Abstract
The auto exhaust and dust derived from increased traffic volumes have led to an increasing level of atmospheric particulates in urban areas, which have become a primary pollutant of ambient air in urban zones. Roadside plants can effectively retain atmospheric particulates and clean the urban air via foliar capture of road dust. Five common roadside plants in Hangzhou were selected to evaluate their capacity for the retention of particulate matter (PM) and the accumulation of metals. The results showed that the PM retention capacity of the different plants varied greatly, as was the case with Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum Yieh, Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Loureiro, Pittosporum tobira (Thunb.) Ait, Photinia × fraseri Dress and Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl. In addition, the amounts of particles retained by the plants varied among seasons, with the highest retention in winter (12.19 g·m−2) and the lowest retention in spring (6.89 g·m−2). The solids on the leaf surface were mainly irregular particles, such as mineral fragments, soot aggregates, and fly ash particles. Meanwhile, these plant species can effectively accumulate heavy metals that attached to the particles. The leaves of the five tree species had the highest amounts of copper (Cu) and the lowest amounts of cadmium (Cd). Among species, L. chinense and P. tobira had the strongest comprehensive capacity to adsorb particulate matter and heavy metals. The results shed light on the rational selection of road plants, both as ornaments and to purify air via dust suppression in subtropical zones.
1. Introduction
Most urban areas in the world face severe air pollution problems because of rapid industrialization and urbanization [1]. As a primary air pollutant, particulate matter (PM) exceeds air quality standards in many cities worldwide, and the situation continues to deteriorate [2]. Atmospheric particulate matter not only deteriorates air quality but also threatens human health. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, atmospheric particulate matter was classified as a group 1 contaminant [3]. The surface of atmospheric particulate matter can adsorb or contain polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PHAs), heavy metals (HM), bacteria and viruses, and other harmful substances [4,5,6,7]. Human activities such as transportation and industry can release particulate matter containing heavy metals into the atmosphere [1,8]. Harmful heavy metals move and resuspend with particulate matter, deteriorating air quality, and entering the human respiratory system, endangering human health [9,10,11,12].
Transportation emissions are one of the most important sources of fine particle in cities [13]. In the EU countries, non-exhaust emissions of PM2.5 increased from 2.9% in 2000 to 5.2% in 2018, and PM10 increased from 4.0% to 6.7% [14]. Harrison et al. [15] found that non-exhaust emissions from vehicles were the largest contributor to particle mass in London. Particulate matter released from traffic emissions carries harmful heavy metals. Hjortenkrans et al. [16] found that cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu) and lead (Pb) emissions from automotive brake linings in Stockholm, Sweden, were 0.061 kg/year, 3800 kg/year, and 35 kg/year, respectively. Particulate matter and heavy metals emitted from road traffic in cities seriously threaten the inhabitants’ health condition. It has been suggested that the exacerbation of worsening respiratory symptoms, impaired lung function, and prevalence of blood pressure is correlated with long-term exposure to air pollution related with traffic [17,18,19,20].
Roadside plants can effectively reduce particulate matter from road traffic [21,22]. Plant leaves can act as natural filters by trapping and retaining the particulate matter from traffic emissions [13,23,24,25]. Zheng et al. [22] believed that dense vegetation could effectively block the penetration of road particulate matter, and the concentration of particulate matter increases significantly in the front part of the vegetation (0–5m). Maher et al. [26] found that particulate matter was reduced by 50% in those houses screened by roadside temporary tree lines. Plants can not only absorb fine particles but also uptake the inherent toxic metals in particles through their leaves [8,27]. Ozdemir et al. [13] also found that the roadside leaves can effectively remove heavy metals. The highest removal rate of nickel (Ni), Pb, Cu, and zinc (Zn) in road particulate matter by dense trees was 42.56%, 26.60%, 19.61%, and 19.12%, respectively.
Plant species can affect the adsorption capacity of leaves for particulate matter and toxic metals. Various factors, such as environment pollution level and leaf surface microstructure, can also influence plant’s capacity to retain particles and metals [8,28,29,30]. It is generally believed that the roughness of the leaf surface, the size of the stomata, the density of the fluff, and the secretions can affect the dust-retaining capacity of the plant [11,31,32]. Zheng et al. [11] found that the maximum particle retention was significantly positive correlated with the density of leaf epidermal hairs, indicating that the hairs of the leaves help to capture particulate matter. The plant leaves can uptake trace elements adhered to particulate matter through stomata [27,33]. Wind speed, temperature, humidity, and pollution conditions can also influence the deposition of airborne particles and the associated trace elements [31,34,35]. Roy et al. [25] found Ficus bengalensis was more capable of accumulating Cu and particulate matter in industrial than commercial zones. Many studies focus on the adsorption of heavy metals and particulate matter on leaves, but less attention has been paid to seasonal differences. To date, the relationship between heavy metal accumulation in plant leaves and particulate matter is unclear under seasonal change.
