Relationship between Soil Burn Severity in Forest Fires Measured In Situ and through Spectral Indices of Remote Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
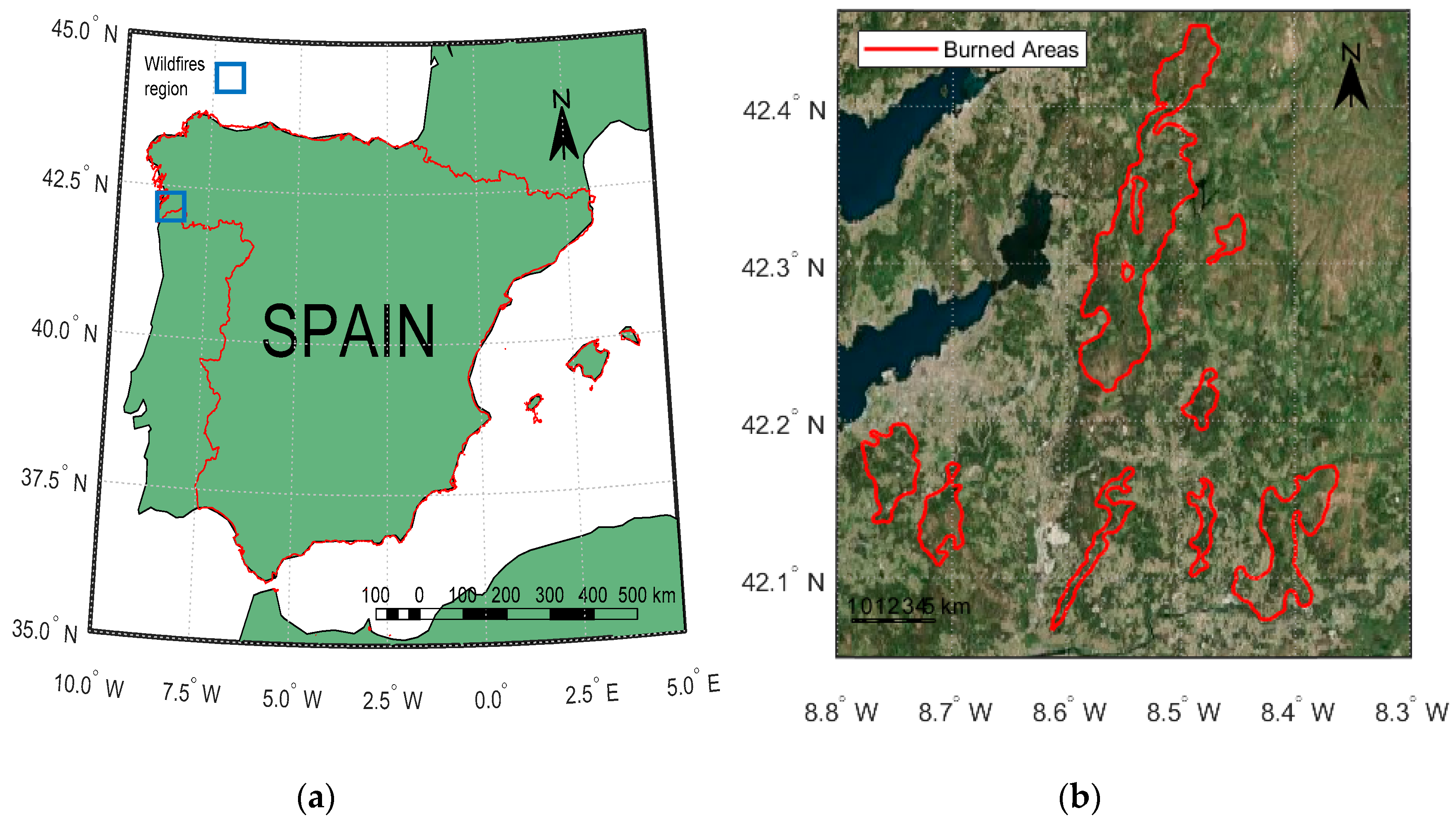
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sentinel-2 Data
2.3. Landsat-8 Data
2.4. Remote Sensing Indices
2.5. Severity Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chuvieco, E.; Aguado, I.; Yebra, M.; Nieto, H.; Salas, J.; Martín, M.P.; Vilar, L.; Martínez, J.; Martín, S.; Ibarra, P.; et al. Development of a framework for fire risk assessment using remote sensing and geographic information system technologies. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Fire Management Global Assessment 2006; FAO Forestry Paper No. 151; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Omi, P.N. Theory and Practice of Wildland Fuels Management. Curr. For. Rep. 2015, 1, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, S.J. Essays on science and society: The fires this time, and next. Science 2001, 294, 1005–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerling, A.L. Warming and Earlier Spring Increase Western U.S. Forest Wildfire Activity. Science 2006, 313, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuvieco, E. Satellite Observation of Biomass Burning. In Earth Observation of Global Change; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 109–142. [Google Scholar]
- Chuvieco, E.; Riaño, D.; Van Wagtendok, J.; Morsdof, F. Fuel loads and fuel type mapping. In Wildland Fire Danger Estimation and Mapping: The Role of Remote Sensing Data; World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd.: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 119–142. [Google Scholar]
- Chuvieco, E. Global impacts of fire. In Earth Observation of Wildland Fires in Mediterranean Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, S.J.; Mack, M.C.; Gurney, K.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Houghton, R.A. Ecosystem responses to recent climate change and fire disturbance at northern high latitudes: Observations and model results contrasting northern Eurasia and North America. Environ. Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 045031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, J.A.; Asner, G.P.; Randerson, J.T.; Tucker, C.; Los, S.; Birdsey, R.; Field, C. Trends in North American net primary productivity derived from satellite observations, 1982–1998. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Cohen, W.B.; Schroeder, T.A. Trajectory-based change detection for automated characterization of forest disturbance dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, N.H.; Kasischke, E.S.; Hall, R.J.; Murphy, K.A.; Verbyla, D.L.; Hoy, E.E.; Allen, J.L. Using Landsat data to assess fire and burn severity in the North American boreal forest region: An overview and summary of results. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape assessment: Remote sensing of severity, the normalized burn ratio and ground measure of severity, the composite burn index. In FIREMON: Fire Effects Monitoring and Inventory System; USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Res. Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kushla, J.D.; Ripple, W.J. Assessing wildfire effects with Landsat thematic mapper data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2493–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Delgado, R.; Lloret, F.; Pons, X. Influence of fire severity on plant regeneration by means of remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsi, J.A.; Lee, K.; Kvaran, G.; Markham, B.L.; Pedelty, J.A. The spectral response of the Landsat-8 operational land imager. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10232–10251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S., Jr. An improved dark-object subtraction technique for atmospheric scattering correction of multispectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L. An improved dark-object subtraction technique for atmospheric correction of Landsat 8. In MIPPR 2015: Remote Sensing Image Processing, Geographic Information Systems, and Other Applications; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.C.; Kaufman, Y.J. Selection of the 1.375 micrometer MODIS Channel for Remote Sensing of Cirrus Clouds and Stratospheric Aerosols from Space. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 4231–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, W.P. The role of disturbance in natural communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1984, 15, 353–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, J.E. Fire intensity, fire severity and burn severity: A brief review and suggested usage. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutes, D.C.; Keane, R.E.; Caratti, J.F.; Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. (Eds.) FIREMON: Fire effects monitoring and inventory system. In Gen. Tech. Rep.; RMRS-GTR-164-Cd; USDA Forest Service; Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- De Santis, A.; Chuvieco, E. GeoCBI: A modified version of the Composite Burn Index for the initial assessment of the short-term burn severity from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.A.; Shakesby, R.A.; Robichaud, P.R.; Cannon, S.H.; Martin, D.A. Current research issues related to post-wildfire runoff and erosion processes. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 122, 10–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Vega, J.A. Modelling the effect of soil burn severity on soil erosion at hillslope scale in the first year following wildfire in NW Spain. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, S.; Vega, J.A.; Rodríguez y Silva, F.; Fernández, C.; Vega-Nieva, D.; Álvarez-González, J.G.; Ruiz-González, A.D. Validación de los índices de teledetección dNBR y RdNBR para determinar la severidad del fuego en el incendio forestal de Oia-O Rosal (Pontevedra) en 2013. Rev. Teledetección 2017, 49, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, Z.A.; Morgan, P.; Evans, J.S. A predictive model of burn severity based on 20-year satellite-inferred burn severity data in a large southwestern US wilderness area. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, A.T.; Morgan, P.; Bobbitt, M.J.; Smith, A.M.S.; Lewis, S.A.; Lentile, L.B.; Robichaud, P.R.; Clark, J.T.; McKinley, R.A. The relationship of multiespectral satellite imagery to immediate fire effects. Fire Ecol. 2007, 3, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Thode, A.E. Quantifying burn severity in a heterogeneous landscape with a relative version of the delta Normalized Burn Ratio (dNBR). Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picotte, J.J.; Robertson, K.M. Validation of remote sensing of burn severity in south-eastern US ecosystems. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2011, 20, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagtendonk, J.W.; Root, R.R.; Key, C.H. Comparison of AVIRIS and Landsat ETM+ detection capabilities for burn severity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraverbeke, S.; Lhermitte, S.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Goossens, R. Evaluation of pre/post-fire differenced spectral indices for assessing burn severity in a Mediterranean environment with Landsat Thematic Mapper. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3521–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.A.; Hudak, A.T.; Ottmar, R.D.; Robichaud, P.R.; Lentile, L.B.; Hood, S.M.; Cronan, J.B.; Morgan, P. Using hyperspectral imagery to estimate forest floor consumption from wildfire in boreal forests of Alaska, USA. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2011, 20, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, E.; Fernández-García, V.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Valbuena, L.; Tárrega, R.; Calvo, L. Evaluation of Composite Burn Index and Land Surface Temperature for Assessing Soil Burn Severity in Mediterranean Fire-Prone Pine Ecosystems. Forests 2018, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, P.R.; Lewis, S.A.; Laes, D.Y.M.; Hudak, A.T.; Kokaly, R.F.; Zamudio, J.A. Postfire soil burn severity mapping with hyperspectral image unmixing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, C.; Dıaz-Fernández, P.; Gil, L. Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza. In Tercer Inventario Forestal Nacional 1997–2006, Barcelona; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, S.A. Remote sensing aerosols using satellite infrared observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17069–17079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA. Sentinel-2 User Handbook; ESA Standard Document. 64; European Spatial Agency: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Copernicus Open Access Hub. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- Kaufman, Y.; Sendra, C. Algorithm for automatic atmospheric corrections to visible and near-IR satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 1357–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascon, F.; Bouzinac, C.; Thépaut, O.; Jung, M.; Francesconi, B.; Louis, J.; Languille, F. Copernicus Sentinel-2A calibration and products validation status. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Wilm, U.; Louis, J.; Richter, R.; Gascon, F.; Niezette, M. Sentinel-2 level 2A prototype processor: Architecture, algorithms and first results. In Proceedings of the 2013 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Edinburgh, UK, 9–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Earthexplorer. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 10 January 2019).
