Airfoil Optimization Design Based on the Pivot Element Weighting Iterative Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Airfoil Parameterization
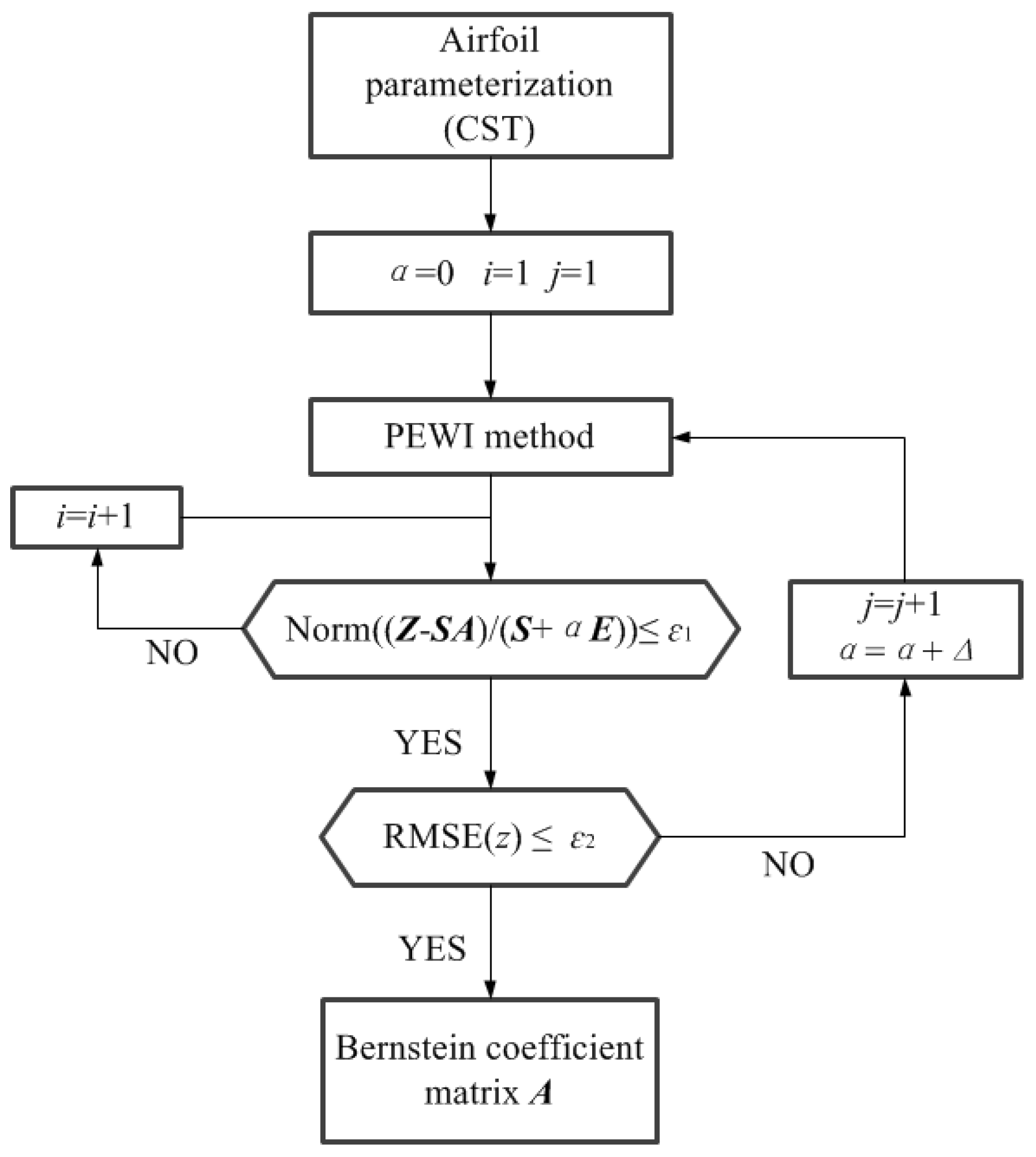
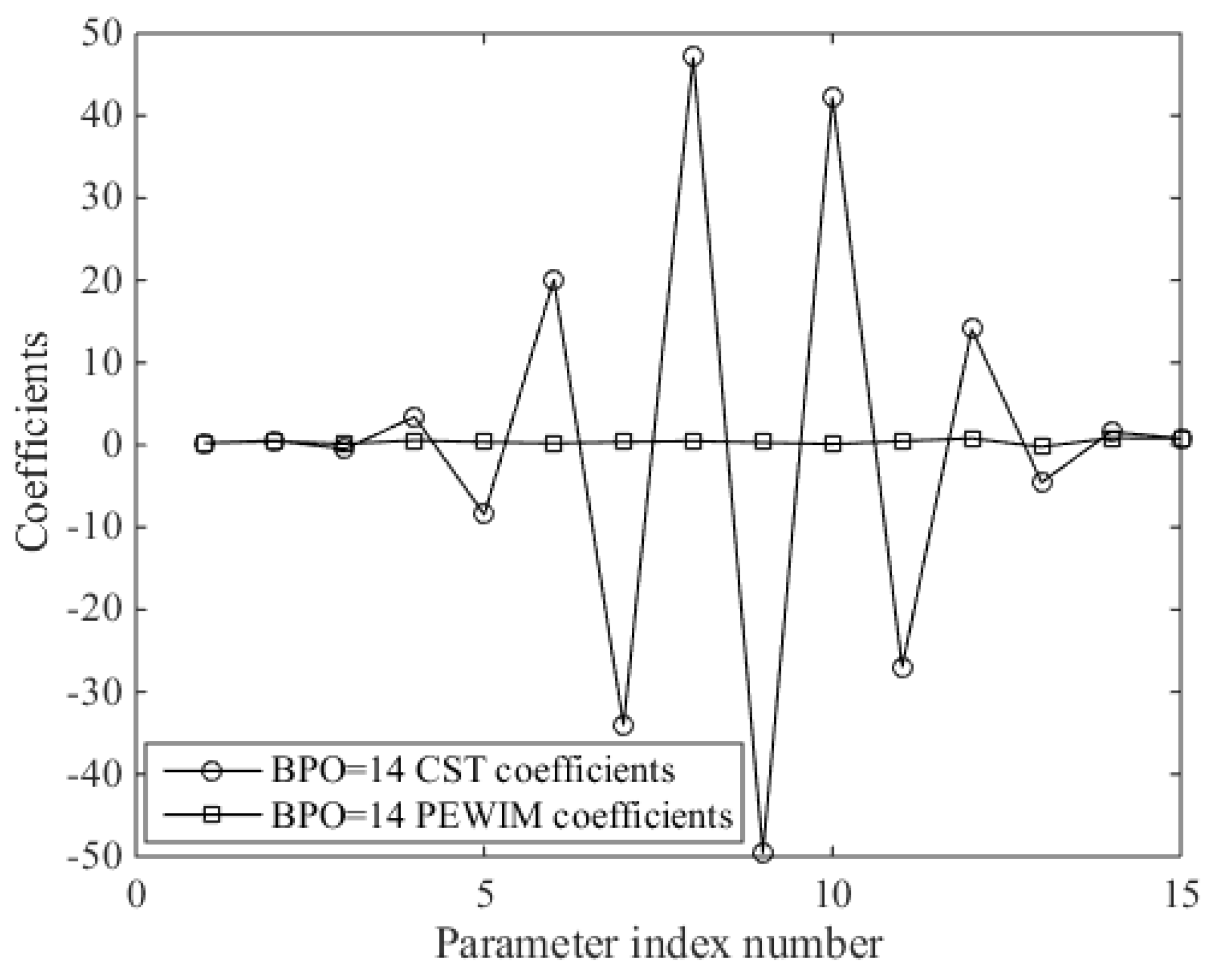
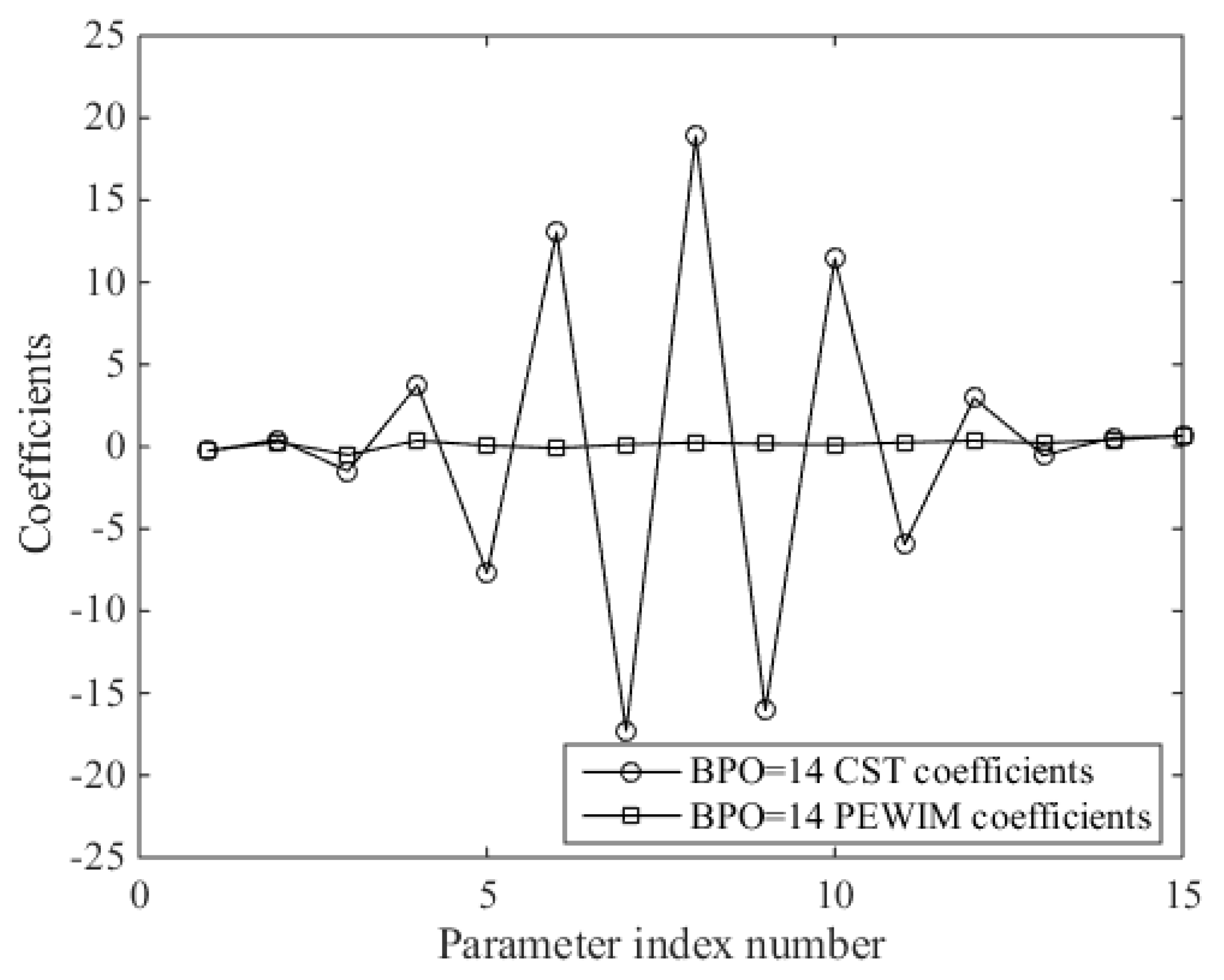
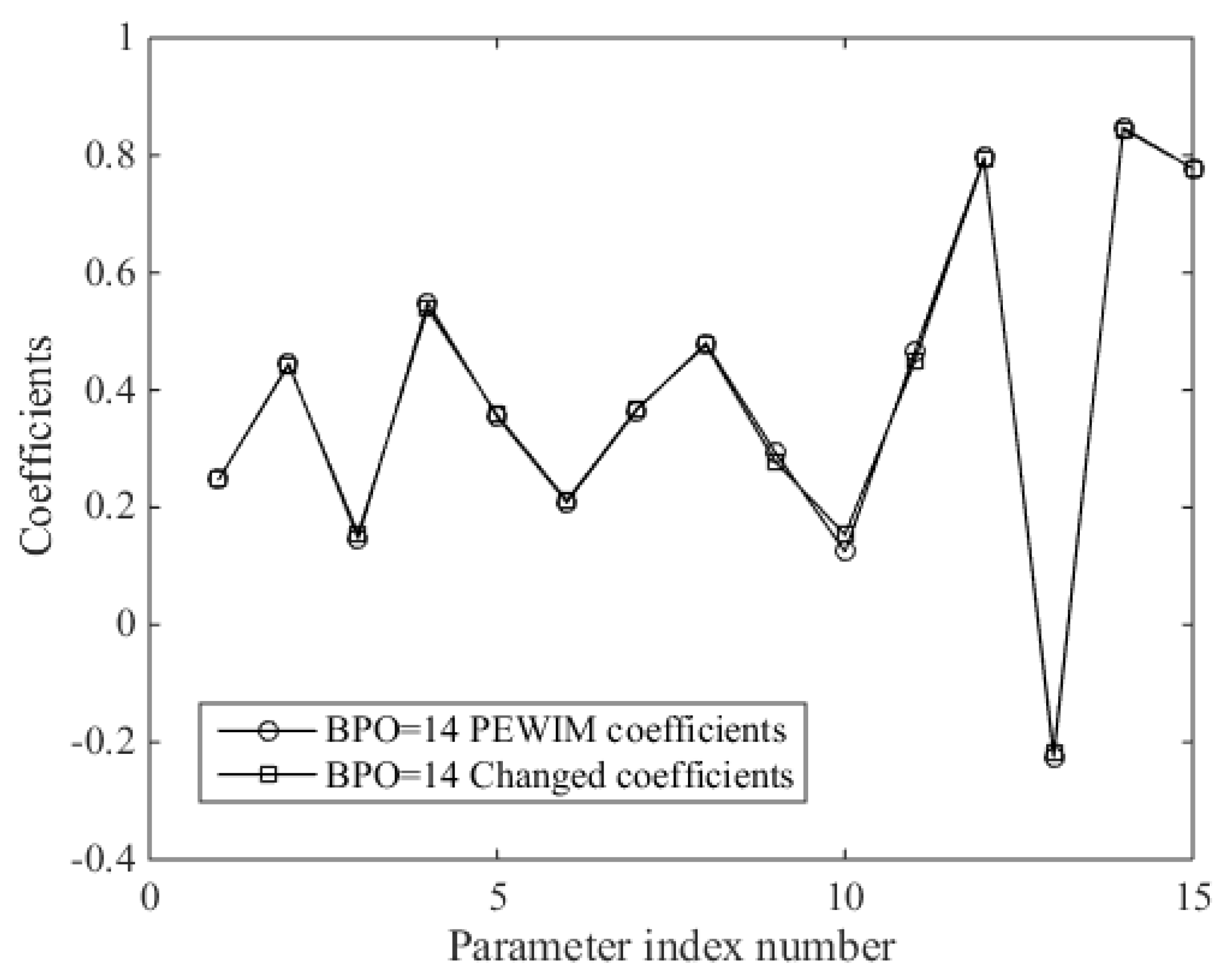
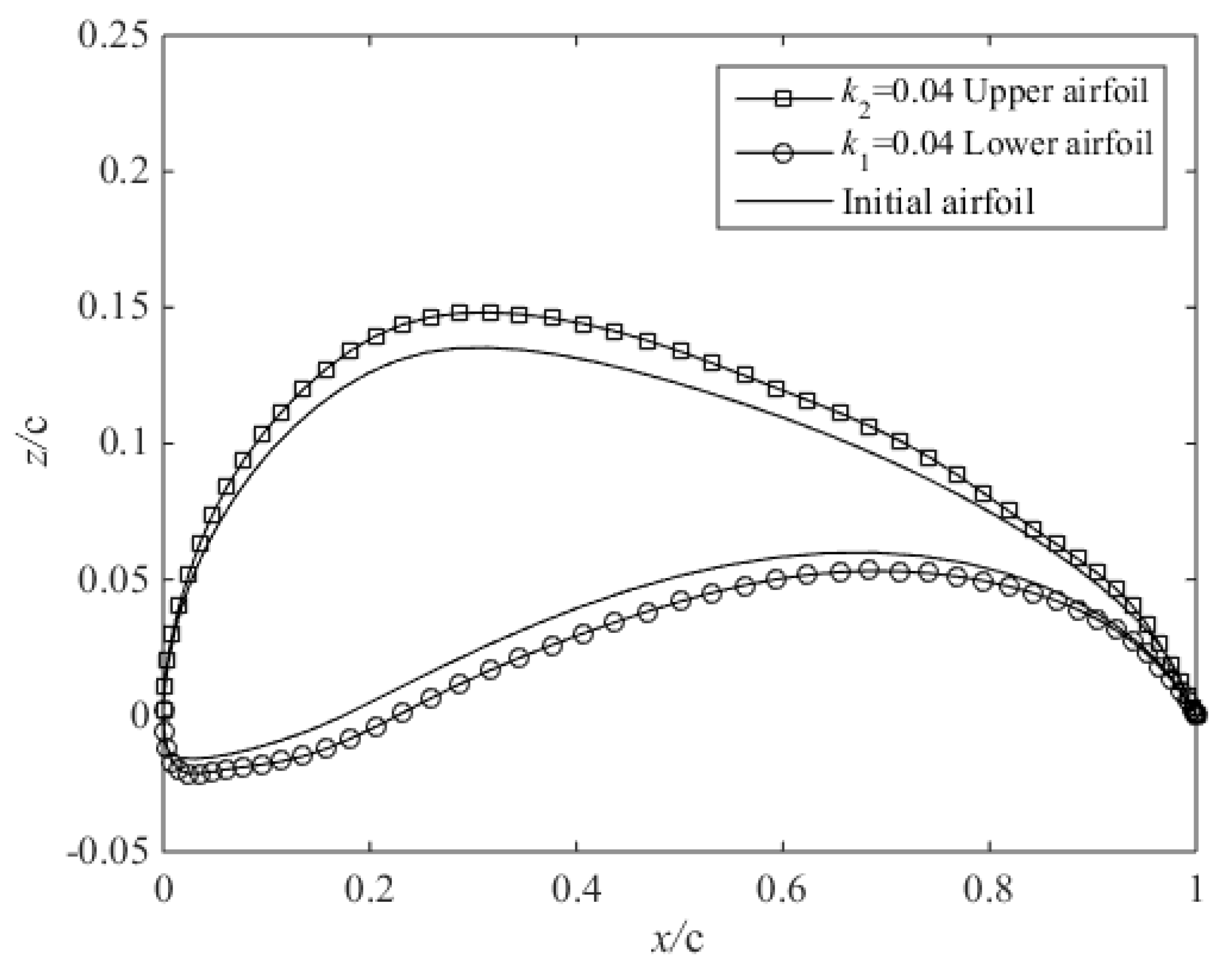
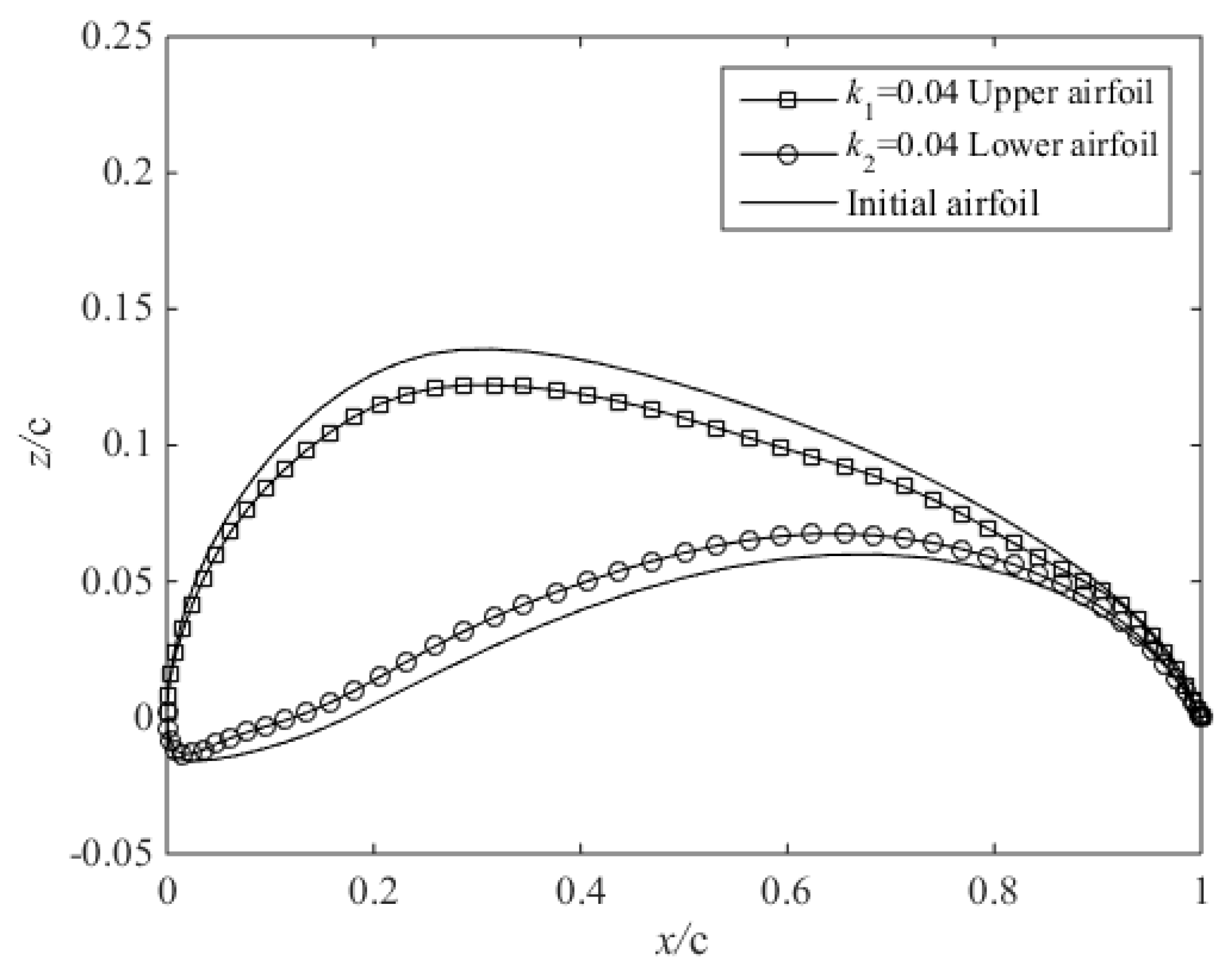
2.1. Airfoil Parameterization Based on the PEWI Method
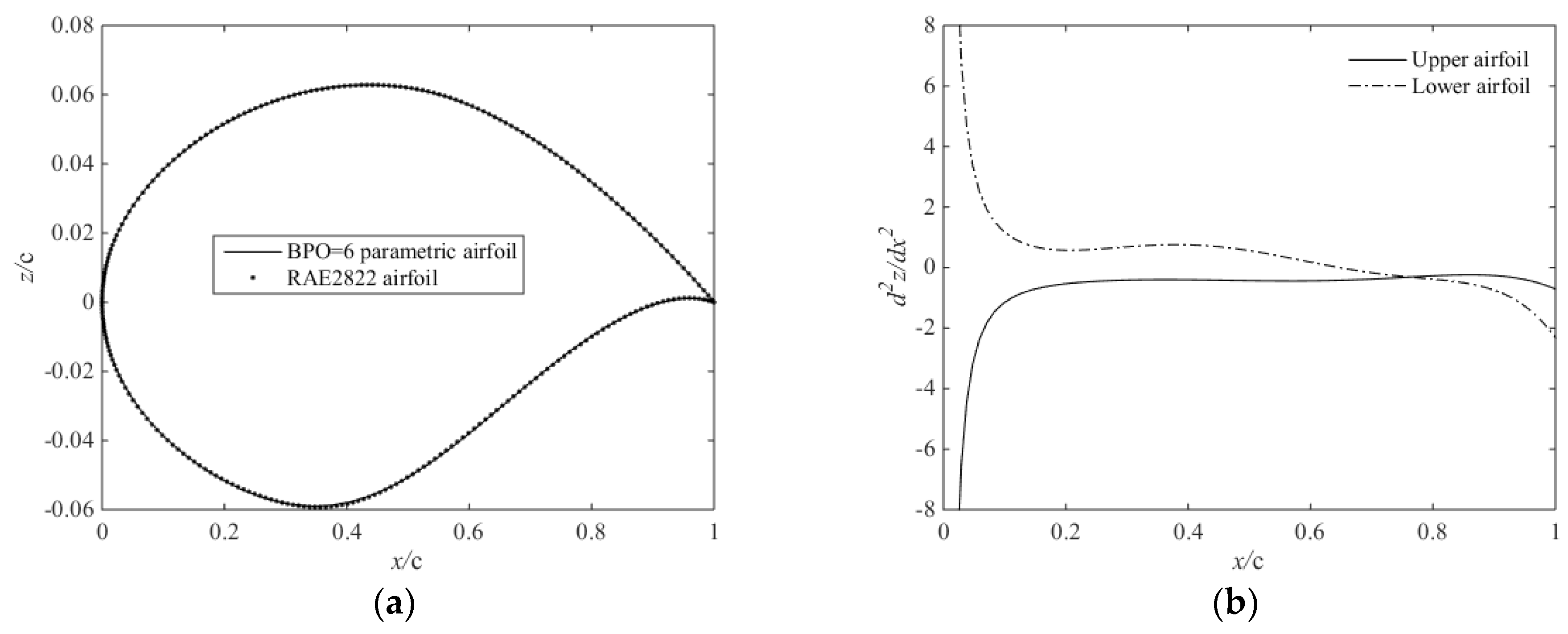
2.2. Fitting Airfoil by the CST Method
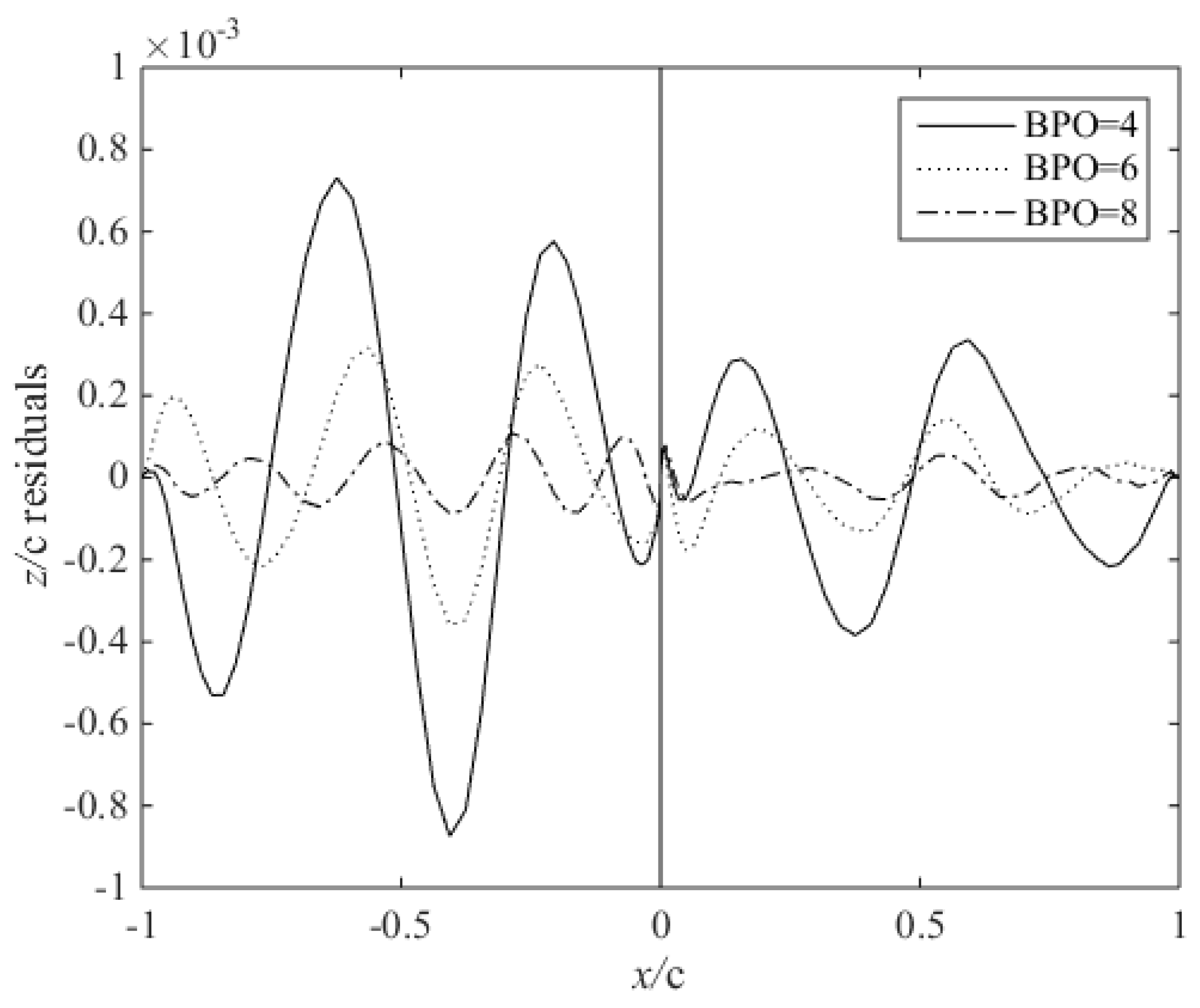
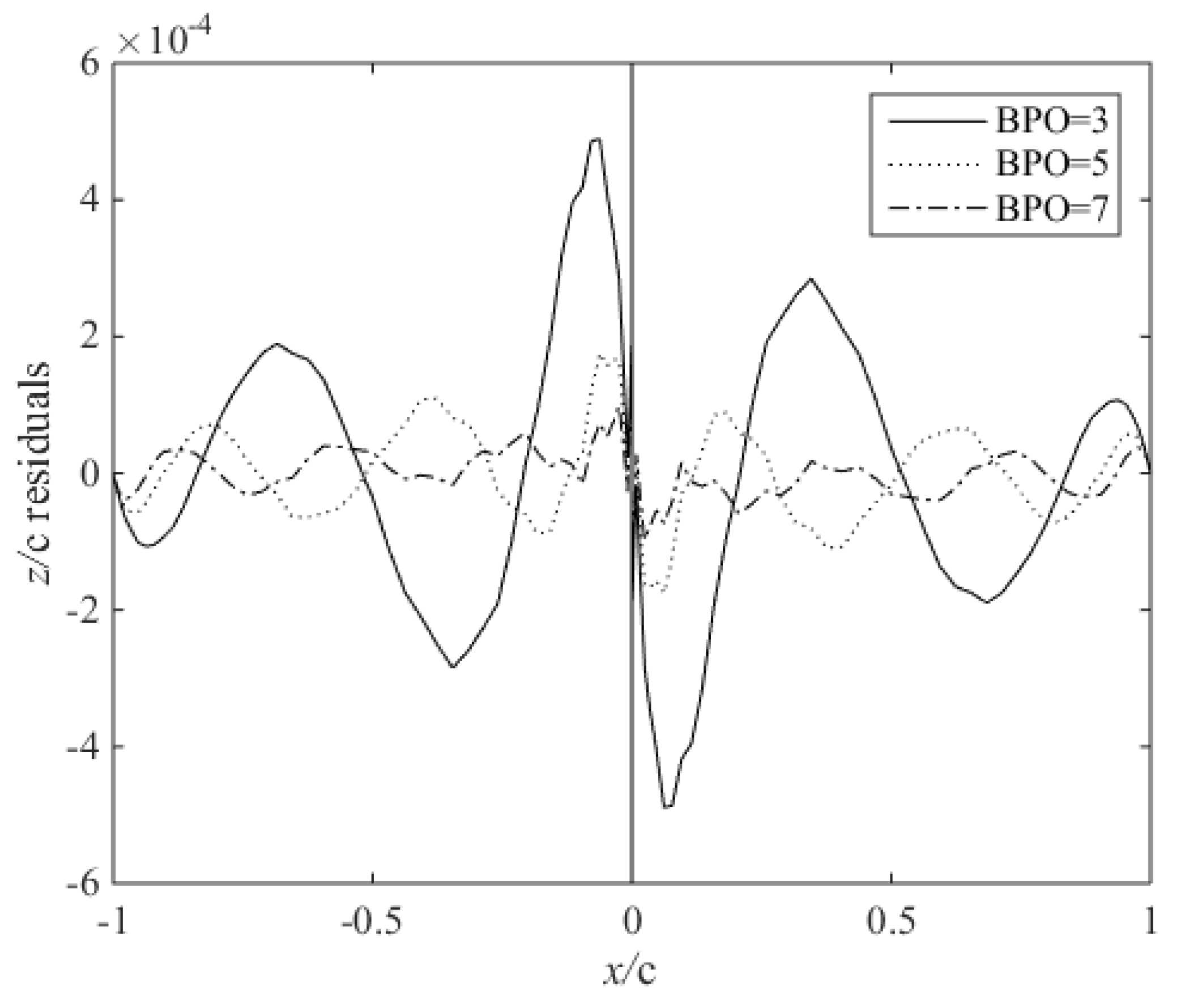
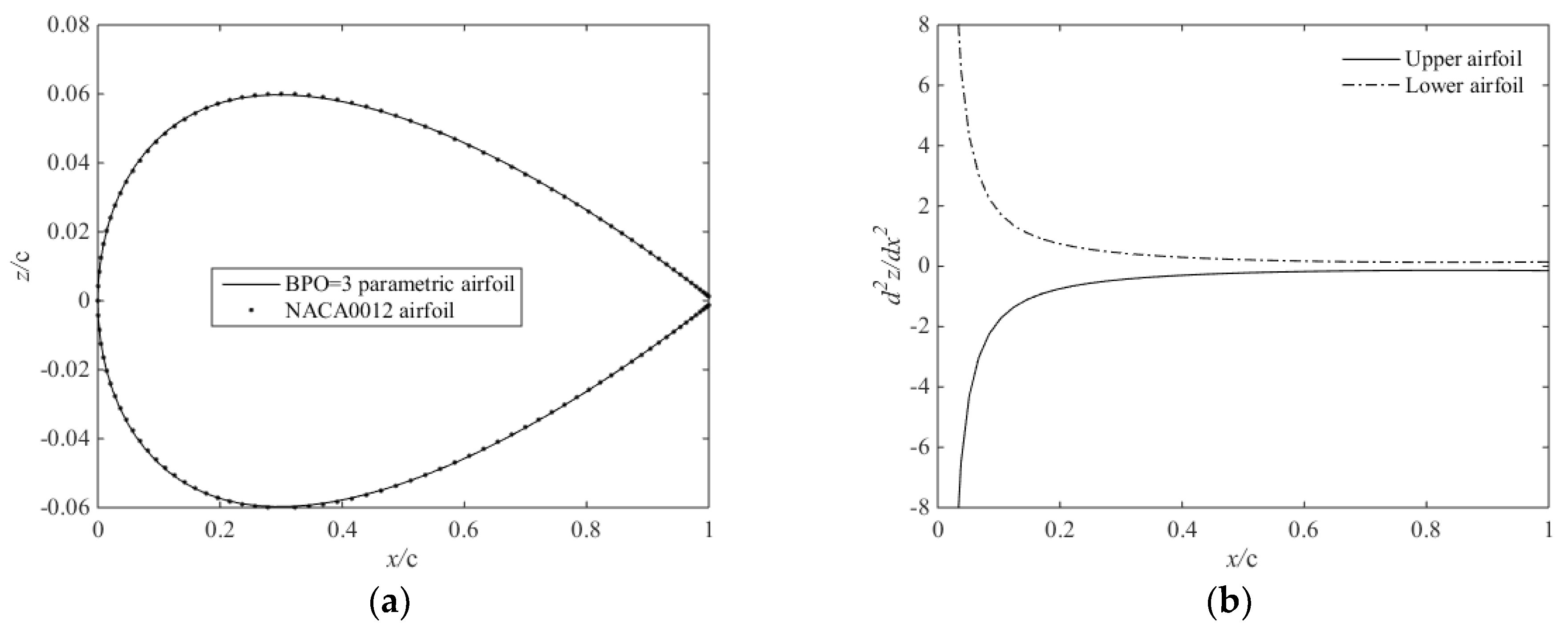
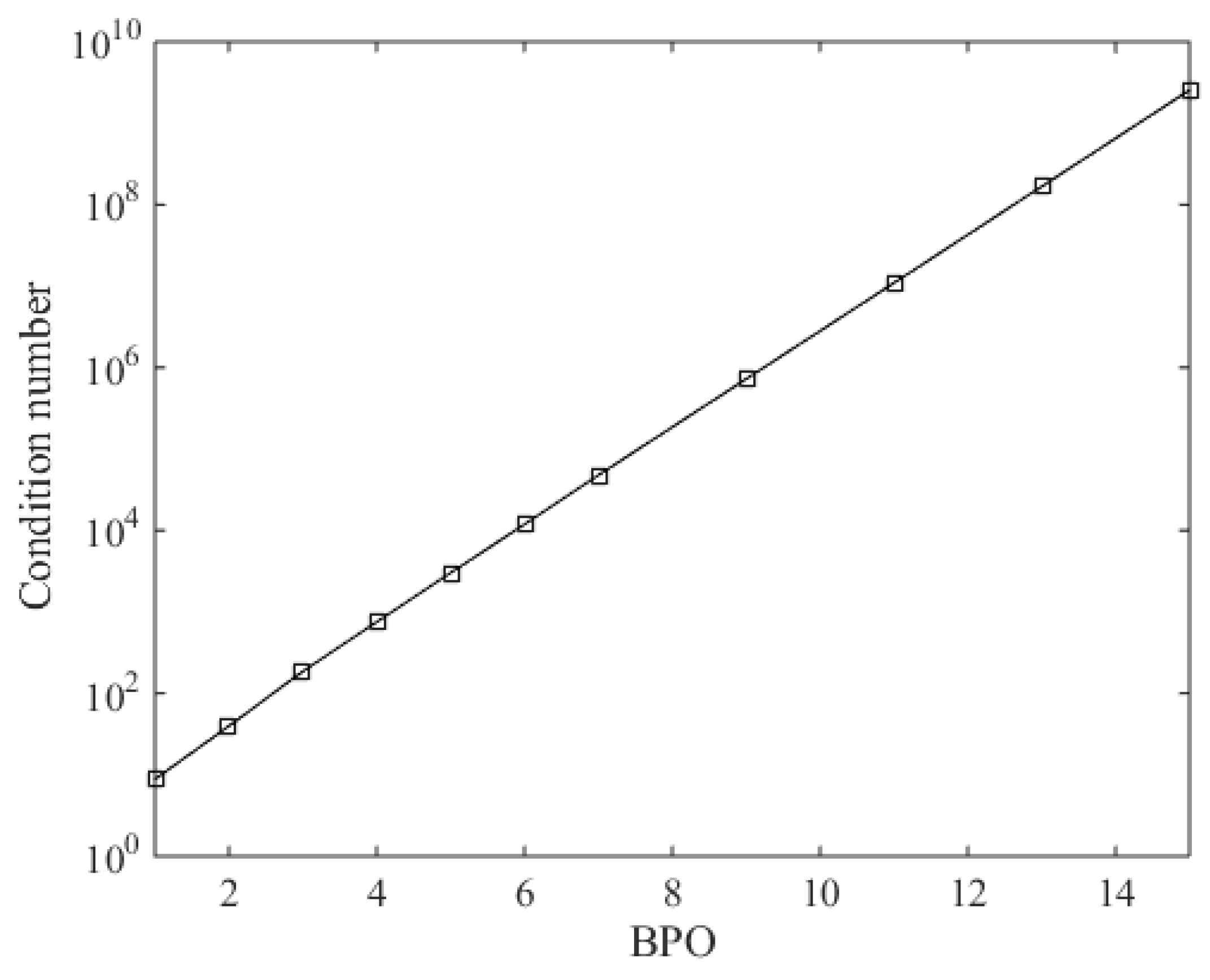
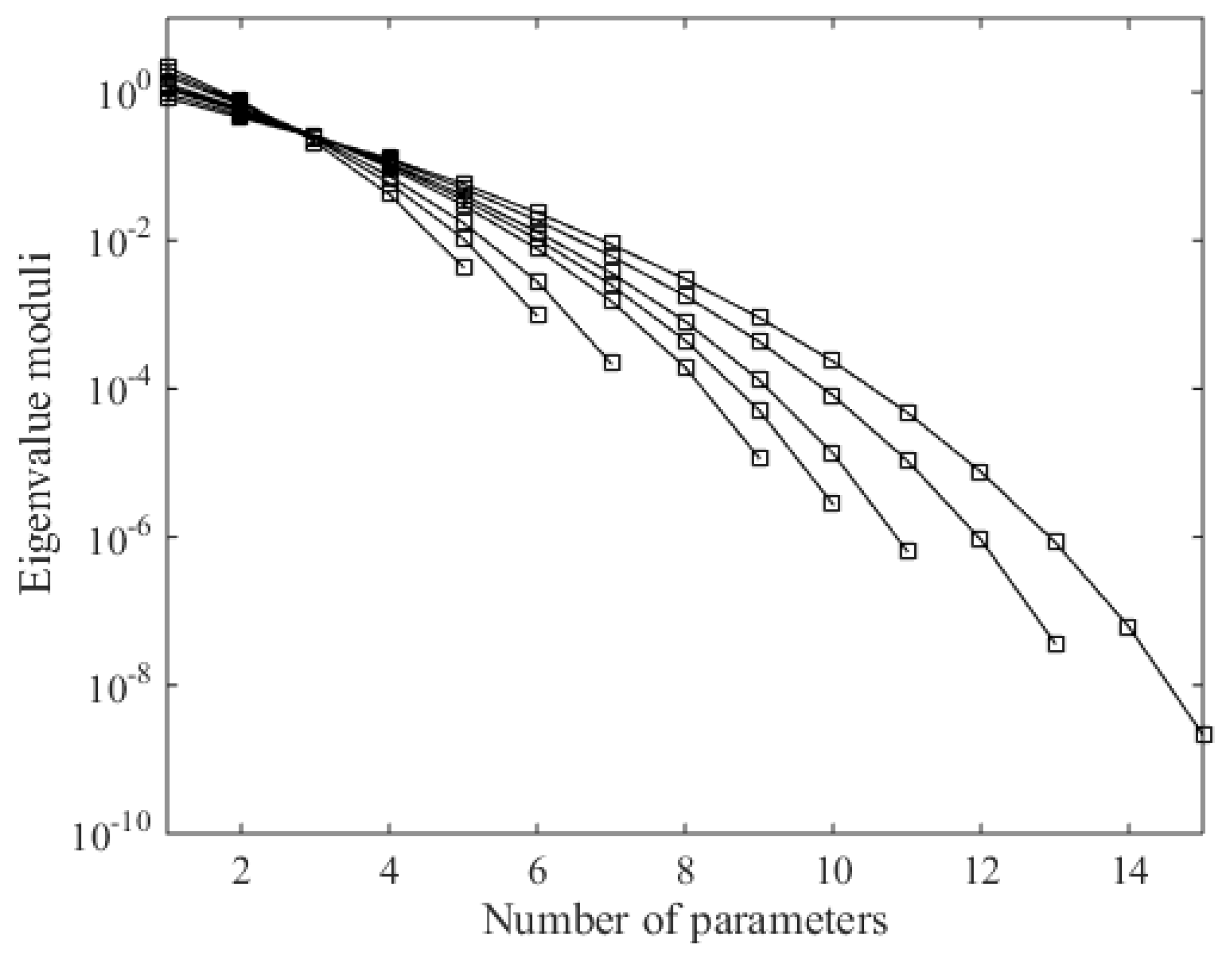
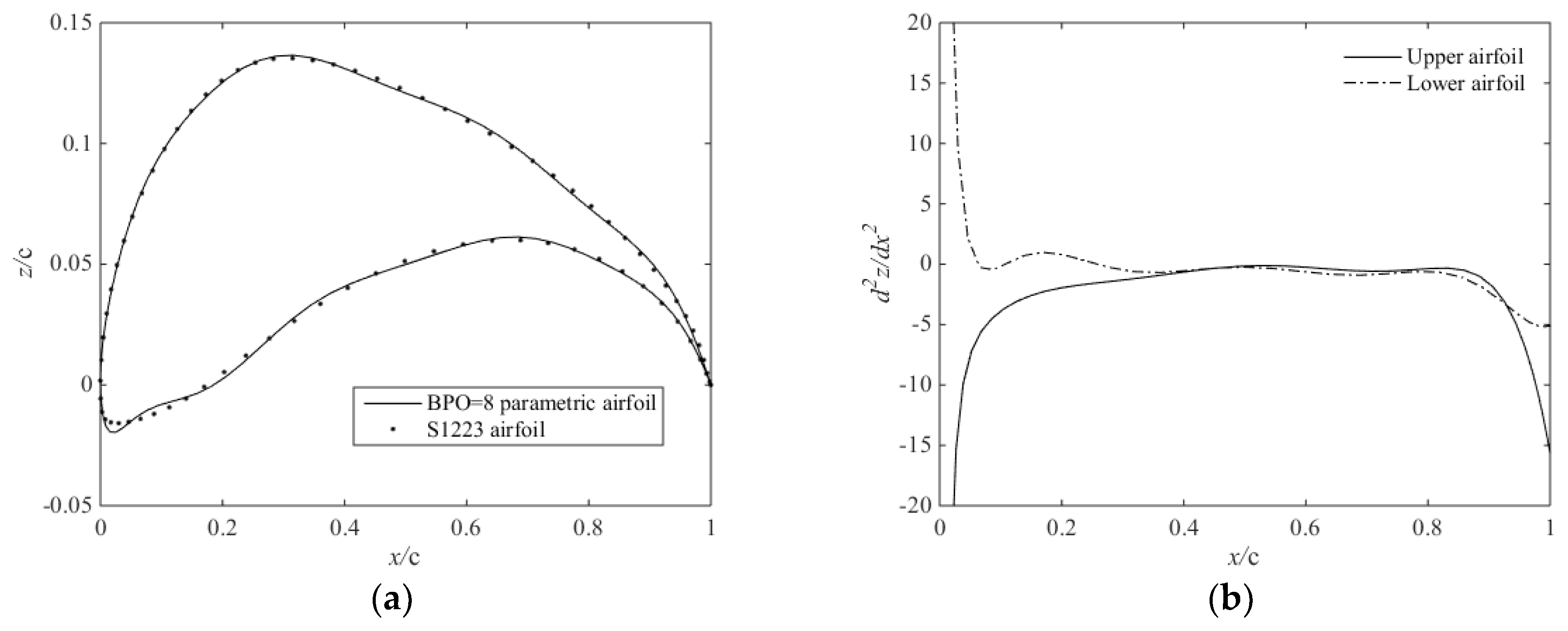
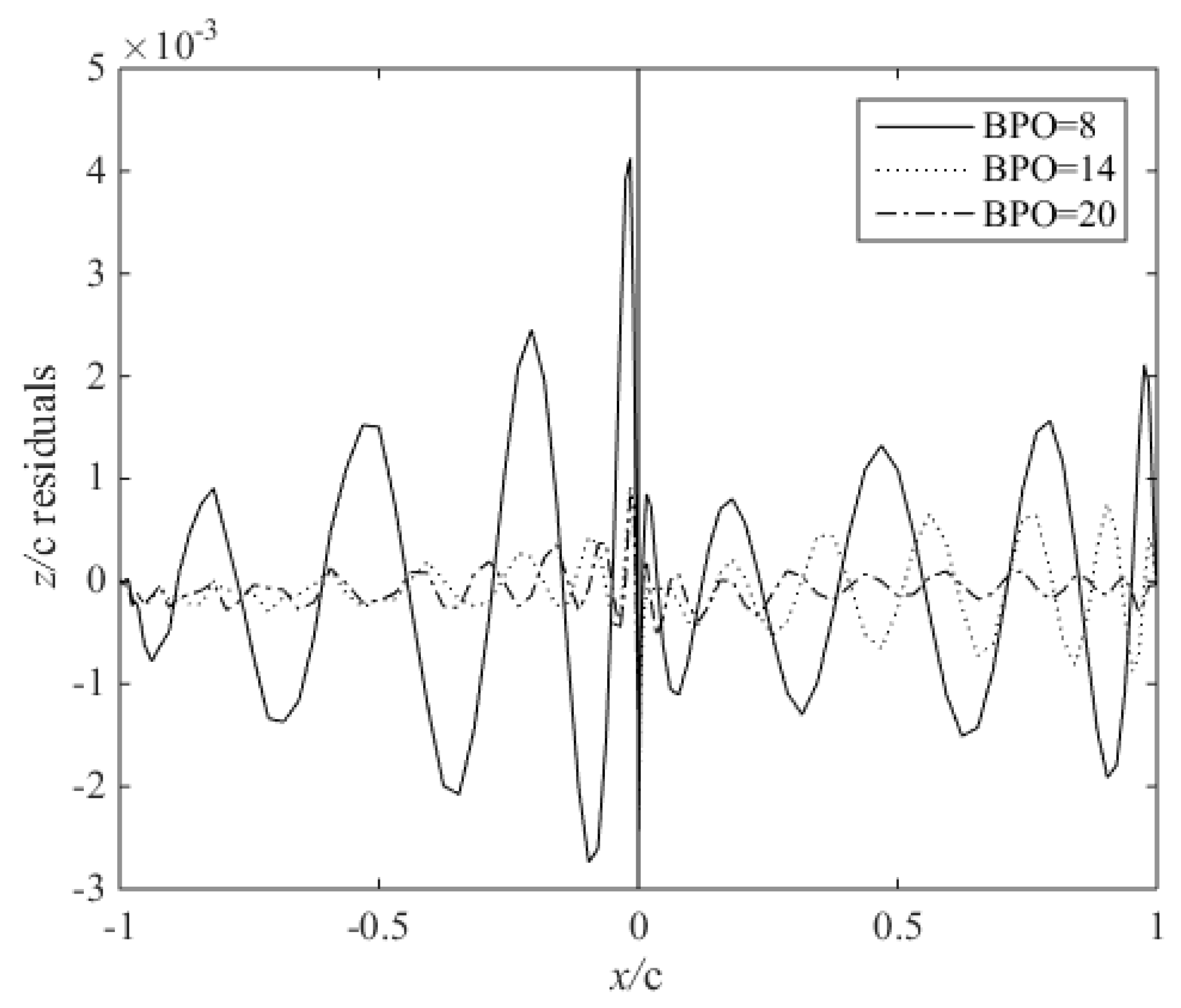
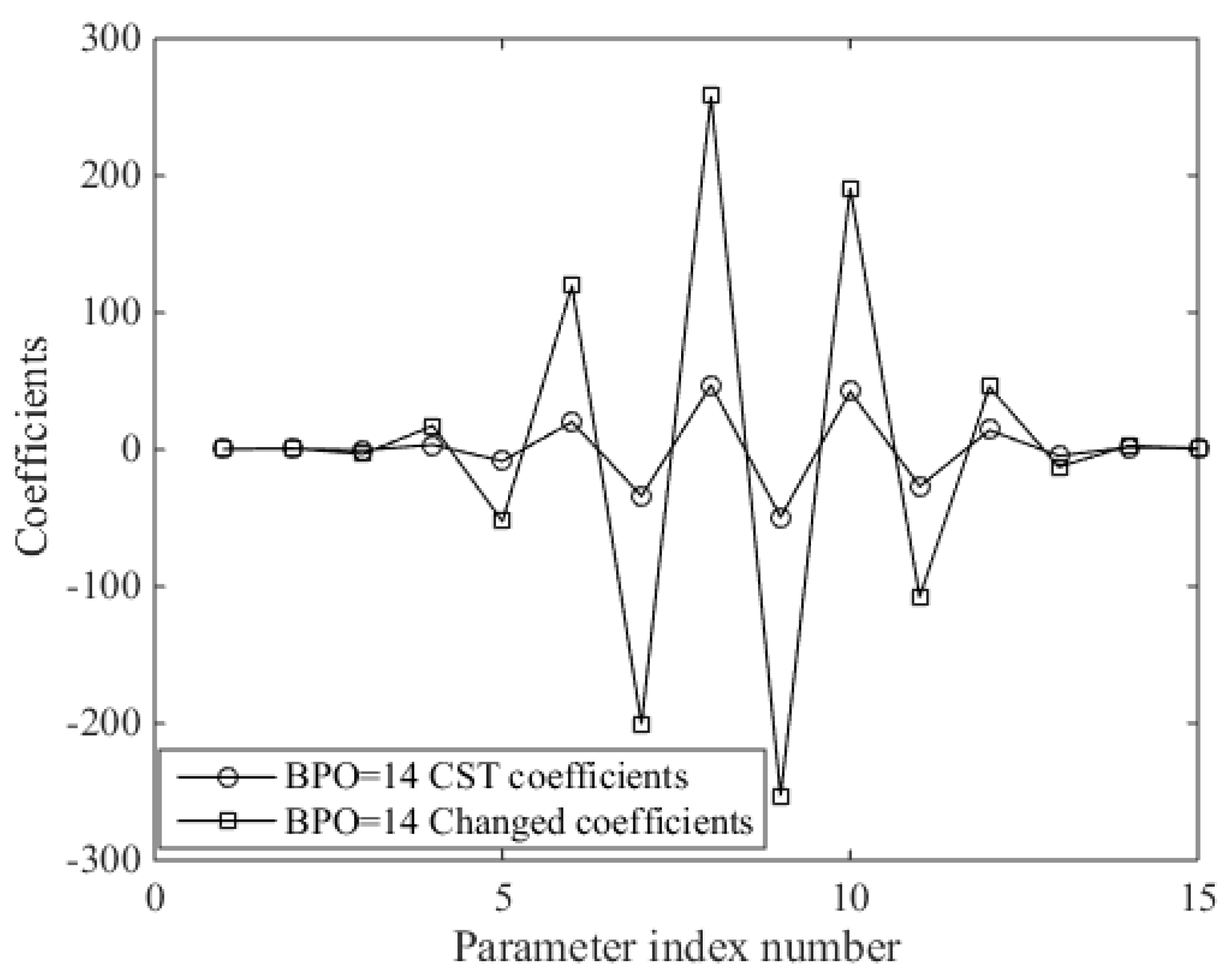
2.3. Parameter Matrix Analysis of the CST Method
3. Aerodynamic Optimization Design of Airfoil
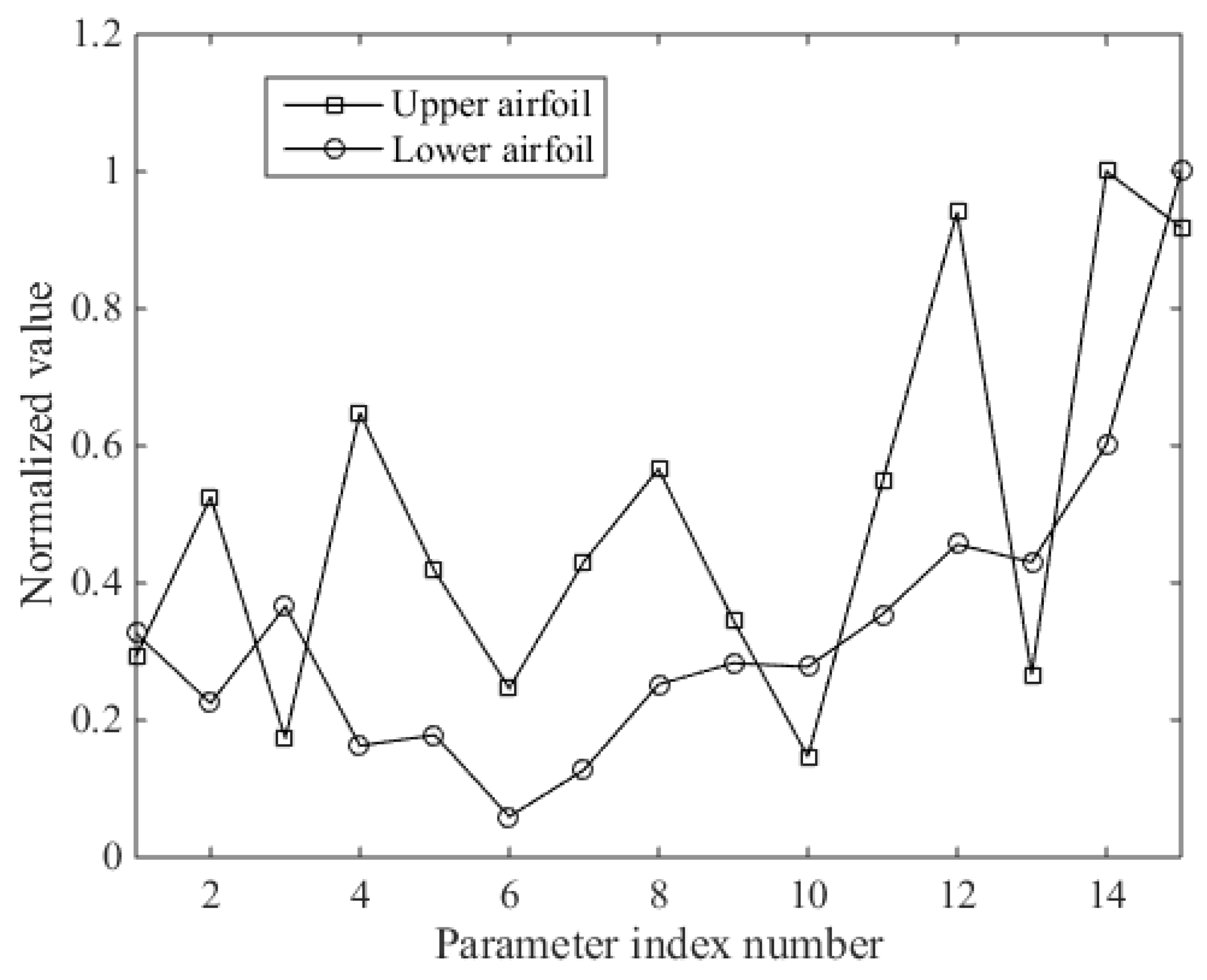
3.1. Normalization of the Design Parameters
3.2. Design of Experiment
3.3. Radial Basis Functions Neural Network Model
3.4. Genetic Algorithms
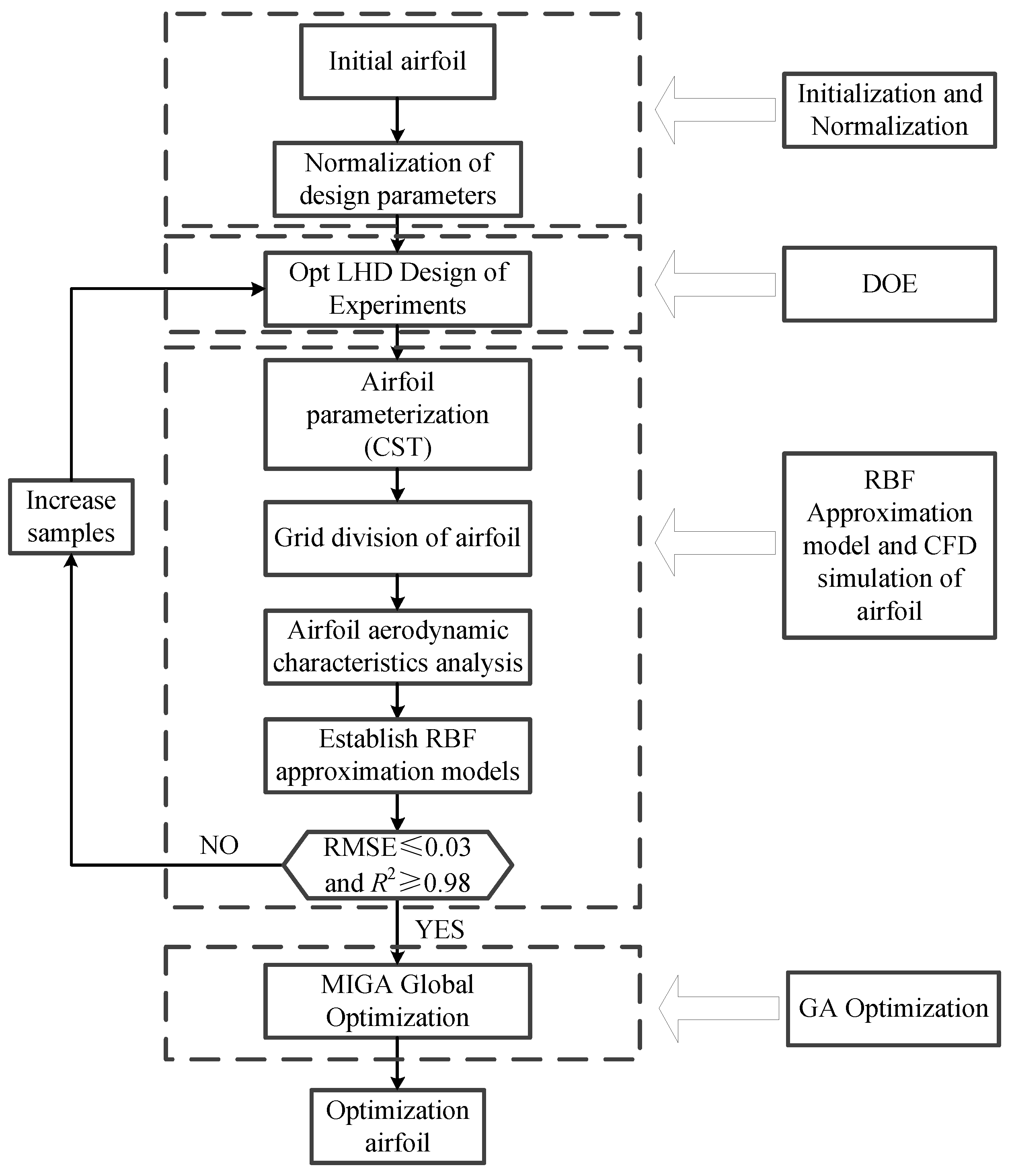
3.5. Optimization Process
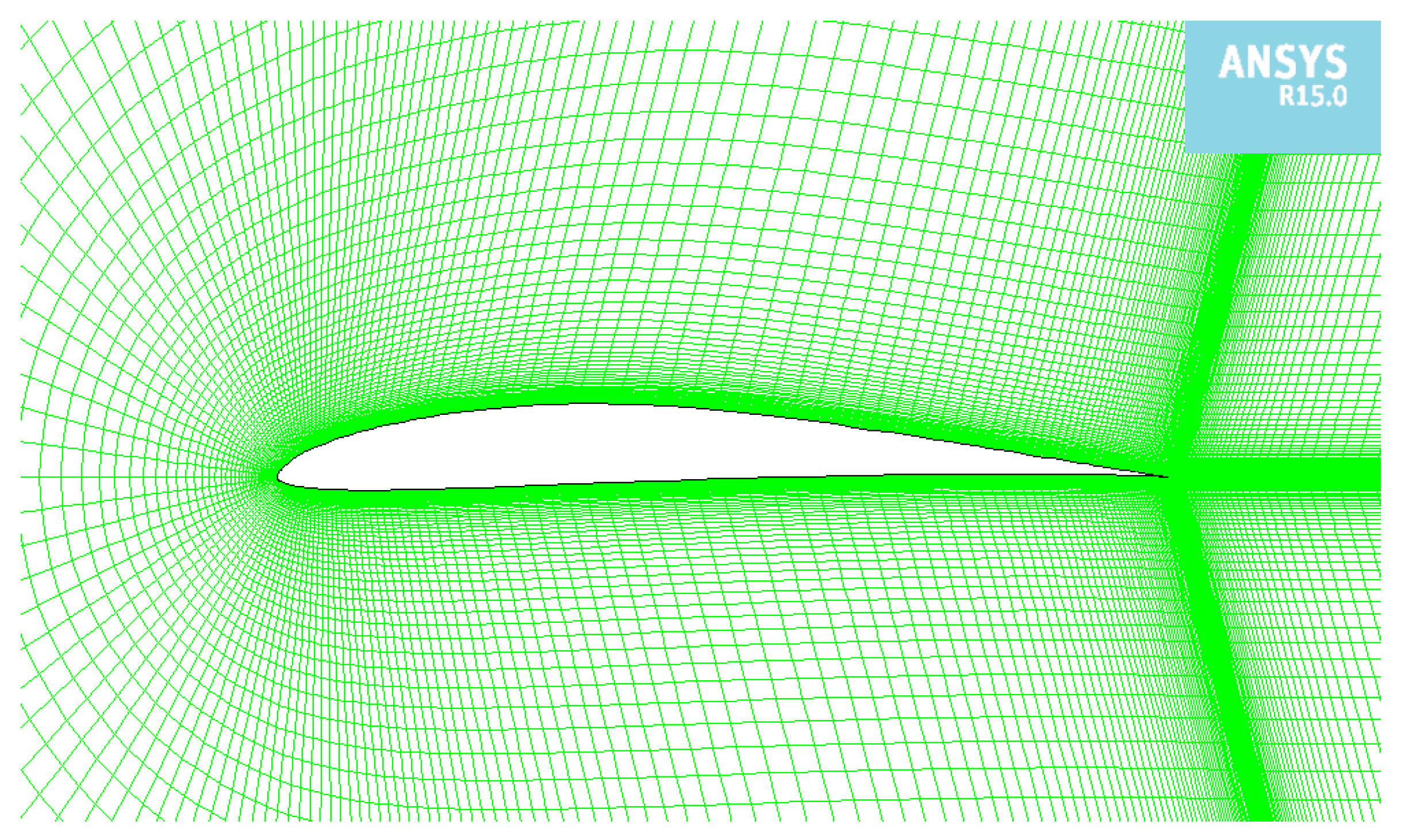
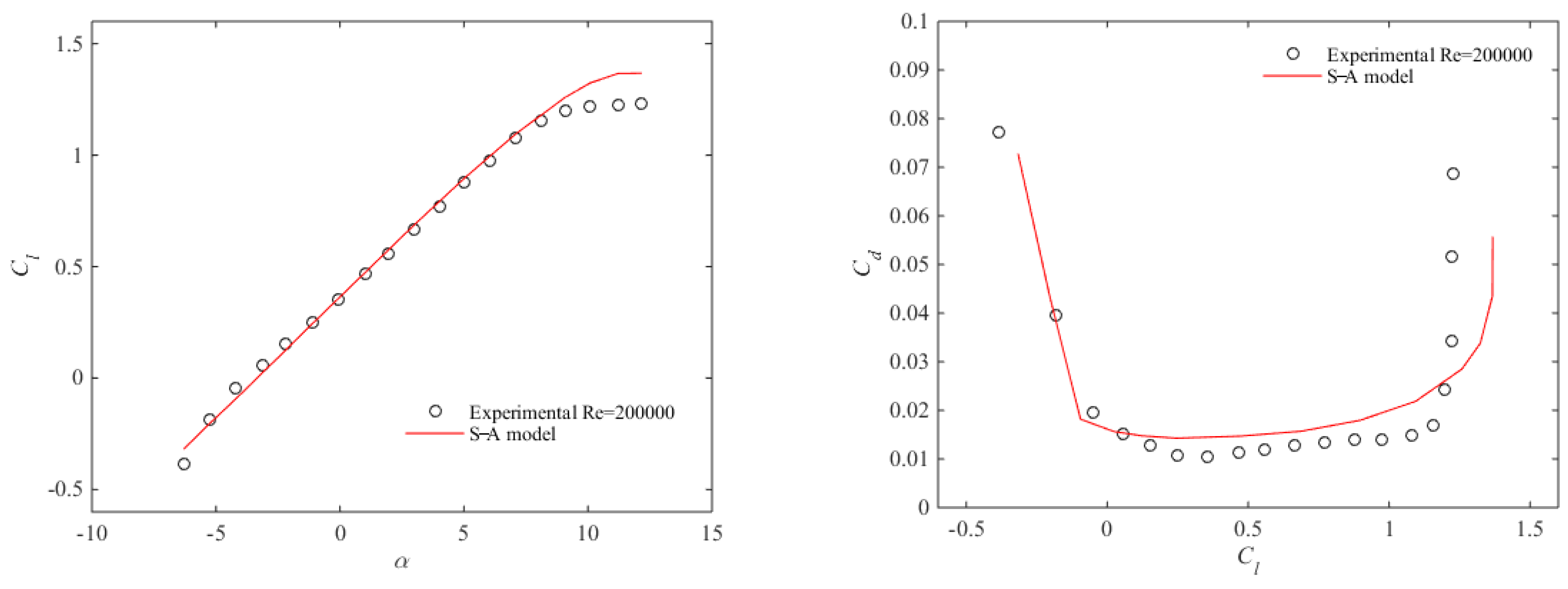
3.6. Validation of CFD Model
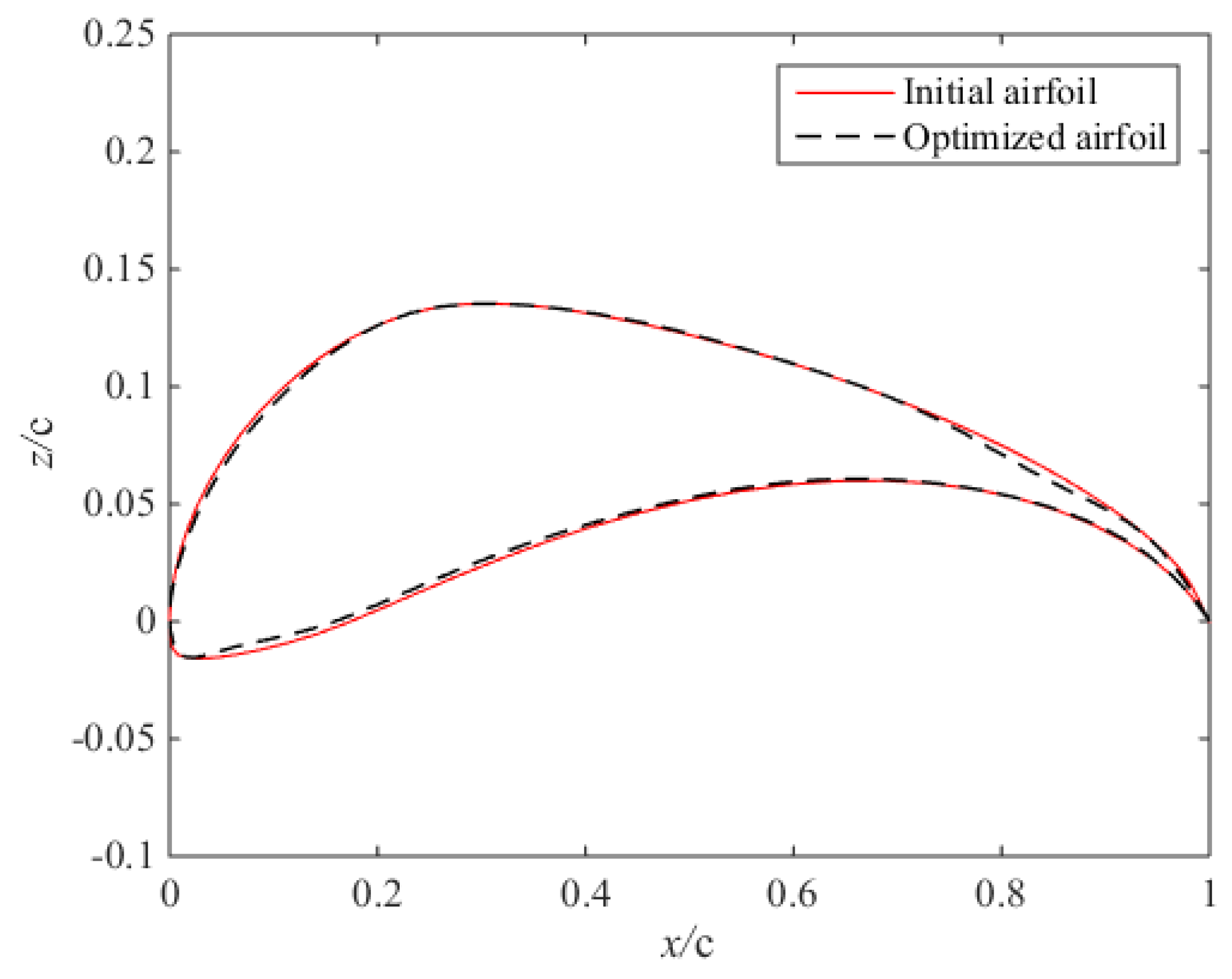
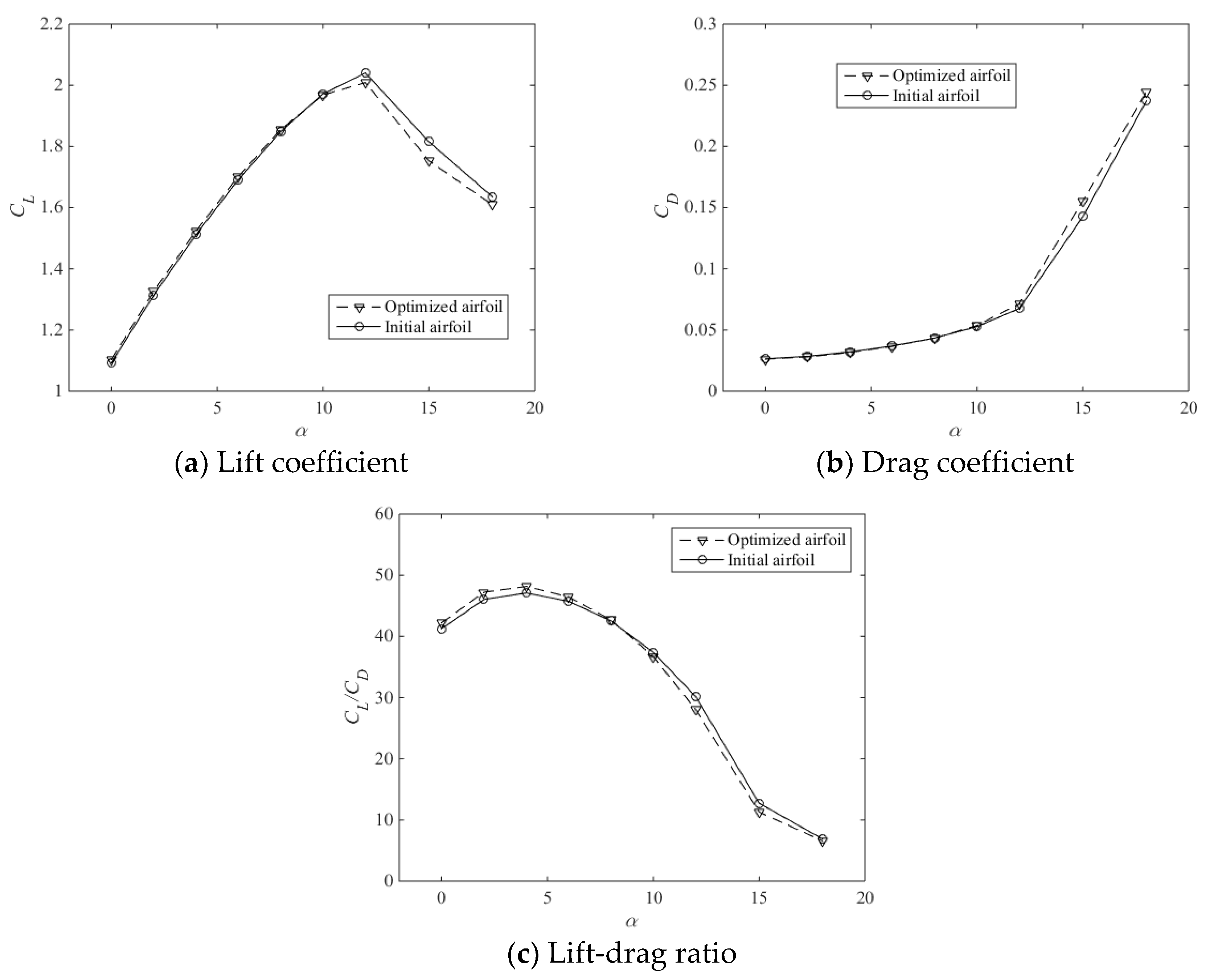
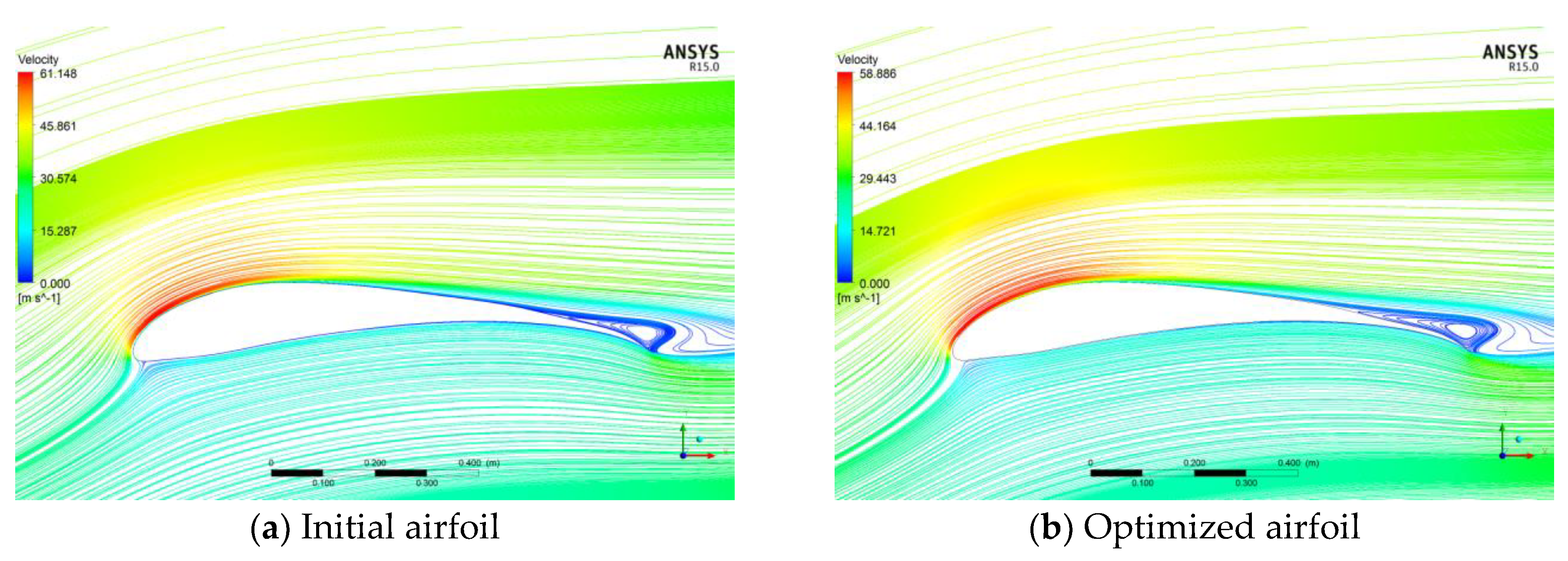
