Abstract
A wide range of species and hybrids of black and balsam poplars or cottonwoods (Populus L., sections Aigeiros and Tacamahaca) grow naturally, or have been introduced to grow in plantations in China. Many species of Melampsora can cause poplar leaf rust in China, and their distributions and host specificities are not entirely known. This study was prompted by the new susceptibility of a previously resistant cultivar, cv. ‘Zhonghua hongye’ of Populus deltoides (section Aigeiros), as well as by the need to know more about the broader context of poplar leaf rust in China. Rust surveys from 2015 through 2018 in Shaanxi, Sichuan, Gansu, Henan, Shanxi, Qinghai, Beijing, and Inner Mongolia revealed some samples with urediniospores with the echinulation pattern of M. medusae. The morphological characteristics of urediniospores and teliospores from poplar species of the region were further examined with light and scanning electron microscopy. Phylogenetic analysis based on sequences of the rDNA ITS region (ITS1, 5.8S rRNA gene, and ITS2) and the nuclear large subunit rDNA (D1/D2) was used to further confirm morphology-based identification. Based on combined analyses, five of the fifteen fully characterized samples were identified as Melampsora medusae: one from Shaanxi and four from Sichuan. Two of the five were from Populus deltoides cv. ‘Zhonghua hongye’. Three others were identified on Populus szechuanica, P. simonii, and P. yunnanensis. Additional samples of M. medusae were collected in Shaanxi in 2017 and 2018, and from Henan in 2015 through 2018. Altogether these findings show that this introduced pathogen is widespread and persistent from year to year in China. This is the first report of this North American poplar leaf rust species, Melampsora medusae, in China. It has previously been reported outside North America in Argentina, Europe, Australia, New Zealand, Japan, and Russia.
1. Introduction
Poplar leaf rust is caused by many species of Melampsora, each of which tends to be host-specific within the genus Populus. Leaf rust can be very damaging to black and balsam poplar species in sections Aigeiros and Tacamahaca, respectively [1,2,3,4]. Melampsora species have native ranges, but many have been inadvertently introduced to other parts of the world [5] since the genus was first described in 1843 [6]. Introductions accompanying the spread of hybrid poplar culture also have provided opportunities for previously isolated species of Melampsora to hybridize [7,8,9]; M. medusae has hybridized with both M. larici-populina [9] and with M. occidentalis [8]. Melampsora medusae is indigenous to Eastern North America in the native range of Populus deltoides [10], but it has also been introduced to Russia [11], Argentina [12], Australia [4], South Africa [4], France [13], India [7], Japan [14], Spain [15], and Portugal [16,17].
Like all rust fungi, Melampsora medusae is an obligate biotrophic plant parasite. It has a heteroecious life cycle in its native range with uredinia, telia, and basidia on P. deltoides, and spermogonia and aecia on Larix laricina. In the European Union, it is an introduced, quarantined fungus [18,19,20,21]. The telial hosts of M. medusae include species of section Aigeiros (e.g., P. deltoides, P. nigra, P. × euramericana) and of section Tacamahaca (e.g., P. maximowiczii, P. simonii, P. trichocarpa). The signs of M. medusae on poplars are typical of many leaf rusts: small, yellow uredinia appear within 10 days of infection on the abaxial surfaces of leaves, or on both sides of the leaves in the case of heavy infections [7,22,23,24].
As recently as five years ago, P. deltoides was largely rust-free in China due to its resistance to the native M. larici-populina. Now, however, P. deltoides and its hybrids experience severe rust from early July until November in Southern China. In Northern China, the new rust season for P. deltoides develops somewhat later. In the mountains of Southern China, some species of section Tacamahaca even become rusted in early July. Unfortunately, the formerly promising cultivar of P. deltoides, ‘Zhonghua hongye’ (Figure 1), is also now rust-susceptible. These recent changes prompted the rust surveys of this study to determine their cause. Between 2015 and 2018, surveys were conducted in Shaanxi, Sichuan, Gansu, Henan, Shanxi, Qinghai, Beijing, and Inner Mongolia. We collected poplar leaf rust specimens and fully characterized 15 collections in this study. By full characterization we mean both morphology- and sequence-based identification [2,25,26]. In addition to the 15, some other samples were identified on the basis of morphology alone.
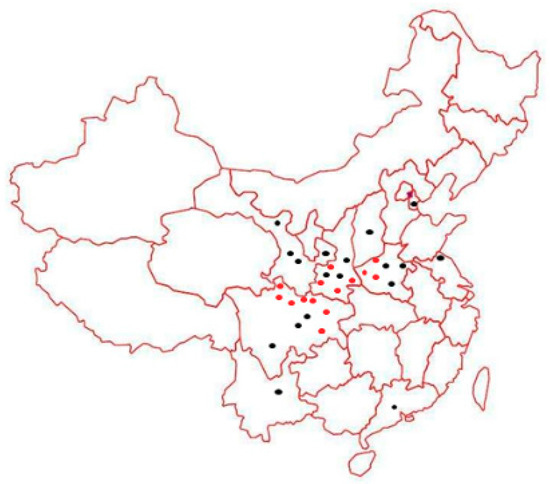
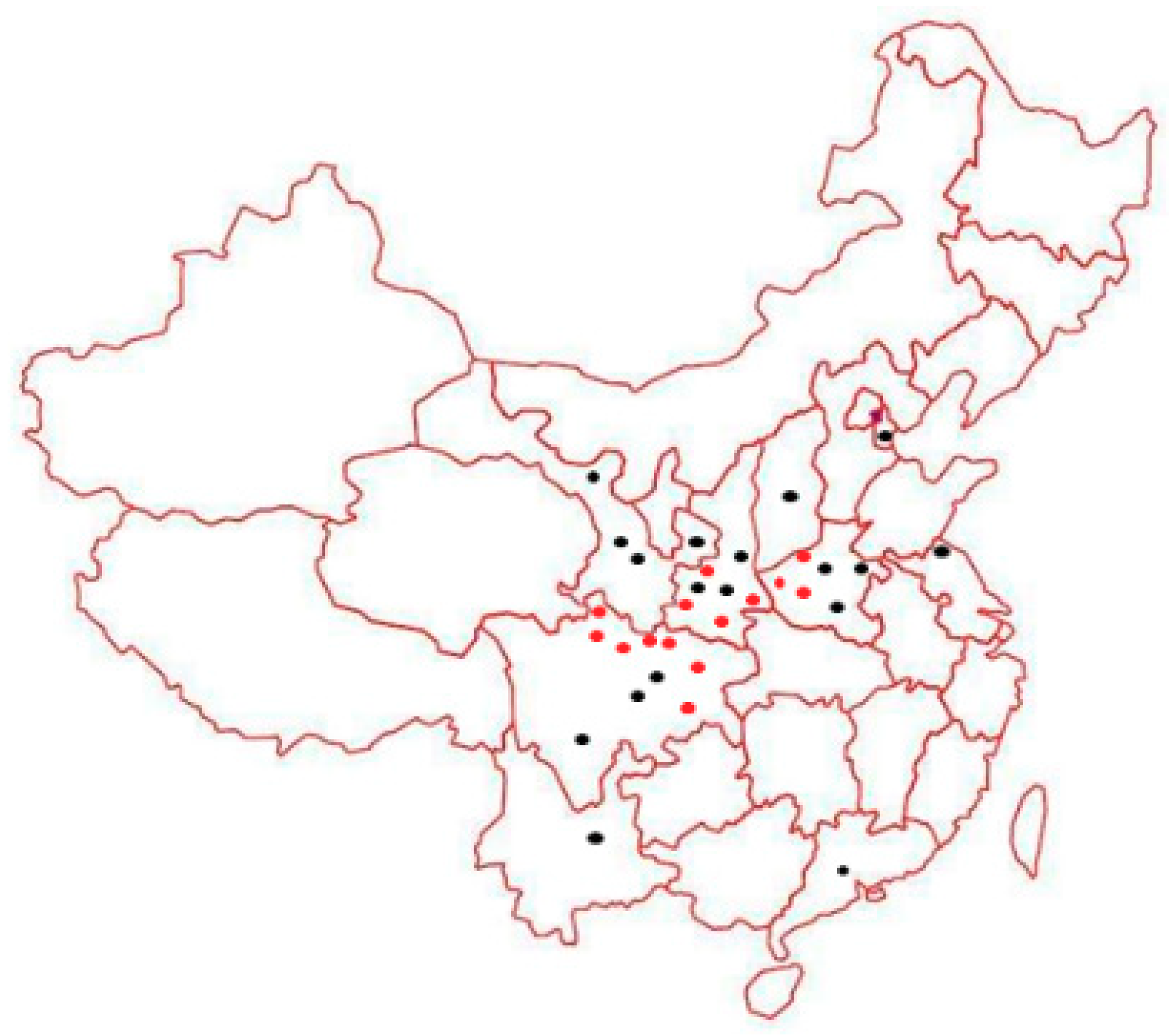
Figure 1.
