Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions on Soil N2O Emissions and CH4 Uptake in a Phosphorus-Limited Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
- (1)
- Control (CK);
- (2)
- Add 15 g N/m2 (HN);
- (3)
- Add 15 g N/m2 and 5 g P/m2 (HNLP);
- (4)
- Add 5 g P/m2 (LP);
- (5)
- Add 15 g N/m2 and 15 g P/m2 (HNHP);
- (6)
- Add 15 g P/m2 (HP).
2.3. Soil Sampling and Chemical Analyses
2.4. Leaf and Litter Sampling and Chemical Analysis
2.5. Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) Data Collection and Measurements
2.6. Measurement of Microclimatic Factors
2.7. Data Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
3.2. Monthly Dynamics of Soil CH4 and N2O Fluxes
3.3. Overall Effects of N and P Addition Treatments
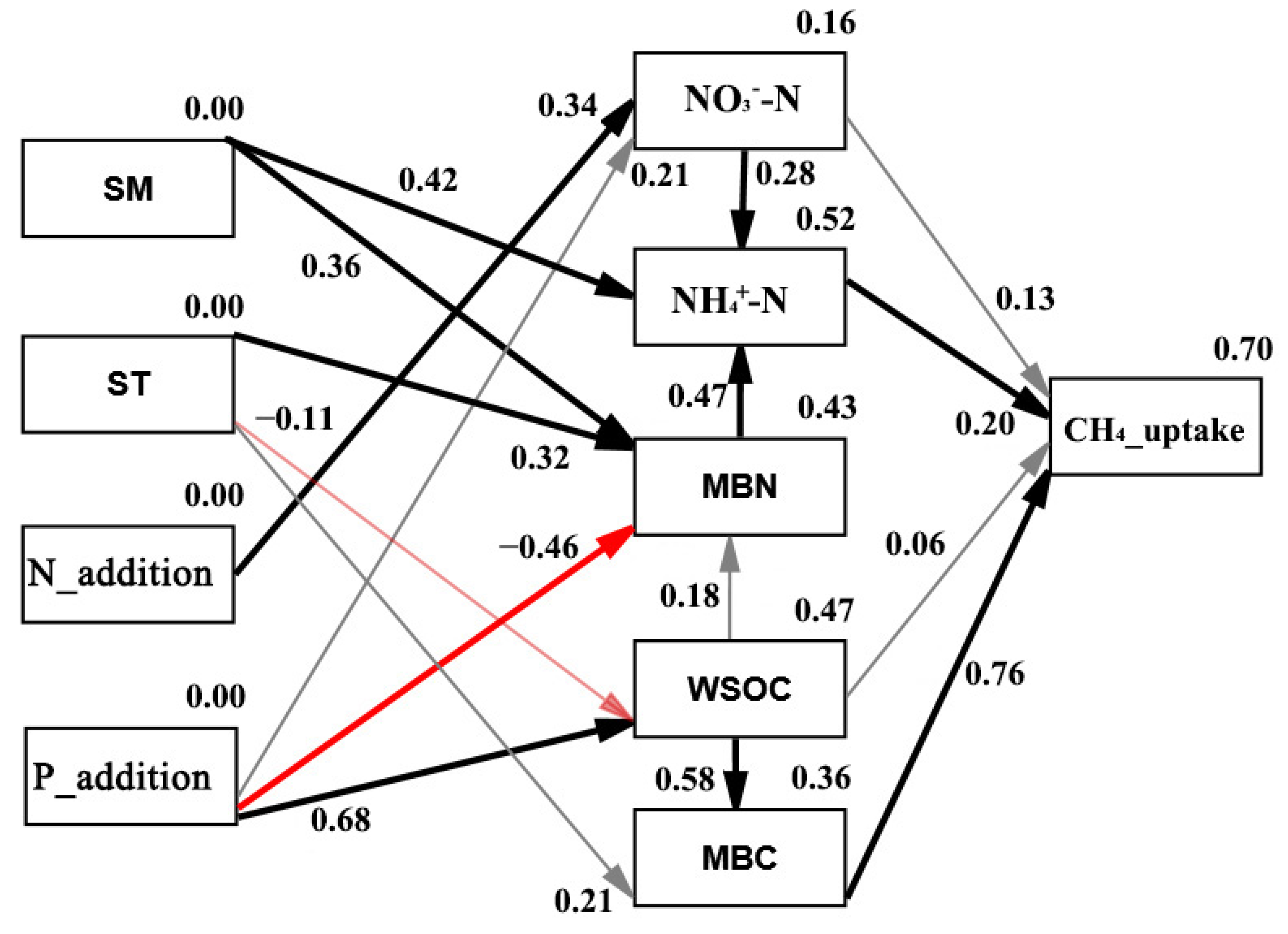
3.4. Pathway Determining N2O Emissions and CH4 Uptakes under N and P Additions
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of N Addition on N2O and CH4 Fluxes and the Controlling Mechanisms
4.2. Effect of P Addition on N2O and CH4 Fluxes and the Controlling Mechanisms
4.3. Interactive Effects of N and P Addition on N2O and CH4 Fluxes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jassal, R.S.; Black, T.A.; Trofymow, J.A.; Roy, R.; Nesic, Z. Soil CO2 and N2O flux dynamics in a nitrogen-fertilized Pacific Northwest Douglas-fir stand. Geoderma 2010, 157, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Lu, C.; Ciais, P.; Michalak, A.M.; Canadell, J.G.; Saikawa, E.; Huntzinger, D.N.; Gurney, K.R.; Sitch, S.; Zhang, B. The terrestrial biosphere as a net source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Nature 2016, 531, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Lu, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Davidson, E.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Arneth, A.; Chang, J.; Ciais, P. Global soil nitrous oxide emissions since the preindustrial era estimated by an ensemble of terrestrial biosphere models: Magnitude, attribution, and uncertainty. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 640–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Xu, R.; Canadell, J.G.; Thompson, R.L.; Winiwarter, W.; Suntharalingam, P.; Davidson, E.A.; Ciais, P.; Jackson, R.B.; Janssens-Maenhout, G. A comprehensive quantification of global nitrous oxide sources and sinks. Nature 2020, 586, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisbet, E.G.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Manning, M.R.; Lowry, D.; Fisher, R.E.; France, J.L.; Michel, S.E.; Miller, J.B.; White, J.W.C.; Vaughn, B. Rising atmospheric methane: 2007–2014 growth and isotopic shift. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 1356–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.D.; Zhang, K.; Su, D.; Lu, F.; Wan, W.X.; Wang, X.K.; Zheng, H. Effects of nitrogen application on soil greenhouse gas fluxes during the growing season of Eucalyptus plantations. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 5931–5939. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.D.; Li, X.R.; Yang, Y.L.; Zheng, Y.H.; Wang, L.S. Analysis of the benefits of greenhouse gas emission reduction in China’s large and medium-sized biogas projects. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mosier, A.R. Soil processes and global change. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 27, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Greaver, T.L. A review of nitrogen enrichment effects on three biogenic GHGs: The CO2 sink may be largely offset by stimulated N2O and CH4 emission. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Lu, C.; Xu, X.; Ren, W.; Zhang, B.; Banger, K.; Tao, B.; Pan, S.; Liu, M. Global methane and nitrous oxide emissions from terrestrial ecosystems due to multiple environmental changes. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2015, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, W.; Mo, J. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on nitrous oxide emission in a nitrogen-rich and two nitrogen-limited tropical forests. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 3503–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Yin, H.; Luo, Y.; Hui, D.F. Differential responses and controls of soil CO2 and N2O fluxes to experimental warming and nitrogen fertilization in a subalpine coniferous spruce (Picea asperata Mast.) plantation forest. Forests 2019, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: How well do we understand the processes and their controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, B. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on soil N2O emission from natural ecosystems: A global meta-analysis. Environ.Pollut. 2022, 301, 118993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Ohta, S.; Ishizuka, S.; Konda, R.; Wicaksono, A.; Heriyanto, J.; Hamotani, Y.; Gobara, Y.; Kawabata, C.; Kuwashima, K. Soil greenhouse gas fluxes and C stocks as affected by phosphorus addition in a newly established Acacia mangium plantation in Indonesia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 310, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.Z.; Terrer, C.; Pellegrini, A.F.A.; Ahlstrom, A.; van Lissa, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Xia, N.; Wu, X.H.; Jackson, R.B. Global patterns of terrestrial nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Ohta, S.; Ishizuka, S.; Konda, R.; Wicaksono, A.; Heriyanto, J.; Hardjono, A. Effects of phosphorus addition on N2O and NO emissions from soils of an Acacia mangium plantation. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zou, B.; Neher, D.A.; Li, Z. Nitrogen and phosphorus addition impact soil N2O emission in a secondary tropical forest of south China. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Ohta, S.; Ishizuka, S.; Konda, R.; Wicaksono, A.; Heriyanto, J. Phosphorus application reduces N2O emissions from tropical leguminous plantation soil when phosphorus uptake is occurring. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Y.; Rafique, R.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Mo, J. Responses of nitrous oxide emissions to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in two tropical plantations with N-fixing vs non-N-fixing tree species. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4941–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, K.; Fukushi, S. Effecfs of phosphate and calcium carbonate application on emission of N2O from soils under aerobic conditions. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1983, 29, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkiner, R.A.; Khanna, P.K.; Raison, R.J. Effect of superphosphate addition on N mineralization in some Australian forest soils. Soil Res. 1993, 31, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, B.R.; Kuyper, T.W.; Van-Groenigen, J.W. Liebig’s law of the minimum applied to a greenhouse gas: Alleviation of P-limitation reduces soil N2O emission. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. Influence of nitrate and phosphorus loading on denitrifying enzyme activity in everglades wetland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1999, 63, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Kou, L. Responses of soil CO2, CH4 and N2O fluxes to N, P, and acid additions in mixed forest in subtropical China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2017, 8, 154–164. [Google Scholar]
- Martinson, G.O.; Müller, A.K.; Matson, A.L.; Corre, M.D.; Veldkamp, E. Nitrogen and phosphorus control soil methane uptake in tropical montane forests. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2020JG005970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R. Microbial ecology of methanogens and methanotrophs. Adv. Agron. 2007, 96, 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mosier, A.R.; Parton, W.J.; Phongpan, S. Long-term large N and immediate small N addition effects on trace gas fluxes in the Colorado shortgrass steppe. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 28, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Q.; Chen, M.; Xu, K.; Tang, J.; Saikawa, E.; Lu, Y.; Melillo, J.M.; Prinn, R.G.; McGuire, A.D. Response of global soil consumption of atmospheric methane to changes in atmospheric climate and nitrogen deposition. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Lee, S.; Zoh, K.D.; Kang, H. Methane concentrations and methanotrophic community structure influence the response of soil methane oxidation to nitrogen content in a temperate forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maljanen, M.; Jokinen, H.; Saari, A.; Strömmer, R.; Martikainen, P.J. Methane and nitrous oxide fluxes, and carbon dioxide production in boreal forest soil fertilized with wood ash and nitrogen. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 22, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, I.; Johnson, M.S.; Jassal, R.S.; Black, T.A.; Grant, N.J.; Smukler, S.M. Application of biochar and nitrogen influences fluxes of CO2, CH4 and N2O in a forest soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reay, D.S.; Nedwell, D.B. Methane oxidation in temperate soils: Effects of inorganic N. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, W.; Mo, J.; Liu, L.; Dong, S. Increased phosphorus availability mitigates the inhibition of nitrogen deposition on CH4 uptake in an old-growth tropical forest, southern China. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2805–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fender, A.C.; Pfeiffer, B.; Gansert, D.; Leuschner, C.; Daniel, R.; Jungkunst, H.F. The inhibiting effect of nitrate fertilisation on methane uptake of a temperate forest soil is influenced by labile carbon. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Inubushi, K. Effects of N sources and methane concentrations on methane uptake potential of a typical coniferous forest and its adjacent orchard soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 40, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-P.; Ineson, P. Methane oxidation in a temperate coniferous forest soil: Effects of inorganic N. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, E.L.; Helliker, B.R. Methane flux in non-wetland soils in response to nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. Ecology 2010, 91, 3242–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.; Conrad, R. Effect of CH4 concentrations and soil conditions on the induction of CH4 oxidation activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelier, P.L.E.; Laanbroek, H.J. Nitrogen as a regulatory factor of methane oxidation in soils and sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 47, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkamp, R.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Papen, H. Methane oxidation by soils of an N limited and N fertilized spruce forest in the Black Forest, Germany. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, G.; Nohrstedt, H. Fast recovery of atmospheric methane consumption in a Swedish forest soil after single-shot N-fertilization. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 134, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraart, A.J.; Steenbergh, A.K.; Ho, A.; Kim, S.Y.; Bodelier, P.L.E. Beyond nitrogen: The importance of phosphorus for CH4 oxidation in soils and sediments. Geoderma 2015, 259, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.J.; Matson, P.A. Nitrogen oxide emissions after nitrogen additions in tropical forests. Nature 1999, 400, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, S.L.; Fang, H.J.; Yu, G.R.; Gao, W.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Dang, X.S.; Li, L.S. Low-level nitrogen addition promotes net methane uptake in a boreal forest across the great Xing’an mountain region. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2014, 60, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.K.; Mo, J.M. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on soil methane uptake in disturbed forests. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 3089–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Working Group 3, Third Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Si, G.; Zhang, T.; Mulder, J.; Duan, L. Nitrogen deposition increases N2O emission from an N-saturated subtropical forest in southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Mulder, J.; Wu, L.P.; Meng, X.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Dörsch, P. Spatial and temporal variability of N2O emissions in a subtropical forest catchment in China. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cui, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Run, Y. Simulating the potential sequestration of three major greenhouse gases in China’s natural ecosystems. Forests 2020, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.R.; Jia, Y.L.; He, N.P.; Zhu, J.X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.F.; Piao, S.L.; Liu, X.J.; He, H.L.; Guo, X.B.; et al. Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Gundersen, P.; Fang, Y.T.; Li, D.J.; Wang, H. Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in a mature tropical forest in southern China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dörsch, P.; Mulder, J. Phosphorus addition mitigates N2O and CH4 emissions in N-saturated subtropical forest, SW China. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 3097–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mo, J.; Yu, G.; Fang, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, X.; Wang, H. Emissions of nitrous oxide from three tropical forests in southern China in response to simulated nitrogen deposition. Plant Soil 2008, 306, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mo, J.; Zhou, G.; Gundersen, P.; Fang, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, T.; Dong, S. Methane