From 2013 to 2014, the exceeded pollutants in Hangzhou were mainly PM2.5 and PM10 [36]. The number of motor vehicles reached 2.44 million in 2017, and traffic emissions have become one of the most critical factors contributing to air pollution in Hangzhou. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the particulate matter emitted by traffic and reduce the health impact on residents. In addition, Hangzhou is famous for its beautiful scenery and landscape with plenty of greening, including roadside plants. The current study aims to: (1) analyze the variations of airborne particle and metals retained by the leaves of common roadside plants; and (2) reveal the relationship between the retention of foliar particles and the accumulation of metals by the common roadside plant. The results will provide some guidance for screening roadside species and improving the accuracy of the assessment on existing urban plant species in the ecosystem services.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Hangzhou city (119°25′–120°19.5′ E,29°44′–30°12′ N) is one of the most famous cities located in the Yangtze River Delta. The resident population of Hangzhou in 2020 was 11.936 million. The motor vehicles were beyond 690,263 in 2010, and traffic emissions have become one of the crucial factors contributing to air pollution in Hangzhou [37]. The area is characterized by a humid subtropical monsoon climate, with an average temperature of 16.0 °C, and an average rainfall of approximately 1613.9 mm annually [38].
2.2. Tested Plants
Five common roadside plants were screened according to our previous survey [39] and studies conducted by others [40]. These five roadside plants are Photinia × fraseri Dress, Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum Yieh, Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl, Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Loureiro and Pittosporum tobira (Thunb.) Ait. (Table S1).
2.3. Sampleanalysis
2.3.1. Leaf Sampling
Daqiao Road (119°57′56.264″ E, 30°3′39.347″ N), one of the main roads in southwest Hangzhou, was selected for sample collection. It is one of the main roads of urban traffic, with a large traffic volume. The road greening is in a common type, with one-board and two-belt. The green belt is mainly located on the sidewalk separation line on both sides of the road. The greening tree species are Cinnamomum camphora, Loropetalum chinense, Ilex cornuta, etc.
Plants of each species with similar age and average crown and that were well developed and healthy were selected for sampling. The leaf was sampled at day 7 after rain (rainfall exceeds 12.55 mm) in August and October 2020 and January and May 2021. The leaves about 1.5 m from the ground with no diseases and no damages were selected and sampled. All collections were repeated three times. For each species, about 30 leaves were selected and packaged separately in a clean ziplock bag. A total of 60 samples (four acquisitions × five samples × three replicates) were collected. The particle retention, particle morphology and elements content were determined. The detailed specific local meteorological parameters are provided in Table S2.
2.3.2. Particulate Matter Density in Leaf Surface
The particulate matter on the leaf surface was measured by the weight difference method [41]. The leaves were soaked in purified water for two hours, then washed clean. The cleaned leaves were put on clean paper towels to dry. The filter membranes were dried to constant weight at 60 °C (W1:10 μm filter membrane weight; W2:2.5 μm filter membrane weight; W3:0.2 μm filter membrane weight). Then, the dust-retaining liquid was filtered through the filter membranes with different pore sizes in turn. The particles were obtained with a particle size greater than 10 μm, between 2.5 and 10 μm, and between 0.2 and 2.5 μm by sequentially filtering with membranes of 10 μm, 2.5 μm, and 0.2 μm, respectively. After filtration, the filter pieces were dried in an oven at 65 °C to a constant weight and then weighed (W4: weight of 10 μm filter membrane after filtration; W5: weight of 2.5 μm filter membrane after filtration; W6: weight of 0.2 μm filter membrane after filtration). The weight of the particle was calculated according to the methods outlined by Dang et al. [39] and briefly described as in Equation (1).
After drying, the leaf was scanned by a scanner (Epson Perfection V700 Photo) and the leaf area was calculated by WinRHIZO Pro2005b (Regent Instruments) to (S).
The particulate matter density in the leaf surface was calculated by:
2.3.3. Particle Morphology and Element Analysis
The particles on the leaf surface were adhered to the conductive glue, and then were placed on the sample stage for gold spraying. Gold spraying can improve the conductivity and the imaging effect. Then the processed samples were placed on the scanning electron microscope (Feina/PHENOM Pro) to observe the morphology of the particles. At the same time, the elemental composition of the particles was analyzed by the energy spectrometer (Feina/PHENOM Pro).