- U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat—Earth Observation Satellites; Version 1.1; U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2015–3081; U.S. Geological Survey: Washingotn, DC, USA, 2016.
- Song, C.; Woodcock, C.E.; Seto, K.C.; Lenney, M.P.; Macomber, S.A. Classification and change detection using Landsat TM data: When and how to correct atmospheric effects? Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Baig, M.H.A.; Liu, S.; Wan, H.; Wu, T.; Yang, Y. Estimating the area burned by agricultural fires from Landsat 8 Data using the Vegetation Difference Index and Burn Scar Index. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2018, 27, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, T.; O’neal, K.J.; Csiszar, I. Regionally adaptable dNBR-based algorithm for burned area mapping from MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez Taboada, M.F.; Rodríguez Pérez, J.R.; Castedo Dorado, F. Semi-Automatización de los Procesos de Monitorización Empleando Imágenes de Satélite en un Entorno Orientado a Objetos. Cartografía, Cuantificación y Clasificación de Áreas Quemadas en Galicia (2006); IX Congreso Nacional Top-Cart: Valencia, España, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Key, C.H.; Benson, N.C. Landscape assessment (LA). In FIREMON: Fire Effects Monitoring and Inventory System; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.A.; Fontúrbel, M.T.; Merino, A.; Fernández, C.; Ferreiro, A.; Jiménez, E. Testing the ability of visual indicators of soil burn severity to reflect changes in soil chemical and microbial properties in pine forests and shrubland. Plant Soil 2013, 369, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.A.; Skowronski, N.S.; Gallagher, M.R. Gallagher High spatial resolution burn severity mapping of the New Jersey Pine Barrens with WorldView-3 near-infrared and shortwave infrared imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epting, J.; Verbyla, D.; Sorbel, B. Evaluation of remotely sensed indices for assessing burn severity in interior Alaska using Landsat TM and ETM+. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.J.; Freeburn, J.T.; De Groot, W.J.; Pritchard, J.M.; Lynham, T.J.; Landry, R. Remote sensing of burn severity: Experience from western Canada boreal fires. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2008, 17, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinis, G.; Mitsopoulos, I.; Chrysafi, I. Evaluating and comparing Sentinel 2A and Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) spectral indices for estimating fire severity in a Mediterranean pine ecosystem of Greece. GISci. Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Caballero, I.; Silva, G.; Parra, P.C.; Vázquez, Á.; Caldeira, R. Evaluation of forest fire on Madeira Island using Sentinel-2A MSI imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth observ. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
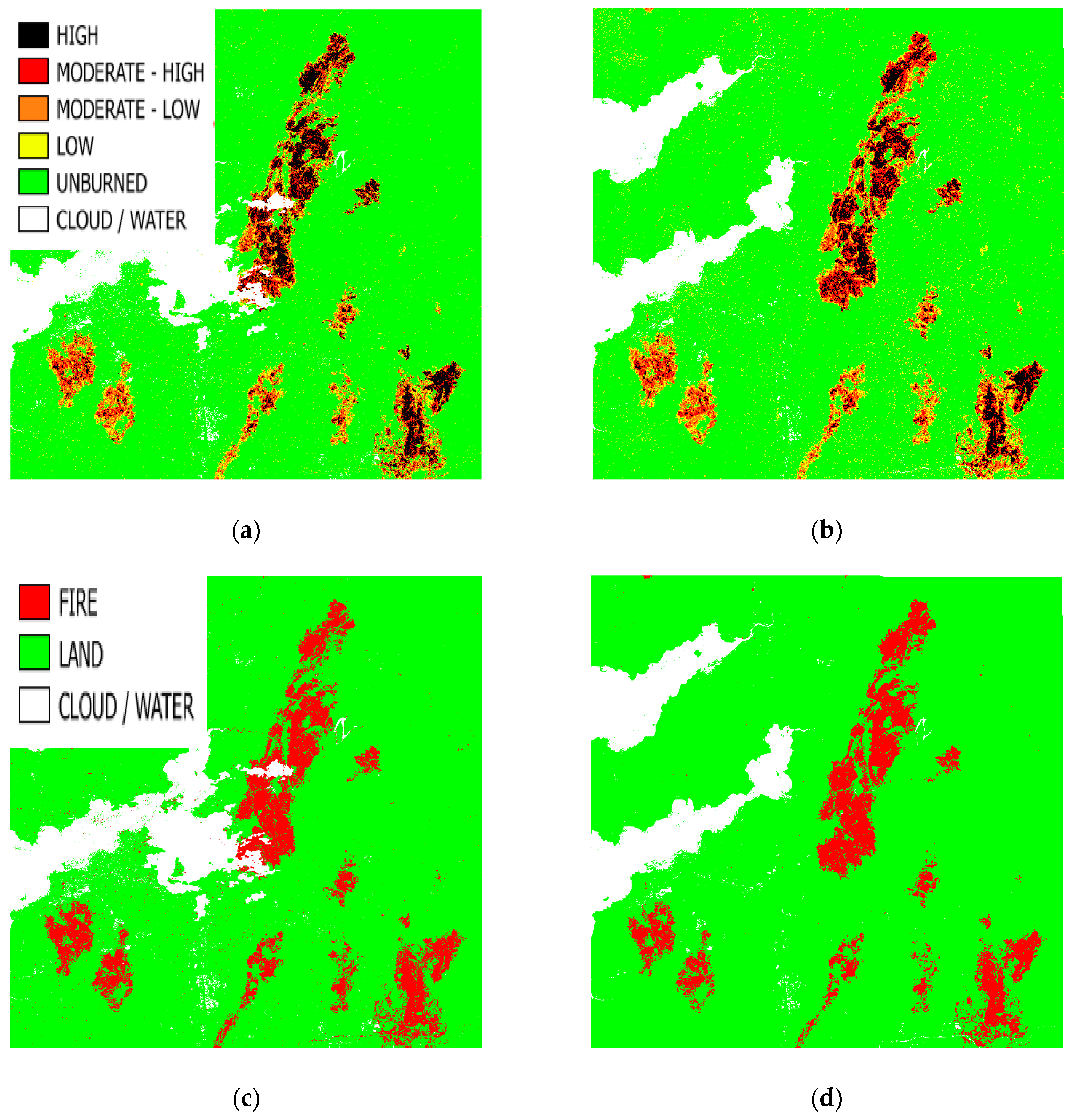
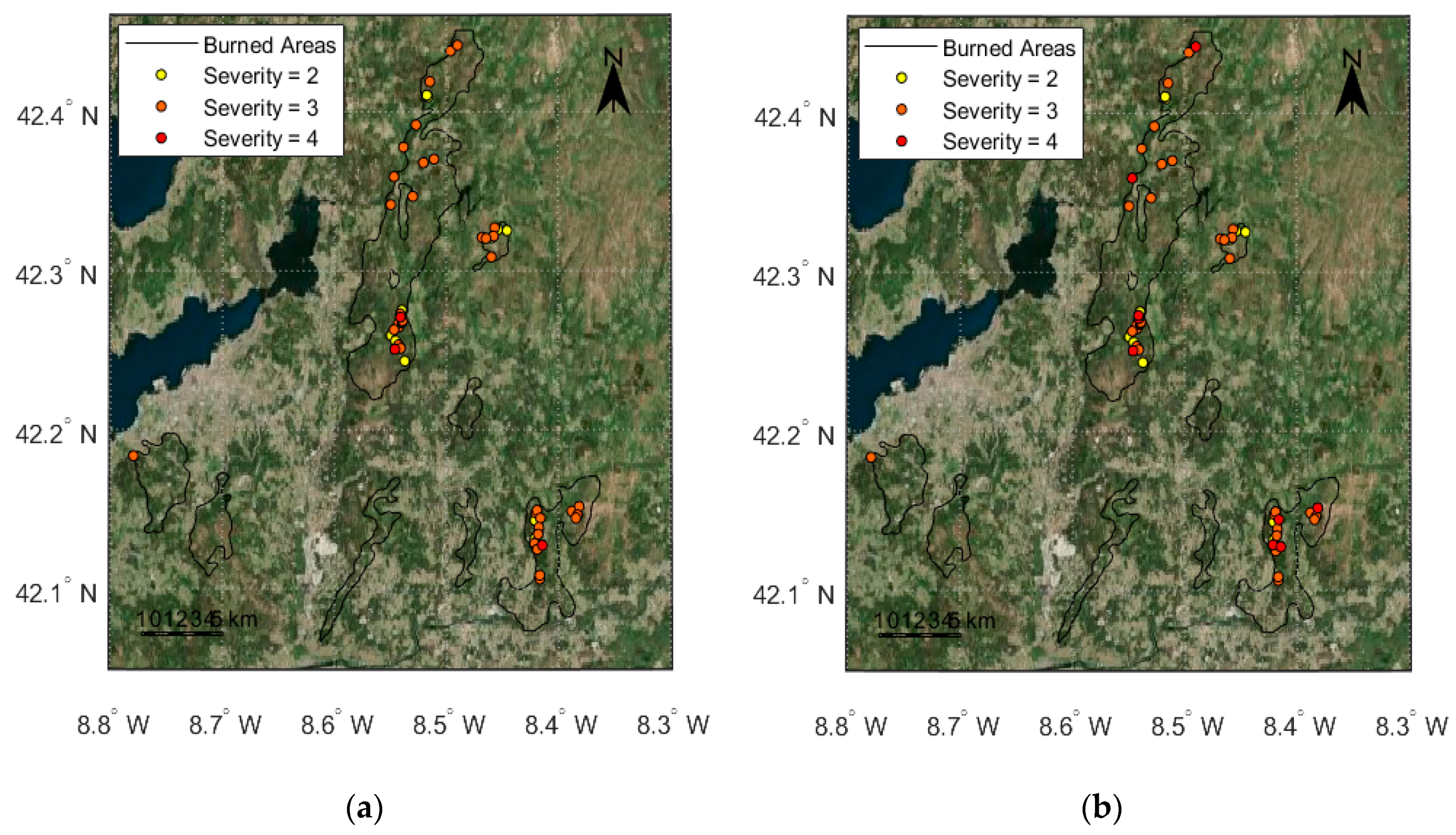
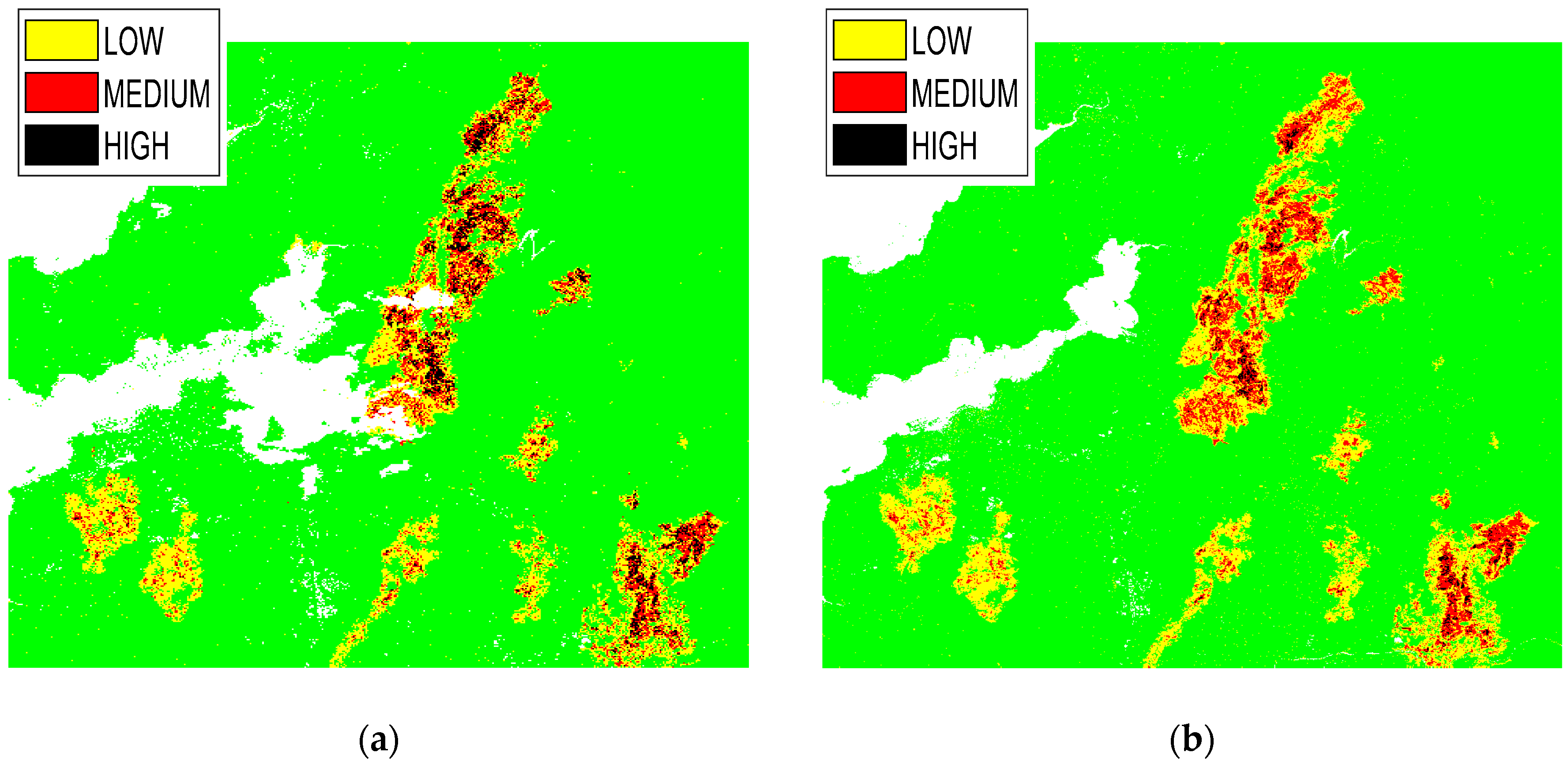
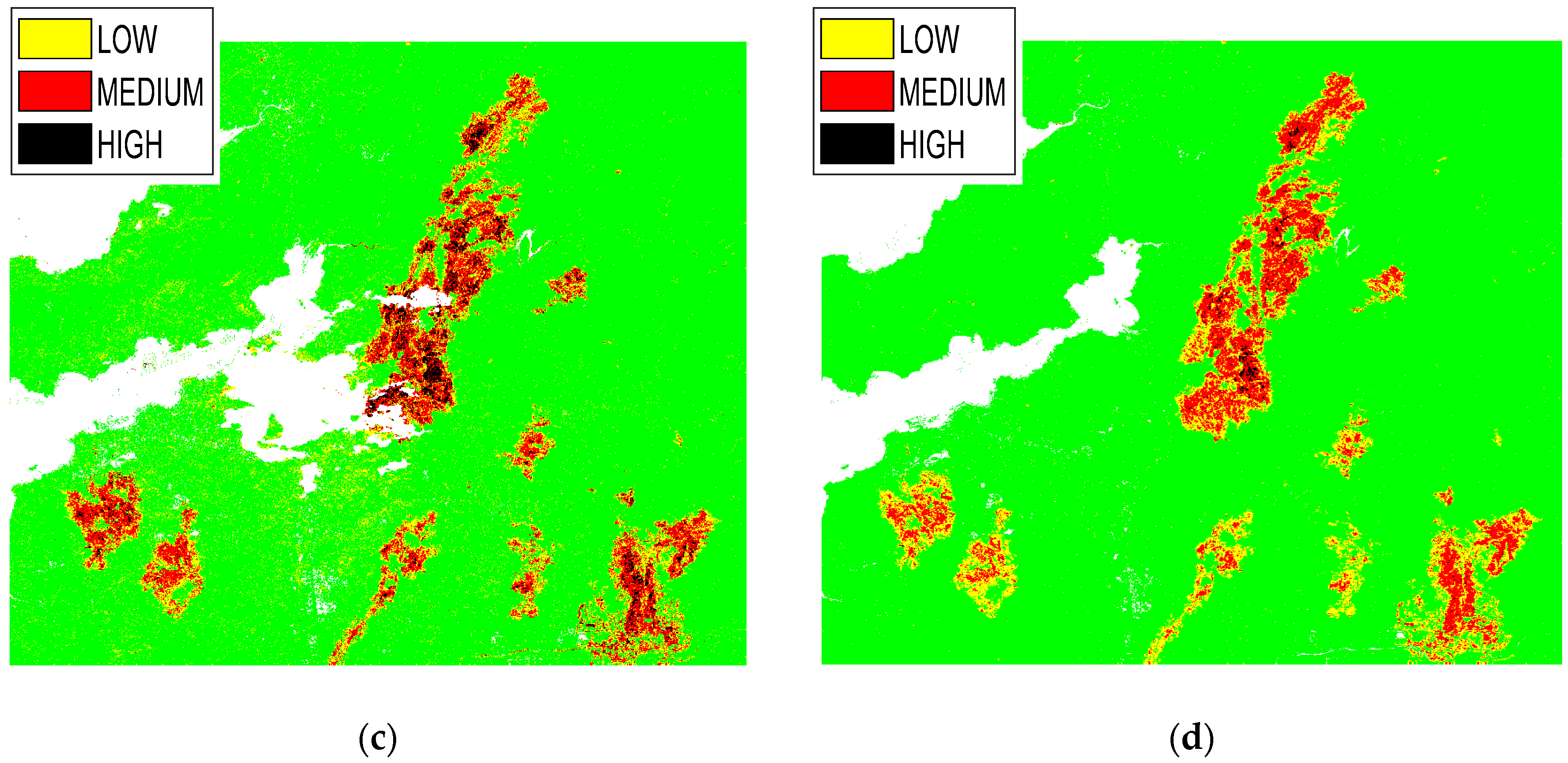
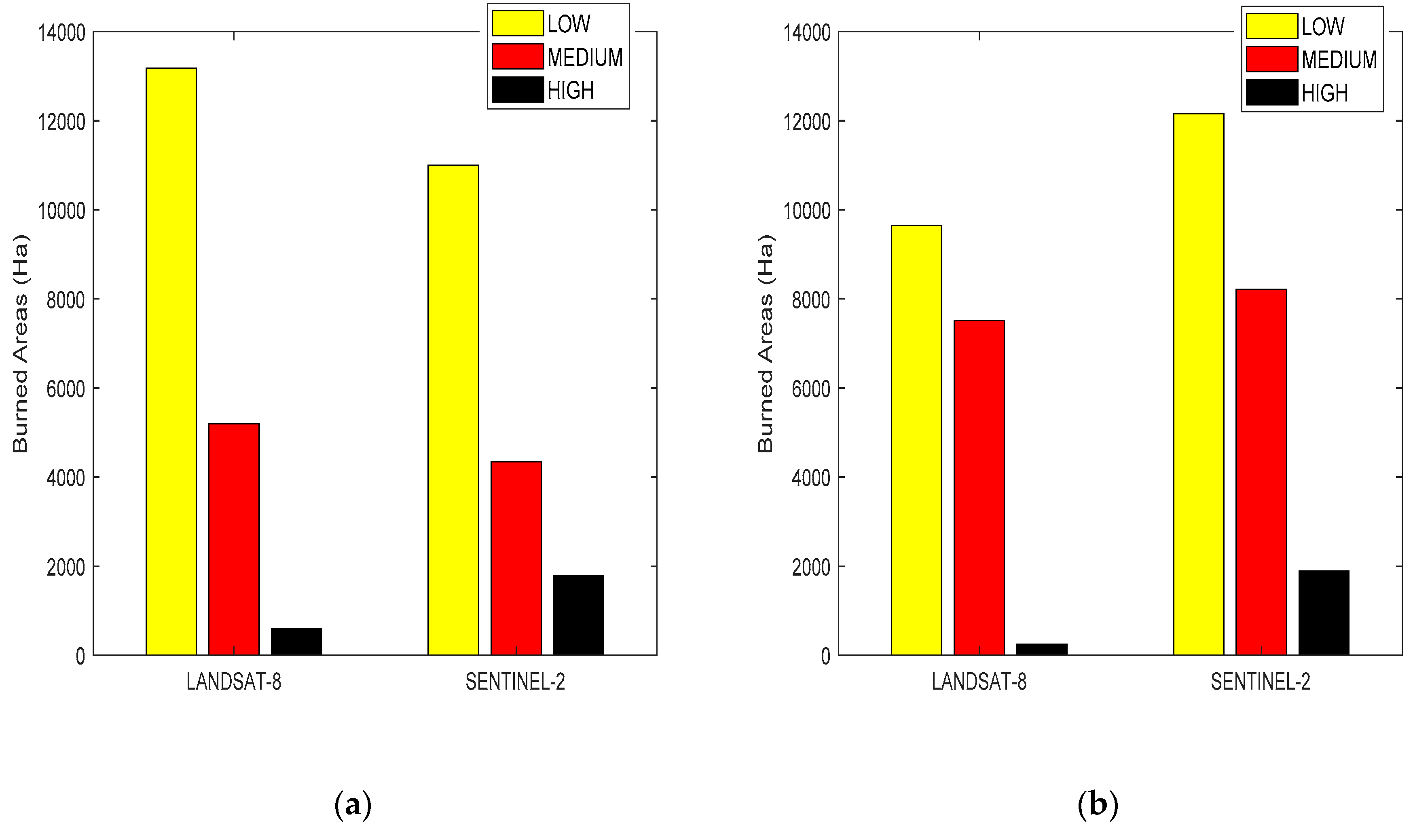
| Pixel Values | Severity Level |
|---|---|
| −0.5 ≤ dNBR < −0.25 | High Regrowth |
