Estimation of Yield Loss Due to Deer Browsing in a Short Rotation Coppice Willow Plantation in Northern Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Deer Browsing Damage to Sprouting Willow Stems
2.3. Willow Yield Measurement
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
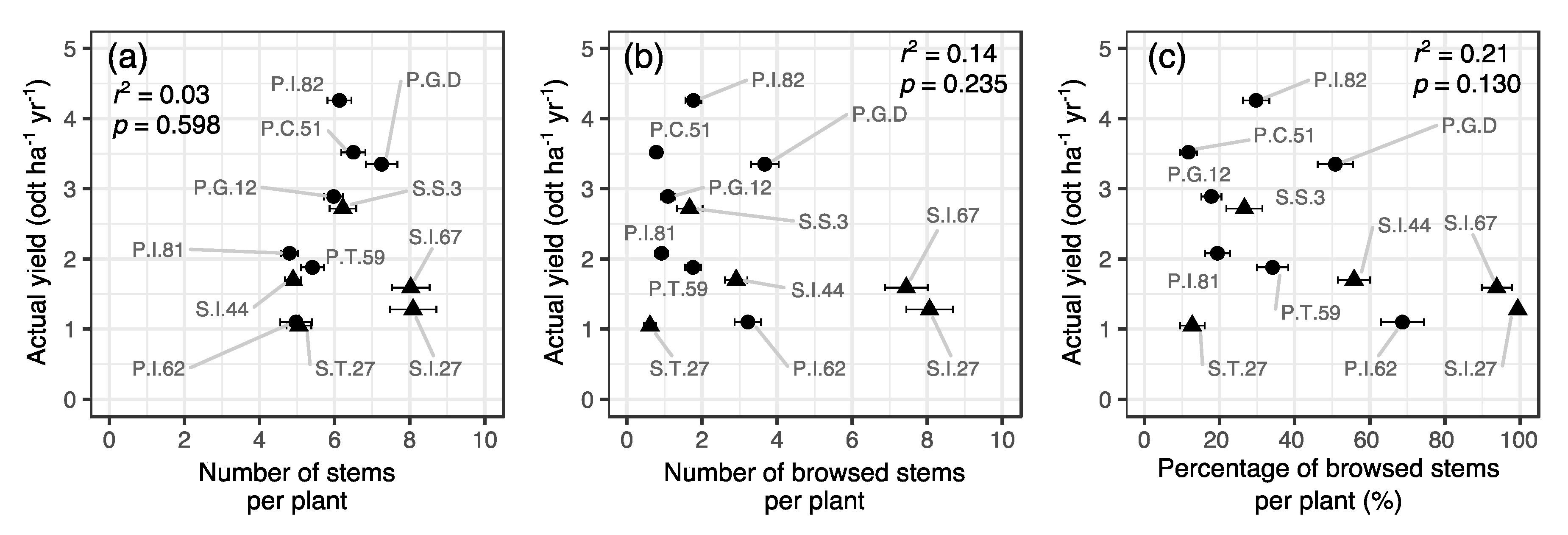
3.1. Deer Browsing and Willow Yield across Clones
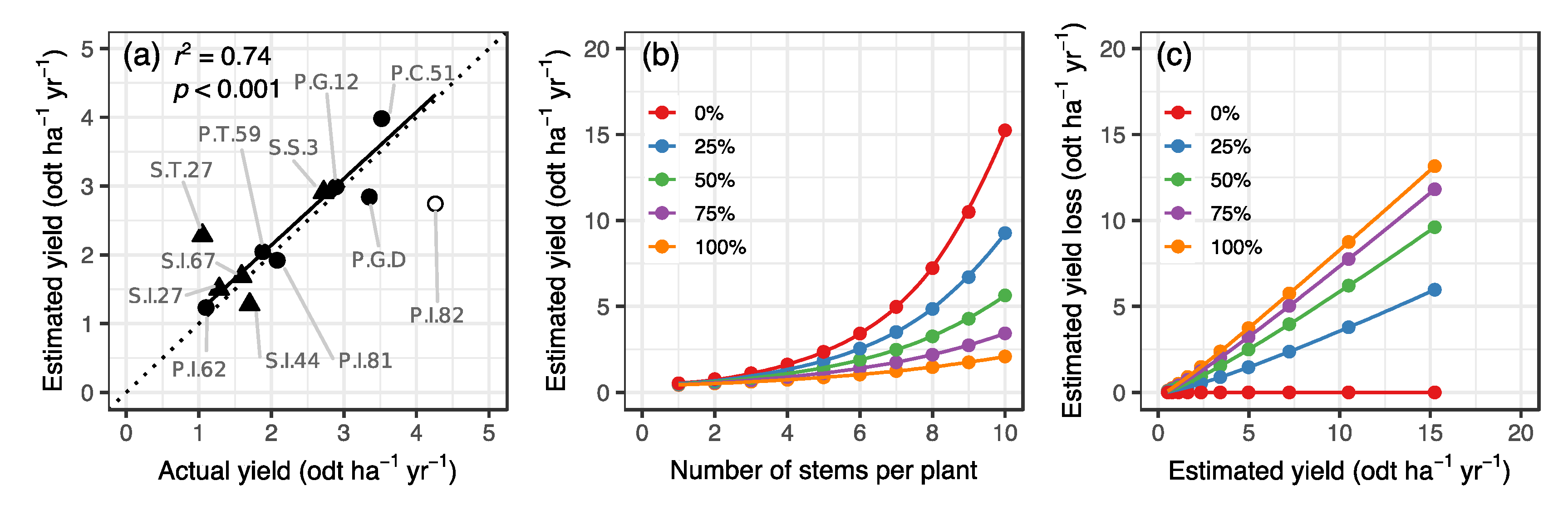
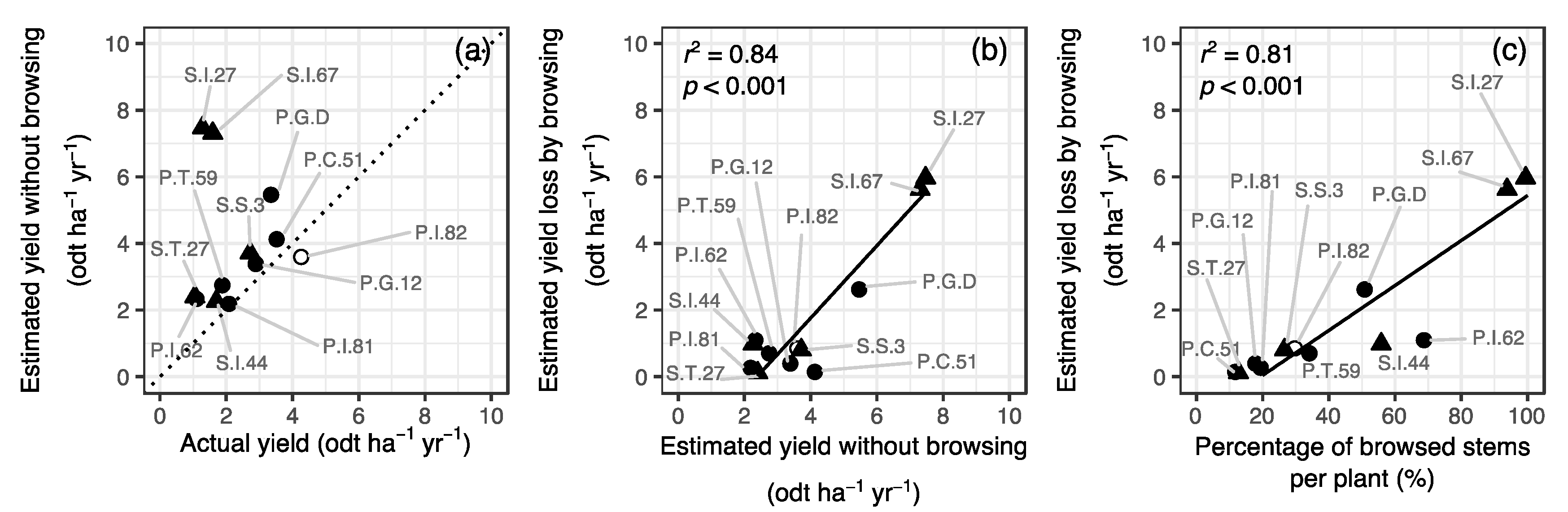
3.2. Estimation of Yield Loss Caused by Deer Browsing
4. Discussion
4.1. Yield Loss Caused by Deer Browsing
4.2. Potential Yield of Studied Willow Clones
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty. 2018. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/download/ (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Environmental Protection Agency. EPA’s Treatment of Biogenic Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Stationary Sources that Use Forest Biomass for Energy Production; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-and-radiation/epas-treatment-biogenic-carbon-dioxide-emissions-stationary-sources-use-forest (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- European Union. Directive 2009/28/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on the Promotion of the Use of Energy from Renewable Sources and