Understanding 34 Years of Forest Cover Dynamics across the Paraguayan Chaco: Characterizing Annual Changes and Forest Fragmentation Levels between 1987 and 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- evaluate annual forest cover changes of the Paraguayan Chaco between 1987 and 2020;
- study the effectiveness of protected areas and natural reserves;
- evaluate the degree of fragmentation of the Paraguayan Chaco, with a special emphasis on forest conservation
2. Materials and Methods
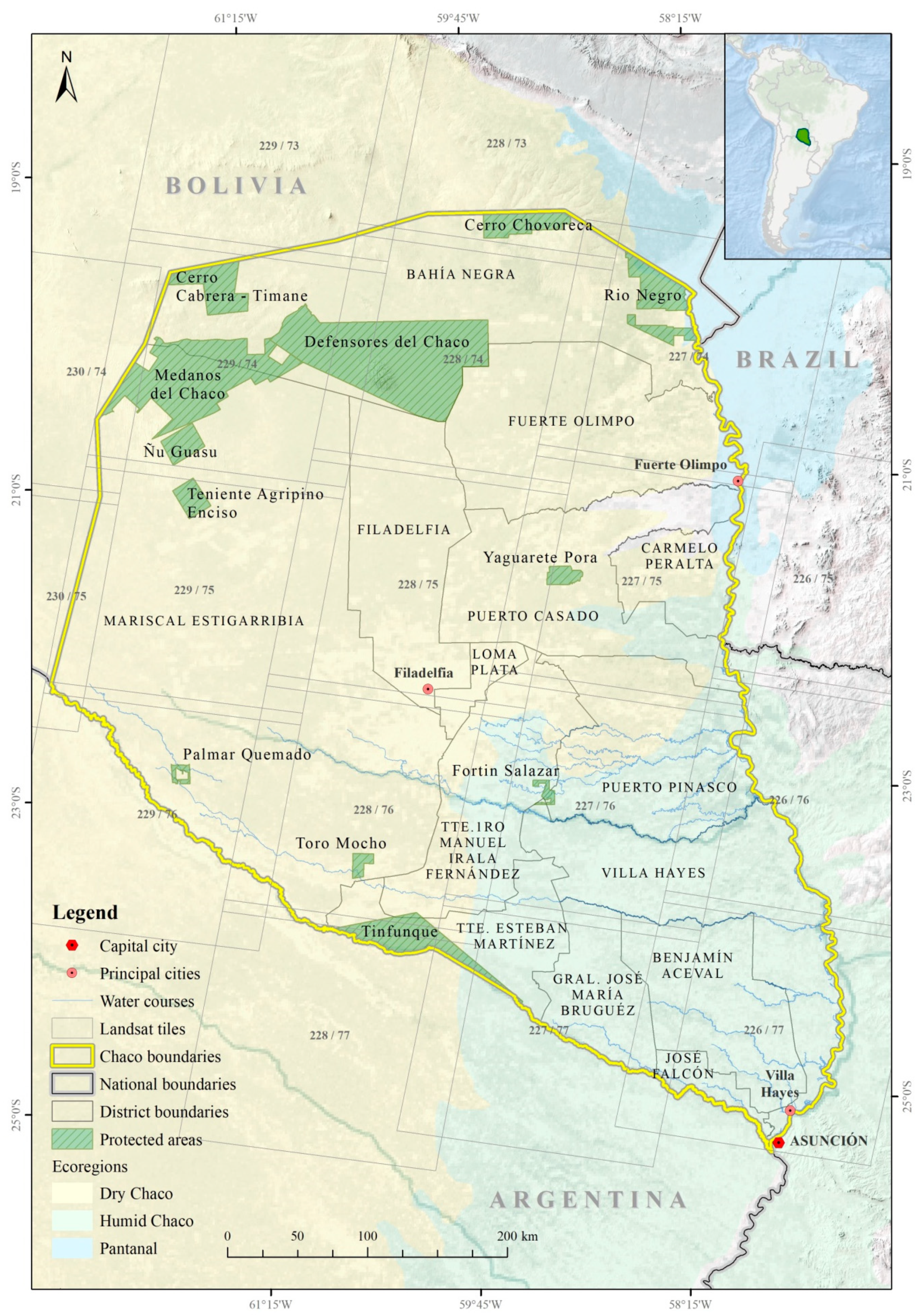
2.1. Study Area
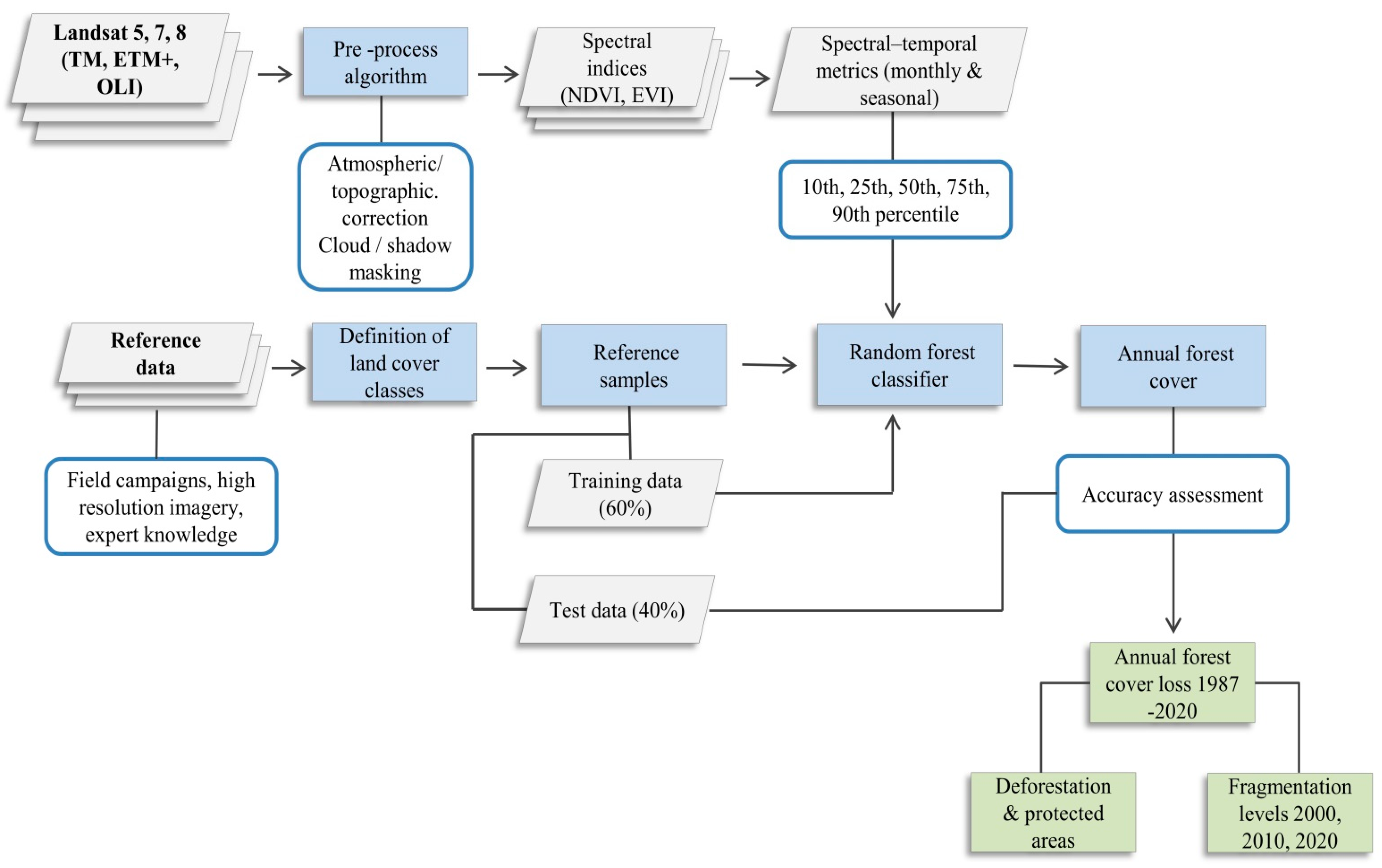
2.2. Image Acquisition and Pre-Processing
2.3. Spectral-Temporal Landsat Time-Series Metrics
2.4. Estimation of Annual Forest Cover between 1987 and 2020
2.5. Fragmentation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Forest-Mask Classification Accuracy
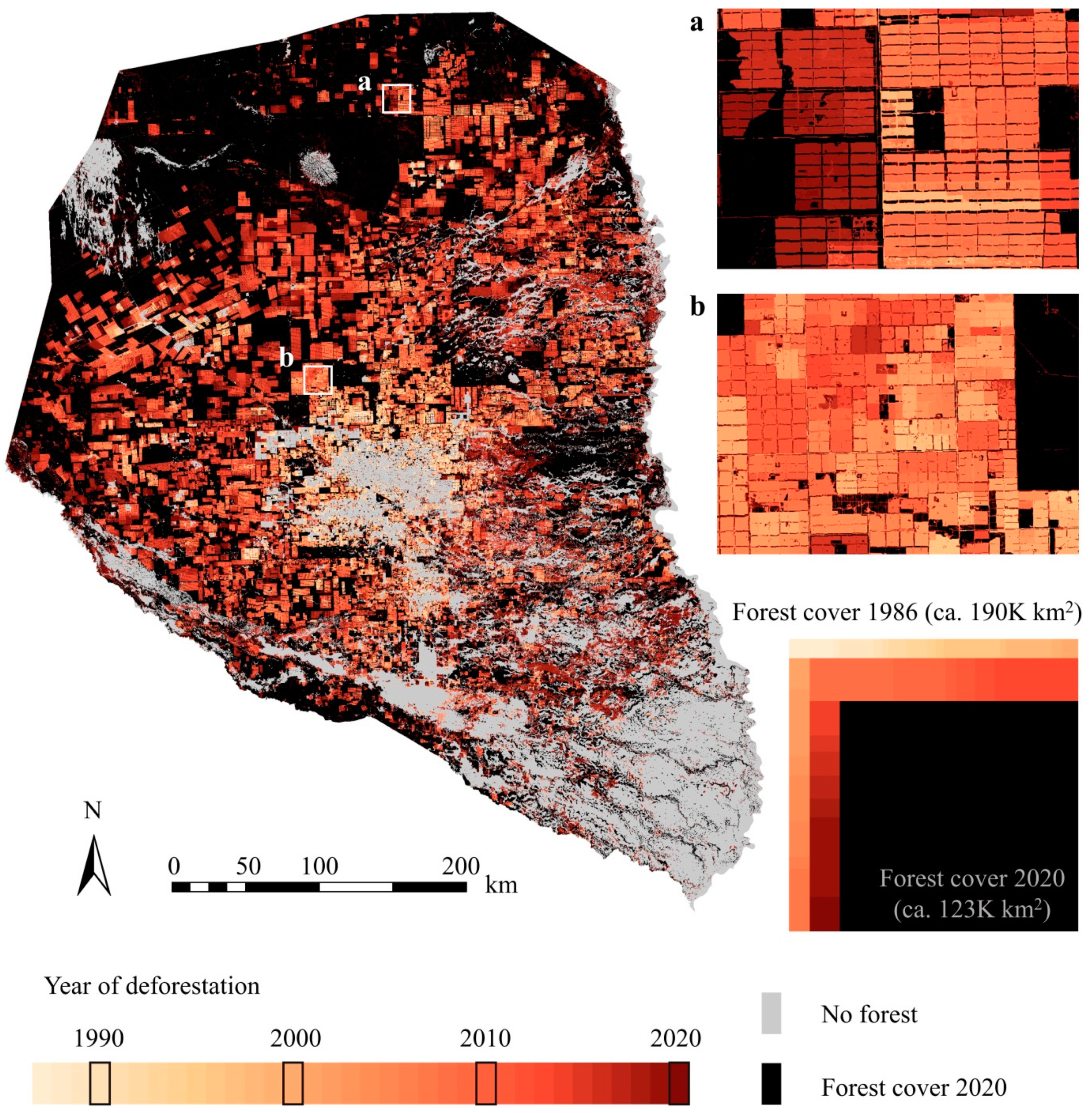
