Pathogenicity of Three Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Isolates in Pinus koraiensis (Siebold & Zucc.) Seedlings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nematodes
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Reproductive Ability of B. xylophilus
2.4. Pathogenicity Test
2.5. Migration of B. xylophilus in Inoculated Trees
2.6. Internal Symptom Observations in Inoculated Trees
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Reproductive Ability of B. xylophilus
3.2. Disease Development in P. koraiensis Seedlings
3.3. Distribution of B. xylophilus in Inoculated Trees
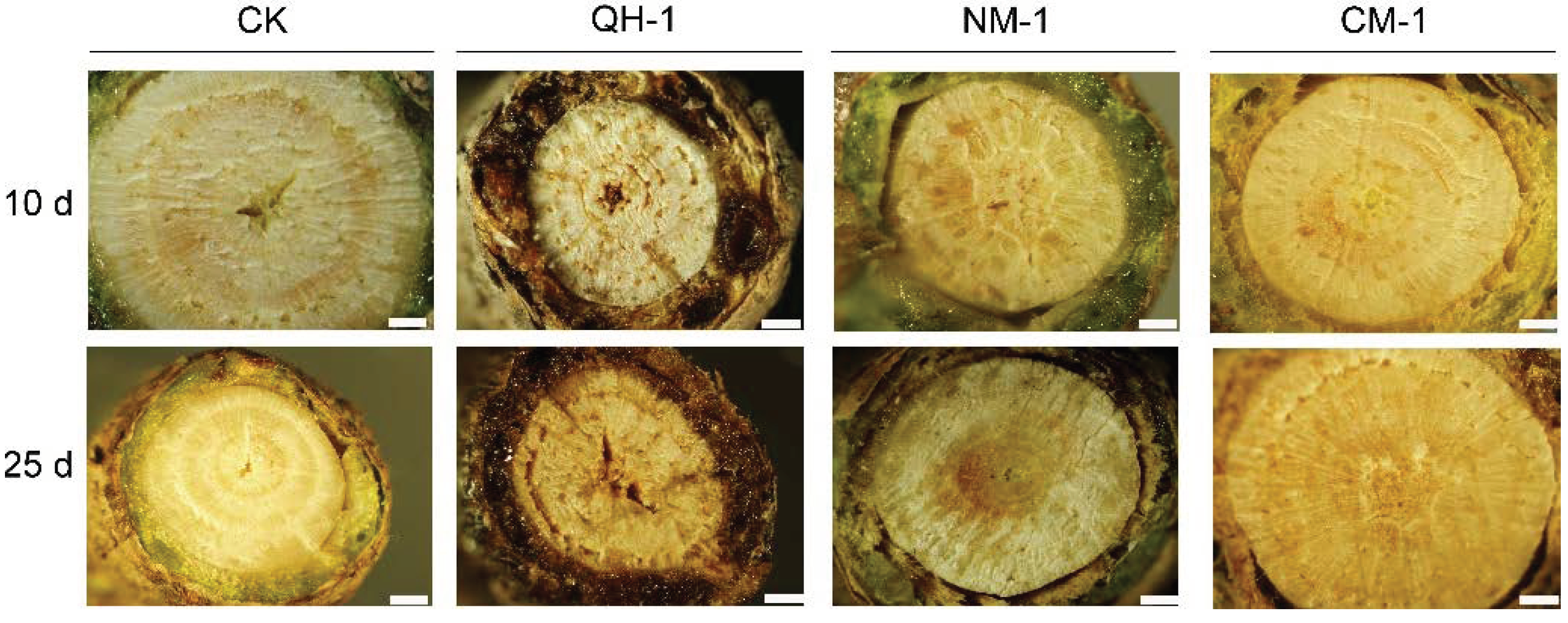
3.4. Internal Symptom Observations in Inoculated Trees
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mota, M.M.; Kazuyoshi, F.; Paulo, V. Pine wilt disease and the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. In Integrated Management of Fruit Crops Nematodes; Mota, M.M., Futai, K., Vieira, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 253–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.G.; Futai, K. Pine Wilt Disease; Sutherland, J.R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Q. Distribution of the pinewood nematode in China and susceptibility of some Chinese and exotic pines to the nematode. Can. J. For. Res. 1989, 19, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, M.M.; Braasch, H.; Bravo, M.A.; Penas, A.C.; Burgermeister, W.; Metge, K.; Sousa, E. First report of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Portugal and in Europe. Nematology 1999, 1, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiya, Y. Pathology of the pine wilt disease caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1983, 21, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamiya, Y. History of pine wilt disease in Japan. J. Nematol. 