Somatic Embryogenesis of Norway Spruce and Scots Pine: Possibility of Application in Modern Forestry
Abstract
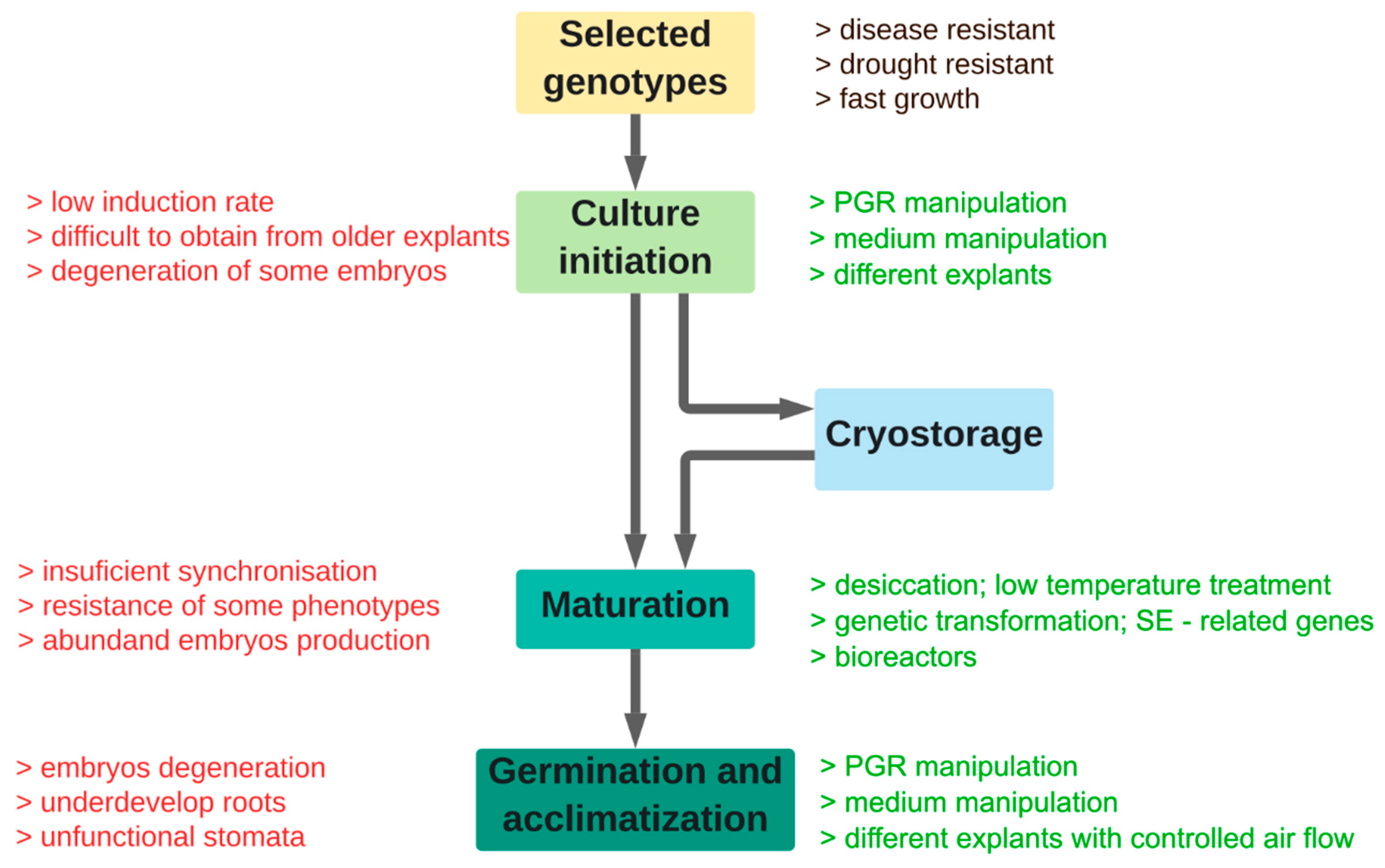
1. Introduction
2. Explants and Initiation of SE
3. Maturation of Somatic Embryos
4. Growth Conditions
4.1. Nutrients
4.2. Light
5. Germination and Acclimatization
6. SE—The Future of Forestry?
6.1. Applied Biotechnology and SE
6.2. Possibility of Automation
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture: Towards 2015/2030: An FAO Study; Earthscan Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2017; p. 431. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, W.R.J. The Need for Planted Forests and the Example of Radiata Pine. New For. 1999, 17, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintilii, R.-D.; Andronache, I.; Diaconu, D.C.; Dobrea, R.C.; Zeleňáková, M.; Fensholt, R.; Peptenatu, D.; Drăghici, C.-C.; Ciobotaru, A.-M. Using Fractal Analysis in Modeling the Dynamics of Forest Areas and Economic Impact Assessment: Maramureș County, Romania, as a Case Study. Forests 2017, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, R.J.; Reams, G.A.; Achard, F.; de Freitas, J.V.; Grainger, A.; Lindquist, E. Dynamics of Global Forest Area: Results from the FAO Global Forest Resources Assessment 2015. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 352, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, K.; Sahariah, D.; Saikia, A. Shrinking Forest and Contested Frontiers: A Case of Changing Human-Forest Interface along the Protected Areas of Nagaon District, Assam, India. Eur. J. Geogr. 2019, 10, 120–136. [Google Scholar]
- Andronache, I.; Marin, M.; Fischer, R.; Ahammer, H.; Radulovic, M.; Ciobotaru, A.-M.; Jelinek, H.F.; Di Ieva, A.; Pintilii, R.-D.; Drăghici, C.-C.; et al. Dynamics of Forest Fragmentation and Connectivity Using Particle and Fractal Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupfer, J.A.; Malanson, G.P.; Franklin, S.B. Not Seeing the Ocean for the Islands: The Mediating Influence of Matrix-Based Processes on Forest Fragmentation Effects. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2006, 15, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Georgescu, M.; Wu, J. Impacts of Landscape Changes on Local and Regional Climate: A Systematic Review. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1269–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, E.L.; de Noblet-Ducoudre, N. Climatic Impact of Global-Scale Deforestation: Radiative versus Nonradiative Processes. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, G.; Kjellström, E. Climate Impacts from Afforestation and Deforestation in Europe. Earth Interact. 2019, 23, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, C.B.; Prevedello, J.A. Does Habitat Fragmentation Affect Landscape-Level Temperatures? A Global Analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Key Concepts and Research Topics in Landscape Ecology Revisited: 30 Years after the Allerton Park workshop. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.P.; Paudel, P.K.; Jnawali, S.R.; Neupane, P.R.; Köhl, M. Can Forest Fragmentation and Configuration Work as Indicators of Human–Wildlife Conflict? Evidences from Human Death and Injury by Wildlife Attacks in Nepal. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazubska-Przybyl, T.; Bojarczuk, K. Tree Somatic Embryogenesis in Science and Forestry. Dendrobiology 2016, 76, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosvall, O. Using Norway Spruce Clones in Swedish Forestry: General Overview and Concepts. Scand. J. For. Res. 2019, 34, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Beaulieu, J.; Bousquet, J. Multi-Varietal Forestry Integrating Genomic Selection and Somatic Embryogenesis. In Vegetative Propagation of Forest Trees; Park, Y.S., Bonga, J.M., Moon, H.-K., Eds.; National Institute of Forest Science (Nifos): Seoul, Korea, 2016; pp. 302–318. [Google Scholar]
- Montwé, D.; Spiecker, H.; Hamann, A. An Experimentally Controlled Extreme Drought in a Norway Spruce Forest Reveals Fast Hydraulic Response and Subsequent Recovery of Growth Rates. Trees Struct. Funct. 2014, 28, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrøppa, T. EUFORGEN Technical Guidelines for Genetic Conservation and Use for Norway Spruce (Picea abies); International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aronen, T. From Lab to Field-Current State of Somatic Embryogenesis in Scots Pine. In Vegetative Propagation of Forest Trees; Park, Y.S., Bonga, J.M., Moon, H.-K., Eds.; National Institute of Forest Science (Nifos): Seoul, Korea, 2016; pp. 515–527. [Google Scholar]