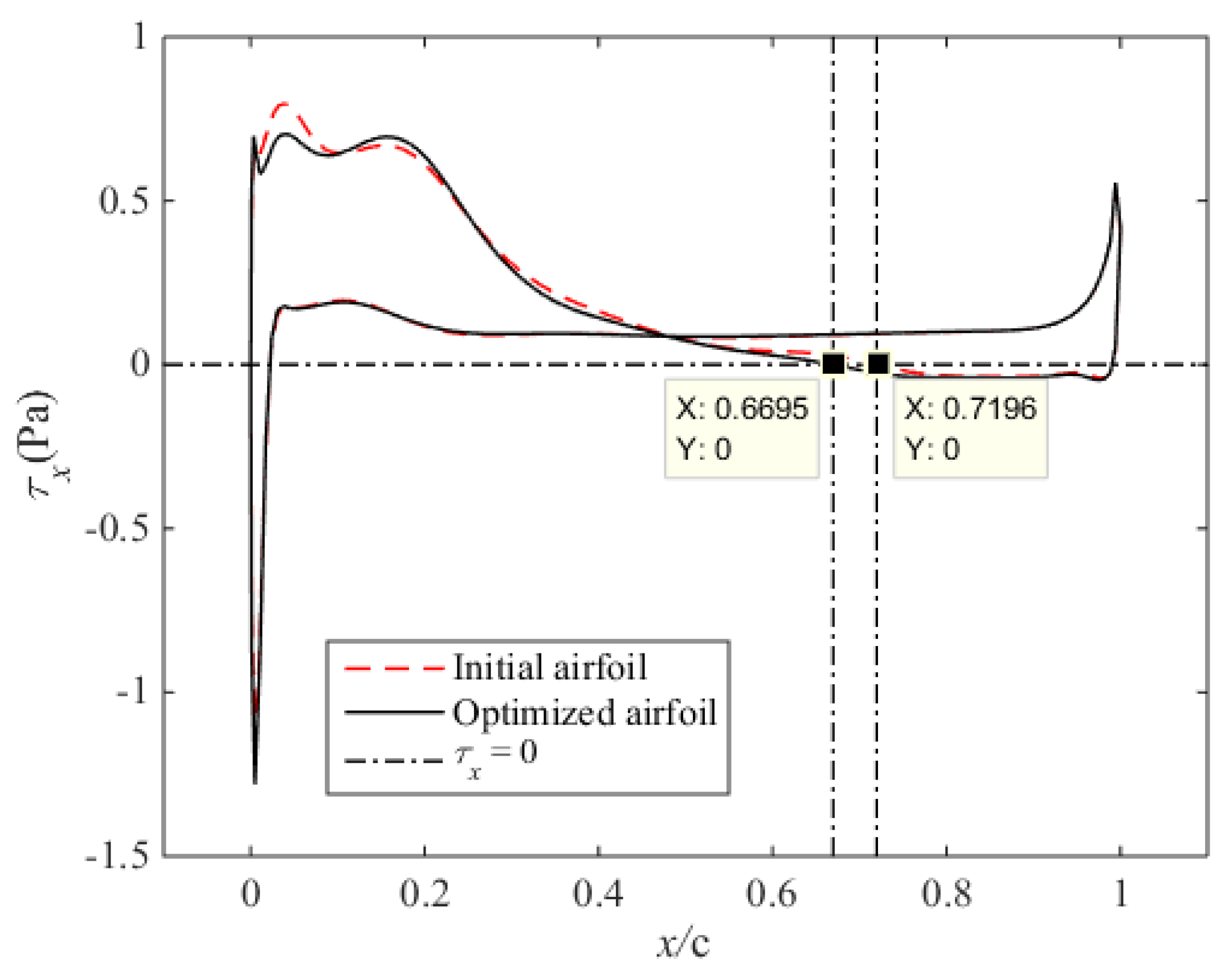
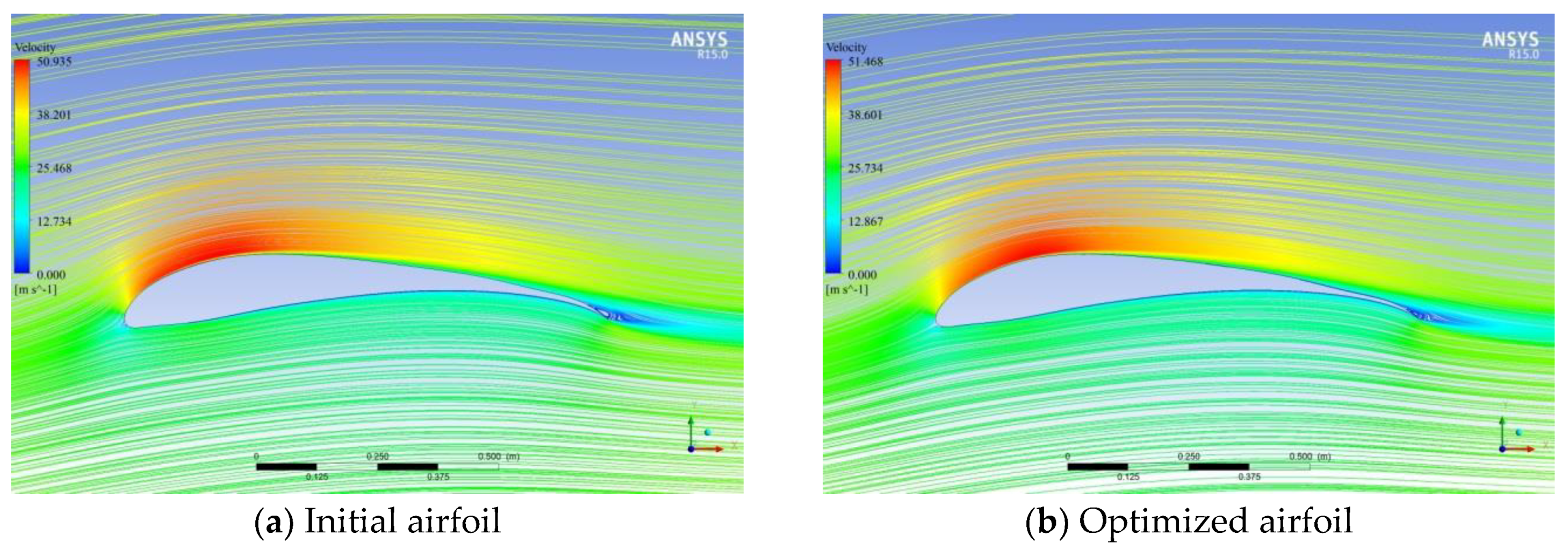
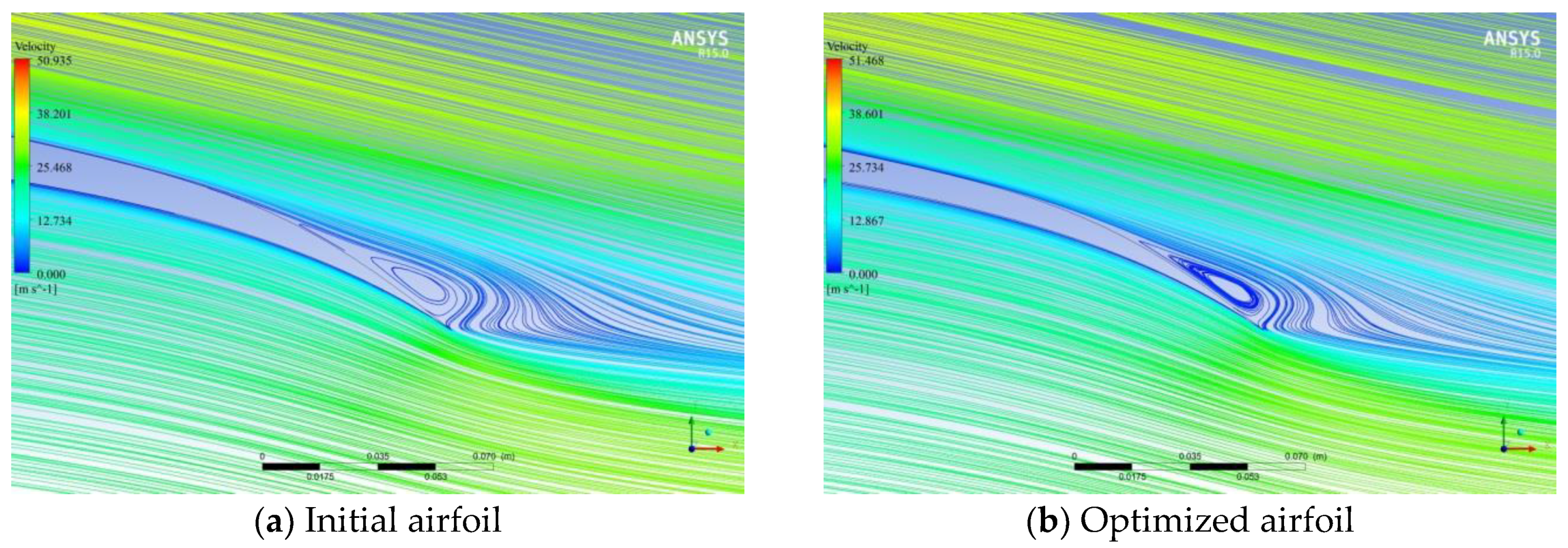
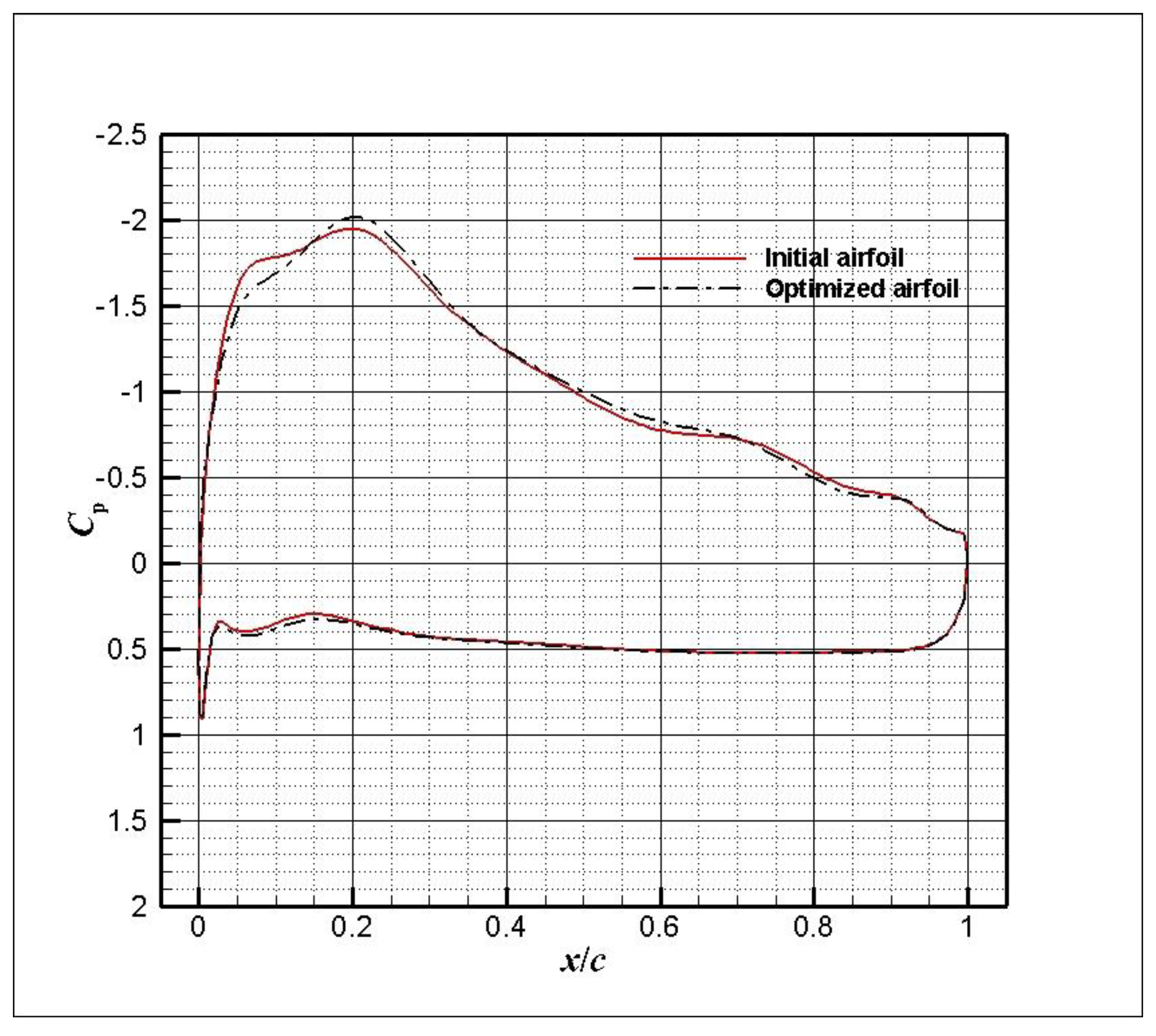
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, F.; Qin, N. Intuitive Class/Shape Function Parameterization for Airfoils. AIAA J. 2013, 52, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.P.; Azevedo, J.L.F. Studies in Aerodynamic Optimization Based on Genetic Algorithms. J. Aircr. 2014, 51, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Yang, C.; Song, X.C. An airfoil parameterization method for the representation and optimization of wind turbine special airfoil. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 24, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, Z.H.; Huang, J.T.; Zhao, K.; Li, J. Smoothing methods based on coordinate transformation in a linear space and application in airfoil aerodynamic design optimization. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2015, 58, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyarit, A.; Kanazaki, M. Multi-Objective Efficient Global Optimization Applied to Airfoil Design Problems. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.C.; Allison, D.L.; Schetz, J.A.; Kapania, R.K.; Sultan, C. Parametric Geometry Model for Design Studies of Tailless Supersonic Aircraft. J. Aircr. 