1988, 20, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, C.; Espada, M.; Vieira, P.; Mota, M.M. Pine wilt disease: A threat to European forestry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiya, Y.; Enda, N. Transmission of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) by Monochamus alternatus (coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Nematologica 1972, 18, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Lin, M.; Qian, R. A study on morphological diagnosis and pathogenicity of the pine wood nematode. J. Nanjing. Agricultural. Univ. 1986, 2, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Chen, F.; Luo, Y.Q.; Xie, B.Y. First isolation of pine wood nematode from Pinus tabuliformis forests in China. For. Pathol. 2013, 43, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.M.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, P.Y. Symptoms of pine wilt disease in Pinus kesiya var. langbianensis caused by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. For. Pest Dis. 2007, 26, 17–18+34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Yan, J.; Fang, G. Economic loss of pine wood nematode disease in mainland China from 1998 to 2017. Forests 2020, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Analysis on the trend of invasion and expansion of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. For. Pest Dis. 2018, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.; Farjon, A. “Pinus Koraiensis”. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2013, e.T42373A2975987. Available online: http://10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42373A2975987.en (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Wolff, R.L.; Bayard, C.C. Fatty acid composition of some pine seed oils. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.K. Pinus koraiensis. In Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 9, pp. 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Meng, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Isolation and identification of pine wood nematode in Pinus koraiensis in Fengcheng. Liaoning Province. For. Pest Dis. 2019, 38, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Sheng, R. The first record of Monochamus saltuarius (coleoptera; cerambycidae) as vector of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and its new potential hosts in china. Insects 2020, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiba, M.; Ishihara, M.; Sahashi, N.; Ohira, M.; Toda, T. Virulence of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus isolated from naturally infested pine forests to five resistant families of Pinus thunbergii. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kondo, E.; Foudin, A.; Linit, M.; Smith, M.; Bolla, R.; Winter, R.; Dropkin, V. Pine Wilt Disease–Nematological, Entomological and Biochemical Investigations; University of Missouri Columbia Agricultural Experiment Station SR 282; University of Missouri Columbia Agricultural: Columbia, Missouri, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bedker, P.; Wingfield, M.; Blanchette, R. Pathogenicity of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus on three species of pine. Can. J. For. Res. 1987, 17, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Hogetsu, T.; Fukuda, K. Cortical responses in Japanese black pine to attack by the pine wood nematode. Can. J. Bot. 1993, 71, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Yamada, T.; Ito, S. Bursaphelenchus xylophilus induced pine wilt: Factors associated with resistance. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 1991, 121, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Suzuki, K. Early symptom development and histological changes associated with migration of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in seedling tissues of Pinus thunbergii. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eo, J.; Takemoto, S.; Otobe, K. Is there a relationship between the intrinsic rate of propagation and in-vitro migration and virulence of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 130, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daub, M. Investigations on Pathogenicity, Invasion Biology and Population Dynamics of the Pine Wood Nematode Bursaphelenchus Xylophilus (Steiner und Buhrer 1934) Nickle 1970 in European Conifers. Bachelor’s Thesis, Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, Braunschweig, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, K. Inhibiting factors of symptom development in several Japanese red pine (Pinus densiflora) families selected as resistant to pine wilt. J. For. Res. 2004, 9, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, C.S.; Ikuyo, Y.; Shinya, R.; Mota, M.M.; Hasegawa, K. Catalases induction in high virulence pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus under hydrogen peroxide-induced stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hooper, D.J. Extraction of Nematodes from Plant Material. In Laboratory Methods for Work with Plant and Soil Nematodes; Southey, J.F., Ed.; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1986; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Amaresan, N.; Sankaranarayanan, A. Extraction of Nematodes from Plant Materials. In Plant-Microbe Interactions Eds.; Springer Protocols Handbooks: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, S.K. Distribution of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in naturally infected Pinus densiflora and P. koraiensis and migration of B. xylophilus