Interaction Enhanced Imperialist Competitive Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Literature Review
2.1. ICA Basic Concept







2.2. Variants of ICA


3. Interaction Enhanced ICA

3.1. Artificial Imperialist



3.2. Crossover Imperialists

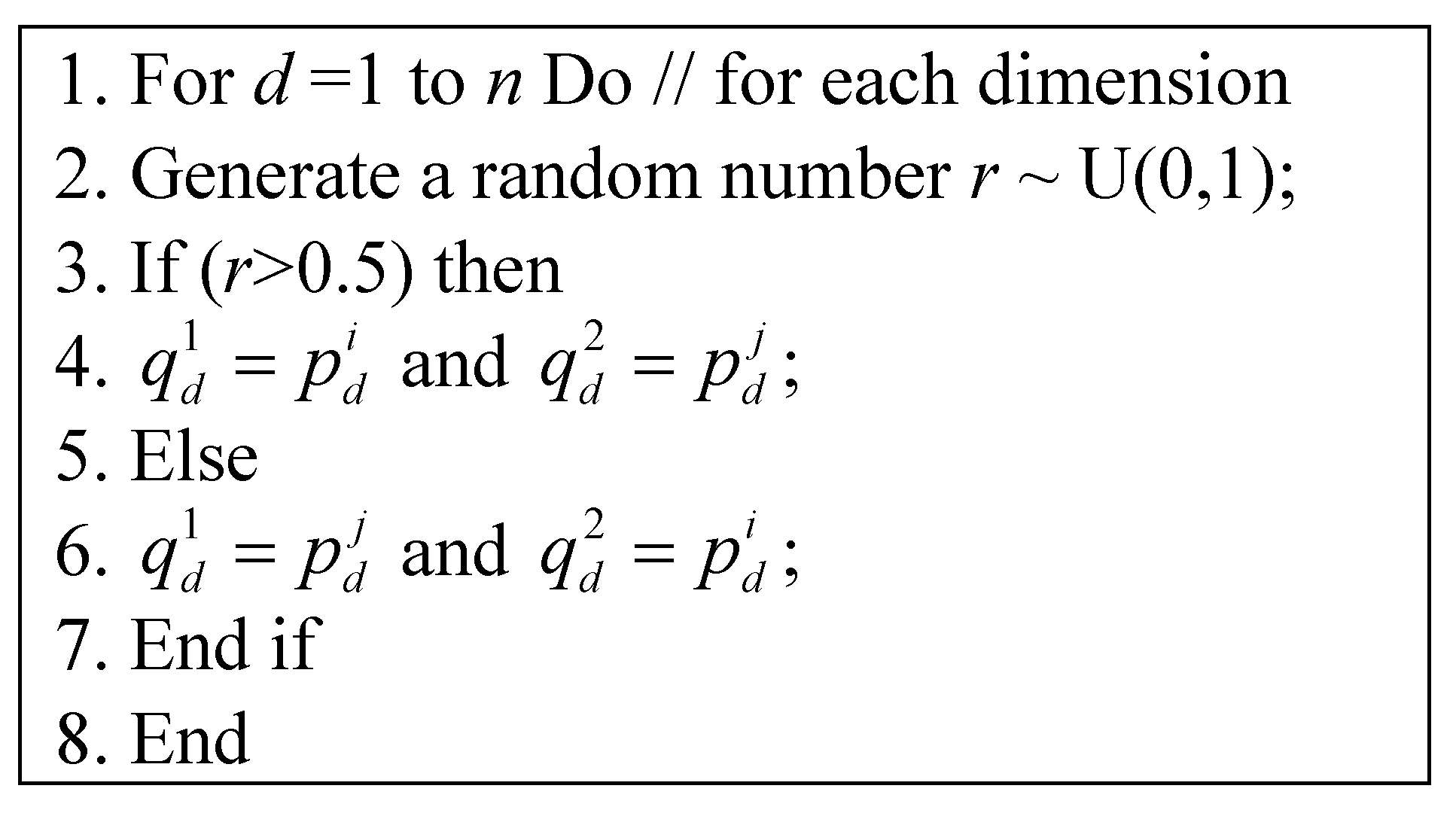
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experiment Settings

| f | Range | fmin |
|---|---|---|
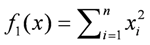 | xi ∈ [−100,100] | f1(0) = 0 |
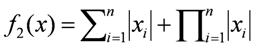 | xi ∈ [−10,10] | f2(0) = 0 |
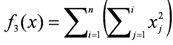 | xi ∈ [−100,100] | f3(0) = 0 |
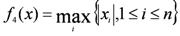 | xi ∈ [−100,100] | f4(0) = 0 |
 | xi ∈ [−100,100] | f5(p) = 0, −0.5 ≤ pi < 0.5 |
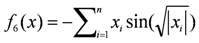 | xi ∈ [−500,500] | f6(420.97) = −418.9829n |
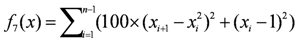 | xi ∈ [−100,100] | f7(1) = 0 |
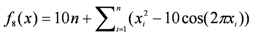 | xi ∈ [−10,10] | f8(0) = 0 |
 | xi ∈ [−600,600] | f9(0) = 0 |
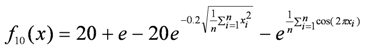 | xi ∈ [−32,32] | f10(0) = 0 |
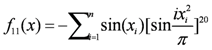 | xi ∈ [0,π] | f11 > −n |
 | xi ∈ [−50,50] | f12(−1) = 0 |
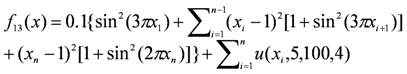 | xi ∈ [−50,50] | f13(1) = 0 |
4.2. Performance Comparison
4.2.1. Experiment 1: Impact of Interaction Operation
| F | PSO | Perturbed ICA [35] | ICAAI | ICACI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | 1.57 × 10−16 (8.6 × 10−16) | 8.312 × 10−6 (1.3 × 10−5) | 3.757 × 10−10 (2 × 10−9) | 2.1 × 10−7 (9.7 × 10−7) |
| f 2 | 1.015 × 10−3 (5.6 × 10−3) | 3.559 × 10−4 (7.48 × 10−4) | 1.103 × 10−7 (2.38 × 10−7) | 5.08 × 10−5 (2.1 × 10−4) |
| f3 | 1.5 × 10−18 (5.8 × 10−18) | 2.687 × 10−4 (4.5 × 10−4) | 1.53 × 10−10 (6.4 × 10−10) | 2.835 × 10−6 (7 × 10−6) |
| f4 | 14.44 (3.7) | 6.607 (2.2) | 1.989 × 10−1 (0.2) | 8.134 (3.1) |
| f5 | 6.67 × 10−2 (0.25) | 19.57 (37.7) | 0.3 (0.79) | 46.27 (146.88) |
| f6 | −1.135 × 104 (367) | −1.140 × 104 (280) | −1.142 × 104 (256) | −1.143 × 104 (304) |