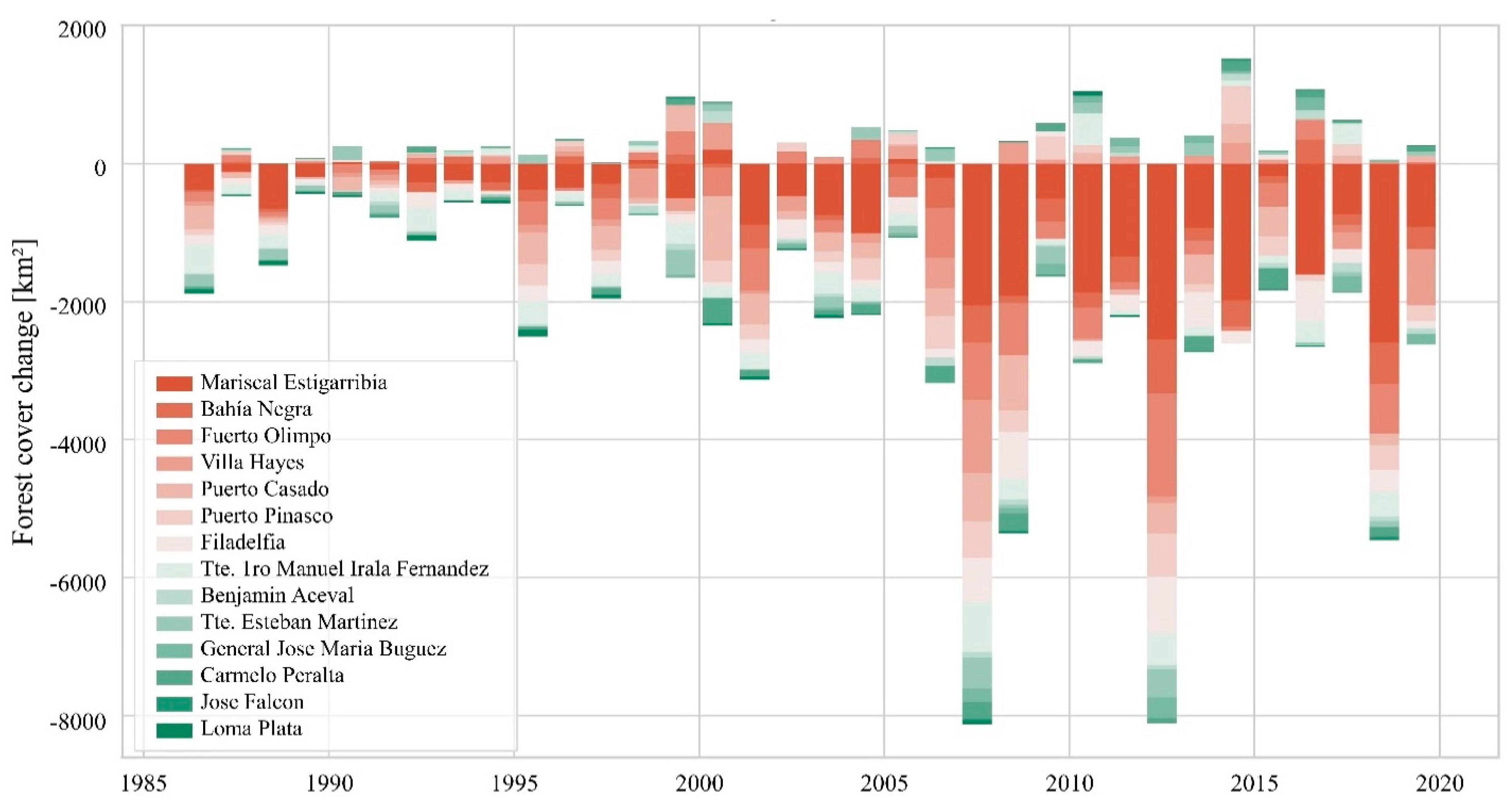
3.2. Deforestation Rates
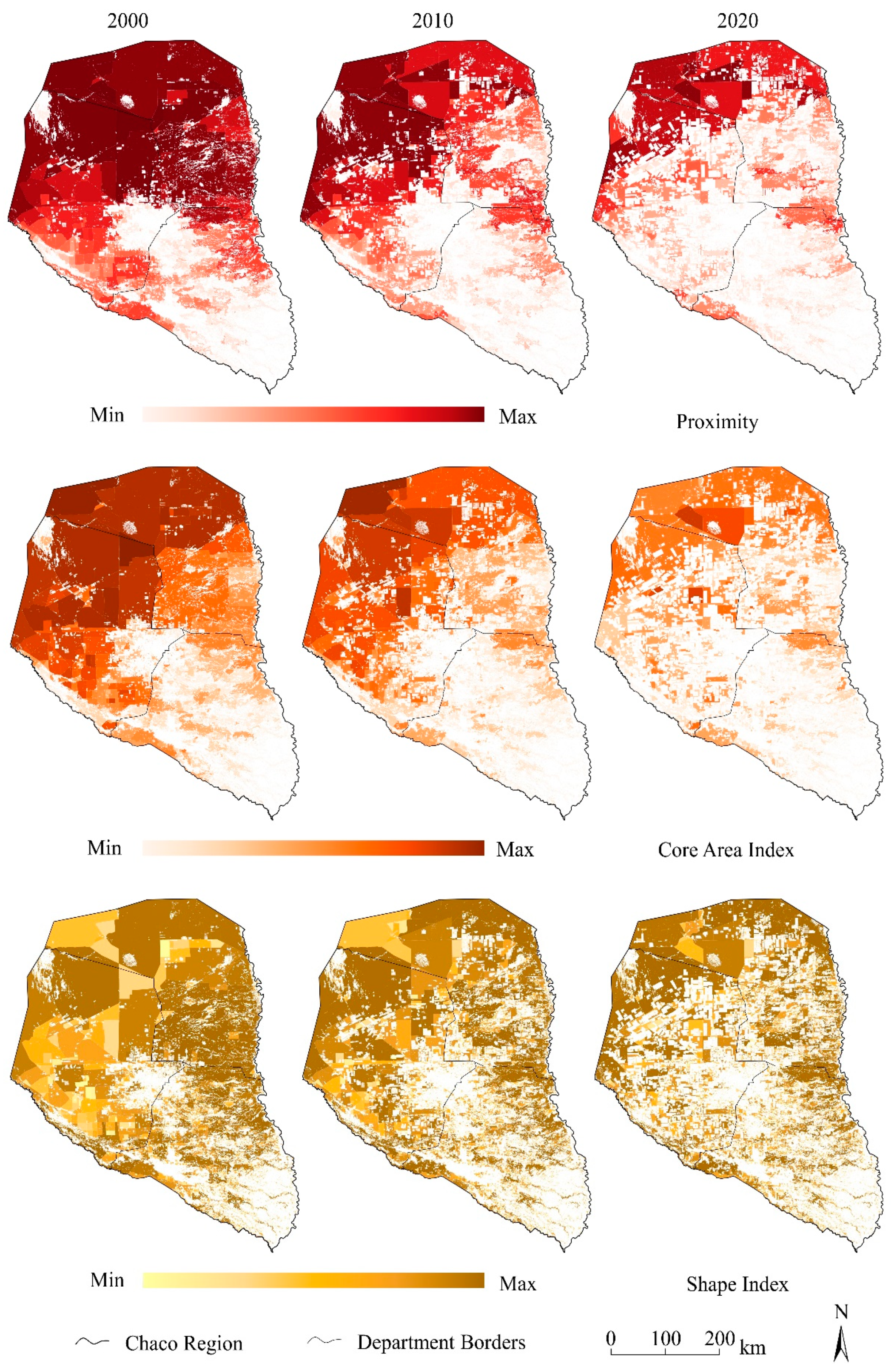
3.3. Forest Fragmentation
4. Discussion
4.1. Forest Cover Change Assesment
4.2. Forest Fragmentation Analysis
5. Conclusions
- The forest characterization based on Landsat data and the subsequent change-detection analysis revealed a forest cover loss of 64,700 km2 between 1987 and 2020, resulting in an annual deforestation rate of 1960 km2. The years between 2013 and 2019 presented the highest values of forest clearings. In the respective years, more than 8000 km2 were lost, which is about four times as much as the average loss in the Chaco region.
- The districts most affected by deforestation activities over the 34-year study period were Mariscal Estigarribia, Fuerte Olimpo, and Filadelfia, accounting for 39%, 11% and 10% of the total area cleared, respectively.