Amending and Subsequently Repealing Directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Japan Woody Bioenergy Association. Wood Biomass Energy Data Book 2018; Japan Woody Bioenergy Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; p. 25. Available online: https://www.jwba.or.jp/app/download/13159696992/Data+book+2018+%28English+version%29.pdf?t=1523342683 (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Ericsson, K.; Rosenqvist, H.; Nilsson, L.J. Energy crop production costs in the EU. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amichev, B.Y.; Hangs, R.D.; Konecsni, S.M.; Stadnyk, C.N.; Volk, T.A.; Bélanger, N.; Vujanovic, V.; Schoenau, J.J.; Moukoumi, J.; Van Rees, K.C.J. Willow short-rotation production systems in Canada and northern United States: A review. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, S168–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindegaard, K.N.; Adams, P.W.; Holley, M.; Lamley, A.; Henriksson, A.; Larsson, S.; von Engelbrechten, H.G.; Esteban Lopez, G.; Pisarek, M. Short rotation plantations policy history in Europe: Lessons from the past and recommendations for the future. Food Energy Secur 2016, 5, 125–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylott, M.J.; Casella, E.; Tubby, I.; Street, N.R.; Smith, P.; Taylor, G. Yield and spatial supply of bioenergy poplar and willow short-rotation coppice in the UK. New Phytol. 2008, 178, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, E.S.; Volk, T.A.; Miller, R.O.; Serapiglia, M.J.; Gauch, H.G.; Van Rees, K.C.J.; Hangs, R.D.; Amichev, B.Y.; Kuzovkina, Y.A.; Labrecque, M.; et al. Genotype × environment interaction analysis of North American shrub willow yield trials confirms superior performance of triploid hybrids. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwijst, T.; Lundkvist, A.; Edelfeldt, S.; Albertsso, J. Development of sustainable willow short rotation forestry in northern Europe. In Biomass Now—Sustainable Growth and Use; Matovic, M.D., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P.A.; Haider, N.; Boby, L.A.; Heavey, J.P.; Miller, T.A. A Roadmap for Poplar and Willow to Provide Environmental Services and to Build the Bioeconomy; Washington State University: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Caslin, B.; Finnan, J.; Johnston, C.; McCracken, A.; Walsh, L. Short Rotation Coppice Willow Best Practice Guidelines; Teagasc and Agri-Food and Biosciences Institute: Carlow, Ireland, 2015; Available online: https://www.teagasc.ie/media/website/publications/2011/Short_Rotation_Coppice_Best_Practice_Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2020).