| −0.25 ≤ dNBR < −0.1 | Low Regrowth |
| −0.1 ≤ dNBR < 0.1 | Unburned |
| 0.1 ≤ dNBR < 0.27 | Low |
| 0.27 ≤ dNBR < 0.44 | Moderate-Low |
| 0.44 ≤ dNBR < 0.66 | Moderate-High |
| 0.66 ≤ dNBR < 1.33 | High |
| Five Burn Severity Degrees Classification | Six Burn Severity Degrees Classification | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severity Degree | Description | Number of Points | Severity Degree | Description | Number of Points |
| 1 | Very Low | 0 | 1 | Very Low | 0 |
| 2 | Low | 13 | 2 | Low | 12 |
| 3 | Medium | 43 | 3 | Medium | 38 |
| 4 | High | 5 | 4 | High (<1 cm) | 11 |
| 5 | High (>1 cm) | 0 | |||
| 5 | Very High | 0 | 6 | Very High | 0 |
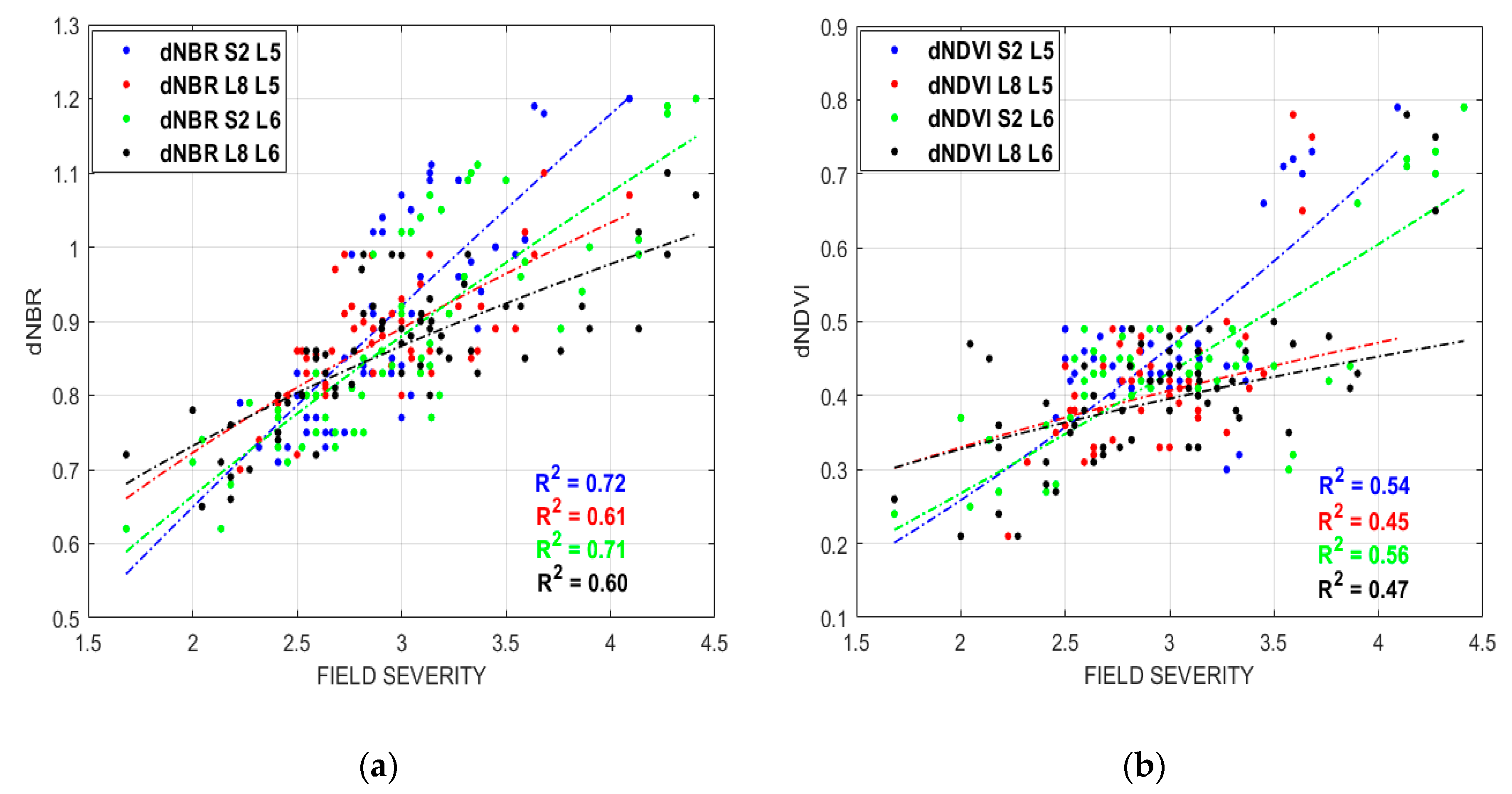
| Satellites | Indices | Burn Severity Degrees Classification | Equations | R2 | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 | dNBR | Five burn severity degrees | 0.357 × (FS0.861) | 0.72 | 0.08 |
| Six burn severity degrees | 0.411 × (FS0.693) | 0.71 | 0.08 | ||
| dNDVI | Five burn severity degrees | 0.095 × (FS1.450) | 0.54 | 0.09 | |
| Six burn severity degrees | 0.119 × (FS1.175) | 0.56 | 0.09 | ||