2014, 51, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Fang, X.M.; Chen, H.X.; Fu, S.; Duan, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.J. Supercritical natural laminar flow airfoil optimization for regional aircraft wing design. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.A.; Lee, J.W.; Shu, J.I. Aerodynamic design optimization of helicopter rotor blades including airfoil shape for hover performance. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2013, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.A.; Lee, J.W. Aerodynamic design optimization of helicopter rotor blades including airfoil shape for forward flight. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2015, 42, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceze, M. A Study of the CST Parameterization Characteristics; Report No.: AIAA-2009-3767; AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.H.; Li, Z.K.; Song, B.F. A study on CST aerodynamic shape parameterization method. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2012, 33, 625–633. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.H.; Song, B.F.; Li, Z.K. Comparison of the CSRT and the CST parameterization methods. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2014, 32, 228–234. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Cai, J.S.; Qu, K.; Liu, C.Z. Airfoil optimization based on improved CST parametric method and transition model. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 2015, 36, 449–461. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Shao, R.; Zhu, Y. New iterative improvement of a solution for an Ill-conditioned system of linear equations based on a linear dynamic system. Comput. Math. Appl. 2002, 44, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkuyeh, D.K.; Fahim, A. A new iterative refinement of the solution of ill-conditioned linear system of equations. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2011, 88, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulfan, B.M.; Bussoletti, J.E. Fundamental parametric geometry representations for aircraft component shapes. In Proceedings of the 11th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, Portsmouth, VA, USA, 6 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kulfan, B.M. Recent Extensions and Applications of the ‘‘CST” Universal Parametric Geometry Representation Method; Report No.: AIAA-2007-7709; AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kulfan, B.M. New Supersonic Wing Far-Field Composite-Element Wave-Drag Optimization Method. J. Aircr. 2009, 46, 1740–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.B. Orthogonal Arrays for Computer Experiments, Integration and Visualization. Stat. Sin. 1992, 2, 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, M.D.; Beckman, R.J.; Conover, W.J. A Comparison of Three Methods for Selecting Values of Input Variables in the Analysis of Output from a Computer Code. Technometrics 1979, 21, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.S. Optimal Latin-hypercube designs for computer experiments. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 1994, 39, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.Y. Parameters Optimization Theory of Isght and Explain of Examples; Beihang University Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 88–102. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sacks, J.; Welch, W.J.; Mitchell, T.J.; Wynn, H.P. Design and analysis of computer experiments. Stat. Sci. 1989, 4, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, T.W.; Lin, D.K.; Chen, W. Sampling strategies for computer experiments: Design and analysis. Int. J. Reliabil. Appl. 2001, 2, 209–240. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, R.L. Multiquadratic equations of topography and other irregular surface. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Chen, W.; Simpson, T.W. Comparative studies of metamodelling techniques under multiple modelling criteria. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2001, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Horstemeyer, M.F. Global response approximation with radial basis functions. Eng. Optim. 2006, 38, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhi, J.Y. Aerodynamic optimization design of adaptive airfoil leading edge based on isight. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. 2014, 48, 1122–1133. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.J.; Wang, Y.K.; Cao, W.W.; Zhou, P. Optimization of suction control on an airfoil using multi-island genetic algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2015, 99, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhong, B.; Liu, P. Optimization design study of low-Reynolds-number high-lift airfoils for the high-efficiency propeller of low-dynamic vehicles in stratosphere. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 2792–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, M.S.; Guglielmo, J.J. High-lift low Reynolds number airfoil design. J. Aircr. 1997, 34, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of generations | 25 |
| Number of sub-populations | 10 |
| Number of individuals on each sub-population | 20 |
| Interval generations of migration | 4 |
| Crossover rate | 0.9 |
| Mutation rate | 0.01 |
| Migration rate | 0.3 |
| Aerodynamic Coefficient | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| CL | 0.00485 | 0.99955 |
| CD | 0.03 | 0.98619 |
| Upper Airfoil Variables | Min | Max | Optimum | Lower Airfoil Variables | Min | Max | Optimum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aup1 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.02188 | Alow1 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.01346 |
| Aup2 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.0246 | Alow2 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.00836 |
