Tracking the Extent and Impacts of a Southern Pine Beetle (Dendroctonus frontalis) Outbreak in the Bienville National Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
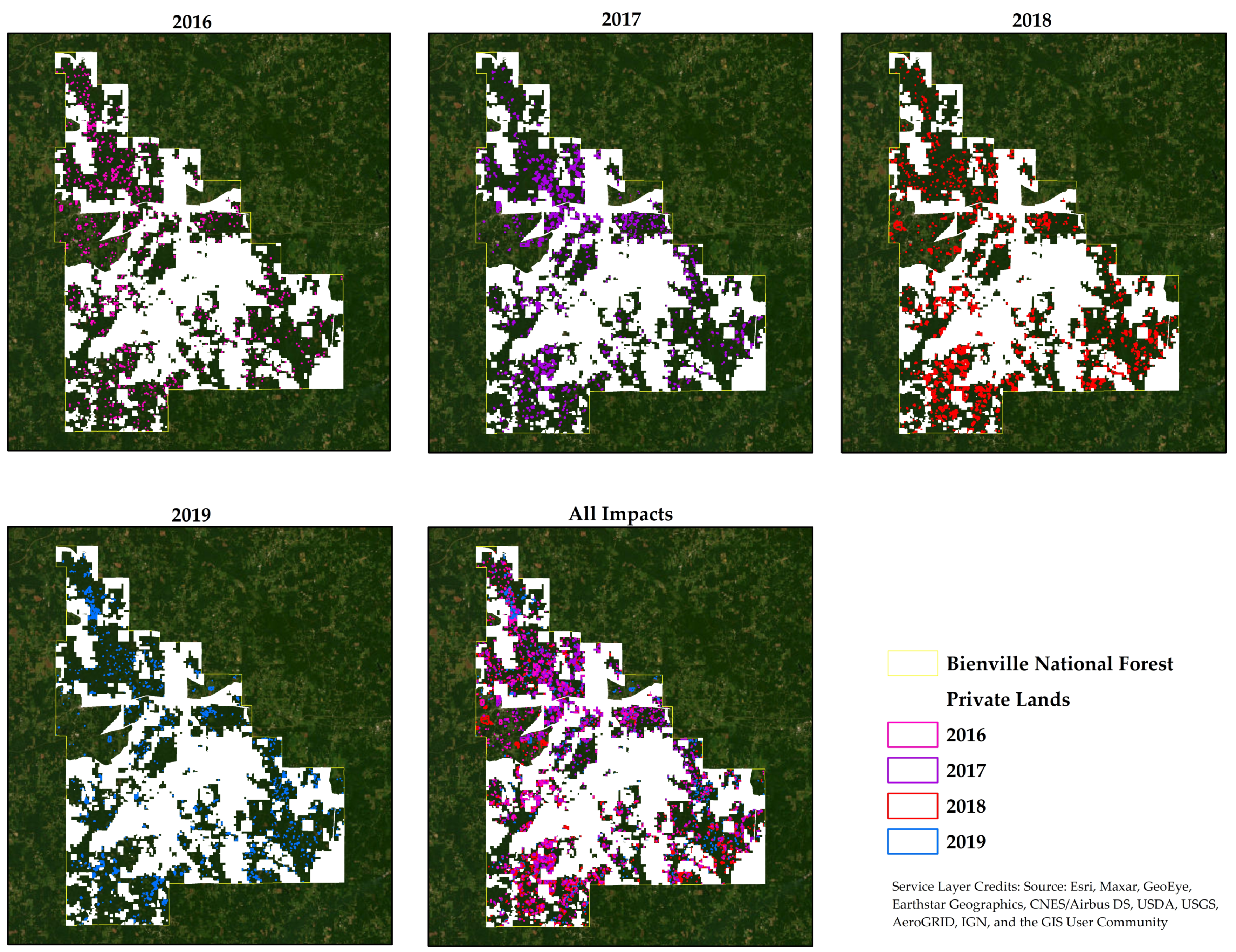
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crosby, M.K.; Fan, Z.; Spetich, M.A.; Leininger, T.; Fan, X. Early indications of drought impacts on forests in the southeastern United States. For. Chron. 2015, 91, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.N.; Naka, K.; Dimov, L.D. Assessment of disturbance across forest inventory plots in the southeastern United States for the period 1995-2018. For. Sci. 2020, 66, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, H.L.; Montes, C.R.; Kinane, S.M.; Gandhi, K.J.K. Through space and time: Predicting numbers of an eruptive pine tree pest and its predator under changing climate conditions. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 483, 118770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.; Asaro, C.; Klepzig, K.; Billings, R. The southern pine beetle initiative: Working for healthier forests. J. For. 2008, 106, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.R.; Nowak, J.T. Southern Pine Beetle. USDA For. Serv., For. Insect and Dis. Leaflet 49, FS-R6-RO-FIDL49, Pacific Northwest Region, Portland, OR. 8 p. 2009. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/fsbdev2_042840.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- Nowak, J.T.; Meeker, J.R.; Coyle, D.R.; Steiner, C.A.; Brownie, C. Southern pine beetle infestations in relation to forest stand conditions, previous thinning, and prescribed burning: Evaluation of the Southern Pine Beetle Prevention Program. J. For. 2015, 113, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushla, J.D.; Dicke, S.G.; Henderson, J.E.; Gordon, J.S.; Londo, A.J.; Meeker, J. Economic impact of a large-scale, collaborative forest health project: A model for making a difference. J. Ext. 2019, 57, 3FEA3. [Google Scholar]
- Krist, F.J., Jr.; Ellenwood, J.R.; Woods, M.E.; McMahan, A.J.; Cowardin, J.P.; Ryerson, D.E.; Sapio, F.J.; Zweifler, M.O.; Romero, S.A. 2014. 2013–2027 National Insect and Disease Forest Risk Assessment. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Fort Collins, Colorado: Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team. Available online: https://www.fs.fed.us/foresthealth/technology/pdfs/2012_RiskMap_Report_web.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- USDA Forest Service. 2022. Forest Products Cut and Sold from the National Forests and Grasslands. Available online: https://www.fs.fed.us/forestmanagement/products/cut-sold/index.shtml (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- USDA Forest Service Forest Inventory and Analysis. 2022. EVALIDator. Available online: https://www.fia.fs.fed.us/tools-data/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Pye, J.M.; Holmes, T.P.; Prestemon, J.P.; Wear, D.N. 2011; Economic Impacts of the Southern Pine Beetle. In: Coulson, R.N.; Klepzig, K.D. 2011. Southern Pine Beetle II. Gen. Tech. Rep. SRS-140. Asheville, NC: U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Southern Research Station. 213-222. Available online: https://www.srs.fs.usda.gov/pubs/gtr/gtr_srs140/gtr_srs140_213.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Clarke, S.R.; Hartshorn, J. Contrasting competitor and predator responses to a short-lived southern pine beetle outbreak: A Case study. For. Sci. 2021, 67, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, R.F.; Pase, H.A. A Field Guide for Checking Southern Pine Beetle Spots; USDA Agriculture Handbook: Washington, DC, USA, 1983; No.558. [Google Scholar]
