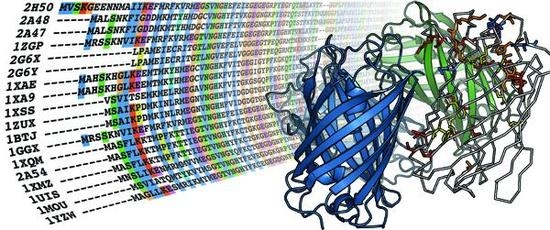
SDPhound, a Mutual Information-Based Method to Investigate Specificity-Determining Positions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Approach
3. Methods
3.1. The estimator for the probability
3.2. Probability estimator for ranking of individual positions
3.3. Probability estimator for ranking of correlated positions
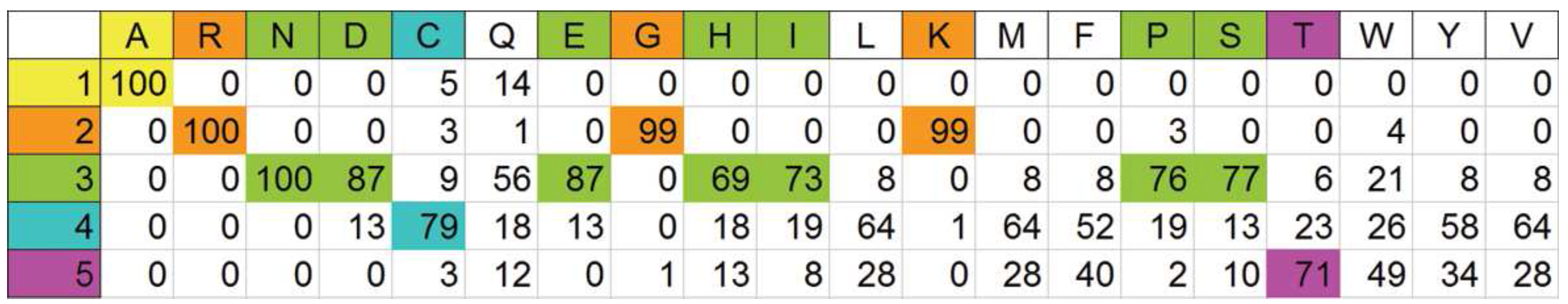
3.4. Probability estimator for ranking based on physical properties of the amino acids
A priori partitioning of amino acids on a physical basis
Optimal automatic pigeonholing
3.5. Statistical significance calculation
4. Results I: MIP and LacI families
4.1. The MIP family
| B45 | S | B62 | S | Id | S | Bloc | S | SDPpred | S | |
| 21 | 21 | 22 | 24 | 24 | ||||||
| 1 | 195 | * | 195 | * | 207 | 195 | * | 207 | ||
| 2 | 232 | 232 | 187 | * | 187 | * | 236 | |||
| 3 | 187 | * | 187 | * | 232 | 159 | * | 48 | * | |
| 4 | 186 | 207 | 236 | 108 | 135 | |||||
| 5 | 236 | 108 | 202 | * | 232 | 159 | * | |||
| 6 | 30 | 211 | 48 | * | 211 | 187 | * | |||
| 7 | 108 | 30 | 201 | * | 236 | 22 | ||||
| 8 | 207 | 159 | * | 159 | * | 135 | 195 | * | ||
| 9 | 211 | 236 | 195 | * | 207 | 191 | * | |||
| 10 | 159 | * | 186 | 191 | * | 191 | * | 201 | * | |
| 11 | 48 | * | 48 | * | 108 | 137 | 108 | |||
| 12 | 135 | 191 | * | 211 | 186 | 137 | ||||
| 13 | 137 | 135 | 137 | 20 | 211 | |||||
| 14 | 194 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 43 | |||||
| 15 | 191 | * | 137 | 208 | 48 | * | 136 | |||
| 16 | 20 | 194 | 186 | 134 | 199 | * | ||||
| 17 | 24 | 24 | 20 | 24 | 194 | |||||
| 18 | 26 | 237 | 135 | 216 | 24 | |||||
| 19 | 216 | 199 | * | 199 | * | 43 | 20 | |||
| 20 | 237 | 34 | 235 | 202 | * | 200 | * | |||
| 21 | 34 | 132 | 34 | 237 | 193 | |||||
| 22 | 233 | 199 | * | 134 | 194 | 194 | ||||
| 23 | 194 | 31 | 26 | 208 | 34 | |||||
| 24 | 100 | 43 | 56 | 34 | 257 |
| Pos. | 195 | 187 | 159 | 48 | 202 | 201 | 191 | 199 | 200 | 207 |
| hyd | 2 | − | − | − | − | 11 | 16 | − | 22 | − |
| crg | − | − | − | 2 | − | 3 | 5 | 19 | − | 7 |
| size | 3 | − | 7 | 14 | 1 | − | 13 | 18 | 38 | 2 |
| Pos. | 232 | 236 | 186 | 108 | 135 | 30 | 211 | 22 | 137 | 20 |
| hyd | 5 | 6 | 3 | 12 | 13 | 7 | 4 | − | 9 | − |
| crg | − | − | − | 13 | − | − | 6 | − | 14 | 4 |
| size | 6 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 19 | 11 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 15 |
4.2. The LacI family
