On the Effects of Hot Forging and Hot Rolling on the Microstructural Development and Mechanical Response of a Biocompatible Ti Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alloy Specimens

| Alloy | Zr | Nb | Ta | Pd | Fe | O | N | H | C | Ti | Tβ (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15.52 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 0.18 | 0.026 | 0.200 | 0.042 | 0.0011 | <0.005 | Bal. | 810 °C |
| B | 16.55 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 0.01 | 0.040 | 0.275 | 0.085 | 0.0010 | 0.007 | Bal. | 830 °C |
2.2. Solution Treatment and Microstructural Observation
2.3. Hot-Forging Test
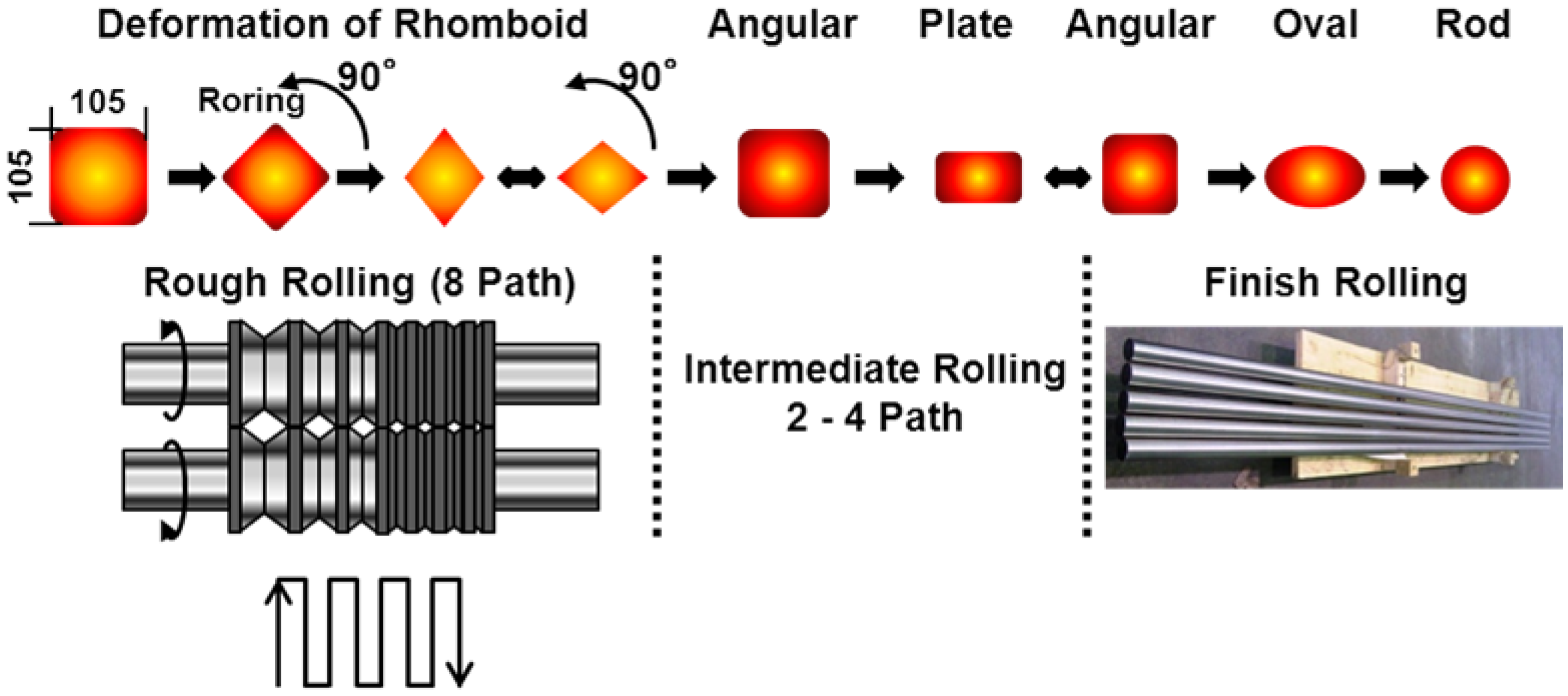
2.4. Hot-Rod-Rolling Test
2.5. Mechanical Tests
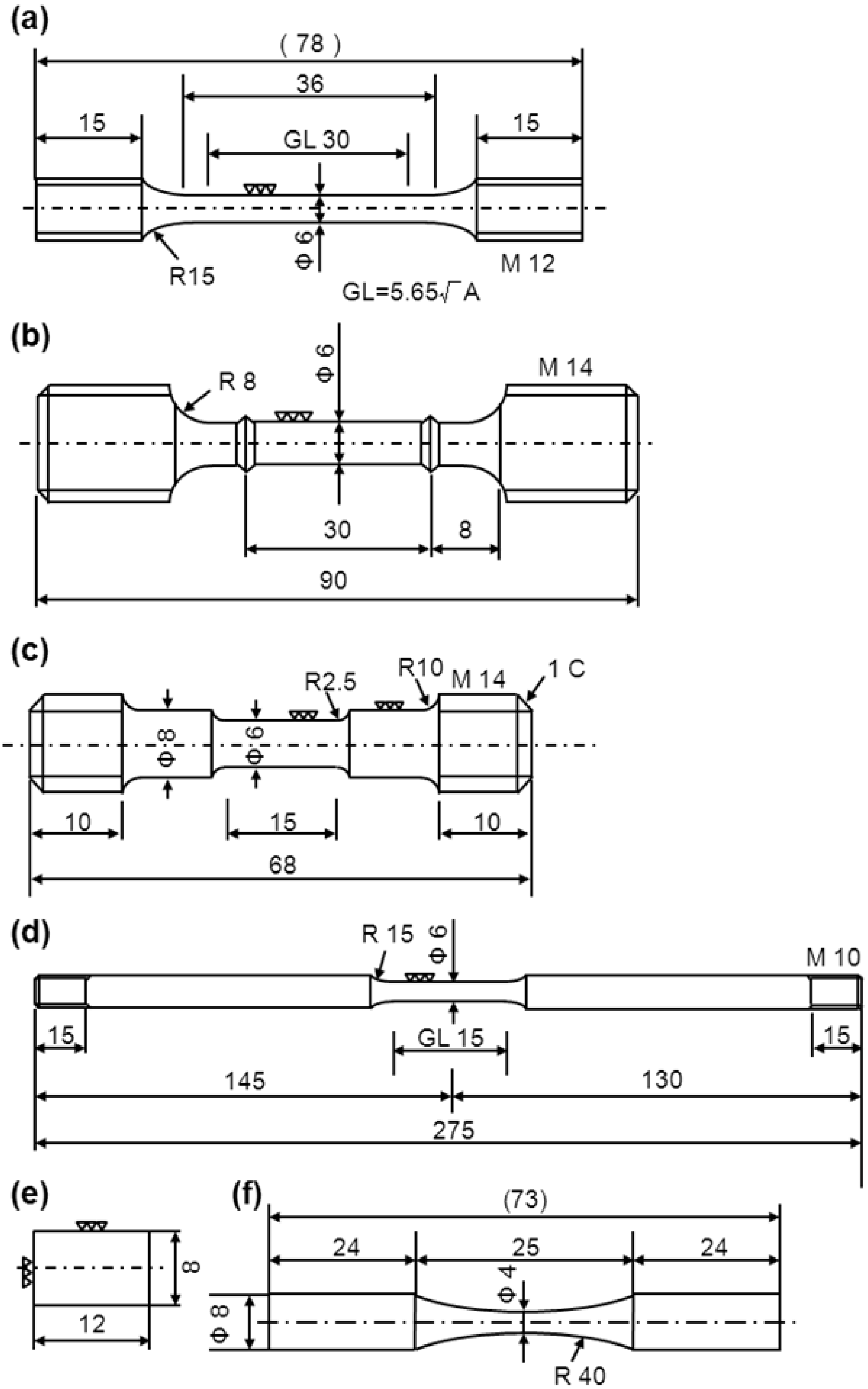
2.6. Fatigue Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Solution-Treatment on Microstructure
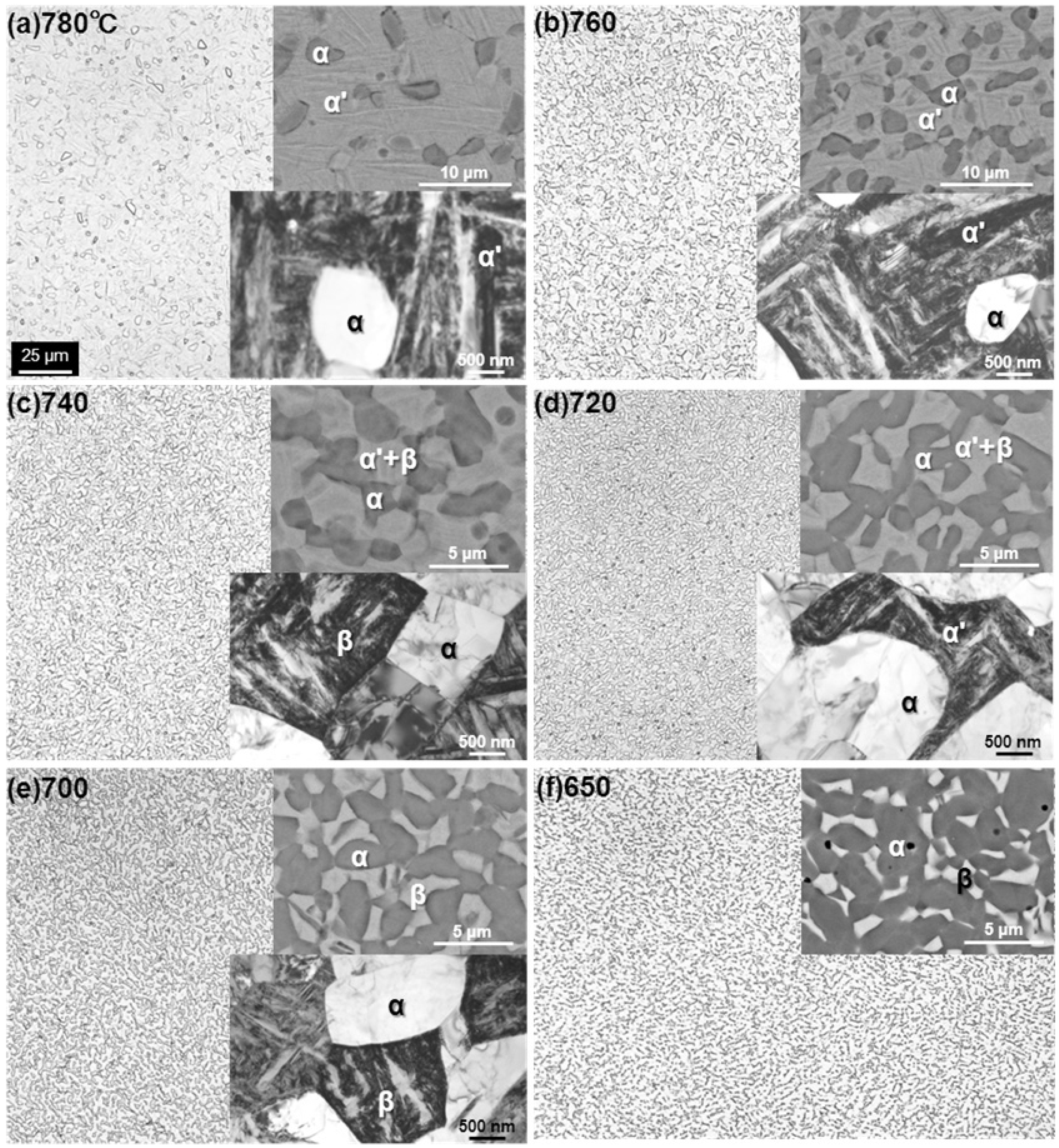
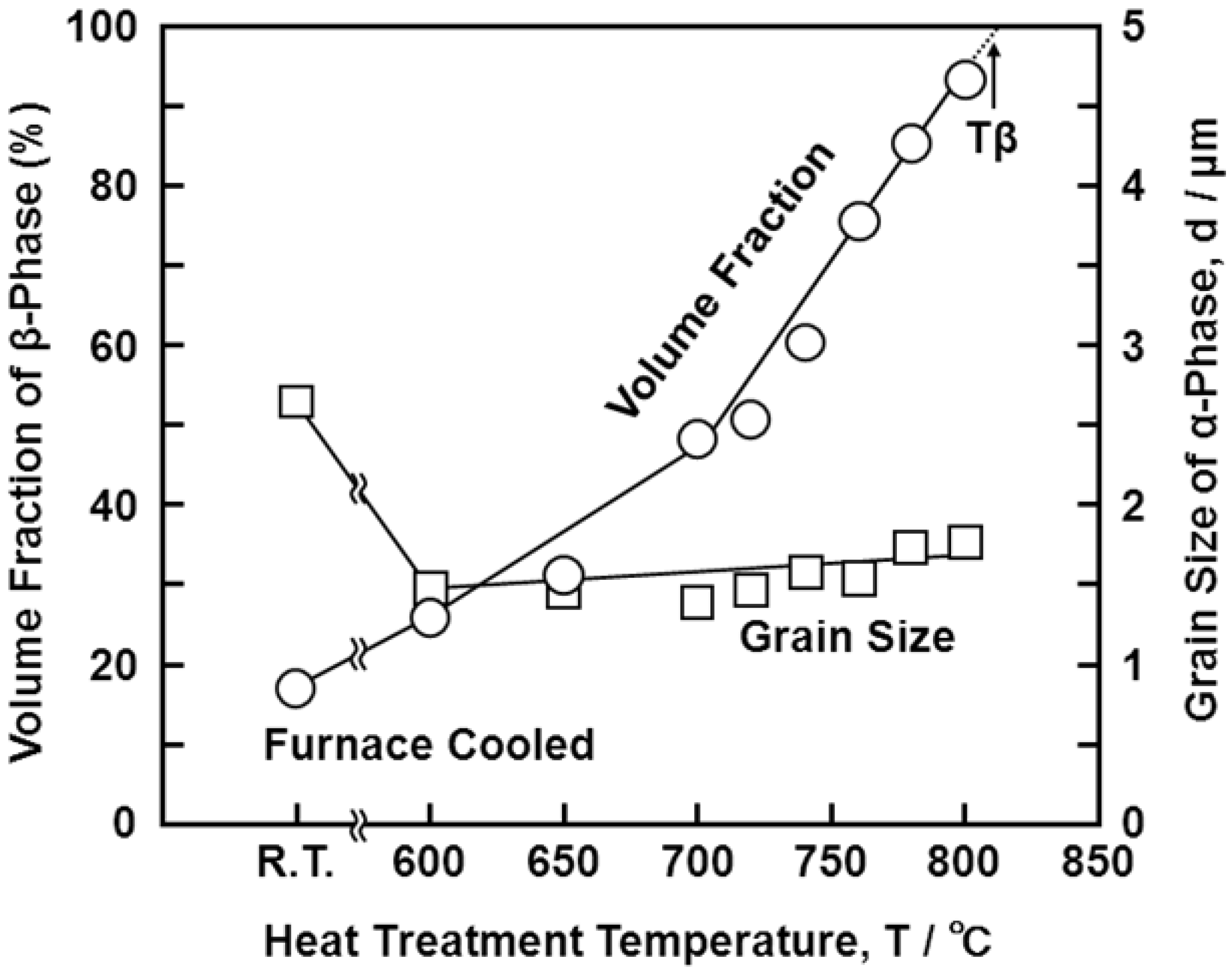

3.2. Effect of Hot Forging on Microstructure
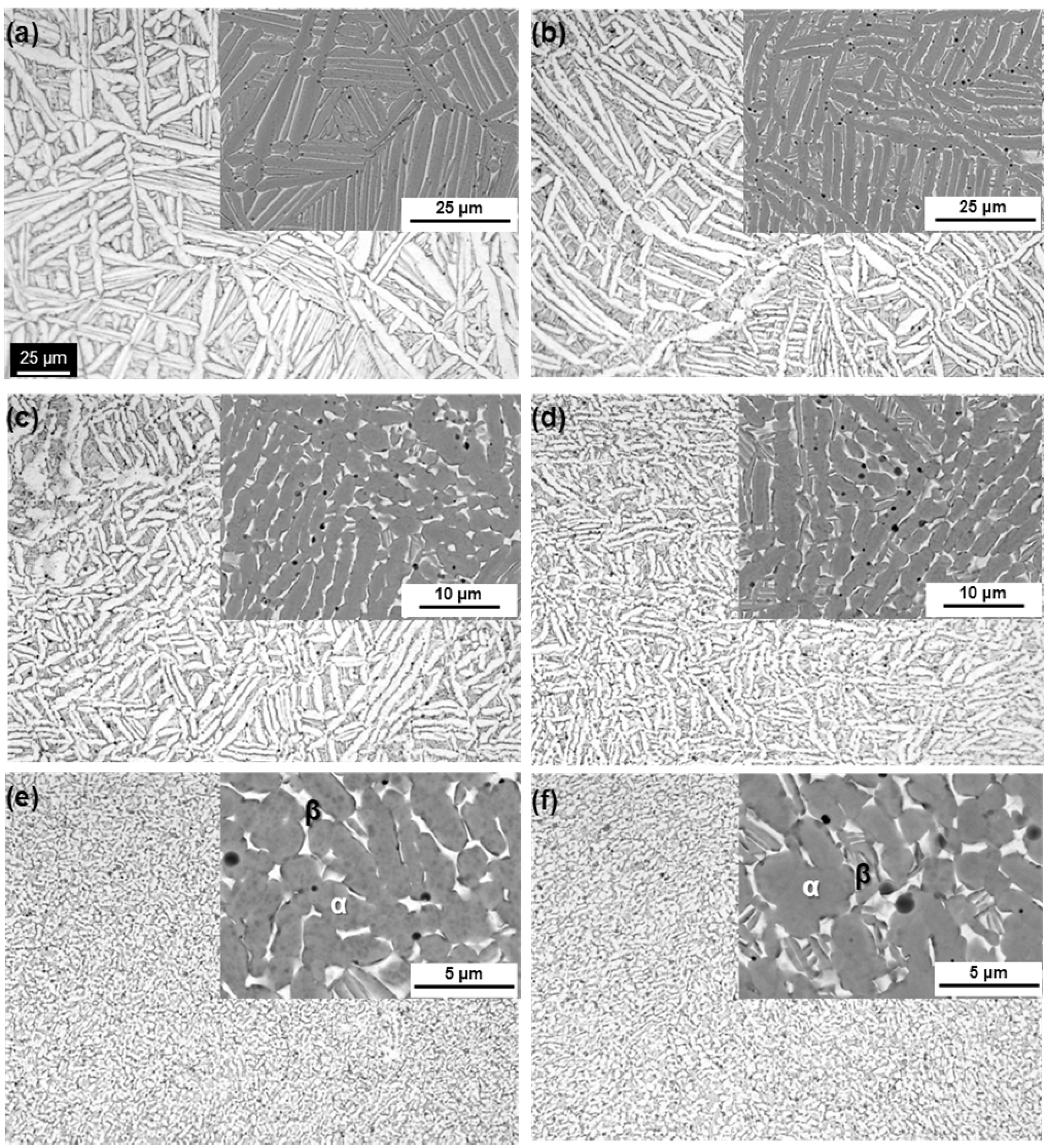
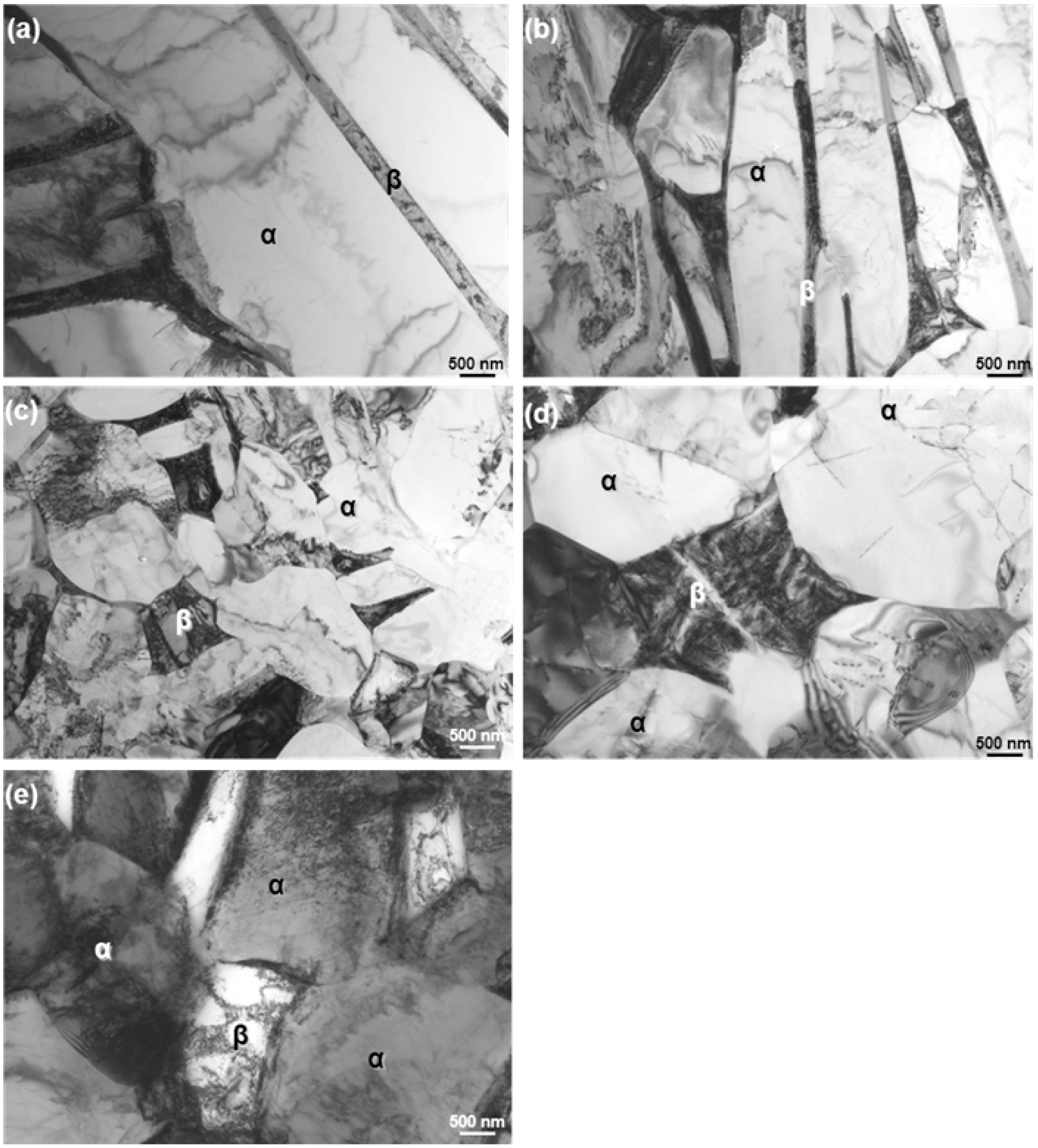
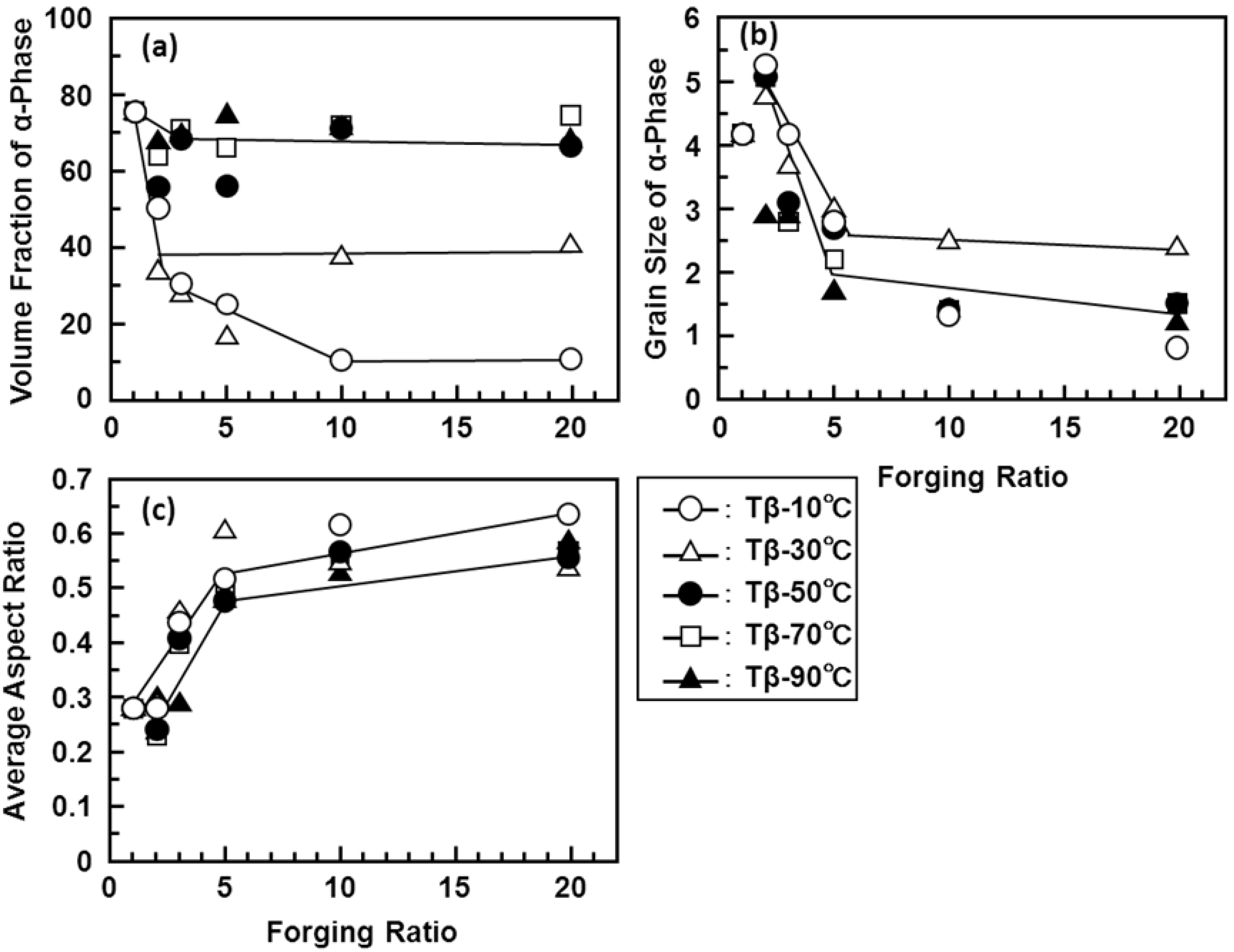
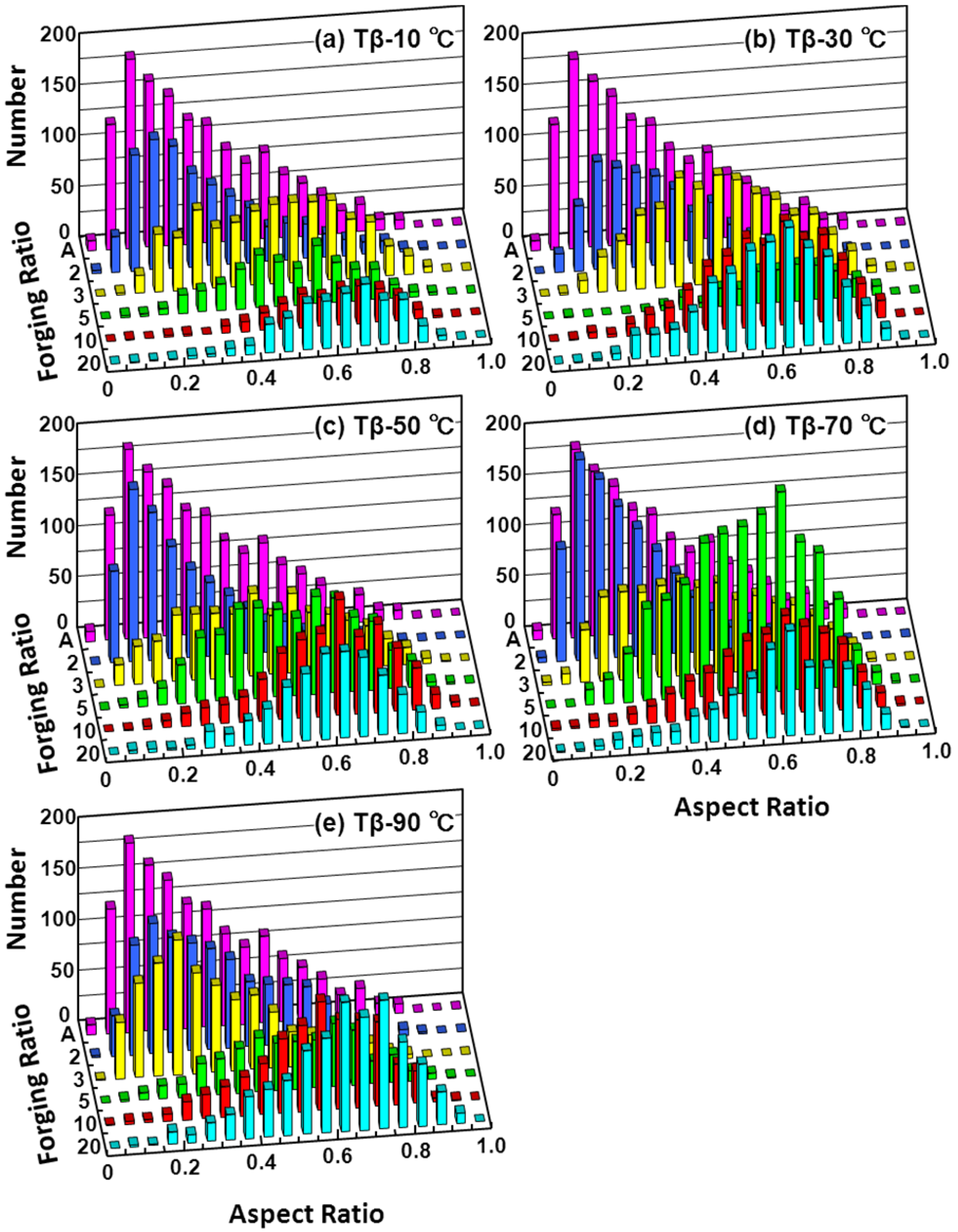