| f7 | 31.2 (16.3) | 230.3 (295.9) | 100.2 (131.3) | 126.7 (145) |
| f8 | 38.5 (10.14) | 5.945 (3.03) | 5.172 (2.94) | 6.008 (2.89) |
| f9 | 1.53 × 10−2 (0.02) | 2.284 × 10−2 (0.03) | 1.23 × 10−2 (0.017) | 3.81 × 10−2 (0.037) |
| f10 | 8.4 × 10−7 (4.55 × 10−6) | 1.203 × 10−3 (1.3 × 10−3) | 4.139 × 10−6 (8.6 × 10−6) | 1.063 × 10−3 (0.002) |
| f11 | −23.757 (1.22) | −27.72 (0.59) | −27.68 (0.89) | −27.58 (0.89) |
| f12 | 1.037 × 10−2 (0.03) | 6.913 × 10−3 (0.026) | 1.037 × 10−2 (0.032) | 6.91 × 10−3 (0.026) |
| f13 | 1.1 × 10−3 (3.35 × 10−3) | 1.810 × 10−3 (4.04 × 10−3) | 1.83 × 10−3 (4.16 × 10−3) | 1.83 × 10−3 (4.16 × 10−3) |
| f | PSO | Perturbed ICA [35] | ICAAI | ICACI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | 1.89 × 10−54 (9.95 × 10−54) | 8.199 × 10−24 (3.3 × 10−23) | 2.89 × 10−28 (1.58 × 10−27) | 2.23 × 10−26 (9.5 × 10−26) |
| f2 | 1.015 × 10−3 (5.56 × 10−3) | 1.726 × 10−15 (3.33 × 10−15) | 2.671 × 10−19 (6.1 × 10−19) | 9.29 × 10−18 (2.2 × 10−17) |
| f3 | 3.17 × 10−56 (1.5 × 10−55) | 1.493 × 10−22 (4.56 × 10−22) | 1.665 × 10−25 (9.1 × 10−25) | 1.1 × 10−24 (3.6 × 10−24) |
| f4 | 6.67 (2.77) | 2.770 × 10−1 (0.19) | 5.242 × 10−3 (6.17 × 10−3) | 3.396 × 10−1 (0.2) |
| f5 | 0 (0) | 19.57 (37.7) | 0.3 (0.79) | 46.1 (146.9) |
| f6 | −1.136 × 104 (368.7) | −1.14 × 104 (280.32) | −1.142 × 104 (263) | −1.143 × 104 (303.6) |
| f7 | 29.96 (16.19) | 87.34 (118.4) | 49.39 (59.02) | 59.07 (84.66) |
| f8 | 28.73 (10.34) | 3.681 (2.22) | 4.676 (3.02) | 5.373 (3.44) |
| f9 | 1.53 × 10−2 (0.02) | 2.282 × 10−2 (0.031) | 1.230 × 10−2 (0.017) | 3.807 × 10−2 (0.037) |
| f10 | 1.8 × 10−14 (4.2 × 10−15) | 6.05 × 10−13 (1.5 × 10−12) | 1.68 × 10−13 (3.22 × 10−13) | 8.79 × 10−13 (1.8 × 10−12) |
| f11 | −24.42 (1.16) | −28.02 (0.74) | −27.93 (0.84) | −27.59 (0.91) |
| f12 | 6.9 × 10−3 (0.026) | 6.911 × 10−3 (0.026) | 1.037 × 10−2 (0.0317) | 6.911 × 10−3 (0.0263) |
| f13 | 7.325 × 10−4 (0.0028) | 1.099 × 10−3 (3.35 × 10−3) | 1.831 × 10−3 (4.17 × 10−3) | 1.831 × 10−3 (4.16 × 10−3) |
