Combining Background Subtraction and Convolutional Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Pumping-Unit Surveillance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem of Pumping-Unit Surveillance
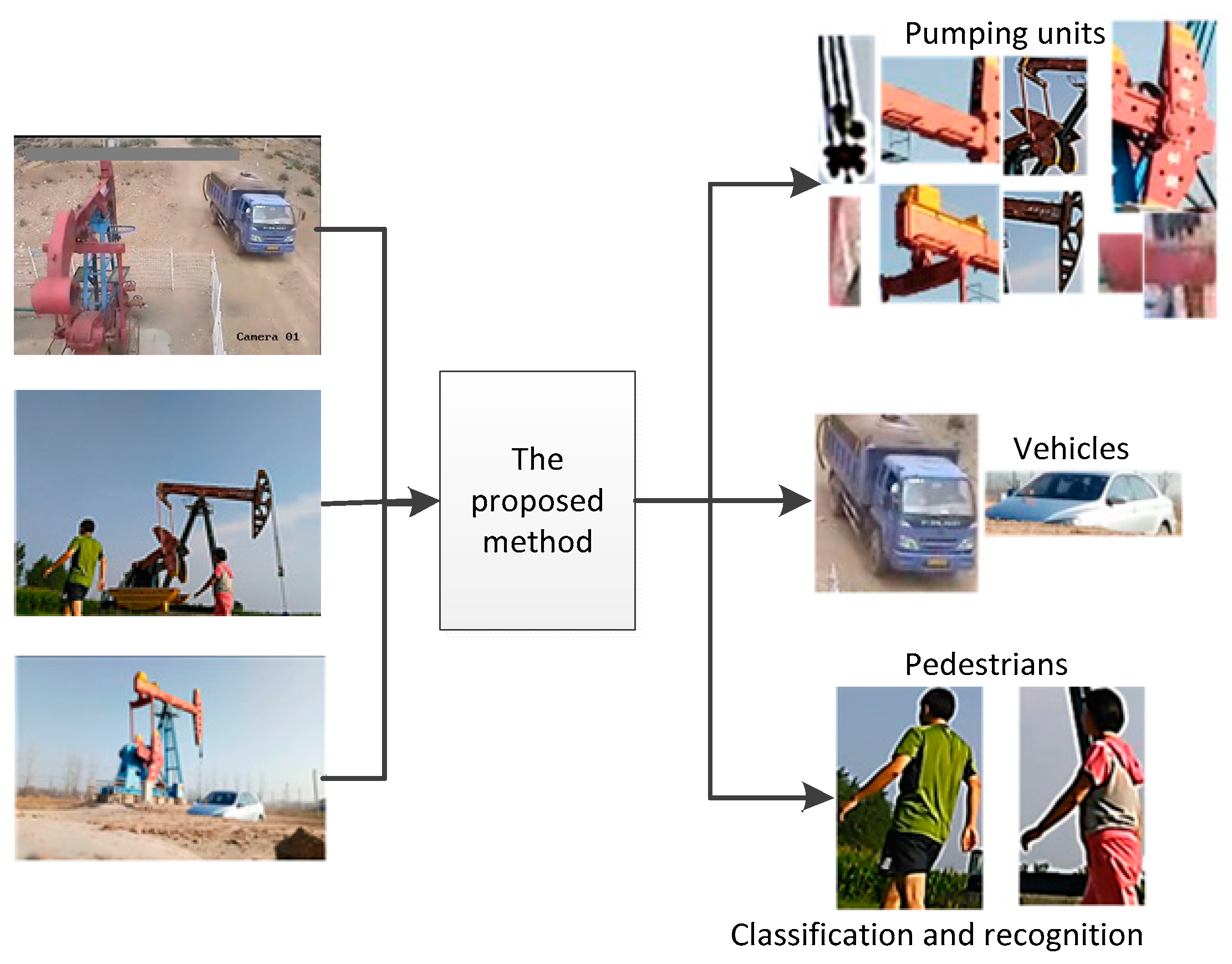
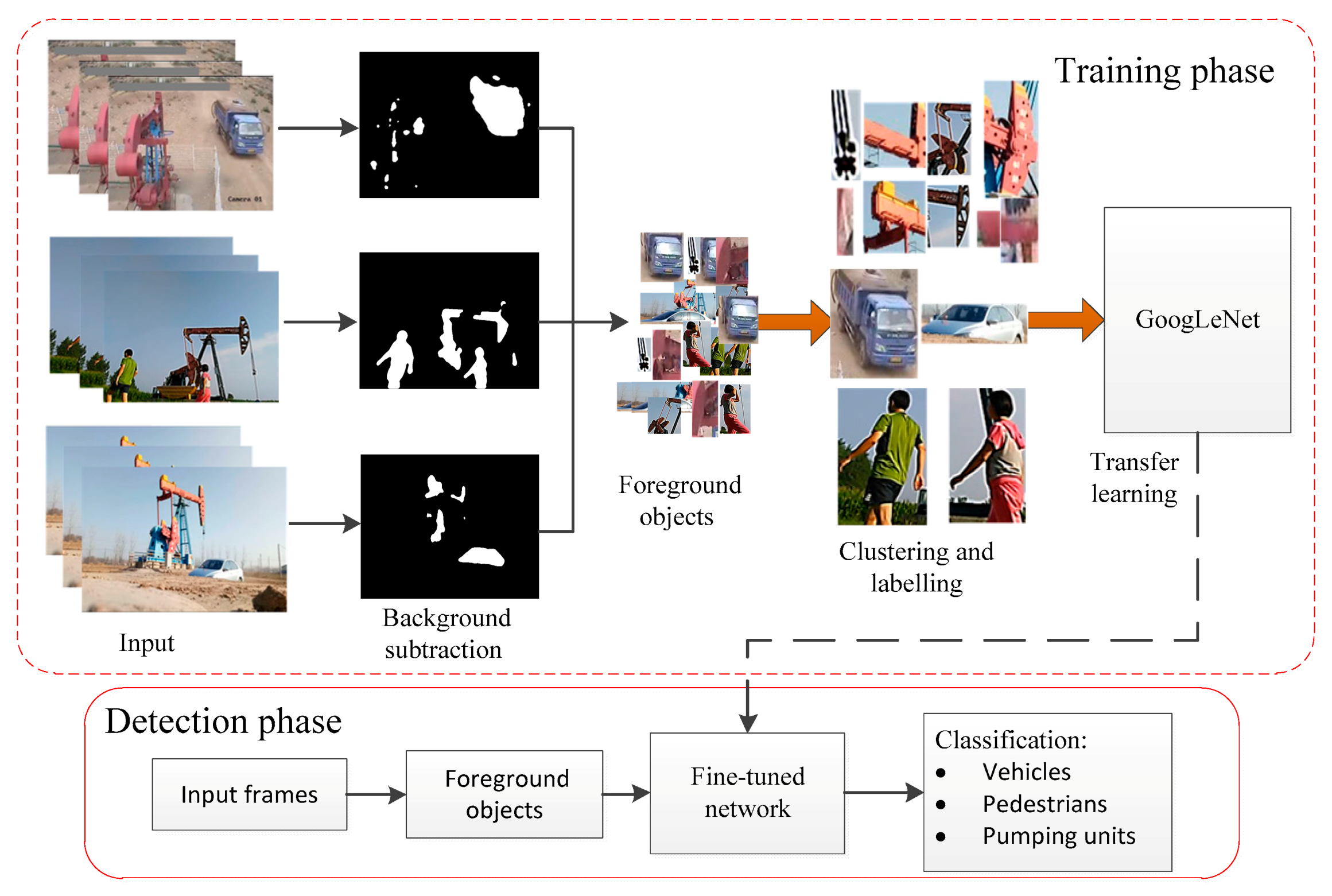
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Moving-Object Extraction
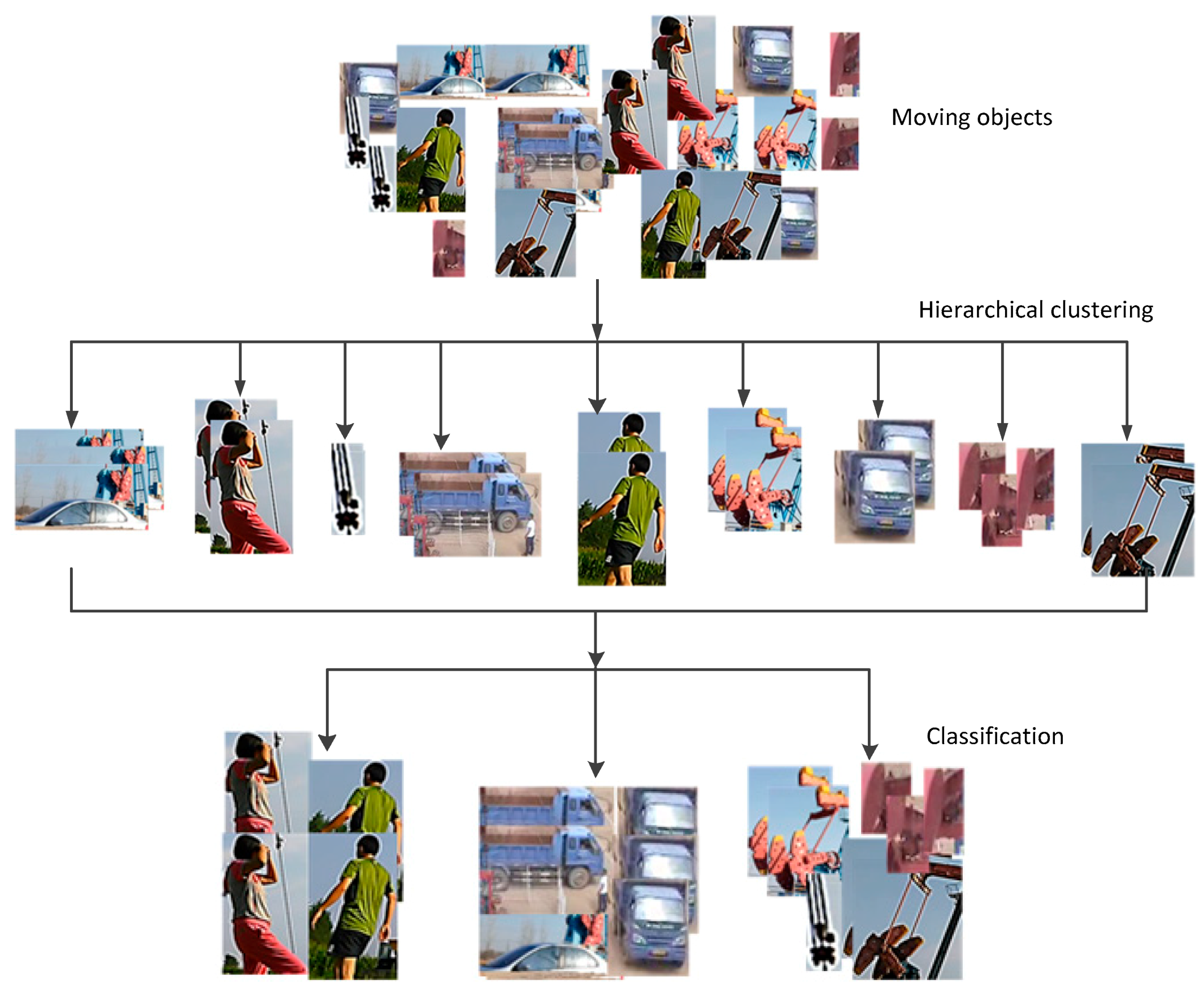
3.2. Clustering and Labeling
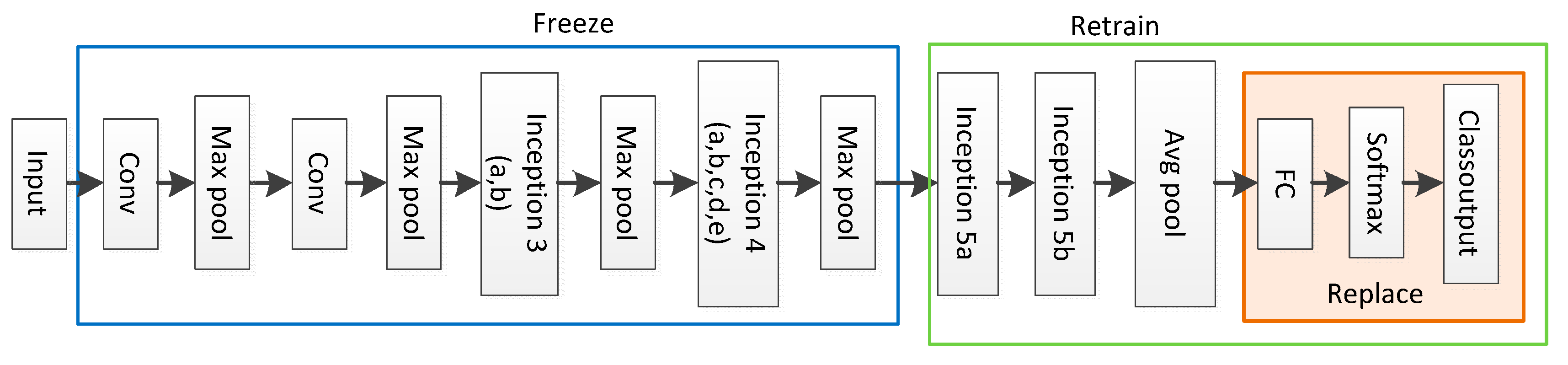
3.3. Transfer Learning
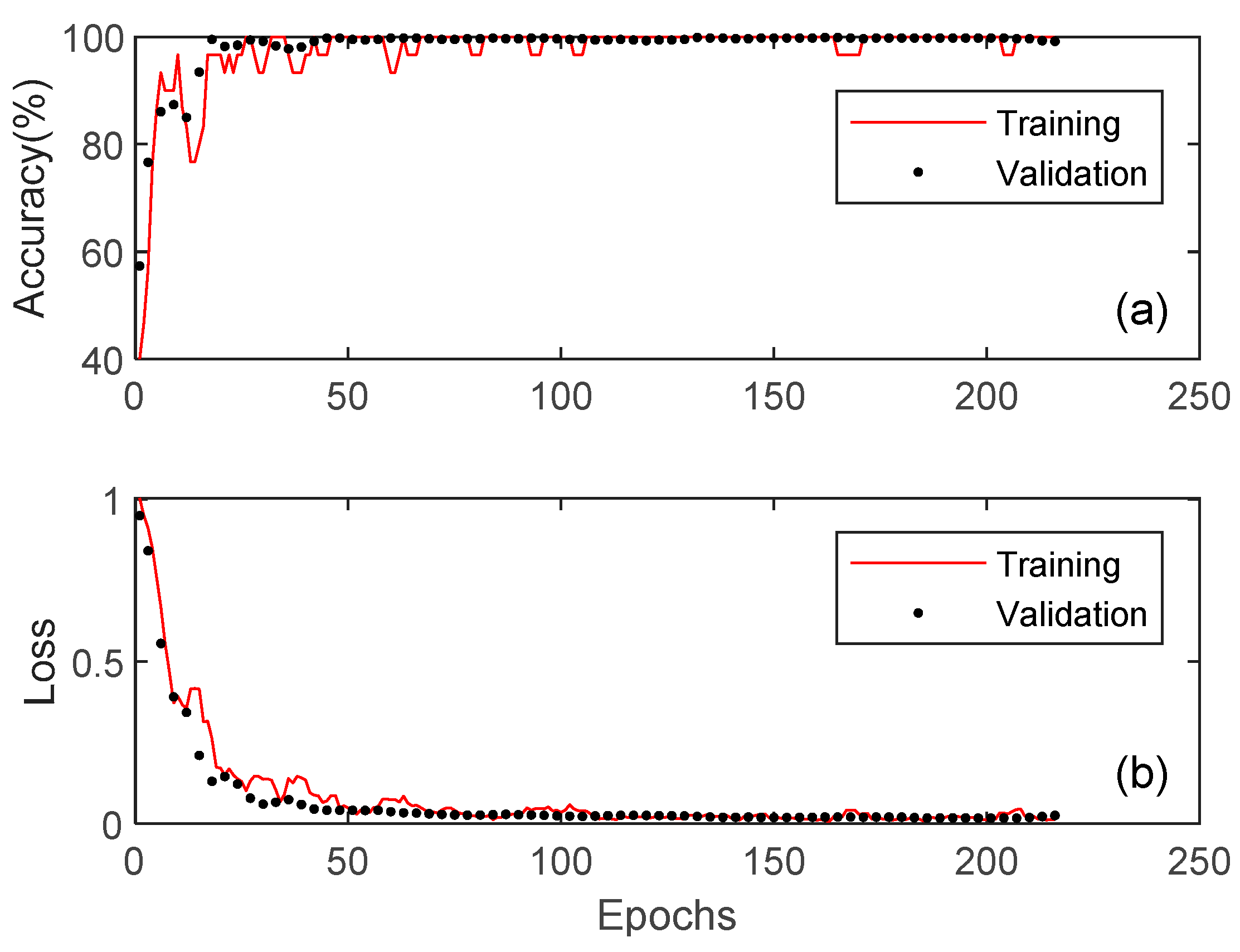
4. Experiments
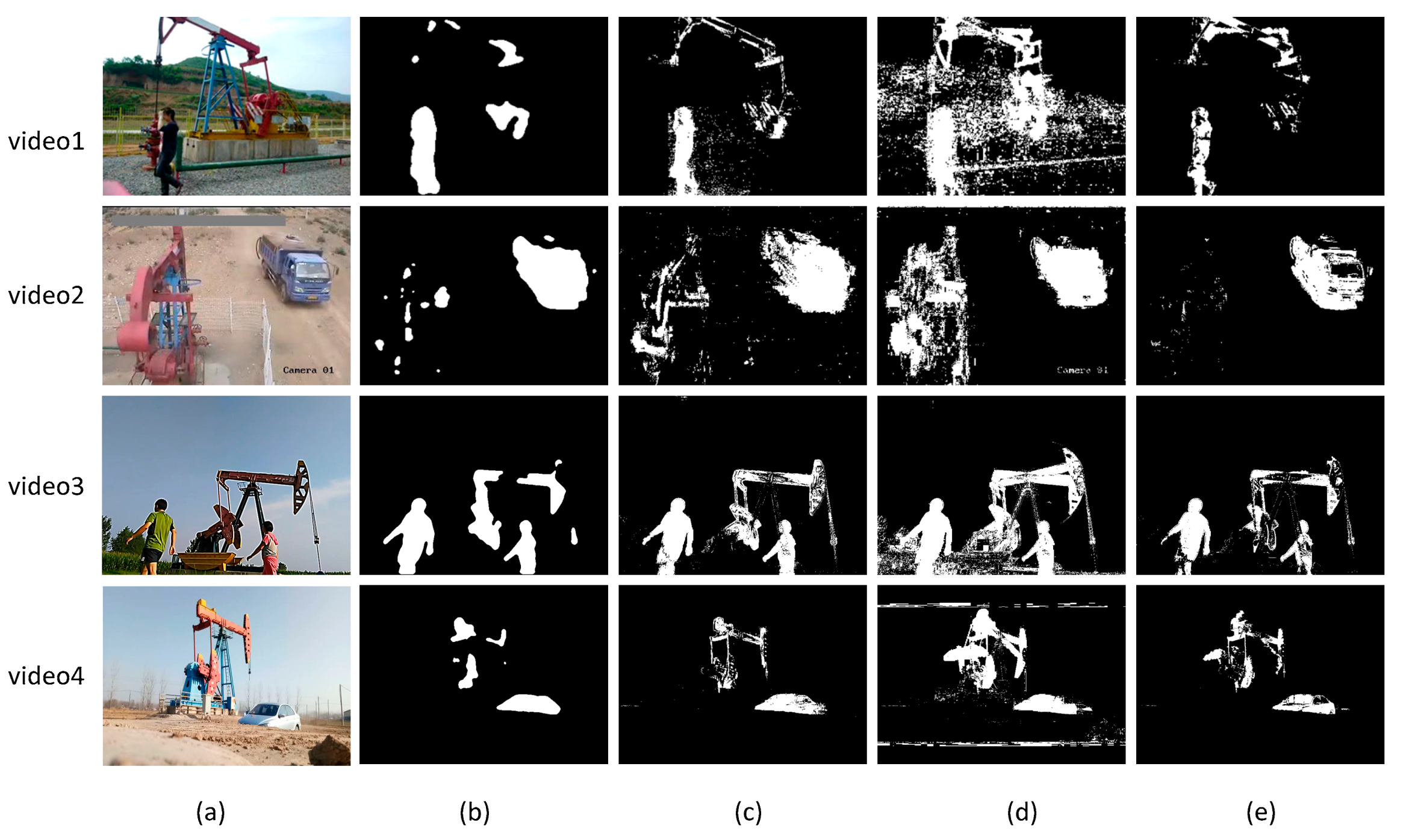
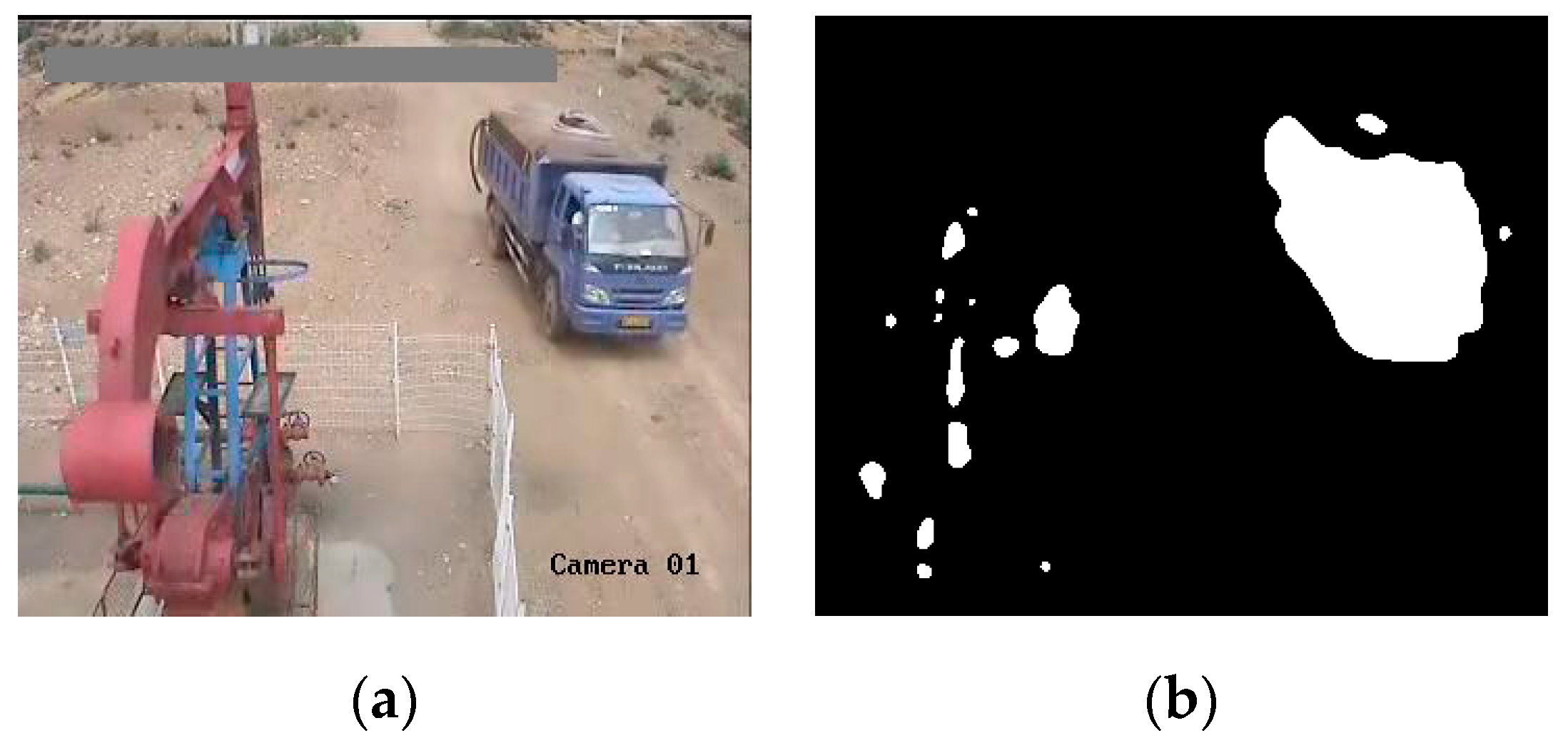
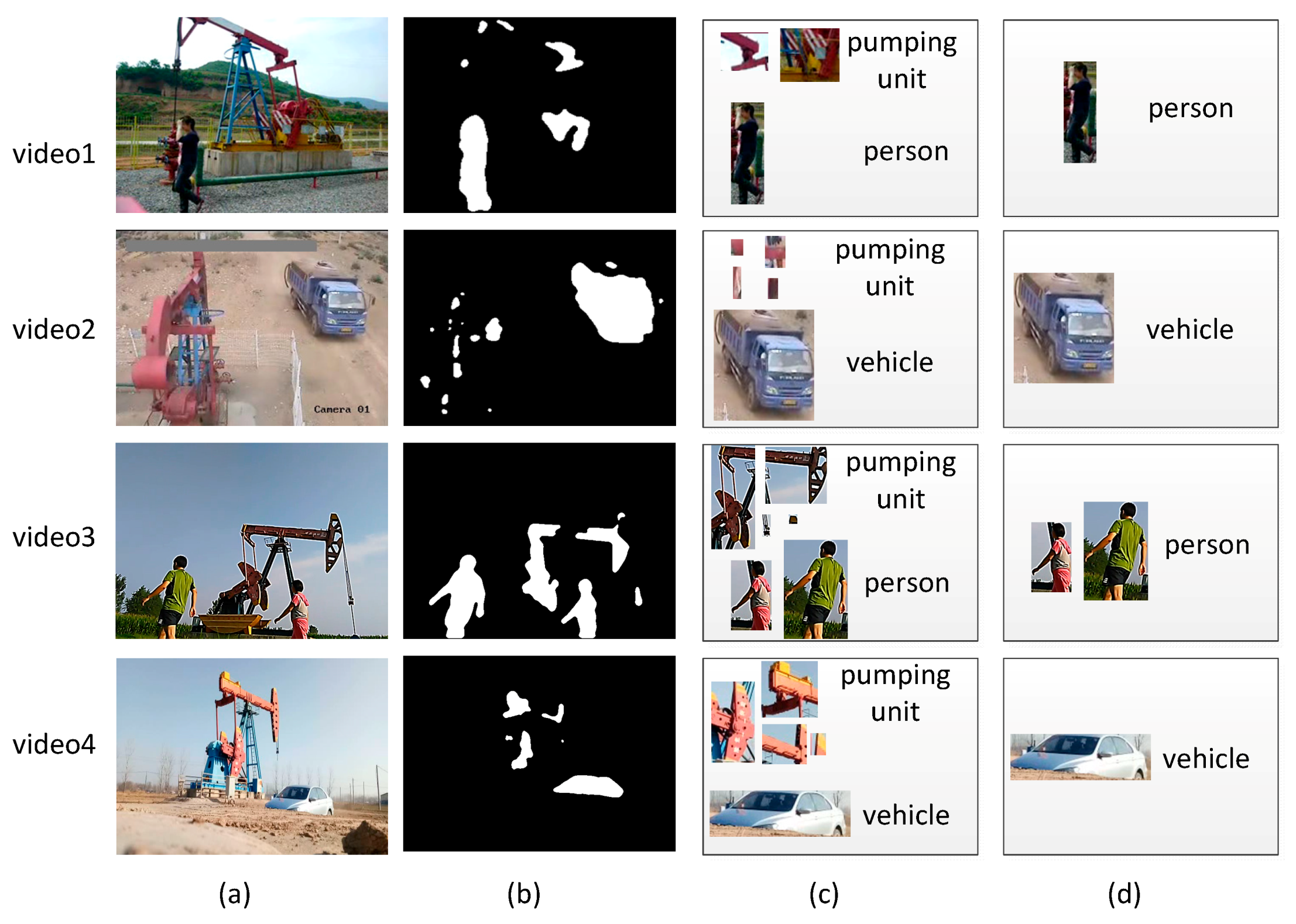
4.1. Foreground Detection
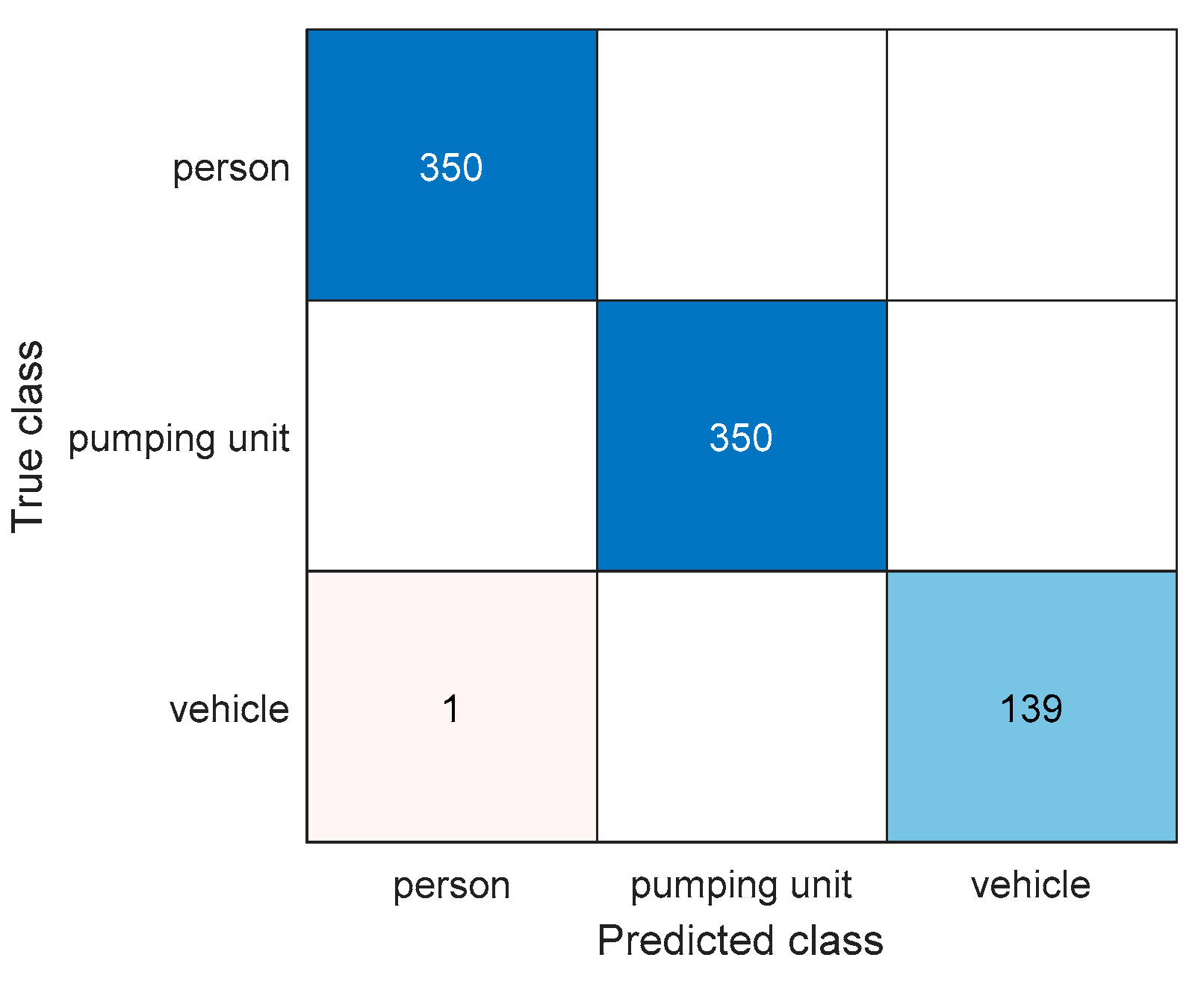
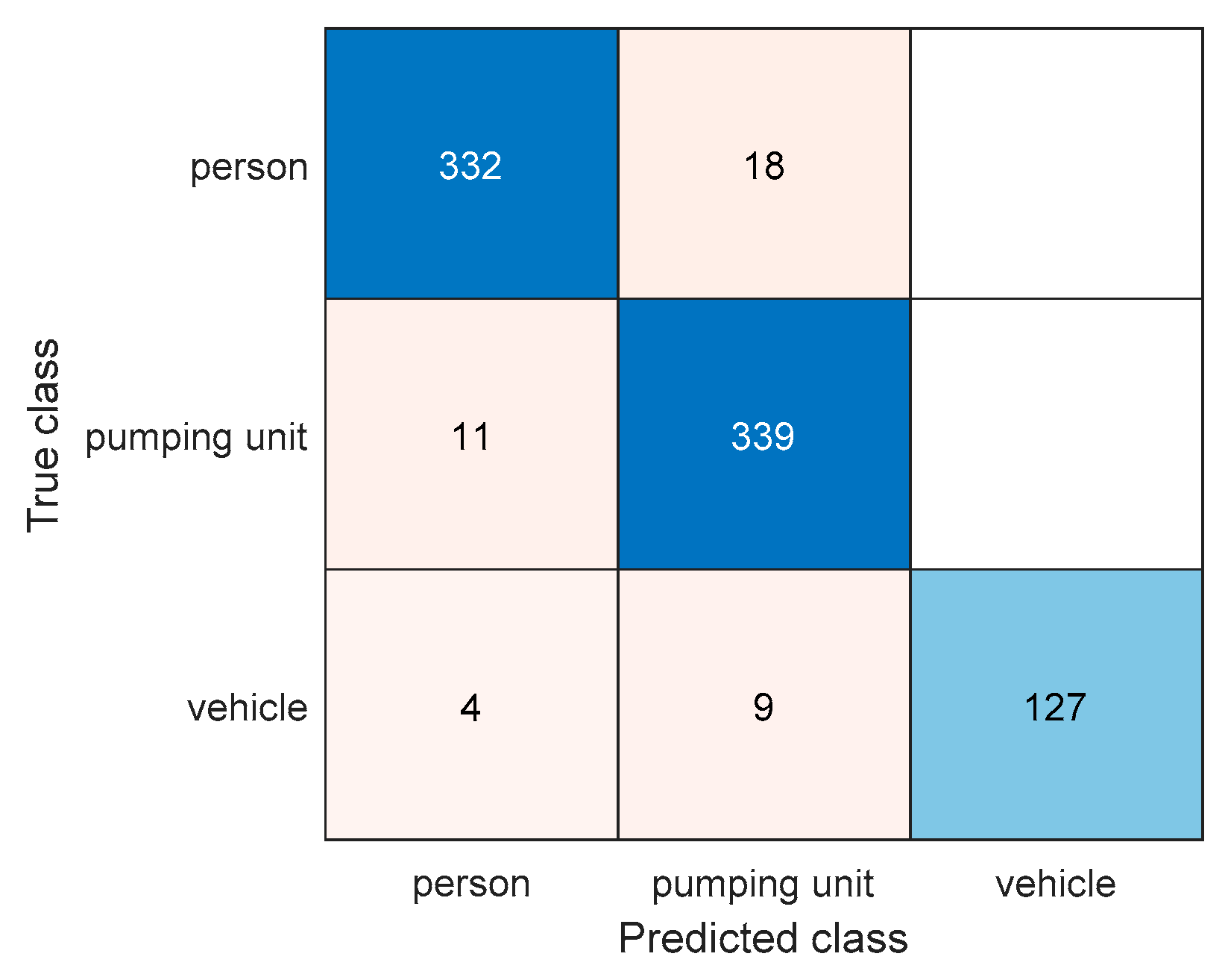
4.2. Object Classifiction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2009, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, P.; Nielsen, L.N.; Steen, K.A.; Jorgensen, R.N.; Karstoft, H. DeepAnomaly: Combining background subtraction and deep learning for detecting obstacles and anomalies in an agricultural field. Sensors 2016, 16, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, B.R.; Thomas, D.M.; Parakkal, R. An overview of deep learning based methods for unsupervised and semi-supervised anomaly detection in videos. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutzer, S.; Höferlin, B.; Heidemann, G. Evaluation of background subtraction techniques for video surveillance. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 32, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar]
- Toyama, K.; Krumm, J.; Brumitt, B.; Meyers, B. Wallflower: Principles and practice of background maintenance. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 1999, 1, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Alan, M.M. Background subtraction techniques. Proc. Image Vis. Comput. 2000, 2, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Babacan, S.D.; Pappas, T.N. Spatiotemporal algorithm for background subtraction. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing—ICASSP ’07, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–20 April 2007; pp. 1065–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer, C.; Grimson, W.E.L. Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 1999, 2, 246–252. [Google Scholar]
- Makantasis, K.; Nikitakis, A.; Doulamis, A.D.; Doulamis, N.D.; Papaefstathiou, I. Data-driven background subtraction algorithm for in-camera acceleration in thermal imagery. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 2090–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnich, O.; Droogenbroeck, M.V. ViBe: A powerful random technique to estimate the background in video sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 945–948. [Google Scholar]
- Barnich, O.; Droogenbroeck, M.V. ViBe: A universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogenbroeck, M.V.; Paquot, O. Background subtraction: Experiments and improvements for ViBe. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Workshops 2012, 71, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Elgammal, A.; Harwood, D.; Davis, L. Non-parametric model for background subtraction. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2000, 1843, 751–767. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, M.; Tiefenbacher, P.; Rigoll, G. Background segmentation with feedback: The pixel-based adaptive segmenter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- St-Charles, P.-L.; Bilodeau, G.-A.; Bergevin, R. Flexible background subtraction with self-balanced local sensitivity. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Montreal, QC, Canada, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 408–413. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 1, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.Q.