Interpretable Machine Learning for Coronary Artery Disease Risk Stratification: A SHAP-Based Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Source
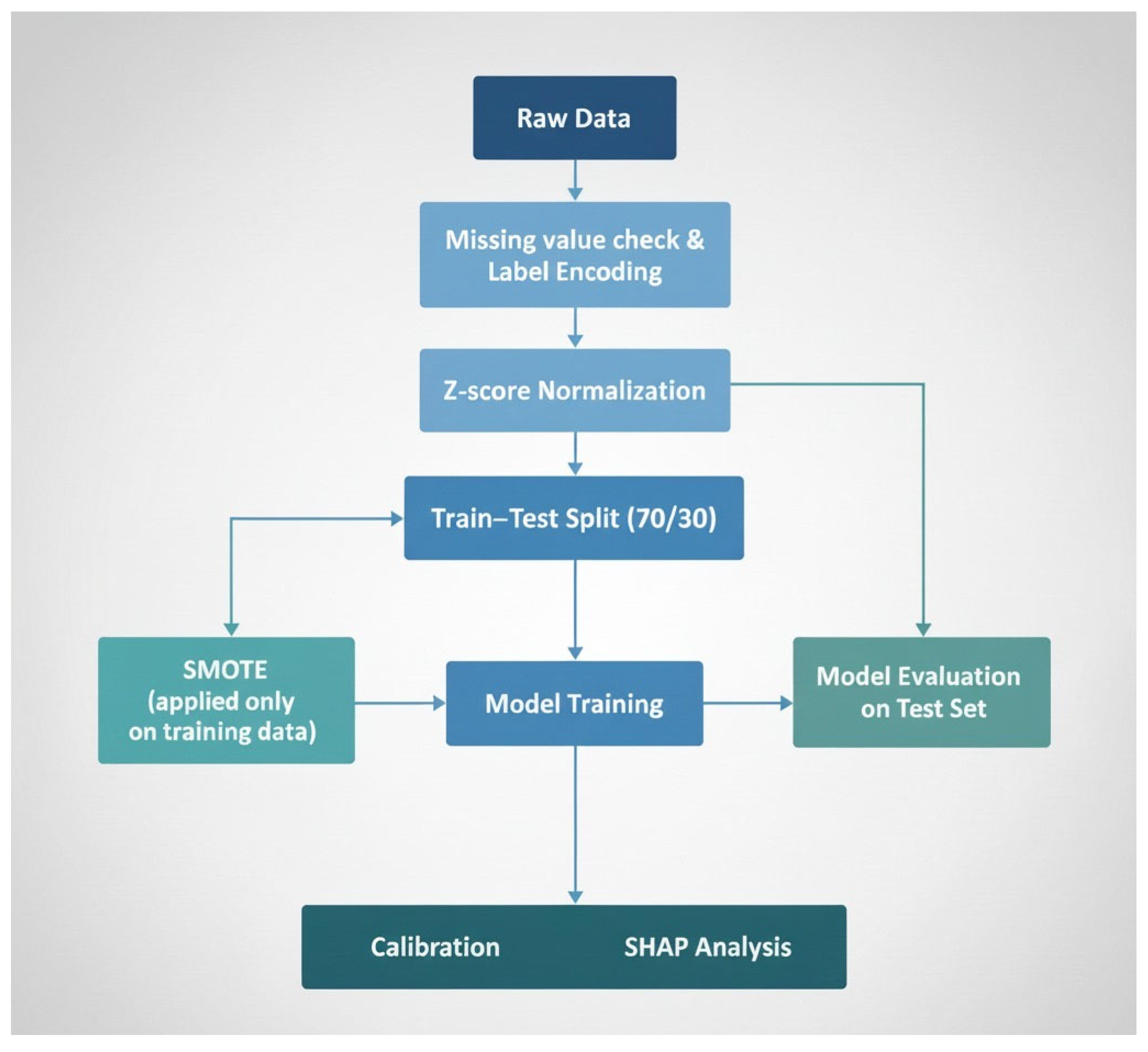
2.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Machine Learning Classification
- 1.
- Support Vector Machine (SVM):
- 2.
- Random Forest (RF):
- 3.
- Extra Trees Classifier (Extremely Randomized Trees):
- 4.
- Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM):
- 5.
- Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost)
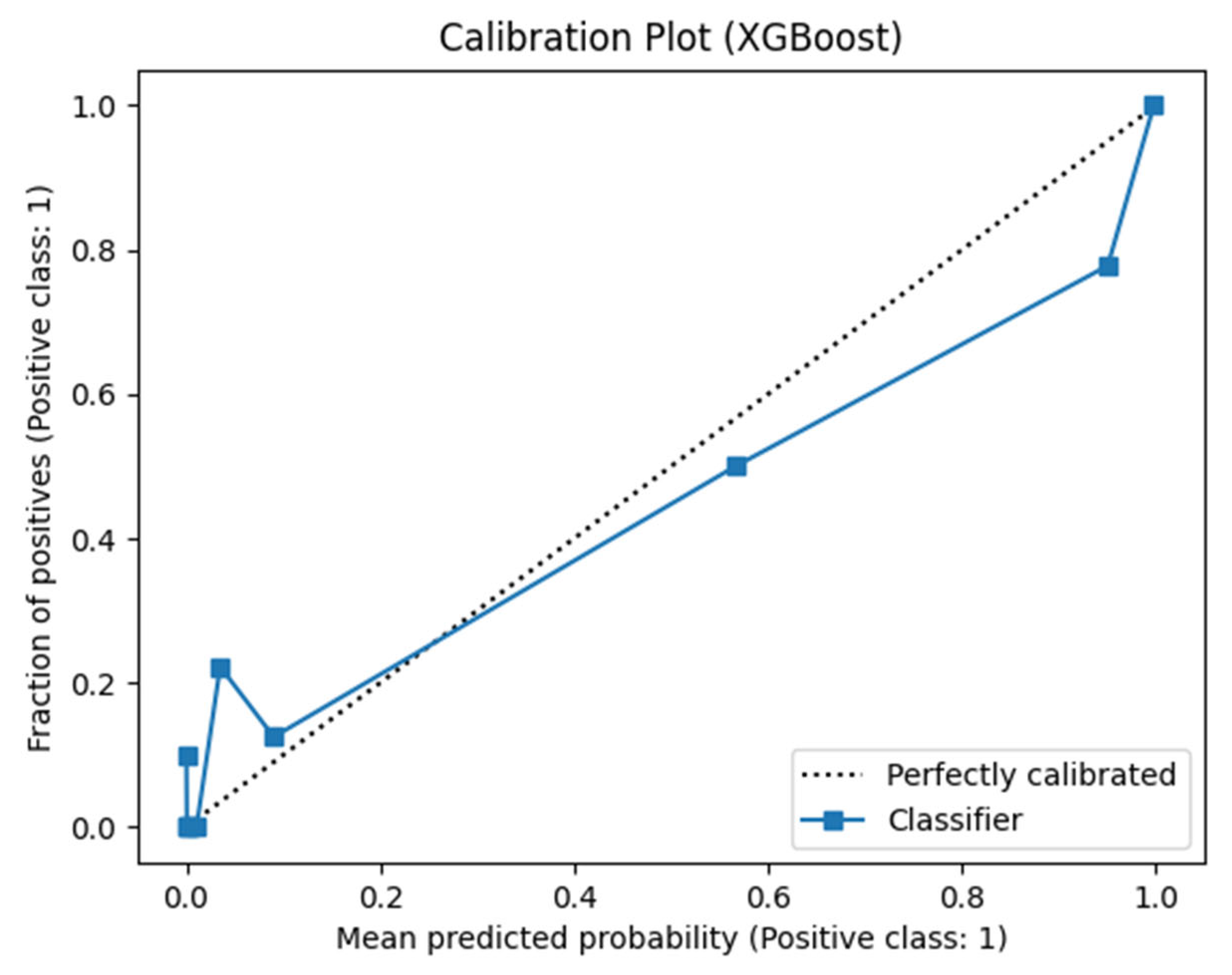
3. Results and Discussion
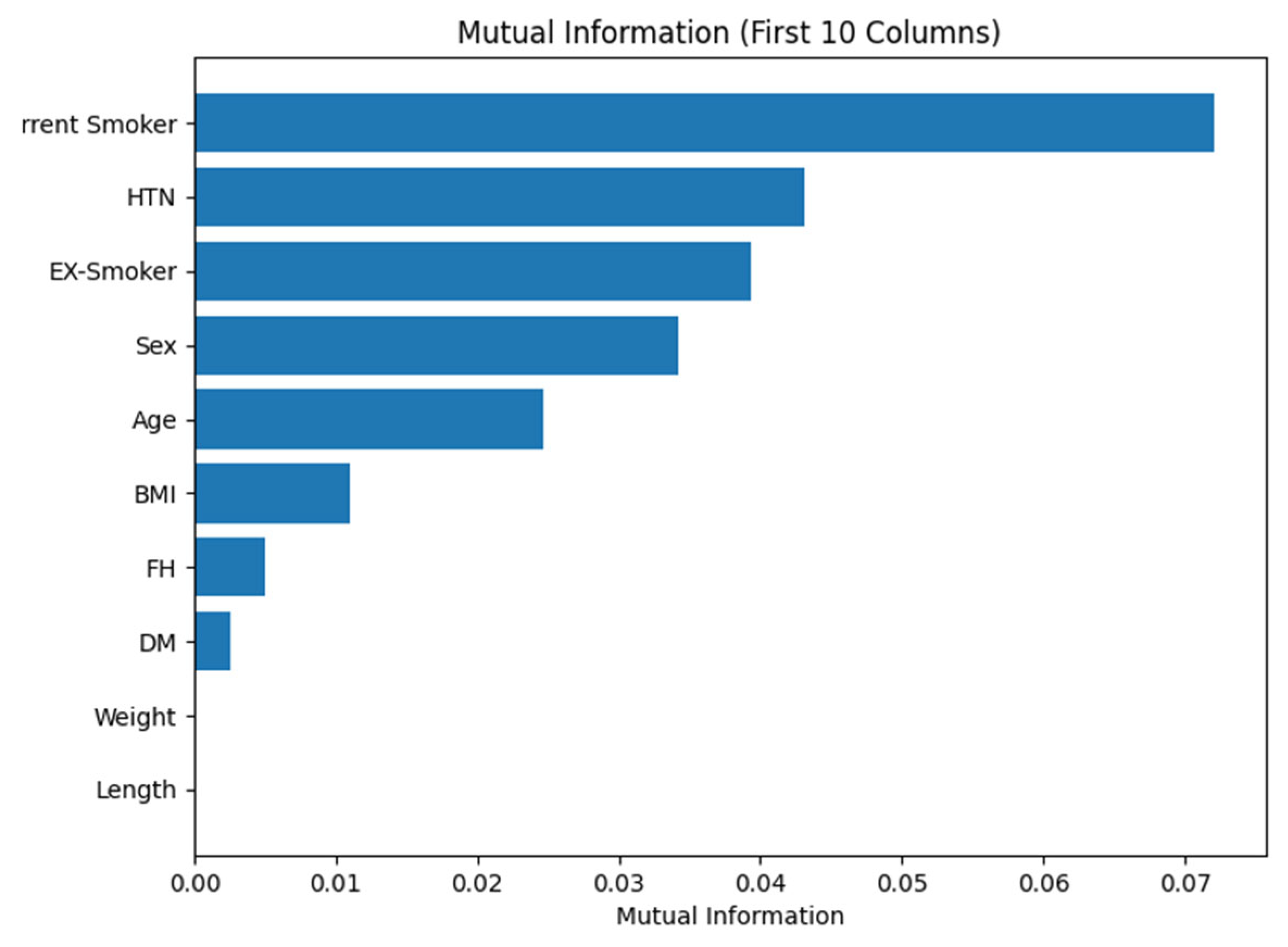
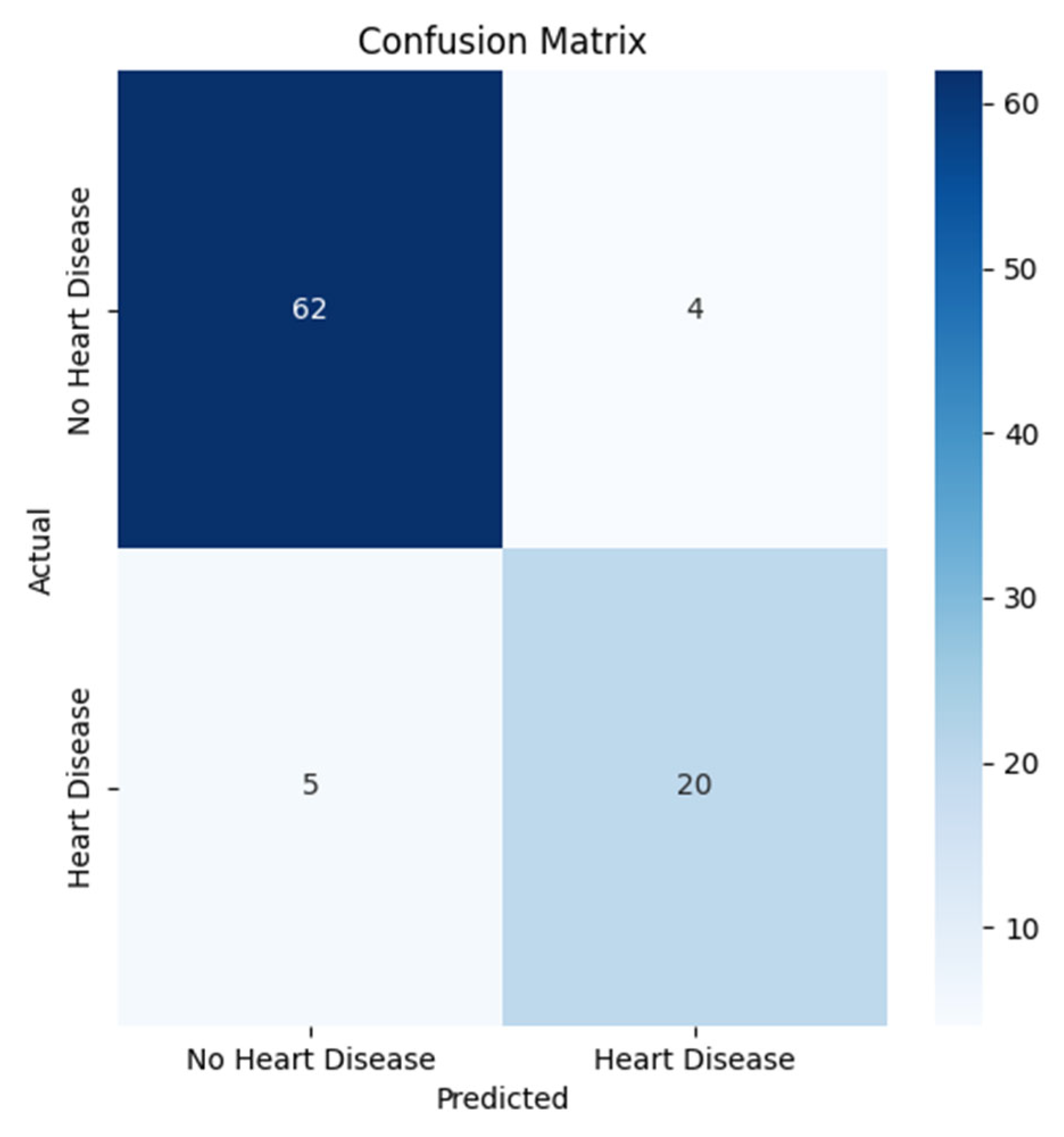
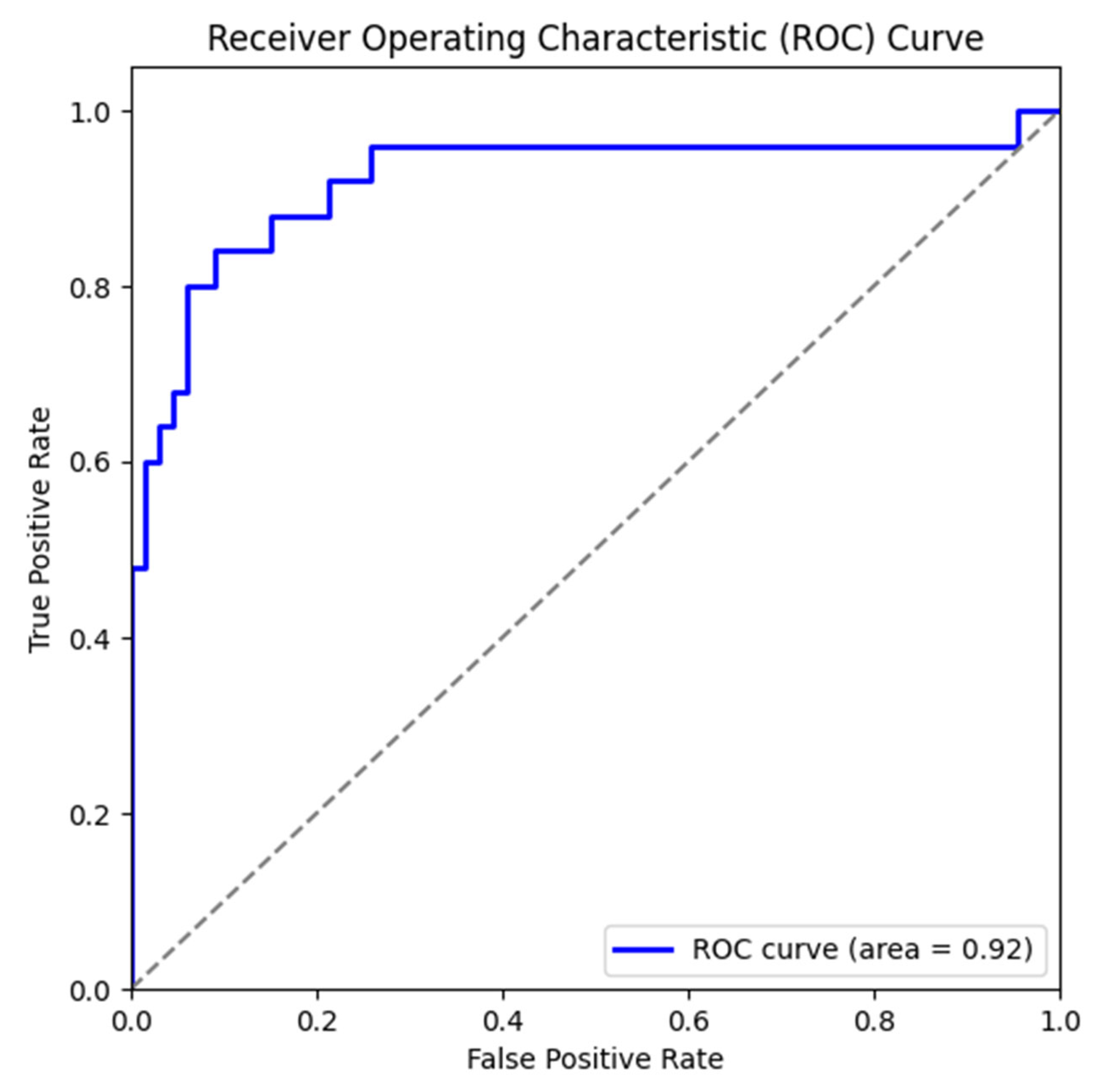
3.1. Results of Machine Learning Models
3.2. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| GB | Gradient Boosting |
| RF | Random Forest |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
References
- Di Lenarda, F.; Balestrucci, A.; Terzi, R.; Lopes, P.; Ciliberti, G.; Marchetti, D.; Schillaci, M.; Doldi, M.; Melotti, E.; Ratti, A.; et al. Coronary Artery Disease, Family History, and Screening Perspectives: An Up-to-Date Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodeboina, M.; Piayda, K.; Jenniskens, I.; Vyas, P.; Chen, S.; Pesigan, R.J.; Ferko, N.; Patel, B.P.; Dobrin, A.; Habib, J.; et al. Challenges and Burdens in the Coronary Artery Disease Care Pathway for Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Contemporary Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralapanawa, U.; Sivakanesan, R. Epidemiology and the Magnitude of Coronary Artery Disease and Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Narrative Review. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lin, L.; Wu, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Li, H. Global, Regional, and National Death, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years (DALYs) for Cardiovascular Disease in 2017 and Trends and Risk Analysis from 1990 to 2017 Using the Global Burden of Disease Study and Implications for Prevention. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 559751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawade, D.B.; Soladoye, A.A.; Omodunbi, B.A.; Aderinto, N.; Adeyanju, I.A. Comparative analysis of machine learning models for coronary artery disease prediction with optimized feature selection. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 436, 133443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen-Uribe, Á.; Kremser, M.; Rohlfing, A.-K.; Castor, T.; Kolb, K.; Dicenta, V.; Emschermann, F.; Li, B.; Borst, O.; Rath, D.; et al. Platelet-Derived PCSK9 Is Associated with LDL Metabolism and Modulates Atherothrombotic Mechanisms in Coronary Artery Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, G.; Subramani, T.; Almanasef, M.; Orayj, K.; Shorog, E.; Alshahrani, A.M.; Alanazi, T.S.; Majeed, A. Exploring Factors Affecting Health-Related Quality of Life in Coronary Artery Disease Patients. Medicina 2025, 61, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, A.; Vasiljević, Z.; Mickovski-Katalina, N.; Mandić-Rajčević, S.; Soldatović, I. Temporal Trends in Acute Coronary Syndrome Mortality in Serbia in 2005–2019: An Age–Period–Cohort Analysis Using Data from the Serbian Acute Coronary Syndrome Registry (RAACS). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauersachs, R.; Zeymer, U.; Brière, J.B.; Marre, C.; Bowrin, K.; Huelsebeck, M. Burden of Coronary Artery Disease and Peripheral Artery Disease: A Literature Review. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2019, 2019, 8295054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasarian, E.; Sharifrazi, D.; Mohsenirad, S.; Tsui, K.; Alizadehsani, R. AI Framework for Early Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease: An Integration of Borderline SMOTE, Autoencoders and Convolutional Neural Networks Approach. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.15339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Arora, H.S.; Kumar, R.; Raman, B. DMHZ: A Decision Support System Based on Machine Computational Design for Heart Disease Diagnosis Using Z-Alizadeh Sani Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 13–16 January 2021; pp. 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadehsani, R.; Roshanzamir, M.; Abdar, M.; Beykikhoshk, A.; Zangooei, M.H.; Khosravi, A.; Nahavandi, S.; Tan, R.S.; Acharya, U.R. Model Uncertainty Quantification for Diagnosis of Each Main Coronary Artery Stenosis. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 10149–10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, R.; Arora, H.S.; Sharma, A.; Al-Turjman, F.; Altrjman, C. C-CADZ: Computational Intelligence System for Coronary Artery Disease Detection Using Z-Alizadeh Sani Dataset. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 2436–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joloudari, J.H.; Azizi, F.; Nematollahi, M.A.; Alizadehsani, R.; Hassannataj, E.; Mosavi, A. GSVMA: A Genetic-Support Vector Machine-Anova Method for CAD Diagnosis Based on Z-Alizadeh Sani Dataset. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 760178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, M.; Varadarajan, V.; Sadoughi, F.; Chopannejad, S.; Langarizadeh, M. A Machine Learning Model for Detection of Coronary Artery Disease Using Noninvasive Clinical Parameters. Life 2022, 12, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D. Investigating the Synthetic Minority Class Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) on an Imbalanced Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Dataset. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 4, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darba, S.; Safaei, N.; Mahboub-Ahari, A.; Nosratnejad, S.; Alizadeh, G.; Ameri, H.; Yousefi, M. Direct and Indirect Costs Associated with Coronary Artery (Heart) Disease in Tabriz, Iran. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2020, 13, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadehsani, R.; Roshanzamir, M.; Sani, Z. Z-Alizadeh Sani [Dataset]. UCI Machine Learning Repository. 2013. Available online: https://doi.org/10.24432/C5Q31T (accessed on 30 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bolikulov, F.; Nasimov, R.; Rashidov, A.; Akhmedov, F.; Cho, Y.-I. Effective Methods of Categorical Data Encoding for Artificial Intelligence Algorithms. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhan, E.C.; Ekmekcioğlu, Ö. Coupling Different Machine Learning and Meta-Heuristic Optimization Techniques to Generate the Snow Avalanche Susceptibility Map in the French Alps. Water 2024, 16, 3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioğlu, A. The Effect of Feature Normalization Methods in Radiomics. Insights Imaging 2024, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-de-León, L.P.; Solís-Martín, D.; Galán-Páez, J.; Borrego-Díaz, J. Text-Conditioned Diffusion-Based Synthetic Data Generation for Turbine Engine Sensor Analysis and RUL Estimation. Machines 2025, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtasham, F.; Pourhoseingholi, M.; Hashemi Nazari, S.S.; Kavousi, K.; Zali, M.R. Comparative Analysis of Feature Selection Techniques for COVID-19 Dataset. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Pencina, M.; Einstein, A.J.; Liang, J.X.; Berman, D.S.; Slomka, P. Impact of Train/Test Sample Regimen on Performance Estimate Stability of Machine Learning in Cardiovascular Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, M.; Atif, D.; Oliva, D.; Abraham, A.; Ventura, S. Handling Imbalanced Medical Datasets: Review of a Decade of Research. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F. A Comparative Study of SMOTE and ADASYN for Multiclass Classification of IoT Anomalies. ResearchGate 2023, 17, 15–24. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/392309026_A_comparative_study_of_SMOTE_and_ADASYN_for_multiclass_classification_of_IoT_anomalies (accessed on 12 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Imani, M.; Beikmohammadi, A.; Arabnia, H.R. Comprehensive Analysis of Random Forest and XGBoost Performance with SMOTE, ADASYN, and GNUS Under Varying Imbalance Levels. Technologies 2025, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Y. XGBoost-Enhanced Graph Neural Networks: A New Architecture for Heterogeneous Tabular Data. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Arshad, M.A.; Luo, G. Decision Trees for Strategic Choice of Augmenting Management Intuition with Machine Learning. Symmetry 2025, 17, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tong, X.; Bai, S.; Zhou, J. A LightGBM-Based Power Grid Frequency Prediction Method with Dynamic Significance–Correlation Feature Weighting. Energies 2025, 18, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-L.; Pai, P.-F. Support Vector Machines with Hyperparameter Optimization Frameworks for Classifying Mobile Phone Prices in Multi-Class. Electronics 2025, 14, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdoost, H. Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Decision-Making Implications. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, T.J.; Huemann, Z.; Hu, J.; Rahmim, A. A Guide to Cross-Validation for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, e220232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Smeden, M.; Heinze, G.; Van Calster, B.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Vardas, P.E.; Bruining, N.; de Jaegere, P.; Moore, J.H.; Denaxas, S.; Boulesteix, A.L.; et al. Critical Appraisal of Artificial Intelligence-Based Prediction Models for Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2921–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, F.S. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve: Overview and Practical Use for Clinicians. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Macheret, F.; Gabriel, R.A.; Ohno-Machado, L. A Tutorial on Calibration Measurements and Calibration Models for Clinical Prediction Models. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2020, 27, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N. From Local Explanations to Global Understanding with Explainable AI for Trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, S.A.; Strümke, I.; Thambawita, V.; Hammou, M.