4.2.2. Experiment 2: Impact of Competition Frequency
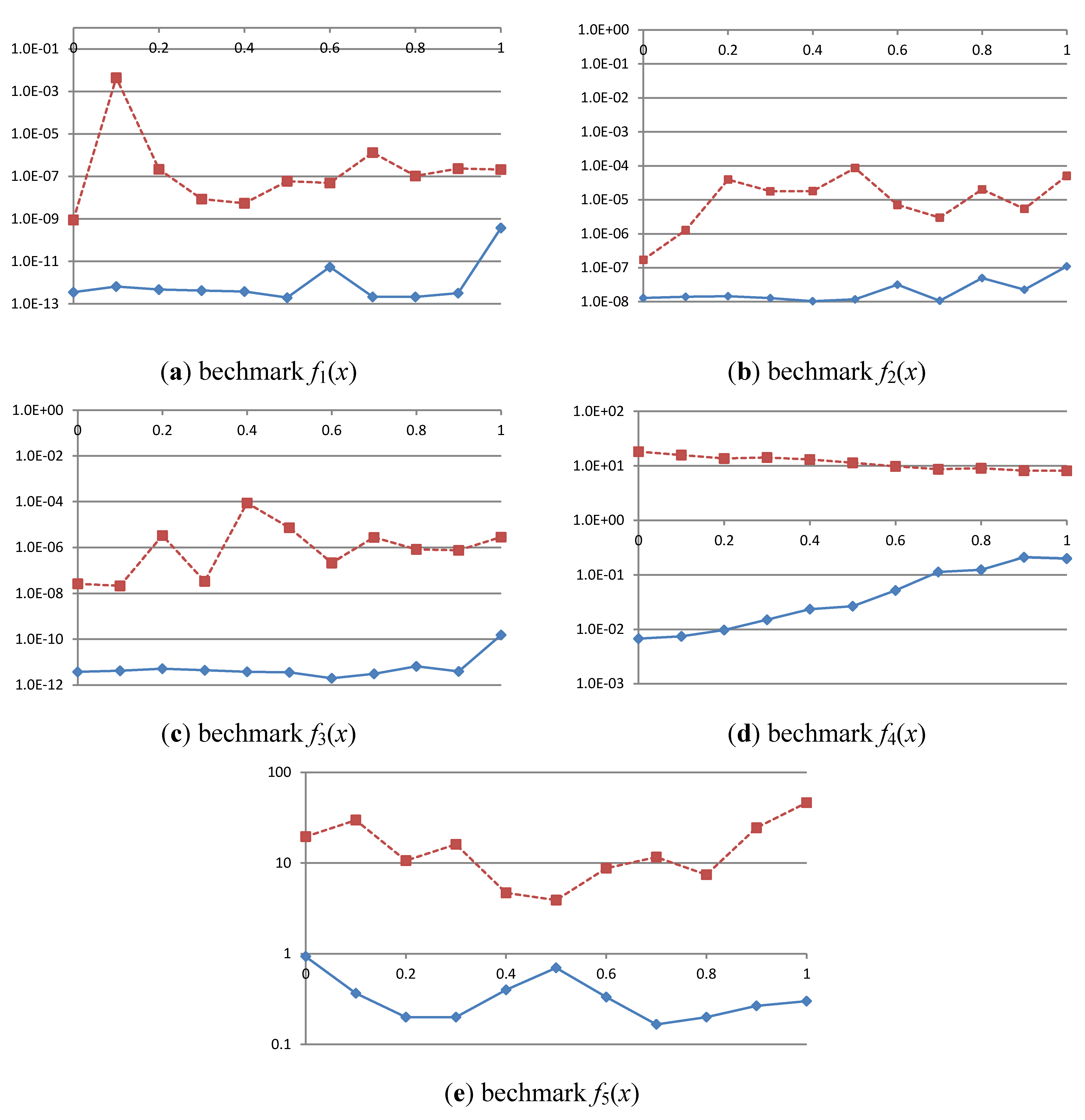
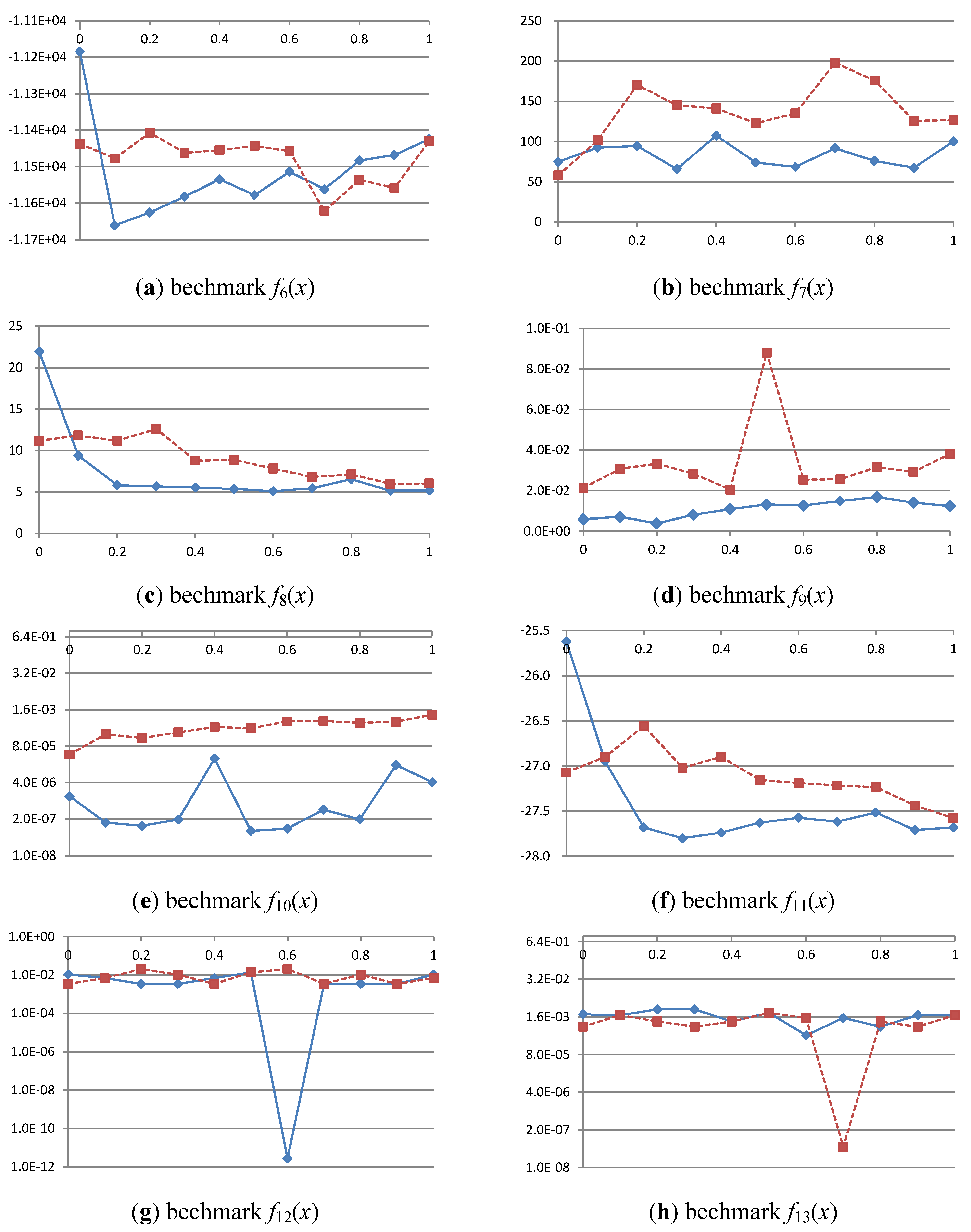
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Holland, J.H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-H.; Chen, M.-C.; Chang, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-M. Ea/g-ga for single machine scheduling problems with earliness/tardiness costs. Entropy 2011, 13, 1152–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, M.; Kennedy, J. The particle swarm—Explosion, stability, and convergence in a multidimensional complex space. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2002, 6, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbil, S.I.; Fang, S.C. An electromagnetism-like mechanism for global optimization. J. Global Optim. 2003, 25, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, D.; Yu, S.H.; Nino, F. Recent advances in artificial immune systems: Models and applications. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.F.; Liu, S.Y.; Huang, L.L. A global best artificial bee colony algorithm for global optimization. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2012, 236, 2741–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, L. Optimal multi-level thresholding based on maximum tsallis entropy via an artificial bee colony approach. Entropy 2011, 13, 841–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Maniezzo, V.; Colorni, A. Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1996, 26, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential evolution—A simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Global Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashpaz-Gargari, E.; Lucas, C. Imperialist competitive algorithm: An algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. In Proceedings of IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Singapore, 25–28 September 2007; pp. 4661–4667.
