Efficacy and Durability in Direct Labeling of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Organosilica, Dextran, and PEG Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
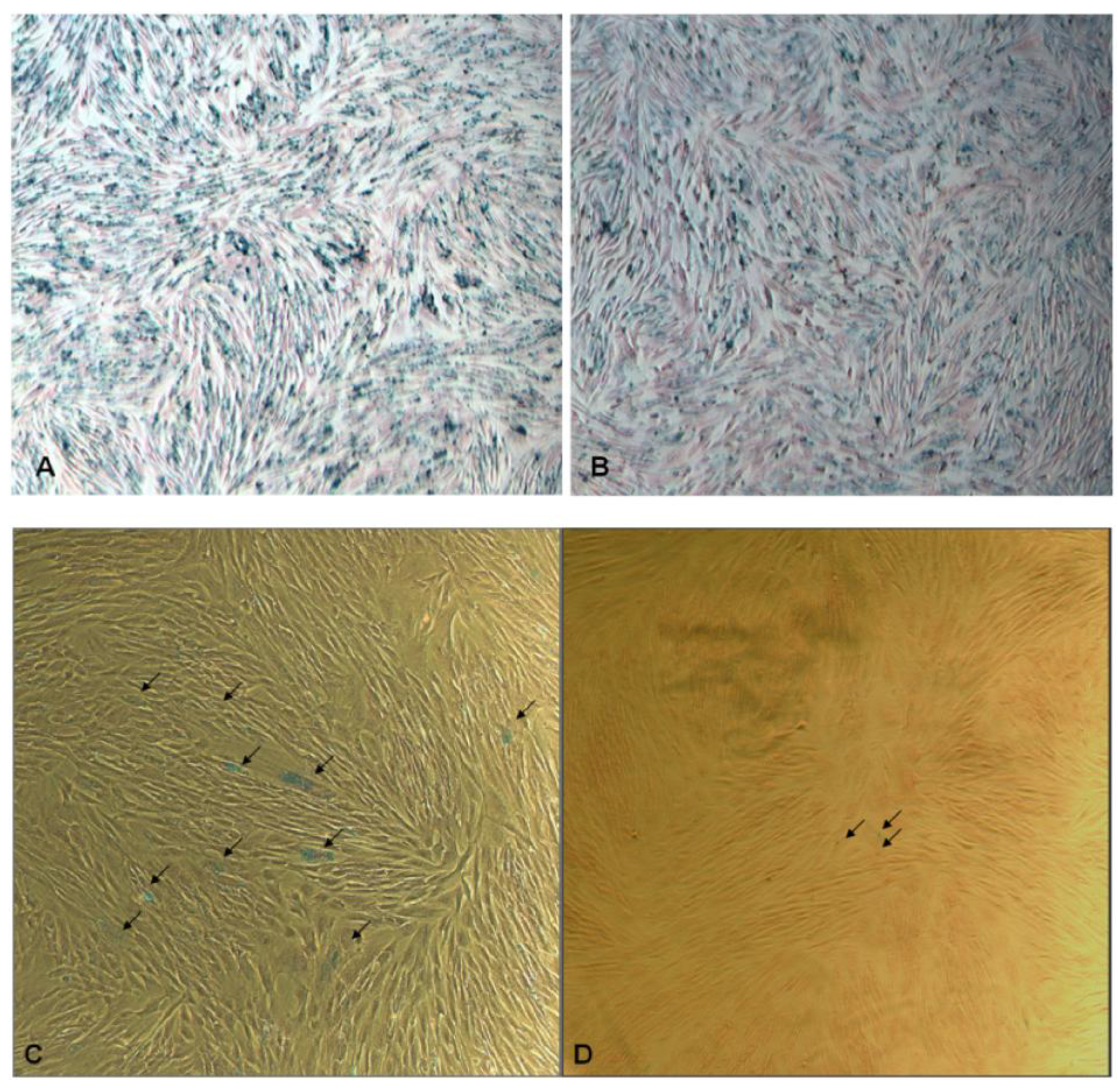
2. Results and Discussion

| ICP-OES | EDX | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe% | Fe% | O% | Si% | C% | |
| SPIO | 63.9 ± 0.1 | 64.8 ± 0.2 | 35.2 ± 0.2 | - | - |
| SPIO@SiO2 | 59.6 ± 0.1 | 57.1 ± 0.3 | 32.3 ± 0.3 | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.3 |
| SPIO@dextran | 50.4 ± 0.1 | 48.8 ± 0.4 | 38.2 ± 0.3 | - | 3.1 ± 0.4 |
| SPIO@PEG | 53.0 ± 0.1 | 51.6 ± 0.3 | 37.4 ± 0.3 | - | 2.0 ± 0.4 |

3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Roco, M.C. Nanotechnology: Convergence with modern biology and medicine. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S.; Lahann, J. Physical approaches to biomaterial design. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Von Maltzahn, G.; Zhang, L.; Derfus, A.M.; Simberg, D.; Harris, T.J.; Ruoslahti, E.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Systematic surface engineering of magnetic nanoworms for in vivo tumor targeting. Small 2009, 5, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.H.; Wang, Y.X.J.; Leung, K.C.F.; Au, D.W.T.; Xuan, S.; Chak, C.P.; Lee, S.K.M.; Sheng, H.; Zhang, G.; Qin, L.; Griffith, J.F.; Ahuja, A.T. Durable mesenchymal stem cell labelling using polyhedral superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 12417–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.C.F.; Wang, Y.X.J.; Wang, H.H.; Xuan, S.; Chak, C.P.; Cheng, C.H.K. Biological and magnetic contrast evaluation of shape-selective Mn–Fe nanowires. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2009, 8, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.C.; Curtis, A.S.G. Functionalisation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R198–R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Hung, Y.; Hsiao, J.K.; Yao, M.; Chung, T.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Wu, S.H.; Hsu, S.C.; Liu, H.M.; Mou, C.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Huang, D.M.; Chen, Y.C. Bifunctional magnetic silica nanoparticles for highly efficient human stem cell labeling. Nano. Lett. 2007, 7, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wängler, B.; Morgenstern, B.; Zentgraf, H.; Eisenhut, M.; Untenecker, H.; Krüger, R.; Huss, R.; Seliger, C.; Semmler, W.; Kiessling, F. Silica- and alkoxysilane-coated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles: A promising tool to label cells for magnetic resonance imaging. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.W.; Seo, J.W.; Cheon, J. Nanoscaling laws of magnetic nanoparticles and their applicabilities in biomedical sciences. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, A.H.; Williams, M.E. Controlling transport and chemical functionality of magnetic nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xuan, S.; Wang, Y.X.J.; Yu, J.C.; Leung, K.C.F. Tuning the grain size and particle size of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 microspheres. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5079–5087. [Google Scholar]
- Alexiou, C.; Arnold, W.; Klein, R.J.; Parak, F.G.; Hulin, P.; Bergemann, C.; Erhardt, W.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Lübbe, A.S. Locoregional cancer treatment with magnetic drug targeting. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6641–6648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skotland, T.; Sontum, P.C.; Oulie, I. In vitro stability analyses as a model for metabolism of ferromagnetic particles (Clariscan), a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 28, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbab, A.S.; Bashaw, L.A.; Miller, B.R.; Jordan, E.K.; Lewis, B.K.; Kalish, H.; Frank, J.A. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labelled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology 2003, 229, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.J.; Leung, K.C.F.; Cheung, W.H.; Wang, H.H.