DAFF-Net: A Dual-Branch Attention-Guided Feature Fusion Network for Vehicle Re-Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a dual-branch attention-guided feature fusion network (DAFF-Net), which introduces a Temperature-Calibration Attention Fusion (TCAF) module and a Multi-Scale Gated Attention (MSGA) module to fully exploit and fuse the complementary information of low-level, mid-level, and high-level features in the backbone network, thereby achieving effective collaboration between local details and global semantics. Additionally, to enhance the intra-class compactness of features, this paper introduces a center loss function during training, further optimizing the model’s representation learning capabilities.
- We employ an integrated mechanism of “align first, fuse then, and adaptively select”, enhancing key scale and directional cues within a unified semantic space. Compared to traditional fusion methods like static concatenation, fixed pyramids, or single-layer attention, this design reduces information dilution and cross-layer interference during multi-level fusion. It achieves a more balanced trade-off between feature alignment, multi-scale modeling, and directional selection at near-linear computational cost, thereby preserving finer-grained component information and enabling more efficient feature collaboration.
- Extensive experimental results on the VeRi-776 and VehicleID datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other relevant approaches in terms of feature expression accuracy and cross-layer fusion effectiveness.
2. Related Work
2.1. Methods for Fusing Global and Local Features
2.2. Methods for Fusing Global and Attribute Features
2.3. Methods for Fusing Global Features and Spatiotemporal Information
3. Proposed Network Model
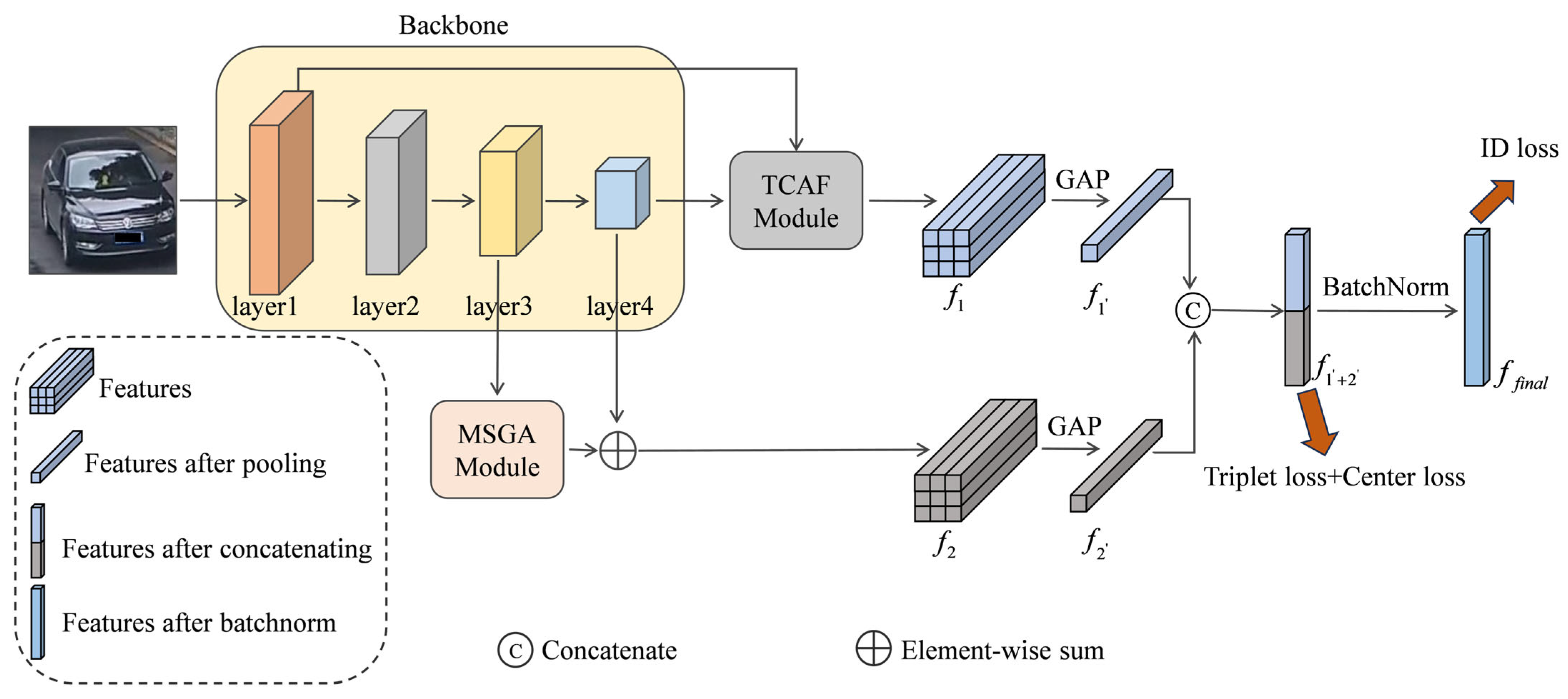
3.1. Model Overview
3.2. Temperature-Calibration Attention Fusion Module
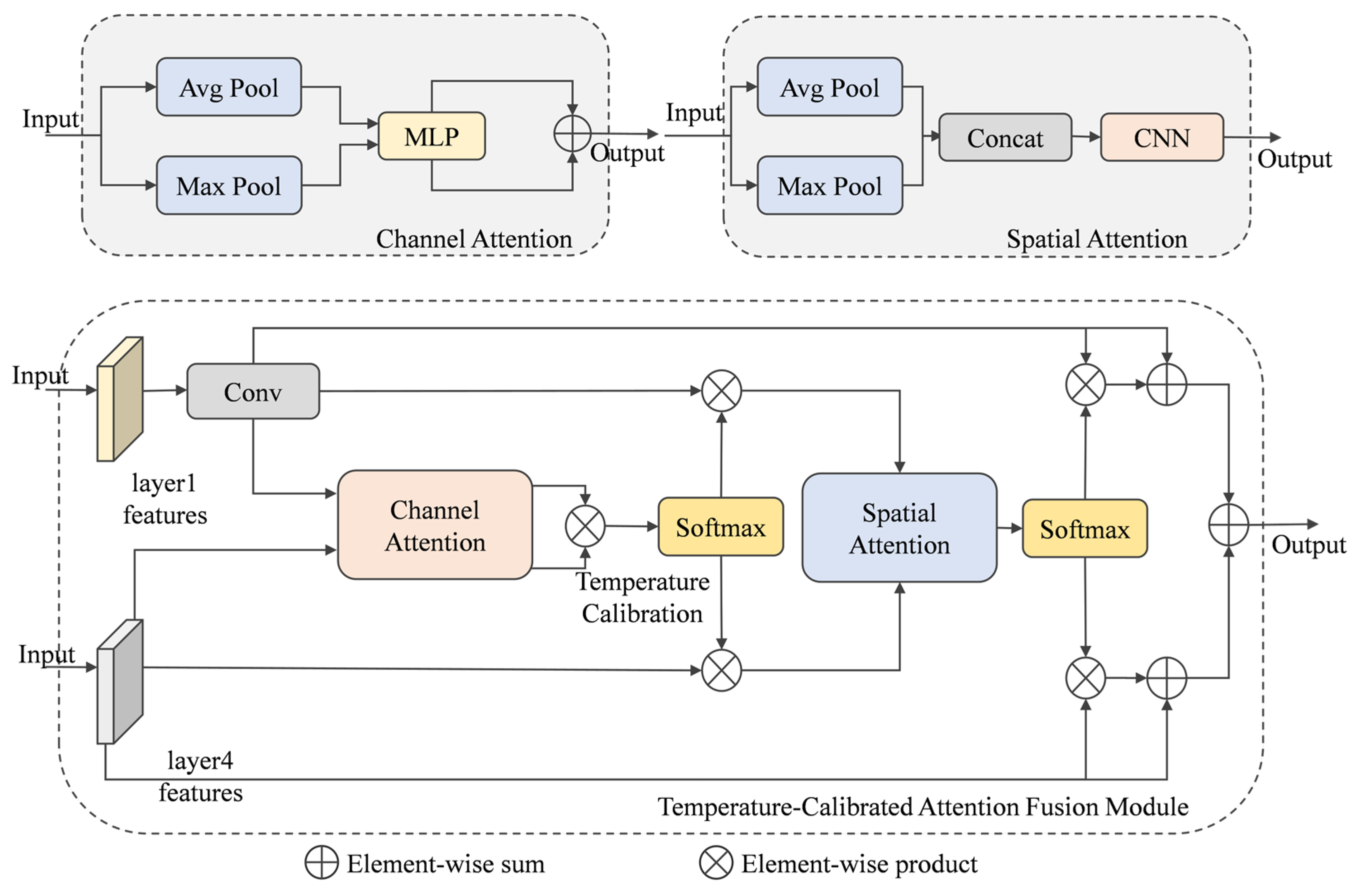
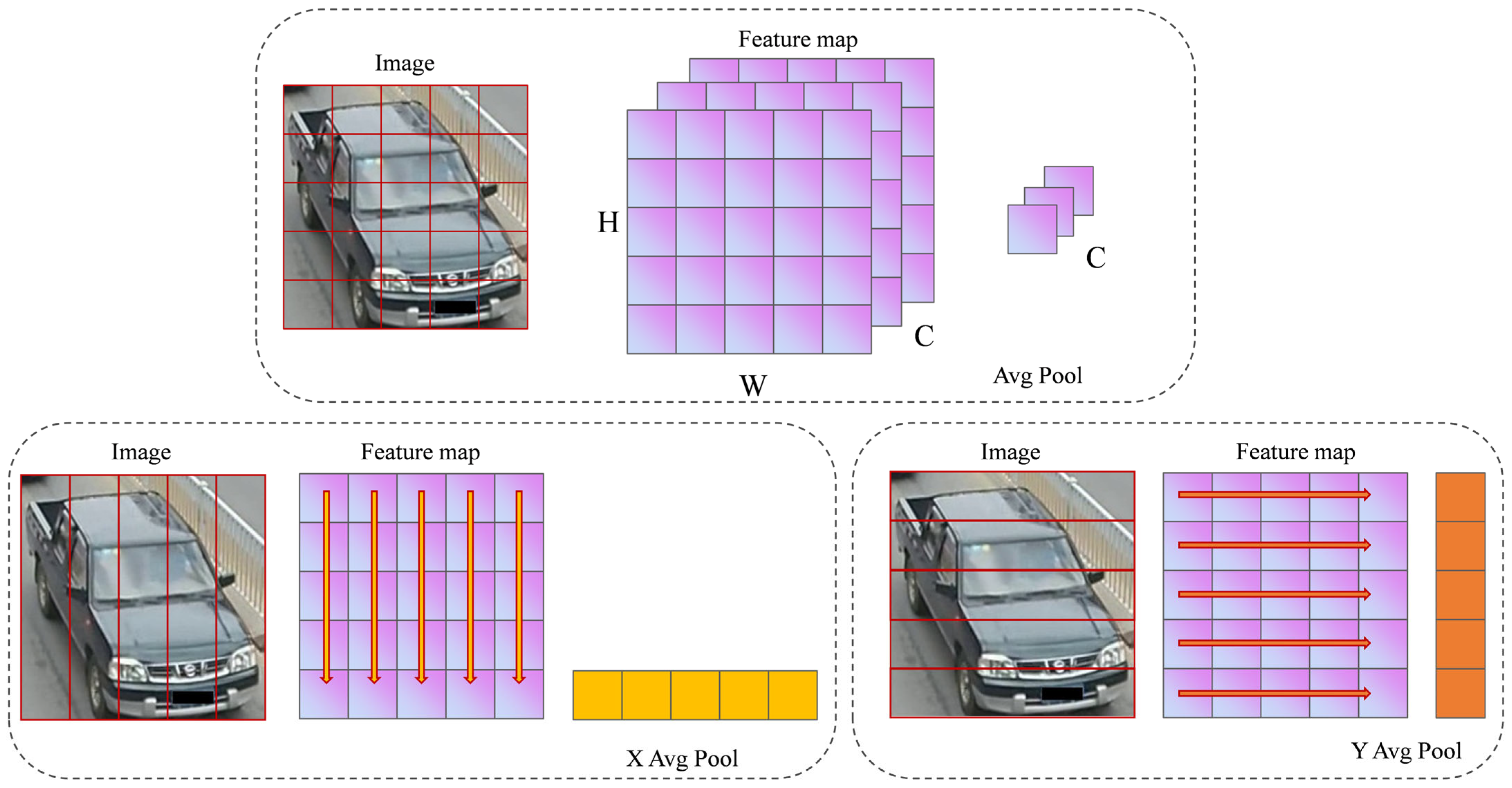
3.3. Multi-Scale Gated Attention Module
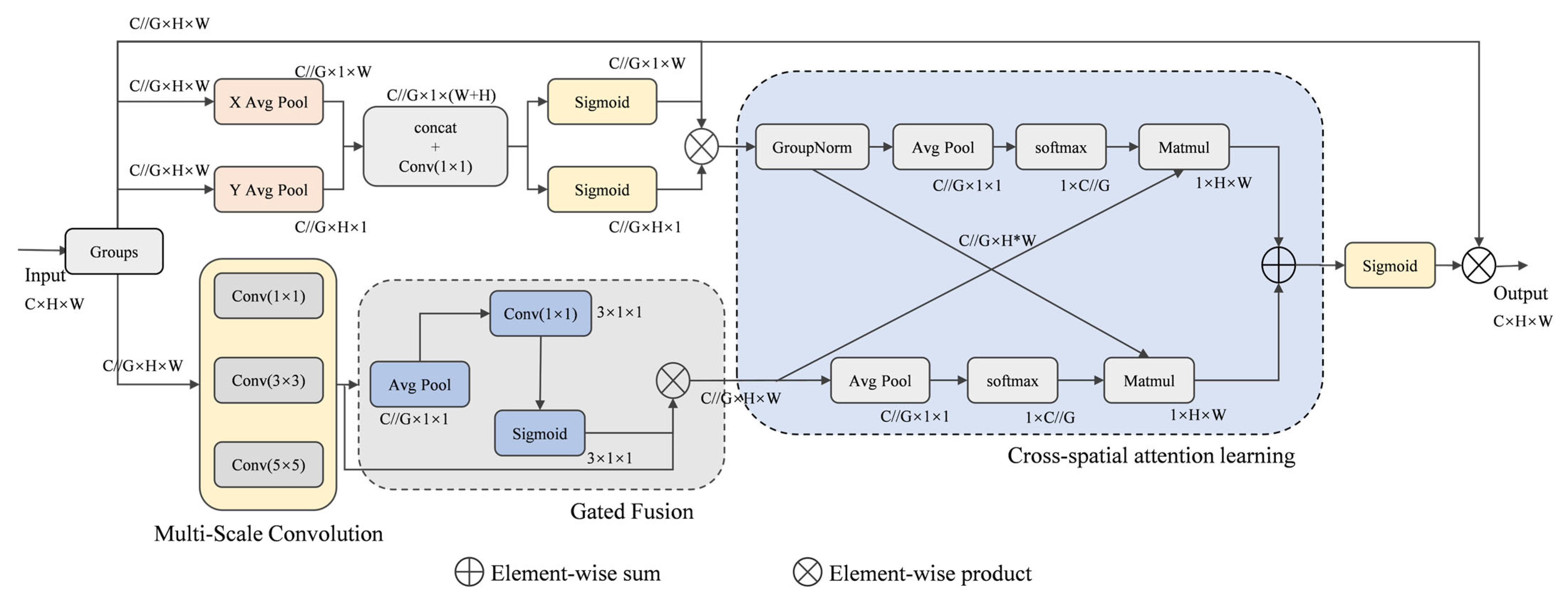
3.4. Center Loss Function
4. Experiment and Results Analysis
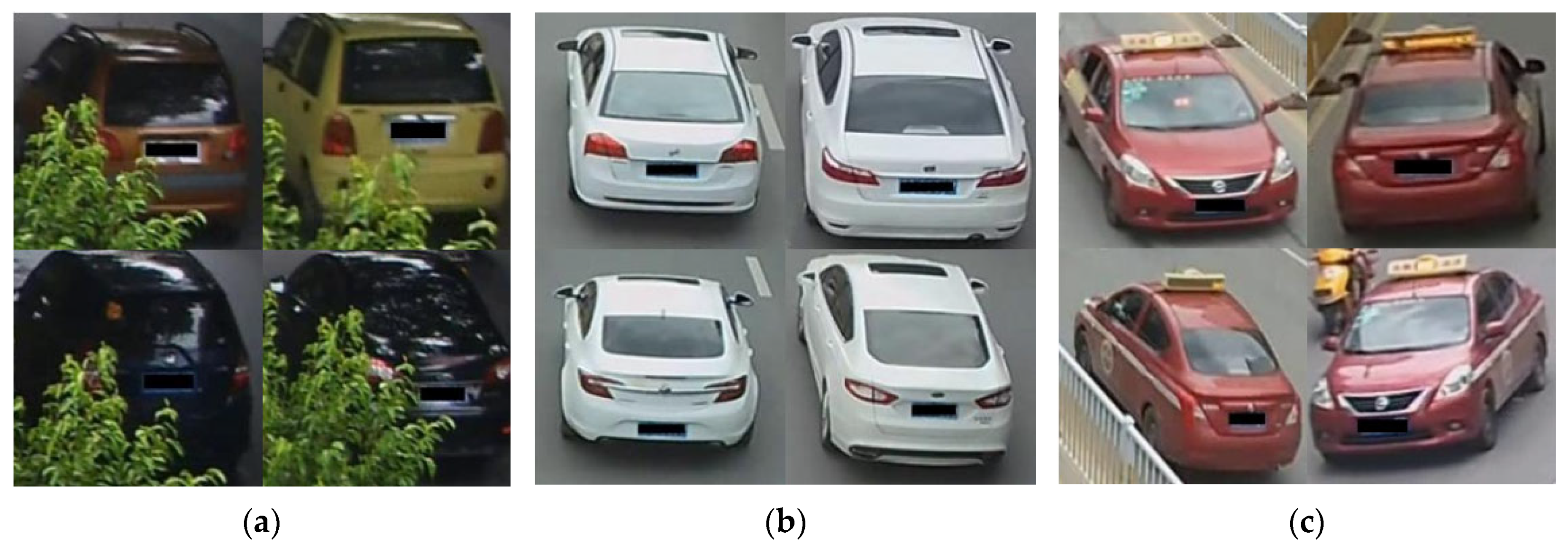
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experiment Settings
4.4. Comparison with Different Mainstream Models
4.5. Ablation Experiments and Analysis
4.5.1. Module Performance Analysis
4.5.2. Experiments on the Combination Methods and Fusion Strategies of the TCAF
4.5.3. MSGA Module Multi-Scale Convolutional Ensemble Ablation Experiment
4.5.4. Experiment on the Selection of Hyperparameter λ in Center Loss
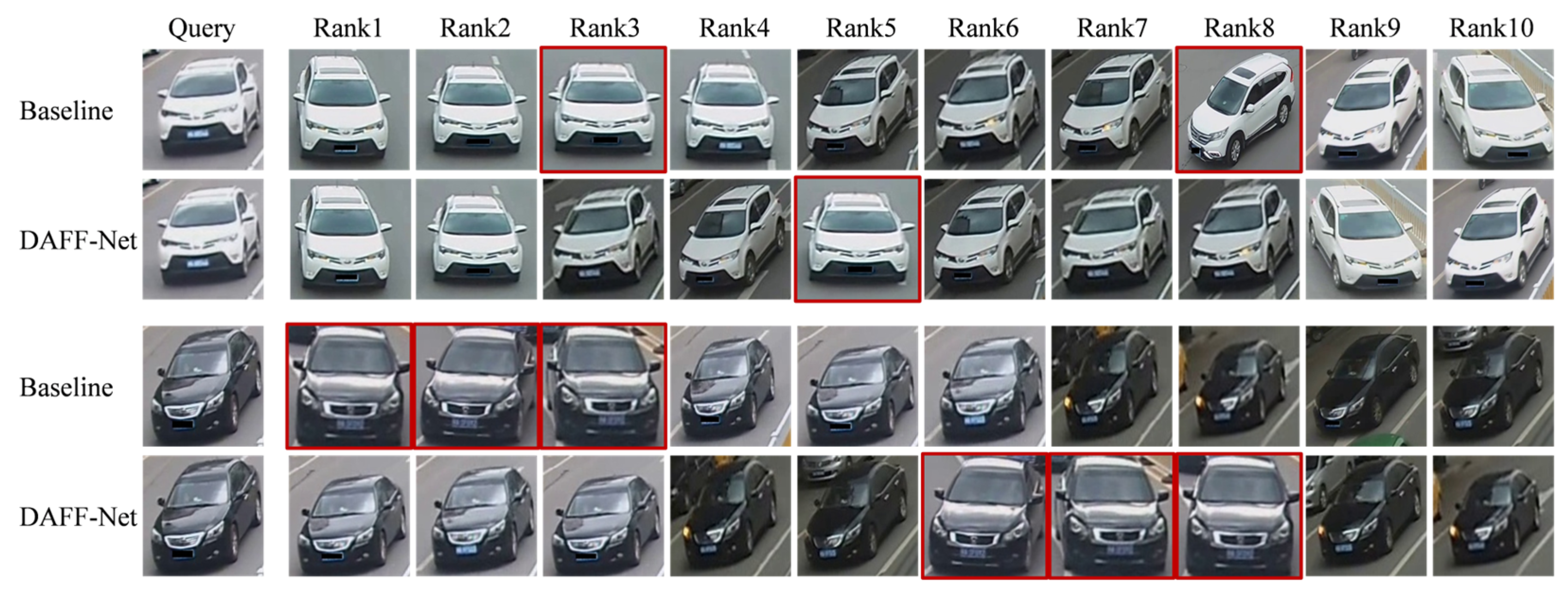
4.6. Visualization of Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H. Research on Vehicle Re-Identification Methods Based on Multi-Perception of Global and Local Features. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Technology and Business University, Yantai, China, 2024. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Dai, G.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Chen, X. TBE-Net: A three-branch embedding network with part-aware ability and feature complementary learning for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 14557–14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Y.; Pang, L.; Huang, T. Deep relative distance learning: Tell the difference between similar vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lou, Y.; Gao, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Duan, L.