A Hybrid Neural Network Transformer for Detecting and Classifying Destructive Content in Digital Space
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
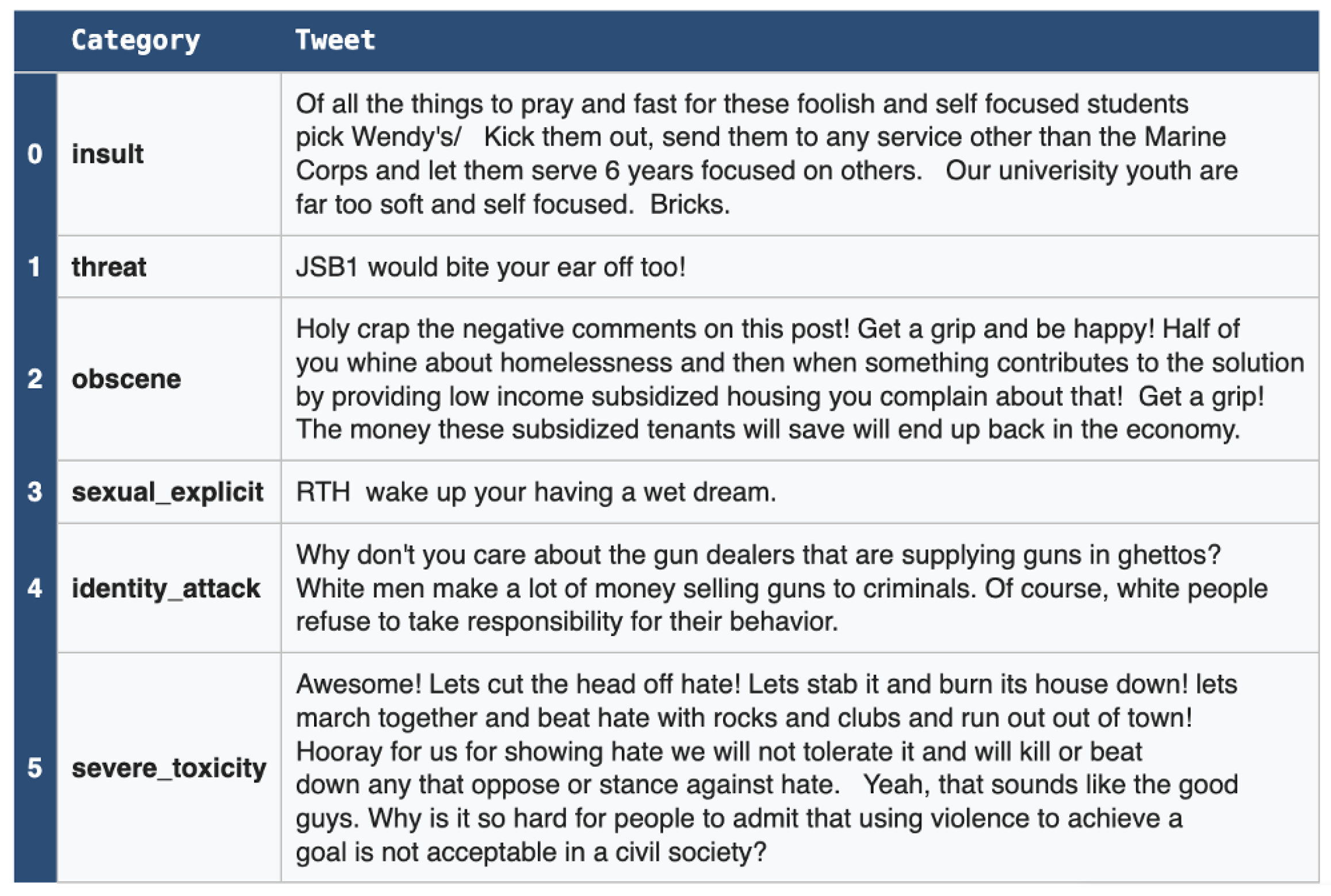
3.1. Dataset
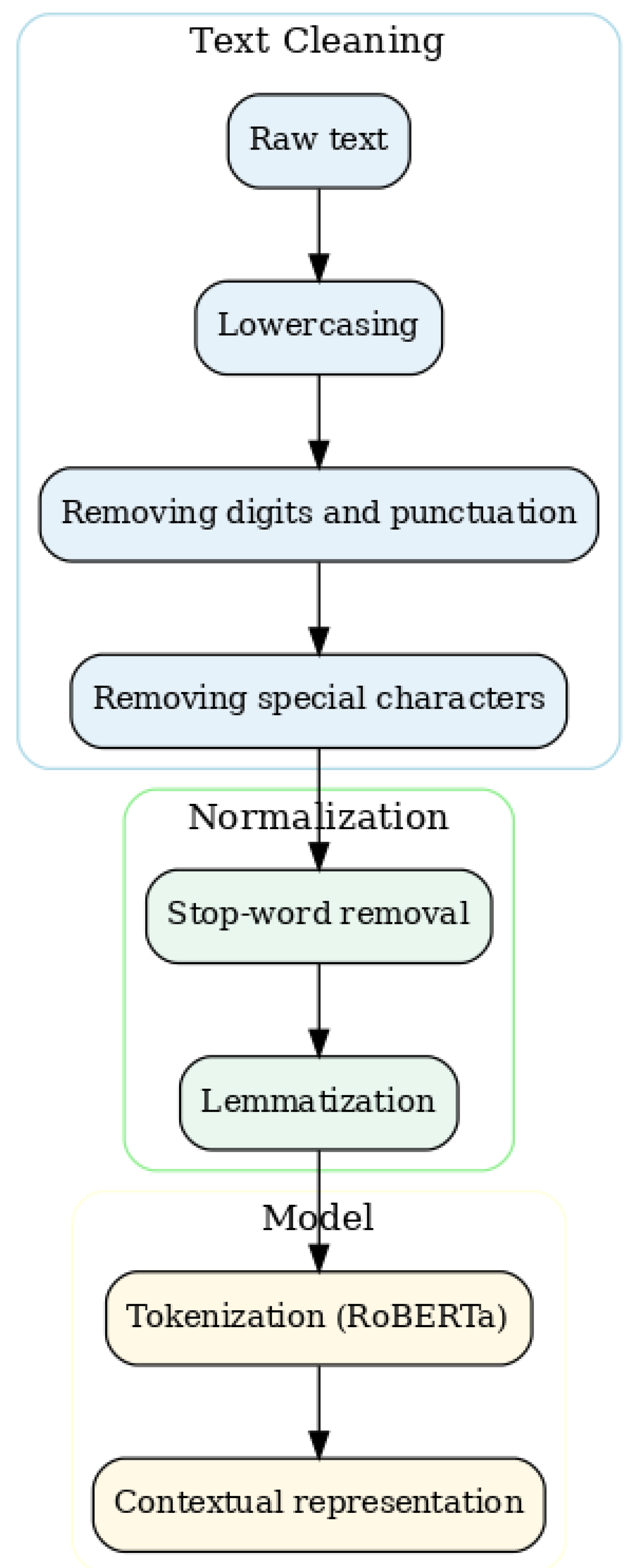
3.2. Data Preparation and Pre-Processing
3.3. Core Algorithmic Components
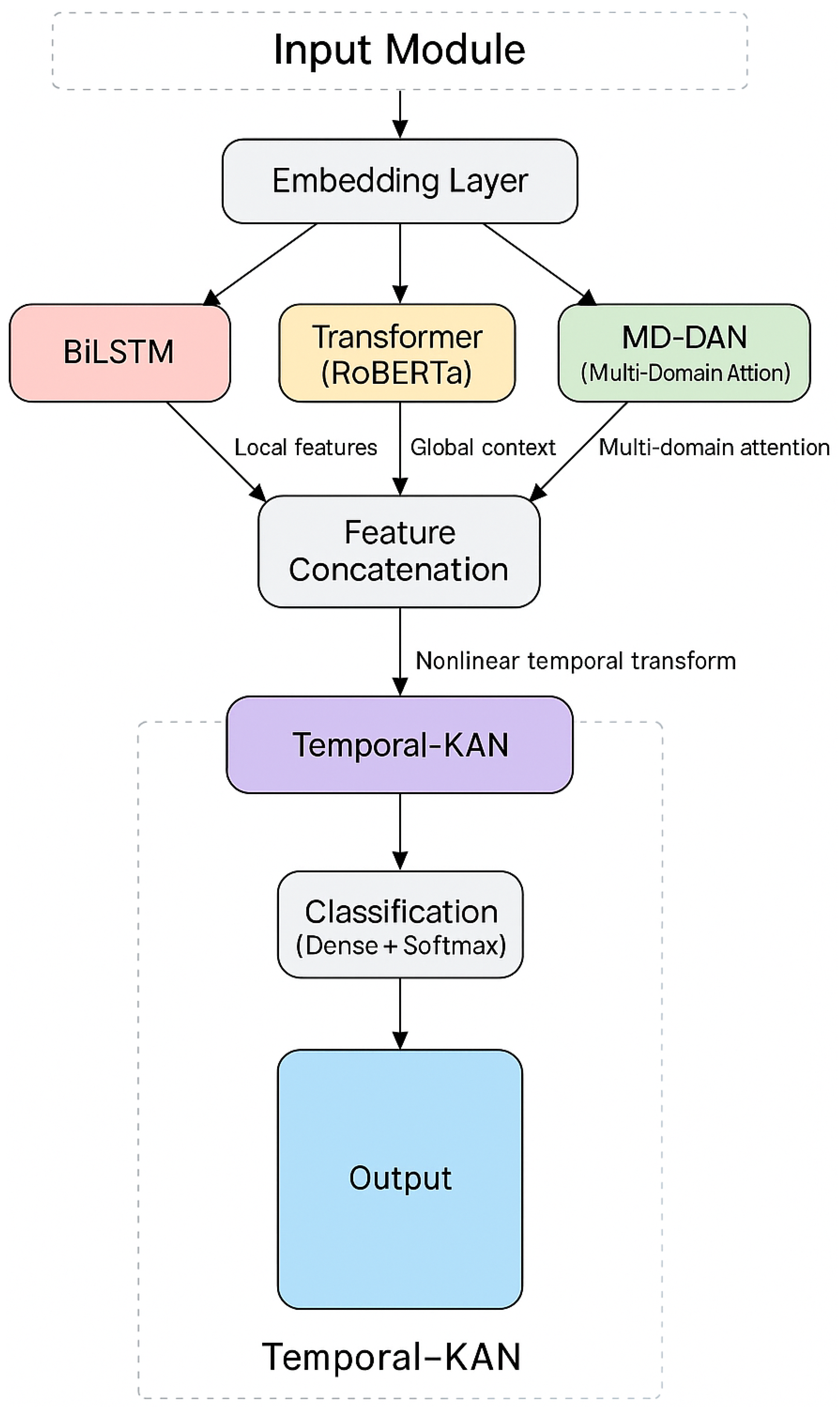
3.4. The Proposed Approach
3.5. Input Data
3.6. Bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM)
3.7. Transformer Module (RoBERTa)
3.8. Multi-Domain Dynamic Attention Network (MD-DAN)
3.9. Temporal-KAN
| Algorithm 1: Hybrid Temporal–KAN Attention (Hyb–TKAN) |
Input: Token sequence , time indices , parameters Output: Predicted class probabilities  |
4. Experimental Results and Evaluation
4.1. Data Processing Tools
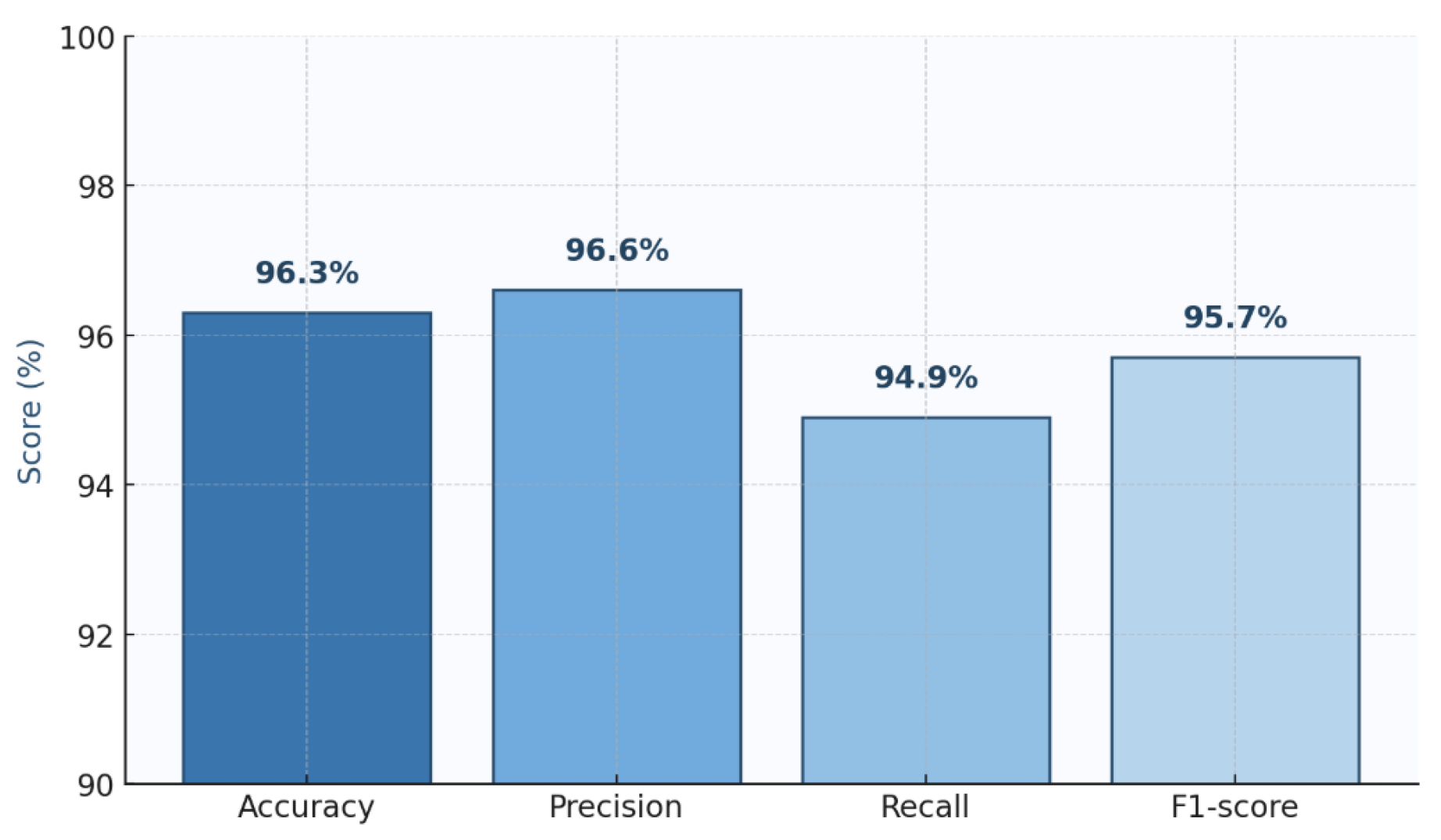
4.2. Model Results
4.3. Discussion on Ablation Studies
4.4. Computational Complexity of the Proposed Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yenduri, G.; Ramalingam, M.; Selvi, G.C.; Supriya, Y.; Srivastava, G.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Raj, G.D.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Prabadevi, B.; Wang, W.; et al. GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer)—A Comprehensive Review on Enabling Technologies, Potential Applications, Emerging Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 54608–54649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleshakova, E.; Osipov, A.; Gataullin, S.; Gataullin, T.; Vasilakos, A. Next Gen Cybersecurity Paradigm Towards Artificial General Intelligence: Russian Market Challenges and