- Hytönen, J.; Jylhä, P. Long-Term Response of Weed Control Intensity on Scots Pine Survival, Growth and Nutrition on Former Arable Land. Eur. J. For. Res. 2011, 130, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly-Wapstra, J.M.; Moore, B.D.; Brewer, M.; Beaton, J.; Sim, D.; Wiggins, N.L.; Iason, G.R. Pinus sylvestris Sapling Growth and Recovery from Mammalian Browsing. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 325, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mátyás, C.; Ackzell, L.; Samuel, C.J.A. EUFORGEN Technical Guidelines for Genetic Conservation and Use for Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris); International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kellomäki, S.; Peltola, H.; Nuutinen, T.; Korhonen, K.T.; Strandman, H. Sensitivity of Managed Boreal Forests in Finland to Climate Change, with Implications for Adaptive Management. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, N.; Bergh, J.; Johansson, U.; Nilsson, U.; Sallnäs, O. Adaptation of Forest Management Regimes in Southern Sweden to Increased Risks Associated with Climate Change. Forests 2016, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierota, Z.; Grodzki, W.; Szczepkowski, A. Abiotic and Biotic Disturbances Affecting Forest Health in Poland over the Past 30 Years: Impacts of Climate and Forest Management. Forests 2019, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyderski, M.K.; Paź, S.; Frelich, L.E.; Jagodziński, A.M. How Much Does Climate Change Threaten European Forest Tree Species Distributions? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Högberg, K.; Varis, S. Vegetative Propagation of Norway Spruce: Experiences and Present Situation in Sweden and Finland. In Vegetative Propagation of Forest Trees; Park, Y.S., Bonga, J.M., Moon, H.-K., Eds.; National Institute of Forest Science (Nifos): Seoul, Korea, 2016; pp. 528–550. [Google Scholar]
- Cyr, D.R.; Attree, S.M.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Ellis, D.D.; Polonenko, D.R.; Sutton, B.C.S. Application of Somatic Embryogenesis to Tree Improvement in Conifers. Prog. Biotechnol. 2001, 18, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu-Walter, M.-A.; Thompson, D.; Harvengt, L.; Sanchez, L.; Toribio, M.; Pâques, L.E. Somatic Embryogenesis in Forestry with a Focus on Europe: State-of-the-Art, Benefits, Challenges and Future Direction. Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egertsdotter, U. Plant Physiological and Genetical Aspects of the Somatic Embryogenesis Process in Conifers. Scand. J. For. Res. 2019, 34, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, T. Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, K.-A.; Hajek, J.; Gailis, A.; Stenvall, N.; Zarina, I.; Teivonen, S.; Aronen, T. Practical Testing of Scots Pine Cutting Propagation—A Joint Metla-Skogforsk-Silava Project; Finnish Forest Research Institute: Vantaa, Finland, 2011; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D. Challenges for the Large-Scale Propagation of Forest Trees by Somatic Embryogenesis–a Review. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference of the IUFRO Unit 2.09.02 on Woody Plant Production Integrating Genetic and Vegetative Propagation Technologies, Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bonga, J. Conifer Clonal Propagation in Tree Improvement Programs. In Vegetative Propagation of Forest Trees; Park, Y.S., Bonga, J.M., Moon, H.-K., Eds.; National Institute of Forest Science (NIFoS): Seoul, Korea, 2016; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Klimaszewska, K.; Miguel, C.; Aronen, T.; Hargreaves, C.; Teyssier, C.; Trontin, J.F. Somatic Embryogenesis for More Effective Breeding and Deployment of Improved Varieties in Pinus spp.: Bottlenecks and Recent Advances. Somat. Embryog. Fundam. AsP. Appl. 2016, 319–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toon, S.M. Somatic Embryogenesis of Lodgepole Pine (Pinus contorta) and Subalpine Larch (Larix Lyallii) for Conservation Purposes. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.S.; Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Harvenght, L.; Trontin, J.F.; MacEacheron, I.; Klimaszewska, K.; Bonga, J.M. Initiation of Somatic Embryogenesis in Pinus Banksiana, P. strobus, P. pinaster, and P. sylvestris at Three Laboratories in Canada and France. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2006, 86, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmersson, A.; von Arnold, S. Embryogenic Cell Lines of Juniperus Communis; Easy Establishment and Embryo Maturation, Limited Germination. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. PCTOC 2009, 96, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, M.; Valladares, S.; Larsson, E.; Clapham, D.; von Arnold, S. Patterning during Somatic Embryogenesis in Scots Pine in Relation to Polar Auxin Transport and Programmed Cell Death. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2012, 109, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Barrett, J.D.; Bonga, J.M. Application of Somatic Embryogenesis in High-Value Clonal Forestry: Deployment, Genetic Control, and Stability of Cryopreserved Clones. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1998, 34, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazubska-Przybył, T.; Ratajczak, E.; Obarska, A.; Pers-Kamczyc, E. Different Roles of Auxins in Somatic Embryogenesis Efficiency in Two Picea Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Cyr, D.R. Conifer Somatic Embryogenesis: I. Development. Dendrobiology 2002, 48, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.-Y.; Thorpe, T.A. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plantlet Regeneration in Cultured Immature Embryos of Picea glauca. J. Plant Physiol. 1987, 128, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramarosandratana, A.V.; Van Staden, J. Tissue Position, Explant Orientation and Naphthaleneacetic Acid (NAA) Affect Initiation of Somatic Embryos and Callus Proliferation in Norway Spruce (Picea abies). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2003, 74, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Overton, C.; Stewart, D.; Rutledge, R.G. Initiation of Somatic Embryos and Regeneration of Plants from Primordial Shoots of 10-Year-Old Somatic White Spruce and Expression Profiles of 11 Genes Followed during the Tissue Culture Process. Planta 2011, 233, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varis, S.; Klimaszewska, K.; Aronen, T. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration from Primordial Shoot Explants of Picea abies (L.) H. Karst. Somatic Trees. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaud, J.-N.; Bercetche, J.; Pâques, M. First Evidence of Somatic Embryogenesis from Needles of 1-Year-Old Picea Abies Plants. Plant Cell ReP. 1992, 11, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, R.G.; Stewart, D.; Caron, S.; Overton, C.; Boyle, B.; MacKay, J.; Klimaszewska, K. Potential Link between Biotic Defense Activation and Recalcitrance to Induction of Somatic Embryogenesis in Shoot Primordia from Adult Trees of White Spruce (Picea glauca). BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronen, T.; Virta, S.; Varis, S. Telomere Length in Norway Spruce during Somatic Embryogenesis and Cryopreservation. Plants 2021, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatelain, M.; Drobniak, S.M.; Szulkin, M. The Association between Stressors and Telomeres in Non-Human Vertebrates: A Meta-Analysis. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keinonen–Mettälä, K.; Jalonen, P.; Eurola, P.; von Arnold, S.; von Weissenberg, K. Somatic Embryogenesis of Pinus sylvestris. Scand. J. For. Res. 1996, 11, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu-Walter, M.-A.; Bernier-Cardou, M.; Klimaszewska, K. Clonal Plant Production from Self- and Cross-Pollinated Seed Families of Pinus sylvestris (L.) through Somatic Embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2008, 92, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xia, X.-R.; Ke, X.; Ye, J.; Zhu, L.