uptake responses to nitrogen deposition in three tropical forests in southern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, M.; Peng, C. Spatial and temporal variations of N2O emissions from global forest and grassland ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 266, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.T.; Wang, N.; Bai, S.B. Short-term response of Chinese fir plantation soil greenhouse gas emissions to Phyllostachys edulis invasion and logging. J. Zhejiang A F Univ. 2021, 38, 703–711. [Google Scholar]
- McGroddy, M.E.; Daufresne, T.; Hedin, L.O. Scaling of C:N:P stoichiometry in forests worldwide: Implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios. Ecology 2004, 85, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, R.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Bahn, M.; Hanson, P.J.; Hosman, K.P.; Kulmala, L.; Pumpanen, J.; Yang, B. On the multi-temporal correlation between photosynthesis and soil CO2 efflux: Reconciling lags and observations. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xue, M. Simultaneous measurement of CO2, CH4 and N2O emission from terrestrial ecosystem with one improved gas chromatography. Tech. Equip. Environ. Pollut. Control 2003, 4, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Lin, D.; Tian, Y.; Hong, S. Thinning intensity affects soil-atmosphere fluxes of greenhouse gases and soil nitrogen mineralization in a lowland poplar plantation. Forests 2016, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, Y. Soil CH4 emission flux from artificial coniferous forest in red soil hilly area of Qianyanzhou. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 32, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Huang, C.B.; Kim, D.G.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Wang, K.B.; Song, X.Z.; Peng, C.H. Soil GHG fluxes are altered by N deposition: New data indicate lower N stimulation of the N2O flux and greater stimulation of the calculated C pools. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2613–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambus, P.; Robertson, G.P. The effect of increased N deposition on nitrous oxide, methane and carbon dioxide fluxes from unmanaged forest and grassland communities in Michigan. Biogeochemistry 2006, 79, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Hojito, M.; Kondo, H.; Matsunami, H.; Scholefield, D. Effects of plant species on CH4 and N2O fluxes from a volcanic grassland soil in Nasu, Japan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2005, 51, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, P.K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Ye, G.; Zhou, G. Effect of fertilization on water-soluble organic C, N, and emission of greenhouse gases in the soil of Phyllostachys edulis stands. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2010, 12, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Friedel, J.K.; Stahr, K. Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Mori, T.; Mao, Q.; Zhou, K.; Zhou, G.; Nie, Y.; Mo, J. Responses of soil microbial community to continuous experimental nitrogen additions for 13 years in a nitrogen-rich tropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Yokoyama, D.; Kitayama, K. Contrasting effects of exogenous phosphorus application on N2O emissions from two tropical forest soils with contrasting phosphorus availability. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenke, G.D.; Herridge, D.F.; Scheer, C.; Rowlings, D.W.; Haigh, B.M.; McMullen, K.G. Greenhouse gas (N2O and CH4) fluxes under nitrogen-fertilised dryland wheat and barley on subtropical Vertosols: Risk, rainfall and alternatives. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Gundersen, P.; Zhang, T.; Mo, J. Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in three forest types in tropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Liu, J.S.; Yu, J.B.; Wang, J.D. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in black soil corn farm ecosystem. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 18, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.; Li, K.; Gong, Y.; Hu, Y.; Mohammat, A.; Christie, P.; Liu, X. A five-year study of the impact of nitrogen addition on methane uptake in alpine grassland. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.H.; Yuan, F.H.; Bai, J.H.; Duan, H.T.; Gu, X.Y.; Hou, L.Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, M.G.; He, J.S.; Zhang, Z.H.; et al. Phosphorus alleviation of nitrogen-suppressed methane sink in global grasslands. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
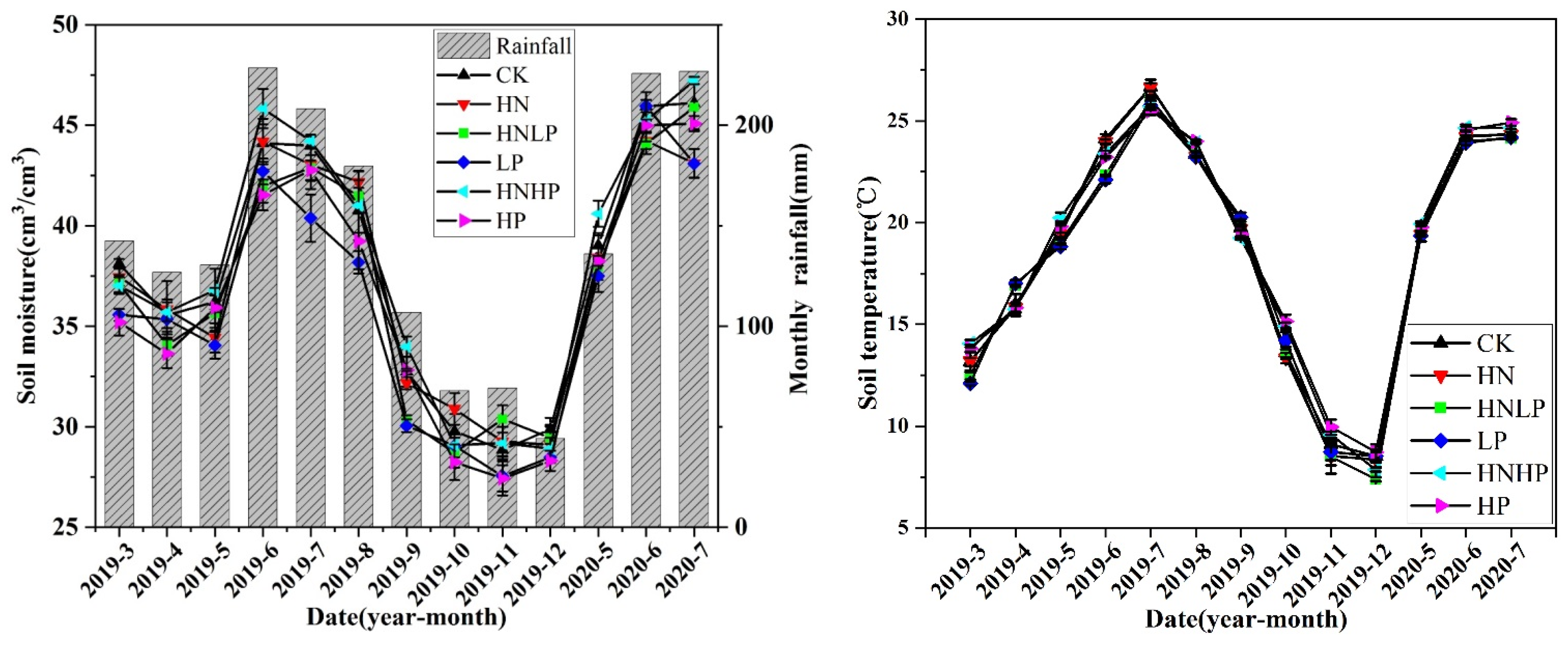
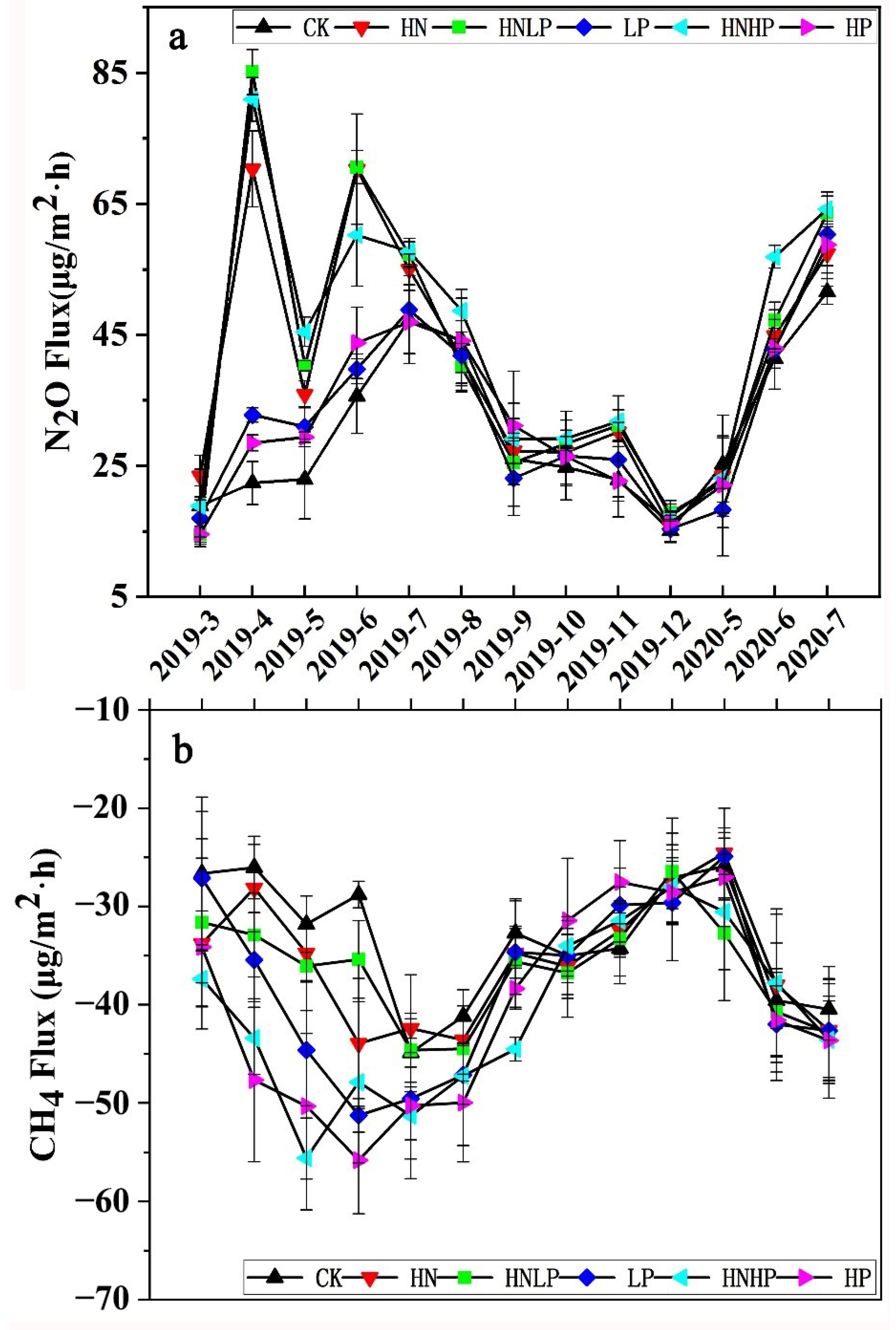
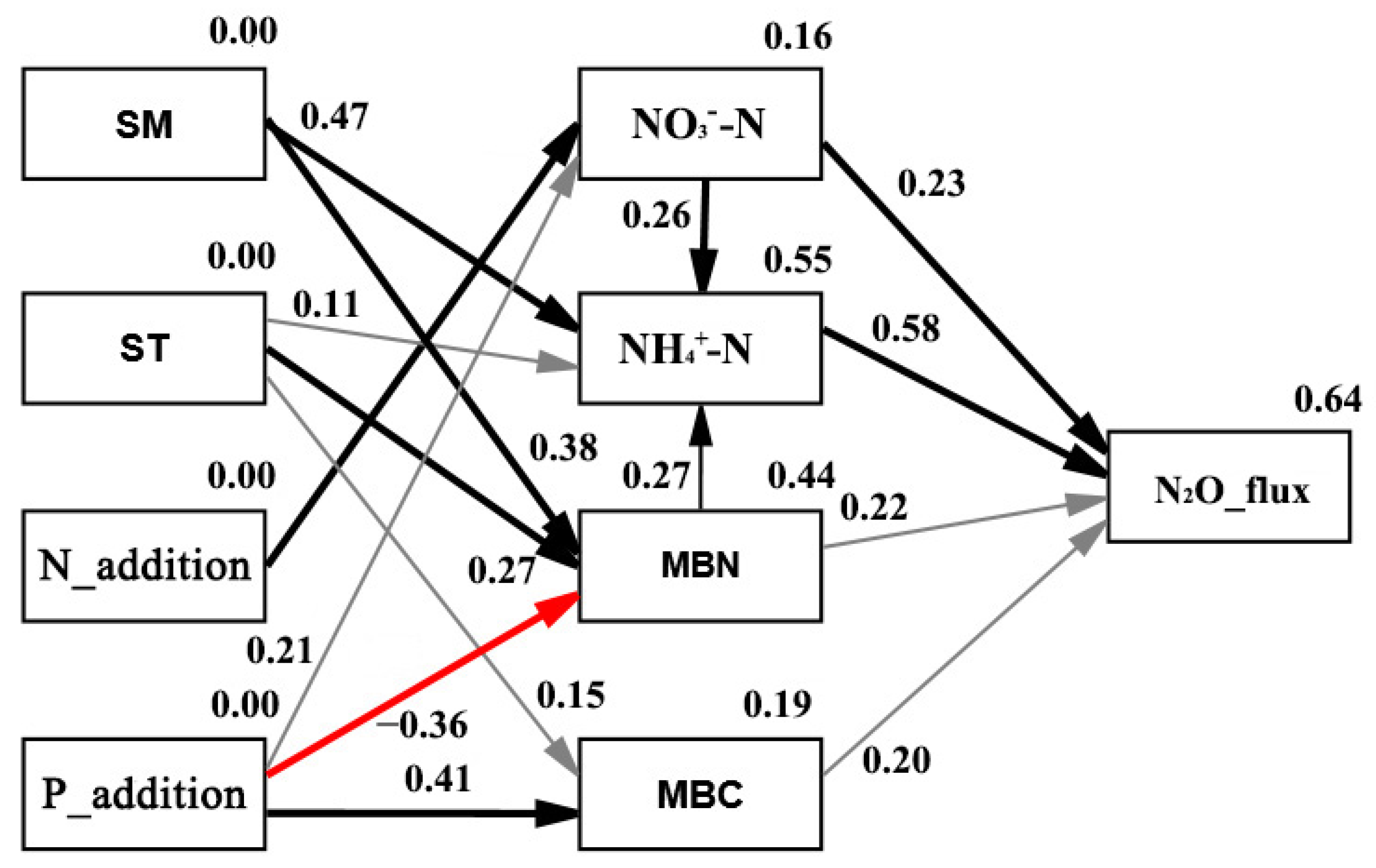
| Variables | CK | LP | HP | HN | HNLP | HNHP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+ (mg/kg) | 12.62 (0.76) b | 11.61 (0.86) b | 12.80 (1.17) b | 14.22 (1.97) a | 14.87 (2.08) a | 12.88 (1.36) b |
| NO3− (mg/kg) | 3.71 (0.076) b | 4.78 (0.42) ab | 3.86 (0.18) b | 4.46 (0.36) b | 4.80 (0.33) ab | 5.89 (0.30) a |
| MBN (mg/kg) | 54.21 (9.47) a | 22.23 (1.35) b | 24.08 (1.17) b | 54.53 (9.26) a | 32.39 (4.36) b | 28.55 (4.18) b |
| MBC (mg/kg) | 137.55 (9.13) b | 173.94 (18.94) a | 206.76 (15.56) a | 158.65 (11.44) ab | 159.07 (7.74) ab | 198.59 (12.70) a |
| WSOC (mg/kg) | 46.93 (2.88) c | 80.20 (3.52) ab | 96.48 (5.85) a | 62.69 (5.16) c | 63.37 (2.02) bc | 91.50 (3.85) a |
