Behavior of Elastoplastic Auxetic Microstructural Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Micromechanical Analysis
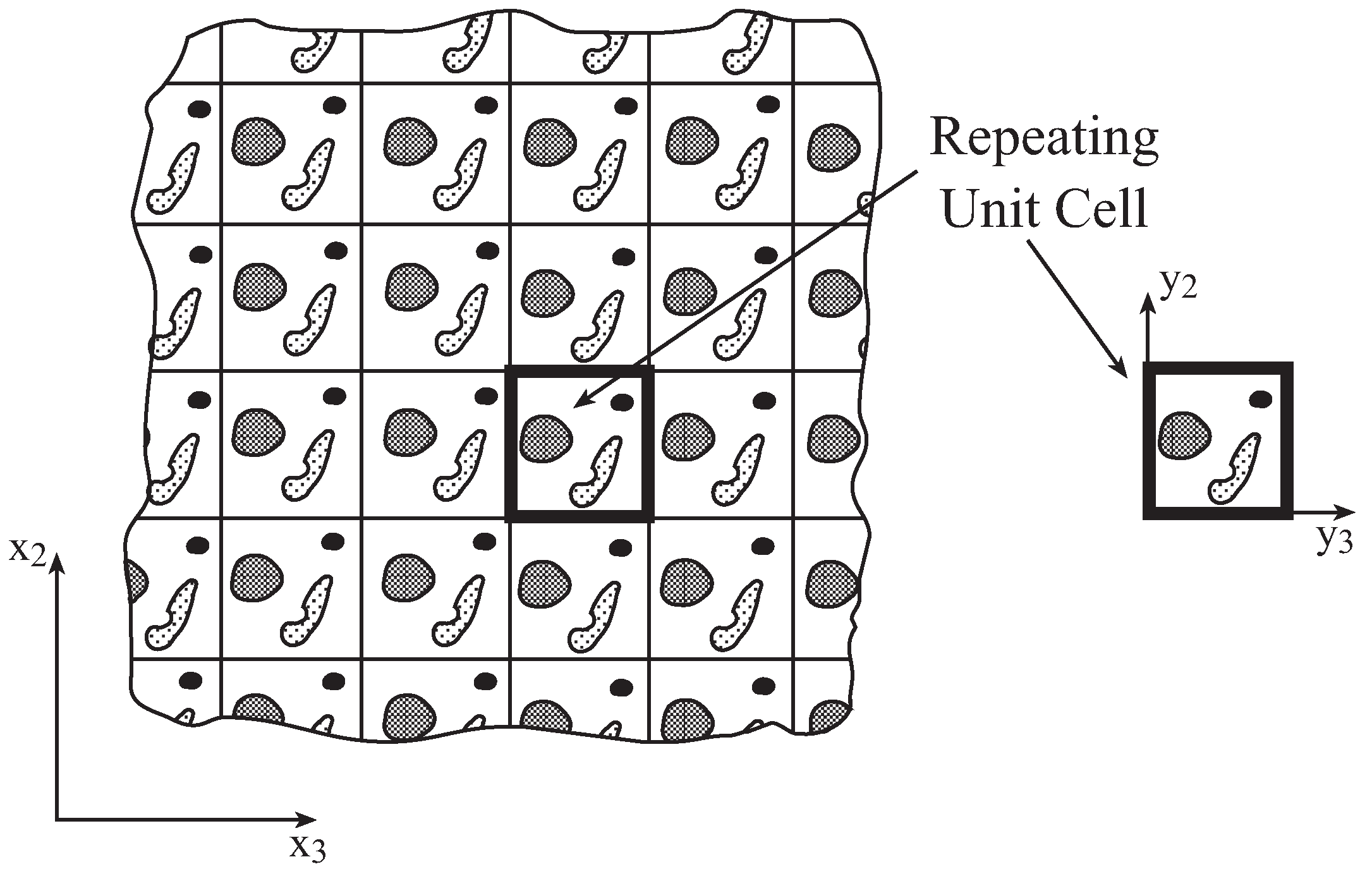
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elasticity Effects
3.1.1. Parametric Study
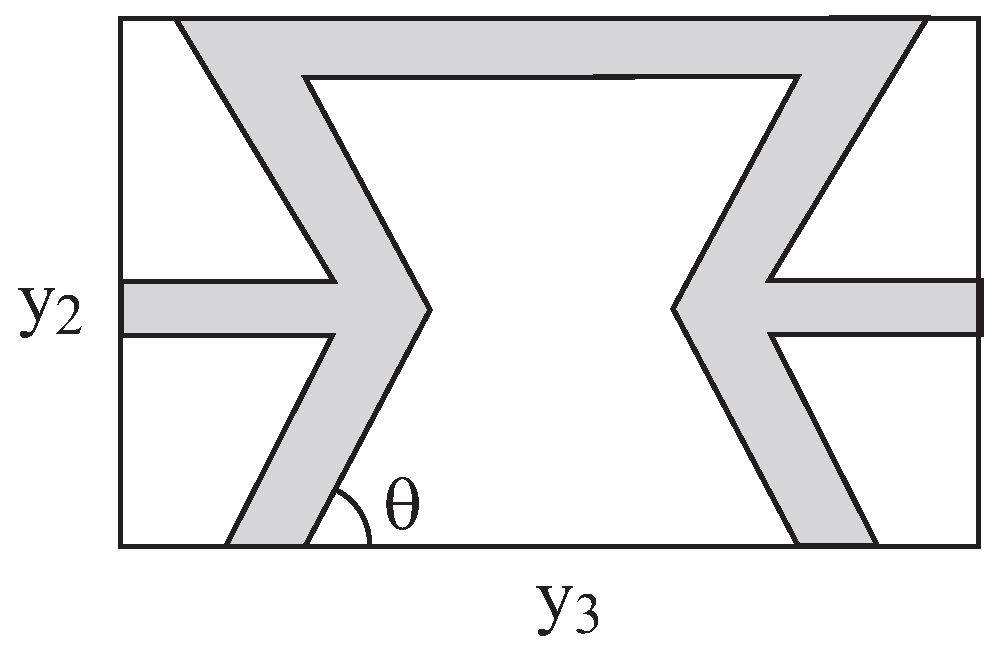
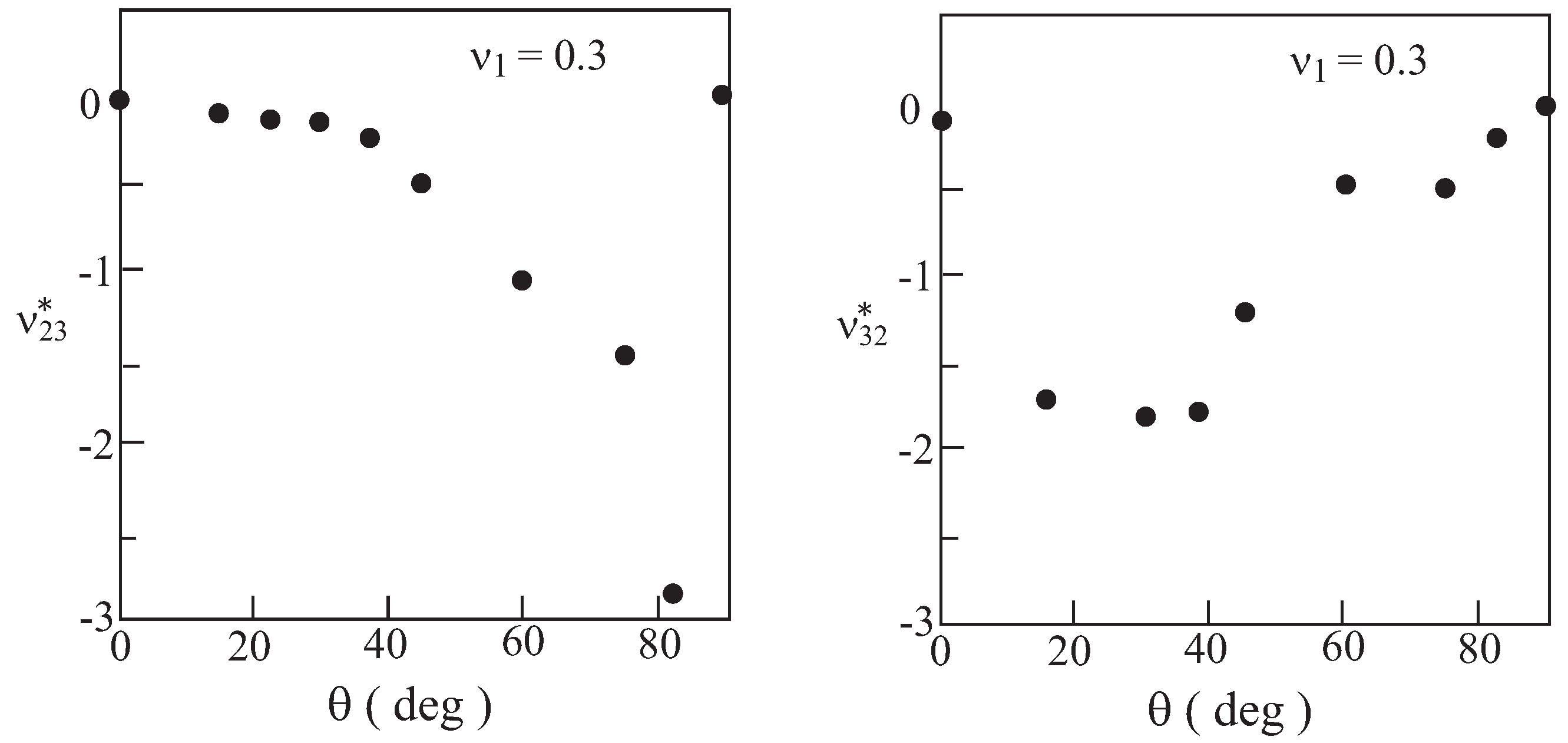
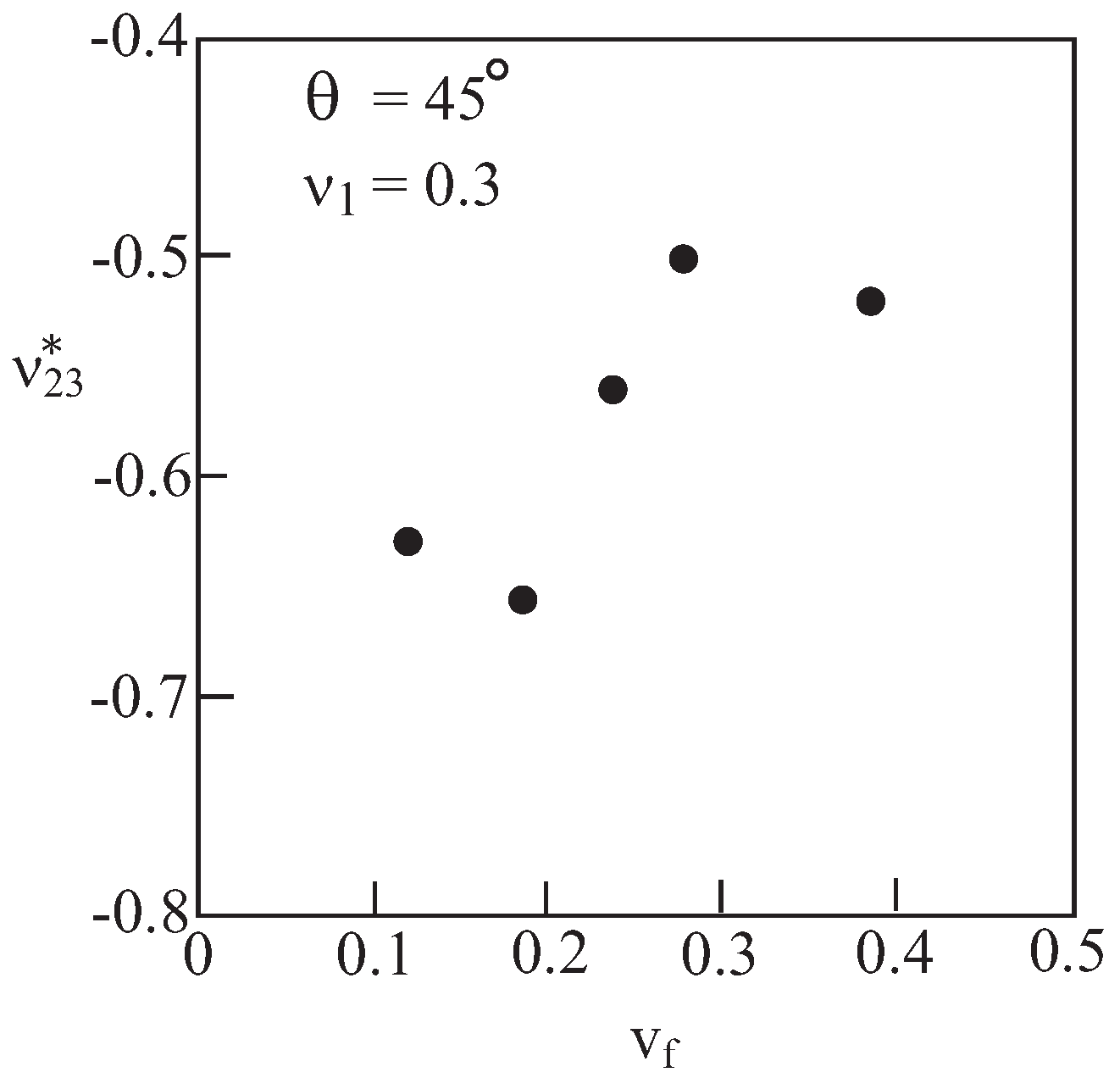
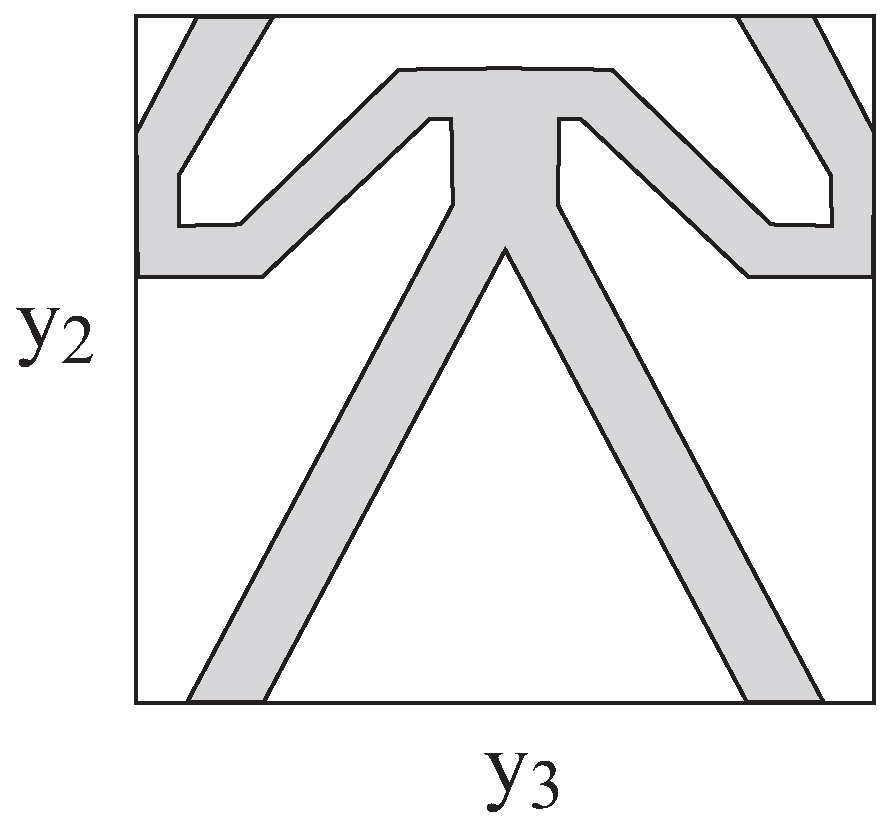
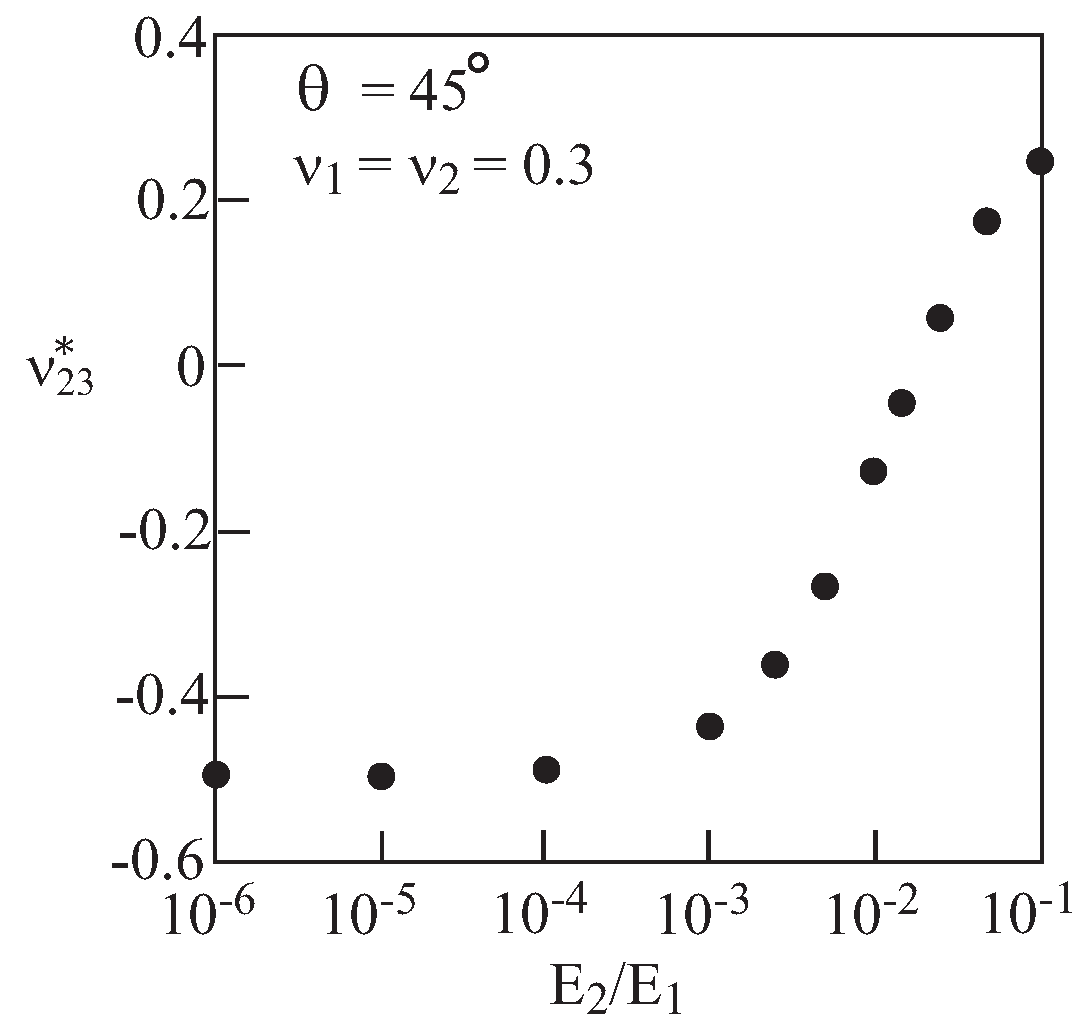
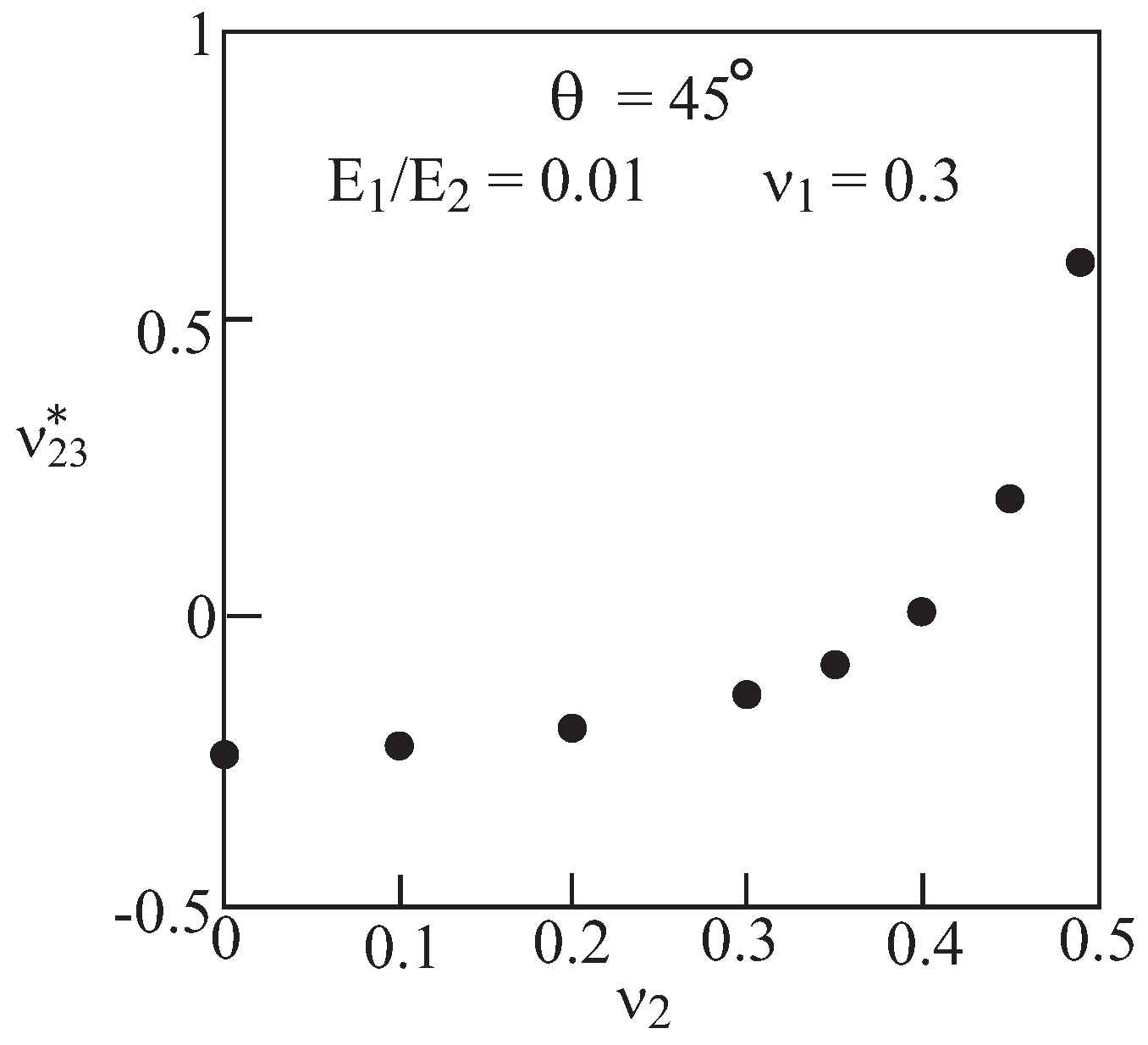
3.1.2. Material Design Strategy
| 0.3 | ||||
| 0.3 | ||||
| 0.3 | ||||
| 0.3 | ||||
| 0 | – | 0 | 0 |
3.2. Plasticity Effects
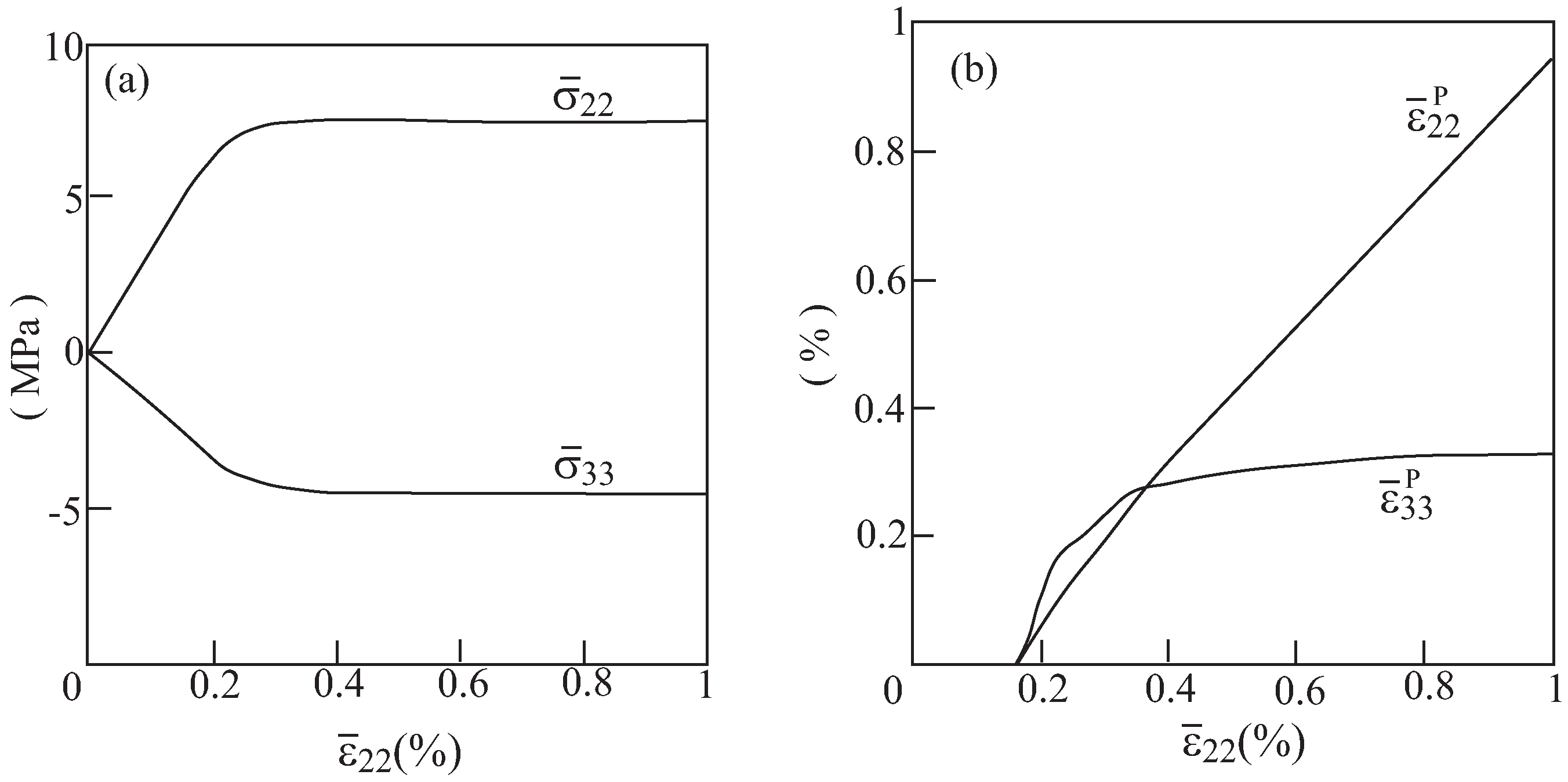
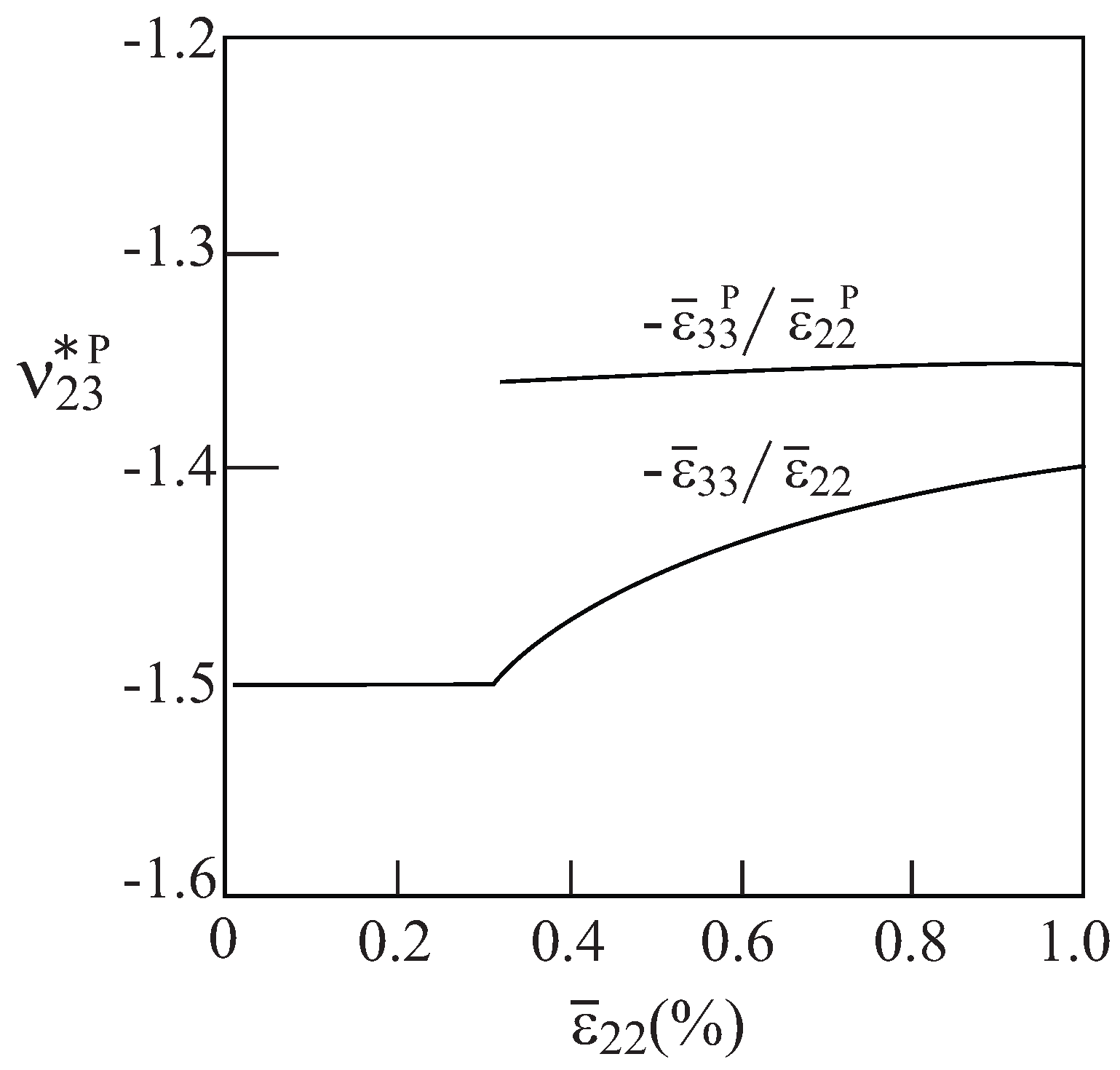
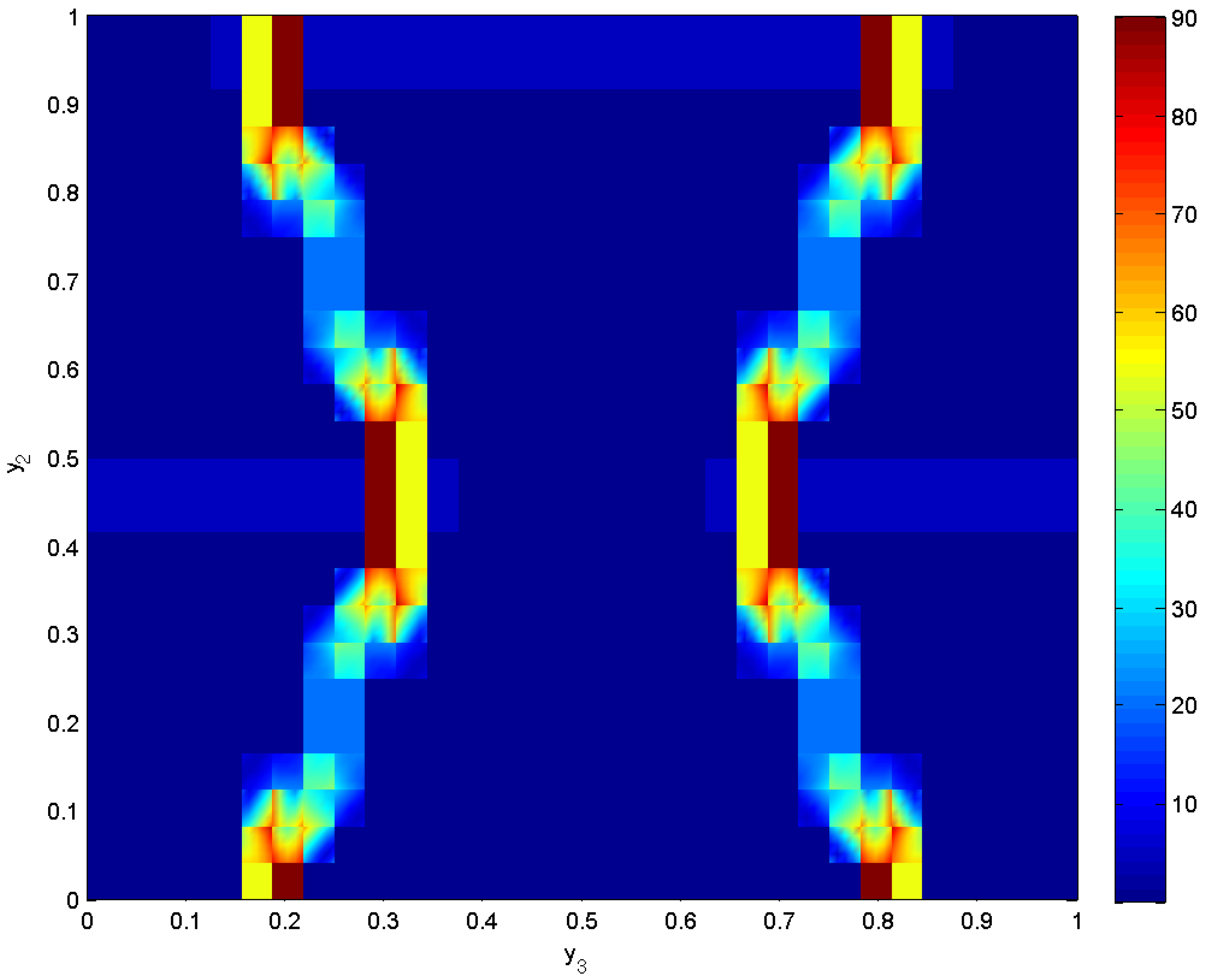
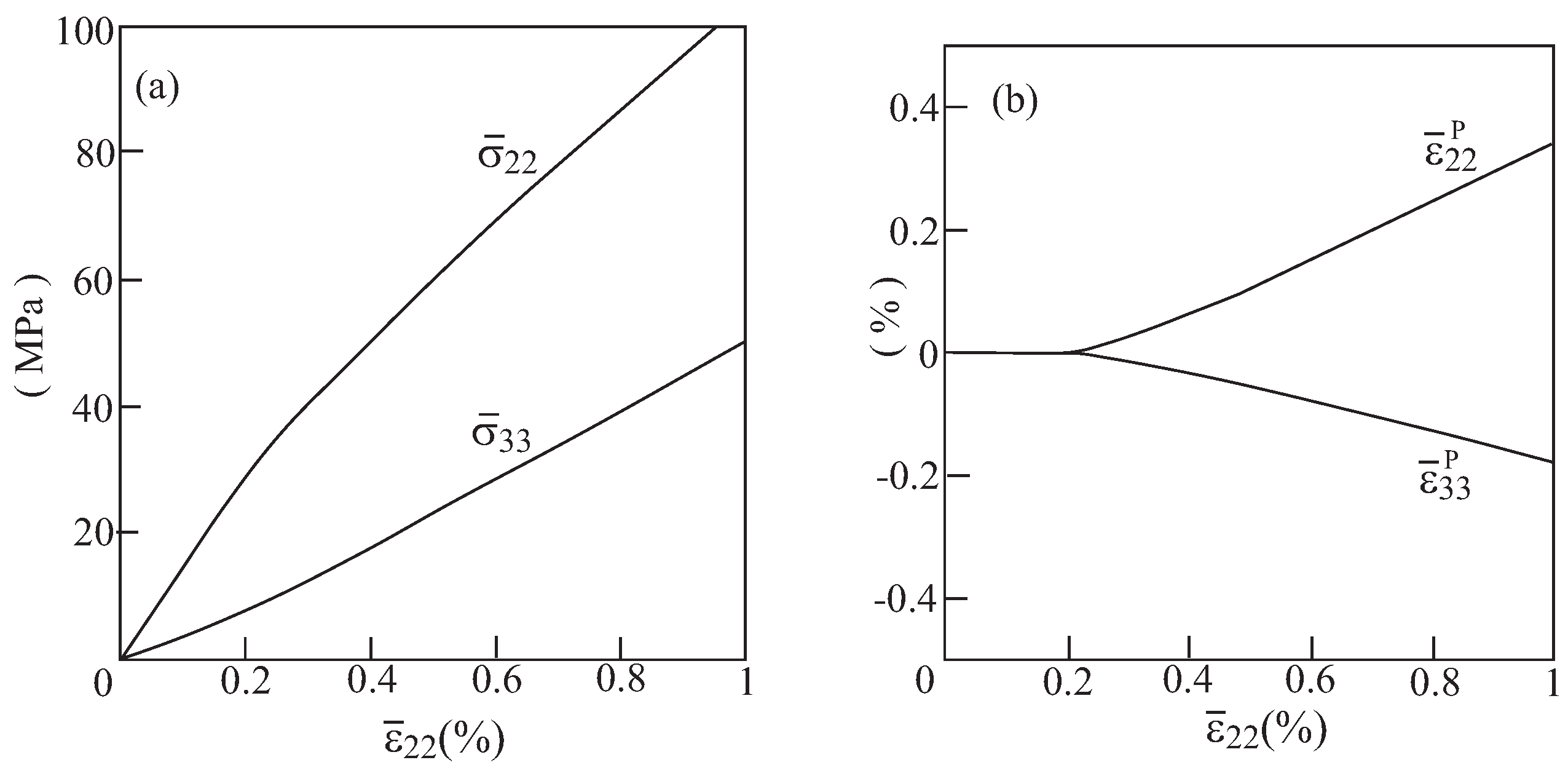