5. Results II: IFP family
| B45 | S | B62 | S | Id | S | Bloc | S | SDPpred | S | |
| 32 | 31 | 35 | 33 | 24 | ||||||
| 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 160 | 2 | 15 | 1 | 146 | 3 |
| 2 | 122 | 2 | 122 | 2 | 15 | 1 | 122 | 2 | 160 | 2 |
| 3 | 144 | 3 | 55 | 1 | 98 | 2 | 160 | 2 | 55 | 1 |
| 4 | 107 | 3 | 56 | 2 | 55 | 1 | 55 | 1 | 85 | 3 |
| 5 | 16 | 1 | 144 | 3 | 146 | 3 | 144 | 3 | 98 | 2 |
| 6 | 55 | 1 | 107 | 3 | 122 | 2 | 249 | 2 | 302 | 3 |
| 7 | 126 | 3 | 85 | 3 | 114 | 2 | 56 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
| 8 | 121 | 3 | 98 | 2 | 249 | 2 | 69 | 3 | 221 | 2 |
| 9 | 56 | 2 | 323 | 3 | 85 | 3 | 85 | 3 | 15 | 1 |
| 10 | 85 | 3 | 16 | 1 | 147 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 122 | 2 |
| 11 | 323 | 3 | 126 | 3 | 16 | 1 | 146 | 3 | 114 | 2 |
| 12 | 123 | 3 | 123 | 3 | 56 | 2 | 302 | 3 | 121 | 3 |
| 13 | 69 | 3 | 160 | 2 | 221 | 2 | 121 | 3 | 69 | 3 |
| 14 | 98 | 2 | 249 | 2 | 323 | 3 | 98 | 2 | 50 | 3 |
| 15 | 146 | 3 | 146 | 3 | 25 | 3 | 147 | 1 | 249 | 2 |
| 16 | 249 | 2 | 69 | 3 | 91 | 3 | 107 | 3 | 147 | 1 |
| 17 | 160 | 2 | 121 | 3 | 302 | 3 | 323 | 3 | 56 | 2 |
| 18 | 20 | 1 | 147 | 1 | 193 | 2 | 233 | 4 | 323 | 3 |
| 19 | 25 | 3 | 25 | 3 | 157 | 4 | 66 | 3 | 186 | 3 |
| 20 | 302 | 3 | 156 | 4 | 148 | 3 | 91 | 3 | 144 | 3 |
| 21 | 156 | 4 | 302 | 3 | 50 | 3 | 50 | 3 | 91 | 3 |
| 22 | 147 | 1 | 91 | 3 | 133 | 3 | 145 | 3 | 123 | 3 |
| 23 | 227 | 2 | 20 | 1 | 69 | 3 | 126 | 3 | 53 | 3 |
| 24 | 21 | 3 | 60 | 2 | 121 | 3 | 25 | 3 | 66 | 3 |
| 25 | 96 | 2 | 193 | 2 | 144 | 3 | 96 | 2 | 157 | 4 |
| 26 | 66 | 3 | 227 | 2 | 107 | 3 | 221 | 2 | 57 | 2 |
| 27 | 50 | 3 | 114 | 2 | 123 | 3 | 156 | 4 | 21 | 3 |
| 28 | 60 | 2 | 50 | 3 | 192 | 2 | 60 | 2 | 145 | 3 |
| 29 | 221 | 2 | 221 | 2 | 20 | 1 | 114 | 2 | 61 | 2 |
| 30 | 91 | 3 | 157 | 4 | 159 | 3 | 294 | 3 | 107 | 3 |
| 31 | 53 | 3 | 96 | 2 | 110 | 2 | 190 | 1 | 193 | 2 |
| 32 | 190 | 1 | 294 | 3 | 53 | 3 | 292 | 2 | 29 | 2 |
| 33 | 73 | 2 | 233 | 4 | 186 | 3 | 123 | 3 | 192 | 2 |
| 34 | 233 | 4 | 73 | 2 | 227 | 2 | 110 | 2 | 78 | 2 |
| 35 | 157 | 4 | 66 | 3 | 57 | 2 | 280 | 3 | 133 | 3 |
| Pos. | 15 | 160 | 122 | 144 | 55 | 98 | 50 | 107 | 56 | 16 |
| hyd | 6 | 15 | 5 | 9 | 14 | − | 7 | 3 | 17 | 4 |
| crg | 2 | 8 | 9 | − | 4 | 1 | 13 | 17 | 29 | 14 |
| size | 5 | 9 | 7 | 25 | 16 | 1 | 12 | − | 4 | 8 |
| Pos. | 146 | 249 | 126 | 85 | 114 | 121 | 123 | 221 | 147 | 323 |