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; Parasa, S. On Evaluation Metrics for Medical Applications of Artificial Intelligence. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, J.; Tamis-Holland, J.; Bangalore, S.; Bates, E.R.; Beckie, T.M.; Bischoff, J.M.; Bittl, J.A.; Cohen, M.G.; DiMaio, J.M.; Don, C.W.; et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, e21–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.-M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes–2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S144–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, W.J.; Khera, A.V.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Shin, J.I.; Won, H.H. Association between Adiposity and Cardiovascular Outcomes: An Umbrella Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational and Mendelian Randomization Studies. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3388–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Collins, G.S.; Debray, T.P.A.; Dhiman, P.; Ma, J.; Schlussel, M.M.; Archer, L.; Van Calster, B.; Harrell, F.E.; Martin, G.P.; et al. Evaluation of Clinical Prediction Models (Part 2): How to Undertake and Report External Validation. BMJ 2024, 384, e074819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.J.; Deedwania, P.; Acharya, T.; Aguilar, D.; Bhatt, D.L.; Chyun, D.A.; Di Palo, K.E.; Golden, S.H.; Sperling, L.S. Comprehensive Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e722–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Newby, L.K.; Arnold, S.V.; Bittner, V.; Brewer, L.C.; Demeter, S.H.; Dixon, D.L.; Fearon, W.F.; Hess, B.; Johnson, H.M.; et al. 2023 AHA/ACC/ACCP/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline for the Management of Patients with Chronic Coronary Disease. Circulation 2023, 148, e9–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Byeon, K.; Jung, M.; Kang, K.-W.; Lee, W.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Lip, G.Y.H. Smoking Cessation and Incident Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2442639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.R.; Brill, I.K.; Gram, I.T.; Brown, P.E.; Jha, P. Smoking Cessation and Short- and Longer-Term Mortality. NEJM Evid. 2024, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losin, I.; Zick, Y.; Peled, Y.; Arbel, Y. The Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Gaps, Challenges and Solutions. Kidney Dis. 2023, 9, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Xie, B.; Dai, H. Prevalence and Impact