-H. Somatic Embryogenesis in Slash Pine (Pinus elliottii Engelm): Improving Initiation of Embryogenic Tissues and Maturation of Somatic Embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 143, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Gao, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Yang, L. Optimization of Maturation Process for Somatic Embryo Production and Cryopreservation of Embryogenic Tissue in Pinus koraiensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2021, 144, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu, M.-A.; Bastien, C.; Drugeault, A.; Gouez, M.-L.; Klimaszewska, K. Somatic Embryogenesis and Plantlet Development in Pinus sylvestris and Pinus pinaster on Medium with and without Growth Regulators. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 105, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohtola, A. Somatic Embryogenesis in Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). In Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants. Forestry Sciences; Jain, S.M., Gupta, P.K., Newton, R.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; Volume 44–46, pp. 269–285. [Google Scholar]
- Aronen, T.; Pehkonen, T.; Ryynänen, L. Enhancement of Somatic Embryogenesis from Immature Zygotic Embryos of Pinus sylvestris. Scand. J. For. Res. 2009, 24, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niskanen, A.-M.; Lu, J.; Seitz, S.; Keinonen, K.; Von Weissenberg, K.; Pappinen, A. Effect of Parent Genotype on Somatic Embryogenesis in Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris). Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trontin, J.F.; Aronen, T.; Hargreaves, C.; Montalbán, I.A.; Reeves, C.; Quoniou, S.; Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Klimaszewska, K. International Effort to Induce Somatic Embryogenesis in Adult Pine Trees. In Vegetative Propagation of Forest Trees; Park, Y.S., Bonga, J.M., Moon, H.-K., Eds.; National Institute of Forest Science (Nifos): Seoul, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson, M.; Valladares, S.; Merino, I.; Larsson, E.; von Arnold, S. Degeneration Pattern in Somatic Embryos of Pinus sylvestris L. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2017, 53, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, I.; Abrahamsson, M.; Larsson, E.; von Arnold, S. Identification of Molecular Processes That Differ among Scots Pine Somatic Embryogenic Cell Lines Leading to the Development of Normal or Abnormal Cotyledonary Embryos. Tree Genet. Genomes 2018, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varis, S.; Tikkinen, M.; Välimäki, S.; Aronen, T. Light Spectra during Somatic Embryogenesis of Norway Spruce—Impact on Growth, Embryo Productivity, and Embling Survival. Forests 2021, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonova, L.H.; Bozhkov, P.V.; Brukhin, V.B.; Daniel, G.; Zhivotovsky, B.; von Arnold, S. Two waves of programmed cell death occur during formation and development of somatic embryos in the gymnosperm, Norway spruce. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 4399–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaj, T.; Blehová, A.; Salaj, J. Embryogenic Suspension Cultures of Pinus Nigra Arn.: Growth Parameters and Maturation Ability. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2007, 29, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahrendorf, J.; Clapham, D.; Egertsdotter, U. Analysis of Nitrogen Utilization Capability during the Proliferation and Maturation Phases of Norway Spruce (Picea abies (L.) H. Karst.) Somatic Embryogenesis. Forests 2018, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.V.; Eriksson, T. In vitro Studies of Adventitious Shoot Formation in Pinus contorta. Can. J. Bot. 1981, 59, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvay, J.D.; Verma, D.C.; Johnson, M.A. Influence of a Loblolly Pine (Pinus taeda L.). Culture Medium and Its Components on Growth and Somatic Embryogenesis of the Wild Carrot (Daucus carota L.). Plant Cell Rep. 1985, 4, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.K.; Durzan, D.J. Shoot Multiplication from Mature Trees of Douglas-Fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) and Sugar Pine (Pinus lambertiana). Plant Cell ReP. 1985, 4, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becwar, M.R.; Nagmani, R.; Wann, S.R. Initiation of Embryogenic Cultures and Somatic Embryo Development in Loblolly Pine (Pinus taeda). Can. J. For. Res. 1990, 20, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith. Growth Medium. U.S. Patent 5,565,355, 15 October 1996.