- Fabio, E.S.; Smart, L.B. Effects of nitrogen fertilization in shrub willow short rotation coppice production—A quantitative review. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Rashid, U.; Nawaz, M.; Ali, S.; Hussain, A.; Gull, M. Biomass production for bioenergy using marginal lands. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2017, 9, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styles, D.; Thorne, F.; Jones, M.B. Energy crops in Ireland: An economic comparison of willow and Miscanthus production with conventional farming systems. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, S.; Holland, R.A.; Lovett, A.; Sunnenberg, G.; Hastings, A.; Smith, P.; Wang, S.; Taylor, G. Potential impacts on ecosystem services of land use transitions to second-generation bioenergy crops in GB. Glob Chang. Biol. Bioenergy 2016, 8, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanbeveren, S.P.P.; Ceulemans, R. Biodiversity in short-rotation coppice. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 111, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, V.; Gauder, M.; Seidl, F.; Nerlich, K.; Claupein, W.; Graeff-Hönninger, S. Impact of different establishment methods in terms of tillage and weed management systems on biomass production of willow grown as short rotation coppice. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 85, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, I.; Rosenqvist, H.; Berndes, G. Slow expansion and low yields of willow short rotation coppice in Sweden; implications for future strategies. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4613–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, I.; Rutz, D. Sustainable Short Rotation Coppice: A Handbook; Rutz, D., Ed.; WIP Renewable Energies: Munich, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, D.; Brunner, J.; Helbig, C. The impact of wild animals on SRC in Germany—A widely underestimated factor. In Proceedings of the BENWOOD: Short rotation forestry and Agroforestry: An Exchange of Experience between CDM Countries and Europe, Conference Proceedings, Barolo, Italy, 20–22 June 2011; pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, R.; Guillet, C. Summer browsing by large herbivores in short-rotation willow plantations. Biomass Bioenergy 2002, 23, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestry Agency Japan. State of Japan’s Forests and Forest Management—3rd Country Report of Japan to the Montreal Process; Forestry Agency Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; p. 153. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/e/policies/forestry/attach/pdf/index-8.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Han, Q.; Harayama, H.; Uemura, A.; Ito, E.; Utsugi, H.; Kitao, M.; Maruyama, Y. High biomass productivity of short-rotation willow plantation in boreal Hokkaido achieved by mulching and cutback. Forests 2020, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Harayama, H.; Uemura, A.; Ito, E.; Utsugi, H. The effect of the planting depth of cuttings on biomass of short rotation willow. J. For. Res. 2017, 22, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, K.; Saitoh, T.; Uno, H.; Matsuda, H.; Yamamura, K. Adaptive management of sika deer populations in Hokkaido, Japan: Theory and practice. Popul. Ecol. 2010, 52, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirozu, T.; Soga, A.; Morishita, Y.K.; Seki, N.; Ko-Ketsu, M.; Fukumoto, S. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of Cryptosporidium infections in Yezo sika deer (Cervus nippon yesoensis) in the Tokachi sub-prefecture of Hokkaido, Japan. Parasitol. Int. 2020, 76, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkaido Goverment. Results of Wildlife Damage Survey. (In Japanese). 2020. Available online: http://www.pref.hokkaido.lg.jp/file.jsp?id=853297 (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Caslin, B.; Finnan, J.; McCracken, A. Willow Varietal Identification Guide; Teagasc & AFBI: Carlow, Ireland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, L.B.; Volk, T.A.; Lin, J.; Kopp, R.F.; Phillips, I.S.; Cameron, K.D.; White, E.H.; Abrahamson, L.P. Genetic improvement of shrub willow (Salix spp.) crops for bioenergy and environmental applications in the United States. Unasylva 2005, 56, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lindegaard, K.; Barker, J.H.A. Breeding willows for biomass. Asp. Appl. Biol. 1996, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, E.; Uemura, A.; Harayama, H.; Han, Q.; Utsugi, H. Root system development and partitioning of nitrogen in short-rotation willow. (In Japanese). Boreal For. Res. 2015, 63, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, M.; Matsuura, Y. The actual condition of animal damage in the willow plantation of Shimokawa town : A tendency of feeding damage and photography frequency by sensor camera about Yezo deer in willow growth period. (In Japanese). Boreal For. Res. 2014, 62, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, 3.6.