| hyd | 18 | − | 1 | 10 | − | − | − | − | − | 30 |
| crg | 11 | 18 | 6 | − | 15 | − | − | − | 7 | − |
| size | 14 | − | − | 3 | − | 2 | 28 | 30 | 17 | 21 |
| B45 | S | B62 | S | Id | S | Bloc | S | SDPpred | S | |
| 19 | 24 | 21 | 18 | 9 | ||||||
| 1 | 194 | 1 | 194 | 1 | 117 | 1 | 117 | 1 | 117 | 1 |
| 2 | 117 | 1 | 117 | 1 | 83 | 2 | 194 | 1 | 83 | 2 |
| 3 | 224 | 1 | 177 | 2 | 194 | 1 | 224 | 1 | 79 | 3 |
| 4 | 177 | 2 | 224 | 1 | 164 | 1 | 175 | 2 | 194 | 1 |
| 5 | 164 | 1 | 164 | 1 | 192 | 1 | 177 | 2 | 184 | 4 |
| 6 | 156 | 1 | 156 | 1 | 156 | 1 | 174 | 1 | 164 | 1 |
| 7 | 44 | 2 | 192 | 1 | 223 | 1 | 124 | 2 | 185 | 4 |
| 8 | 197 | 2 | 197 | 2 | 175 | 2 | 192 | 1 | 192 | 1 |
| 9 | 192 | 1 | 174 | 1 | 153 | 1 | 164 | 1 | 156 | 1 |
| 10 | 125 | 1 | 44 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 153 | 1 | 175 | 2 |
| 11 | 174 | 1 | 175 | 2 | 177 | 2 | 162 | 1 | 177 | 2 |
| 12 | 162 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 224 | 1 | 197 | 2 | 72 | 4 |
| 13 | 4 | 3 | 125 | 1 | 124 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 153 | 1 |
| 14 | 175 | 2 | 153 | 1 | 162 | 1 | 83 | 2 | 124 | 2 |
| 15 | 124 | 2 | 124 | 2 | 147 | * | 44 | 2 | 8 | 3 |
| 16 | 127 | 1 | 162 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 156 | 1 | 147 | * |
| 17 | 153 | 1 | 150 | 2 | 174 | 1 | 71 | 2 | 150 | 2 |
| 18 | 72 | 4 | 127 | 1 | 72 | 4 | 150 | 2 | 174 | 1 |
| 19 | 150 | 2 | 92 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 72 | 4 | 44 | 2 |
| 20 | 92 | 3 | 72 | 3 | 44 | 2 | 78 | 4 | 21 | 1 |
| 21 | 78 | 4 | 83 | 2 | 21 | 1 | 223 | 1 | 219 | 4 |
| 22 | 85 | 3 | 85 | 3 | 71 | 2 | 147 | * | 162 | 1 |
| 23 | 6 | 1 | 78 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 125 | 1 | 75 | 4 |
| 24 | 83 | 2 | 118 | 4 | 197 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 57 | 4 |
| 20 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 18 |
5.1. Sequence alignment
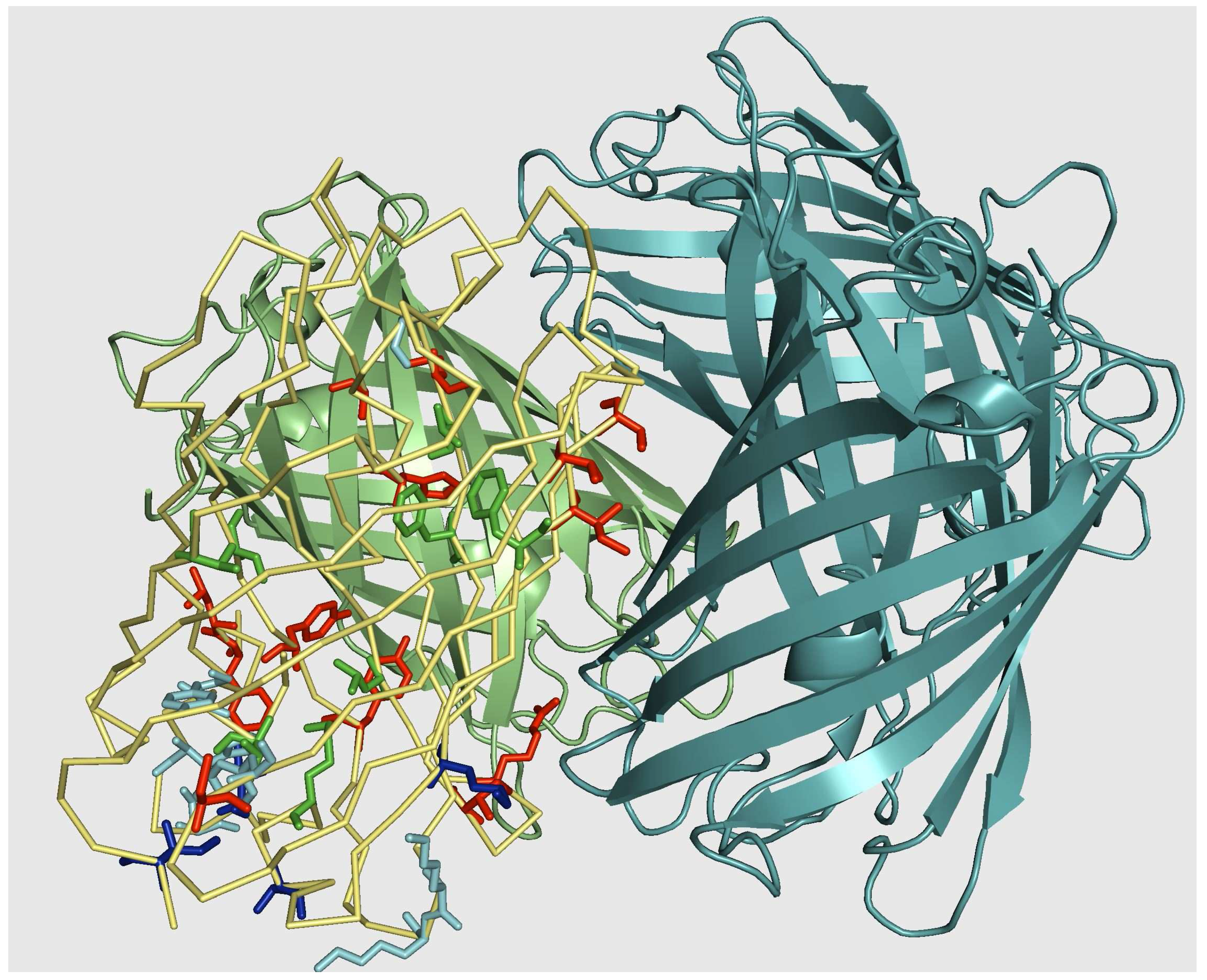
5.2. Monomerization of multimeric IFP
| Pos. | 117 | 83 | 194 | 164 | 192 | 156 | 223 | 175 | 153 | 5 |
| hyd | 4 | − | 1 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 22 | 7 | 15 | − |
| crg | 3 | − | 5 | 1 | 8 | − | 4 | − | 2 | 7 |
| size | 1 | − | 2 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 19 | 11 | − | 21 |
| Pos. | 177 | 224 | 124 | 162 | 147 | 4 | 174 | 72 | 8 | 44 |
| hyd | − | 11 | − | − | 34 | − | − | − | − | 6 |
| crg | − | − | − | 19 | 37 | − | 6 | 12 | − | − |