- Teasdale, R.; Buxton, P.A. Culture of Pinus radiata embryos with reference to artificial seed production. NZJ For. Sci. 1986, 16, 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Montalbán, I.A.; Setién-Olarra, A.; Hargreaves, C.L.; Moncaleán, P. Somatic Embryogenesis in Pinus halepensis Mill.: An Important Ecological Species from the Mediterranean Forest. Trees 2013, 27, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaj, T.; Klubicová, K.; Matusova, R.; Salaj, J. Somatic Embryogenesis in Selected Conifer Trees Pinus nigra Arn. And Abies Hybrids. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mendiguren, O.; Montalbán, I.A.; Goicoa, T.; Ugarte, M.D.; Moncaleán, P. Environmental Conditions at the Initial Stages of Pinus radiata Somatic Embryogenesis Affect the Production of Somatic Embryos. Trees Struct. Funct. 2016, 30, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, I.A.; García-Mendiguren, O.; Goicoa, T.; Ugarte, M.D.; Moncaleán, P. Cold Storage of Initial Plant Material Affects Positively Somatic Embryogenesis in Pinus radiata. New For. 2015, 46, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Peng, C.; Wang, H.; Tretyakova, I.N.; Nosov, A.M.; Shen, H.; Yang, L. Key Techniques for Somatic Embryogenesis and Plant Regeneration of Pinus koraiensis. Forests 2020, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malabadi, R.B.; Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Nataraja, K. Salic Acid Induces Somatic Embryogenesis from Mature Trees of Pinus roxburghii (Chir Pine) Using TCL Technology. In Tree Forest Science and Biotechnology; Global Science Books Ltd: East Sussex, UK; Ikanobe: Takamatsu, Japan, 2008; pp. 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kocsy, G.; Tari, I.; Vanková, R.; Zechmann, B.; Gulyás, Z.; Poór, P.; Galiba, G. Redox Control of Plant Growth and Development. Plant Sci. 2013, 211, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonova, L.H.; Bozhkov, P.V.; Von Arnold, S. Developmental Pathway of Somatic Embryogenesis in Picea Abies as Revealed by Time-Lapse Tracking. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudec, L.; Konrádová, H.; Hašková, A.; Lipavská, H. Norway Spruce Embryogenesis: Changes in Carbohydrate Profile, Structural Development and Response to Polyethylene Glycol. Tree Physiol. 2016, 36, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, L.; Tremblay, F.M. Carbohydrate Requirements for the Development of Black Spruce (Picea Mariana (Mill.) B.S.P.) and Red Spruce (P. rubens Sarg.) Somatic Embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1991, 27, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Yi, S. Somatic Embryogenesis in Mature Zygotic Embryos of Picea likiangensis. Biologia 2010, 65, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasolla, C.; Yeung, E.C. Recent Advances in Conifer Somatic Embryogenesis: Improving Somatic Embryo Quality. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2003, 74, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazubska-Przybył, T.; Wawrzyniak, M. Stimulation of Somatic Embryo Growth and Development in Picea spp. by Polyethylene Glycol. Dendrobiology 2017, 78, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stasolla, C. The Effect of Reduced Glutathione on Morphology and Gene Expression of White Spruce (Picea glauca) Somatic Embryos. J. ExP. Bot. 2004, 55, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.E. The Effect of Temperature on Conversion of White Spruce Somatic Embryos. Propag Ornam Plants 2005, 5, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Tikkinen, M.; Varis, S.; Peltola, H.; Aronen, T. Improved Germination Conditions for Norway Spruce Somatic Cotyledonary Embryos Increased Survival and Height Growth of Emblings. Trees 2018, 32, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varis, S.; Ahola, S.; Jaakola, L.; Aronen, T. Reliable and Practical Methods for Cryopreservation of Embryogenic Cultures and Cold Storage of Somatic Embryos of Norway Spruce. Cryobiology 2017, 76, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, I.A.; De Diego, N.; Moncaleán, P. Bottlenecks in Pinus radiata Somatic Embryogenesis: Improving Maturation and Germination. Trees Struct. Funct. 2010, 24, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, H.M.; Sarjala, T.; Jokela, A.; Häggman, H.; Vuosku, J. Moderate Stress Responses and Specific Changes in Polyamine Metabolism Characterize Scots Pine Somatic Embryogenesis. Tree Physiol. 2016, 36, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakau, U.-K.; Liesebach, M.; Aronen, T.; Lelu-Walter, M.-A.; Schneck, V. Scots Pine (Pinus Sylvestris L.). In Forest Tree Breeding in Europe: Current State-of-the-Art and Perspectives; Pâques, L.E., Ed.; Managing Forest Ecosystems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 267–323. ISBN 978-94-007-6146-9. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, J.; Egertsdotter, U.; Ganeteg, U.; Svennerstam, H. Nitrogen Utilization during Germination of Somatic Embryos of Norway Spruce: Revealing the Importance of Supplied Glutamine for Nitrogen Metabolism. Trees Struct. Funct. 2019, 33, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llebrés, M.T.; Avila, C.; Cánovas, F.M.; Klimaszewska, K. Root Growth of Somatic Plants of Hybrid Pinus strobus (L.) and P. wallichiana (A. B. Jacks.) Is Affected by the Nitrogen Composition of the Somatic Embryo Germination Medium. Trees Struct. Funct. 