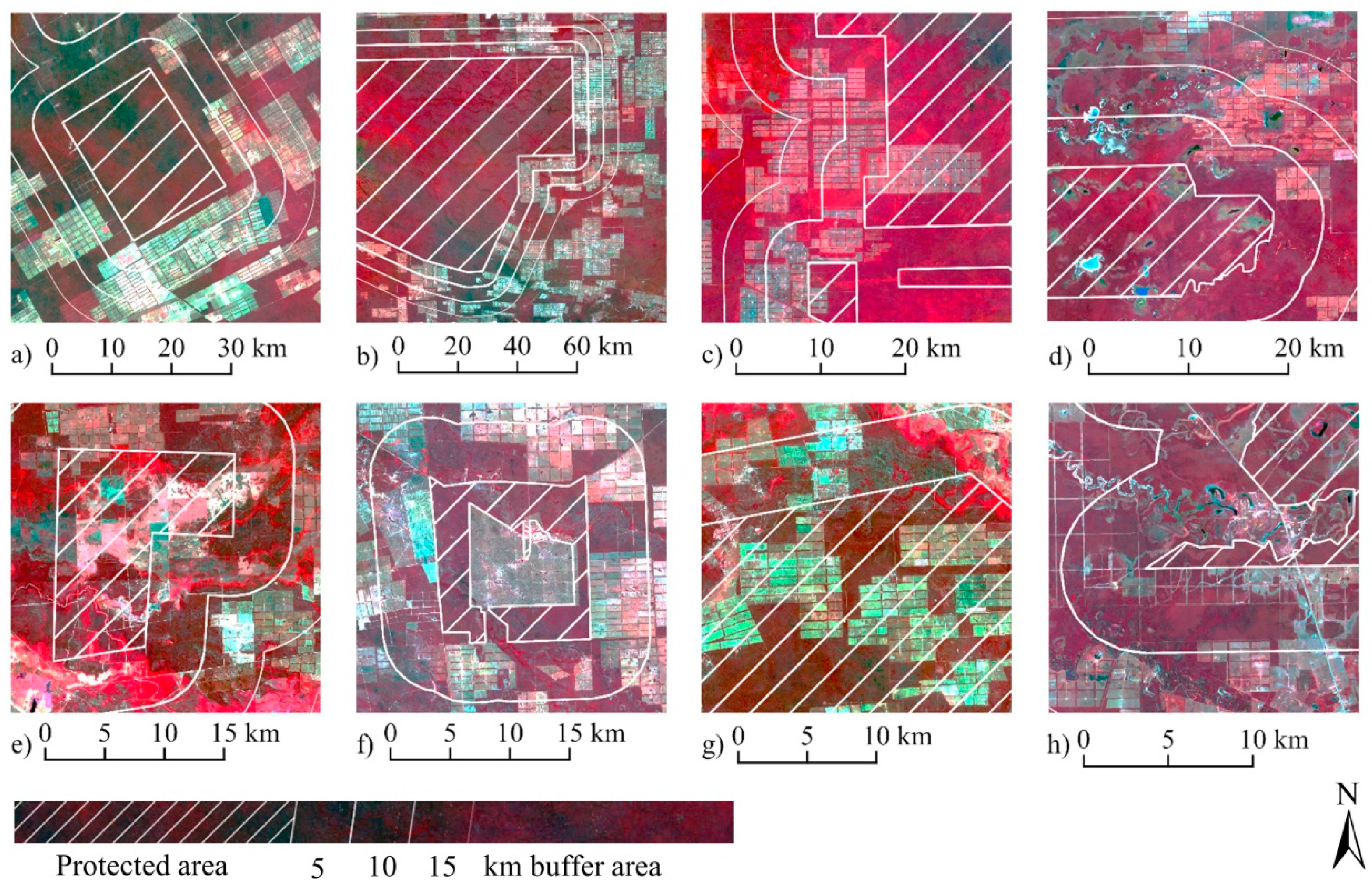
- The results in this study demonstrate a sound effectivity of most protected areas to preserve the forest. However, the natural reserves of Toro Mocho, Tinfunqué, Río Negro, and Fortin Salazar exhibited severe deforestation rates, varying from 14 up to 25%. Moreover, a drastic increment of forest loss was observed in the buffer zones of 5, 10, and 15 km, with values ascending up to 65%. These trends indicate that there is a constant pressure on protected areas, which therefore reveals the necessity of stronger law-enforcement strategies to successfully protect these natural sites.
- Ongoing deforestation activities increase forest fragmentation and compromise biodiversity conservation in the Paraguayan Chaco region. Levels of fragmentation increase in larger patches. While a certain connectivity between forest patches still remains, particularly in the north, a continuous decrease in forest cover would result in the generation of forest islands, which would dramatically endanger the possibility of animals to moving between the main reserves.