-Y. Group-sensitive triplet embedding for vehicle reidentification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 2385–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, R.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Y. Vehicle re-identification with viewpoint-aware metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8282–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Gong, D.; You, M.; Shen, C. Part-guided attention learning for vehicle instance retrieval. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 23, 3048–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y. Part-regularized near-duplicate vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3997–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, C.; Li, L.; Liu, D.; Lin, H.; Shi, J. Research Progress on Vehicle Re-Identification Based on Deep Learning. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2025, 61, 1–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z. Self-supervised Geometric Features Discovery via Interpretable Attention for Vehicle Re-Identification and Beyond (Complete Version). arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.11169. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Woo, T.; Lee, S.H. Multi-attention-based soft partition network for vehicle re-identification. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2023, 10, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shen, Z.Y. Transformer vehicle re-identification of intelligent transportation system under carbon neutral target. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 185, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kuang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Ding, X.; Huang, Y. AIVR-Net: Attribute-based invariant visual representation learning for vehicle re-identification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 289, 111455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Zheng, A.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. Attribute and state guided structural embedding network for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 5949–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Pei, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Multi-attribute adaptive aggregation transformer for vehicle re-identification. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, R.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Pedrini, H. Attributenet: Attribute enhanced vehicle re-identification. Neurocomputing 2021, 465, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Peng, J.; Chen, D.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, T.; Fu, X. Attribute-guided feature learning network for vehicle reidentification. IEEE Multimed. 2020, 27, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Jiang, W.; Luo, H.; Yu, H. Stripe-based and attribute-aware network: A two-branch deep model for vehicle re-identification. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 095401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ruan, T.