| Leaf N (g/kg) | 7.55 (0.11) a | 8.00 (0.27) a | 7.05 (0.30) a | 7.96 (0.81) a | 8.75 (0.99) a | 9.22 (0.86) a |
| Soil TN (g/kg) | 0.86 (0.036) a | 0.90 (0.040) a | 0.91 (0.043) a | 1.04 (0.095) a | 1.00 (0.097) a | 1.00 (0.082) a |
| SOC (%) | 1.55 (0.031) ab | 1.67 (0.10) ab | 1.86 (0.12) a | 1.47 (0.06) b | 1.81 (0.11) ab | 1.57 (0.048) ab |
| Soil TP (g/kg) | 0.13 (0.014) b | 0.14 (0.010) b | 0.23 (0.024) a | 0.13 (0.011) b | 0.13 (0.008) b | 0.15 (0.025) ab |
| Treatments | N2O (μg/m2·h) | CH4 (μg/m2·h) | N2O (μg/m2·h) | CH4 (μg/m2·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Months | All Months | |||
| CK | 32.06 (11.69) b | −34.92 (7.74) a | 30.63 (12.42) a | −35.06 (7.22) a |
| HN | 57.86 (15.13) a | −35.37 (6.47) a | 40.17 (17.98) b | −35.58 (7.12) a |
| HNLP | 63.30 (16.73) a | −39.74 (7.03) ab | 41.83 (21.23) b | −37.23 (8.07) ab |
| LP | 38.08 (8.02) b | −43.42 (8.51) bc | 32.57 (13.93) a | −38.28 (9.04) ab |
| HNHP | 61.09 (13.52) a | −49.94 (6.52) c | 43.346 (19.55) b | −40.75 (9.76) b |
| HP | 37.15 (9.09) b | −51.03 (7.37) c | 32.88 (13.39) a | −40.60 (10.83) b |
| Treatments | N Effect | P Effect | N × P Interaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | ||
| N2O | 4 months | 86.44 | <0.05 | 1.62 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.96 |
| All months | 25.92 | <0.05 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.04 | 0.96 | |
| CH4 | 4 months | 0.87 | 0.35 | 33.30 | <0.05 | 0.61 | 0.54 |
| All months | 0.02 | 0.90 | 9.52 | <0.05 | 0.22 | 0.80 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Chen, G.; Lu, X.; Jiao, H. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions on Soil N2O Emissions and CH4 Uptake in a Phosphorus-Limited Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation. Forests 2022, 13, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050772
Li B, Chen G, Lu X, Jiao H. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions on Soil N2O Emissions and CH4 Uptake in a Phosphorus-Limited Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation. Forests. 2022; 13(5):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050772
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Binjie, Guangsheng Chen, Xiaochen Lu, and Hongbo Jiao. 2022. "Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions on Soil N2O Emissions and CH4 Uptake in a Phosphorus-Limited Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation" Forests 13, no. 5: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050772
APA StyleLi, B., Chen, G., Lu, X., & Jiao, H. (2022). Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Additions on Soil N2O Emissions and CH4 Uptake in a Phosphorus-Limited Subtropical Chinese Fir Plantation. Forests, 13(5), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050772