- Whereas this study analyzes forest fragmentation based on exemplary values obtained from previous regional studies, concrete figures must be defined for each main group of species from the Paraguayan Chaco. As an example, while birds can easily migrate along patches, additional effort is required by other invertebrates. Therefore, the distance between patches might not have an equal significance to bird populations as it does for other species.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Scale | Metric [Units] | Description | Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area Metrics | Total Area (TA) [km2] | Total area of the forest class | Landscape |
| Core Area (CA) [km2] | The sum of areas within patch beyond some specified edge distance or buffer (500m). | Landscape | |
| Core Area Index (CAI) [%] | Percentage of the patch that is comprised of core area. | Landscape, patch | |
| Number of patches (NP) | Number of patches in the forest class. | Landscape | |
| Edge Metrics | Total Edge (TE) [km] | Measure of total edge length of a particular patch type (class level) or of all patch types (landscape level). | Landscape |
| Mean Patch Edge [km] | Measures the average edge length of a forest patch. | Landscape | |
| Form Metrics | (Mean) Shape Index (MSI) | Measures the average patch shape for a particular patch type (class) or for all patches in the landscape. | Landscape (mean), patch |
| Mean Perimeter-Area Ratio (MPAR) | Measures the average Perimeter-Area Ratio for a particular patch type (class) or for all patches in the landscape. | Landscape | |
| Mean Fractal Dimension (MFRACT) | Mean of the fractal dimension index of all patches belonging to a class. | Landscape | |
| Nearest Neighbor Metrics: | (Mean) Proximity Index (PROX) | Measures the degree of isolation and fragmentation of the corresponding patch type. | Landscape (mean), patch |
| Subdivision Metrics | Division | Refers to the degree to which the landscape is broken up into separate patches. | Landscape |
| Split | Number of patches one gets when dividing the total landscape into patches of equal size. | Landscape | |
| Mesh [km2] | Size of the patches one gets when dividing the total landscape into patches of equal size. | Landscape |
| Year | Class | OA | Producers Accuracy | User Accuracy | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1987 | Forest | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.84 |
| No Forest | 0.85 | 0.92 | |||
| 1988 | Forest | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.74 |
| No Forest | 0.72 | 0.87 | |||
| 1989 | Forest | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.79 |
| No Forest | 0.87 | 0.84 | |||
| 1990 | Forest | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.89 |
| No Forest | 0.89 | 0.96 | |||
| 1991 | Forest | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.87 |
| No Forest | 0.83 | 0.97 | |||
| 1992 | Forest | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.88 |
| No Forest | 0.86 | 0.94 | |||
| 1993 | Forest | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.89 |
| No Forest | 0.87 | 0.95 | |||
| 1994 | Forest | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.87 |
| No Forest | 0.86 | 0.93 | |||
| 1995 | Forest | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.83 |
| No Forest | 0.81 | 0.94 | |||
| 1996 | Forest | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.86 |
| No Forest | 0.88 | 0.92 | |||
| 1997 | Forest | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.76 |
| No Forest | 0.83 | 0.87 | |||
| 1998 | Forest | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.76 |
| No Forest | 0.84 | 0.87 | |||
| 1999 | Forest | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.92 |
| No Forest | 0.94 | 0.93 | |||
| 2000 | Forest | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.87 |
| No Forest | 0.90 | 0.90 | |||
| 2001 | Forest | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.85 |
| No Forest | 0.90 | 0.87 | |||
| 2002 | Forest | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| No Forest | 0.97 | 1.00 | |||
| 2003 | Forest | 0. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 |
| No Forest | 1.00 | 0.99 | |||
| 2004 | Forest | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.95 |
| No Forest | 0.94 | 0.99 | |||
| 2005 | Forest | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| No Forest | 0.98 | 1.00 | |||
| 2006 | Forest | 0.90 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.78 |
| No Forest | 0.89 | 0.82 | |||
| 2007 | Forest | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.84 |
| No Forest | 0.92 | 0.95 | |||
| 2008 | Forest | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.91 |
| No Forest | 0.99 | 0.99 | |||
| 2009 | Forest | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.98 | 0.89 |
| No Forest | 0.96 | 0.93 | |||
| 2010 | Forest | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.88 |
| No Forest | 0.94 | 0.91 | |||
| 2011 | Forest | 0.94 | 0.72 | 0.91 | 0.90 |
| No Forest | 0.95 | 0.99 | |||
| 2012 | Forest | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.90 |
| No Forest | 0.97 | 0.90 | |||
| 2013 | Forest | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.81 |
| No Forest | 0.85 | 0.91 | |||
| 2014 | Forest | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.84 |
| No Forest | 0.86 | 0.94 | |||
| 2015 | Forest | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.84 |
| No Forest | 0.91 | 0.89 | |||
| 2016 | Forest | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.91 |
| No Forest | 0.85 | 0.94 | |||
| 2017 | Forest | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.95 |
| No Forest | 0.94 | 0.96 | |||
| 2018 | Forest | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.93 |
| No Forest | 0.95 | 0.97 | |||
| 2019 | Forest | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.82 |
| No Forest | 0.87 | 0.94 | |||
| 2020 | Forest | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.70 |
| No Forest | 0.81 | 0.89 |
References