| size | 9 | 7 | 18 | − | 13 | 12 | 16 | − | − | 15 |
Looking for primary physical features
| B45 | S | B62 | S | Id | S | Bloc | S | SDPpred | S | |
| 24 | 16 | 22 | 20 | 221 | ||||||
| 1 | 124 | * | 124 | * | 127 | ‡ | 124 | * | 127 | ‡ |
| 2 | 127 | ‡ | 127 | ‡ | 153 | * | 172 | 124 | * | |
| 3 | 156 | * | 172 | 125 | ‡ | 127 | ‡ | 172 | ||
| 4 | 172 | 158 | 172 | 156 | * | 153 | * | |||
| 5 | 21 | † | 156 | * | 124 | * | 21 | † | 114 | |
| 6 | 158 | 21 | † | 114 | 114 | 217 | † | |||
| 7 | 114 | 6 | † | 6 | † | 180 | † | 125 | ‡ | |
| 8 | 6 | † | 114 | 158 | 6 | † | 154 | |||
| 9 | 44 | † | 181 | 156 | * | 160 | † | 156 | * | |
| 10 | 225 | * | 211 | 154 | 158 | 76 | ||||
| 11 | 181 | 64 | 225 | * | 62 | 118 | ||||
| 12 | 146 | 87 | 176 | 170 | 167 | |||||
| 13 | 211 | 225 | * | 217 | † | 4 | 158 | |||
| 14 | 64 | 44 | † | 209 | 211 | 21 | † | |||
| 15 | 87 | 146 | 39 | 36 | 87 | |||||
| 16 | 160 | 168 | 168 | 94 | 45 | |||||
| 17 | 192 | * | 180 | † | 45 | 202 | 39 | |||
| 18 | 47 | 47 | 21 | † | 154 | 82 | ||||
| 19 | 170 | 192 | * | 208 | 175 | * | 155 | |||
| 20 | 45 | 39 | 162 | * | 168 | 181 | ||||
| 21 | 107 | 4 | 163 | † | 192 | * | 62 | |||
| 22 | 117 | † | 170 | 118 | 64 | 209 | ||||
| 23 | 147 | 160 | 180 | † | 209 | 163 | † | |||
| 24 | 4 | 202 | 167 | 225 | * | 176 |
Pairwise correlation
5.3. From tetrameric to dimeric form
| Pos. | 172 | 158 | 114 | 181 | 211 | 154 | 64 | 62 | 146 | 87 |
| hyd | 1 | − | − | 16 | − | − | 32 | 6 | 14 | − |
| crg | 19 | 17 | 30 | 24 | 2 | 27 | − | 6 | − | − |
| size | 30 | 9 | 2 | 20 | − | − | 28 | − | 25 | 21 |
| Pos. | 176 | 170 | 4 | 209 | 39 | 36 | 160 | 168 | 94 | 45 |
| hyd | 29 | − | 31 | 25 | − | 21 | − | − | − | − |
| crg | − | − | 29 | 10 | 8 | − | 15 | − | 34 | 21 |
| size | − | 34 | 33 | − | − | 15 | 31 | − | 23 | 24 |
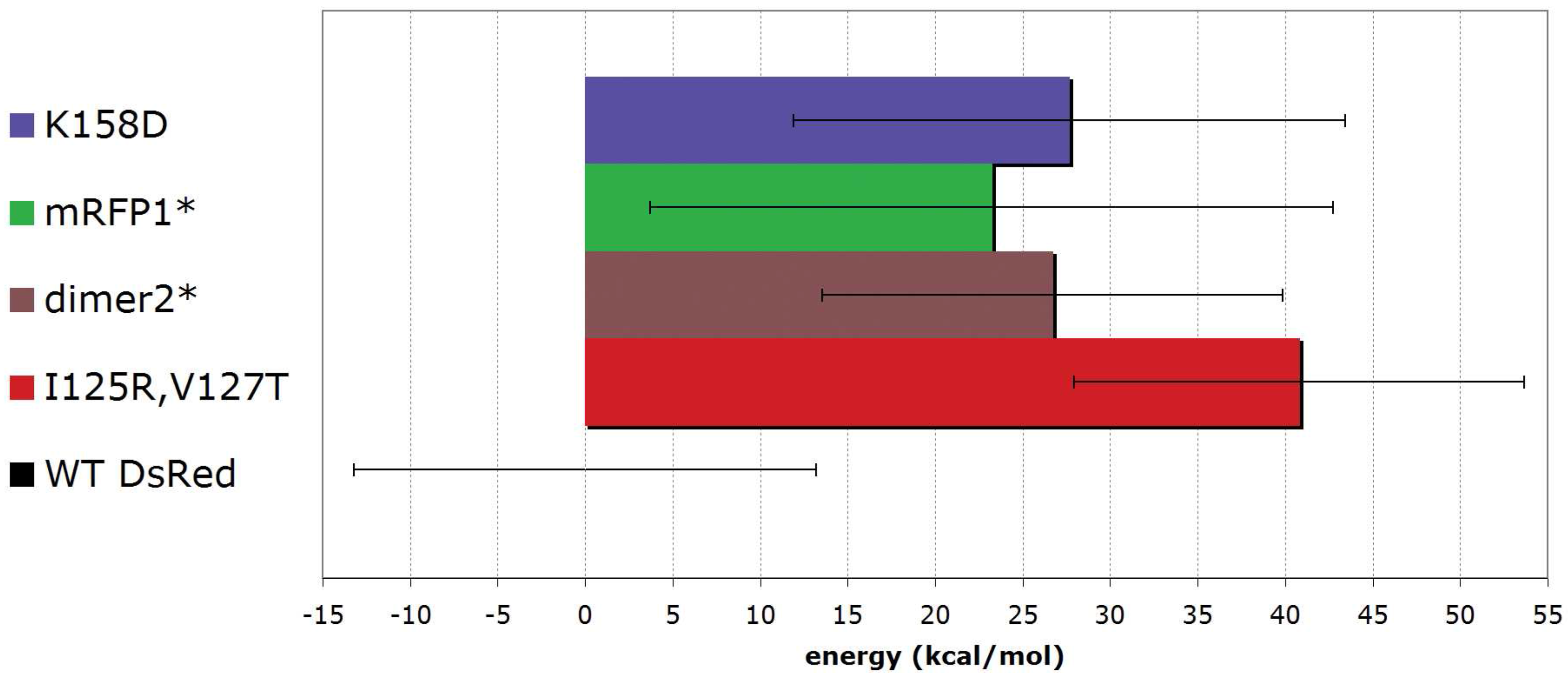
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Pazos, F.; Bang, J.-W. Computational prediction of functionally important regions in proteins. Curr. Bioinf. 2006, 1, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinina, O.V.; Mironov, A.A; Gelfand, M.S; Rakhmaninova, A.B. Automated selection of positions determining functional specificity of proteins by comparative analysis of orthologous groups in protein families. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 443–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, J.E.; Shakhnovich, E.I. Predicting specificity residues in two large eukaryotic transcription factor families. Nucl. Acids Res. 2005, 33, 4455–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarri, R.; Nifosi, R.; Pingue, P.; Tozzini, V.; Beltram, F. Nano-Sized Optical "Devices" for Applications in Proteomics and Biomolecular Electronics: Engineered Green Fluorescent Proteins. In Functional Nanomaterials; Geckeler, K.E., Rosenberg, E., Eds.; American Scientific Publisher: California, 2006; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie, M.; Tu, Y.; Euskirchen, G.; Ward, W.W.; Prasher, D.C. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 1994, 263, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozzini, V.; Pellegrini, v.; Beltram, F. Handbook of organic photochemistry and photobiology; Horsphool, W. M., Lenci, F., Eds.; CRC: Washington DC, 2004; Chapter 139. [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura, O.; Johnson, F.H.; Saiga, Y. Extraction, purification and properties of aequorin, a bioluminescent protein from the luminous hydromedusan, Aequorea. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 1962, 59, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagin, D.A; Barsova, E.V.; Yanushevich, Y.G.; Fradkov, A.F.; Lukyanov, K.A.; Labas, Y.A.; Semenova, T.N.; Ugalde, J.A.; Meyers, A.; Nunez, J.M.; Widder, E.A.; Lukyanov, S.A.; Matz, M.V. GFP-like proteins as ubiquitous metazoan superfamily: evolution of functional features and structural complexity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaner, N.C.; Steinbach, P.A.; Tsien, R.Y. A guide to choosing fluorescent proteins. Nature Methods 2005, 2, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollman, P.A.; Massova, I.; Reyes, C.; Kuhn, B.; Huo, S.; Chong, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; Donini, O.; Cieplak, P.; Srinivasan, J.; Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd. Calculating structures and free energies of complex molecules: combining molecular mechanics and continuum models. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henikoff, S.; Henikoff, J.G. Amino acid substitution matrices from protein blocks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 96, 10915–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirny, L.A.; Gelfand, M.S. Using orthologous and paralogous proteins to identify specificity-determining residues in bacterial transcription factors. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 321, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.J.; Goldstein, R.A. Predicting solvent accessibility: higher accuracy using bayesian statistics and optimized residue substitution classes. Prot. Struct. Funct. Gen. 1996, 25, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzini, V. Coarse Graine Models for Proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henikoff, S.; Henikoff, J.G. Position-based sequence weights. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 243, 574578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujishita, T. On triple mutual information. Advances in applied mathematics 1995, 16, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, W.J. Multivariate Information Transmission. IEEE Trans. Information Theory 1954, 4, 93–111. [Google Scholar]
- Good, P. Permutation Tests: A Practical Guide to Resampling Methods for Testing Hypotheses; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: New York, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mirny, L.A.; Gelfand, M.S. Using orthologous and paralogous proteins to identify specificity-determining residues in bacterial transcription factors. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 321, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirovano, W.; Feenstra, K.A.; Heringa, J. Sequence comparison by sequence harmony identifies subtype-specific functional sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 6540–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinina, O.V.; Novichkov, P.S.; Mironov, A.A.; Gelfand, M.S.; Rakhmaninova, A.B. SDPpred: a tool for prediction of amino acid residues that determine differences in functional specificity of homologous proteins. Nucleic Acid Research 2004, 32, W424–W428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Libson, A.; Miercke, L.J.; Weitzman, C.; Nollert, P.; Krucinski, J.; Stroud, R.M. Structure of a glycerol-conducting channel and the basis for its selectivity. Science 2000, 290, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Han, B.G.; Lee, J.K.; Walian, P.; Jap, B.K. Structural basis of water-specific transport through the AQP1 water channel. Nature 2001, 414, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Schumacher, M.A.; Arvidson, D.N.; Haldimann, A.; Wanner, B.L.; Zalkin, H.; Brennan, R.G. Structure-Based Redesign of Corepressor Specificity of the Escherichia coli Purine Repressor by Substitution of Residue 190. Biochem. 