2.3.4. Metal Accumulation of Blade and Foliar Particles
The metal contents (Cd, Ni, Pb and Cu) in the PMs and leaves were measured. The HNO3-HCl digestion method and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry were used for the determination (refer to Dang et al. [39] for specific methods).
2.3.5. Comprehensive Evaluation
To assess the pollution level caused by the metals in leaf particulate matter, the Geo-accumulation index (Igeo) of four metals (Cd, Ni, Pb and Cu) was calculated as Equation (2).
where Cn and Bn represent the metal concentration in particulate matter and soil background, respectively. The soil background value adopts the soil element background value of Zhejiang Province (Cd: 0.17, Ni: 23.93, Pb: 35.70, and Cu 22.63 mg·kg−1) [42]. Muller’s [43] method was used to classify metal contamination categories (Table S3).
The capacity for particulate matter retention and for metal accumulation of foliar particles was comprehensively evaluated by the membership function in fuzzy mathematics [44]. The basic calculation method was as follows:
where Xμ is the membership function of the measured value tolerance capacity, which is a value between 0 and 1. Xmax and Xmin are the maximum and minimum values of the measured value of the index, respectively.
2.3.6. Data Analysis
SPSS 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analyses. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a least significant difference (LSD) was applied to determine the statistical differences (α = 0.05 or 0.01). Figures were mainly drawn using Microsoft Excel 2019 (Microsoft Corp, Redmond, Washington, USA) and Adobe Photoshop CC2019 software (Adobe System Inc., San Jose, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Surface Morphology and Elements of Particle
Aerosol particulate matter mainly comes from natural and anthropogenic sources, such as soil and surface geological sediments, biological materials, and fossil fuel burning [45,46,47]. Particles from soil and surface sediments were irregular blocks with similar shapes, such as gravel pieces of nature [47]. Biological particles were pollen, spores, and plant fragments [48]. The particulate matter produced by fossil fuel burning was primarily spherical and circular [47,49].
The particles adsorbed by plant leaves were observed by a scanning electron microscope (Figure 1). The particles retained by leaves in this study mainly appeared as regular and irregular shapes. Irregular-shaped particles were mostly fluffy polymer, chain polymer, irregular block, and irregular flake. Regular-shaped particles were mostly spherical and cylindrical. An irregular flake, layered, and smooth surface particle can be seen in Figure 1A. The main element oxygen (O) was detected, followed by carbon (C), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), calcium (Ca), and other elements. Figure 1B represents an irregular block particle mainly containing O, C, and Si. Irregular-shaped particles (Figure 1A,B) were mainly formed from the mechanical abrasion of soil and surface geological deposits [49,50]. Figure 1C shows the particle with an oval shape, which was divided into biological particles with C, nitrogen (N) and O as the main elements. Figure 1D shows a long stripe of particulate matter originating from the earth and possibly transformed from secondary aerosol formation from atmospheric reactions [51]. Figure 1E shows a fluffy polymer belonging to soot aggregates. Figure 1F represents spherical particles with a smooth surface, which were fly ash particles. The soot aggregates and spherical particles in the urban atmosphere were primarily from fossil fuel burning (industrial or automotive) and automobile exhaust [52,53,54]. In summary, the particles retained by plants were mainly biological, mineral, fly ash particles, and soot aggregates. The significant sources of road particulate matter were soil and surface sediments, fuel combustion, vehicle exhaust emissions, and biological debris. This was consistent with the findings of other scientists on the composition of leaf dust particles [48].
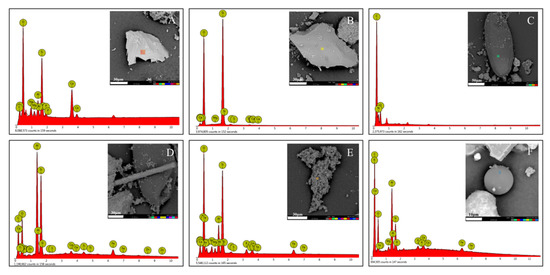
Figure 1.
Morphology and energy spectrum of single particle retained by leaf.