Sites (red dots) for rust sampling of P. deltoides cv. ‘Zhonghua hongye’. Dark dots represent the potential distribution of this formerly rust-free cultivar.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surveys and Specimens
Poplar leaf rust samples were collected during surveys from 2015 through 2018 in Shaanxi, Sichuan, Gansu, Shanxi, Qinghai, Beijing and Inner Mongolia in China. Specimens were dried in plant presses and deposited in State Key Laboratory of Mycology Institute of Microbiology Chinese Academy of Sciences. Sequences were deposited in GenBank with accession numbers as in Table 1.

Table 1.
Fifteen fully characterized samples of Melampsora in China identified as species, with host plants, sampling locations, years, and voucher and GenBank accession numbers. The two samples of rust on P. deltoides are both from cv. ‘Zhonghua hongye’.
2.2. Morphological Observations
Morphological characteristics of uredinia and telia were examined under the light microscope (LM) and the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Fifty spores of each sample were randomly selected and examined with a Leica DM4000B. Length, width, and wall thickness both apically and laterally were measured. The measurements obtained from samples were compared with published descriptions of taxa of Melampsora [2,7,8,19]. The surface echinulation of urediniospores was observed with a SEM. For the SEM, samples were coated with platinum-palladium prior to observations with an S-4800 scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) operated at 10kV, as in Zhao et al [27].
2.3. Germination of Urediospores on the Surface of 2% Agar
Fresh urediniospores were collected to test germination and to observe nuclei. Dry fresh urediniospores were sprayed on the surface of 2% agar water and sealed in the dish with a little water to maintain 100% relative humidity. After 6 h, 10 h, and 16 h incubation at 25 °C in the dark, urediniospores and germination tubes were dyed by DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole∙2HCl, Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO, USA) ethanol solution and observed with a Leica DM4000B [28,29].
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
DNA extraction of urediniospores followed Virtudazo et al [30]. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed with the universal primers ITS1F and ITS4 [31,32], LSU primer [33], under the reaction system of 30 μL volume, containing 0.2 μM primer, 1 unit of TaKaRa Taq DNA polymerase, a 2.5 mM commercial deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) mixture, and 2 mM Mg2+ Taq reaction buffer. PCR reactions were carried out in a GeneAmp PCR TC-96 (Bioer Technology Co. Ltd., Hangzhou, China) under the following conditions: 95 °C for denaturing for 3 min, then 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 1 min, 72 °C for 1 min, and a final step of 72 °C for 10 min. Products were checked in 1% agarose gel electrophoresis under the UV transilluminator. PCR products were purified and sequenced by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). Sequences were aligned in BioEdit version 7.0.9 and searched in GenBank [34]. All sequences were compared and submitted to NCBI to obtain accession numbers. Other homologous sequences from the GenBank database were downloaded for species comparisons. Multiple alignments were performed using ClustalX version 1.8 [35]. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the software PAUP* v4.0b10 with the Maximum likelihood (ML) method [36]. Clade support was analyzed with 1000 bootstrap replicates.
2.5. Confirmation of M. medusae
As there still is confusion surrounding the identity of the species of Melampsora on P. tremuloides in North America [37], to confirm M. medusae two sets of specific primers were employed [37]. DNA extraction and PCR amplification were carried out as Section 2.4; annealing temperatures of PCR are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Primer sequences for M. medusae.
3. Results
3.1. Surveyed Poplar Leaf Rust in China, 2015–2018
Five of the fifteen fully characterized samples were identified as Melampsora medusae (Table 1): Two of the five were from Populus deltoides (section Aigeiros) cv. ‘Zhonghua hongye’. Three others were identified on three species of section Tacamahaca: Populus szechuanica, P. simonii, and P. yunnanensis. Additional samples of M. medusae were collected in Shaanxi in 2017 and 2018, and from Henan and Sichuan in 2015 through 2018. The only other rust species recorded on sections Aigeiros and Tacamahaca was M. laricic-populina. The sole representative of section Leucoides in the survey was P. wilsonii, and it revealed M. abietis-populi. Samples of section Populus (i.e., P. alba and P. tomentosa) yielded M. magnusiana. The rust of the sole representative of section Turanga, P. euphratica, from Inner Mongolia, was M. pruinosae. Thus, in all, there were five species of Melampsora.
