Comparative Analyses of 35 Complete Chloroplast Genomes from the Genus Dalbergia (Fabaceae) and the Identification of DNA Barcodes for Tracking Illegal Logging and Counterfeit Rosewood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Complete Chloroplast Genomes
2.2. Repeat Analysis
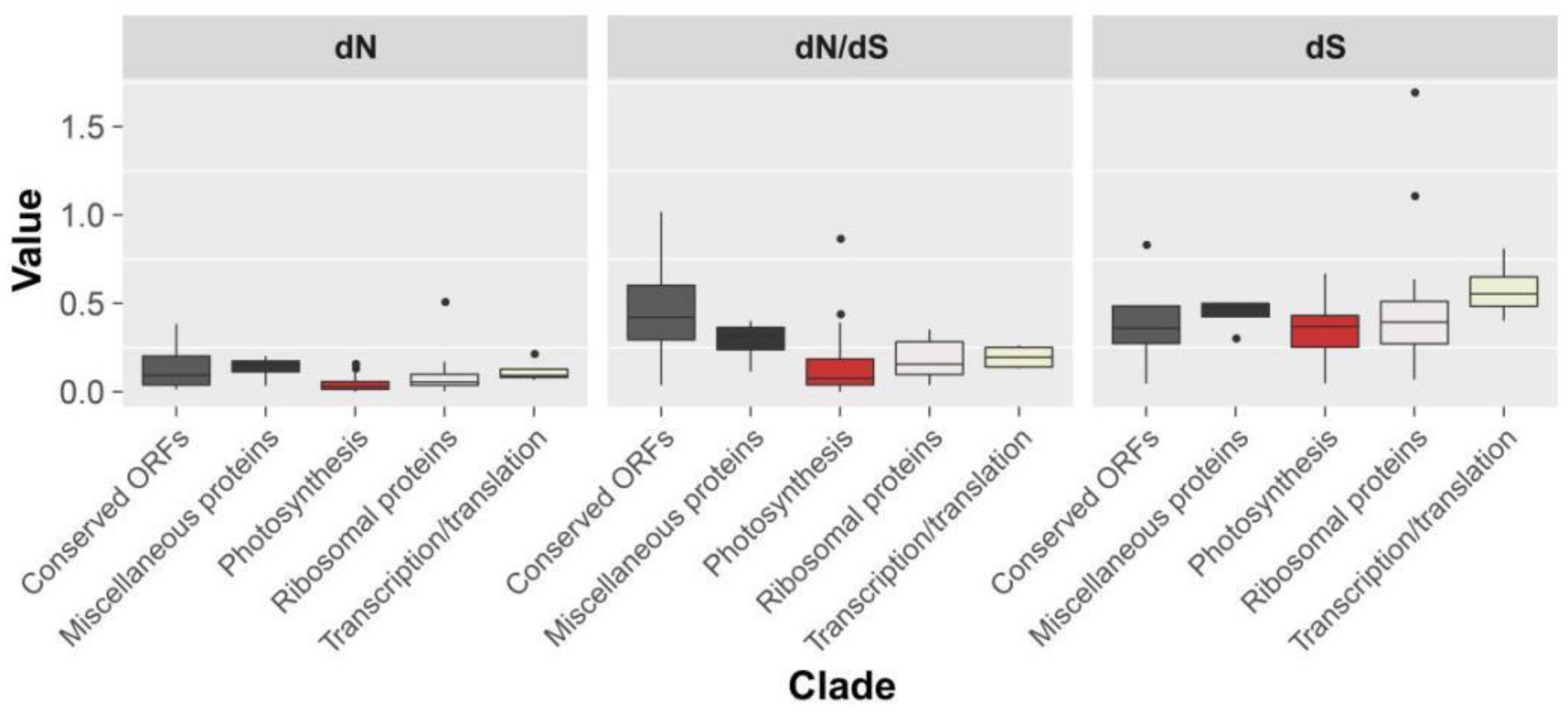
2.3. Genome Sequence Divergence
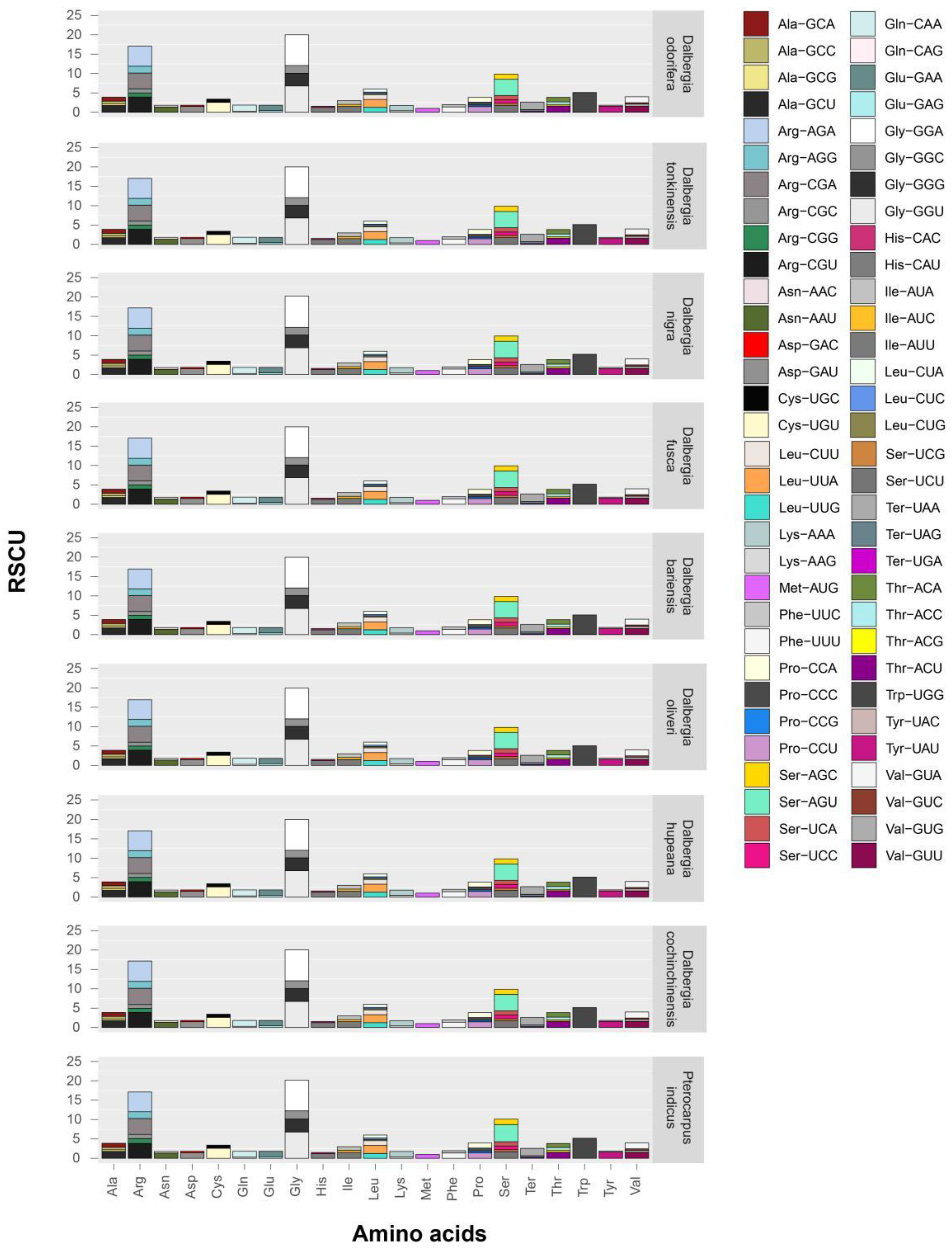
2.4. Codon Usage in Dalbergia Chloroplast Genes
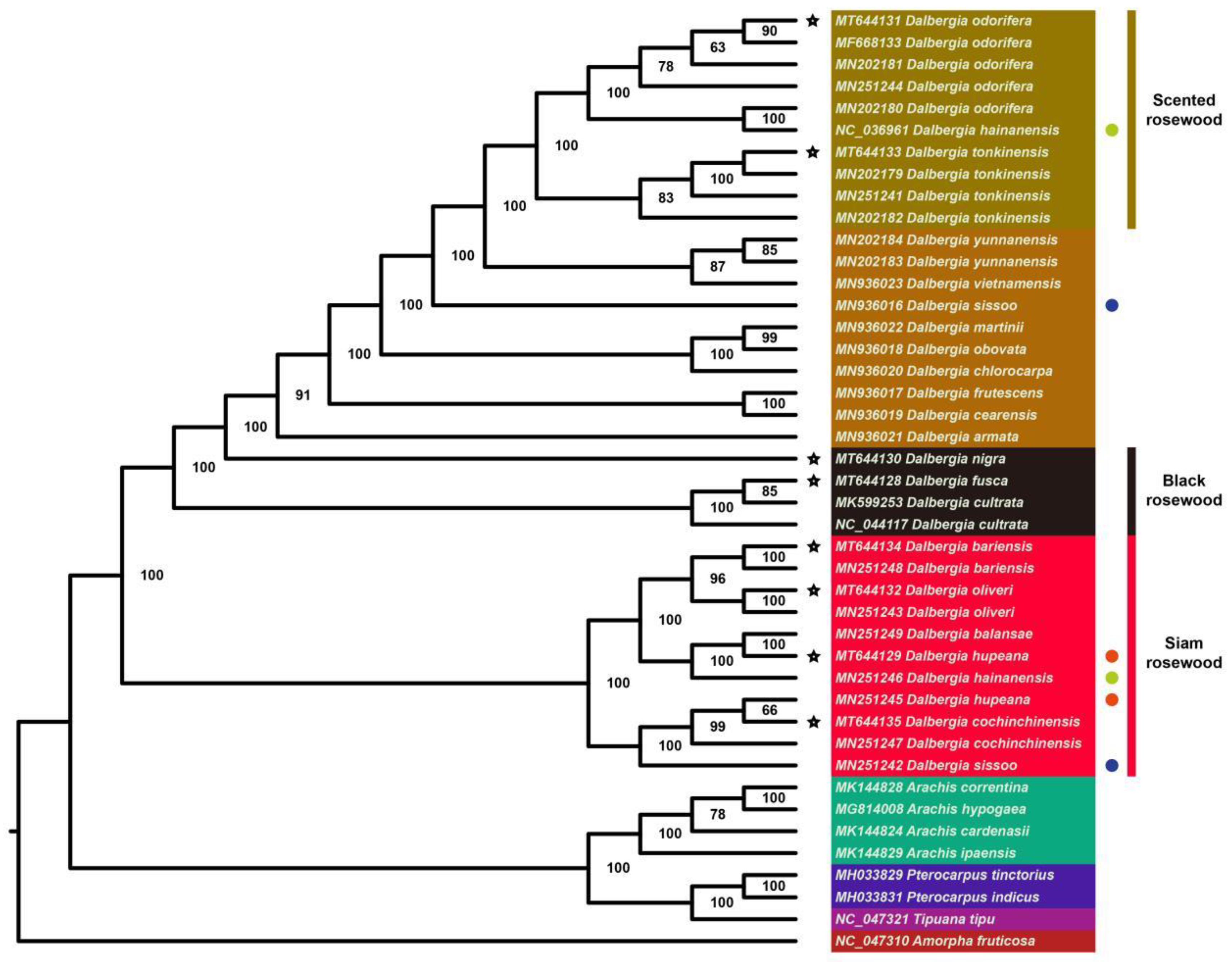
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis and Barcode Selection
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Tissue Samples and DNA Extraction
3.2. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
3.3. Genome Annotation
3.4. Genome Structure Analysis
3.5. Genome Nucleotide Diversity
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis and Nucleotide Substitutions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Lian, J.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Xu, D. The chromosome-level draft genome of Dalbergia odorifera. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Li, M. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome sequence of Dalbergia species and its phylogenetic implications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.L. China’s rosewood boom: A cultural fix to capital overaccumulation. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2020, 1, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Everything old is new again: Classical chinese furniture. China Today 2011, 11, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sriudorn, N.; Benchawattananon, R. Morphology and anatomy of rosewood (Dalbergia cochinchinensis) and relationship between its elemental components and soil properties for identification of endemic species. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2018, 14, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, E.O.; Wiemann, M.C.; Barajas-Morales, J.; Chavarria, G.D.; McClure, P.J. Forensic analysis of cites-protected dalbergia timber from the americas. IAWA J. 2015, 36, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeman, E.; Velásquez Runk, J. Panama’s illegal rosewood logging boom from Dalbergia retusa. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J. Madagascar rosewood, illegal logging and the tropical timber trade. Madag. Conserv. Dev. 2010, 5, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul-Rahaman, I.; Kabanda, J.; Braimah, M.M. Desertification of the savanna: Illegal logging of rosewood, causes and effects on the people of kabonwule, northern region. Saudi J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2016, 1, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwat, P.; Nijman, V. Using online media-sourced seizure data to assess the illegal wildlife trade in Siamese rosewood. Environ. Conserv. 2018, 45, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.P.; Chi, N.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Thuong, B.H.; Ban, D.V.; Dell, B. 2020. Market and policy setting for the trade in Dalbergia tonkinensis, a rare and valuable rosewood, in Vietnam. Trees For. People 2020, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puy, D.D. The Leguminosae of madagascar. Curtis’s Bot. Mag. 1997, 14, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, E.R. Logging of rare rosewood and palisandre (Dalbergia spp.) within Marojejy National Park. Madag. Madag. Conserv. Dev. 2007, 2, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randriamalala, H.; Liu, Z. Rosewood of Madagascar: Between democracy and conservation. Madag. Conserv. Dev. 2010, 5, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. World Wildlife Crime Report: Trafficking in Protected Species; United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- CITES. 2020. Available online: https://cites.org/eng/disc/species.php (accessed on 30 May 2020).