3.2. Characteristics of Metals in Particle
The metal contents in the particles retained by plant leaves were different (Table 1). The content of Cu (262.60 to 2825.00 mg·kg−1) in the particles was the highest, followed by Pb (52.78 to 601.67 mg·kg−1) and Ni (37.35 to 227.26 mg·kg−1), whereas Cd (1.68 to 23.44 mg·kg−1) was the lowest level. The heavy metal contents in the different leaf particles varied greatly among seasons. Ni and Cd were at the highest level in summer and lowest in spring. By contrast, the contents of Cu and Pb were highest in winter and lowest in spring. Zhu et al. [55] observed that the enrichment factor (EF) at moderate pollution levels in winter was higher than in other seasons, especially for Cu and Pb, which was similar to our findings. The Geo-accumulation index suggested that the pollution level in leaf particulate matter was caused by heavy metals (Table S5). Cadmium and Cu had higher contamination levels, and Ni had lower contamination levels. Traffic sources can emit large amounts of heavy metals [13,55], and tire wear has been suggested to be a significant source of Cd [56]. Copper was a tracer for vehicle fuel burn and brake wear [56,57,58].

Table 1.
Metal content in leaf particulate matter (mg·kg-1).
3.3. The Particle Retained by Plant Leaf
The retention capacity for different particle sizes varied among all species of plants (Figure 2). The L. chinense plants consistently retained the most total suspended particles (TSP) (2.25–4.66 g·m−2), PM10 (1.27–1.39 g·m−2), and PM2.5 (0.18–0.74 g·m−2) in comparison to the other four plants (p < 0.05). The lowest retentions of PM10 and PM2.5 were detected in Photinia × fraseri and C. camphora plants. Liu et al. [59] also noted that the L. chinense plants showed the largest amount of particulate matter retention, which was obviously higher than those of Photinia × fraseri and C. camphor plants. These differences in leaf particulate matter retention among species can be ascribed to leaf morphologic structure and leaf area [24,60,61,62]. A rough surface, a high stomatal density, and dense surface villi are factors that may contribute to the higher particulate matter retention capacity in L. chinense plants [63,64]. On the other hand, the smooth leaf surface of C. camphora plants might not be facilitated to absorb particulate matter [65].

Figure 2.
Foliar particulate matter retention of different plants. Note: (A) TSP, (B) PM10, (C) PM2.5, CC: Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl; LC: Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum Yieh; OF: Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Loureiro; PF: Photinia × fraseri Dress; PT: Pittosporum tobira (Thunb.) Ait. Different lowercase letters in the figure indicate significant differences among different tree species in the same season (p < 0.05).
The particulate matter retained on the leaf surface was classified by size as fine particles (d ≤ 2.5 μm), coarse particles (2.5 μm < d ≤ 10 μm), and large particles (d > 10 μm). Particles captured by plant leaves were predominantly large, accounting for 43.70%–90.78% of TSP, followed by coarse particles (7.60%–36.04% of TSP) and fine particles (16.2%–22.73% of TSP) (Figure 3). Kończak et al. [48] reported that large particles accounted for the greatest proportion of particulate matter retained by roadside plants. O. fragrans plants accumulated 80.02% to 90.78% of the large particles.

Figure 3.
Size distribution of particulate matter deposition on the leaf of five plants. Note: (A) spring, (B) summer, (C) autumn, (D) winter; CC: Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl; LC: Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum Yieh; OF: Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Loureiro; PF: Photinia × fraseri Dress; PT: Pittosporum tobira (Thunb.) Ait.
Climate, weather, and pollution all affect plant retention of particulates in different seasons [35]. The seasonal variation of TSP retention by different plants was in descending order of winter (12.19 g·m−2) > summer (10.42 g·m−2) > autumn (7.86 g·m−2) > spring (6.89 g·m−2). According to the local “Zhejiang Water Resources Bulletin,” air pollution was most severe in winter. When air pollution is severe, plants tend to retain more particulate matter [66]. Prajapati et al. [67] reported that particulate matter retention was highest in winter. Particulate matter accumulation in winter is attributed to wet leaves, as well as foggy conditions that prevent particulate matter from dispersing. This led to plants retaining more particulate matter during winter.
3.4. The Metal Accumulation in Leaf
The sampled roadside plants showed significant heavy metal accumulation variations (Figure 4). Copper content was the highest in the plant leaves, whereas Cd and Pb contents were the lowest. The higher Cu content in the leaves may be due to the role of essential metals as micronutrients in plant biosynthesis of enzymes, auxins, and proteins [68]. The L. chinense plants had an outstanding performance absorbing Ni and Pb because plants accumulated the most significant amount of these two heavy metals in autumn and summer. The greatest Cd content was more evident in the P. tobira plants than in other plants. The Cu contents in the leaves of five plant species were similar, and no significant differences were observed (p > 0.05). The level of heavy metals in the leaves was affected by the growth status of the plant itself, the level of metals in particulate matter, and the leaf structural characteristics [1,21,69]. According to Lorenzini et al. [70] and Cao et al. [63], L. chinense and P. tobira plants had a more vital capacity for accumulating heavy metals, which may have been attributed to their particulate matter retention capacity and physiological growth behaviors.