Future Global Technological Trends. J. Comput. Virol. Hacking Tech. 2024, 20, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Huang, Z.; Bergman, A.; Shen, D.; Gao, P.; Lingelbach, M.; Sun, K.; Bian, W.; Song, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Phased Consistency Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 83951–84009. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Hu, M.; Fan, Z.; Wang, C.; Ding, C.; Tao, D.; Cham, T.J. Trajectory Consistency Distillation. CoRR 2024. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=aDJXCgfkf4 (accessed on 20 November 2025).
- Geng, Z.; Pokle, A.; Luo, W.; Lin, J.; Kolter, J.Z. Consistency Models Made Easy. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.14548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, M.; Qu, X.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, W. A Survey of Attacks on Large Vision–Language Models: Resources, Advances, and Future Trends. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 19525–19545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zeng, G.; Wang, T.; Lu, W. TinyLLaMA: An Open-Source Small Language Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.02385. [Google Scholar]
- Schick, T.; Schütze, H. It’s Not Just Size That Matters: Small Language Models Are Also Few-Shot Learners. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Online, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 2339–2352. [Google Scholar]
- Magister, L.C.; Mallinson, J.; Adamek, J.; Malmi, E.; Severyn, A. Teaching Small Language Models to Reason. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 1773–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Mo, T.; Lu, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Tang, X.; et al. A Comprehensive Survey of Small Language Models in the Era of Large Language Models: Techniques, Enhancements, Applications, Collaboration with LLMs, and Trustworthiness. In ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Tu, Y.; Han, X.; He, C.; Cui, G.; Long, X.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, W.; et al. MiniCPM: Unveiling the Potential of Small Language Models with Scalable Training Strategies. In Proceedings of the First Conference on Language Modeling, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–9 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Dong, Z.; Yang, C.; Qiao, Y. Weak-to-Strong Search: Align Large Language Models via Searching over Small Language Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 4819–4851. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Pertsch, K.; Karamcheti, S.; Xiao, T.; Balakrishna, A.; Nair, S.; Rafailov, R.; Foster, E.; Lam, G.; Sanketi, P.; et al. OpenVLA: An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2406.09246. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Tang, Z.; Wu, K.; Xu, Z.; Liu, N.; Cheng, R.; Shen, C.; et al. TinyVLA: Towards Fast, Data-Efficient Vision-Language-Action Models for Robotic Manipulation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 3988–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.; Liang, D.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Kirchhoff, K. Masked Language Model Scoring. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Dong, L.; Wei, F.; Wang, W.; Yang, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Piao, S.; Zhou, M.; et al. UNILMv2: Pseudo-Masked Language Models for Unified Language Model Pre-Training. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, S.; Arriola, M.; Schiff, Y.; Gokaslan, A.; Marroquin, E.; Chiu, J.; Rush, A.; Kuleshov, V. Simple and Effective Masked Diffusion Language Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 130136–130184. [Google Scholar]
- Arriola, M.; Chiu, J.; Gokaslan, A.; Kuleshov, V.; Marroquin, E.; Rush, A.; Sahoo, S.; Schiff, Y. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Jiao, R. Segment Anything Model for Medical Image Segmentation: Current Applications and Future Directions. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 171, 108238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurowski, M.A.; Dong, H.; Gu, H.; Yang, J.; Konz, N.; Zhang, Y. Segment Anything Model for Medical Image Analysis: An Experimental Study. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 89, 102918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Luzi, F.; Lahrichi, S.; Kassaw, K.; Collins, L.M.; Bradbury, K.; Malof, J.M. Segment Anything, from Space? In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, L.; Ye, M.; Danelljan, M.; Tai, Y.W.; Tang, C.K.; Yu, F. Segment Anything in High Quality. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 29914–29934. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Du, B.; Xu, M.; Liu, L.; Tao, D.; Zhang, L. SAMRS: Scaling-Up Remote Sensing Segmentation Dataset with Segment Anything Model. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 8815–8827. [Google Scholar]