- Maingi, J.K.; Luhn, W.M. Mapping insect-induced pine mortality in the Daniel Boone National Forest, Kentucky using Landsat TM and ETM+ Data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2005, 42, 224–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, R.; Smith, L.A.; Zhu, J.; Verma, S.; Kouchoukos, N.; Heo, J. Developing and validating a method for monitoring and tracking changes in southern pine beetle hazard at the landscape level. In Advances in Threat Assessment and Their Application to Forest and Rangeland Management; Pye, J.M., Rauscher, H.M., Sands, Y., Lee, D.C., Beatty, J.S., Eds.; Gen. Tech. Rep. PNW-GTR-802; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest and Southern Research Stations: Portland, OR, USA, 2010; pp. 541–549. [Google Scholar]
- Bright, B.C.; Hudak, A.T.; Meddens, A.J.H.; Egan, J.M.; Jorgensen, C.L. Mapping multiple insect outbreaks across large regions annually using Landsat time series data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näsi, R.; Honkavaara, E.; Blomqvist, M.; Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, P.; Hakala, T.; Viljanen, N.; Kantola, T.; Holopainen, M. Remote sensing of bark beetle damage in urban forests at individual tree level using a novel hyperspectral camera from UAV and aircraft. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 30, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hais, M.; Wild, J.; Berec, L.; Brůna, J.; Kennedy, R.; Braaten, J.; Brož, Z. Landsat imagery spectral trajectories-important variables for spatially predicting the risks of bark beetle disturbance. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, C.; Seidl, R.; Hostert, P. Remote sensing of forest insect disturbances: Current state and future directions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 60, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.F.; Ritger, H.M.W.; Pearce, C.; Eickwort, J.; Hulcr, J. Ability of remote sensing systems to detect bark beetle spots in the Southeastern US. Forests 2020, 11, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, T.E. Ranking agricultural and natural resources contributions to Mississippi. J. Agribus. 2021, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, J.S.; Handfield, R.B.; Daystar, J.S.; McConnell, T.E. An Economic Impact Analysis of the U.S. Biobased Products Industry: A Report to the Congress of the United States of America. In A Joint Publication of the Duke Center for Sustainability & Commerce and the Supply Chain Resource Cooperative at North Carolina State University; USDA: Washington DC, WA, USA, 2015; 127p. [Google Scholar]
- Mississippi Forestry Commission. Mississippi’s Forest Action Plan 2020. Jackson, MS, Mississippi Forestry Commission. 241 p. 2020. Available online: https://www.mfc.ms.gov/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Mississippi-Forest-Action-Plan-January-2021-compressed.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2021).
