Effects of Scion Variety on the Phosphorus Efficiency of Grafted Camellia oleifera Seedlings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
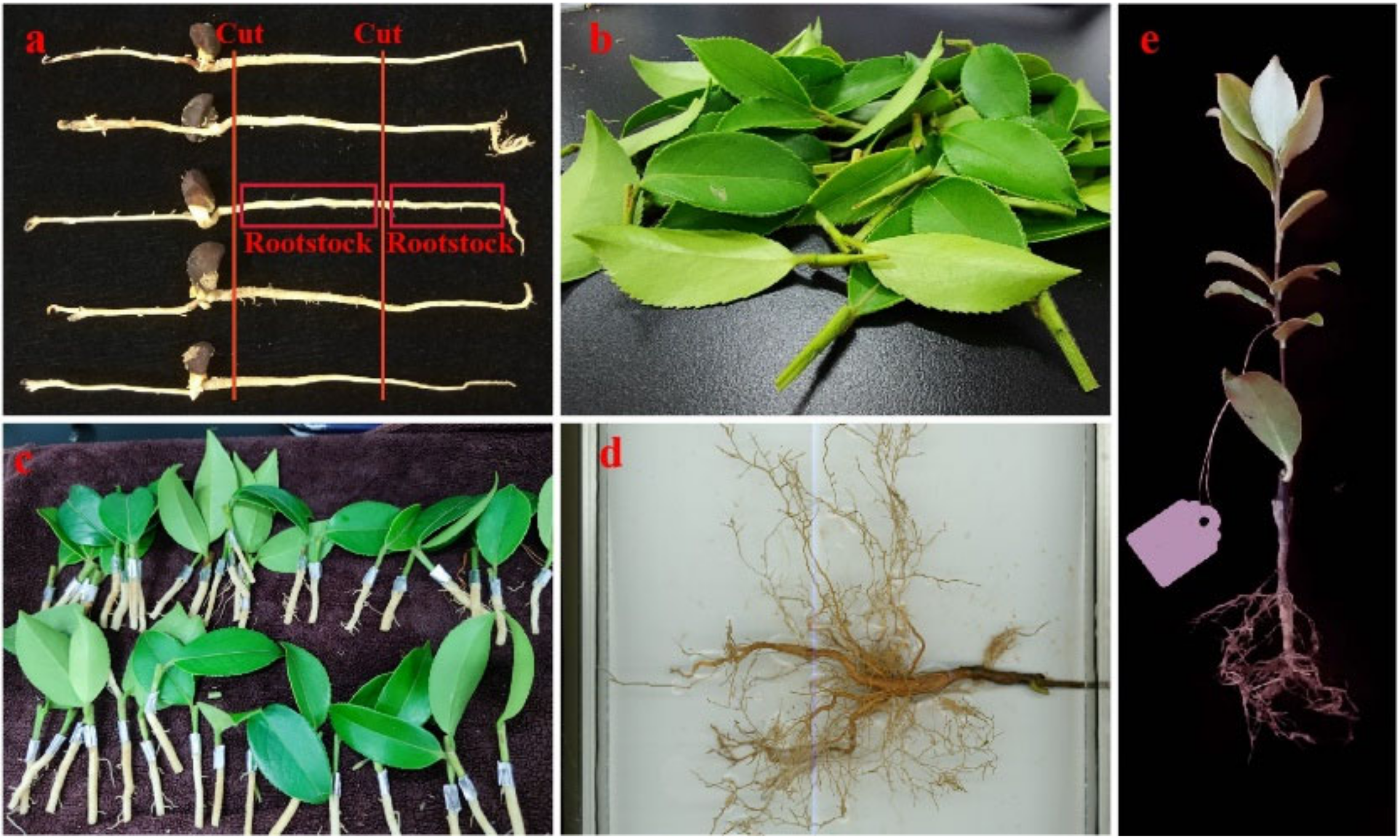
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Biomass and Tissue Phosphorus Concentration
2.4. Root Morphology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Scions Affected the Dry Weight of Grafted C. oleifera
3.2. Scions Affected Root Morphology of Grafted C. oleifera
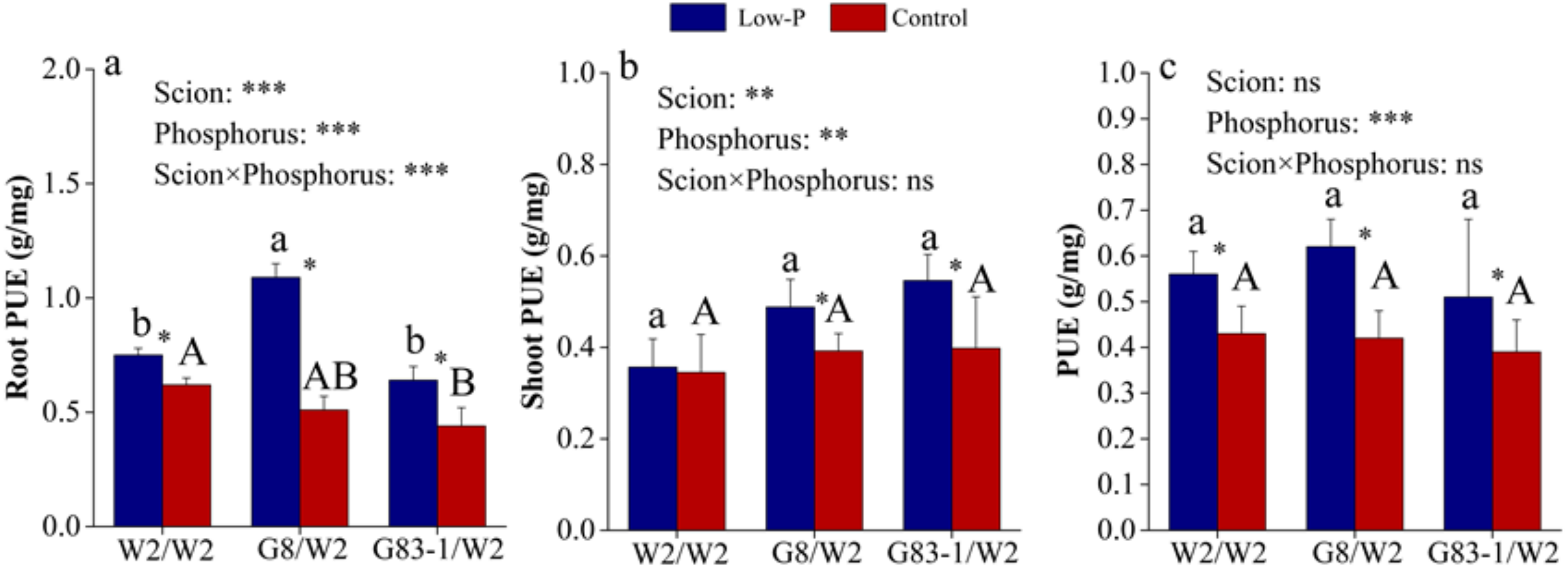
3.3. Scions Affected P Accumulation and P Utilization Efficiency (PUE) of the Root of Grafted C. oleifera
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vance, C.P.; Uhde-Stone, D. Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol. 2003, 157, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merbach, W.; Deubel, A.; Gransee, A.; Ruppel, A.S. Phosphorus solubilization in the rhizosphere and its possible importance to determine phosphate plant availability in soil. A review with main emphasis on German results. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2010, 56, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbard, L.P. Estimation of plant available phosphate in soil. Soil Sci. 1933, 35, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchenbuch, R.O.; Buczko, U. Re-visiting potassium- and phosphate-fertilizer responses in field experiments and soil-test interpretations by means of data mining. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sc. 2011, 174, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, C.R.I. Soil phosphorus: Its measurement, and its uptake by plants. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinefsky, M.J.; Assuero, S.G.; Mollier, A.S.; Pellerin, S. Analysis of the response of two tall fescue cultivars of different origin to P deficiency. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 69, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fita, A.; Nuez, F.; Picó, B. Diversity in root architecture and response to P deficiency in seedlings of Cucumis melo L. Euphytica. 2011, 181, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundim, G.B.; Viana, J.M.S.; Maia, C. Early evaluation of popcorn inbred lines for phosphorus use efficiency. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, G.; Ciotta, M.N.; Brunetto, G. ‘Fuji’ apple tree response to phosphorus fertilization. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2017, 39, 17369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonou-gbo, Z.; Djedatin, G.; Dansi, A.; Tamo, M. Screening of 134 maize genotypes collected in Benin for tolerance to phosphorus deficiency. Int. J. Curr. Res. Biosci. Plant Biol. 2017, 4, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, H.L.; Zhang, S.X. Differences of rhizosphere characteristics of two P-efficient wheat genotypes on two calcareous soils. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2009, 4, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.Y.; He, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, F.M. High Phosphorus acquisition and allocation strategy is associated with soybean seed yield under water- and P-limited conditions. Agronomy 2021, 11, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilo, S.; Odindo, A.O.; Kondwakwenda, A.; Sibiya, J. Root traits related with drought and phosphorus tolerance in common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; Zang, X.L.; Sun, L.L.; Zhai, H. Comparison of phosphorus efficiency on different rootstocks and their grafted seedlings with cabernet sauvignon. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2014, 41, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Jia, Z.M.; Wang, D.B. Effects of limited phosphorus supply on growth, root morphology and phosphorus uptake in citrus rootstocks seedlings. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, I.; Strever, A.; Myburgh, P.A.; Deloire, A. Review: The interaction between rootstocks and cultivars (Vitis vinifera L.) to enhance drought tolerance in grapevine. Aust. J. Grape Wine R. 2014, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Imtiaz, M.; Kong, Q.; Cheng, F.; Ahmed, W.; Huang, Y.; Bie, Z. Grafting: A technique to modify ion accumulation in horticultural crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautier, A.T.; Merlin, I.; Doumas, P.; Cochetel, N.; Cookson, S.J. Identifying roles of the scion and the rootstock in regulating plant development and functioning under different phosphorus supplies in grapevine. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 185, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollat, N.; Peccoux, A.; Papura, D.; Esmenjaud, D.; Marguerit, E.; Tandonnet, J.P.; Bordenave, L.; Cookson, S.J.; Barrieu, F.; Rossdeutsch, L.; et al. Rootstocks as a Component of Adaptation to Environment; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2015; pp. 68–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zambrosi, F.C.B.; Mattos, D.; Quaggio, J.A.; Cantarella, H.; Boaretto, R.M. Phosphorus uptake by young citrus trees in low-P soil depends on rootstock varieties and nutrient management. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2013, 44, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Andújar, C.