The uredinia of M. medusae were mainly hypophyllous; a few uredinia were epiphyllous with small or more scattered pustules. Uredinia were roundish and golden orange to orange in color. Abundant capitate paraphyses were intermixed with urediniospores in the uredinia (Figure 2a). Paraphyses were 25.21–43.76 μm in length with stalks of 3.95–5.53 μm in width and swollen apices which were roughly spherical and 12.43–17.95 μm in diameter. Echinulate urediniospores were obovate or oval, with rounded apices; they were typically flattened laterally (Figure 2b,c), 20.64–31.45 × 14.39–20.38 μm, with golden yellow cytoplasm. Urediniospore walls were colorless, and germ pores were indistinct. The wall of the equatorial area of the urediniospores was slightly thickened at 1.76–3.62 μm thickness. Urediniospores were echinulate, except for the smooth equatorial area characteristic of M. medusae that commonly extended from one half to three-quarters of the way around the spore (Figure 2b,c). Spines were smaller near the smooth patch (Figure 2d). Telia were mainly hypophyllous. Their initial color was pale amber brown, but that eventually became deep reddish brown or almost black. Telia were raised slightly above the leaf surface, roughly circular to irregular in outline. Teliospores were roughly cylindrical to angular in shape in the cross-section, and the walls were pale reddish-brown. They were 31.69–44.12 (38.30) μm in length × 10.12–14.50 (11.65) μm in width. The morphological characterizations of all five species of Melampsora found in the surveys are summarized in Table 3.
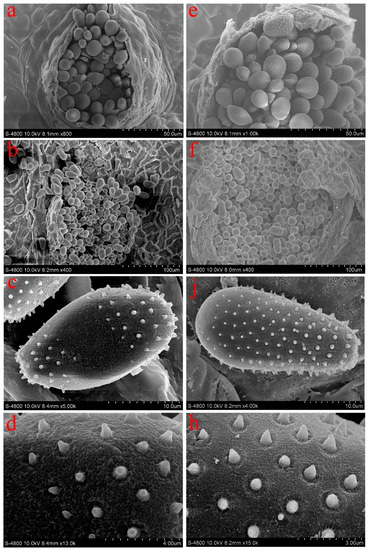
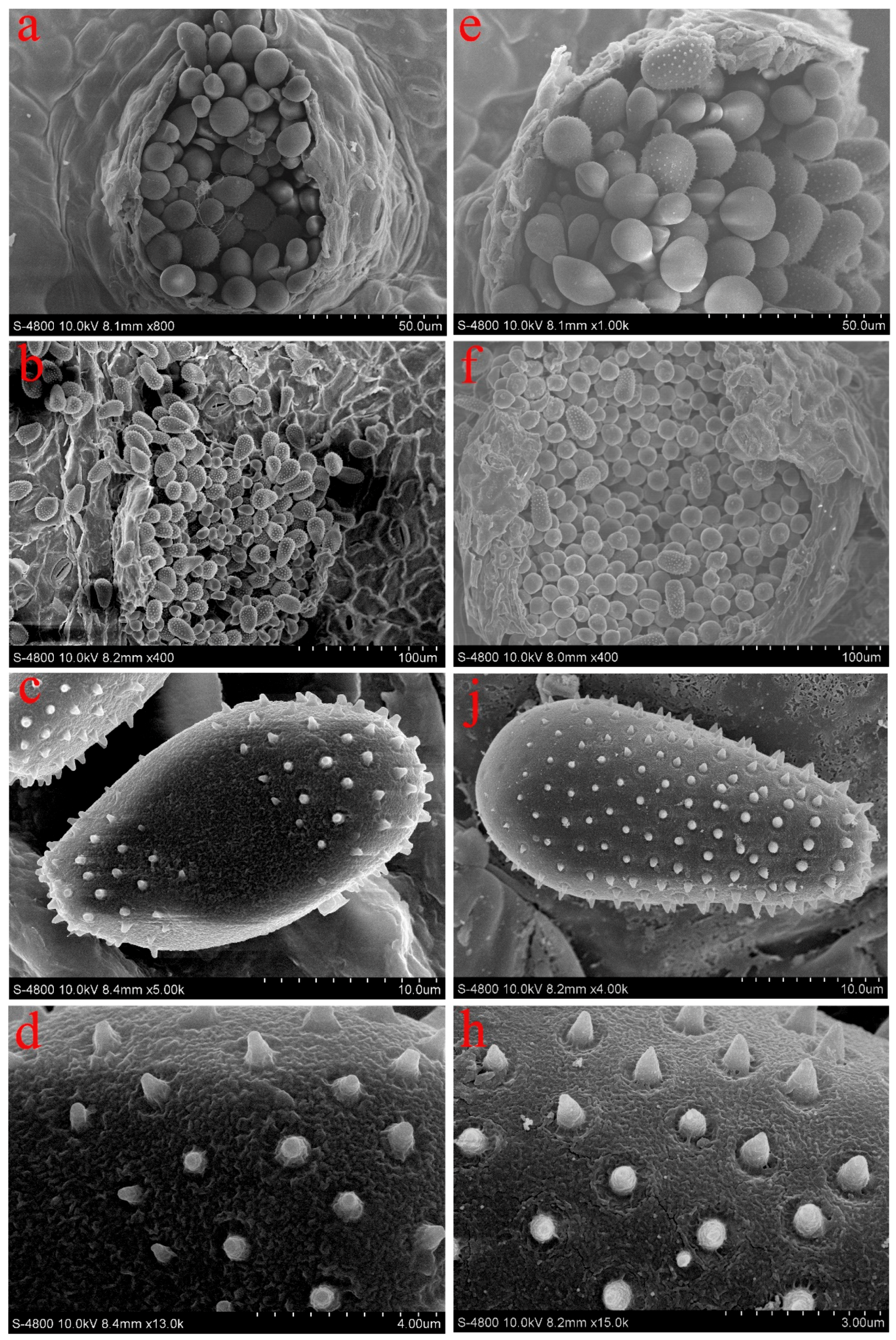
Figure 2.
Echinulation patterns of urediniospores and associated paraphyses of Melampsora medusae and Melampsora larici-populina (the two species of Melampsora found on sections Tacamahaca and Aigeiros in our surveys in China) as observed in the SEM. (a–d) Melampsora medusae; (e–h) Melampsora larici-populina; (a, e) abundant paraphyses under SEM; (b, f) Uredinium under SEM; (c, j) urediniospores with echinulate spines under SEM; (d, h) spines on the surface of urediniospores under SEM.