| Aup3 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | 0.01508 | Alow3 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.00994 |
| Aup4 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.00465 | Alow4 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.02331 |
| Aup5 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | 0.0144 | Alow5 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | −0.01926 |
| Aup6 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.01463 | Alow6 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.0073 |
| Aup7 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | 0.01213 | Alow7 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.00906 |
| Aup8 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.03027 | Alow8 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.02173 |
| Aup9 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | 0.02574 | Alow9 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | −0.02401 |
| Aup10 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | 0.02347 | Alow10 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.01487 |
| Aup11 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.00374 | Alow11 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 9.00×10−5 |
| Aup12 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.02438 | Alow12 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | −0.0015 |
| Aup13 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.02732 | Alow13 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.00396 |
| Aup14 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.03367 | Alow14 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 9.70×10−4 |
| Aup15 | −0.0339 | 0.0339 | −0.02324 | Alow15 | −0.0263 | 0.0263 | 0.00871 |
| CL | CD | CL/CD | ΔCL | ΔCD | ΔCL/CD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial airfoil | 1.5119 | 0.0321 | 47.1 | |||
| Optimized airfoil (RBF) | 1.5247 | 0.03165 | 48.17 | 0.85% | −1.40% | 2.27% |
| CFD | 1.5244 | 0.03165 | 48.16 | 0.83% | −1.40% | 2.25% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; He, W. Airfoil Optimization Design Based on the Pivot Element Weighting Iterative Method. Algorithms 2018, 11, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100163
Liu X, He W. Airfoil Optimization Design Based on the Pivot Element Weighting Iterative Method. Algorithms. 2018; 11(10):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100163
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinqiang, and Weiliang He. 2018. "Airfoil Optimization Design Based on the Pivot Element Weighting Iterative Method" Algorithms 11, no. 10: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100163
APA StyleLiu, X., & He, W. (2018). Airfoil Optimization Design Based on the Pivot Element Weighting Iterative Method. Algorithms, 11(10), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/a11100163