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M.; Dodd, I.C.; Albacete, A.; Pérez-Alfocea, F. Hormonal and nutritional features in contrasting rootstock-mediated tomato growth under low-phosphorus nutrition. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Ai, W.; Chen, L. Plantation quality assessment of Camellia oleifera in mid-subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 186, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Zhou, J.; Masabni, J.; Yuan, J. Phosphorus relieves aluminum toxicity in oil tea seedlings by regulating the metabolic profiling in the roots. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 152, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, X. Comparative transcriptomic analysis identifies genes responsible for fruit count and oil yield in the oil tea plant Camellia chekiangoleosa. Sci. Rep. UK 2018, 8, 6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, G.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, J. Effect of aluminum toxicity and phosphorus deficiency on the growth and photosynthesis of oil tea (Camellia oleifera Abel.) seedlings in acidic red soils. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Tan, X.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, X.; Ye, S.; Zhou, J. Effect of phosphates on the growth, photosynthesis, and P content of oil tea in acidic red soils. J. Sustain. Forest. 2013, 32, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Feng, J.L.; Chen, H. Anatomical study on healing process of grafting port of Camellia oleifera seedling stock. Plant. Sci. J. 2013, 31, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.P.; Lin, W.J.; Yang, Z.J. Relationship between graft healing and endogenous hormones in Camellia oleifera seedling stock. J. Forest Environ. 2018, 38, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Liu, G.; You, L.; Yu, S.Q.; Lian, L.N.; Wang, H.K.; Yan, M.; Hu, D.N. Temporal and spatial distribution dynamics of fine roots of different Camellia oleifera varieties. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 3927–3933. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.M.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.N.; Wu, N.S.; Huang, H.N. Evaluation on fruit characters of 10 clonesof young Camellia oleifera group gan. Study on phenotypic variation and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of young trees of Gan Camellia oleifera clone. Jiangxi Agric. Univ. 2011, 33, 0906–0910. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.L.; Xing, W.N.; Lei, X.L.; Liu, S.; Yi, W.H.; Zhou, W.C.; Gong, C.; Ao, W.C.; Xu, L.C. Growth performance of one year old Camellia oleifera clones. Eco. For. R. 2009, 27, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Chen, H. Signaling pathway in development of Camellia oleifera nurse seedling grafting union. Trees 2017, 31, 1543–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.S.; Chen, Y.Z.; Yang, X.H.; Tang, L.T.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.N.; Peng, S.F. Effects of low phosphorus stress on the growth and nutrient utilization efficiency of different Camellia oleifera clones. J. Nanjing Univ. 2014, 38, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Jing, L.; Hua, B.; Liu, Z.; Bie, Z. Grafting onto different rootstocks as a means to improve watermelon tolerance to low potassium stress. Sci. Hortic-Amst. 2013, 149, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tandonnet, J.P.; Cooksoon, S.J.; Vivin, P.; Ollat, N. Scion genotype controls biomass allocation and root development in grafted grapevine. Aust. J. Grape Wine R. 2010, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, S.; Tisdall, J.M.; Tang, C.; Walker, R.R. Accumulation of potassium in grapevine rootstocks (Vitus) as affected by dry matter partitioning, root traits and transpiration. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2010, 16, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhao, X.; Liang, N.; He, L.; Yu, L.; Zhan, Y. Phosphorus deficiency promotes the lateral root growth of Fraxinus mandshurica seedlings. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sc. 2019, 182, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.; Öztekin, G.B.; Tüzel, Y.; Brückner, B.; Krumbein, A. Rootstocks can enhance tomato growth and quality characteristics at low potassium supply. Sci. Hortic. Amst. 2013, 149, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, A.; Bie, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q. Effects of scion and rootstock genotypes on the anti-oxidant defense systems of grafted cucumber seedlings under NaCl stress. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 56, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Bie, Z.; Xie, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H. Genotypic variation for potassium efficiency in wild and domesticated watermelons under ample and limited potassium supply. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sc. 2013, 176, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.T.; Hu, D.N.; You, L.; Zhong, L.S.; Shen, J.; Luo, H.D.; Meng, F.H.; Wang, X.X. Variation analysis of growth characters of 19 Camellia oleifera strains in Ganmao series. J. Jiangxi Agric. Univ. 2016, 38, 905–912. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhl, E.H. Uptake and distribution of potassium by grapevine rootstocks and its implication for grape juice pH of scion varieties. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1989, 29, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. Systemic long-distance signaling and communication between rootstock and scion in grafted vegetables. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenicano, S.; Coll, L.; Messier, C.; Berninger, F. Nitrogen forms affect root structure and water uptake in the hybrid poplar. New Forest. 2011, 42, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doi, R.; Tanikawa, T.; Miyatani, K.; Hirano, Y. Intraspecific variation in morphological traits of root branch orders in Chamaecyparis obtusa. Plant Soil 2017, 416, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Gong, L. The morphological and chemical properties of fine roots respond to nitrogen addition in a temperate Schrenk’s spruce (Picea schrenkiana) forest. Sci. Rep. UK 2021, 11, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.C.; Martin, A.R. Carbon Content of Tree Tissues: A Synthesis. Forests 2012, 3, 332–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Chen, X.; Huang, B.; Chi, G. Distribution changes of phosphorus in soil–plant systems of larch plantations across the chronosequence. Forests 2018, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Versiani, M.A.; De-Deus, G.; Dummer, P.M.H. A new system for classifying root and root canal morphology. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Placido, D.F.; Sandhu, J.; Sato, S.J.; Nersesian, N.; Quach, T.; Clemente, T.E.; Staswick, P.E.; Walia, H. The lateral root density gene regulates root growth during water stress in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, L.; Peng, L.; Lie, X.; Kuxia, Y.; Wen, W. High heterogeneity of root carbon allocation affects root turnover rate and production of bothriochloa ischaemum under drought stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 40, 226–239. [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayaka, D.; Plaxton, W.C.; Hans, L.; Meike, S.; Buddhi, M.W.; Jun, W. Molecular mechanisms underpinning phosphorus-use efficiency in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafsi, C.; Atia, A.; Lakhdar, A.; Debez, A.; Abdelly, C. Differential responses in potassium absorption and use efficiencies in the halophytes Catapodium rigidum and Hordeum maritimum to various potassium concentrations in the medium. Plant Prod. Sci. 2011, 14, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, J.B.; Tomkins, B. Chapter 13-Genotypic differences in potassium translocation in ryegrass. Transp. Transf. Process Plants 1976, 221, 145–152. [Google Scholar]