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Charles, P.-L.; Bilodeau, G.-A.; Bergevin, R. Subsense: A universal change detection method with local adaptive sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shapiro, L.G. Computer and Robot Vision; Addison-Wesley: Readimg, Boston, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 1, pp. 28–48. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Tian, Y. A comprehensive survey of clustering algorithms. Ann. Data Sci. 2015, 2, 165–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapadakis, E.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, A.; Doulamis, N.; Dres, D.; Bimpas, M. Stacked autoencoders for outlier detection in over-the-horizon radar signals. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protopapadakis, E.; Niklis, D.; Doumpos, M.; Doulamis, A.; Zopounidis, C. Sample selection algorithms for credit risk modelling through data mining techniques. Int. J. Data Min. Model. Manag. 2019, 11, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lior, R.; Maimon, O. Clustering methods. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 321–352. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.M.; Gopalan, R.; Li, R.; Chellappa, R. Visual domain adaptation: A survey of recent advances. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2015, 32, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Transfer Adaptation Learning: A Decade Survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.04687. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jodoin, P.-M.; Porikli, F.; Janusz, K.; Benezeth, Y.; Ishwar, P. CDnet 2014: An expanded change detection benchmark dataset. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 1, 886–893. [Google Scholar]


| Data | Frame Dimension | FPS | Number of Frames | Objects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| video 1 | 320 × 240 | 24 | 1677 | Pumping unit, person |