3.3. Effects of Forging on Room-Temperature Mechanical Properties of Ti-15Zr-4Nb-4Ta Alloy
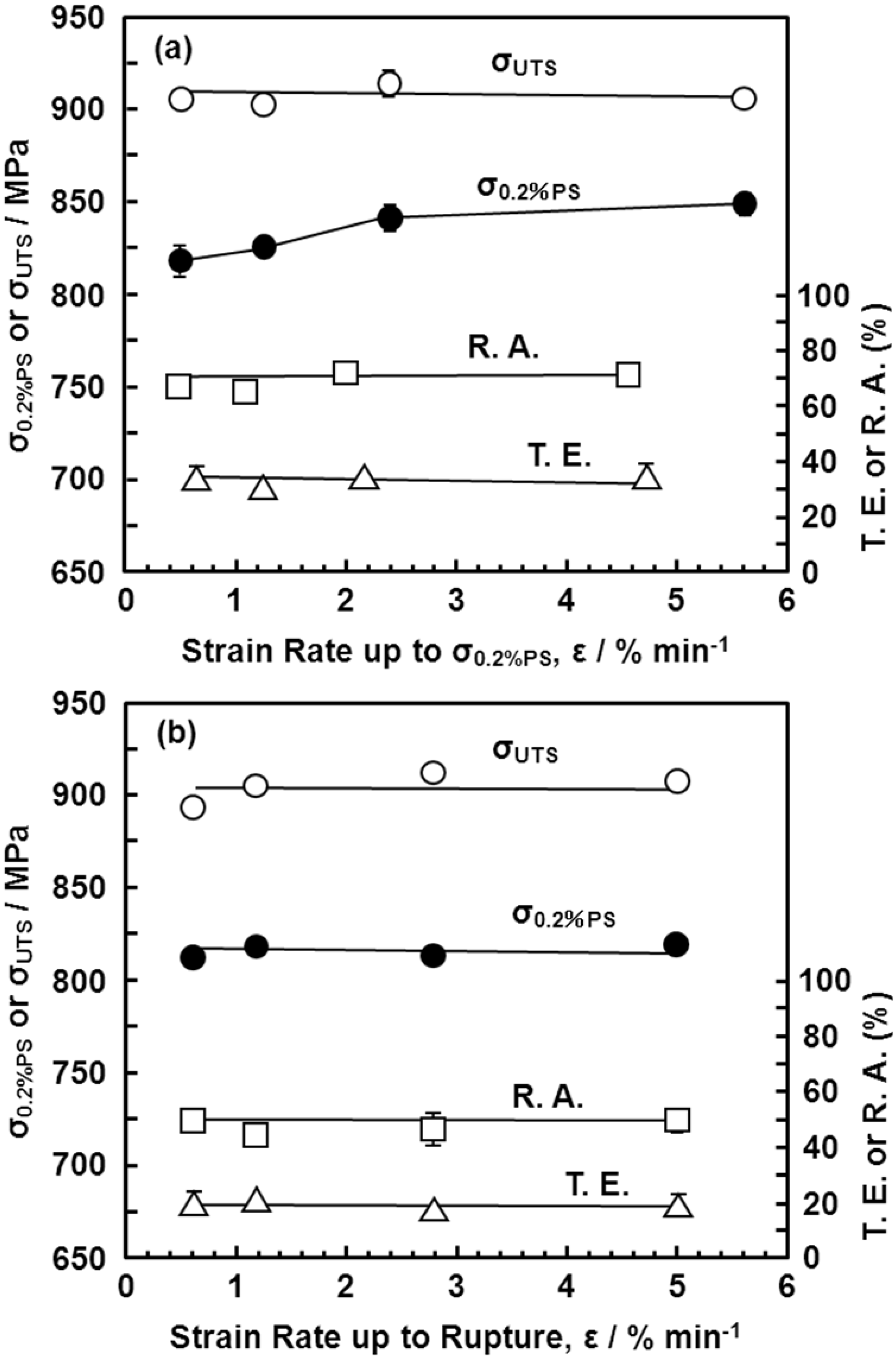

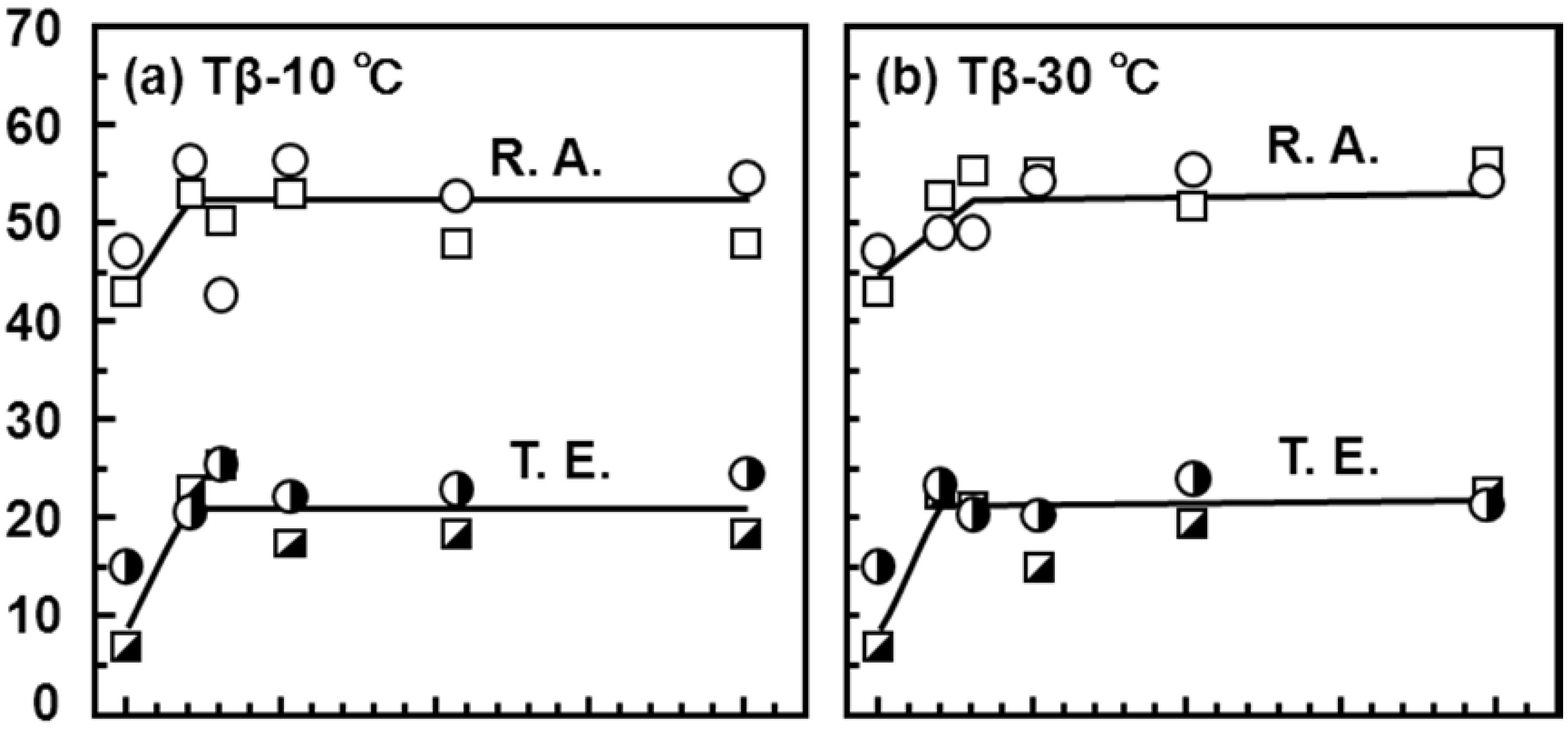
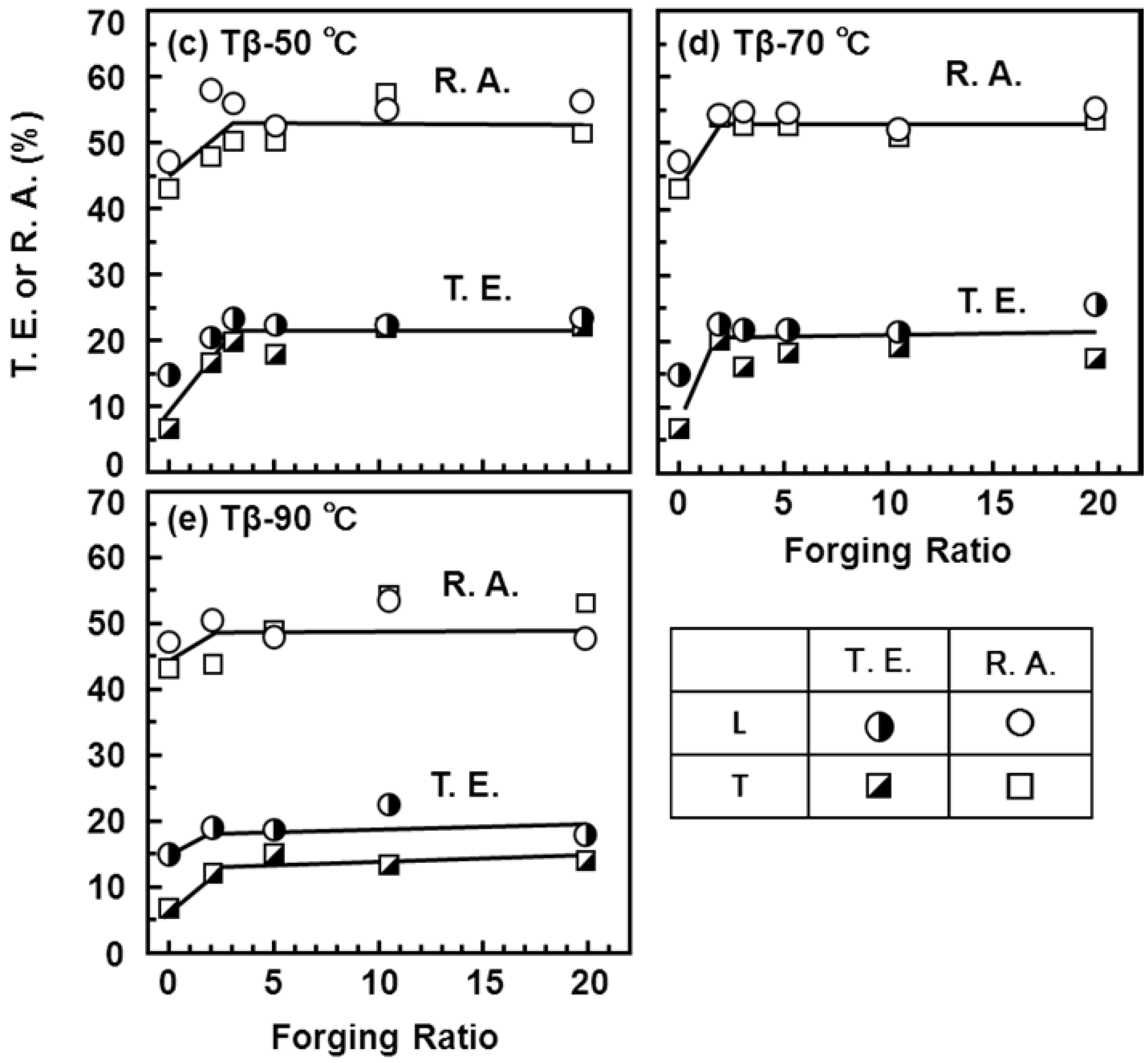
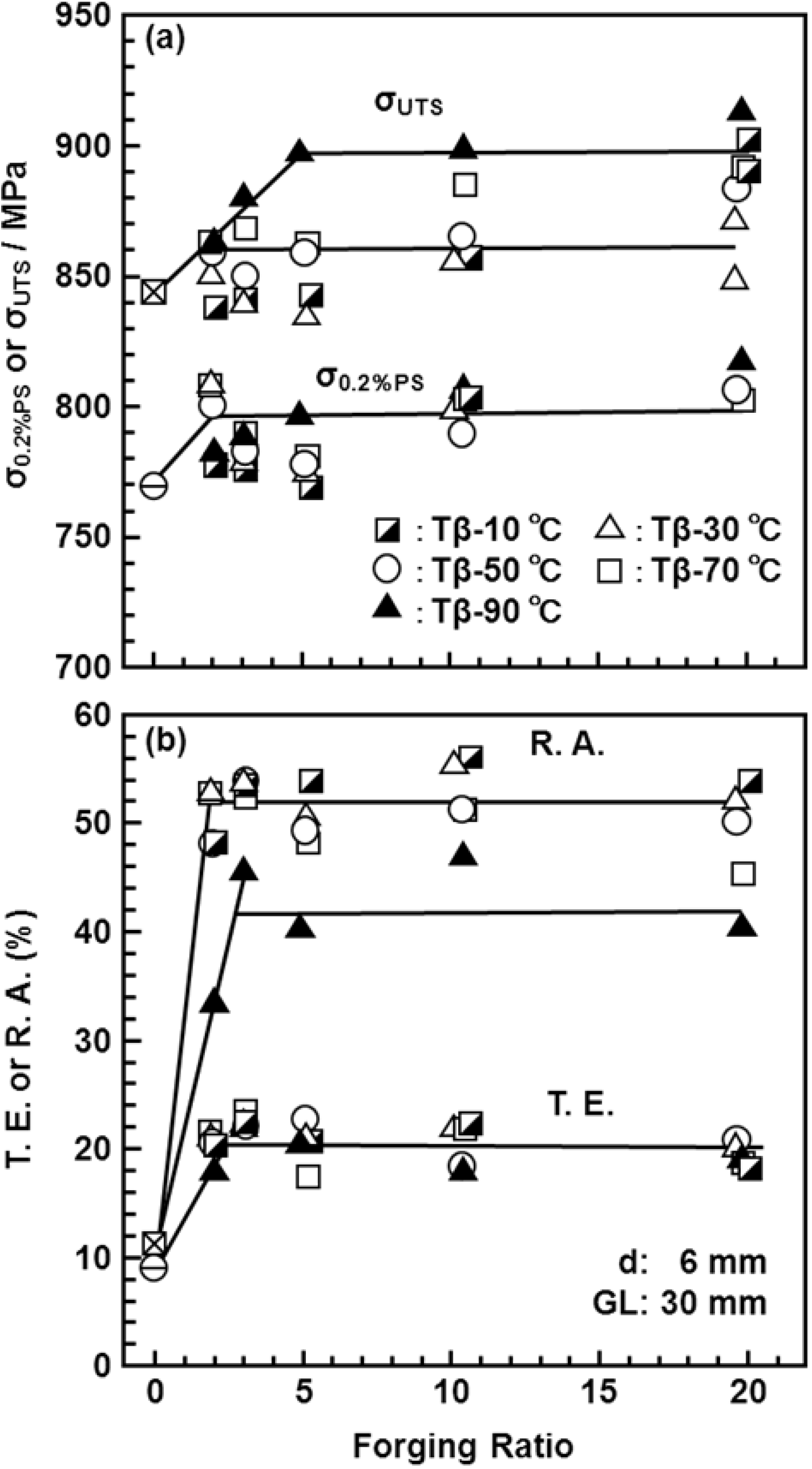
3.4. Effect of Forging on Fatigue Strength
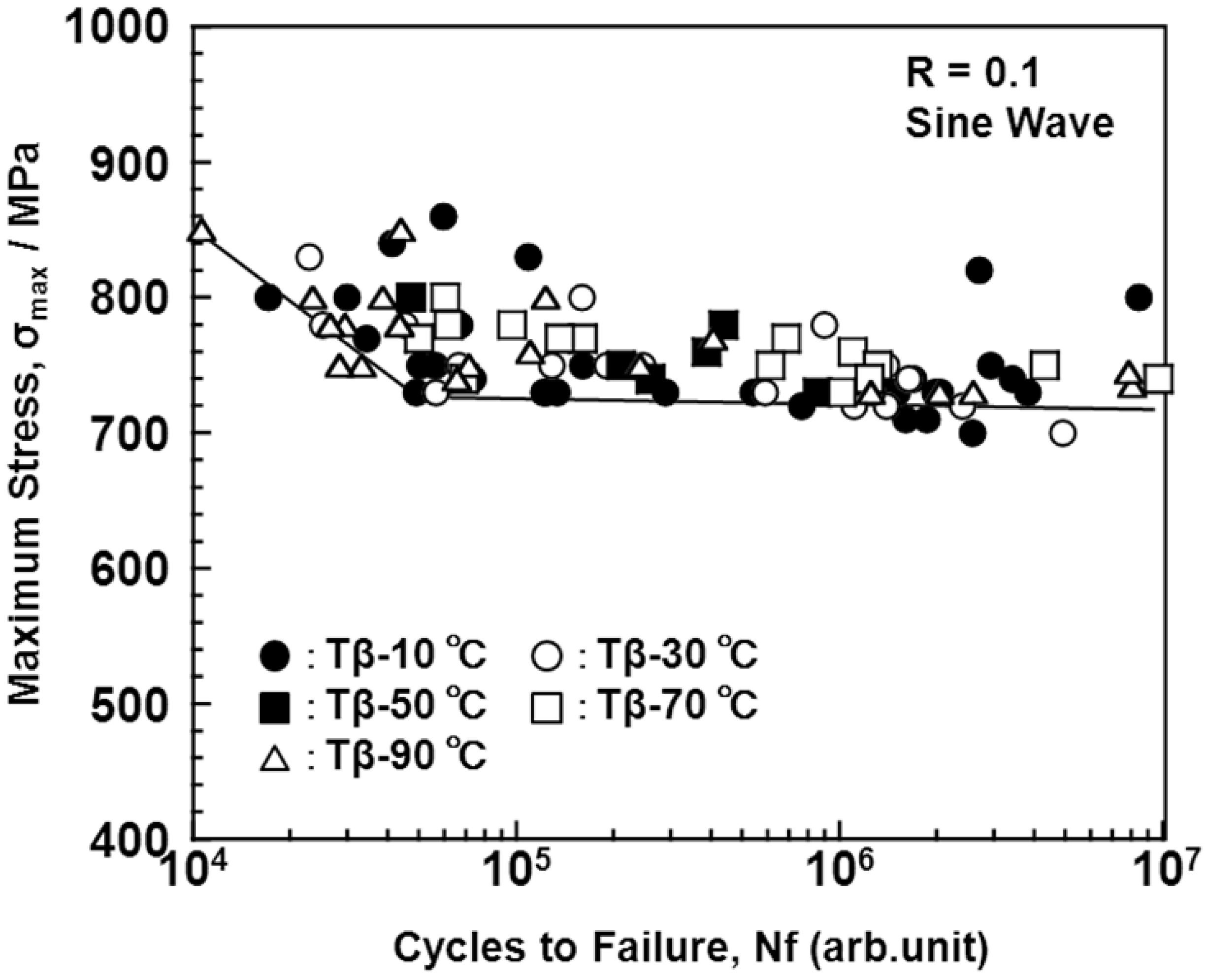
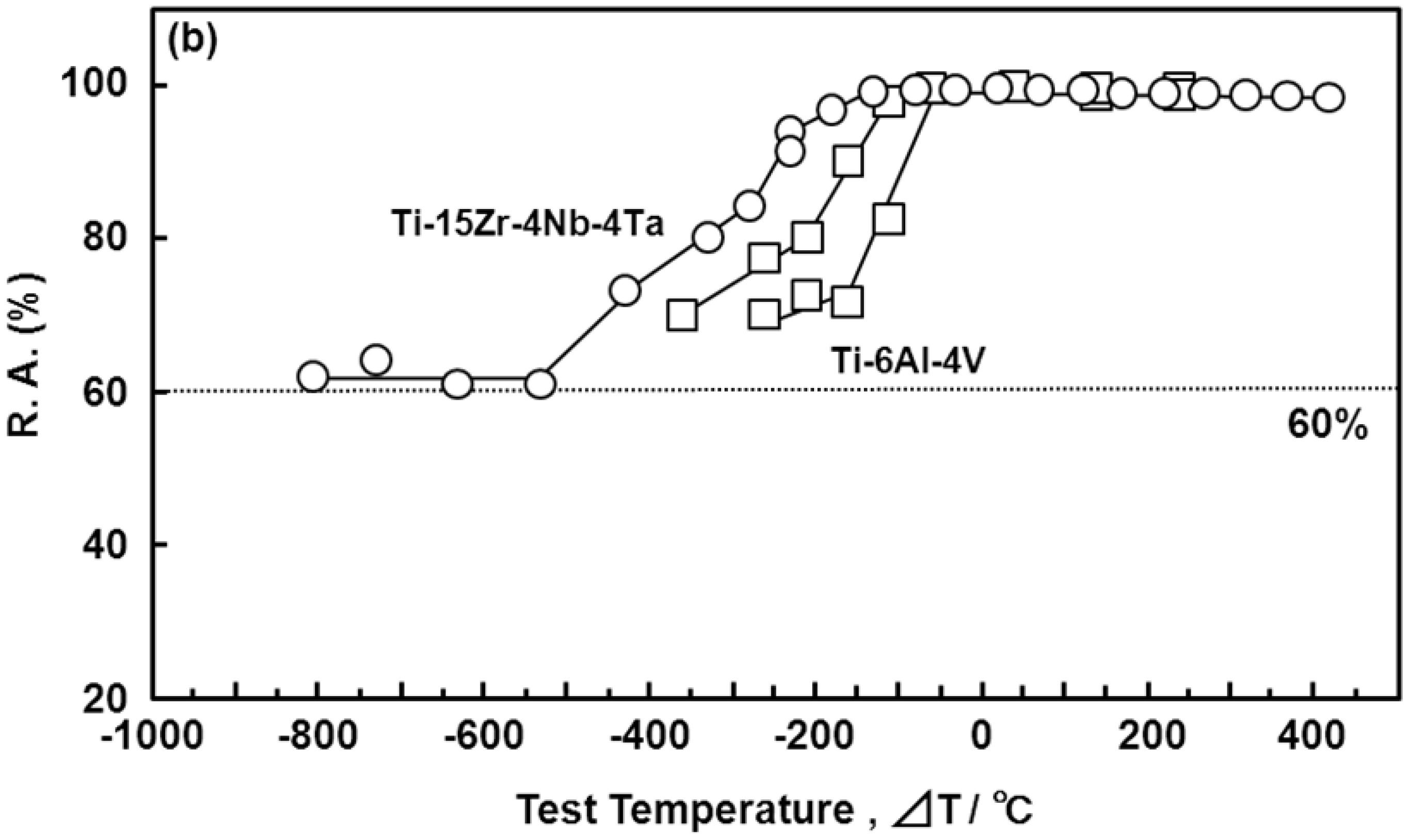
3.5. Manufacturing Equivalency of Ti-15Zr-4Nb-4Ta Alloy
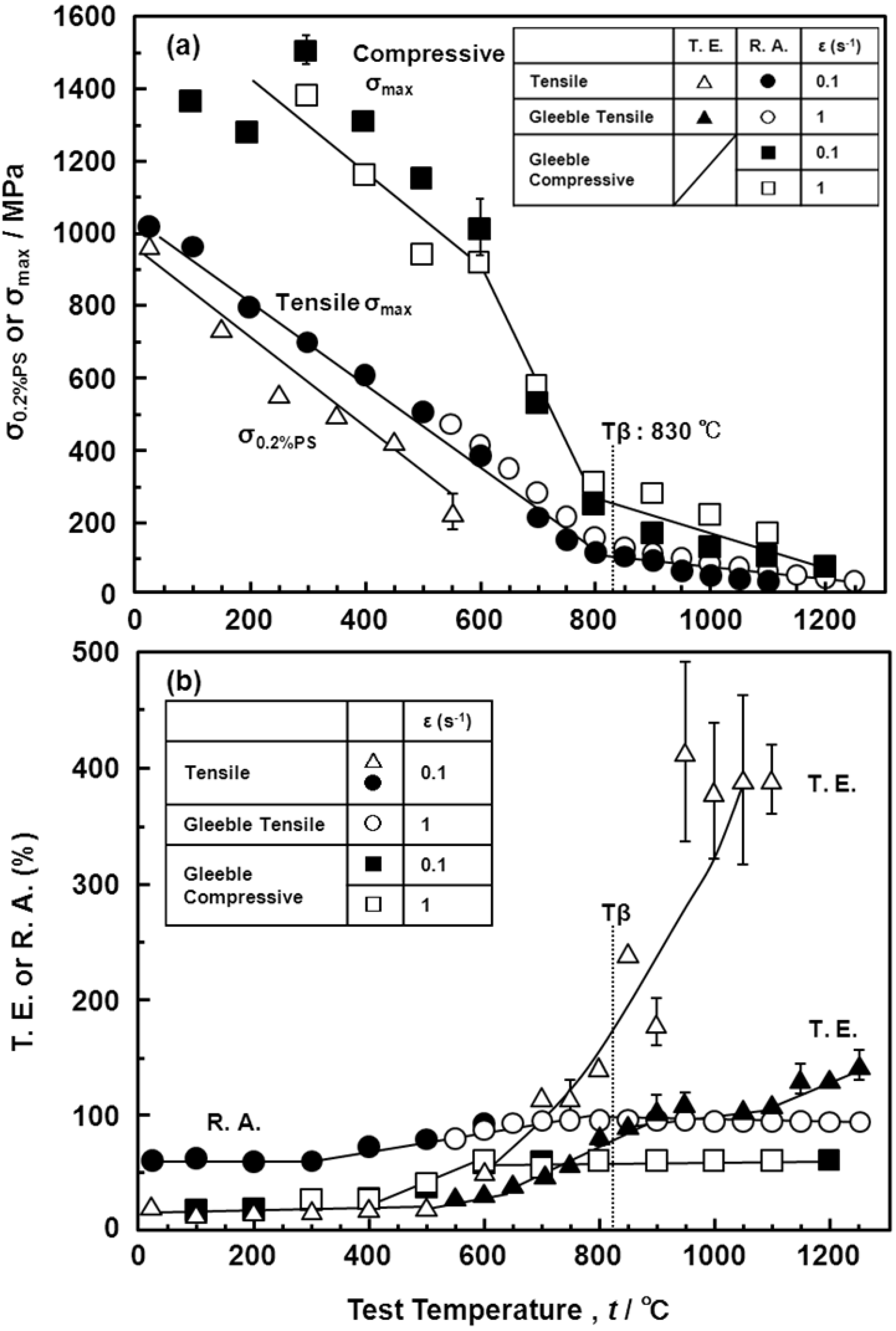
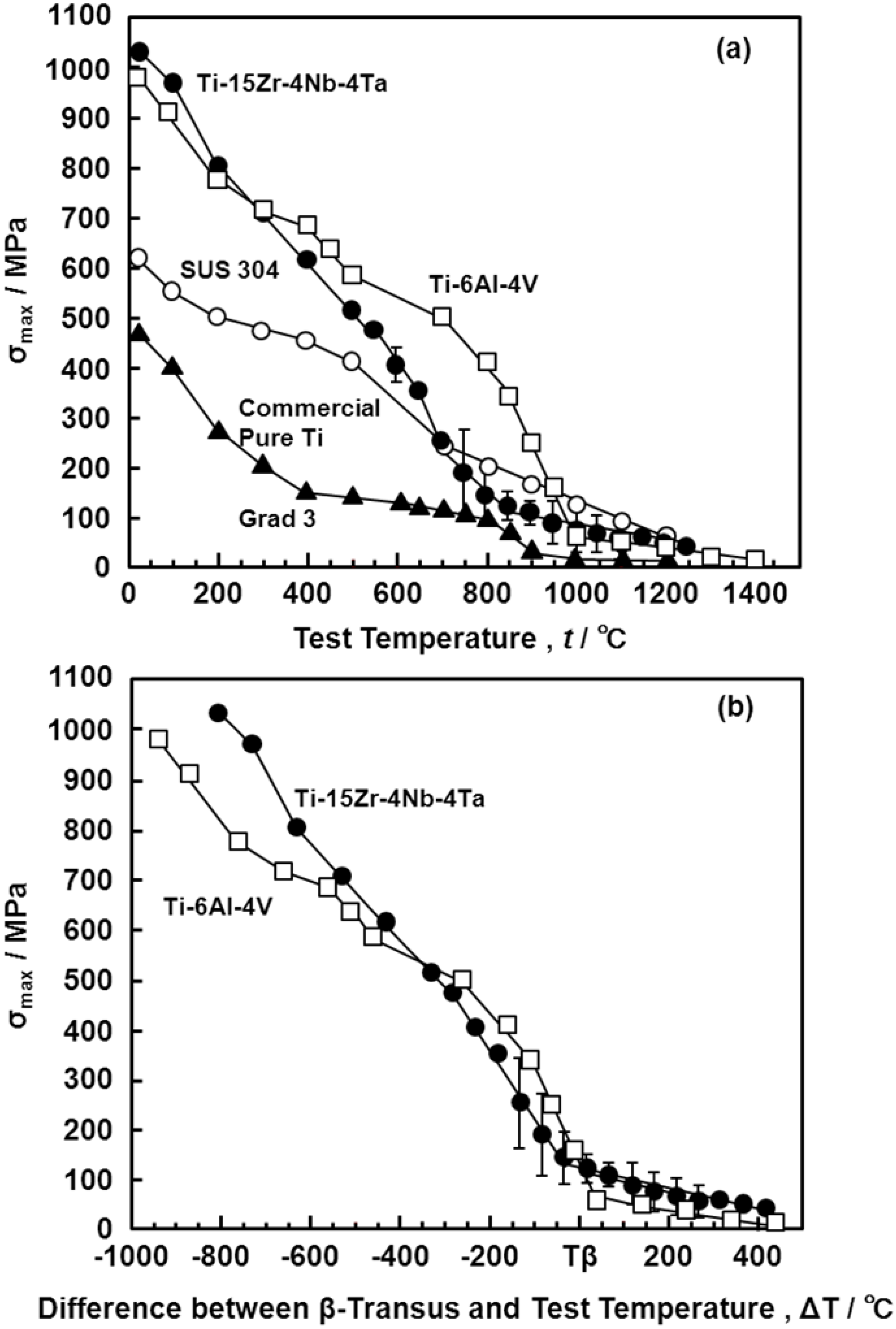
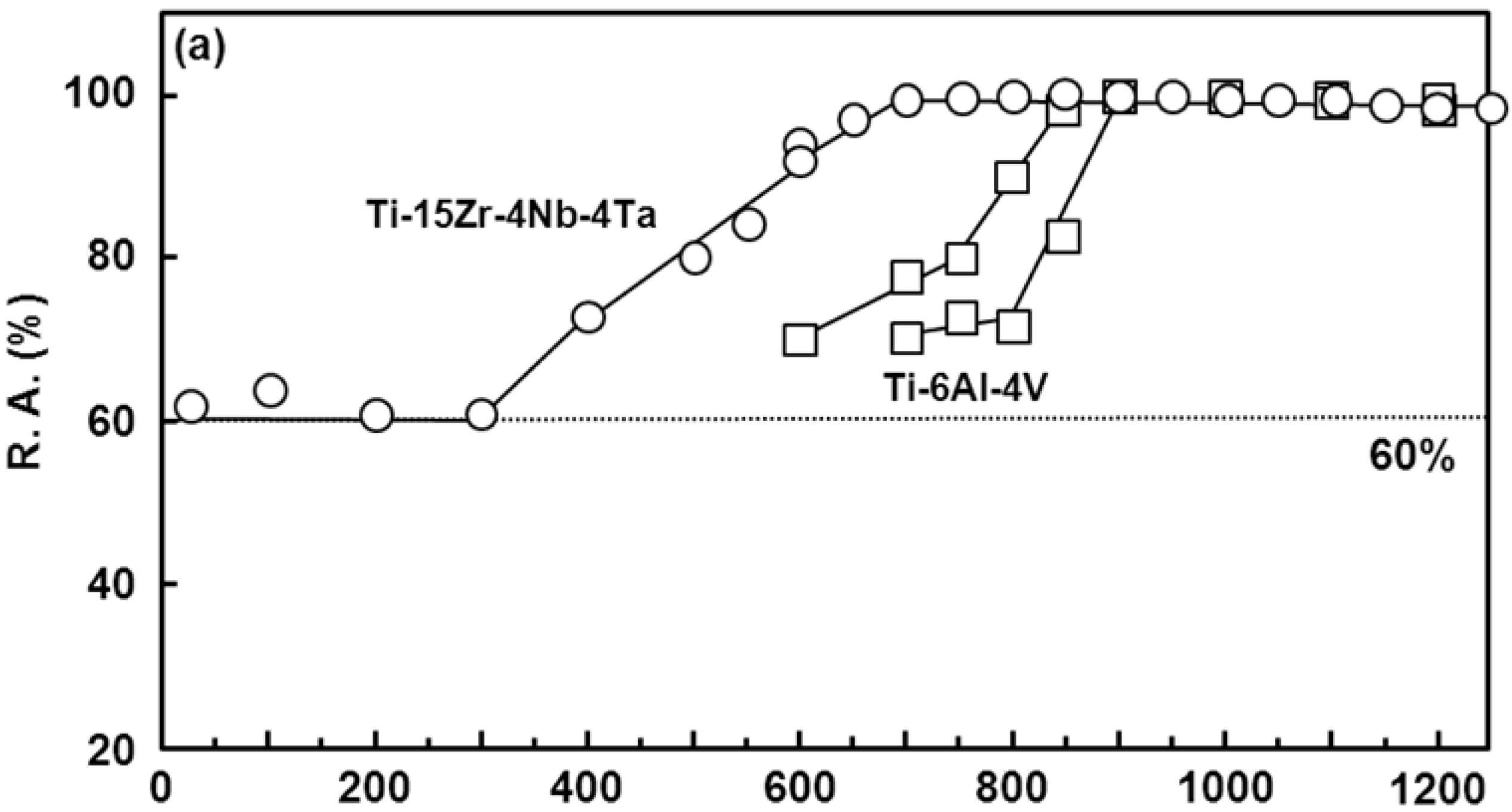
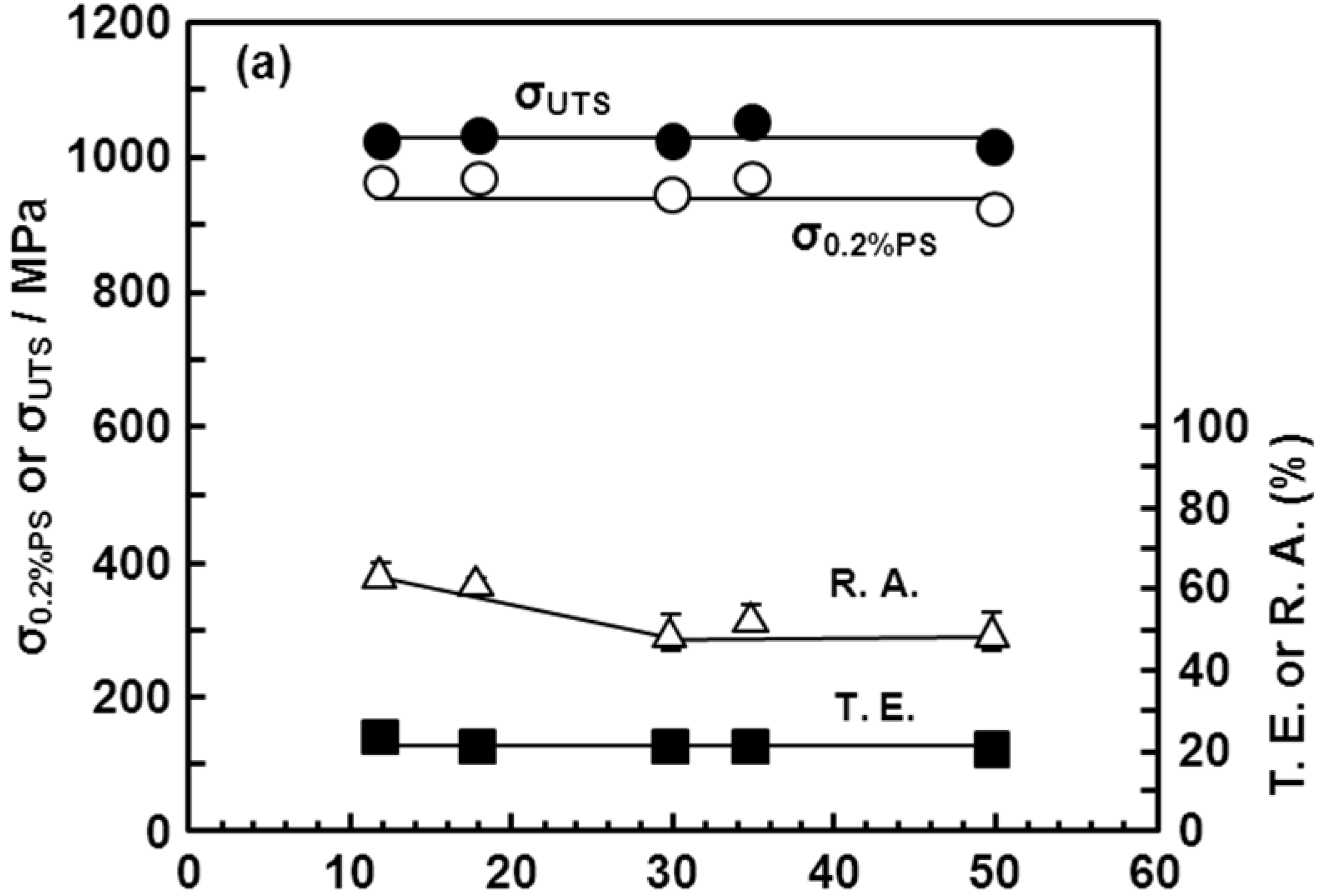
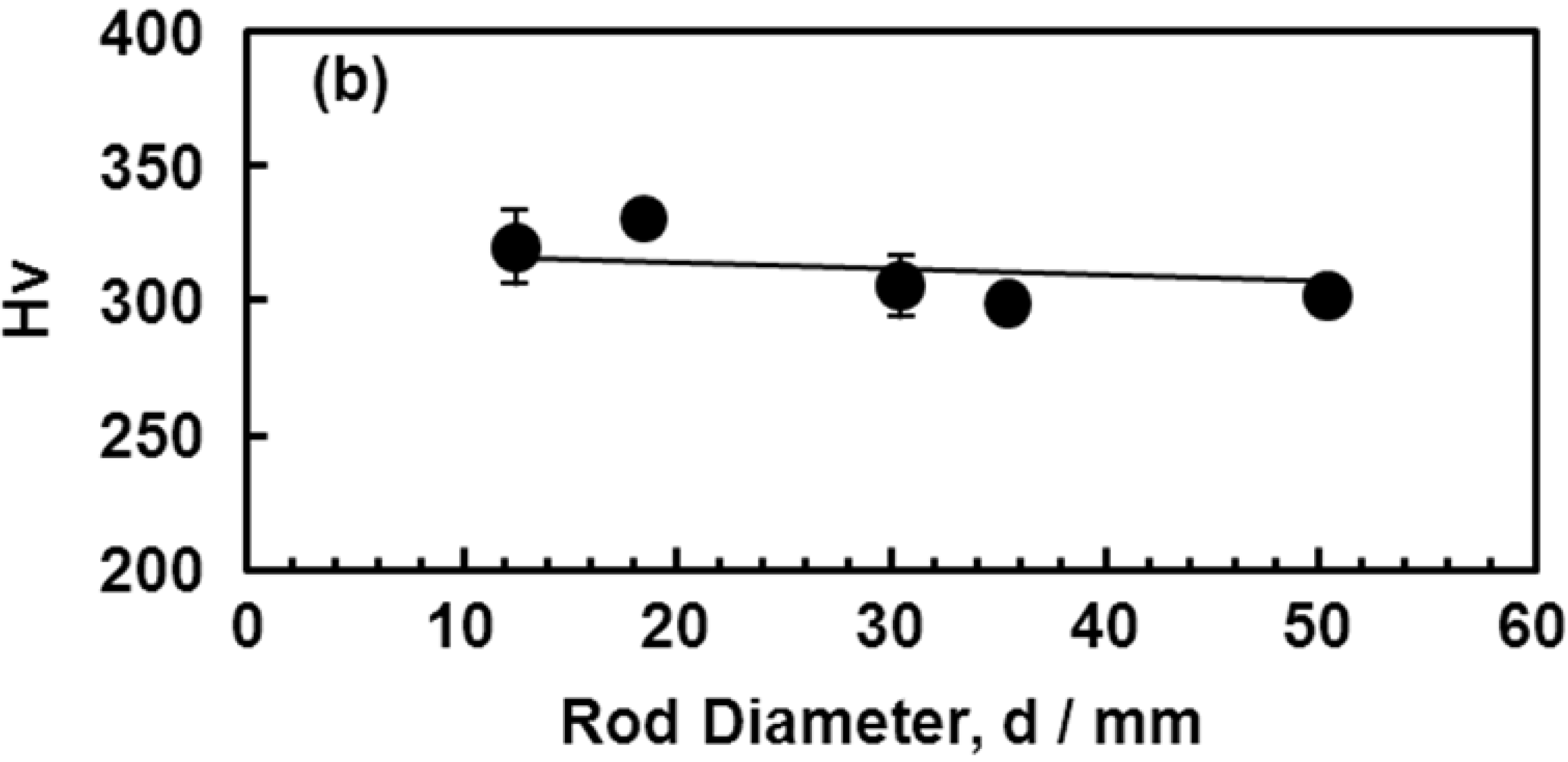
3.6. Room-Temperature Mechanical Properties of Hot-rolled Ti-15Zr-4Nb-4Ta Alloy
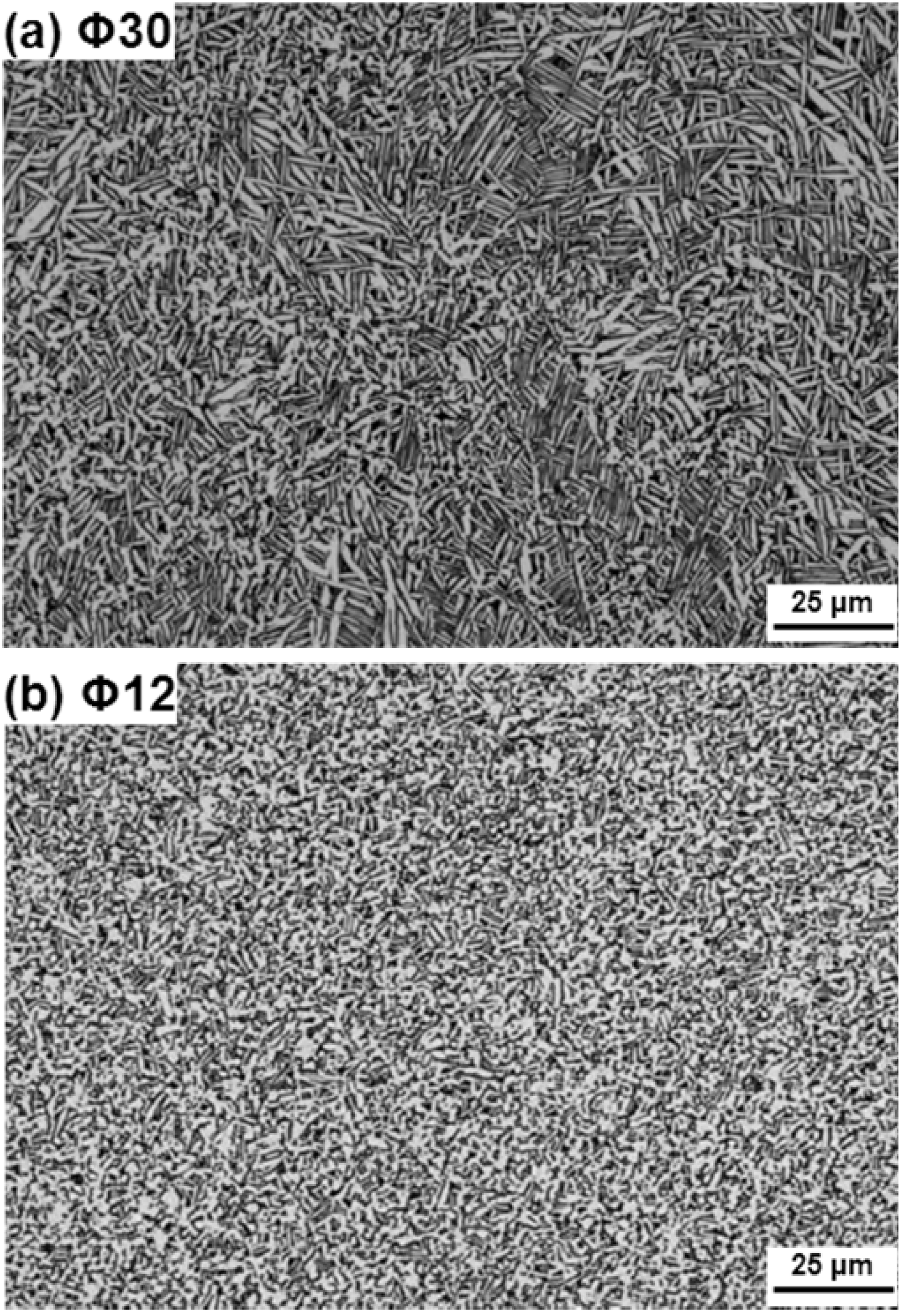
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Li, S.J.; Cui, T.C.; Hao, Y.L.; Yang, R. Fatigue properties of a metastable β-type titanium alloy with reversible phase transformation. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Ju, C.P.; Lin, J.H.C. A comparison of the fatigue behavior of cast Ti-7.5Mo with C.P. titanium, Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-13Nb-13Zr alloys. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niinomi, M. Fatigue characteristics of metallic biomaterials. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S.; Laube, W.; Vécsei, V. The fatigue strength of small diameter tibial nails. Injury 2001, 32, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; López, V. Failure analysis of a Ti6Al4V cementless HIP prosthesis. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.S.; Postak, P.D.; Greenwald, A.S. Femoral stem fatigue characteristics of modular hip designs. In Modularity of Orthopedic Implants; Marlowe, D.E., Parr, J.E., Mayor, M.B., Eds.; American Society for Testing and Materials Special Technical Publication: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997; pp. 226–243. [Google Scholar]
- Steinemann, S.G. Corrosion of surgical implants-in Vivo and in Vitro tests. In Evaluation of Biomaterials; Winter, G.D., Leray, J.L., de Groot, K., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1980; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Steinemann, S.G. Compatibility of titanium in soft and hard tissue—The ultimate is osseointegration. In Materials for Medical Engineering; Stallforth, H., Revell, P., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1999; pp. 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, Y.; Ito, Y.; Ito, A.; Tateishi, T. Effect of alloying elements on mechanical properties of titanium alloys for medical implants. Mater. Trans. JIM 1993, 34, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Rao, S.; Asao, S.; Tateishi, T.; Katsuda, S.; Furuki, Y. Effects of Ti, Al and V concentrations on cell viability. Mater. Trans. JIM 1998, 39, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Kyo, K.; Ito, Y.; Tateishi, T. Effects of Mo and Pd on corrosion resistance of V-free titanium alloys for medical implants. Mater. Trans. JIM 1997, 38, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Tateishi, T.; Ito, Y. Corrosion resistance of implant alloys in pseudo physiological solution and role of alloying elements in passive films. Mater. Trans. JIM 1997, 38, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Okazaki, Y.; Tateishi, T.; Ito, Y. In vitro biocompatibility, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance of Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Pd and Ti-Sn-Nb-Ta-Pd alloys. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, Y.; Ito, Y.; Ito, A.; Tateishi, T. New titanium alloys to be considered for medical implants. In Medical Applications of Titanium and Its Alloys: The Material and Biological Issues; Brown, S.A., Lemons, J.E., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, Y.; Rao, S.; Tateishi, T.; Ito, Y. Cytocompatibility of various metals and development of new titanium alloys for medical implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1998, 243, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Ito, Y. New Ti alloy without Al and V for medical implants. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2000, 2, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Nishimura, E. Effect of metal released from Ti alloy wear powder on cell viability. Mater. Trans. JIM 2000, 41, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Nishimura, E.; Nakada, H.; Kobayashi, K. Surface analysis of Ti-15Zr-4Nb-4Ta alloy after implantation in rat tibia. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, Y. Effect of friction on anodic polarization properties of metallic biomaterials. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2071–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, Y.; Gotoh, E. Comparison of metal release from various metallic biomaterials in vitro. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, Y.; Gotoh, E.; Nishimori, M.; Katsuda, S.; Manabe, T.; Kobayashi, K. Osteocompatibility of stainless steel, Co-Cr-Mo, Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-15Zr-4Nb-4Ta alloy implants in rat bone tissue. Mater. Trans. JIM 2005, 46, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Gotoh, E.; Manabe, T.; Kobayashi, K. Comparison of metal concentrations in rat tibia tissues with various metallic implants. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5913–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titanium Materials for Surgical Implant Applications Part 4 Wrought Titanium 15-Zirconium 4-Niobium 4-Tantalum Alloy, version 7401-4-2002; Japanese Industrial Standards Committee: Tokyo, Japan, 2002.