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. A coefficient of determination for generalized linear models. Am. Stat. 2016, 71, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokely, T.D.; Betts, M.G.; Macinnis-Ng, C. Deer-mediated ecosystem service versus disservice depends on forest management intensity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 57, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helby, P.; Rosenqvist, H.; Roos, A. Retreat from Salix—Swedish experience with energy crops in the 1990s. Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, M.J.; Mustill, S.J.; Carver, P.; Nixon, P.M.I. Yield improvements through modification of planting density and harvest frequency in short rotation coppice Salix spp.—2. Resource capture and use in two morphologically diverse varieties. Biomass Bioenergy 2002, 22, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amichev, B.Y.; Volk, T.A.; Hangs, R.D.; Bélanger, N.; Vujanovic, V.; Van Rees, K.C.J. Growth, survival, and yields of 30 short-rotation willow cultivars on the Canadian Prairies: 2nd rotation implications. New For. 2018, 49, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.; Rice, B.; Finnan, J.; McConnon, R. A Review of Past and Current Research on Short Rotation Coppice in Ireland and Abroad; COFORD: Dublin, Ireland, 2010; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, S.U.; Jørgensen, U.; Kjeldsen, J.B.; Lærke, P.E. Effect of fertilisation on biomass yield, ash and element uptake in SRC willow. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 86, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, P.D.; Bryant, J.P.; Chapin, F.S., 3rd. Resource availability and plant antiherbivore defense. Science 1985, 230, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herms, D.A.; Mattson, W.J. The dilemma of plants: To grow or defend. Q. Rev. Biol. 1992, 67, 283–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iijima, H. The Effects of Landscape Components, Wildlife Behavior and Hunting Methods on Hunter Effort and Hunting Efficiency of Sika Deer. Wildl. Biol. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charles, J.G.; Nef, L.; Allegro, G.; Collins, C.M.; Delplanque, A.; Gimenez, R.; Höglund, S.; Jiafu, H.; Larsson, S.; Luo, Y.; et al. Insect and other pests of poplars and willows. In Poplars and Willows: Trees for Society and the Environment; Isebrands, J.G., Richardson, J., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2014; pp. 459–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, H.; Kaji, K.; Tamada, K. Sika Deer Population Irruptions and Their Management on Hokkaido Island, Japan. In Sika Deer: Biology and Management of Native and Introduced Populations; McCullough, D.R., Takatsuki, S., Kaji, K., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2009; pp. 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Factor | Estimate | SE | t Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM for 12 clones (including an outlier) 1 | ||||
| Intercept | −1.113 (0.33) | 0.616 | −1.808 | 0.104 |
| Number of stems per plant | 0.411 (1.51) | 0.118 | 3.488 | 0.007 |
| Number of browsed stems per plant | −0.223 (0.80) | 0.055 | −4.037 | 0.003 |
| GLM for 9 clones (excluding an outlier) 2 | ||||
| Intercept | −1.009 (0.36) | 0.519 | −1.943 | 0.088 |
| Number of stems per plant | 0.373 (1.45) | 0.100 | 3.724 | 0.006 |
| Number of browsed stems per plant | −0.199 (0.82) | 0.048 | −4.186 | 0.003 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harayama, H.; Han, Q.; Ishihara, M.; Kitao, M.; Uemura, A.; Sasaki, S.; Yamada, T.; Utsugi, H.; Maruyama, Y. Estimation of Yield Loss Due to Deer Browsing in a Short Rotation Coppice Willow Plantation in Northern Japan. Forests 2020, 11, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11080809
Harayama H, Han Q, Ishihara M, Kitao M, Uemura A, Sasaki S, Yamada T, Utsugi H, Maruyama Y. Estimation of Yield Loss Due to Deer Browsing in a Short Rotation Coppice Willow Plantation in Northern Japan. Forests. 2020; 11(8):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11080809
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarayama, Hisanori, Qingmin Han, Makoto Ishihara, Mitsutoshi Kitao, Akira Uemura, Shozo Sasaki, Takeshi Yamada, Hajime Utsugi, and Yutaka Maruyama. 2020. "Estimation of Yield Loss Due to Deer Browsing in a Short Rotation Coppice Willow Plantation in Northern Japan" Forests 11, no. 8: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11080809
APA StyleHarayama, H., Han, Q., Ishihara, M., Kitao, M., Uemura, A., Sasaki, S., Yamada, T., Utsugi, H., & Maruyama, Y. (2020). Estimation of Yield Loss Due to Deer Browsing in a Short Rotation Coppice Willow Plantation in Northern Japan. Forests, 11(8), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11080809