2018, 32, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhkov, P.V.; Mikhlina, S.B.; Shiryaeva, G.A.; Lebedenko, L.A. Influence of Nitrogen Balance of Culture Medium on Norway Spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst] Somatic Polyembryogenesis: High Frequency Establishment of Embryonal-Suspensor Mass Lines from Mature Zygotic Embryos. J. Plant Physiol. 1993, 142, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.D.; Park, Y.S.; Bonga, J.M. The Effectiveness of Various Nitrogen Sources in White Spruce [Picea glauca (Moench) Voss] Somatic Embryogenesis. Plant Cell ReP. 1997, 16, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, J.; Svennerstam, H.; Moritz, T.; Egertsdotter, U.; Ganeteg, U. Nitrogen Uptake and Assimilation in Proliferating Embryogenic Cultures of Norway Spruce—Investigating the Specific Role of Glutamine. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.; Hu, L.; Yuan, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, W.; He, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis between Somatic Embryos (SEs) and Zygotic Embryos in Cotton: Evidence for Stress Response Functions in SE Development. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nic-Can, G.I.; Avilez-Montalvo, J.R.; Aviles-Montalvo, R.N.; Márquez-López, R.E.; Mellado-Mojica, E.; Galaz-Ávalos, R.M.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. The Relationship between Stress and Somatic Embryogenesis. In Somatic Embryogenesis: Fundamental Aspects and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 121–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-G.; Han, S.-Y.; Yang, W.-H.; Wei, H.-L.; Zhang, M.; Qi, L.-W. Changes in H2O2 Content and Antioxidant Enzyme Gene Expression during the Somatic Embryogenesis of Larix leptolepis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2010, 100, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salajova, T.; Salaj, J.; Kormutak, A. Initiation of Embryogenic Tissues and Plantlet Regeneration from Somatic Embryos of Pinus nigra Arn. Plant Sci. 1999, 145, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvaalen, H.; Appelgren, M. Light Quality Influences Germination, Root Growth and Hypocotyl Elongation in Somatic Embryos but Not in Seedlings of Norway Spruce. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1999, 35, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latkowska, M.J.; Kvaalen, H.; Appelgren, M. Genotype Dependent Blue and Red Light Inhibition of the Proliferation of the Embryogenic Tissue of Norway Spruce. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2000, 36, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, S.A.; Montello, P.M.; Xia, X.; Upchurch, B.L.; Smith, D.R. Light Quality Treatments Enhance Somatic Seedling Production in Three Southern Pine Species. Tree Physiol. 2006, 26, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbán, I.A.; Moncaleán, P. Rooting of Pinus radiata Somatic Embryos: Factors Involved in the Success of the Process. J. For. Res. 2019, 1, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonga, J.M.; Klimaszewska, K.K.; von Aderkas, P. Recalcitrance in Clonal Propagation, in Particular of Conifers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. PCTOC 2010, 100, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, M.F.; Yeung, E.C. The Effects of Reduced and Oxidized Glutathione on White Spruce Somatic Embryogenesis. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2004, 40, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullman, G.S.; Zeng, X.; Copeland-Kamp, B.; Crockett, J.; Lucrezi, J.; May, S.W.; Bucalo, K. Conifer Somatic Embryogenesis: Improvements by Supplementation of Medium with Oxidation-Reduction Agents. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, T.E.; Hosoi, Y. Progress in Somatic Embryogenesis of Japanese Pines. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Chavez, A.; Flinn, B.S.; Egertsdotter, U. Initiation of Somatic Embryogenesis from Immature Zygotic Embryos of Oocarpa Pine (Pinus oocarpa Schiede Ex Schlectendal). Tree Physiol. 2011, 31, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.K.; Amerson, H.V. Slash Pine (Pinus elliottii Engelm.) Somatic Embryogenesis I. Initiation of Embryogenic Cultures from Immature Zygotic Embryos. New For. 1995, 10, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.K.; Juan, I.-P. Improving the Germination of Somatic Embryos of Picea morrisonicola Hayata: Effects of Cold Storage and Partial Drying. J. For. Res. 2015, 20, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullman, G.S.; Olson, K.; Fischer, T.; Egertsdotter, U.; Frampton, J.; Bucalo, K. Fraser Fir Somatic Embryogenesis: High Frequency Initiation, Maintenance, Embryo Development, Germination and Cryopreservation. New For. 2016, 47, 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.A.; Gella, R.; Herrero, M. Stomatal Structure and Functioning as a Response to Environmental Changes in Acclimatized Micropropagated Prunus cerasus L. Ann. Bot. 1988, 62, 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Pospóšilová, J.; Tichá, I.; Kadleček, P.; Haisel, D.; Plzáková, Š. Acclimatization of Micropropagated Plants to Ex Vitro Conditions. Biol. Plant. 