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.K.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 106, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Liao, X.Z.; Zhang, X.N.; Tembrock, L.R.; Broz, A. Genomic architectural variation of plant mitochondria—a review of multichromosomal structuring. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 60, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CBOL Plant Working Group. A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12794–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassold, S.; Lowry, P.N.; Bauert, M.R.; Razafintsalama, A.; Ramamonjisoa, L.; Widmer, A. DNA barcoding of malagasy rosewoods: Towards a molecular identification of cites-listed dalbergia species. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e157881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Li, D.Z.; van der Bank, M.; Twyford, A.D. Telling plant species apart with DNA: From barcodes to genomes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ge, F.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L. PCIR: A database of plant chloroplast inverted repeats. Database 2019, 1, 2019–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Zou, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Yang, X.; Zhou, S. DNA barcoding of Oryza: Conventional, specific, and super barcodes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 105, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, Z.Q.; Bystriakova, N.; Ansell, S.W.; Xiang, Q.P.; Heinrichs, J.; Schneider, H.; Zhang, X.C. Phylogeography of the Sino-Himalayan fern Lepisorus clathratus on “the roof of the world”. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.N.; Wu, C.S.; Ye, L.J.; Mo, Z.Q.; Liu, J.; Chang, Y.W.; Li, D.Z.; Chaw, S.M.; Gao, L.M. Prevalence of isomeric plastomes and effectiveness of plastome super-barcodes in yews (Taxus) worldwide. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.S.; Liu, J.Q. Are nuclear loci ideal for barcoding plants? A case study of genetic delimitation of two sister species using multiple loci and multiple intraspecific individuals. J. Syst. Evol. 2011, 3, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, H.; Ai, B.; Gao, W.; Zhang, C.; Fei, Q.; Yuan, D.; Wu, Z.; et al. Chloroplast genomes in Populus (Salicaceae): Comparisons from an intensively sampled genus reveal dynamic patterns of evolution. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmayanti, Y.; Leinemann, L.; Gailing, O.; Finkeldey, R. DNA from processed and unprocessed wood: Factors influencing the isolation success. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2009, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltonstall, K.; Lambertini, C. The value of repetitive sequences in chloroplast DNA for phylogeographic inference: A comment on Vachon & Freeland 2011. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Brazda, V.; Lysek, J.; Bartas, M.; Fojta, M. 2018. Complex analyses of short inverted repeats in all sequenced chloroplast dnas. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1097018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Ma, L.; Wu, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y. Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes from 22 Lythraceae species: Inferences for phylogenetic relationships and genome evolution within Myrtales. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanparast, M.; Klitgård, B.B.; Adema, F.A.C.B.; Pennington, R.T.; Yahara, T.; Kajita, T. First molecular phylogeny of the pantropical genus Dalbergia: Implications for infrageneric circumscription and biogeography. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 89, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teruel, M.; Ruíz-Ruano, F.J.; Marchal, J.A.; Sánchez, A.; Cabrero, J.; Camacho, J.P.; Perfectti, F. Disparate molecular evolution of two types of repetitive DNAs in the genome of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Heredity 2014, 112, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:arXiv:1303.3997v2. [Google Scholar]
- Nurk, S.; Bankevich, A.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Pyshkin, A.; Sirotkin, A.; Sirotkin, Y.; et al. Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 714–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.J.; Moore, M.J.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. The codon Adaptation Index-a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudno, M.; Do, C.B.; Cooper, G.M.; Kim, M.F.; Davydov, E.; Green, E.D.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S. LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: Efficient tools for large-scale multiple alignment of genomic DNA. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Notredame, C.; Higgins, D.G.; Heringa, J. T-Coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martinez, J.M.; Gabaldon, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z. PAML: A program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput. Appl. Biosci. CABIOS 1997, 13, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