- Behnamian, J.; Zandieh, M. A discrete colonial competitive algorithm for hybrid flowshop scheduling to minimize earliness and quadratic tardiness penalties. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 14490–14498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouharfard, S.; Zandieh, M. An imperialist competitive algorithm to schedule of receiving and shipping trucks in cross-docking systems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2010, 51, 1179–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, N.; Zandieh, M.; Najafi, A.A. Group scheduling in flexible flow shops: A hybridised approach of imperialist competitive algorithm and electromagnetic-like mechanism. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2011, 49, 4965–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahpour, E.; Zandieh, M.; Dorri, B. A novel imperialist competitive algorithm for bi-criteria scheduling of the assembly flowshop problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2011, 49, 3087–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, K.; Zhang, C.; Gao, L.; Shao, X. A modified colonial competitive algorithm for the mixed-model u-line balancing and sequencing problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- MousaviRad, S.J.; Akhlaghian Tab, F.; Mollazade, K. Application of imperialist competitive algorithm for feature selection: A case study on bulk rice classification. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 40, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, S.; Shokouhi, S.B. Application of imperialist competitive algorithm for automated classification of remote sensing images. Int. J. Comput. Theory Eng. 2012, 4, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Bagher, M.; Zandieh, M.; Farsijani, H. Balancing of stochastic u-type assembly lines: An imperialist competitive algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2011, 54, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.D.S.; Afonso, L.D.; Alotto, P. A modified imperialist competitive algorithm for optimization in electromagnetics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, A.; Talatahari, S. Optimum design of skeletal structures using imperialist competitive algorithm. Comput.Struct. 