Figure 4.
Metal content in leaves of different plants. Note: (A) spring, (B) summer, (C) autumn, (D) winter; CC: Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl; LC: Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum Yieh; OF: Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Loureiro; PF: Photinia × fraseri Dress; PT: Pittosporum tobira (Thunb.) Ait. Different lowercase letters indicate the significant differences among different plant species in the same season (p < 0.05).
Plant leaves accumulate heavy metals differently according to the season. A leaf can uptake more heavy metals in spring and winter, with slight differences among species (Figure 4). C. camphora, L. chinense, and O. fragrans accumulated more Cd in summer and autumn and less in spring and winter. The O. fragrans and Photinia × fraseri plants showed the highest foliar Cu uptake in summer, and other plants had the highest Cu uptake in autumn. Seasonal differences in the leaf metals were affected by plant physiological activity and pollution level of metals in the atmosphere [8,71]. It has been demonstrated that plants in spring have stronger physiological activity and a larger stomatal opening, and therefore have a stronger capacity for capturing heavy metals in spring [72]. In general, the higher the concentration of metals in air particulates, the higher accumulation of metals in plant leaves [73]. Heavy metal contents were higher in the sampled particulates collected during winter (Table 1). Therefore, plant leaves were able to accumulate more heavy metals in winter. These results are in line in the findings of Liu et al. [74], who found that the higher level of metals in the leaf particles correlated with the higher capacity of plants to absorb metals in winter.
3.5. Relationship between Leaf Metals and Particulate Matter Retention
In the event that the particulate matter carrying heavy metals was deposited on the leaf surface, the metals could then transfer to the leaf [27,75]. The level of the leaf metals positively correlated with the leaf particulate matter (Table 2). For example, in L. chinense and Photinia × fraseri plants, foliar Cu and Pb uptake were mainly correlated with PM2.5 amounts. In P. tobira plants, Cd accumulation was positively correlated with PM>10 retentions in the leaves. A positive correlation between leaf heavy metal concentration and particulate matter heavy metal concentration was also found in some cases (Table 2). For L. chinense, Cu in leaves and particulate matter was significantly positively correlated. There was a significant positive correlation between Cd in leaves and particulate matter, such as P. tobira. The results showed that sampled roadside plants could absorb Cd, Cu, and Pb in atmospheric particulates through stomata, cuticle cracks, and lenticels, which was supported by Gajbhiye et al. [76] and Sharma et al. [27].

Table 2.
Correlations of metal content in leaves and leaf particulate matter.
3.6. Comprehensive Evaluation of Tested Plants
The comprehensive evaluation of tested plants in particulate matter retention and metal accumulation using the membership function method is provided in Table 3. The L. chinense plants were superior in terms of particulate matter retention. In contrast, C. camphora plants were inferior in retaining particles than other plants. Cadmium and Cu were the most polluted by road particulate matter (Table S5). The P. tobira plants had the greatest accumulation capacity for Cd and Cu, whereas Photinia × fraseri plants had the lowest accumulation capacity of heavy metals. The comprehensive evaluation results suggest that, in regard to the retention of particulate matter and the accumulation of metals, the plants had the descending order of L. chinense > P. tobira > O. fragrans > Photinia × fraseri > C. camphora.

Table 3.
A comprehensive evaluation of the capacity of plant leaves to retain particulate matter and accumulate heavy metals.