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.F.; Qin, L.; Ahuja, A.T. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound increases cellular uptake of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanomaterial: Results from human osteosarcoma cell line U2OS. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 2010, 31, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Hussain, S.M.; Krestin, G.P. Superparamagnetic iron oxide contrast agents: physicochemical characteristics and applications in MR imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corot, C.; Robert, P.; Idée, J.M.; Port, M. Recent advances in iron oxide nanocrystal technology for medical imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1471–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syková, E.; Jendelová, P.; Herynek, V. MR tracking of stem cells in living recipients. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 549, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk-Wolthuis, W.N.E.; Hoogeboom, J.A.M.; Van Steenbergen, M.J.; Tsang, S.K.Y.; Hennink, W.E. Degradation and release behavior of dextran-based hydrogels. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 4639–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Xu, H.; Anker, J.; Kopelman, R.; Ross, B.; Rehemtulla, A.; Reddy, R. Synthesis and characterization of silica-embedded iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L.; Wilson, J. Ceramic Transactions; Clarke, E.D., Simmons, J., Folz, D., Eds.; American Ceramic Society: Westerville, OH, USA, 1999; p. 101. [Google Scholar]
- Coradin, T.; Lopez, P.J. Biogenic silica patterning: Simple chemistry or subtle biology? Chembiochem 2003, 4, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Moon, W.K.; Kim, Y.; Lim, D.; Song, I.C.; Yoon, B.W. Labeling efficacy of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles to human neural stem cells: Comparison of ferumoxides, monocrystalline iron oxide, cross-linked iron oxide (CLIO)-NH2 and tat-CLIO. Korean J. Radiol. 2007, 8, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.W.; Liu, X.Z.; Qu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mickey, S.K.; Turetsky, D.; Gottlieb, D.I.; Choi, D.W. Transplanted embryonic stem cells survive, differentiate and promote recovery in injured rat spinal cord. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnecchi, M.; He, H.; Liang, O.D.; Melo, L.G.; Morello, F.; Mu, H.; Noiseux, N.; Zhang, L.; Pratt, R.E.; Ingwall, J.S.; Dzau, V.J. Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernigou, P.; Poignard, A.; Manicom, O.; Mathieu, G.; Rouard, H. The use of percutaneous autologous bone marrow transplantation in nonunion and avascular necrosis of bone. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. Vol. 2005, 87, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimelman, N.; Pelled, G.; Helm, G.A.; Huard, J.; Schwarz, E.M.; Gazit, D. Gene- and stem cell-based therapeutics for bone regeneration and repair. Tissue Eng. A 2007, 13, 1135–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, B.L.; Ryan, T.L.; In’t Veld, P.; Kulseng, B.; Rokstad, A.M.; Skjak-Brek, G.; Espevi, T. Poly-l-Lysine induces fibrosis on alginate microcapsules via the induction of cytokines. Cell Transplant. 2001, 10, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, C.; Billotey, C.; Roger, J.; Pons, J.N.; Bacri, J.C.; Gazeau, F. Intracellular uptake of anionic superparamagnetic nanoparticles as a function of their surface coating. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X. In vivo MR imaging tracking of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle labelled, engineered, autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells following intra-articular injection. Joint Bone Spine 2009, 76, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, A.; Galderisi, U.; Marino, I.R. From the laboratory bench to the patient's bedside: an update on clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 211, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mays, R.W.; van’t Hof, W.; Ting, A.E.; Perry, R.; Deans, R. Development of adult pluripotent stem cell therapies for ischemic injury and disease. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2007, 7, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauer, B.E.; Brehm, M.; Zeus, T.; Köstering, M.; Hernandez, A.; Sorg, R.V.; Kögler, G.; Wernet, P. Repair of infarcted myocardium by autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in humans. Circulation 2002, 106, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmus, B.; Schächinger, V.; Teupe, C.; Britten, M.; Lehmann, R.; Döbert, N.; Grünwald, F.; Aicher, A.; Urbich, C.; Martin, H.; Hoelzer, D.; Dimmeler, S.; Zeiher, A.M. Transplantation of progenitor cells and regeneration enhancement in acute myocardial infarction (TOPCARE-AMI). Circulation 2002, 106, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangji, V.; Toungouz, M.; Hauzeur, J.P. Stem cell therapy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, O.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, P.H.; Lee, G. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blanc, K.; Frassoni, F.; Ball, L.; Locatelli, F.; Roelofs, H.; Lewis, I.; Lanino, E.; Sundberg, B.; Bernardo, M.E.; Remberger, M.; Dini, G.; Egeler, R.M.; Bacigalupo, A.; Fibbe, W.; Ringdén, O. On behalf of the developmental committee of the european group for blood and marrow transplantation, mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: A phase II study. Lancet 2008, 371, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbab, A.S.; Wilson, L.B.; Ashari, P.; Jordan, E.K.; Lewis, B.K.; Frank, J.A. A model of lysosomal metabolism of dextran coated superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles: Implications for cellular magnetic resonance imaging. NMR Biomed. 2005, 18, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Man, G.C.; Heng, P.A.; Griffith, J.F.; Ahuja, A.T. Color quantification for evaluation of stained tissues. Cytometry A 2011, 79, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Wang, H.H.; Au, D.W.T.; Zuo, B.S.; Teng, L.S. Pitfalls in employing superparamagnetic iron oxide particles for stem cell labeling and in vivo MRI tracking. Br. J. Radiol. 2008, 81, 987–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-X.J.; Quercy-Jouvet, T.; Wang, H.-H.; Li, A.-W.; Chak, C.-P.; Xuan, S.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.-F.; Lee, S.-F.; Leung, P.-C.; et al. Efficacy and Durability in Direct Labeling of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Organosilica, Dextran, and PEG Coatings. Materials 2011, 4, 703-715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4040703
Wang Y-XJ, Quercy-Jouvet T, Wang H-H, Li A-W, Chak C-P, Xuan S, Shi L, Wang D-F, Lee S-F, Leung P-C, et al. Efficacy and Durability in Direct Labeling of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Organosilica, Dextran, and PEG Coatings. Materials. 2011; 4(4):703-715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4040703
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi-Xiang J., Thibault Quercy-Jouvet, Hao-Hao Wang, Ak-Wai Li, Chun-Pong Chak, Shouhu Xuan, Lin Shi, De-Feng Wang, Siu-Fung Lee, Ping-Chung Leung, and et al. 2011. "Efficacy and Durability in Direct Labeling of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Organosilica, Dextran, and PEG Coatings" Materials 4, no. 4: 703-715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4040703
APA StyleWang, Y.-X. J., Quercy-Jouvet, T., Wang, H.-H., Li, A.-W., Chak, C.-P., Xuan, S., Shi, L., Wang, D.-F., Lee, S.-F., Leung, P.-C., Lau, C. B. S., Fung, K.-P., & Leung, K. C.-F. (2011). Efficacy and Durability in Direct Labeling of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Organosilica, Dextran, and PEG Coatings. Materials, 4(4), 703-715. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma4040703