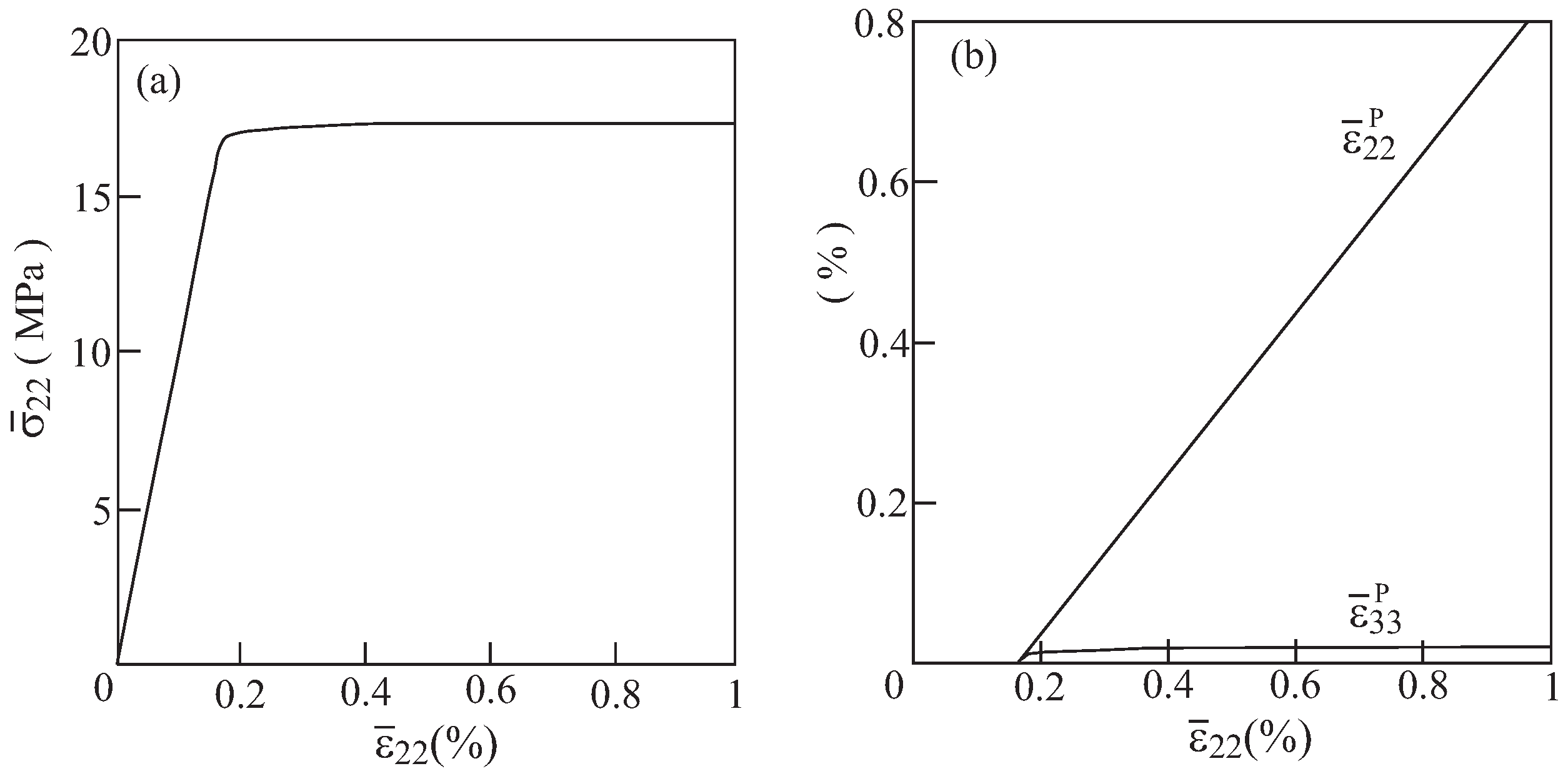
4. Conclusions
References
- Lakes, R. Foam structures with a negative Poisson’s ratio. Science 1987, 235, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.B.; Lakes, R.S. Nonlinear properties of polymer cellular materials with a negative Poisson’s ratio. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 4678–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.B.; Lakes, R.S. Analysis of elastic modulus of conventional foams and of re-entrant foam materals with a negative Poisson’s ratio. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1995, 37, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almgren, R.F. An isotropic three-dimensional structure with negative Poisson’s ratio = −1. J. Elast. 