- Mittermeier, R.A.; Myers, N.; Mittermeier, C.G. Hotspots: Earth’s Biologically Richest and Most Endangered Terrestrial Ecoregions; CEMEX: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fao. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2010. Main Report; FAO Forestry Paper 163; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010; Volume 163, 350p. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, R. Tropical Deforestation as a Source of Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Amazon Institute for Environmental Research: Pará, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- WWF. Paraguay Extends Zero Deforestation Law to 2018; WWF: Grand, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Arino, O.; Gross, D.; Ranera, F.; Leroy, M.; Bicheron, P.; Brockman, C.; Defourny, P.; Vancutsem, C.; Achard, F.; Durieux, L.; et al. GlobCover: ESA service for Global land cover from MERIS. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 2412–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, S.; Murthy, M.S.R.; Thomas, A.P. The progress on remote sensing technology in identifying tropical forest degradation: A synthesis of the present knowledge and future perspectives. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedl, M.A.; McIver, D.K.; Hodges, J.C.F.; Zhang, X.; Muchoney, D.; Strahler, A.H.; Woodcock, C.E.; Gopal, S.; Schneider, A.; Cooper, A.; et al. Global land cover mapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global Forest Resource Assesment; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, G.; Obermeier, W.; Gerique, A.; Sandoval, M.; Lehnert, L.; Thies, B.; Bendix, J. Land Cover Change in the Andes of Southern Ecuador—Patterns and Drivers. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2509–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebhardt, S.; Wehrmann, T.; Ruiz, M.A.M.; Maeda, P.; Bishop, J.; Schramm, M.; Kopeinig, R.; Cartus, O.; Kellndorfer, J.; Ressl, R.; et al. MAD-MEX: Automatic wall-to-wall land cover monitoring for the mexican REDD-MRV program using all landsat data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3923–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giri, C.; Long, J. Land Cover Characterization and Mapping of South America for the Year 2010 Using Landsat 30 m Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9494–9510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hightower, J.; Butterfield, A.; Weishampel, J. Quantifying Ancient Maya Land Use Legacy Effects on Contemporary Rainforest Canopy Structure. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10716–10732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, M.; Itoh, T.; Motooka, T.; Watanabe, M.; Shiraishi, T.; Thapa, R.; Lucas, R. New global forest/non-forest maps from ALOS PALSAR data (2007–2010). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Kuemmerle, T.; Baumann, M.; Radeloff, V.C.; Abrudan, I.V.; Lieskovsky, J.; Munteanu, C.; Ostapowicz, K.; Hostert, P. Forest disturbances, forest recovery, and changes in forest types across the Carpathian ecoregion from 1985 to 2010 based on Landsat image composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 151, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Volante, N.; Kuemmerle, T.; Jose, G.G.; Gavier-pizarro, G. Deforestation and cattle expansion in the Paraguayan Chaco. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sancha, U.; Boyle, S.A.; Mcintyre, N.E.; Brooks, D.M.; Yanosky, A.; Cuellar, E.; Mereles, F.; Camino, M.; Stevens, R.D. The disappearing Dry Chaco, one of the last dry forest systems on earth. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2997–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Ponte, E.; Fleckenstein, M.; Leinenkugel, P.; Parker, A.; Oppelt, N.; Kuenzer, C. Tropical forest cover dynamics for Latin America using Earth observation data: A review covering the continental, regional, and local scale. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 3196–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.; Da Ponte, E.; Insfran, K.; Gonzales, L.; World Wildlife Fund; German Aesrospace Center. Atlas del Chaco Paraguayo; Musa, K., Ed.; Asuncion-Paraguay, WWF: Grand, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mereles, M.F.; Rodas, O. Assessment of rates of deforestation classes in the Paraguayan Chaco (Great South American Chaco) with comments on the vulnerability of forests fragments to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2014, 127, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, M.M.; Goodin, D.; Sherwood, S.; Campos Krauer, J.M.; Wisely, S.M. Land-cover change in the Paraguayan Chaco: 2000–2011. J. Land Use Sci. 2013, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direccion Nacional de Encuestas y Estadisticas (DGEEC). Atlas censal del Paraguay; Asuncion-Paraguay; 2002; Volume 1, p. 143. Available online: http://www.dgeec.gov.py/ (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Da Ponte, E.; Mack, B.; Wohlfart, C.; Rodas, O.; Oppelt, N.; Dech, S.; Kuenzer, C. Assessing Forest Cover Dynamics and Forest Perception in the Atlantic Forest of Paraguay, Combining Remote Sensing and Household Level Data. Forests 2017, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohlfart, C.; Mack, B.; Liu, G.; Kuenzer, C. Multi-faceted land cover and land use change analyses in the Yellow River Basin based on dense Landsat time series: Exemplary analysis in mining, agriculture, forest, and urban areas. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 85, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, K.; Gessner, U.; Fensholt, U.; Kuenzer, C. Agricultural Expansion in Burkina Faso over 14 Years with 30 m Resolution Time Series: The Role of Population Growth and Implications for the Environment. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Object-based cloud and cloud shadow detection in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.; Griffiths, P.; Hostert, P. Long-term deforestation dynamics in the Brazilian Amazon—Uncovering historic frontier development along the Cuiabá–Santarém highway. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 44, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, B.; Leinenkugel, P.; Kuenzer, C.; Dech, S. A semi-automated approach for the generation of a new land use and land cover product for Germany based on Landsat time-series and Lucas in-situ data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A. Monitoring land cover change in urban and peri-urban areas using dense time stacks of Landsat satellite data and a data mining approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation, 6th ed.; Sons, J.W., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Da Ponte, E.; Roch, M.; Leinenkugel, P.; Dech, S.; Kuenzer, C. Paraguay’s Atlantic Forest cover loss–Satellite-based change detection and fragmentation analysis between 2003 and 2013. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, C.; Thompson, D.; Kelly, M.; Lopez-Gonzalez, C.A. Puma concolor. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015; Global Biodiversity Information Facility: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Kim, S.; Song, K.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Davis, P.; Altstatt, A.; Rodas, O.; Yanosky, A.; Clay, R.; Tucker, C.J.; et al. Assessment of Paraguay’s forest cover change using Landsat observations. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarical, K.; Marks, B.J. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; Gen. Tech. Rep. PNW-GTR-351. US; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station: Portland, OR, USA, 1994; Volume 97331, p. 134.