2010, 88, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.; Ghorbani, A.; Hashemi, S.N. Deployment of the meta heuristic colonial competitive algorithm in synthesis of unequally spaced linear antenna array. IEICE Electron. Express 2011, 8, 2048–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Nasiri-Gheidari, Z.; Tootoonchian, F. Application of an imperialist competitive algorithm to the design of a linear induction motor. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Shirkouhi, S.; Eivazy, H.; Ghodsi, R.; Rezaie, K.; Atashpaz-Gargari, E. Solving the integrated product mix-outsourcing problem using the imperialist competitive algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 7615–7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanpoor, H.; Nozarian, S.; VafaeiJahan, M. Solving the graph bisection problem with imperialist competitive algorithm. Int. Conf. Sys. Eng. Model. 2012, 34, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, E.; Karami, A.; Shahhosseni, M. The use of imperialist competitive algorithm for the optimization of heat transfer in an air cooler equipped with butterfly inserts. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 6, 293–301. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-L.; Yu, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-H. PSO-based imperialist competitive algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2012, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- Niwa, T.; Tanaka, M. Analysis on the island model parallel genetic algorithms for the genetic drifts. Simul. Evolut. Learn. 1999, 1585, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashpaz-Gargari, E. Imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA). Available online: http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/22046-imperialist-competitive-algorithm-ica (accessed on 10 January 2012).