1985, 15, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.B.; Lakes, R.S. Nonlinear analysis of the Poisson’s ratio of negative Poisson’s ratio foams. J. Compos. Mater. 1995, 29, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P.; Lakes, R.S. Micromechanical analysis of dynamic behavior of conventional and negative Poisson’s ratio foams. J. Eng. Mater. Tech. 1996, 118, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.-C. Constitutive relationship of a material with unconventional Poisson’s ratio. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2003, 22, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, G.W. Composite materials with Poisson’s ratios close to −1. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1992, 40, 1105–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assidi, M.; Ganghoffer, J.F. Composites with auxetic inclusions showing both an auxetic behavior and enhancement of their mechanical properties. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overaker, D.W.; Cuitino, A.M.; Langrana, N.A. Elastoplastic micromechanical modeling of two-dimensiona irregular convex and nonconvex (re-entrant) hexagonal foams. J. Appl. Mech. 1998, 65, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.S.; Fleck, N.A. Isotropic constitutive models for mettalic foams. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2000, 48, 1253–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirrenberger, J.; Forest, S.; Jeulin, D; Colin, C. Homogenization of periodic auxetic materials. Proced. Eng. 2011, 10, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirrenberger, J.; Forest, S.; Jeulin, D. Elastoplasticity of auxetic materials. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 64, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.B.; Choi, K. Application of homogenization FEM analysis to regular and re-entrant honeycomb structures. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 4105–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawoto, Y. Seeing auxetic materoals from the mechanical point of view: A structural review on the negative Poisson ratio. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 58, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoti, W.L.; Koutsawa, Y.; Bonfoh, N.; Lipinski, P.; Belouettar, S. On the capability of micromechanics models to capture the auxetic behavior of fibers/particles reinforced composite materials. Compos. Struct. 2011, 94, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudi, J.; Arnold, S.M.; Bednarcyk, B.A. Micromechanics of Composite Materials: A Generalized Multiscale Analysis Approach; Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aboudi, J. The generalized method of cells and high-fidelity generalized method of cells micromechanical models—A review. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2004, 11, 329–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudi, J.; Gilat, R. Micromechanical analysis of lattice blocks. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 4372–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamkarov, A.L.; Kolpakov, A.G. Analysis, Design and Optimization of Composite Structures; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Arias, F.; Brittain, S.T.; Zhao, X.-M.; Grzybowski, B.; Torquato, S.; Whitesides, G.M. Making negative Poisson’s ratio microstructures by soft lithography. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 1186–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.M. Mechanics of Composite Materials; Scripta Book Company: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, U.D.; Sigmund, O.; Bouwsta, S. Design and fabrication of compliant micromechanisms and structures with negative Poisson’s ratio. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1997, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Topology Optimization; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Haj-Ali, R.; Aboudi, J. Formulation of the high-fidelity generalized method of cells with arbitrary cell geometry for refined micromechanics and damage in composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 3447–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gilat, R.; Aboudi, J. Behavior of Elastoplastic Auxetic Microstructural Arrays. Materials 2013, 6, 726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6030726
Gilat R, Aboudi J. Behavior of Elastoplastic Auxetic Microstructural Arrays. Materials. 2013; 6(3):726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6030726
Chicago/Turabian StyleGilat, Rivka, and Jacob Aboudi. 2013. "Behavior of Elastoplastic Auxetic Microstructural Arrays" Materials 6, no. 3: 726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6030726
APA StyleGilat, R., & Aboudi, J. (2013). Behavior of Elastoplastic Auxetic Microstructural Arrays. Materials, 6(3), 726-737. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6030726




