One-Year Monitoring of Daily Earthworm Cast Production: Surface Cast Contribution to Soil Fertility in a Subtropical Forest
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
2.3. Chemical Properties Analysis
2.4. Microbial Properties Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
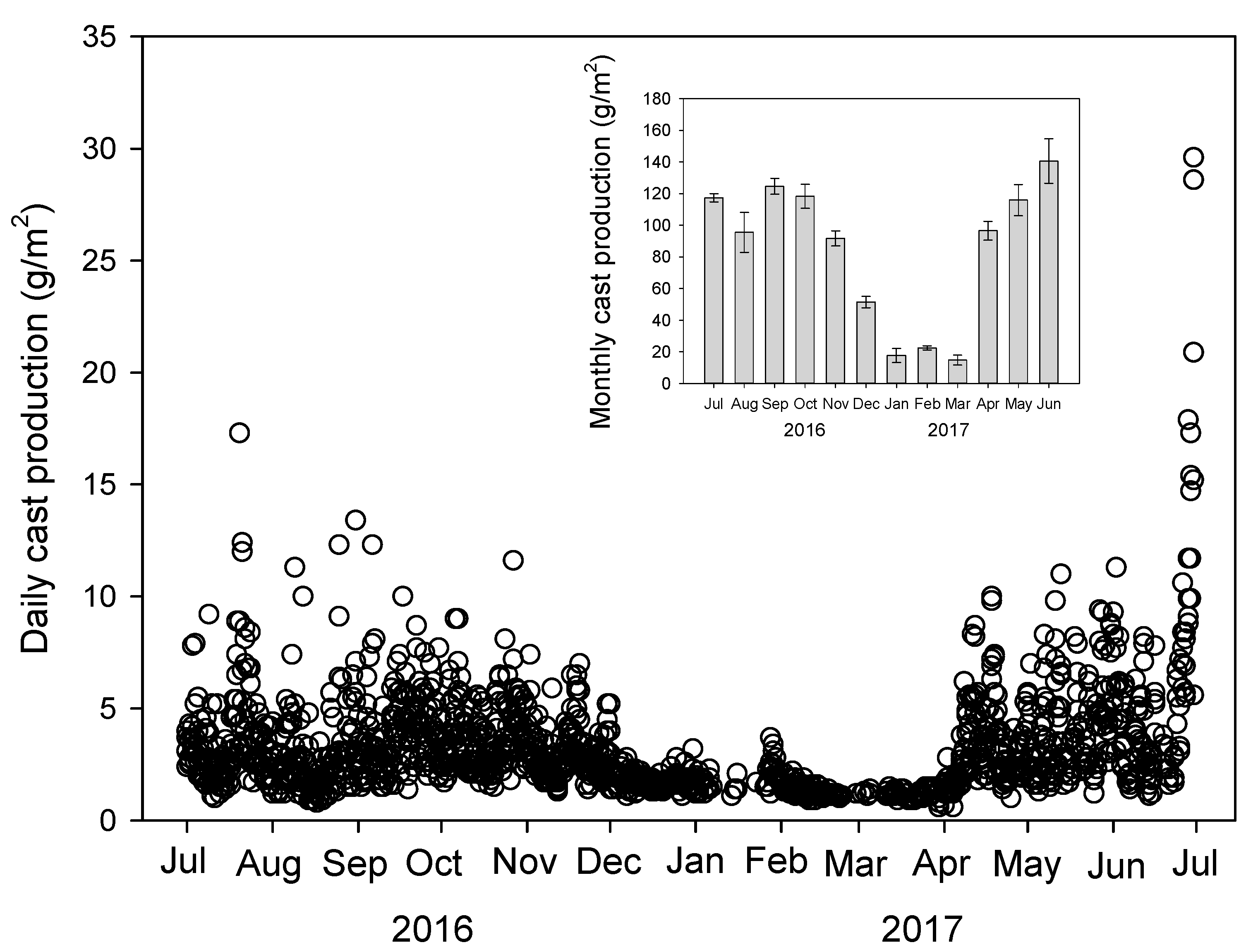
3.1. Earthworm Cast Production
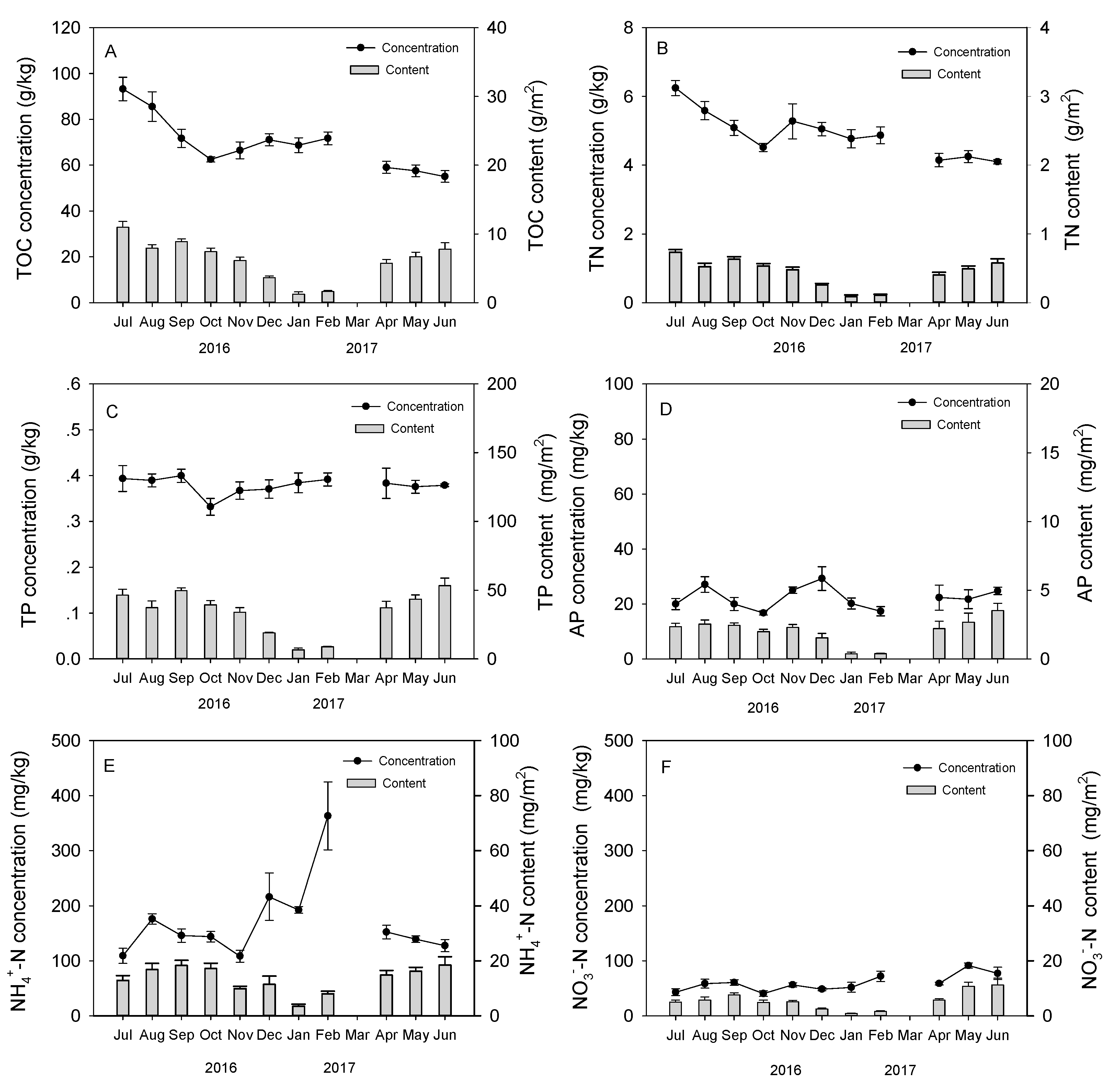
3.2. Seasonal Dynamics of Earthworm Cast Nutrients
3.3. Chemical Properties in Casts and Soil
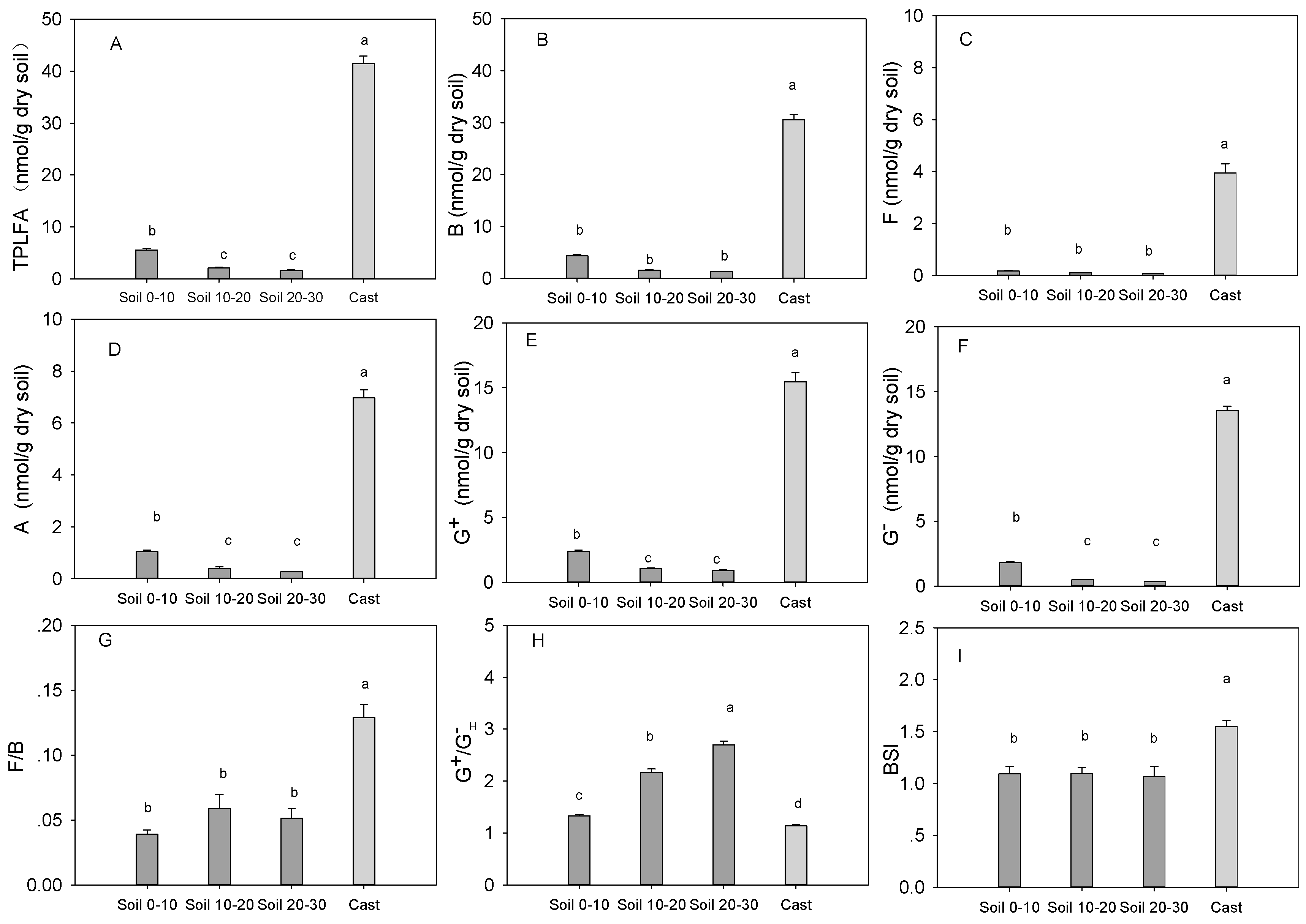
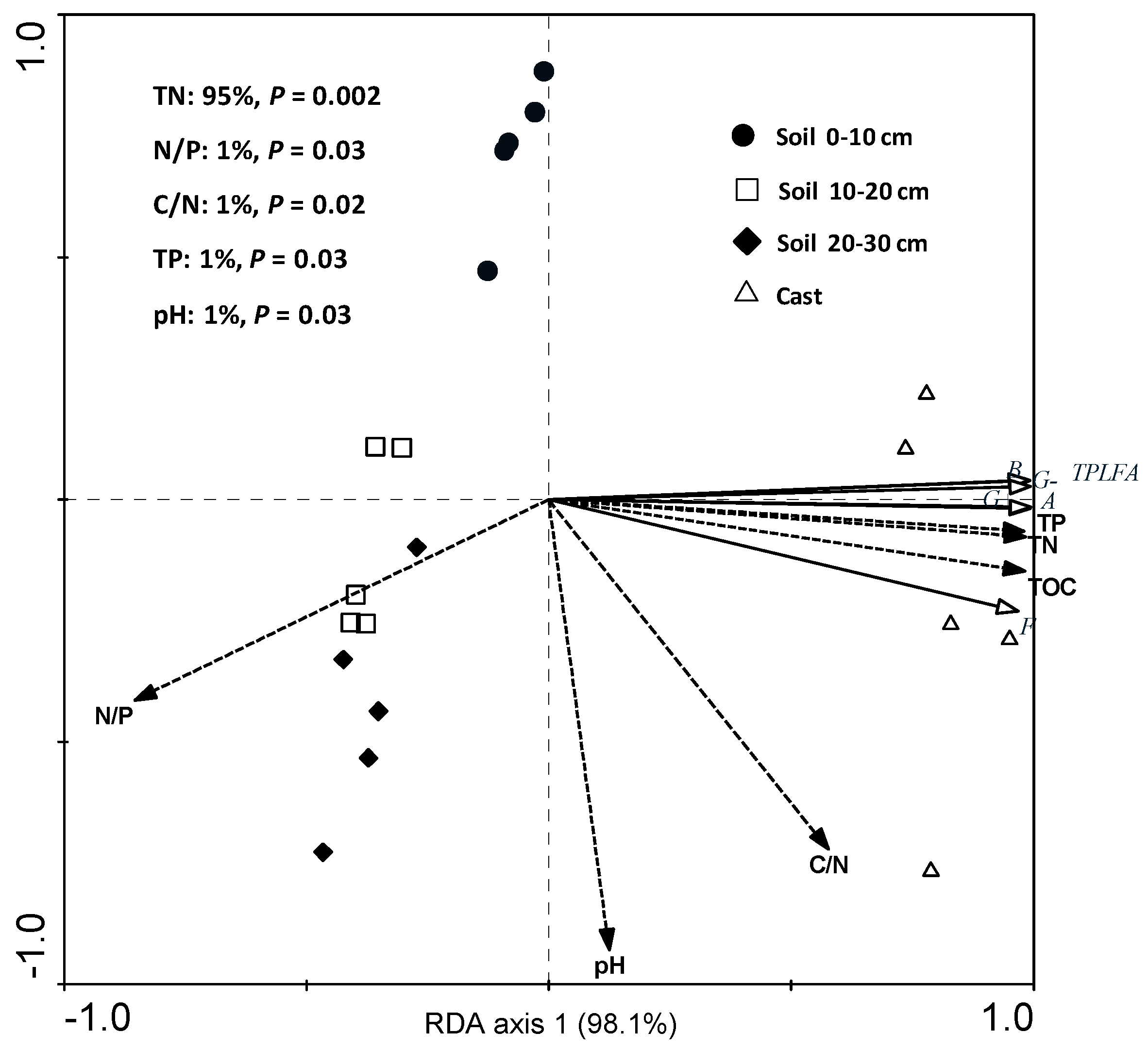
3.4. Microbial Community Characteristics in Cast and Soil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Groenigen, J.W.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Koopmans, G.F.; Stokkermans, L.; Vos, H.M.J.; Lubbers, I.M. How fertile are earthworm casts? A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2018, 338, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Martin, A. Small-scale and large-scale effects of endogeic earthworms on soil organic matter dynamics in soils of the humid tropics. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.A. Historical overview of vermicomposting. Biocycle 1995, 36, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chaoui, H.I.; Zibilske, L.M.; Ohno, T. Effects of earthworm casts and compost on soil microbial activity and plant nutrient availability. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Palacios, P.; Maestre, F.T.; Bradford, M.A.; Reynolds, J.F. Earthworms modify plant biomass and nitrogen capture under conditions of soil nutrient heterogeneity and elevated atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, C. Microbial activity was greater in soils added with herb residue vermicompost than chemical fertilizer. Soil. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 2, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Dutta, D.; Ray, D.P.; Karmakar, R. Vermicompost and Soil Quality. In Farming for Food and Water Security; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barley, K.P.; Jennings, A.C. Earthworms and soil fertility. III. The influence of earthworms on the availability of nitrogen. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1959, 10, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.W. Soil, nitrogen, phosphorus, and organic matter processing by earthworms in tallgrass prairie. Ecology 1991, 72, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barois, I.; Villemin, G.; Lavelle, P.; Toutain, F. Transformation of the soil structure through Pontoscolex corethrurus (Oligochaeta) intestinal tract. Geoderma 1993, 56, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharin, S.A.; Kurakov, A.V. Transformation of nitrogen compounds and dynamics of microbial biomass in fresh casts of Aporrectodea caliginosa. Eurasian. Soil Sci. 2009, 42, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, L.; Juan, J.; Jiménez Asakawa, N.; Thomas, R.J.; Decaëns, T. What happens to earthworm casts in the soil? A field study of carbon and nitrogen dynamics in Neotropical savannahs. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S. Microbial activity and nutrient dynamics in earthworm casts (Lumbricidae). Biol. Fert. Soils 1987, 5, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashanasi, B.; Melendez, G.; Szott, L.; Lavelle, P. Effect of inoculation with the endogeic earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae) on N availability, soil microbial biomass and the growth of three tropical fruit tree seedlings in a pot experiment. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1992, 24, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechitaylo, T.Y.; Yakimov, M.; Godinho, M.; Timmis, K.N.; Belogolova, E.; Byzov, B.A.; Kurakov, A.V.; Jones, D.L.; Golyshin, P. Effect of the Earthworms Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea caliginosa on Bacterial Diversity in Soil. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 59, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, Y.; Luizão, F.; Barros, E. Effect of earthworm addition on soil nitrogen availability, microbial biomass and litter decomposition in mesocosms. Biol. Fert. Soils 2004, 39, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groffman, P.M.; Bohlen, P.J.; Fahey, F.T.J. Exotic earthworm invasion and microbial biomass in temperate forest soils. Ecosystems 2004, 7, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, J.H.C.; Wong, M.H. Effects of earthworm activity and p-solubilizing bacteria on P availability in soil. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2004, 167, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Pashanasi, B.; Charpentier, F.; Gilot, C.; Rossi, J.P.; Derouard, L.; Jean André, J.; Ponge, J.F.; Bernier, N. Large-scale effects of earthworms on soil organic matter and nutrient dynamics. In Earthworm Ecology; Edwards, C.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 103–122. [Google Scholar]
- Decaëns, T.; Mariani, L.; Betancourt, N.; Jiménez, J.J. Seed dispersion by surface casting activities of earthworms in Colombian grasslands. Acta Oecol. 2003, 24, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, H.; Six, J.; Hendrix, P.F. Protection of soil carbon by microaggregates within earthworm casts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Gunina, A.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Shao, Y.; Shi, L.; Yao, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Cooperation of earthworm and arbuscular mycorrhizae enhanced plant N uptake by balancing absorption and supply of ammonia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S. The role of substrate feeding earthworms (Lumbricidae) for bioturbation in a beechwood soil. Oecologia 1987, 72, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrot, J.; Brussaard, L. Abundance, casting activity, and cast quality of earthworms in an acid ultisol under alley-cropping in the humid tropics. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1997, 6, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.N.; Rumpel, C.; Tureaux, T.H.D.; Bardoux, G.; Billou, D.; Duc, T.T.; Jouquet, P. How do earthworms influence organic matter quantity and quality in tropical soils? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. World reference base for soil resources 2006. In World Soil Resources Reports No. 103; FAO, UN: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.X.; Li, J.X.; Guo, M.F.; Liao, C.H. Seasonal variation of earthworm community structure as correlated with environmental factors in three plantation of Heshan, Guangdong, China. Acta Ecol. Sinica 2005, 25, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Description of Soil Profiles; China Standard: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.T.; Gundersen, P.; Mo, J.M.; Zhu, W.X. Input and output of dissolved organic and inorganic nitrogen in subtropical forests of South China under high air pollution. Biogeosciences 2008, 5, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Scow, K.M. Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: Phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, Å.; Bååth, E. The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 1996, 22, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bååth, E.; Anderson, T.H. Comparison of soil fungal/bacterial ratios in a pH gradient using physiological and PLFA-based techniques. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Liu, Z.F.; Sun, Y.X.; Zhou, L.X.; Lin, Y.B.; Fu, S.L. Introduced Eucalyptus urophylla plantations change the composition of the soil microbial community in subtropical china. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 24, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.C.; Tiwari, B.K.; Mishra, R.R. Microbial populations, enzyme activities and nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium enrichment in earthworm casts and in the surrounding soil of a pineapple plantation. Biol. Fert. Soils 1989, 8, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Lazcano, C.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Domínguez, J. Ageing effects of casts of Aporrectodea caliginosa on soil microbial community structure and activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aira, M.; Domínguez, J. Changes in nutrient pools, microbial biomass and microbial activity in soils after transit through the gut of three endogeic earthworm species of the genus Postandrilus Qui and Bouché, 1998. J. Soil Sediment 2014, 14, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, C.; Pawluk, S. Faecal microbiology of Octolasion tyrtaeum, Aporrectodea turgida and Lumbricus terrestris and its relation to the carbon budgets of three artificial soils. Pedobiologia 1986, 29, 377–389. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.X.; Hendrix, P.F.; Damem, L.E.; Burke, R.A.; Wu, J.P.; Neher, D.A.; Li, J.X.; Shao, Y.H.; Fu, S.L. Earthworms facilitate carbon sequestration through unequal amplification of carbon stabilization compared with mineralization. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdale, S.L.; Nelson, W.L. Soil fertility and fertilizers. Q. Rev. Biol. 1966, 101, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högberg, M.N.; Chen, Y.; Högberg, P. Gross nitrogen mineralisation and fungi-to-bacteria ratios are negatively correlated in boreal forests. Biol. Fert. Soils 2007, 44, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseeva, T.; Besse, P.; Françoise, B.; Delort, A.M.; Tixier, C. Effect of earthworm