Table 3.
Morphology of the five Melampsora species found on Populus in China during 2015–2018 surveys.
3.2. Germination of Urediniospores on 2% Agar
Urediniospores of M. medusae germinated after 6 h on 2% agar. As Spiers (1994) described [9], the nuclei moved into germ tubes from the spores. After 10 h, there were typically two nuclei in the germ tubes, and the tops of the germ tubes were swollen; after 16 h, some germ tubes fused together. Usually, there were more than three nuclei in the fusion cell. Whereas urediniospores of M. larici-populina contained 4 germ pores and mostly had more than 2 germ tubes developed (Figure 3d,e), tubes were rope-like without swollen appressorium (Figure 3e), branched randomly, and typically found with 2 nuclei (Figure 3f).
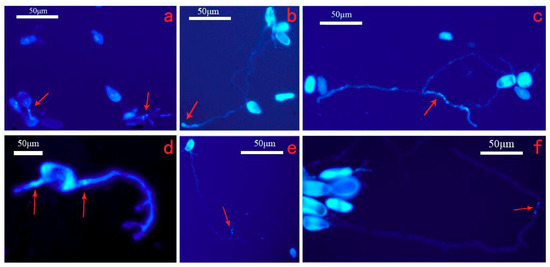
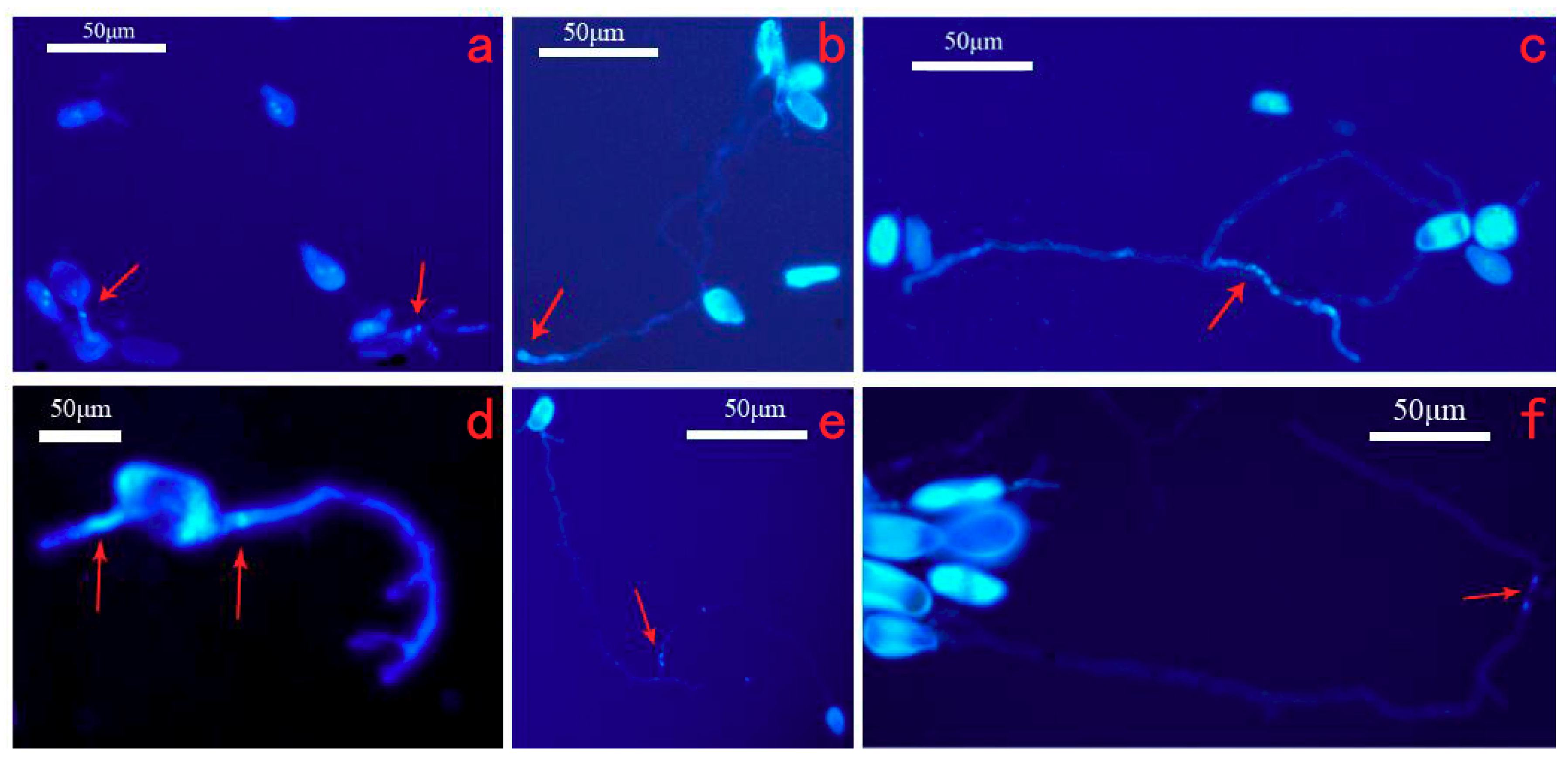
Figure 3.
Germination of urediniospores of M. medusae and M. larici-populina on a medium of 2% agar. (a–c) M. medusae; (d–f) M. larici-populina; (a) the flowing nuclei (arrows) after 6 h; (b) the swollen top of the germ tube (arrows) after 10 h; (c) germ nucleates (arrows) with 4 nucleates after 16 h; (d) the flowing nuclei of MLP (arrows) after 8 h; (e) the germ tube with 2 nuclei (arrows) after 10 h; (f) the germ tube with 2 nuclei (arrows) after 16 h.