- Dahal, R.P.; Henderson, J.E.; Munn, I.A.; Grala, R.K. Forestry in Mississippi-the Contribution of the Industry to the Mississippi Economy: An Input-Output Analysis. Forest and Wildlife Research Center, Research Bulletin FO464, Mississippi State University. 32 pp. 2017. Available online: https://www.fwrc.msstate.edu/pubs/foinms2017.pdf (accessed on 18 August 2021).
- USDA. National Agricultural Imaging Program, USDA-FSA-APFO Digital Ortho Mosaic. Imagery from the USDA-FSA-APFO Aerial Photography Field Office, Salt Lake City, UT. 2017. Available online: https://www.maris.state.ms.us/NAIP_2016/ (accessed on 23 May 2021).
- Mississippi Automated Resource Information System (MARIS). 2021. 2016 Mississippi NAIP. Available online: https://www.maris.state.ms.us/HTML/DATA/data_Aerial/NAIP/NAIP2016.html#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- SAS, Version 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2022.
- Clarke, S.R.; Riggins, J.J.; Stephen, F.M. Forest management and southern pine beetle outbreaks: A historical perspective. For. Sci. 2016, 62, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutner, M.H.; Nachtsheim, C.J.; Neter, J. Applied Linear Regression Models, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Irwin: New York, NY, USA, 2004; 701p. [Google Scholar]
- Billings, R.F. Mechanical Control of Southern Pine Beetle Infestations. In Southern Pine Beetle II. Gen. Tech. Rep. SRS-140; Coulson, R.N., Klepzig, K.D., Eds.; U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Southern Research Station: Asheville, NC, USA, 2011; pp. 399–413. [Google Scholar]
- Immitzer, M.; Atzberger, C. Early detection of bark beetle infestation in Norway spruce (Picea abies, L.) using WorldView-2 data. Photogramm. -Fernerkund. -Geoinf. 2014, 5, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte, M.; Solano-Correa, Y.T.; Frizzera, L.; Gianelle, D. Mapping a European spruce beetle outbreak using Sentinel-2 remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, B.C.; Hudak, A.T.; Egan, J.M.; Jorgensen, C.L.; Rex, F.E.; Hicke, J.A.; Meddens, A.J.H. Using satellite imagery to evaluate bark beetle-caused tree mortality reported in aerial surveys in a mixed conifer forest in Northern Idaho, USA. Forests 2020, 11, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Gao, R.; Zhao, F.; Huang, C.; Sun, R.; Lv, Z.; Huang, Z. Landsat-based monitoring of southern pine beetle infestation severity and severity change in a temperate mixed forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietzsch, B.W.; Peter, F.J.; Berger, U. The effect of sanitation felling on the spread of European spruce bark beetle-an individual-based modeling approach. Front. For. Glob. Change 2021, 4, 704930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobor, L.; Hlásny, T.; Rammer, W.; Zimová, S.; Barka, I.; Seidl, R. Spatial configuration matters when removing windfelled trees to manage bark beetle disturbances in central European forest landscapes. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meddens, A.J.H.; Hicke, J.A.; Vierling, L.A.; Hudak, A.T. Evaluating methods to detect bark beetle-caused tree mortality using single-date and multi-date Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestemon, J.P.; Abt, K.L.; Potter, K.M.; Koch, F.H. An economic assessment of mountain pine beetle timber salvage in the West. West. J. Appl. For. 2013, 28, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Little, N.S.; McConnell, T.E.; Irby, N.E.; Shi, S.Q.; Riggins, J.J. Surface free energy of blue-stained southern pine sapwood from bark-beetle attacked trees. Wood Fiber Sci. 2013, 45, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hlásny, T.; König, L.; Krokene, P.; Lindner, M.; Montagné-Huck, C.; Müller, J.; Qin, H.; Raffa, K.F.; Schelhaas, M.; Svoboda, M.; et al. Bark beetle outbreaks in Europe: State of knowledge and ways forward for management. Curr. For. Rep. 2021, 7, 138–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, J.; Tyukavina, A.; Khan, A.; Potapov, P.; Adusei, B.; Hansen, M.C.; Lima, A. Using multi-resolution satellite data to quantify land dynamics: Applications of PlanetScope imagery for cropland and tree-cover loss area estimation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.P.; Samalens, J.C.; Guyon, D.; van Halder, I.; Jactel, H.; Menassieu, P.; Piou, D. Multiscale spatial variation of the bark beetle Ips sexdentatus damage in a pine plantation forest (Landes de Gascogne, Southwestern France). For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.R.; Meeker, J.R.; Dodds, K.A. Revised and potential new tactics for the suppression of southern pine beetle infestations. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2021, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, I.A.; Rucker, R.R. An economic analysis of the differences between bid prices on forest service and private timber sales. For. Sci. 1995, 41, 823–840. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, D.R.; Newman, D.H. The impact of reserve prices on sealed bid federal timber sale auctions. For. Sci. 1988, 44, 485–495. [Google Scholar]
- Sendak, P.E. Timber Sale Value as a Function of Sale Characteristics and Number of Bidders; Res. Pap. NE-657; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Northeastern Forest Experiment Station: Radnor, PA, USA, 1991; 7p. [Google Scholar]
- Leefers, L.A.; Potter-Witter, K. Timber sale characteristics and competition for public lands stumpage: A case study from the Lake States. For. Sci. 2006, 52, 460–467. [Google Scholar]




| Year | Active Infestation | Standing Dead | Cut and Leave | Cut and Remove | Hazard Mitigation | Yearly Totals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 607 | 476 | 63 | 2 | 0 | 1148 |
| 2017 | 485 | 574 | 176 | 7 | 1 | 1243 |
| 2018 | 487 | 1087 | 60 | 166 | 164 | 1964 |
| 2019 | 607 | 700 | 4 | 41 | 15 | 1367 |
| Spot Status Totals | 2186 | 2837 | 303 | 216 | 180 | 5722 |
| Year | Estimate | Difference from 2016 | Incident Rate Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 3.9912 | ---- | 1.0000 |
| 2017 | 4.4457 | 0.4545 | 1.5736 |
| 2018 | 6.0981 | 2.1069 | 8.2231 |
| 2019 | 4.6118 | 0.6206 | 1.8601 |
| Status | Estimate | Difference from ACTIVEINF | Incident Rate Ratio |
| ACTIVEINF | 6.5790 | ---- | 1.0000 |
| CUTLEAVE | 4.6211 | −1.9579 | 0.1412 |
| CUTREMOVE | 3.3095 | −3.2695 | 0.0380 |
| HAZARDMIT | 2.8080 | −3.771 | 0.0230 |
| STDEAD | 6.6159 | 0.0368 | 1.0375 |
| Year | Class/Treatment | # Events | Area (ha) | Total/Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Active Infestation | 607 | 337.10 | 547.37 |
| Standing Dead | 476 | 66.36 | ||
| Cut & Leave | 63 | 75.38 | ||
| Cut & Remove | 2 | 68.53 | ||
| 2017 | Active Infestation | 485 | 952.79 | 2921.86 |
| Standing Dead | 574 | 665.66 | ||
| Cut & Leave | 176 | 1149.26 | ||
| Cut & Remove | 7 | 149.27 | ||
| Hazard Tree Mitigation | 1 | 4.88 | ||
| 2018 | Active Infestation | 487 | 355.52 | 4422.47 |
| Standing Dead | 1087 | 1546.97 | ||
| Cut & Leave | 60 | 173.26 | ||
| Cut & Remove | 166 | 2027.96 | ||
| Hazard Tree Mitigation | 164 | 318.77 | ||
| 2019 | Active Infestation | 607 | 315.53 | 1063.67 |
| Standing Dead | 700 | 227.35 | ||
| Cut & Leave | 4 | 8.62 | ||
| Cut & Remove | 41 | 467.70 | ||
| Hazard Tree Mitigation | 15 | 44.48 | ||
| Total | 8955.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crosby, M.K.; McConnell, T.E.; Holderieath, J.J.; Meeker, J.R.; Steiner, C.A.; Strom, B.L.; Johnson, C. Tracking the Extent and Impacts of a Southern Pine Beetle (Dendroctonus frontalis) Outbreak in the Bienville National Forest. Forests 2023, 14, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14010022
Crosby MK, McConnell TE, Holderieath JJ, Meeker JR, Steiner CA, Strom BL, Johnson C. Tracking the Extent and Impacts of a Southern Pine Beetle (Dendroctonus frontalis) Outbreak in the Bienville National Forest. Forests. 2023; 14(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrosby, Michael K., T. Eric McConnell, Jason J. Holderieath, James R. Meeker, Chris A. Steiner, Brian L. Strom, and Crawford (Wood) Johnson. 2023. "Tracking the Extent and Impacts of a Southern Pine Beetle (Dendroctonus frontalis) Outbreak in the Bienville National Forest" Forests 14, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14010022
APA StyleCrosby, M. K., McConnell, T. E., Holderieath, J. J., Meeker, J. R., Steiner, C. A., Strom, B. L., & Johnson, C. (2023). Tracking the Extent and Impacts of a Southern Pine Beetle (Dendroctonus frontalis) Outbreak in the Bienville National Forest. Forests, 14(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14010022