in artificially inoculated P. densiflora seedlings. Res. Plant Dis. 2012, 18, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mamiya, Y.; Shoji, T. Pathogenicity of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, to Japanese larch, Larix kaempferi, seedlings. J. Nematol. 2009, 41, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Kanzaki, N.; Tanaka, R.; Sahashi, N. Mortality of shaded pine trees inoculated with virulent and less-virulent isolates of pine wood nematodes. Environ. Entomol. 2012, 41, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menéndez-Gutiérrez, M.; Villar, L.; Díaz, R. Virulence of seven pathogenic Bursaphelenchus xylophilus isolates in Pinus pinaster and Pinus radiata seedlings and its relation with multiplication. For. Pathol. 2021, 51, e12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, T.; Kikuchi, T. Estimation of virulence of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) based on its reproductive ability. Nematology 2007, 9, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, E. Relationship between the anatomical characteristics of cortical resin canals and migration of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in stem cuttings of Pinus thunbergii seedlings. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 2006, 88, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oku, H.; Shiraishi, T.; Chikamatsu, K. Active defense as a mechanism of resistance in pine against pine wilt disease. Jpn. J. Phytopathol. 1989, 55, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Chung, Y.J.; Shin, S.C. First report of pine wilt disease on Pinus koraiensis in Korea. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, K.S.; Lee, D.H.; Koo, B.Y.; Yeo, K.J. Inoculation of seven pine species or hybrid seedlings with Korean isolates of pinewood nematode under greenhouse conditions. Ann. For. Sci. 2008, 65, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