3.3. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
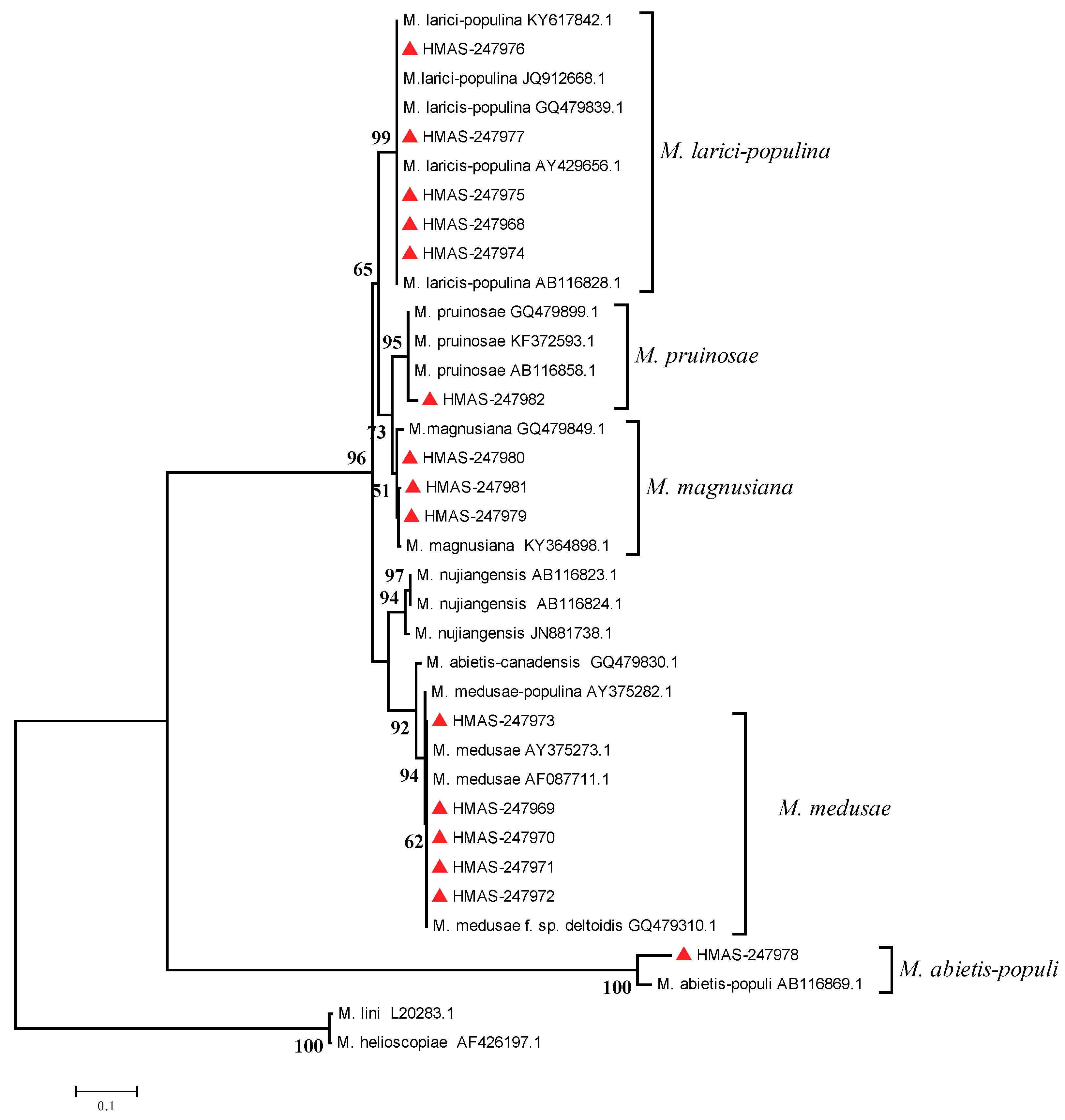
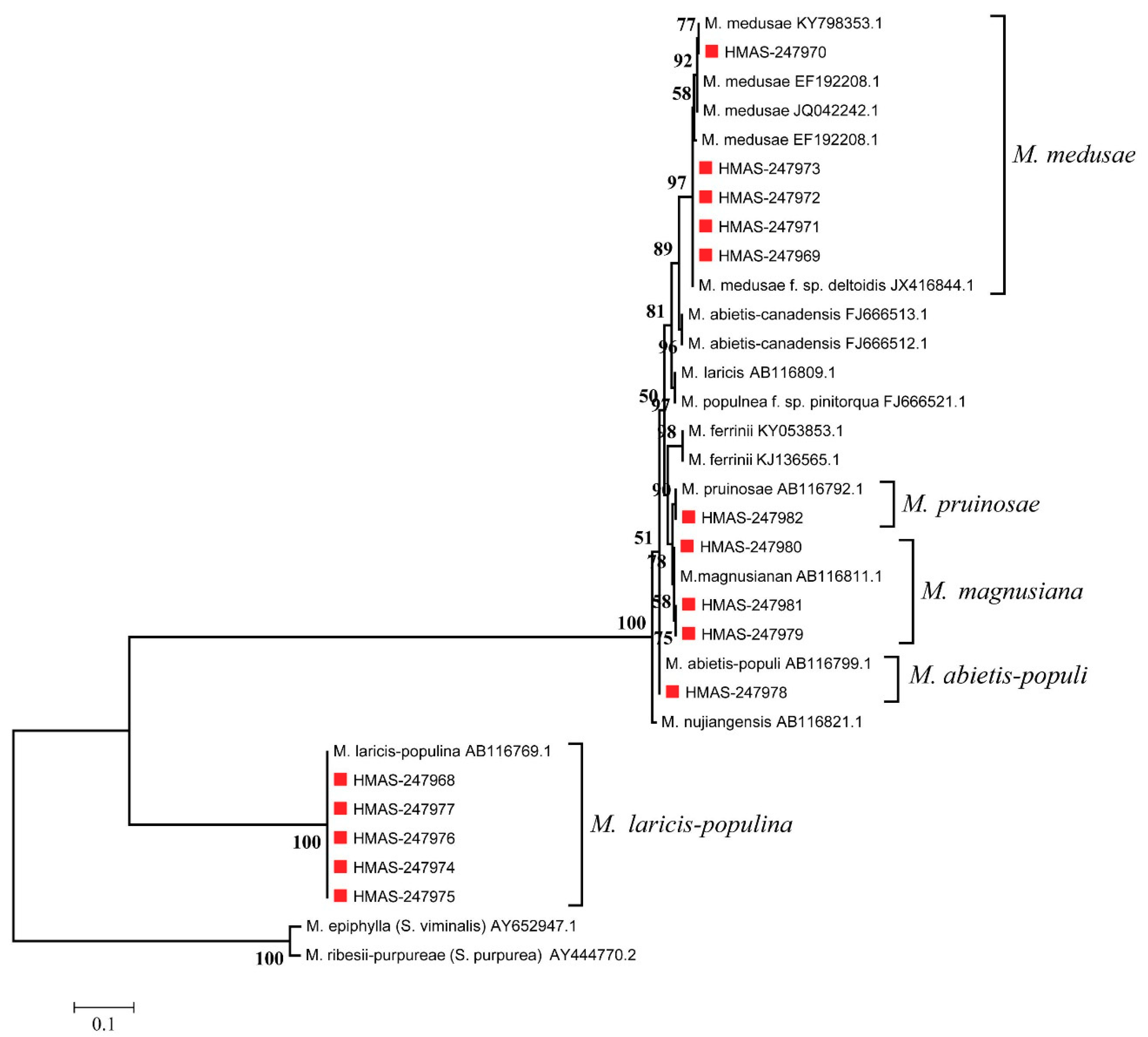
Phylogenetic analysis of rDNA ITS regions is shown in Figure 4. The Chinese samples belonged to five clades when M. lini (GenBank accessions: L20283 [38]) and M. helioscopiae (GenBank accessions: AF426197 [39]) were used as outgroups (Figure 4). The analysis revealed that five samples (HMAS-247973, HMAS-247969, HMAS-247970, HMAS-247971 and HMAS-247972) belonged to the clade anchored by M. medusae given the following GenBank accessions: AY375273 (representative of M. medusae in France), AF087711 (M. medusae in U.S.A. [8]), GQ479310 (also a French sample of M. medusae [7]). Five specimens (HMAS-247976, HMAS-247977, HMAS-247975, HMAS-247968, HMAS-247974) belonged to the clade with M. larici-populina given the following GenBank accessions: AY429656 (M. larici-populina in Canada [40]), AB116828 (M. larici-populina in China [2]). Three specimens (HMAS-247979, HMAS-247980, HMAS-247981) were grouped in a clade with M. magnusiana given the following GenBank accessions: GQ479849 (representative of M. magnusiana in Germany [7]), KY364898 (M. magnusiana in Italy [41]). M. pruinosae and M. allii-populina were divided into two separate clades anchored by GenBank accessions AB116858 (M. pruinosae in China [2]) and AB116869 (M. allii-populina in China [2]), respectively (Figure 4), M. pruinosae is closely related to M. magnusiana. nrDNA-ITS phylogeny clearly distinguished M. medusae from the other four Melampsora species of poplars that were found in these surveys in China.
