The Effect of Land Use/Cover Change on Soil Erosion Change by Spatial Regression in Changwu County on the Loess Plateau in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
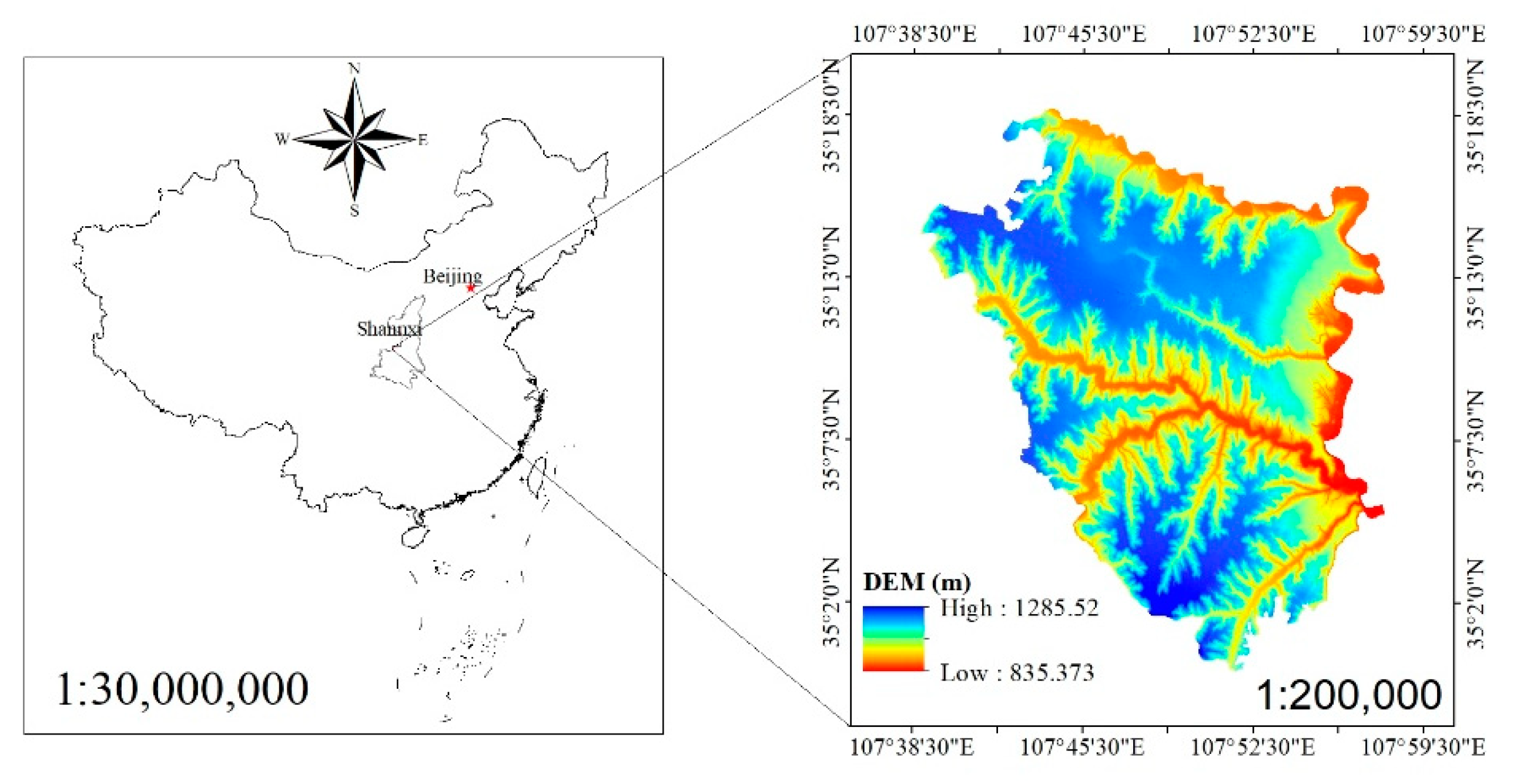
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. LULCC Analysis
2.4. Soil Erosion Estimation
2.4.1. R, Rainfall Erosivity Factor
2.4.2. K, Soil Erodibility Factor
2.4.3. LS, Slope Length and Steepness Factor
2.4.4. C, Crop Management Factor
2.4.5. P, Conservation Supporting Practice Factor
2.5. Soil Erosion Analysis
2.6. Regression Models
2.6.1. Ordinary Least Squares (OLS)
2.6.2. Spatial Regression Model
3. Results
3.1. LULCC Classification and Accuracy Evaluation
3.2. LULCC Analysis
3.3. Soil Erosion Estimation and Analysis
3.4. LULCC Effect on Soil Erosion Change and Model Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minta, M.; Kibret, K.; Thorne, P.; Nigussie, T.; Nigatu, L. Land use and land cover dynamics in Dendi-Jeldu hilly-mountainous areas in the central Ethiopian highlands. Geoderma 2018, 314, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schutt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, J.C.; Liu, H.P.; Liu, X.P.; Zhang, Y.H. Spatiotemporal evolution analysis of time-series land use change using self-organizing map to examine the zoning and scale effects. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 76, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change: Local Processes and Global Impacts; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Handavu, F.; Chirwa, P.W.C.; Syampungani, S. Socio-economic factors influencing land-use and land-cover changes in the miombo woodlands of the Copperbelt province in Zambia. For. Policy Econ. 2019, 100, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phiri, D.; Morgenroth, J.; Xu, C. Long-term land cover change in Zambia: An assessment of driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schielein, J.; Borner, J. Recent transformations of land-use and land-cover dynamics across different deforestation frontiers in the Brazilian Amazon. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.V.R.; Escobar-Silva, E.V.; Chaves, M.E.D.; Mataveli, G.A.V.; Bourscheidt, V.; de Oliveira, G.; Picoli, M.C.A.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Moschini, L.E. Assessing Land Use and Land Cover Changes in the Direct Influence Zone of the Braco Norte Hydropower Complex, Brazilian Amazonia. Forests 2020, 11, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; dos Santos, A.C.A.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Effects of land use and land cover on water quality of low-order streams in Southeastern Brazil: Watershed versus riparian zone. Catena 2018, 167, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Cao, Y. Quantifying landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes: A case study at the county level in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstegen, J.A.; van der Laan, C.; Dekker, S.C.; Faaij, A.P.C.; Santos, M.J. Recent and projected impacts of land use and land cover changes on carbon stocks and biodiversity in East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Alexander, P.; Evans, T.; Magliocca, N.R.; Malek, Z.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; van Vliet, J. Beyond land cover change: Towards a new generation of land use models. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sust. 2019, 38, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.R.; Liu, R.M.; Men, C.; Guo, L.J. Application of genetic algorithm to land use optimization for non-point source pollution control based on CLUE-S and SWAT. J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickson, R.J. Can control of soil erosion mitigate water pollution by sediments? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.J.; Wen, Q.K.