1999, 42, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Bandopadhyay, R.; Kumar, V.; Chandra, R. Acclimatization of Tissue Cultured Plantlets: From Laboratory to Land. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragonezi, C.; Caldeira, A.T.; Martins, M.R.; Dias, L.S.; Santos-Silva, C.; Ganhão, E.; Miralto, O.; Pereira, I.; Louro, R.; Klimaszewska, K.; et al. Pisolithus arhizus (Scop.) Rauschert Improves Growth of Adventitious Roots and Acclimatization of in vitro Regenerated Plantlets of Pinus pinea L. Propag. Ornam. Plants 2012, 12, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Jayawickrama, K.J.S.; Carson, M.J. A Breeding Strategy for the New Zealand Radiata Pine Breeding Cooperative. Silvae Genet. Ger. 2000, 49, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dungey, H.S.; Brawner, J.T.; Burger, F.; Carson, M.; Henson, M.; Jefferson, P.; Matheson, A.C. A New Breeding Strategy for Pinus Radiata in New Zealand and New South Wales. Silvae Genet. 2009, 58, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.H.; Park, Y.S.; Krasowski, M.J.; Mullin, T.J. Allocation of Varietal Testing Efforst for Implementing Conifer Multi-Varietal Forestry Using White Spruce as a Model Species. Ann. For. Sci. 2011, 68, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, Y.-S. Implementation of Conifer Somatic Embryogenesis in Clonal Forestry: Technical Requirements and Deployment Considerations. Ann. For. Sci. 2002, 59, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomion, C.; Bastien, C.; Bogeat-Triboulot, M.-B.; Bouffier, L.; Déjardin, A.; Duplessis, S.; Fady, B.; Heuertz, M.; Le Gac, A.-L.; Le Provost, G.; et al. Forest Tree Genomics: 10 Achievements from the Past 10 Years and Future Prospects. Ann. For. Sci. 2016, 73, 77–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltunis, B.S.; Wu, H.X.; Dungey, H.S.; Mullin, T.J.; Brawner, J.T. Comparisons of Genetic Parameters and Clonal Value Predictions from Clonal Trials and Seedling Base Population Trials of Radiata Pine. Tree Genet. Genomes 2009, 5, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danell, Ö. Breeding Programmes in Sweden. General Approach. In Proceedings of the Progeny Testing and Breeding Strategies. Proceedings from a Meeting with the Nordic Group for Tree Breeding, Edinburg, UK, 6–10 October 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rosvall, O. Review of the Swedish Tree Breeding Program. Skogforsk Upps. Swed. 2011, 4–37. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, G.; Hansen, J.K.; Haapanen, M.; Kvaalen, H.; Steffenrem, A. The Genetic and Economic Gains from Forest Tree Breeding Programmes in Scandinavia and Finland. Scand. J. For. Res. 2017, 32, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Find, J.I.; Charity, J.A.; Grace, L.J.; Kristensen, M.M.M.H.; Krogstrup, P.; Walter, C. Stable genetic transformation of embryogenic cultures of Abies nordmanniana (Nordmann fir) and regeneration of transgenic plants. In vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2005, 41, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.C.; Shyamkumar, B.; Anjaneyulu, C. Progress in tissue culture, genetic transformation and applications of biotechnology to trees: An overview. Trees Struct. Funct. 2004, 18, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-L.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Yan, J.-D.; Gao, Y.-R.; Li, X.-W.; Sun, J.-C.; Fang, K.-F.; Zhang, Q.; Xing, Y.; et al. Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2020, 140, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereso, S.; Miguel, C.; Zoglauer, K.; Valle-Piquera, C.; Oliveira, M.M. Stable Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic tissues from Pinus pinaster Portuguese genotypes. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 50, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Kher, M.M.; Soner, D.; Page, T.; Zhang, X.; Nataraj, M.; Ma, G. Sandalwood: Basic biology, tissue culture, and genetic transformation. Planta 2016, 243, 847–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, L.; Fernandes, P.; Oakes, A.; Stewart, K.; Powell, W. Transformation of American chestnut (Castanea dentata (marsh.) borkh) using Rita® temporary immersion bioreactors and in vitro containers. Forests 2020, 11, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska, K.; Lachance, D.; Pelletier, G.; Lelu, M.-A.; Séguin, A. Regeneration of transgenic Picea glauca, P. mariana, and P. abies after cocultivation of embryogenic tissue with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. In Vitro Cell.-Dev. Biol.-Plant 2001, 37, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenck, R.A.; Quinn, M.; Whetten, R.W.; Pullman, G.; Sederoff, R. High-efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and loblolly pine (Pinus taeda). Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 39, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, C.; Grace, L.J.; Donaldson, S.S.; Moody, J.; Gemmell, J.E.; van der Maas, S.; Kvaalen, H.; Lönneborg, A. An efficient Biolistic® transformation protocol for Picea abies embryogenic tissue and regeneration of transgenic plants. Can. J. For. Res. 1999, 29, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavingerová, D.; Bříza, J.; Niedermeierová, H.; Vlasák, J. Stable Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Norway spruce embryogenic tissues using somatic embryo explants. J. For. Sci. 2011, 57, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bříza, J.; Pavingerová, D.; Vlasák, J.; Niedermeierová, H. Norway spruce (Picea abies) genetic transformation with modified Cry3A gene of Bacillus thuringiensis. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2013, 60, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadenbäck, J.; Von Arnold, S.; Egertsdotter, U.; Walter, M.H.; Grima-Pettenati, J.; Goffner, D.; Gellerstedt, G.; Gullion, T.; Clapham, D. Lignin biosynthesis in transgenic Norway spruce plants harboring an antisense construct for cinnamoyl CoA reductase (CCR). Transgenic Res. 2008, 17, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggman, H.M.; Aronen, T.S.; Nikkanen, T.O. Gene transfer by particle bombardment to Norway spruce and Scots pine pollen. Can. J. For. Res. 1997, 27, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronen, T.S.; Nikkanen, T.O.; Häggman, H.M. The Production of Transgenic Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) via the Application of Transformed Pollen in Controlled Crossings. Transgenic Res. 2003, 12, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, L.J.; Charity, J.A.; Gresham, B.; Kay, N.; Walter, C. Insect-resistant transgenic Pinus radiata. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.M.; Ordás, R.J. Stable Agrobacterium -mediated transformation of maritime pine based on kanamycin selection. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 681792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamun, N.H.A.; Egertsdotter, U.; Aidun, C.K. Bioreactor Technology for Clonal Propagation of Plants and Metabolite Production. Front. Biol. 2015, 10, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egertsdotter, U.; Ahmad, I.; Clapham, D. Automation and Scale Up of Somatic Embryogenesis for Commercial Plant Production, With Emphasis on Conifers. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aidun, C.K.; Egertsdotter, U. SE Fluidics System. In Step Wise Protocols for Somatic Embryogenesis of Important Woody Plants.; Jain, S.M., Gupta, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume I, pp. 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Businge, E.; Trifonova, A.; Schneider, C.; Rödel, P.; Egertsdotter, U. Evaluation of a New Temporary Immersion Bioreactor System for Micropropagation of Cultivars of Eucalyptus, Birch and Fir. Forests 2017, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, F.; Varis, S.; Aronen, T.S. From Petri Dishes to Bioreactors—First Experiences on Optimization of Norway Spruce SE-Process for Bioreactors. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of the IUFRO Unit 2.09.02. on Development and Application of Vegetative Propagation Technologies in Plantation Forestry to Cope with a Changing Climate and Environment, La Plata, Argentina, 19–23 September 2016; pp. 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Välimäki, S.; Paavilainen, L.; Tikkinen, M.; Salonen, F.; Varis, S.; Aronen, T. Production of Norway Spruce Embryos in a Temporary Immersion System (TIS). Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2020, 56, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoeup, P.K.; Chakrabarty, D. Micropropagation of Woody Plants Using Bioreactor. In Micropropagation of Woody Trees and Fruits; Jain, S.M., Ishii, K., Eds.; Forestry Sciences; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 735–755. ISBN 978-94-010-0125-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, N.H.A.; Aidun, C.K.; Egertsdotter, U. Improved and Synchronized Maturation of Norway Spruce (Picea abies (L.) H. Karst.) Somatic Embryos in Temporary Immersion Bioreactors. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2018, 54, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.-C.; Weerasekara, A.B.; Ranade, S.S.; Egertsdotter, E.-M.U. Evaluation of Parameters to Characterize Germination-Competent Mature Somatic Embryos of Norway Spruce (Picea abies). Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 203, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hazubska-Przybył, T.; Wawrzyniak, M.K.; Kijowska-Oberc, J.; Staszak, A.M.; Ratajczak, E. Somatic Embryogenesis of Norway Spruce and Scots Pine: Possibility of Application in Modern Forestry. Forests 2022, 13, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020155
Hazubska-Przybył T, Wawrzyniak MK, Kijowska-Oberc J, Staszak AM, Ratajczak E. Somatic Embryogenesis of Norway Spruce and Scots Pine: Possibility of Application in Modern Forestry. Forests. 2022; 13(2):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020155
Chicago/Turabian StyleHazubska-Przybył, Teresa, Mikołaj Krzysztof Wawrzyniak, Joanna Kijowska-Oberc, Aleksandra Maria Staszak, and Ewelina Ratajczak. 2022. "Somatic Embryogenesis of Norway Spruce and Scots Pine: Possibility of Application in Modern Forestry" Forests 13, no. 2: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020155
APA StyleHazubska-Przybył, T., Wawrzyniak, M. K., Kijowska-Oberc, J., Staszak, A. M., & Ratajczak, E. (2022). Somatic Embryogenesis of Norway Spruce and Scots Pine: Possibility of Application in Modern Forestry. Forests, 13(2), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020155