of COPD in Ischemic Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2024, 19, 2333–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibbler, J.; Stefan, M.S.; Thanassoulis, G.; Ripley, D.P.; Bourke, S.C.; Steer, J. Prevalence of Undiagnosed Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction in COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00548–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, W.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.-F.; An, Z.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.-Y.; Hao, M.-D.; Jin, Y.-J.; Li, D.; et al. Association between Asthma and All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease Morbidity and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 861798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Hernández, C.A.; Del Greco, M.F.; Sundaram, V.; Portas, L.; Minelli, C.; Bloom, C.I. Asthma and Incident Coronary Heart Disease: An Observational and Mendelian Randomisation Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, 2301788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomii, D.; Pilgrim, T.; Borger, M.A.; De Backer, O.; Lanz, J.; Reineke, D.; Siepe, M.; Windecker, S. Aortic Stenosis and Coronary Artery Disease: Decision-Making between Surgical and Transcatheter Management. Circulation 2024, 150, 2046–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Gill, D. Mendelian Randomization for Cardiovascular Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3278–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zúñiga, D.; Balasubramanian, S.; Mehmood, K.T.; Al-Baldawi, S.; Salazar, G.Z. Hypothyroidism and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e52512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evron, J.M.; Papaleontiou, M. Decision Making in Subclinical Thyroid Disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 105, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure. Circulation 2022, 145, e895–e1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, N.; Myllis, G.; Tsimpiris, A.; Vrana, V. The Role of Mutual Information Estimator Choice in Feature Selection: An Empirical Study on mRMR. Information 2025, 16, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Rizvi, S.S.H.; Adil, S.H. Enhancing Software Quality with AI: A Transformer-Based Approach for Code Smell Detection. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.R.; Guedes, A.; Sanchez-Gendriz, I. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) for Efficient Feature Selection in Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2024, 6, 316–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable Group | Number of Variables | Type (Numerical/Categorical/Yes-No) | Examples | Representation in Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | 5 | Numerical + Categorical | Age (numerical), Sex (categorical) | Continuous/Discrete |
| Risk Factors | 10 | Yes/No (binary) | DM, HTN, Smoking, FH | Binary (0/1) |
| Clinical Findings | 8 | Numerical + Yes/No | BP (numerical), Dyspnea (Yes/No) | Mixed |
| ECG Variables | 7 | Yes/No (binary) | Q Wave, ST Elevation, LVH | Binary (0/1) |
| Laboratory | 15 | Numerical | FBS, LDL, HDL, HB, CR | Continuous |
| Echocardiographic | 6 | Numerical + Yes/No | EF-TTE (numerical), VHD (Yes/No) |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1_Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGBMClassifier | 0.8791 | 0.7917 | 0.7600 | 0.7755 |
| ExtraTreesClassifier | 0.8681 | 0.7826 | 0.7200 | 0.7500 |
| RandomForest | 0.8901 | 0.8947 | 0.6800 | 0.7727 |
| SVM | 0.8681 | 0.7826 | 0.7200 | 0.7500 |
| XGBoost | 0.9011 | 0.8333 | 0.8000 | 0.8163 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tasmurzayev, N.; Baigarayeva, Z.; Amangeldy, B.; Imanbek, B.; Kurmanbek, S.; Dikhanbayeva, G.; Amirkhanova, G. Interpretable Machine Learning for Coronary Artery Disease Risk Stratification: A SHAP-Based Analysis. Algorithms 2025, 18, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110697
Tasmurzayev N, Baigarayeva Z, Amangeldy B, Imanbek B, Kurmanbek S, Dikhanbayeva G, Amirkhanova G. Interpretable Machine Learning for Coronary Artery Disease Risk Stratification: A SHAP-Based Analysis. Algorithms. 2025; 18(11):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110697
Chicago/Turabian StyleTasmurzayev, Nurdaulet, Zhanel Baigarayeva, Bibars Amangeldy, Baglan Imanbek, Shugyla Kurmanbek, Gulmira Dikhanbayeva, and Gulshat Amirkhanova. 2025. "Interpretable Machine Learning for Coronary Artery Disease Risk Stratification: A SHAP-Based Analysis" Algorithms 18, no. 11: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110697
APA StyleTasmurzayev, N., Baigarayeva, Z., Amangeldy, B., Imanbek, B., Kurmanbek, S., Dikhanbayeva, G., & Amirkhanova, G. (2025). Interpretable Machine Learning for Coronary Artery Disease Risk Stratification: A SHAP-Based Analysis. Algorithms, 18(11), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110697







