fiji | Coffea sp. | JX010185 | JX010412 | JX009890 | JX009490 | JX010036 | JX010334 | |
| C. salsolae | ICMP19051 * | Hungary | Salsola tragus | JX010242 | JX010403 | JX009863 | JX009562 | JX009916 | JX010325 |
| CBS 119296, ICMP18693 | Hungary | Glycine max | JX010241 | --- | JX009791 | JX009559 | JX009917 | --- | |
| C. siamense | ICMP12567 | Australia | Perseaa mericana | JX010250 | JX010387 | JX009761 | JX009541 | JX009940 | JX010309 |
| ICMP18121 | Nigeria | Dioscor earotundata | JX010245 | JX010402 | JX009845 | JX009460 | JX009942 | JX010324 | |
| C. theobromicola | MUCL42295, ICMP17958, CBS 124250 | Australia | Stylosanthes guianensis | JX010291 | JX010381 | JX009822 | JX009498 | JX009948 | JX010303 |
| ICMP17895 | Mexico | Annona diversifolia | JX010284 | JX010382 | JX009828 | JX009568 | JX010057 | JX010304 | |
| C. ti | ICMP 5285 | New Zealand | Cordyline australis | JX010267 | JX010441 | JX009897 | JX009553 | JX009910 | JX010363 |
| ICMP 4832 * | New Zealand | Cordyline sp. | JX010269 | JX010442 | JX009898 | JX009520 | JX009952 | JX010362 | |
| C. tropicale | MAFF 239933, ICMP 18672 | Japan | Litchi chinensis | JX010275 | JX010396 | JX009826 | JX009480 | JX010020 | JX010318 |
| CBS 124949 *, ICMP 18653 | Panama | Theobroma cacao | JX010264 | JX010407 | JX009870 | JX009489 | JX010007 | JX010329 | |
| C. xanthorrhoeae | BRIP 45094 *, ICMP 17903 | Australia | Xanthorrhoea preissii | JX010261 | JX010448 | JX009823 | JX009478 | JX009927 | JX010369 |
| IMI 350817a, ICMP 17820 | Australia | Xanthorrhoea sp. | JX010260 | --- | JX009814 | JX009479 | JX010008 | --- | |
| Gene Datasets | ITS | TUB | GAPDH | ACT | CHS-1 | SOD2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best-fit evolutionary model | SYM + I + G | HKY + I | HKY + I | HKY + I | SYM + G | GTR + I + G |
| Groups | Isolates | Colony Characteristics | Conidia | Appressorium | Growth Rate (mm/day) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (µm) | Width (µm) | Shape | Length (µm) | Width (µm) | Shape | ||||
| 1 | yc01–yc18 | White to pale, less fluffy mycelia, reverse light yellowish, less sporulation | 12.40 ± 1.29 (10.00–15.70) | 4.51 ± 0.61 (3.20–6.00) | Cylindrical | 9.20 ± 0.94 (8.00–10.70) | 5.62 ± 0.45 (4.20–6.00) | Ovoid or irregular | 9.60 ± 0.50 (8.20–10.70) |
| 2 | yc19–yc29 | White to grey to dark grey aerial mycelia, with orange visible conidial masses, reverse dark brownish, fast growing | 13.02 ± 0.85 (11.20–14.40) | 4.63 ± 0.35 (4.00–5.20) | Fusiform | 7.51 ± 0.99 (6.00–9.10) | 5.62 ± 0.61 (4.60–6.20) | Spherical to cylindrical | 11.40 ± 0.60 (10.90–13.00) |
| 3 | yc30–yc45 | White, dense fluffy mycelia with floccose aerial mycelia in center, reverse slightly greenish to brownish | 13.65 ± 0.92 (11.80–15.40) | 5.22 ± 0.41 (4.60–6.30) | Fusiform | 13.50 ± 0.75 (12.50–14.70) | 7.15 ± 1.32 (4.80–8.00) | Clavate or irregular | 8.56 ± 0.49 (8.10–9.27) |
| 4 | yc46–yc51 | Cottony, dense grey aerial mycelium, with orange visible conidial masses, reverse slightly brownish, fast growing | 13.22 ± 0.69 (12.00–14.40) | 4.55 ± 0.34 (4.00–5.10) | Fusiform | 7.83 ± 0.75 (6.20–8.50) | 6.10 ± 0.77 (4.50–6.80) | Spherical to cylindrical | 11.14 ± 0.86 (10.10–12.70) |
| Groups | Isolate No. | Leaf | Fruit | Groups | Isolate No. | Leaf | Fruit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | yc01 | 100 | 20 | 2 | yc27 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc02 | 100 | 6.7 | 2 | yc28 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc03 | 100 | 53.3 | 2 | yc29 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc04 | 100 | 0 | 3 | yc30 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc05 | 100 | 13.3 | 3 | yc31 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc06 | 100 | 6.7 | 3 | yc32 | 60 | 0 |
| 1 | yc07 | 100 | 0 | 3 | yc33 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 1 | yc08 | 100 | 10 | 3 | yc34 | 80 | 0 |
| 1 | yc09 | 100 | 0 | 3 | yc35 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc10 | 100 | 0 | 3 | yc36 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc11 | 100 | 3.3 | 3 | yc37 | 63.3 | 0 |
| 1 | yc12 | 100 | 3.3 | 3 | yc38 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc13 | 100 | 0 | 3 | yc39 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc14 | 100 | 50 | 3 | yc40 | 76.7 | 0 |
| 1 | yc15 | 100 | 6.7 | 3 | yc41 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 1 | yc16 | 100 | 0 | 3 | yc42 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc17 | 100 | 0 | 3 | yc43 | 100 | 0 |
| 1 | yc18 | 100 | 3.3 | 3 | yc44 | 100 | 0 |
| 2 | yc19 | 100 | 6.7 | 3 | yc45 | 100 | 0 |
| 2 | yc20 | 100 | 0 | 4 | yc46 | 63.3 | 10 |
| 2 | yc21 | 100 | 0 | 4 | yc47 | 66.7 | 0 |
| 2 | yc22 | 100 | 0 | 4 | yc48 | 60 | 10 |
| 2 | yc23 | 73.3 | 10 | 4 | yc49 | 60 | 0 |
| 2 | yc24 | 76.7 | 0 | 4 | yc50 | 100 | 6.7 |
| 2 | yc25 | 100 | 0 | 4 | yc51 | 100 | 0 |
| 2 | yc26 | 100 | 6.7 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; He, C. Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Causing Tea-Oil Camellia (Camellia oleifera C.Abel) Anthracnose in Hainan, China. Forests 2023, 14, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051030
Zhu H, He C. Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Causing Tea-Oil Camellia (Camellia oleifera C.Abel) Anthracnose in Hainan, China. Forests. 2023; 14(5):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051030
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hui, and Chaozu He. 2023. "Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Causing Tea-Oil Camellia (Camellia oleifera C.Abel) Anthracnose in Hainan, China" Forests 14, no. 5: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051030
APA StyleZhu, H., & He, C. (2023). Identification and Characterization of Colletotrichum Species Causing Tea-Oil Camellia (Camellia oleifera C.Abel) Anthracnose in Hainan, China. Forests, 14(5), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14051030