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.Y.; Hu, S.G.; Liu, B. Assessment of soil erosion change and its relationships with land use/cover change in China from the end of the 1980s to 2010. Catena 2016, 137, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.Q.; Sun, R.H.; Chen, L.D. A global comparison of soil erosion associated with land use and climate type. Geoderma 2019, 343, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, A.; Pisciotta, A.; Minacapilli, M.; Maltese, A.; Capodici, F.; Cerda, A.; Gristina, L. The impact of soil erosion on soil fertility and vine vigor. A multidisciplinary approach based on field, laboratory and remote sensing approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, F.; Yang, W.; Fu, J.; Li, Z. Effects of vegetation and climate on the changes of soil erosion in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, A.; Zhang, D.; Su, X.; Chen, J. Responses of Soil Erosion to Land-Use Changes in the Largest Tableland of the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2007, 107, 2411–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Wu, F.Q.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L.F.; Zhao, L.S. Application of PCA integrated with CA and GIS in eco-economic regionalization of Chinese Loess Plateau. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhen, L. Soil erosion control practices in the Chinese Loess Plateau: A systematic review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Liu, W.Z. Simulating potential response of hydrology, soil erosion, and crop productivity to climate change in Changwu tableland region on the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 131, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qian, H. Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall and extreme values in Shaanxi, China, since the 1950s. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2582–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Kim, D.G.; Li, M.Y.; Huang, C.B.; Liu, Q.Y.; Cheng, M.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Peng, C.H. Land-use changes driven by ’Grain for Green’ program reduced carbon loss induced by soil erosion on the Loess Plateau of China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 177, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Meng, Q.H.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, W.W.; Zhang, Q.J.; Davidson, D.A. Effects of land use on soil erosion and nitrogen loss in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Y.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C. A comparison of explicit and implicit spatial downscaling of GCM output for soil erosion and crop production assessments. Clim. Chang. 2007, 84, 337–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Mu, X.M.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G.J. Analysis of extreme temperature events in the Qinling Mountains and surrounding area during 1960–2012. Quatern. Int. 2016, 392, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.H.; Kelly, M.; Gong, P.; Liu, D.S. An object-based classification approach in mapping tree mortality using high spatial resolution imagery. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2007, 44, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Xia, F. Assessing object-based classification: Advantages and limitations. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 1, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Saha, S.K. Multi-resolution Segmentation for Object-based Classification and Accuracy Assessment of Land Use/Land Cover Classification using Remotely Sensed Data. Photonirvachak-J. Ind. 2008, 36, 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Langley, S.K.; Cheshire, H.M.; Humes, K.S. A comparison of single date and multitemporal satellite image classifications in a semi-arid grassland. J. Arid. Environ. 2001, 49, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.S. Spatio-temporal changes in oases in the Heihe River Basin of China: 1963–2013. Ecoscience 2015, 22, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M. The sankey diagram in energy and material flow management. J. Ind. Ecol. 2008, 12, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuba, N. Research note: Sankey diagrams for visualizing land cover dynamics. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2015, 139, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushanjiang, A.; Zhang, F.; Kung, H.T.; Li, Z. Spatial-temporal variation of ecosystem service values in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Natural Reserve from 1972 to 2016, Xinjiang, arid region of China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, J.J.; Ellis, P.; Gandrud, C. Package ‘NetworkD3’. D3 JavaScript Network Graphs from R. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/eliztang/networkD3 (accessed on 8 July 2021).