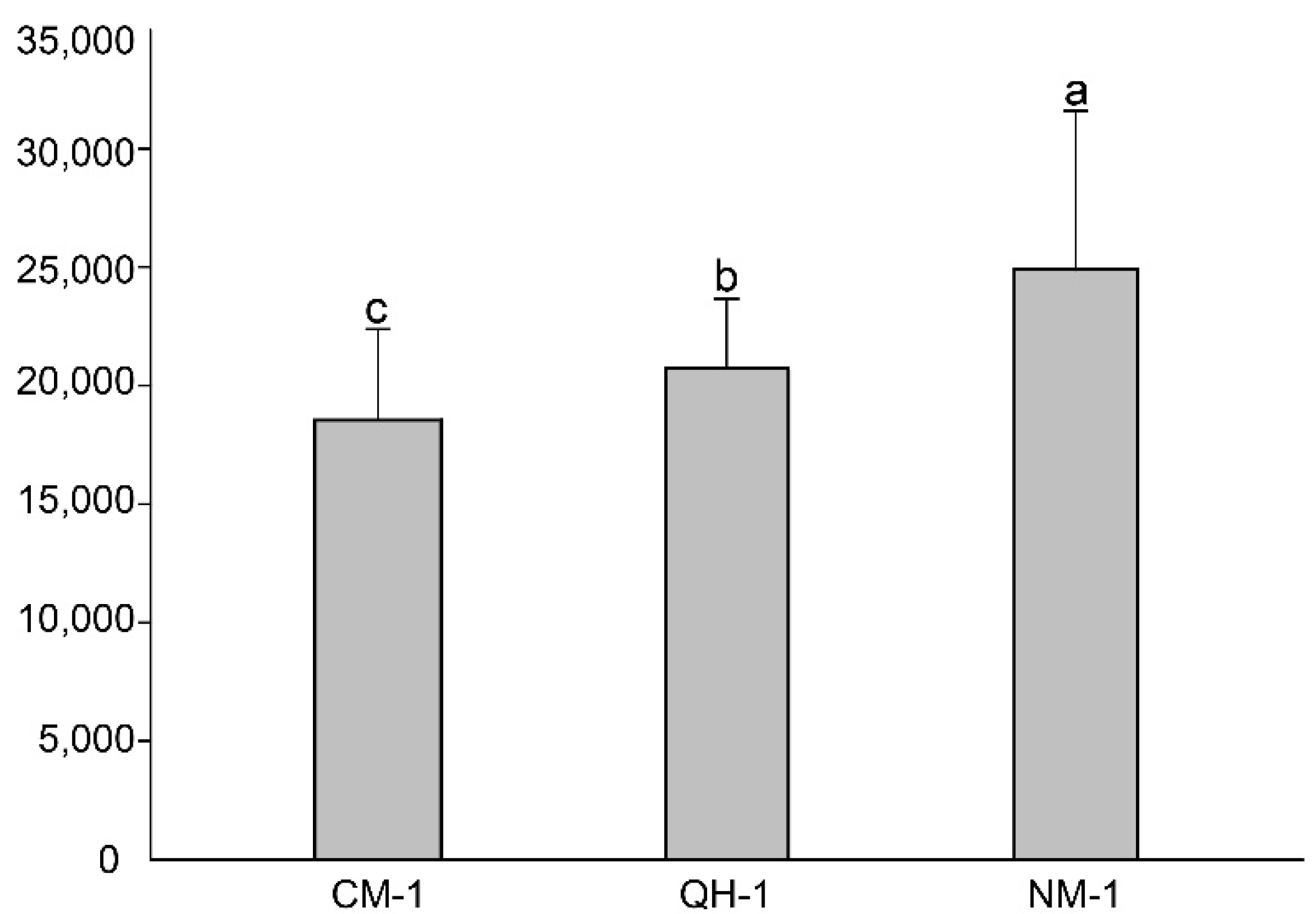
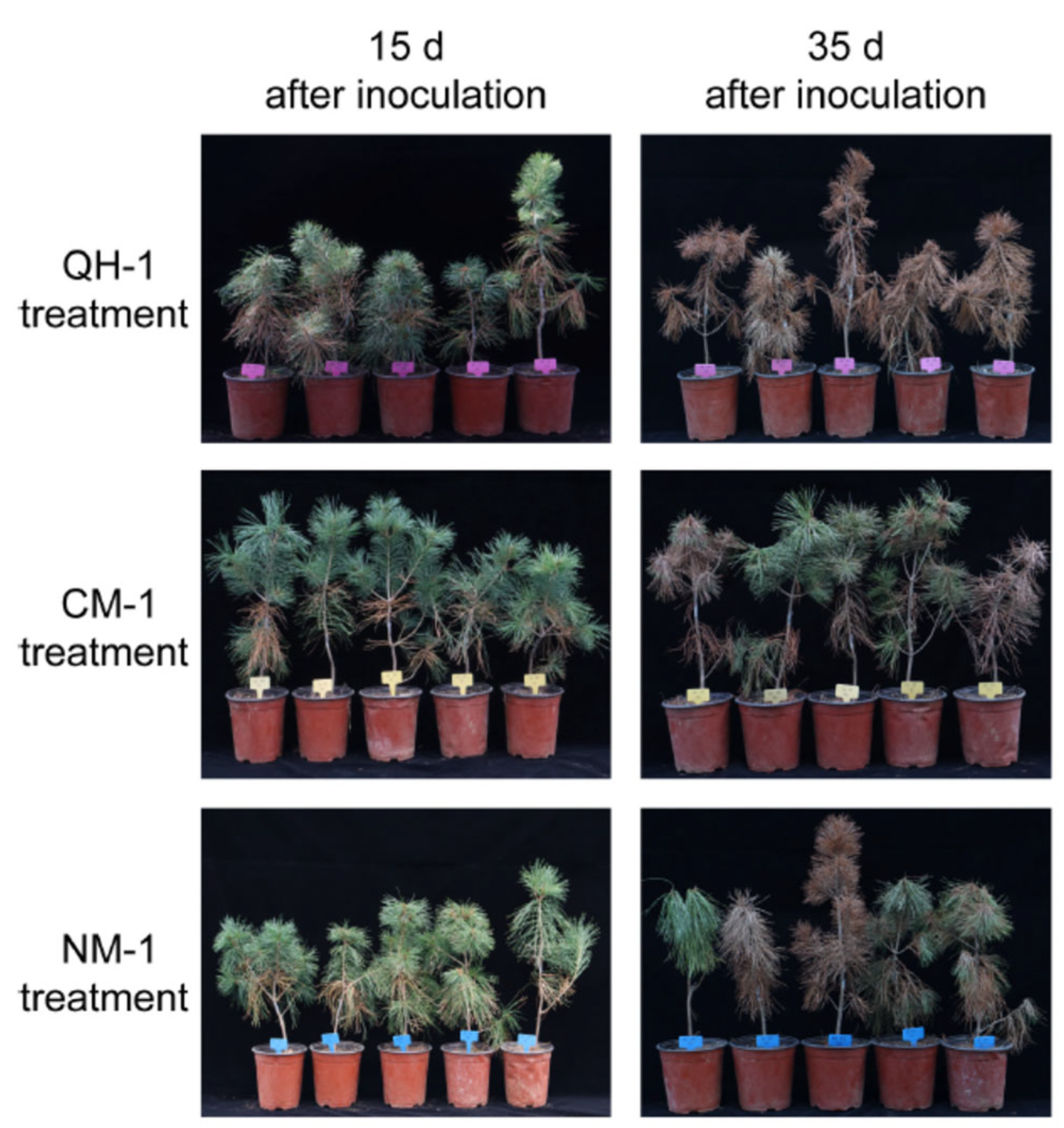
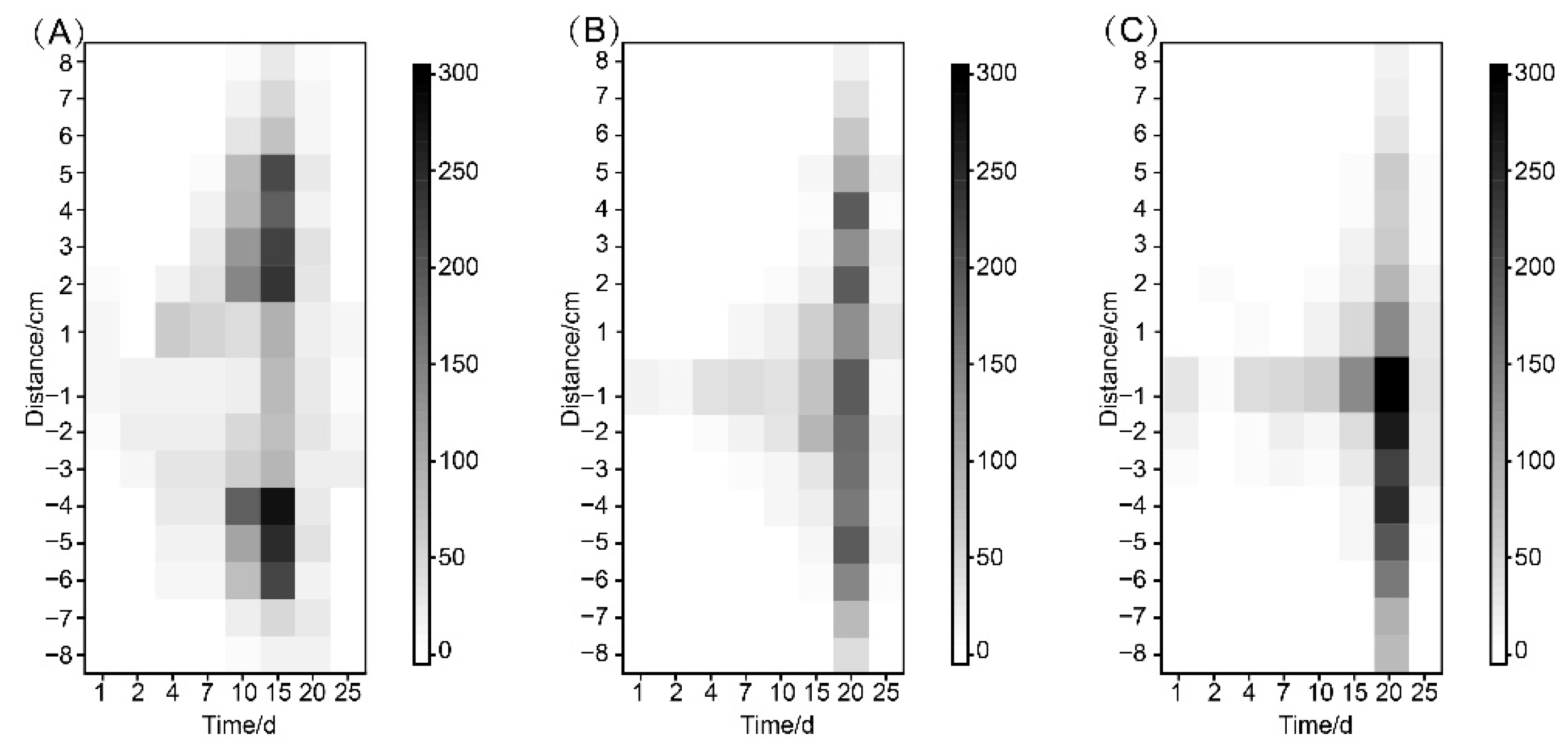
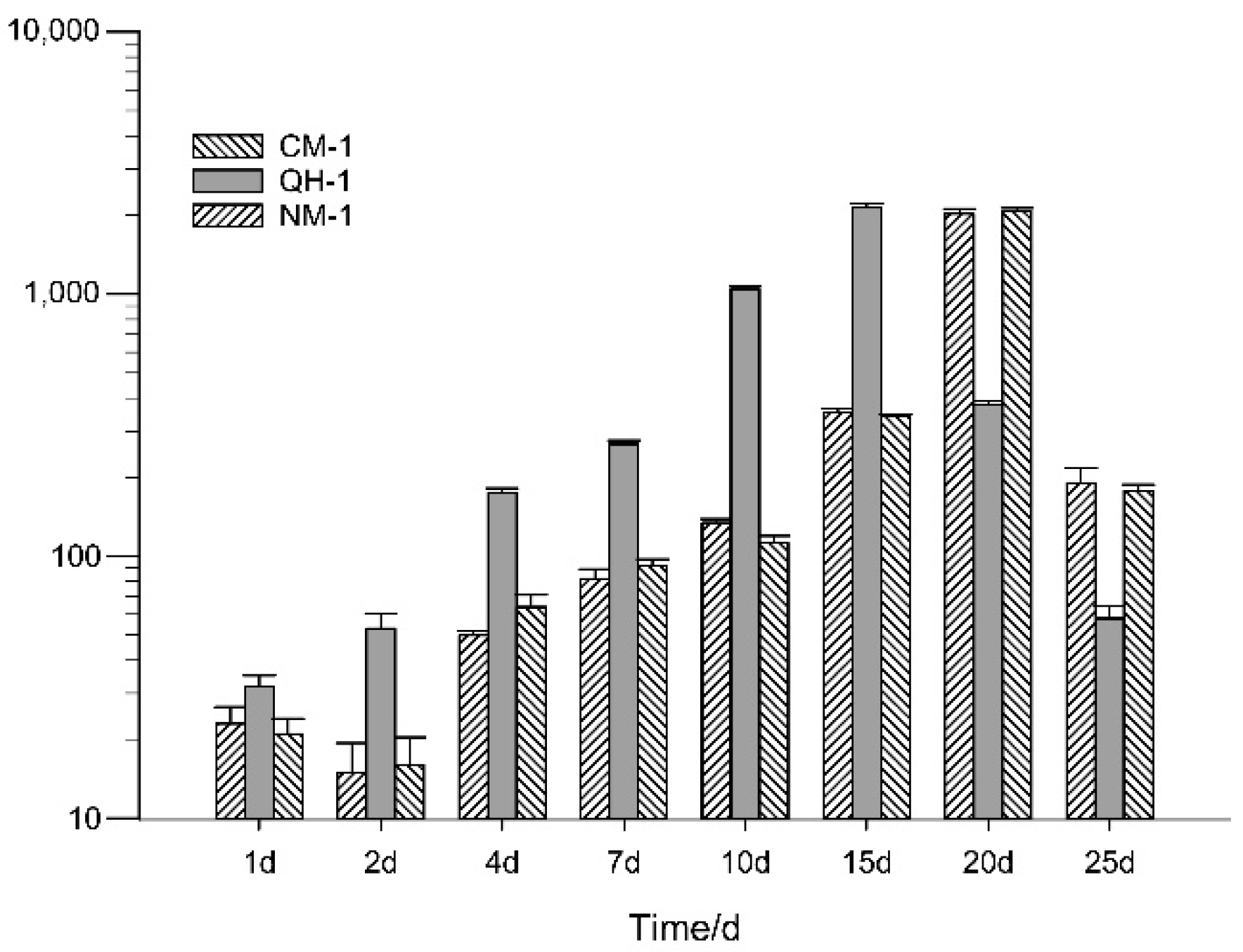
| Nematode Isolate | Seedling Species | Number of Seedlings | Mortality Rate (%) | Nematodes in Seedlings 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QH-1 | 4-year-old seedlings P. koraiensis (Siebold & Zucc.) | 10 | 100 | 28,776 ± 4774 a |
| NM-1 | 10 | 60 | 19,290 ± 3502 b | |
| CM-1 | 10 | 40 | 19,737 ± 3501 b | |
| CK | 10 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.-F.; Wang, L.-F.; Wang, X.-Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, M. Pathogenicity of Three Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Isolates in Pinus koraiensis (Siebold & Zucc.) Seedlings. Forests 2022, 13, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13081197
Cao Y-F, Wang L-F, Wang X-Z, Wang X, Xu M. Pathogenicity of Three Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Isolates in Pinus koraiensis (Siebold & Zucc.) Seedlings. Forests. 2022; 13(8):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13081197
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Ye-Fan, Lai-Fa Wang, Xi-Zhuo Wang, Xiang Wang, and Ming Xu. 2022. "Pathogenicity of Three Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Isolates in Pinus koraiensis (Siebold & Zucc.) Seedlings" Forests 13, no. 8: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13081197
APA StyleCao, Y.-F., Wang, L.-F., Wang, X.-Z., Wang, X., & Xu, M. (2022). Pathogenicity of Three Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner & Buhrer) Nickle. Isolates in Pinus koraiensis (Siebold & Zucc.) Seedlings. Forests, 13(8), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13081197