activity (Aporrectodea giardi) on atrazine adsorption and biodegradation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagodatskaya, E.V.; Anderson, T.H. Interactive effects of pH and substrate quality on the fungal-to-bacterial ratio and qCO2 of microbial communities in forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Oba, Y. Effect of fungal to bacterial biomass ratio on the relationship between CO2 evolution and total soil microbial biomass. Biol. Fert. Soils 1994, 17, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Shao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liang, C.; Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S. Plants modify the effects of earthworms on the soil microbial community and its activity in a subtropical ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Fu, S.L.; Shao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.P.; Zhang, W.X. Earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus stimulated soil CO2 emission by enhancing substrate availability rather than changing microbiota community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Eisenhauer, N.; Liu, T.; Erlian, O.F.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Liang, C.; Fu, S. Exotic earthworms maintain soil biodiversity by altering bottom-up effects of plants on the composition of soil microbial groups and nematode communities. Biol. Fert. Soils 2019, 55, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, S. Special issue on the biodiversity and ecological functions of soil fauna. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 3, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Layer | Cast | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 cm | 10–20 cm | 20–30 cm | ||
| pH | 4.01 ± 0.05 b | 4.14 ± 0.03 a | 4.21 ± 0.03 a | 4.19 ± 0.11 a |
| TOC (g/kg) | 20.8 ± 1.03 b | 8.90 ± 0.38 c | 7.57 ± 0.8 c | 89.5 ± 6.61 a |