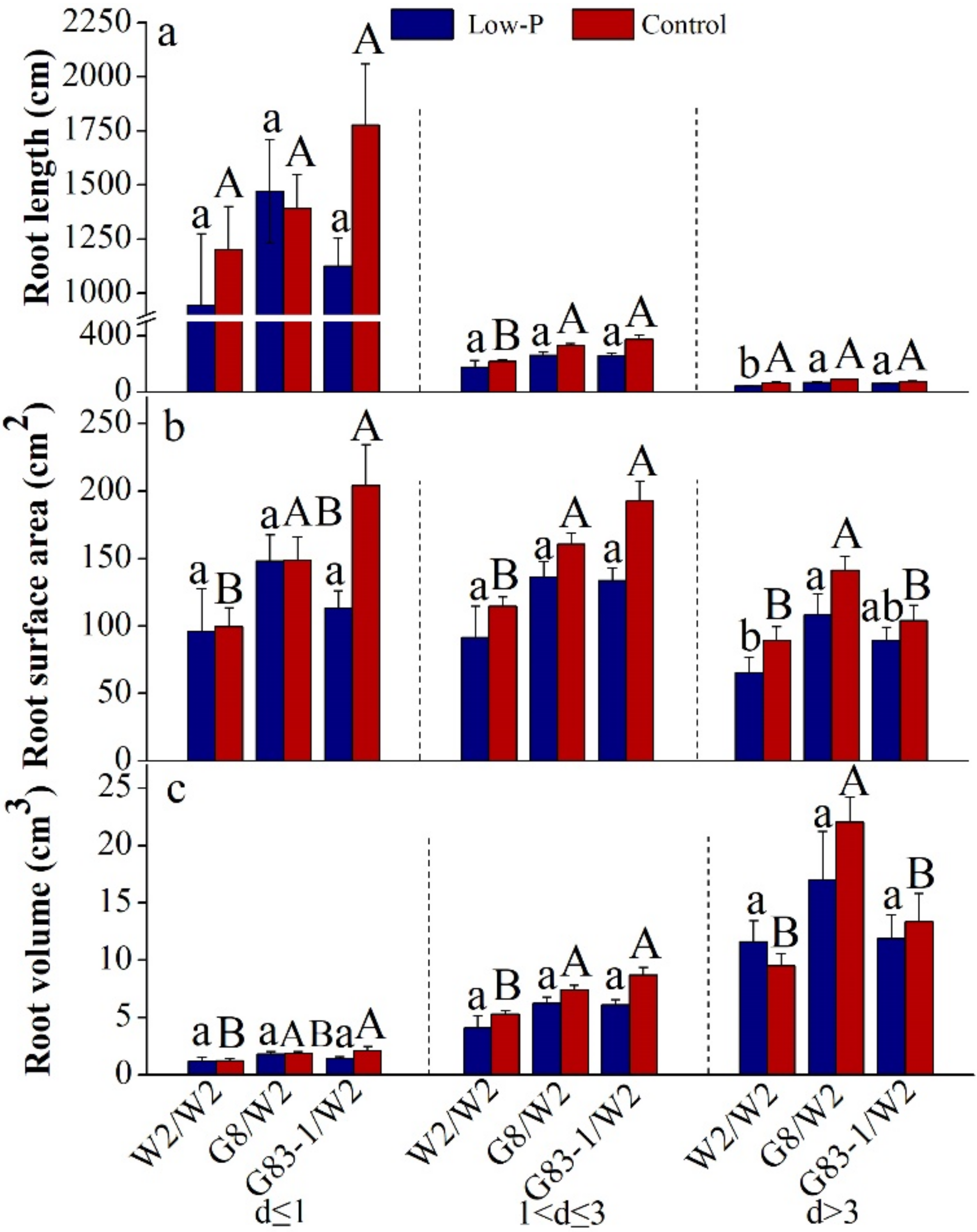
| Root Diameter (mm) | Factor | Root Length | Root Surface Area | Root Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total roots | Scion | ns | <0.01 | <0.05 |
| Phosphorus | ns | ns | ns | |
| Scion × Phosphorus | ns | ns | ns | |
| d ≤ 1 | Scion | ns | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Phosphorus | ns | ns | ns | |
| Scion × Phosphorus | ns | ns | ns | |
| 1 < d ≤ 3 | Scion | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Phosphorus | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| Scion × Phosphorus | ns | ns | ns | |
| d > 3 | Scion | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Phosphorus | <0.01 | <0.05 | ns | |
| Scion × Phosphorus | ns | ns | ns |
| Scion/Rootstock | P Availability | Root P Accumulation | Shoot P Accumulation | Plant P Uptake Efficiency | Root P Accumulation/Plant P Uptake Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mM | mg | mg | mg | % | |
| W2/W2 | Control | 3.30 ± 0.46 B | 6.70 ± 2.07 A | 10.00 ± 3.92 B | 33.00 |
| Low-P | 2.98 ± 0.36 ab | 5.74 ± 1.36 ab | 8.72 ± 2.36 a | 34.17 | |
| G8/W2 | Control | 5.03 ± 0.20 AB * | 9.82 ± 1.44 A | 14.85 ± 1.44 AB * | 33.87 |
| Low-P | 2.22 ± 0.36 b | 7.40 ± 1.68 a | 9.62 ± 2.10 a | 23.08 | |
| G83-1/W2 | Control | 7.76 ± 0.55 A * | 8.86 ± 2.96 A * | 16.62 ± 3.00 A * | 46.69 |
| Low-P | 4.27 ± 0.88 a | 3.85 ± 2.2 b | 8.12 ± 2.61 a | 52.59 | |
| Significance | |||||
| Scion (S) | ** | ** | ns | ||
| Phosphorus (P) | ** | ** | *** | ||
| S × P | ns | ns | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Liu, J.; Lian, L.; Xu, A.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Hu, D. Effects of Scion Variety on the Phosphorus Efficiency of Grafted Camellia oleifera Seedlings. Forests 2022, 13, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020203
Zeng J, Liu J, Lian L, Xu A, Guo X, Zhang L, Zhang W, Hu D. Effects of Scion Variety on the Phosphorus Efficiency of Grafted Camellia oleifera Seedlings. Forests. 2022; 13(2):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jin, Juan Liu, Lunan Lian, Aowen Xu, Xiaomin Guo, Ling Zhang, Wenyuan Zhang, and Dongnan Hu. 2022. "Effects of Scion Variety on the Phosphorus Efficiency of Grafted Camellia oleifera Seedlings" Forests 13, no. 2: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020203
APA StyleZeng, J., Liu, J., Lian, L., Xu, A., Guo, X., Zhang, L., Zhang, W., & Hu, D. (2022). Effects of Scion Variety on the Phosphorus Efficiency of Grafted Camellia oleifera Seedlings. Forests, 13(2), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020203