4. Conclusions
The capacity for particulate matter retention and metal accumulation by the leaves of five road plant species were comprehensively evaluated in this study. The particulate matter retained by plants were mainly soot aggregates, fly ash particles, mineral particles, and biological particles. Cadmium and Cu in the particulate matter had the highest contamination levels. L. chinense and O. fragrans displayed great potential to retain particulate matter, followed by P. tobira, Photinia × fraseri, and C. camphora. Among species, L. chinense showed a higher foliar Cd and Ni uptake, and P. tobira absorbed the highest Pb in the leaf. The results revealed that these road plant species could effectively capture particulate matter and heavy metals. Taken together, L. chinense and P. tobira showed a high capacity for the retention particulate matter, which is why they should be a recommended roadside greening species in urban zones in east China for improving air quality.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/f13081290/s1, Table S1: Biological characteristics of tree species used in the experiment; Table S2: Meteorological parameters of the sampling point; Table S3: The grades of geo-accumulation indexes; Table S4: Morphological characteristics and chemical composition of residual single particles in blades; Table S5: Geo-accumulation index and pollution type of different heavy metals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.C.; Data curation, N.D. and H.Z.; formal analysis, N.D. and H.Z.; funding acquisition, G.C.; investigation, Ning Dang; methodology, N.D. and G.C.; resources, H.L.; supervision, G.C.; visualization, N.D., H.Z. and H.L.; writing—original draft, N.D. and H.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.M.A.S. and G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Special Fund for Cooperation of Zhejiang Province and the Chinese Academy of Forestry (2021SY12), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41807151&31971718).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alahabadi, A.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Miri, M.; Aval, H.E.; Yousefzadeh, S.; Ghaffari, H.R.; Ahmadi, E.; Talebi, P.; Fahabadi, Z.A.; Babai, F.; et al. A comparative study on capability of different tree species in accumulating heavy metals from soil and ambient air. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Air Pollution Levels Rising in Many of the World’s Poorest Cities. 2016, WHO News Release. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2016/air-pollution-rising/en/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Sun, Y.; Xin, H.; Wu, J.; Lian, H.; Chen, Y. Fractionation and health risks of atmospheric particle-bound as and heavy metals in summer and winter. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donham, K.J.; Popendorf, W.; Palmgren, U.; Larsson, L. Characterization of dusts collected from swine confinement buildings. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1986, 10, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.L.; Bi, X.H.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Yao, L.; Jiao, L.; Feng, Y.C. Characterization and source identification of heavy metals in ambient PM10 and PM2.5 in an integrated iron and steel industry zone compared with a background site. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, L.; Lou, S.; Ma, Y.; Yan, N. Investigation of fungal spore characteristics in PM2.5 through organic tracers in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, M.; Gu, L.; Wu, M.; Xua, D.; Xu, G.; Ma, L. Seasonal variation, sources and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in different particle fractions of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.Y.; Zhou, D.Q.; Lu, S.P.; Yu, J.P. Assessment of foliar dust particle retention and toxic metal accumulation ability of fifteen roadside tree species: Relationship and mechanism. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, C.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Role of particle size and composition in metal adsorption by solids deposited on urban road surfaces. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Keshavarzik, B.; Moore, F.; Tavakol, T.; Lahijanzadeh, A.R.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Kermani, M. Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis. Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.L.; Li, P. Resuspension of settled atmospheric particulate matter on plant leaves determined by wind and leaf surface characteristics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19606–19614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopke, P.K.; Hill, E.L. Health and charge benefits from decreasing PM2.5 concentrations in New York State: Effects of changing compositions. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, H. Mitigation impact of roadside trees on fine particle pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.M.; Allan, J.; Carruthers, D.; Heal, M.R.; Lewis, A.C.; Marner, B.; Murrells, T.; Williams, A. Non-exhaust vehicle emissions of particulate matter and voc from road traffic: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Jones, A.M.; Gietl, J.; Yin, J.; Green, D.C. Estimation of the Contributions of Brake Dust, Tire Wear, and Resuspension to Nonexhaust Traffic Particles Derived from Atmospheric Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6523–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjortenkrans, D.S.T.; Bergbäck, B.G.; Häggerud, A.V. Metal Emissions from Brake Linings and Tires: Case Studies of Stockholm, Sweden 1995/1998 and 2005. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierse, N.; Rushton, L.; Harris, R.S.; Kuehni, C.E.; Silverman, M.; Grigg, J. Locally generated particulate pollution and respiratory symptoms in young children. Thorax 2006, 61, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenlund, M.; Forastiere, F.; Porta, D.; De Sario, M.; Badaloni, C.; Perucci, C.A. Traffic-related air pollution in relation to respiratory symptoms, allergic sensitisation and lung function in schoolchildren. Thorax 2009, 64, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Effects Institute (HEI). Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure and Health Effects; Panel on the Health Effects of Traffic-Related Air Pollution; Special Report 17; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fuks, K.B.; Weinmayr, G.; Foraster, M.; Dratva, J.; Hampel, R.; Houthuijs, D.; Oftedal, B.; Oudin, A.; Panasevich, S.; Penell, J.; et al. Arterial blood pressure and long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution: An analysis in the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Singh, H.; Kumar, N. Adaptation and mitigation potential of roadside trees with bio-extraction of heavy metals under vehicular emissions and their impact on physiological traits during seasonal regimes—Sciencedirect. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 58, 126900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.B.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Z.R. Impacts of vegetation on particle concentrations in roadside environments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæbø, A.; Popek, R.; Nawrot, B.; Hanslin, H.M.; Gawronska, H.; Gawronski, S.W. Plant species differences in particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukowski, A.; Popek, R.; Karolewski, P. Particulate matter on foliage of Betula pendula, Quercus robur, and Tilia cordata: Deposition and ecophysiology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10296–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Kumari, M. Air pollution tolerance, metal accumulation and dust capturing capacity of common tropical trees in commercial and industrial sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Davison, B.; Karloukovski, V.; Clarke, R. Impact of roadside tree lines on indoor concentrations of traffic-derived particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13737–13744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Yadav, P.; Ghosh, C.; Singh, B. Heavy metal capture from the suspended particulate matter by morus alba and evidence of foliar uptake and translocation of pm associated zinc using radiotracer (65Zn). Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.N.; Zhang, G.; An, H.L.; Yin, W.L.; Xia, X.L. Quantifying the particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces of urban plants in Beijing, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meravi, N.; Singh, P.K.; Prajapati, S.K. Seasonal variation of dust deposition on plant leaves and its impact on various photochemical yields of plants. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.C.; Jo, Y.G.; Son, J.A.; Kim, I.; Yook, S.J. Deposition characteristics of soot and tire-wear particles on urban tree leaves. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 155, 105768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.W.; Yang, X.B.; Li, S.N.; Chen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, L. Effects of plant leaf surface and different pollution levels on PM2.5 adsorption capacity. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 34, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, W.J. Response of the particulate matter capture ability to leaf age and pollution intensity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34258–34269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.P.; Xue, P.Y.; Dong, J.W.; Zhang, X.M.; Sun, H.X.; Geng, L.P.; Luo, S.X.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, W.J. Contribution of PM2.5-Pb in atmospheric fallout to Pb accumulation in Chinese cabbage leaves via stomata. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, X.; Qian, H. Comparison of particle concentration vertical profiles between downtown and urban forest park in Nanjing (China). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Cong, L.; Yan, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Z. Dry deposition of particulate matter and ions in forest at different heights. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Luo, H.J.; Feng, X.; Gu, L.N.Z.; Jia, L.; Huang, W.; Wan, L.D. Analysis on characteristics of aerosol air pollutant levels in Beijing and Hangzhou. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 41, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.X.; Sun, G.J.; Wang, X.W.; Tian, W.L.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Jiao, L. Vehicle exhausts emission characteristics and contributions in Hangzhou district. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Lin, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, D.; Li, M. Atmospheric particle retention capacity and photosynthetic responses of three common greening plant species under different pollution levels in Hangzhou. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 20, e00783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.; Zhang, H.D.; Mir Md Abdus Salam, M.M.A.; Li, H.M.; Chen, G.C. Foliar dust particle retention and metal accumulation of five garden tree species in Hangzhou: Seasonal changes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Lv, C.; Wei, W.; Feng, R.; Luo, K.; Wu, X.H.; Shen, Y.M.; Yan, S.J. Investigation and diversity analysis of road greening tree species in major urban areas of Hangzhou city. For. Resour. Manag. 2019, 3, 74–79+93. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.D.; Li, H.M.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.K.; Li, S.M. Capacity of six shrub species to retain atmospheric particulates with different diameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Q. Background characteristics of soil elements in four plains of Zhejiang Province. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 33, 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, G. Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veran-derungen seitt 1971. Umschan 1979, 79, 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.X.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, J.F.; Chen, G.C. Growth, physiological responses, and copper accumulation in seven willow species exposed to cu—A hydroponic experiment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19875–19886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric aerosols: Composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, K.A.; Prather, K.A. Mass spectrometry of atmospheric aerosols—Recent developments and applications. Part II: On-Line mass spectrometry techniques. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2011, 31, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.Q.; Chen, W.; Dai, Q.W.; Deng, Y.Q.; He, P.; He, X.C.; Tang, J.; Liu, L.Z.; He, H. Characterization of mineralogy and surface zeta potential of atmospheric dust fall in northwest China. Miner. Petrol. 2015, 109, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kończak, B.; Cempa, M.; Pierzchała, Ł.; Deska, M. Assessment of the ability of roadside vegetation to remove particulate matter from the urban air. Environ. Poll. 2021, 268, 115465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.K.; Seip, H.M.; Leinum, J.R.; Winje, T.; Xiao, J.S. Chemical characterizations of individual particles (PM10) form ambient air in Guiyang City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 343, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaegi, R. Chemical and morphological analysis of airborne particles at a tunnel construction site. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Shao, L.; Jones, T.P.; Whittaker, A.G.; Lu, S.; Bérubé, K.A.; He, T.; Richardsc, R.J. Characterization of airborne individual particles collected in an urban area, a satellite city and a clean air area in Beijing, 2001. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4097–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, T.L.; Norris, G.A.; Landis, M.S.; Williams, R.W. Individual particle analysis of indoor, outdoor, and community samples from the 1998 Baltimore particulate matter study. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3935–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Shao, L.; Wang, Z.; Tang, U.; Shen, R.; Li, W. Investigations of microscopic morphology of individual inhalable particulates in Macao in summer. Environ. Sci. 2009, 30, 1514–1519. [Google Scholar]
- González, L.T.; Longoria-Rodríguez, F.E.; Sánchez-Domínguez, M.; LeyvaPorras, C.; Acuña-Askar, K.; Kharissov, B.I.; Arizpe-Zapata, A.; AlfaroBarbosa, J.M. Seasonal variation and chemical composition of particulate matter: A study by XPS, ICP-AES and sequential microanalysis using Raman with SEM/EDS. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 74, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, W.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, R. Spatio-temporal distribution and source identification of heavy metals in particle size fractions of road dust from a typical industrial district. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miri, M.; Allahabadi, A.; Ghaffari, H.R.; Fathabadi, Z.A.; Raisi, Z.; Rezai, M.; Rezai, M.; Aval, M.Y. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal (hm) pollution in the ambient air using a new bio-indicator. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 14210–14220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, C.; Norman, M.; Burman, L. Road traffic emission factors for heavy metals. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4681–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Harrison, R.M. Estimation of the contribution of road traffic emissions to particulate matter concentrations from field measurements: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Hou, Y.J.; Shu, D.Y.; Yang, B.; Cui, Y.C.; Ding, F.J. Properties and spatio-temporal variation of leaf retained particulate matters of the main tree species planted in Guiyang city. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2020, 56, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Guan, D.; Peart, M. The morphological structure of leaves and the dust-retaining capability of afforested plants in urban Guangzhou, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3440–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Zhang, T.R.; Song, X.M.; Zhang, Y.K.; Huang, F.; Yu, H.; Zhang, G.H.; Qi, F.; Shao, F. The relationship between particulate matter retention capacity and leaf surface micromorphology of ten tree species in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgrigna, G.; Baldacchini, C.; Dreveck, S.; Cheng, Z.; Calfapietra, C. Relationships between air particulate matter capture efficiency and leaf traits in twelve tree species from an Italian urban-industrial environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.N.; Wu, H.; Shen, L.M.; Chen, G.C.; Zhang, J.F. Analysis on the Dust Retention and Heavy Metal Absorption Ability of Leaves: A Case Study in Yuyao, Zhejiang Province. For. Res. 2016, 29, 662–669. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.M.; Shi, F.Q.; Li, M.; Zhu, Y.L. Study on dust retention rank and pattern recognition of typical garden plant leaves in Changsha. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, F.; Wang, L.H.; Sun, F.B.; Li, G.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zeng, X.R.; Yan, H.; Dong, L.; Bao, Z.Y. Study on different particulate matter retention capacities of the leaf surfaces of eight common garden plants in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybysz, A.; Sæbø, A.; Hanslin, H.M.; Gawroński, S.W. Accumulation of particulate matter and trace elements on vegetation as affected by pollution level, rainfall and the passage of time. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Tripathi, B.D. Seasonal variation of leaf dust accumulation and pigment content in plant species exposed to urban particulates pollution. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, Y.; Mokhtari, M.; Faraji, M.; Abdolahnejad, A.; Mohammadi, A. Biomonitoring of airborne metals using tree leaves: Protocol for biomonitor selection and spatial trend. MethodsX 2019, 6, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, L.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, F.; Lun, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, X. Assessing the capacity of plant species to accumulate particulate matter in Beijing, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzini, G.; Grassi, C.; Nali, C.; Petiti, A.; Loppi, S.; Tognotti, L. Leaves of pittosporum tobira as indicators of airborne trace element and PM10 distribution in central Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4025–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wang, C. Research status and prospects on functions of urban forests in regulating the air particulate matter. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.N.; Kong, L.W.; Lu, S.W.; Chen, B.; Gao, C.; Shi, Y. Beijing Common Green Tree Leaves’ Accumulation Capacity for Heavy Metals. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Fang, H.L.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, Y.D. Heavy metal in leaves of twelve plant species from seven different areas in Shanghai, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 27, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Q.; Chen, Q.B.; Deng, Z.H.; Yang, H.Z. Enrichment of atmospheric heavy metals by urban forest. Environ. Chem. 2017, 36, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Heavy metals and metalloids: Sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, T.; Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.H.; Szulejko, J.E.; Prasad, S. Airborne foliar transfer of PM bound heavy metals in Cassia siamea: A less common route of heavy metal accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