1998, 37, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasfeld, A.; Koehler, A.N.; Schumacher, M.A.; Brennan, R.G. The role of lysine 55 in determining the specificity of the purine repressor for its operators through minor groove interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 291, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, M.A.; Choi, K.Y.; Zalkin, H.; Brennan, R.G. Crystal structure of LacI member PurR, bound to DNA: minor groove binding by alpha helices. Science 1994, 266, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.E.; Tour, O.; Palmer, A.E.; Steinbach, P.A.; Baird, G.S.; Zacharias, D.A.; Tsien, R.Y. A monomeric fluorescent protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002, 99, 7877–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD - Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Molec. Graphics 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.B.; Barton, G.J. Multiple protein sequence alignment from tertiary structure comparison: assignment of global and residue confidence levels. Proteins 1992, 14, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, G.S. PhD Thesis (University of California, San Diego) 2001.
- Taylor, W. The classification of amino acid conservation. J. Theor. Biol. 1986, 119, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonella, S.; Rocchia, W.; Amat, P.; Nifosí, R.; Tozzini, V. SDPhound, a Mutual Information-Based Method to Investigate Specificity-Determining Positions. Algorithms 2009, 2, 764-789. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2020764
Bonella S, Rocchia W, Amat P, Nifosí R, Tozzini V. SDPhound, a Mutual Information-Based Method to Investigate Specificity-Determining Positions. Algorithms. 2009; 2(2):764-789. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2020764
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonella, Sara, Walter Rocchia, Pietro Amat, Riccardo Nifosí, and Valentina Tozzini. 2009. "SDPhound, a Mutual Information-Based Method to Investigate Specificity-Determining Positions" Algorithms 2, no. 2: 764-789. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2020764
APA StyleBonella, S., Rocchia, W., Amat, P., Nifosí, R., & Tozzini, V. (2009). SDPhound, a Mutual Information-Based Method to Investigate Specificity-Determining Positions. Algorithms, 2(2), 764-789. https://doi.org/10.3390/a2020764