- Lang, S.; Tiede, D. vLATE Extension für ArcGIS—Vektorbasiertes Tool zur quantitativen Landschaftsstrukturanalyse. In Proceedings of the Esri European User Conference 2003, Innsbruck, Austria, 8–10 October 2003; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, E.N.; Asner, G.P.; Keller, M.; Knapp, D.E.; Oliveira, P.J.C.; Silva, J.N. Forest fragmentation and edge effects from deforestation and selective logging in the Brazilian Amazon. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchimol, M.; Peres, C. Predicting local extinctions of Amazonian vertebrates in forest islands created by a mega dam. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 187, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, M. Revealing Forest Cover Loss in Paraguay’s Atlantic Forest Region—A Remote Sensing and GIS Based Forest Monitoring. Master’s Thesis, Universität Salzburg, Salzburg, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Programa Nacional Conjunto (ONU-REDD + Paraguay). Metodología de Elaboración de Mapas de Cambio de Uso de la Tierra en el Paraguay: Informe del Equipo Técnico. Available online: http://www.infona.gov.py/application/files/5314/3092/8338/Presentacion_IFN_PARAGUAY_06.05.2015.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Huang, C.; Kim, S.; Altstatt, A.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Davis, P.; Song, K.; Tucker, C.J.; Rodas, O.; Yanosky, A.; Clay, R.; et al. Rapid loss of Paraguay’s Atlantic forest and the status of protected areas—A Landsat assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsik, M.; Stevens, F.R.; Southworth, J. Amazon deforestation: Rates and patterns of land cover change and fragmentation in Pando, northern Bolivia, 1986 to 2005. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 35, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Landsat Image Data Sets | Value | Overall Accuracy (%) | User’s Accuracy (%) | Producer’s Accuracy (%) | Kappa Statistics (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Non-Forest | Forest | Non-Forest | ||||
| Landsat 5 (1987–1998) | Min | 88.44 | 89.17 | 84.42 | 91.81 | 72.65 | 0.74 |
| Max | 97.04 | 97.42 | 97.73 | 99.54 | 89.04 | 0.89 | |
| Mean | 93.65 | 94.27 | 92.00 | 96.78 | 84.76 | 0.83 | |
| Landsat 5 & 7 (1999–2012) | Min | 89.81 | 86.71 | 82.0 | 71.73 | 89.00 | 0.77 |
| Max | 99.71 | 100.00 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 0.99 | |
| Mean | 95.58 | 95.62 | 94.10 | 92.30 | 94.56 | 0.90 | |
| Landsat 8 (2013–2020) | Min | 85.33 | 81.80 | 89.21 | 89.23 | 81.76 | 0.71 |
| Max | 97.42 | 97.50 | 97.23 | 98.50 | 95.03 | 0.95 | |
| Mean | 92.01 | 93.36 | 94.45 | 96.60 | 86.45 | 0.84 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Da Ponte, E.; García-Calabrese, M.; Kriese, J.; Cabral, N.; Perez de Molas, L.; Alvarenga, M.; Caceres, A.; Gali, A.; García, V.; Morinigo, L.; et al. Understanding 34 Years of Forest Cover Dynamics across the Paraguayan Chaco: Characterizing Annual Changes and Forest Fragmentation Levels between 1987 and 2020. Forests 2022, 13, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010025
Da Ponte E, García-Calabrese M, Kriese J, Cabral N, Perez de Molas L, Alvarenga M, Caceres A, Gali A, García V, Morinigo L, et al. Understanding 34 Years of Forest Cover Dynamics across the Paraguayan Chaco: Characterizing Annual Changes and Forest Fragmentation Levels between 1987 and 2020. Forests. 2022; 13(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleDa Ponte, Emmanuel, Monserrat García-Calabrese, Jennifer Kriese, Nestor Cabral, Lidia Perez de Molas, Magali Alvarenga, Arami Caceres, Alicia Gali, Vanina García, Luis Morinigo, and et al. 2022. "Understanding 34 Years of Forest Cover Dynamics across the Paraguayan Chaco: Characterizing Annual Changes and Forest Fragmentation Levels between 1987 and 2020" Forests 13, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010025
APA StyleDa Ponte, E., García-Calabrese, M., Kriese, J., Cabral, N., Perez de Molas, L., Alvarenga, M., Caceres, A., Gali, A., García, V., Morinigo, L., Ríos, M., & Salinas, A. (2022). Understanding 34 Years of Forest Cover Dynamics across the Paraguayan Chaco: Characterizing Annual Changes and Forest Fragmentation Levels between 1987 and 2020. Forests, 13(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13010025