- Duan, H.B.; Xu, C.F.; Liu, S.Q.; Shao, S. Template matching using chaotic imperialist competitive algorithm. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2010, 31, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.; Nigam, M.J. Synergy of evolutionary algorithm and socio-political process for global optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 3706–3713. [Google Scholar]
- Khorani, V.; Razavi, F.; Ghoncheh, A. A new hybrid evolutionary algorithm based on ICA and GA: Recursive-ICA-GA. In IC-AI; Arabnia, H.R., de la Fuente, D., Kozerenko, E.B., Olivas, J.A., Chang, R., LaMonica, P.M., Liuzzi, R.A., Solo, A.M.G., Eds.; CSREA Press: Las Vegas, NV, USA; pp. 131–140, 12–15 July 2010.
- Talatahari, S.; Azar, B.F.; Sheikholeslami, R.; Gandomi, A.H. Imperialist competitive algorithm combined with chaos for global optimization. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2012, 17, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, H.; Faez, K.; Abdechiri, M. Imperialist competitive algorithm using chaos theory for optimization (cica). In Proceedings of the 2010 12th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation (UKSim), Cambridge, UK, 24–26 March 2010; pp. 98–103, IEEE Computer Society Conference Publishing Service.
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, C. Improved imperialist competitive algorithm for constrained optimization. In Proceedings of the International Forum on Computer Science-Technology and Applications, 2009, Chongqing, China, 25–27 December 2009; 1, pp. 204–207.
- Lin, J.-L.; Cho, C.-W.; Chuan, H.-C. Imperialist competitive algorithms with perturbed moves for global optimization. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- Nozarian, S.; Jahan, M.V. A novel memetic algorithm with imperialist competition as local search. IPCSIT 2012, 30, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, H.; Abdechiri, M.; Meybodi, M.R. Imperialist competitive algorithm with adaptive colonies movement. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2012, 2, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, Y.; Chi, H. Differential evolution using opposite point for global numerical optimization. J. Intell. Learn. Syst. Appl. 2012, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Worasucheep, C. A particle swarm optimization with stagnation detection and dispersion. In Proceedings of IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, Hong Kong, China, 1–6 June 2008; pp. 424–429.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.-L.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Yu, C.-Y.; Li, M.-S. Interaction Enhanced Imperialist Competitive Algorithms. Algorithms 2012, 5, 433-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/a5040433
Lin J-L, Tsai Y-H, Yu C-Y, Li M-S. Interaction Enhanced Imperialist Competitive Algorithms. Algorithms. 2012; 5(4):433-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/a5040433
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jun-Lin, Yu-Hsiang Tsai, Chun-Ying Yu, and Meng-Shiou Li. 2012. "Interaction Enhanced Imperialist Competitive Algorithms" Algorithms 5, no. 4: 433-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/a5040433
APA StyleLin, J.-L., Tsai, Y.-H., Yu, C.-Y., & Li, M.-S. (2012). Interaction Enhanced Imperialist Competitive Algorithms. Algorithms, 5(4), 433-448. https://doi.org/10.3390/a5040433