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Mei, T. VehicleNet: Learning robust visual representation for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; He, J.; Guan, X. Discriminative feature representation with spatio-temporal cues for vehicle re-identification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.06852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Nie, X.; Bi, X.; Wang, S.; Yin, Y. Detail enhancement-based vehicle re-identification with orientation-guided re-ranking. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 137, 109304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, C.; Gao, X.; Gong, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Liu, H. TVG-ReID: Transformer-based vehicle-graph re-identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 4644–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Zha, Z.-J.; Gao, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q. Parsing-based view-aware embedding network for vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Luo, F.; Zhuang, H.; Weng, Z.; Gong, X.; Lin, Z. Attention multihop graph and multiscale convolutional fusion network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, A.; Beyer, L.; Leibe, B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.07737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sabuncu, M. Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 8792–8802. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016, 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, part VII 14. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, W.; Mei, T.; Ma, H. Provid: Progressive and multimodal vehicle reidentification for large-scale urban surveillance. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 20, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Khorramshahi, P.; Kumar, A.; Peri, N.; Rambhatla, S.S.; Chen, J.-C.; Chellappa, R. A dual-path model with adaptive attention for vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6132–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gu, K.; Qi, L.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, W. Multi-scale deep feature fusion for vehicle re-identification. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J. Exploring spatial significance via hybrid pyramidal graph network for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 8793–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 15013–15022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Nie, X.; Xi, X.; Yin, Y. CFVMNet: A multi-branch network for vehicle re-identification based on common field of view. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 3523–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Zheng, A.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. MsKAT: Multi-scale knowledge-aware transformer for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 19557–19568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, Q.; Han, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Analyzing Travel and Emission Characteristics of Hazardous Material Transportation Trucks Using BeiDou Satellite Navigation System Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


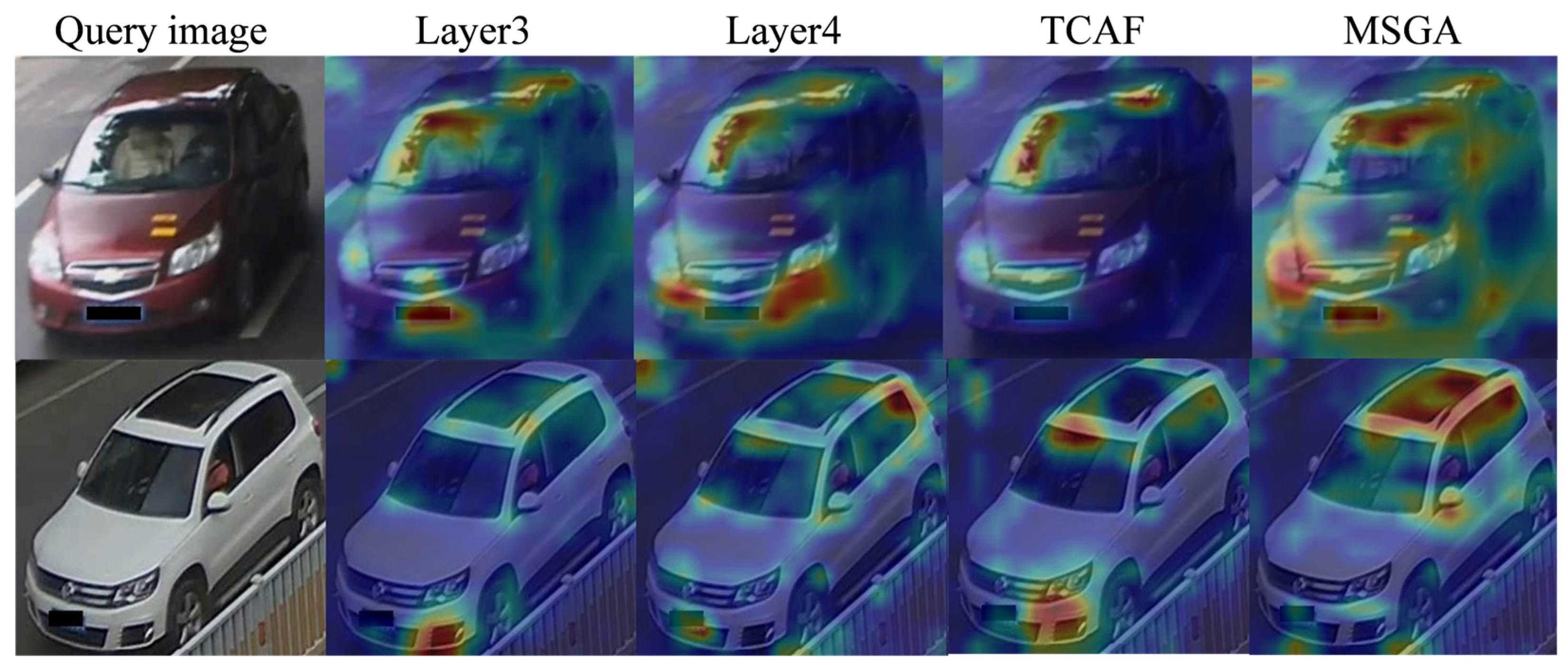