- Petushkov, G.V.; Sigov, A.S. Analysis and selection of the structure of a multiprocessor computing system according to the performance criterion. Russ. Technol. J. 2024, 12, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Vaidya, S.; Ruehle, F.; Halverson, J.; Soljačić, M.; Hou, T.Y.; Tegmark, M. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.19756. [Google Scholar]
- Kozyrev, A.N. Data Economy, Neural Network Training, and Multidimensional Geometry. Digit. Econ. 2024, 3, 5–13. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thant, A.M.; Panitanarak, T. Emotion Recognition Through Advanced Signal Fusion and Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 93259–93270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Z.; Song, A. KAN-GCNN: EEG-Based Emotion Recognition with a Kolmogorov-Arnold Network-Enhanced Graph Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Robotics and Control Engineering, Linköping, Sweden, 7–10 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Saha, S.; Jana, N.D. KANGAN-AVSS: Kolmogorov-Arnold Network Based Generative Adversarial Networks for Audio–Visual Speech Synthesis. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025—IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zainal, A.; Siraj, M.M.; Ghaleb, F.A.; Hao, X.; Han, S. An Intrusion Detection Model Based on Convolutional Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Cao, M.; Zhang, C. ICKAN: A Deep Musical Instrument Classification Model Incorporating Kolmogorov-Arnold Network. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayed, A.; Li, C.; Abdalsalam, M.; Fat’hAlalim, A. A Hybrid Model for Arabic Character Recognition Using CNN and Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs). Multimed. Tools Appl. 2025, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, F.; Rizk, R.; Rizk, D.; Rizk, P.; Chu, C.-H.H. KAN-MID: A Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks-Based Framework for Malicious URL and Intrusion Detection in IoT Systems. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 160855–160873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleshakova, E.S.; Gataullin, S.T. KAN-BiLSTM: Hybrid Neural Network Model with Multi-Domain Attention for Threat Analysis in Digital Space; Certificate of State Registration of Computer Program No. 2025619243; EDN ORSBNY; Rospatent Federal Service on Intellectual Property: Moscow, Russia, 2025. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Toscano, J.D.; Wang, L.L.; Karniadakis, G.E. KKANs: Kurkova-Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks and Their Learning Dynamics. Neural Netw. 2025, 191, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT: A Distilled Version of BERT—Smaller, Faster, Cheaper and Lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.R.; Le, Q.V. XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-Supervised Learning of Language Representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11942. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, K.; Luong, M.T.; Le, Q.V.; Manning, C.D. ELECTRA: Pre-Training Text Encoders as Discriminators Rather Than Generators. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10555. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Gao, J.; Chen, W. DeBERTaV3: Improving DeBERTa Using ELECTRA-Style Pre-Training with Gradient-Disentangled Embedding Sharing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.09543. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, Y. A Graph Neural Network-Based Context-Aware Framework for Sentiment Analysis Classification in Chinese Microblogs. Mathematics 2025, 13, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaca-Rubio, C.J.; Blanco, L.; Pereira, R.; Caus, M. Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) for Time Series Analysis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.08790. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.L.; Ding, J.J. Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks with Trainable Activation Functions for Data Regression and Classification. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Fukuoka, Japan, 18–21 February 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L. G-KAN: Graph Kolmogorov-Arnold Network for Node Classification Using Contrastive Learning. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 100287–100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
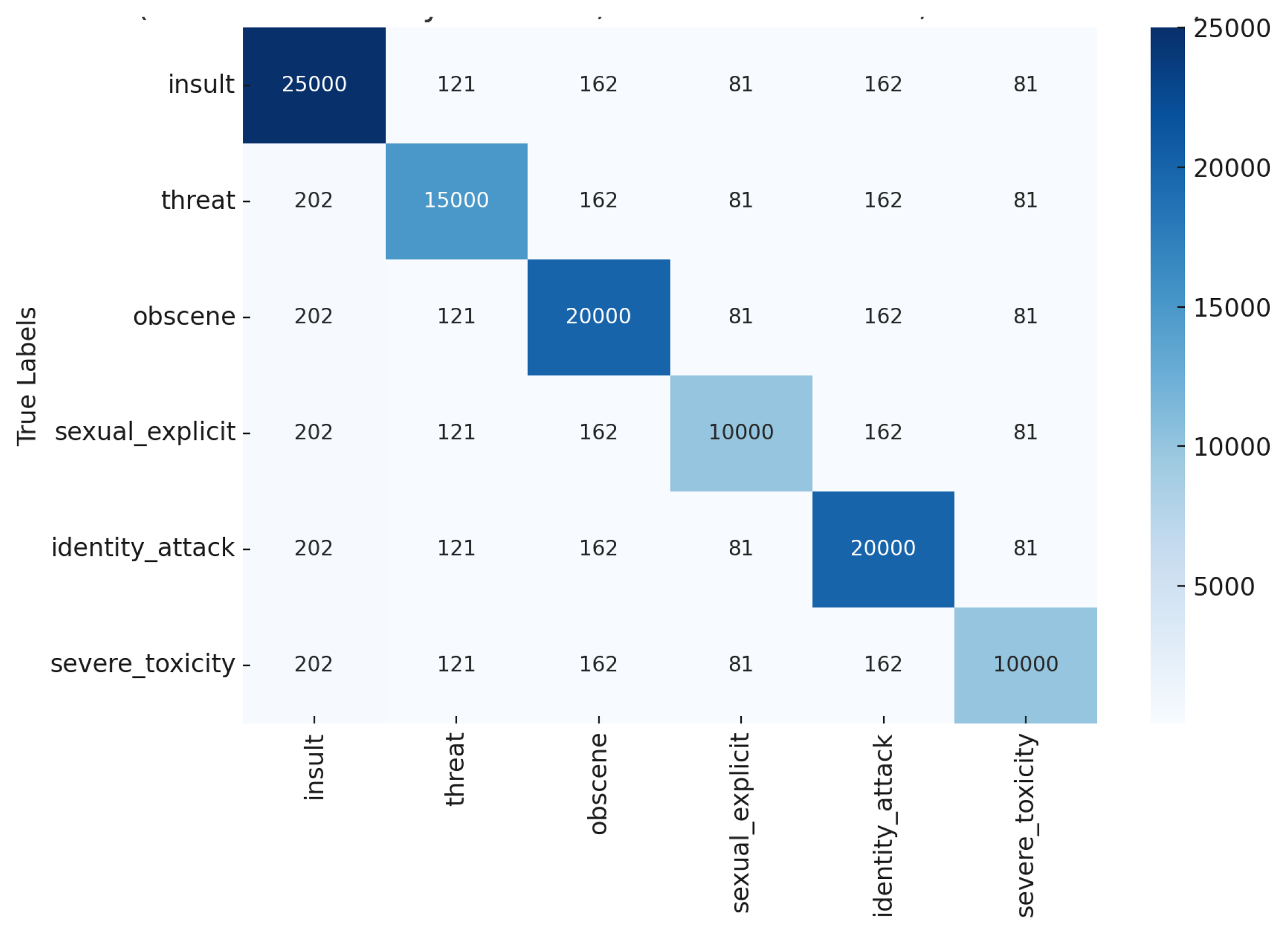
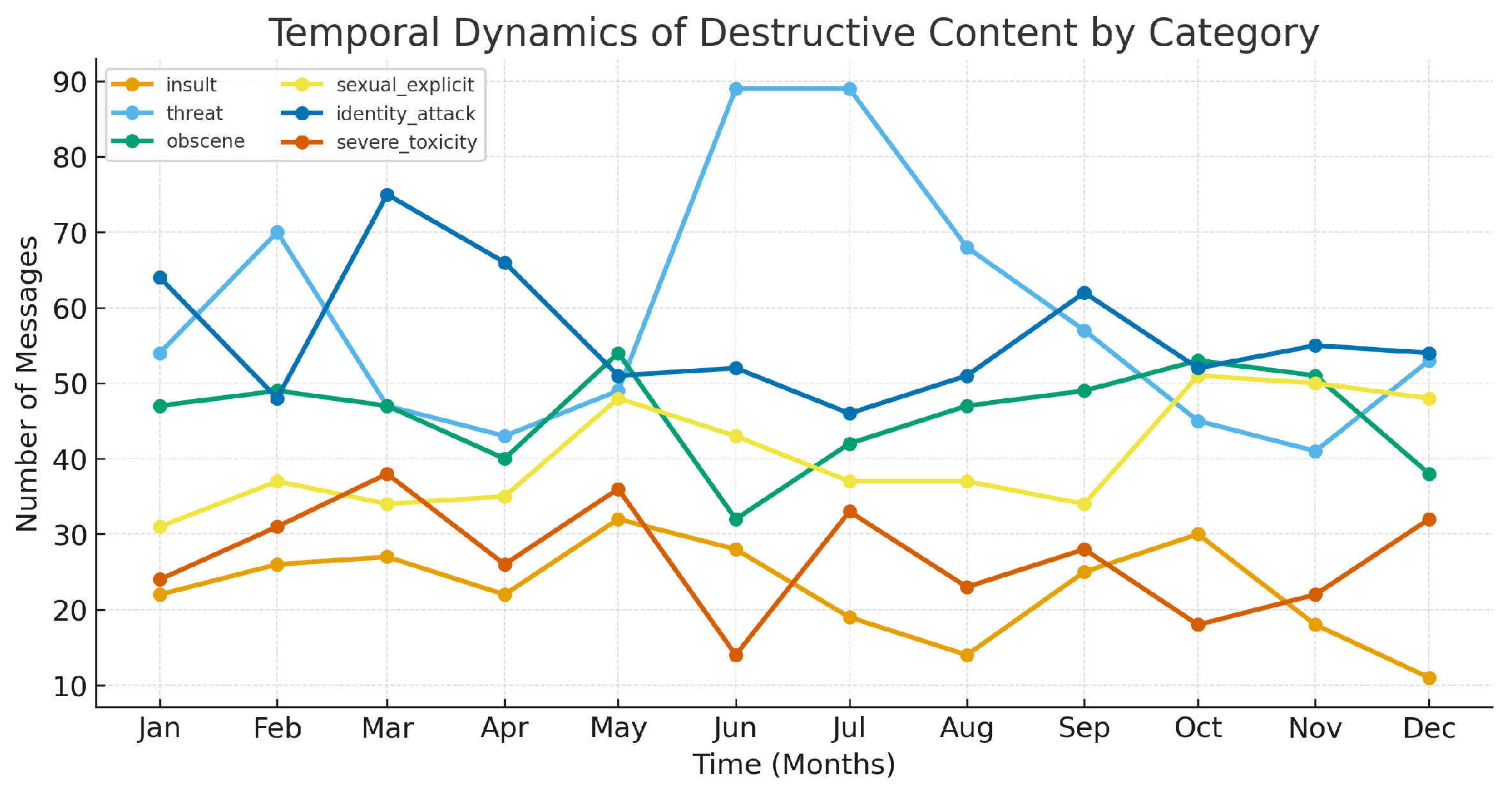
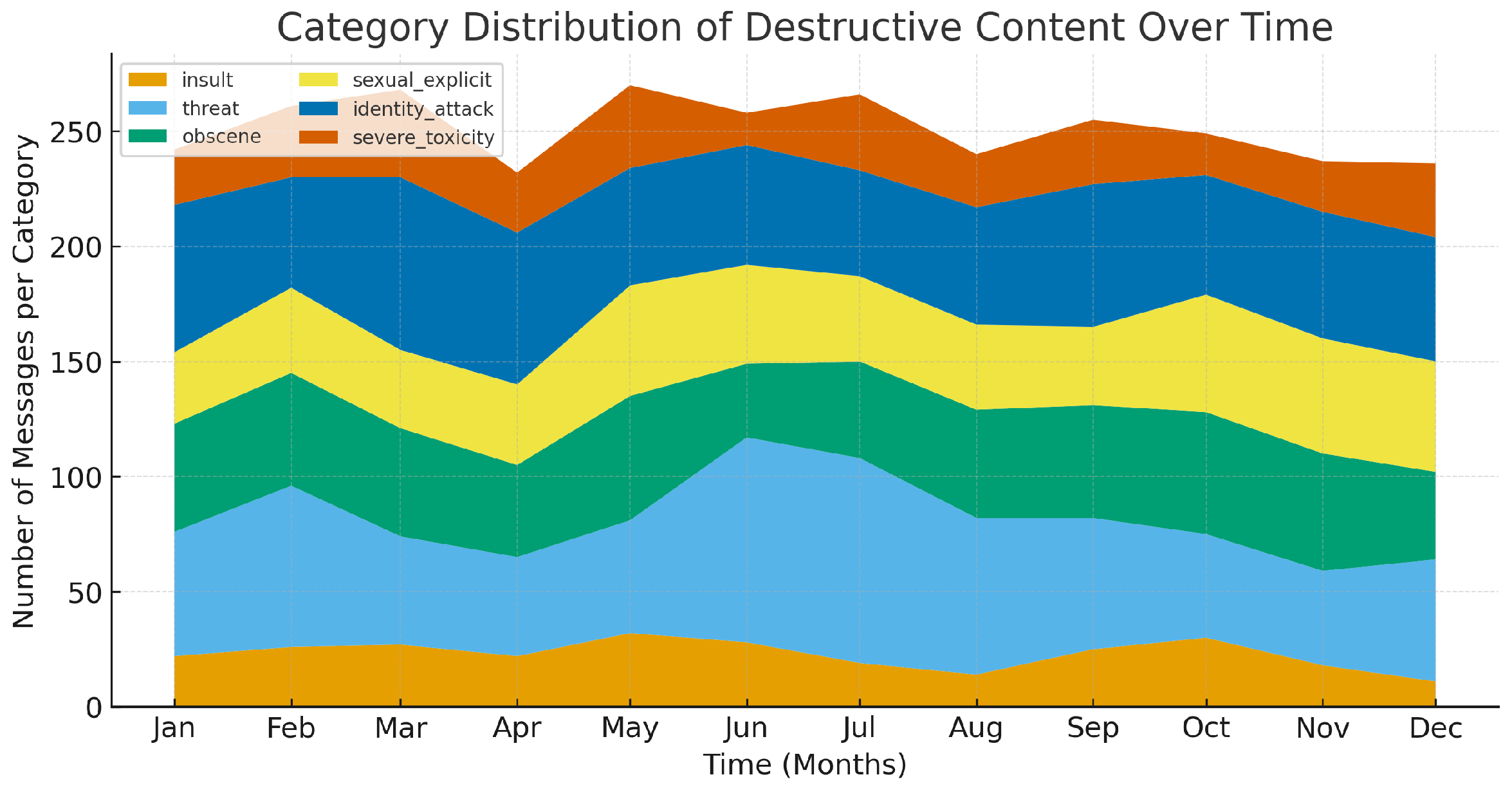
| Models | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-base | 90.1% | 94.7% | 89.2% | 91.9% |
| RoBERTa-base | 92.8% | 94.2% | 94.2% | 93.2% |
| RoBERTa-large | 93.0% | 94.9% | 93.9% | 94.4% |
| DistilBERT | 89.0% | 93.5% | 88.7% | 90.1% |
| ALBERT-xxlarge | 91.5% | 95.1% | 91.3% | 93.0% |