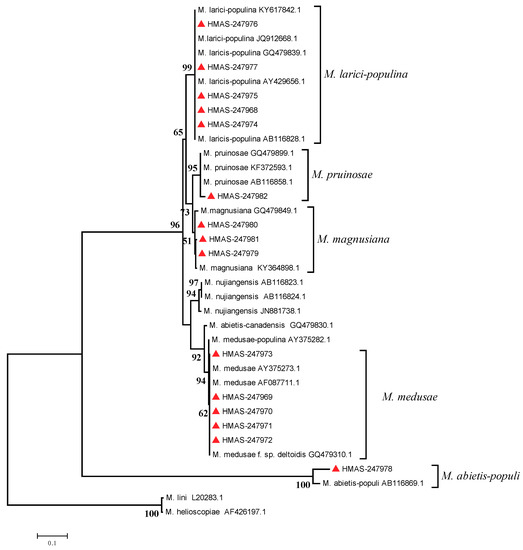
Figure 4.
Maximum Likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of nrDNA-ITS sequences of species of Melampsora from HMAS collections (red triangles) made during poplar leaf rust surveys in China, 2015–2018. Bootstrap values >50% are shown.
Phylogenetic analysis of D1/D2 regions showed almost the same results as nrDNA-ITS, in that the 15 specimens were distributed in five clades when M. epiphylla (GenBank accessions: AY652947 [26]) and M. ribesii-purpureae (GenBank accessions: AY444770 [26]) were used as outgroups (Figure 5).
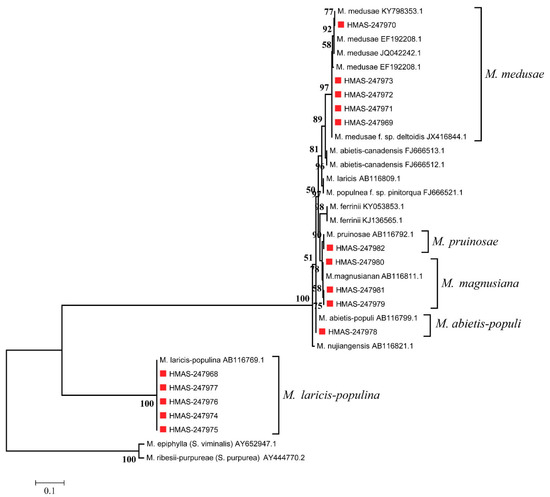
Figure 5.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenic tree of 28S rDNA(D1/D2) regions. Note: Bootstrap values >50% are shown and red marks are specimens we collected.
3.4. Formae Speciales Identification
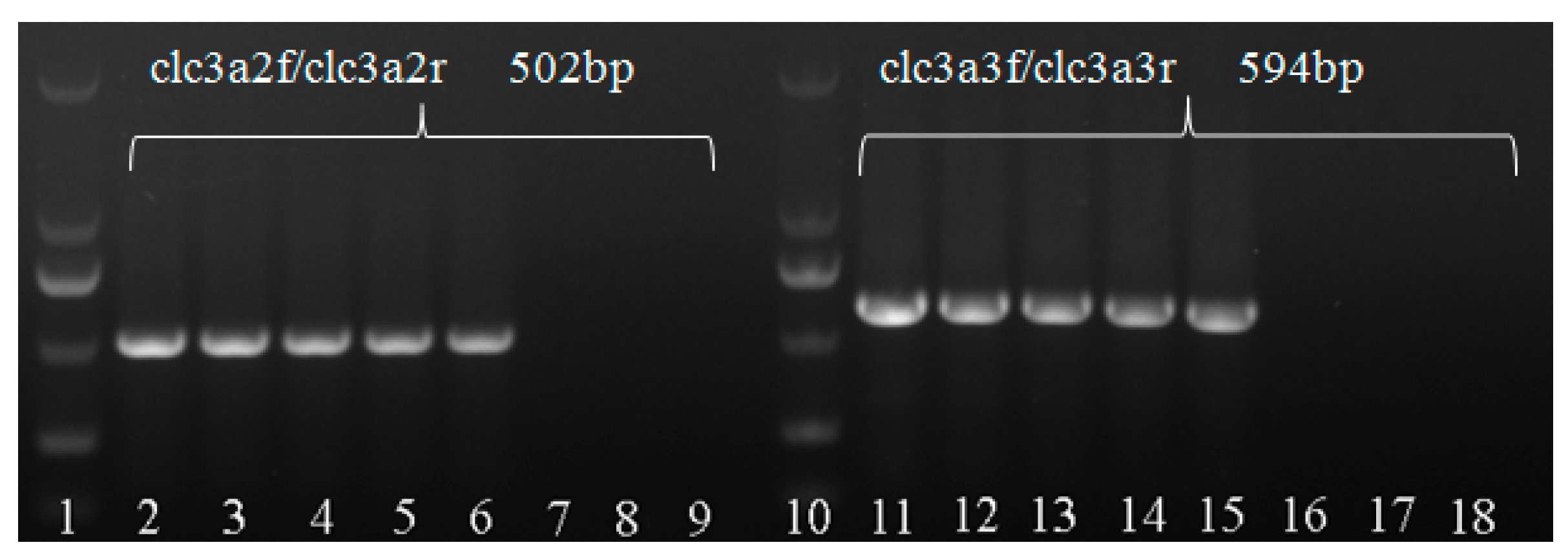
The two pairs of primer both showed a single-specified PCR DNA band for the putative five M. medusae specimens, with clc3a2f/clc3a2r primer 502 bps and clc3a3f/clc3a3r primer 594 bps, respectively, and the positive of M. larici-populina and negative controls of ddH2O without products (Figure 6), which implied the 5 specimens were M. medusae f.sp. deltoidae.