| Method | mAP | CMC@1 | CMC@5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AAVER [34] | 0.612 | 0.890 | 0.947 |
| PRN [7] | 0.743 | 0.943 | 0.989 |
| MSDeep [35] | 0.745 | 0.951 | - |
| PVEN [6] | 0.794 | 0.956 | 0.984 |
| TBE-Net [2] | 0.795 | 0.960 | 0.985 |
| HPGN [36] | 0.802 | 0.967 | - |
| LSFR [11] | 0.808 | 0.964 | - |
| TransReID [37] | 0.806 | 0.969 | - |
| ASSEN [13] | 0.813 | 0.969 | - |
| DAFF-Net (Ours) | 0.822 | 0.975 | 0.982 |
| Method | Small | Medium | Large | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMC@1 | CMC@5 | CMC@1 | CMC@5 | CMC@1 | CMC@5 | |
| AAVER [34] | 0.747 | 0.938 | 0.686 | 0.900 | 0.635 | 0.856 |
| PRN [7] | 0.784 | 0.923 | 0.750 | 0.883 | 0.742 | 0.864 |
| MSDeep [35] | 0.812 | 0.954 | 0.780 | 0.918 | 0.756 | 0.893 |
| CFVMNet [38] | 0.814 | 0.941 | 0.773 | 0.904 | 0.747 | 0.887 |
| HPGN [36] | 0.839 | - | 0.799 | - | 0.773 | - |
| PVEN [6] | 0.847 | 0.970 | 0.806 | 0.945 | 0.778 | 0.920 |
| TBE-Net [2] | 0.860 | 0.984 | 0.823 | 0.966 | 0.807 | 0.949 |
| MsKAT [39] | 0.863 | 0.974 | 0.818 | 0.955 | 0.794 | 0.939 |
| GLNet [1] | 0.872 | 0.978 | 0.829 | 0.956 | 0.803 | 0.934 |
| DAFF-Net (Ours) | 0.907 | 0.972 | 0.846 | 0.965 | 0.821 | 0.956 |
| Method | mAP | CMC@1 | CMC@5 |
|---|---|---|---|
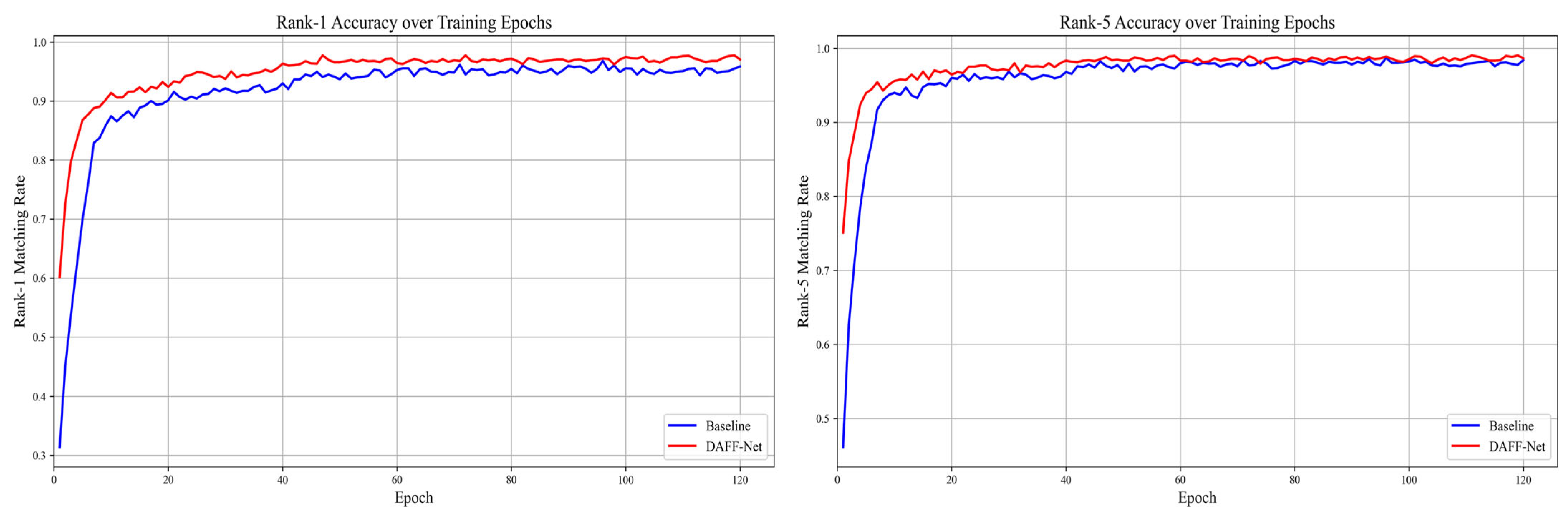
| Baseline | 0.778 | 0.963 | 0.978 |
| DAFF-Net w/o MSGA | 0.808 | 0.969 | 0.980 |
| DAFF-Net w/o TCAF | 0.803 | 0.968 | 0.983 |
| DAFF-Net | 0.822 | 0.975 | 0.982 |
| Method | mAP | CMC@1 | CMC@5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sum (layer1 + layer4) | 0.804 | 0.963 | 0.983 |
| TCAF (layer1 + layer4) | 0.813 | 0.973 | 0.985 |
| TCAF (layer2 + layer4) | 0.808 | 0.968 | 0.986 |