| Landsat-8 | dNBR | Five burn severity degrees | 0.506 × (FS0.512) | 0.61 | 0.06 |
| Six burn severity degrees | 0.548 × (FS0.417) | 0.56 | 0.06 | ||
| dNDVI | Five burn severity degrees | 0.231 × (FS0.515) | 0.45 | 0.12 | |
| Six burn severity degrees | 0.237 × (FS0.466) | 0.47 | 0.12 |
| Thresholds | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellites | Indices | Low | Medium | High |
| Sentinel-2 | dNBR | X ≤ 0.7 | 0.7 < X ≤ 0.9 | X > 0.9 |
| dNDVI | X ≤ 0.35 | 0.35 < X ≤ 0.55 | X > 0.55 | |
| Landsat-8 | dNBR | X ≤ 0.7 | 0.7 < X ≤ 0.95 | X > 0.95 |
| dNDVI | X ≤ 0.35 | 0.35 < X ≤ 0.5 | X > 0.5 |
| Satellites | Indices | Low (%) | Medium (%) | High (%) | Global (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 | dNBR | 77 | 65 | 100 | 81 |
| dNDVI | 62 | 86 | 80 | 76 | |
| Landsat-8 | dNBR | 54 | 98 | 60 | 71 |
| dNDVI | 62 | 81 | 60 | 68 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobrino, J.A.; Llorens, R.; Fernández, C.; Fernández-Alonso, J.M.; Vega, J.A. Relationship between Soil Burn Severity in Forest Fires Measured In Situ and through Spectral Indices of Remote Detection. Forests 2019, 10, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050457
Sobrino JA, Llorens R, Fernández C, Fernández-Alonso JM, Vega JA. Relationship between Soil Burn Severity in Forest Fires Measured In Situ and through Spectral Indices of Remote Detection. Forests. 2019; 10(5):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050457
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobrino, Jose Antonio, Rafael Llorens, Cristina Fernández, José M. Fernández-Alonso, and José Antonio Vega. 2019. "Relationship between Soil Burn Severity in Forest Fires Measured In Situ and through Spectral Indices of Remote Detection" Forests 10, no. 5: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050457
APA StyleSobrino, J. A., Llorens, R., Fernández, C., Fernández-Alonso, J. M., & Vega, J. A. (2019). Relationship between Soil Burn Severity in Forest Fires Measured In Situ and through Spectral Indices of Remote Detection. Forests, 10(5), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10050457