- Okazaki, Y.; Gotoh, E. Comparison of fatigue strengths of biocompatible Ti-15Zr-4Nb-4Ta alloy and other materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 31, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM. Alpha-beta alloy, Ti-6Al-4V: Fraction of phase constituents after quenching. In Titanium Alloys; Boyer, R., Welsch, G., Collings, E.W., Eds.; The Materials Information Society: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1994; pp. 490–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, S.; Oyama, H. α-β Type Titanium Alloy. US Patent 6,849,231-B2, 1 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kobe Homepage. Available online: http://www.kobelco.co.jp/titan/characteristic/index.html (accessed on 18 August 2012).
- Suzuki, H.; Takeo, A.; Aoyagi, K.; Fujii, H.; Tanabe, K. Hot workability of Ti-6Al-4V alloys. J. Iron Steel 1986, 72, 587–594. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Fujii, H. Hot workability of various kinds of titanium alloys. In Proceedings of the 114th ISIJ Meeting, Kumamoto, Japan, 11 October 1987.
- Okazaki, Y.; Rao, S.; Ito, Y.; Tateishi, T. Corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, corrosion fatigue strength and cytocompatibility of new Ti alloys without Al and V. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1197–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Okazaki, Y. On the Effects of Hot Forging and Hot Rolling on the Microstructural Development and Mechanical Response of a Biocompatible Ti Alloy. Materials 2012, 5, 1439-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5081439
Okazaki Y. On the Effects of Hot Forging and Hot Rolling on the Microstructural Development and Mechanical Response of a Biocompatible Ti Alloy. Materials. 2012; 5(8):1439-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5081439
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkazaki, Yoshimitsu. 2012. "On the Effects of Hot Forging and Hot Rolling on the Microstructural Development and Mechanical Response of a Biocompatible Ti Alloy" Materials 5, no. 8: 1439-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5081439
APA StyleOkazaki, Y. (2012). On the Effects of Hot Forging and Hot Rolling on the Microstructural Development and Mechanical Response of a Biocompatible Ti Alloy. Materials, 5(8), 1439-1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5081439