| XLNet-large | 90.5% | 94.2% | 90.5% | 91.7% |
| ELECTRA-base | 91.6% | 95.6% | 92.0% | 93.7% |
| DeBERTa-v3-small | 92.4% | 96.0% | 95.7% | 93.8% |
| Hyb-TKAN | 96.3% | 96.4% | 94.7% | 95.3% |
| Model | Train Time per Epoch (s) | Inference (ms/Sample) | GPU Memory (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DistilBERT | 52–57 | 2.9–3.4 | 2.4–2.7 |
| BERT-base | 88–94 | 4.2–4.8 | 3.9–4.3 |
| RoBERTa-base | 78–84 | 3.8–4.4 | 4.1–4.6 |
| XLNet-base | 112–119 | 5.0–5.6 | 4.8–5.3 |
| ELECTRA-base | 71–76 | 3.4–3.9 | 3.6–3.9 |
| Hyb-TKAN | 98–104 | 4.6–5.2 | 4.4–4.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chechkin, A.; Pleshakova, E.; Gataullin, S. A Hybrid Neural Network Transformer for Detecting and Classifying Destructive Content in Digital Space. Algorithms 2025, 18, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120735
Chechkin A, Pleshakova E, Gataullin S. A Hybrid Neural Network Transformer for Detecting and Classifying Destructive Content in Digital Space. Algorithms. 2025; 18(12):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120735
Chicago/Turabian StyleChechkin, Aleksandr, Ekaterina Pleshakova, and Sergey Gataullin. 2025. "A Hybrid Neural Network Transformer for Detecting and Classifying Destructive Content in Digital Space" Algorithms 18, no. 12: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120735
APA StyleChechkin, A., Pleshakova, E., & Gataullin, S. (2025). A Hybrid Neural Network Transformer for Detecting and Classifying Destructive Content in Digital Space. Algorithms, 18(12), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18120735