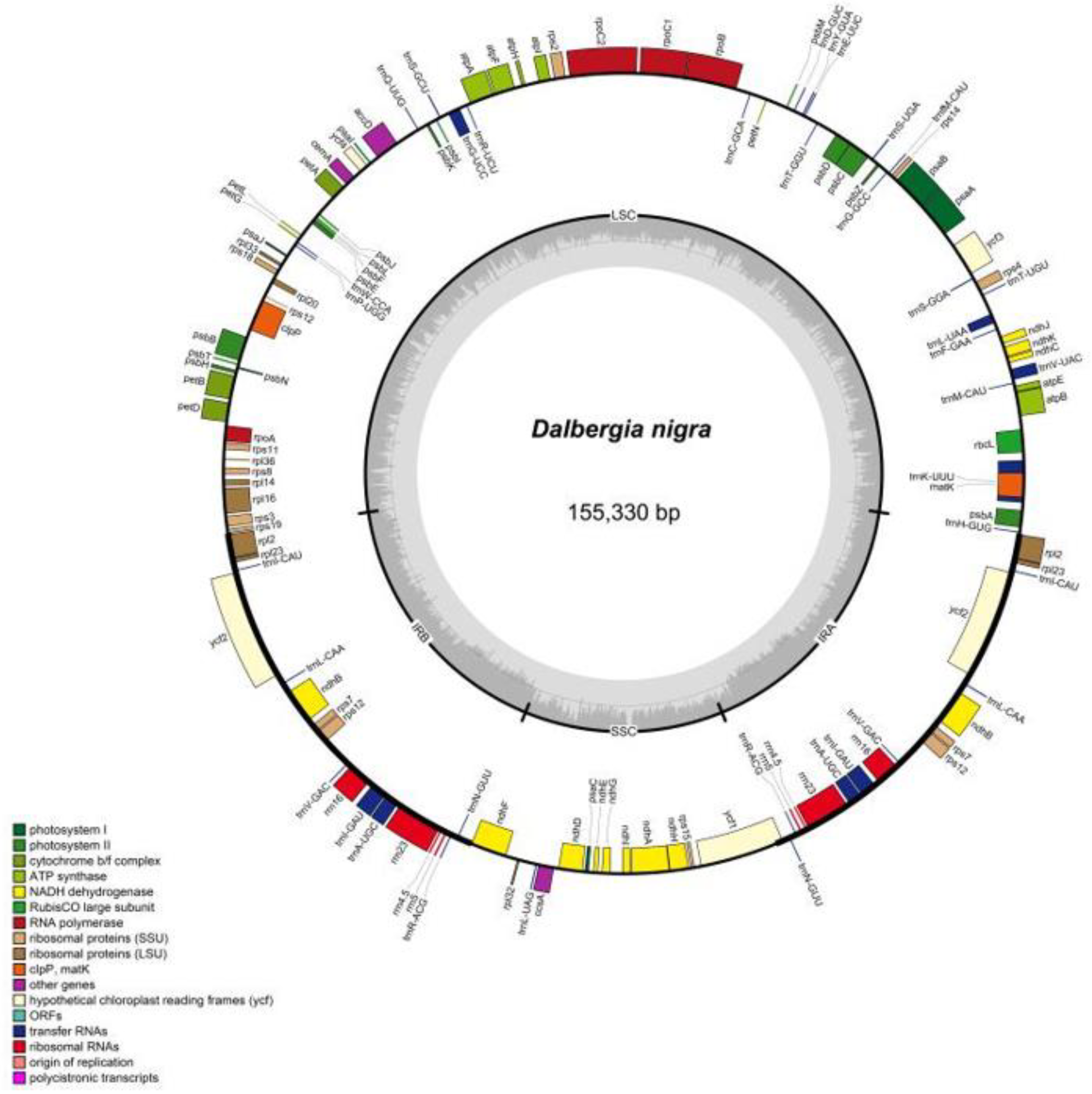
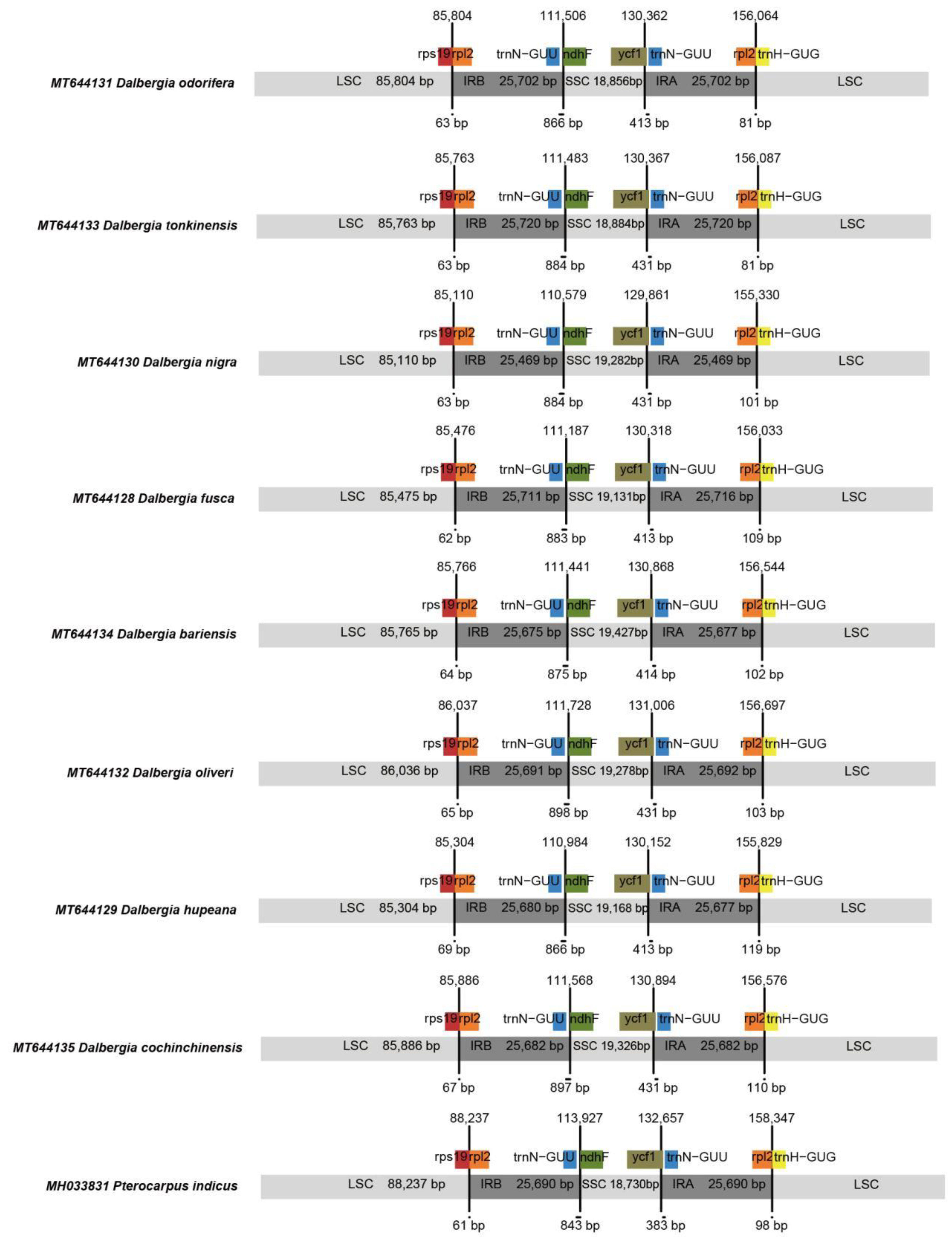

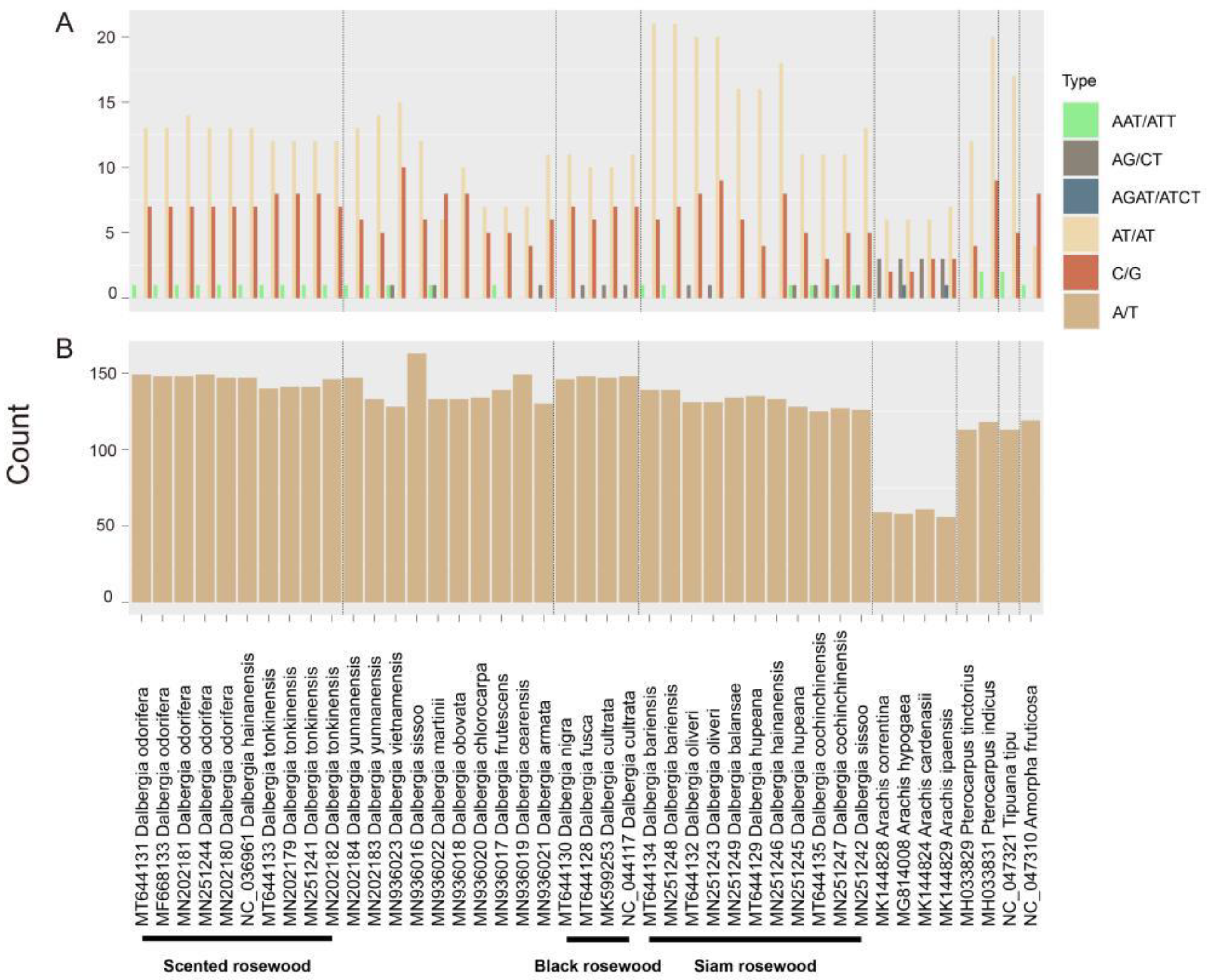
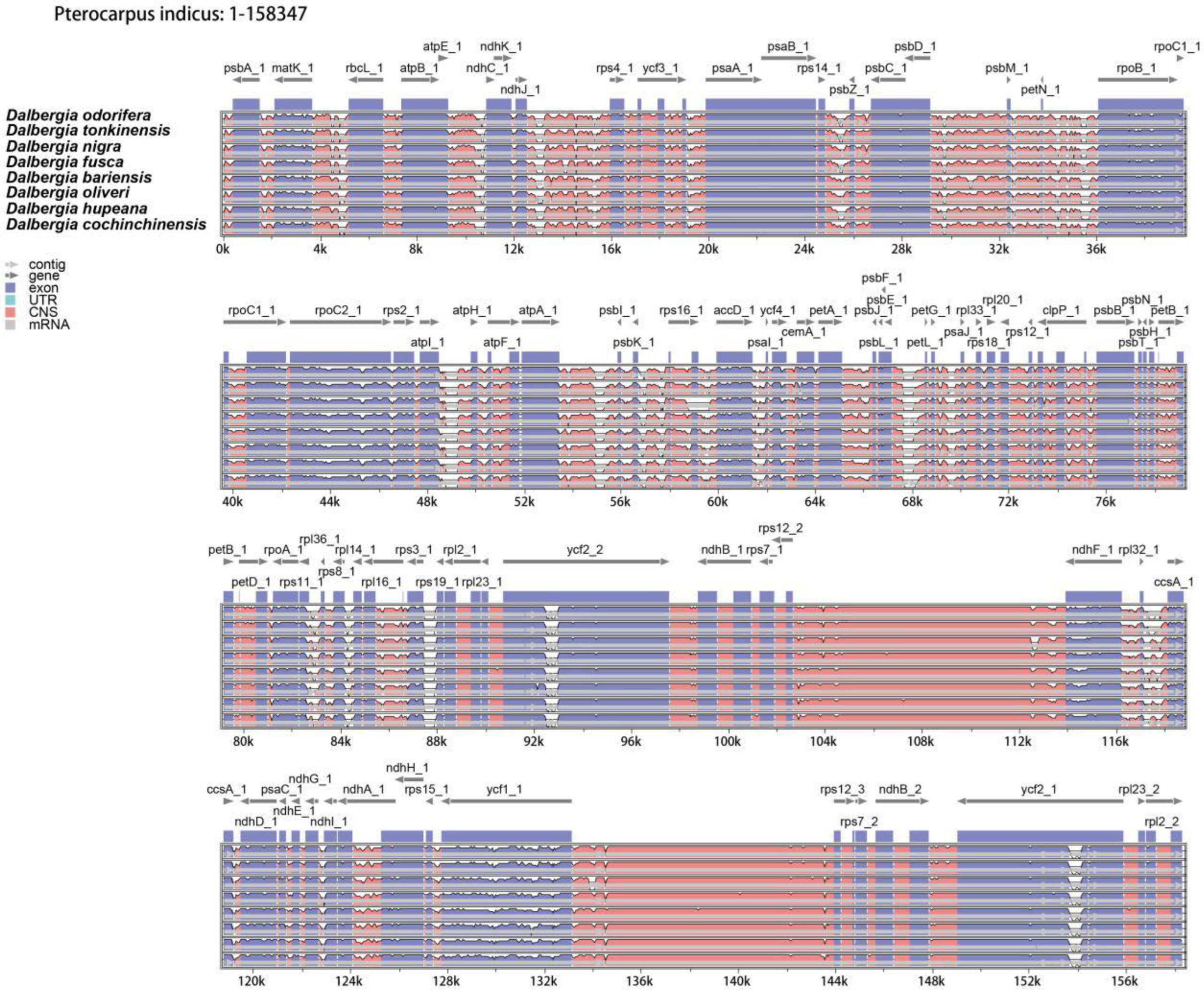

| GB ID | Species | TL | Genes | tRNA | rRNA | GC% | LSC | IRB | SS | IRA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT644128 | Dalbergia fusca | 156,033 | 83 | 37 | 8 | 36.08 | 85,475 | 25,711 | 19,131 | 25,716 |
| MT644129 | Dalbergia hupeana | 155,829 | 83 | 37 | 8 | 36.19 | 85,304 | 25,680 | 19,168 | 25,677 |
| MT644130 | Dalbergia nigra | 155,330 | 82 | 37 | 8 | 36.05 | 85,110 | 25,469 | 19,282 | 25,469 |
| MT644131 | Dalbergia odorifera | 156,064 | 83 | 37 | 8 | 36.09 | 85,804 | 25,702 | 18,856 | 25,702 |
| MT644132 | Dalbergia oliveri | 156,697 | 82 | 37 | 8 | 35.96 | 86,036 | 25,691 | 19,278 | 25,692 |
| MT644133 | Dalbergia tonkinensis | 156,087 | 83 | 37 | 8 | 36.09 | 85,763 | 25,720 | 18,884 | 25,720 |
| MT644134 | Dalbergia bariensis | 156,544 | 83 | 37 | 8 | 35.94 | 85,765 | 25,675 | 19,427 | 25,677 |
| MT644135 | Dalbergia cochinchinensis | 156,576 | 83 | 37 | 8 | 36.08 | 85,886 | 25,682 | 19,326 | 25,682 |
| Group | Species Contained | Unique INDELs | Unique SNVs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black rosewood | D. fusca, D. cultrata, D. nigra | 1 | 2 |
| Black rosewood | D. fusca, D. cultrata | 49 | 229 |
| Black rosewood | D. nigra | 69 | 94 |
| Siam rosewood | As shown in Figure 9 | 10 | 58 |