| video 2 | 352 × 288 | 24 | 1708 | Pumping unit, person, vehicle |
| video 3 | 640 × 480 | 24 | 1643 | Pumping unit, person |
| video 4 | 640 × 480 | 24 | 4031 | Pumping unit, person, vehicle |
| Classes | Methods | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | Specificity | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| person | proposed | 0.9988 | 1.0000 | 0.9972 | 0.9980 | 0.9986 |
| SVM | 0.9607 | 0.9486 | 0.9568 | 0.9694 | 0.9527 | |
| pumping unit | proposed | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| SVM | 0.9548 | 0.9686 | 0.9262 | 0.9449 | 0.9469 | |
| vehicle | proposed | 0.9988 | 0.9929 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9964 |
| SVM | 0.9845 | 0.9071 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9513 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, T.; Yang, J.; Lu, W. Combining Background Subtraction and Convolutional Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Pumping-Unit Surveillance. Algorithms 2019, 12, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060115
Yu T, Yang J, Lu W. Combining Background Subtraction and Convolutional Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Pumping-Unit Surveillance. Algorithms. 2019; 12(6):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060115
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Tianming, Jianhua Yang, and Wei Lu. 2019. "Combining Background Subtraction and Convolutional Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Pumping-Unit Surveillance" Algorithms 12, no. 6: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060115
APA StyleYu, T., Yang, J., & Lu, W. (2019). Combining Background Subtraction and Convolutional Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Pumping-Unit Surveillance. Algorithms, 12(6), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12060115