| TCAF (layer3 + layer4) | 0.805 | 0.969 | 0.981 |
| Method | mAP | CMC@1 | CMC@5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conv-1 × 1 | 0.791 | 0.963 | 0.980 |
| Conv-3 × 3 | 0.813 | 0.972 | 0.982 |
| Conv-5 × 5 | 0.810 | 0.973 | 0.982 |
| Conv-1 × 1 + 3 × 3 | 0.815 | 0.973 | 0.984 |
| Conv-1 × 1 + 5 × 5 | 0.808 | 0.969 | 0.980 |
| Conv-3 × 3 + 5 × 5 | 0.815 | 0.970 | 0.983 |
| Conv-All | 0.819 | 0.974 | 0.985 |
| λ(×10−3) | mAP | CMC@1 | CMC@5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.781 | 0.954 | 0.979 |
| 0.25 | 0.798 | 0.957 | 0.983 |
| 0.5 | 0.813 | 0.972 | 0.986 |
| 0.75 | 0.811 | 0.968 | 0.983 |
| 1 | 0.807 | 0.963 | 0.981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Yuan, G.; Li, W.; Li, H. DAFF-Net: A Dual-Branch Attention-Guided Feature Fusion Network for Vehicle Re-Identification. Algorithms 2025, 18, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110690
Guo Y, Yuan G, Li W, Li H. DAFF-Net: A Dual-Branch Attention-Guided Feature Fusion Network for Vehicle Re-Identification. Algorithms. 2025; 18(11):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110690
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yi, Guowu Yuan, Wen Li, and Hao Li. 2025. "DAFF-Net: A Dual-Branch Attention-Guided Feature Fusion Network for Vehicle Re-Identification" Algorithms 18, no. 11: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110690
APA StyleGuo, Y., Yuan, G., Li, W., & Li, H. (2025). DAFF-Net: A Dual-Branch Attention-Guided Feature Fusion Network for Vehicle Re-Identification. Algorithms, 18(11), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18110690