| Scented rosewood | D. odorifera, D. tonkinensis, D. hainanensis (NC_036961) | 13 | 29 |
| Scented rosewood | D. odorifera | 3 | 7 |
| Scented rosewood | D. tonkinensis | 3 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, Z.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Tembrock, L.R.; Wu, Z.; Xu, D.; Liao, X. Comparative Analyses of 35 Complete Chloroplast Genomes from the Genus Dalbergia (Fabaceae) and the Identification of DNA Barcodes for Tracking Illegal Logging and Counterfeit Rosewood. Forests 2022, 13, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13040626
Hong Z, He W, Liu X, Tembrock LR, Wu Z, Xu D, Liao X. Comparative Analyses of 35 Complete Chloroplast Genomes from the Genus Dalbergia (Fabaceae) and the Identification of DNA Barcodes for Tracking Illegal Logging and Counterfeit Rosewood. Forests. 2022; 13(4):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13040626
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Zhou, Wenchuang He, Xiaojing Liu, Luke R. Tembrock, Zhiqiang Wu, Daping Xu, and Xuezhu Liao. 2022. "Comparative Analyses of 35 Complete Chloroplast Genomes from the Genus Dalbergia (Fabaceae) and the Identification of DNA Barcodes for Tracking Illegal Logging and Counterfeit Rosewood" Forests 13, no. 4: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13040626
APA StyleHong, Z., He, W., Liu, X., Tembrock, L. R., Wu, Z., Xu, D., & Liao, X. (2022). Comparative Analyses of 35 Complete Chloroplast Genomes from the Genus Dalbergia (Fabaceae) and the Identification of DNA Barcodes for Tracking Illegal Logging and Counterfeit Rosewood. Forests, 13(4), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13040626