| TN (g/kg) | 1.71 ± 0.14 b | 0.84 ± 0.12 c | 0.71 ± 0.10 c | 5.08 ± 0.90 a |
| TP (g/kg) | 0.26 ± 0.02 b | 0.21 ± 0.02 c | 0.22 ± 0.02 c | 0.41 ± 0.03 a |
| C/N | 12.2 ± 0.5 b | 10.8 ± 0.7 b | 10.7 ± 0.8 b | 17.8 ± 0.9 a |
| C/P | 82.0 ± 5.2 b | 43.0 ± 3.1 c | 35.8 ± 4.9 c | 216.0 ± 10.2 a |
| N/P | 6.7 ± 0.2 b | 4.0 ± 0.2 c | 3.3 ± 0.3 c | 12.2 ± 0.6 a |
| C/N/P | 82/7/1 | 43/4/1 | 36/3/1 | 216/12/1 |
| Soil Layer | Cast | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 cm | 10–20 cm | 20–30 cm | ||
| MBC (mg/kg) | 247.6 ± 30.3 b | 114.0 ± 20.3 c | 118.3 ± 52.3 c | 1785.4 ± 277.0 a |
| MBN (mg/kg) | 44.3 ± 7.3 b | 17.1 ± 6.7 c | 22.7 ± 8.1 c | 365.0 ± 75.3 a |
| MBC/MBN | 5.6 ± 0.2 a | 8.4 ± 2.6 a | 5.6 ± 1.1 a | 5.1 ± 0.7 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Fu, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. One-Year Monitoring of Daily Earthworm Cast Production: Surface Cast Contribution to Soil Fertility in a Subtropical Forest. Forests 2021, 12, 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070865
Wang X, Fu S, Wang X, Li Z, Li J, Zhang W. One-Year Monitoring of Daily Earthworm Cast Production: Surface Cast Contribution to Soil Fertility in a Subtropical Forest. Forests. 2021; 12(7):865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070865
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoling, Shenglei Fu, Xiaoli Wang, Zhigang Li, Jianxiong Li, and Weixin Zhang. 2021. "One-Year Monitoring of Daily Earthworm Cast Production: Surface Cast Contribution to Soil Fertility in a Subtropical Forest" Forests 12, no. 7: 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070865
APA StyleWang, X., Fu, S., Wang, X., Li, Z., Li, J., & Zhang, W. (2021). One-Year Monitoring of Daily Earthworm Cast Production: Surface Cast Contribution to Soil Fertility in a Subtropical Forest. Forests, 12(7), 865. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070865