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture; Science and Education Administration; United States Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Shi, P.J.; Jia, Z.W. Slope length effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Bennett, S.J.; Li, Y. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: A case study of the Yangou watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Xie, Y. Effect of different vegetation types on soil erosion by water. Acta Bot. Sin. 2003, 45, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Baoyuan, L.; Peijun, S.; Zhongshan, J.J.A.E.S. Crop cover factor estimating for soil loss prediction. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2001, 21, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.D.; Li, Z.B.; Jia, L.L.; Li, P.; Xu, G.C.; Ren, Z.P.; Pang, G.W.; Zhao, B.H. Capacity of soil loss control in the Loess Plateau based on soil erosion control degree. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollalo, A.; Vahedi, B.; Rivera, K.M. GIS-based spatial modeling of COVID-19 incidence rate in the continental United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 2015, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Spatial econometrics: Methods and models. Econ. Geogr. 1988, 65, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, M.A.; Auch, R.F.; Karstensen, K.A.; Sayler, K.L.; Taylor, J.L.; Loveland, T.R. Land change variability and human-environment dynamics in the United States Great Plains. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.W.; Zhang, K.; Yang, X.D. A 110-year pollen record of land use and land cover changes in an anthropogenic watershed landscape, eastern China: Understanding past human-environment interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2906–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.G.; Ma, Z.G.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.H.; Mahmood, R. Land use/land cover changes and regional climate over the Loess Plateau during 2001–2009. Part II: Interrelationship from observations. Clim. Chang. 2015, 129, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, K.; Wei, J.Z.; Pei, J.Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.L.; Huang, F.Q.; Li, F.M.; Ye, J.S. Impacts of climate change and human activities on grassland vegetation variation in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, C.; Jiang, W.J.G.R. Rural transformation from the perspective of regime shifts of socio-ecological systems in the Loess Plateau: A case study of Hongjia town in Changwu county, China. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 1510–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Návar, J. Modeling rainfall interception loss components of forests. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunicke, S.; Queck, R.; Bernhofer, C. Long-term investigation of forest canopy rainfall interception for a spruce stand. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 292, 108125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.Y.; Shen, Y.J.; Ge, J.F.; Tateishi, R.; Tang, C.Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Huang, Z.Y. Evaluating urban expansion and land use change in Shijiazhuang, China, by using GIS and remote sensing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 75, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wei, W.; Pan, D.L. Effects of rainfall and terracing-vegetation combinations on water erosion in a loess hilly area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.Q.; Hu, C.H.; Zhang, G.D.; Zhang, J.P. Study on the throughfall, stemflow, and interception of two shrubs in the semiarid Loess region of China. Agr. For. Meteorol. 2019, 279, 107713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fu, B.J.; Gao, G.Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, N.; Wang, S. Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid environment in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H. Impact of land use changes on catchment soil erosion and sediment yield in the northeastern China: A panel data model application. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Orchard | Agricultural land for planting fruit trees |
| Cropland | All agricultural land used for growing food crops |
| Forest land | The trees closed to canopy or have closed canopy |
| Planted land | Including open forest, bushes, shrubs and grass |
| Water body | Including river and reservoir |
| Construction land | Including settlements, roads and buildings |
| Code | Erosion Intensity Ton km−2 year−1 | Erosion Intensity Class |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | <1000 | slight |
| 2 | 1000–2500 | light |
| 3 | 2500–5000 | moderate |
| 4 | 5000–8000 | severe |
| 5 | 8000–15,000 | very severe |
| 6 | >15,000 | extremely severe |
| Period | OLS | GWR | SLM | SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1987–1997 | 0.025 | 0.203 | 0.653 | 0.659 |
| 1997–2007 | 0.047 | 0.211 | 0.644 | 0.639 |
| 2007–2017 | 0.004 | 0.300 | 0.627 | 0.639 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Wang, F.; Qu, M.; Yu, B.; Zhao, Z. The Effect of Land Use/Cover Change on Soil Erosion Change by Spatial Regression in Changwu County on the Loess Plateau in China. Forests 2021, 12, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091209
Yu S, Wang F, Qu M, Yu B, Zhao Z. The Effect of Land Use/Cover Change on Soil Erosion Change by Spatial Regression in Changwu County on the Loess Plateau in China. Forests. 2021; 12(9):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091209
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shichuan, Fei Wang, Mei Qu, Binhou Yu, and Zhong Zhao. 2021. "The Effect of Land Use/Cover Change on Soil Erosion Change by Spatial Regression in Changwu County on the Loess Plateau in China" Forests 12, no. 9: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091209
APA StyleYu, S., Wang, F., Qu, M., Yu, B., & Zhao, Z. (2021). The Effect of Land Use/Cover Change on Soil Erosion Change by Spatial Regression in Changwu County on the Loess Plateau in China. Forests, 12(9), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12091209