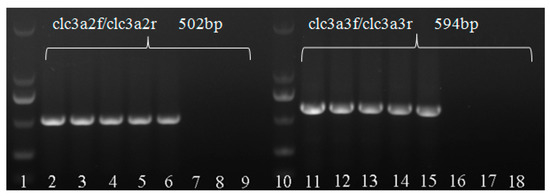
Figure 6.
Amplification with primer clc3a2f/clc3a2r and primer clc3a3f/clc3a3r. Lanes 1 and 10: Marker DM2000; lanes 2–6: Amplification from uredinia of the five specimens of M. medusae (HMAS 247969-71, HMAS 247972-73) using primers clc3a2f/clc3a2r; Lanes 11–15: Amplification from uredinia of the five specimens of M. medusae (HMAS 247969-71, HMAS 247972-73) using primers clc3a3f/clc3a3r; Lanes 7–8 and 16–17(HMAS247968, HMAS247978): The positive control with DNA of M. larici-populina; Lanes 9 and 18: The negative control with ddH2O.
4. Discussion
Two of the five fully characterized samples of M. medusae were collected from Populus deltoides cv. ‘Zhonghua hongye’, a bud mutation propagated from Populus deltoides in China. ‘Zhonghua hongye’ has been regarded as fast-growing, rust-resistant and ornamental, so it has been widely planted in inland China since 2000. We have sampled the rust disease on ‘Zhonghua hongye’ from 2017–2018 in Shaanxi, and from 2015 through 2018 in Hennan, and 2016–2018 in Sichuan. Its new susceptibility to introduced M. medusae may change its trajectory of expansion and commercialization. The susceptibility to M. medusae of species in section Tacamahaca (i.e., P. yunnanensis, P. simonii and P. szechuanica) is not surprising, as North American species in this section of the genus are also susceptible to varying extents [8]. The susceptibility of these same Asian species in Tacamahaca has also been reported before from New Zealand [42]. The host specificity of M. medusae as reported in its original description [10] was limited to P. deltoides; it did not include P. tremuloides nor any other species of section Populus. Thus, the confirmation here of the absence of M. medusae on surveyed P. alba and P. tomentosa in China is not surprising.
The aecial host of M. medusae in its native range in Eastern North America is Larix laricina, but Pseudotsuga menziesii can also be a host [43]. In China, the aecial host is not yet known. The most likely hosts in China would be species of Larix, Pseudotsuga and possibly Cathaya. These three genera belong to subfamily Laricoideae of Pinaceae, although Cathaya may be closer to Pinus than to Larix/Pseudotsuga [44]. No rust fungi have ever been reported on Cathaya [11], although this absence is likely a function of a lack of attention. For example, only recently was the first pathogen of Cathaya described as a new species [45].
The involvement of M. medusae in inter-specific hybridization complicates its introduction into China. In our survey, we frequently found Melampsora larici-populina in close proximity to M. medusae. We have not yet surveyed for the hybrid M. medusae-populina, but its existence in China is now a distinct possibility that should be researched.
5. Conclusions
Our combined morphology- and sequence-based approach led to the identification of five species of Melampsora in surveys in China. The most important discovery was that of the introduction of North American M. medusae that is now both widespread and persistent from year to year in China.
Author Contributions
Materials collection: Y.Z., P.Z. and C.Z.; experiments: Y.Z. and Z.W.; investigation: H.D. and P.Z.; writing-original draft preparation: Z.W. and Y.Z.; writing-review and editing: G.N.
Funding
This research was funded by “the national key research projects, grant number 2017YFD0600103-4-2” and National natural science committee, grant number “31670650”.
Acknowledgments
We thank Liu Xiaoyong from the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences for help with morphological identification and voucher specimen reserving. We thank Zhang Chunni for help collecting in Yulin City.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pinon, J.; Frey, P. Interaction between poplar clones and Melampsora populations and their implication for breeding for durable resistance. In Rust Diseases of Willow and Poplar; CABI: Oxford, England, 2005; Volume 12, pp. 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.M.; Shang, Y.Z.; Zhuang, J.Y.; Wang, Q.; Kakishima, M. Morphological and molecular phylogenetic analysis of Melampsora species on poplars in China. Mycoscience 2004, 45, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenackers, J.; Steenackers, M.; Steenackers, V.; Stevens, M. Poplar diseases, consequences on growth and wood quality. Biomass Bioenerg. 1996, 10, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galović, V.; Orlović, S.; Pap, P.; Kovačević, B.; Marković, M. Specificity of SSR Loci for Melampsora Species on Poplars. Genetika-Belgrade 2010, 42, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, G.; Dugan, F.M. Fungal pathogens of plants in the Homogocene. In Molecular Identification of Fungi; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Castagne, L. Observations sur quelques plantes acotylédonées de la famille des uredinées. In recueillies dans le département des Bouches-du-Rhône; impr. de Achard: Marseille, France, 1843. [Google Scholar]
- Vialle, A.; Frey, P.; Hambleton, S. Poplar rust systematics and refinement of Melampsora species delineation. Fungal Divers. 2011, 50, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, G.; Stirling, B.; Mcdonald, S.; Bradshaw, H.D. Melampsora × columbiana, a natural hybrid of M. medusae and M. occidentalis. Mycol. Res. 2000, 104, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiers, A.G.; Hopcroft, D.H. Comparative studies of the poplar rusts Melampsora medusae, M. larici-populina and their interspecific hybrid M. medusae-populina. Mycol. Res. 1994, 98, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thümen, F.v. New species of North American Uredinei. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1878, 6, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, D.F.; Rossman, A.Y. Fungal Databases; U.S. National Fungus Collections, ARS, USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 6 December 2018. Available online: https://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/ (accessed on 25 October 1984).
- Fresa, R. Argentine Republic: Melampsora larici-populina in the Delta of Paraná. Int. Bull. Pl. Prot. 1936, 10, 145–146. [Google Scholar]
- Dupias, G. Contribution à l'étude des Urédinées de la Haute-Garonne. Bull. Soc. Hist.Nat. Toulouse. 1943, 78, 32–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka, N. Miscellaneous notes on the East Asiatic Uredinales with special reference to the Japanese species (VI). J. Jap. Bot. 1939, 15, 621–627. [Google Scholar]
- Hennebert, G.L. L'identification des rouilles du peuplier. Agricultura 1964, 12, 661–670. [Google Scholar]
- Pinon, J. Situation of Melampsora medusae in Europe. Bull 1986, 16, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinon, J. Eléments de répartition des rouilles des peupliers cultivés en France. C. R. Acad. Agric. Fr. 1991, 77, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- OEPP/EPPO. Data sheets on quarantine organisms no. 33, Melampsora medusae. Bull 1982, 12, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Husson, C.; Loos, R.; Andrieux, A.; Frey, P. Development and use of new sensitive molecular tools for diagnosis and detection of Melampsora rusts on cultivated poplar. For. Pathol. 2013, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Hartigan, D.; Bertus, A.L. Poplar rusts in Australia with comments on potential conifer rusts. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1974, 4, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of the European Union. Council Directive 2000/29/EC of 8 May 2000 on Protective Measures against the Introduction into the Community of Organisms Harmful to Plants or Plant Products and against their Spread within the Community. O.J.L.. 2000, Volume 169. Available online: https://publications.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/6aab39f3-60ec-4851-99cf-d676e093b8a7/language-en (accessed on 28 June 2007).
- Feau, N.; Vialle, A.; Allaire, M.; Tanguay, P.; Joly, D.L.; Frey, P.; Callan, B.E.; Hamelin, R.C. Fungal pathogen (mis-) identifications: A case study with DNA barcodes on Melampsora rusts of aspen and white poplar. Mycol. Res. 2009, 113, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutigny, A.L.; Guinet, C.; Vialle, A.; Hamelin, R.; Frey, P.; Ioos, R. A sensitive real-time PCR assay for the detection of the two Melampsora medusae formae speciales on infected poplar leaves. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 136, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinon, J.; Frey, P. Structure of Melampsora larici-populina populations on wild and cultivated poplar. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1997, 103, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Kaneko, S.; Yamaoka, Y.; Kakishima, M. Differentiation of Melampsora rust species on willows in Japan using PCR-RFLP analysis of ITS regions of ribosomal DNA. Mycoscience 1998, 39, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.H.; Bayon, C.; Ruiz, C. Phylogenetic relationships in some Melampsora rusts on Salicaceae assessed using rDNA sequence information. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tian, C.M.; Yao, Y.J.; Wang, Q.; Kakishima, M.; Yamaoka, Y. Melampsora salicis-sinicae (Melampsoraceae, Pucciniales), a new rust fungus found on willows in China. Mycoscience 2014, 55, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, M.C.; Xu, H.X.; Eilam, T. Nuclear behavior of the cowpea rust fungus during the early stages of basidiospore- or urediospore- derived growth in resistant or susceptible cowpea cultivars. Phytopathology 1996, 86, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.D.; Liang, J.; Cao, Z.M. Nuclear behavior in the life cycle of Melompsor larici-populina Kleb. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2009, 7, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtudazo, E.V.; Nakamura, H.; Kakishima, M. Phylogenetic analysis of sugarcane rusts based on sequences of ITS, 5.8 S rDNA and D1/D2 regions of LSU rDNA. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2001, 67, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes: application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequence of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, K. Fusarium and its near relatives. In The Fungal Holomorph: Mitotic, Meiotic and Pleomophic Speciation in Fungal Systematics; Reynolds, D.R., Taylor, J.W., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1993; pp. 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP 4.0: Phylogenetic Analysis using Parsimony, version 4.0b10; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, M.; Bernier, L.; Hamelin, R.C. Direct genotyping of the poplar leaf rust fungus, Melampsora medusae f. sp. deltoidae, using codominant PCR-SSCP markers. Forest Pathol. 2005, 35, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, W.; Begerow, D.; Weiß, M.; Oberwinkler, F. Phylogeny of the rust fungi: an approach using nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Can. J. Bot. 2003, 81, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihrmark, K.; Bodeker, I.T.M.; Cruz-Martinez, K.; Friberg, H.; Kubartova, A.; Schenck, J.; Strid, Y.; Stenlid, J.; Brandstrom-Durling, M.; Clemmensen, K.E.; et al. New primers to amplify the fungal ITS2 region—evaluation by 454-sequencing of artificial and natural communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, L.; Marchand, L.; Frey, P.; Bourassa, M.; Hamelin, R.C. First report of Melampsora larici-populina on Populus spp. in eastern North America. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, L.; Giorcelli, A.; Gonthier, P.; Gullino, M.L. First report of leaf rust caused by Melampsora magnusiana on Populus alba in Italy. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 535. [Google Scholar]
- Gadgil, P.D. Fungi on trees and shrubs in New Zealand. In Fungi of New Zealand; Fungal Diversity Press: Hong Kong, China, 2005; Volume 4, p. 437. [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe, G.; Chastagner, G.A.; McDonald, S.K. Additional coniferous aecial hosts of the poplar leaf rusts, Melampsora larici-populina and M. medusae f. sp. deltoidae. Plant Dis. 1994, 78, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.P.; Huang, J.P.; Wu, C.S.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chaw, S.M. Comparative chloroplast genomics reveals the evolution of Pinaceae genera and subfamilies. Genome Biol. Evol. 2010, 2, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.M.; Lin, Y.R.; Huang, H.Y.; Hou, C.L. A new species of Lophodermium associated with the needle cast of Cathay silver fir. Mycol. Prog. 2013, 12, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).