Chemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Sol-Gel Materials †
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Sol-Gel Technology
3. Sol-Gel Based Chemical Sensors
3.1. Optical Sensors for pH Determination
3.2. Sensors for Ionic Compounds
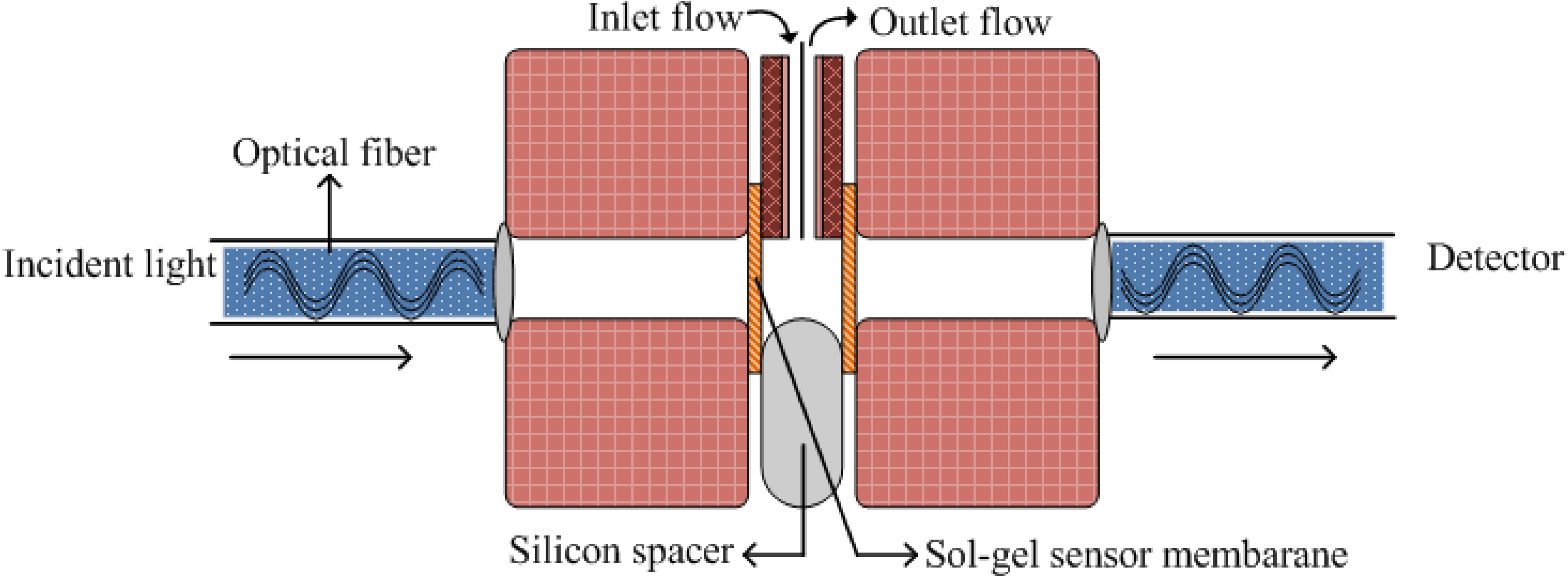
3.3. Gas Phase Sensing
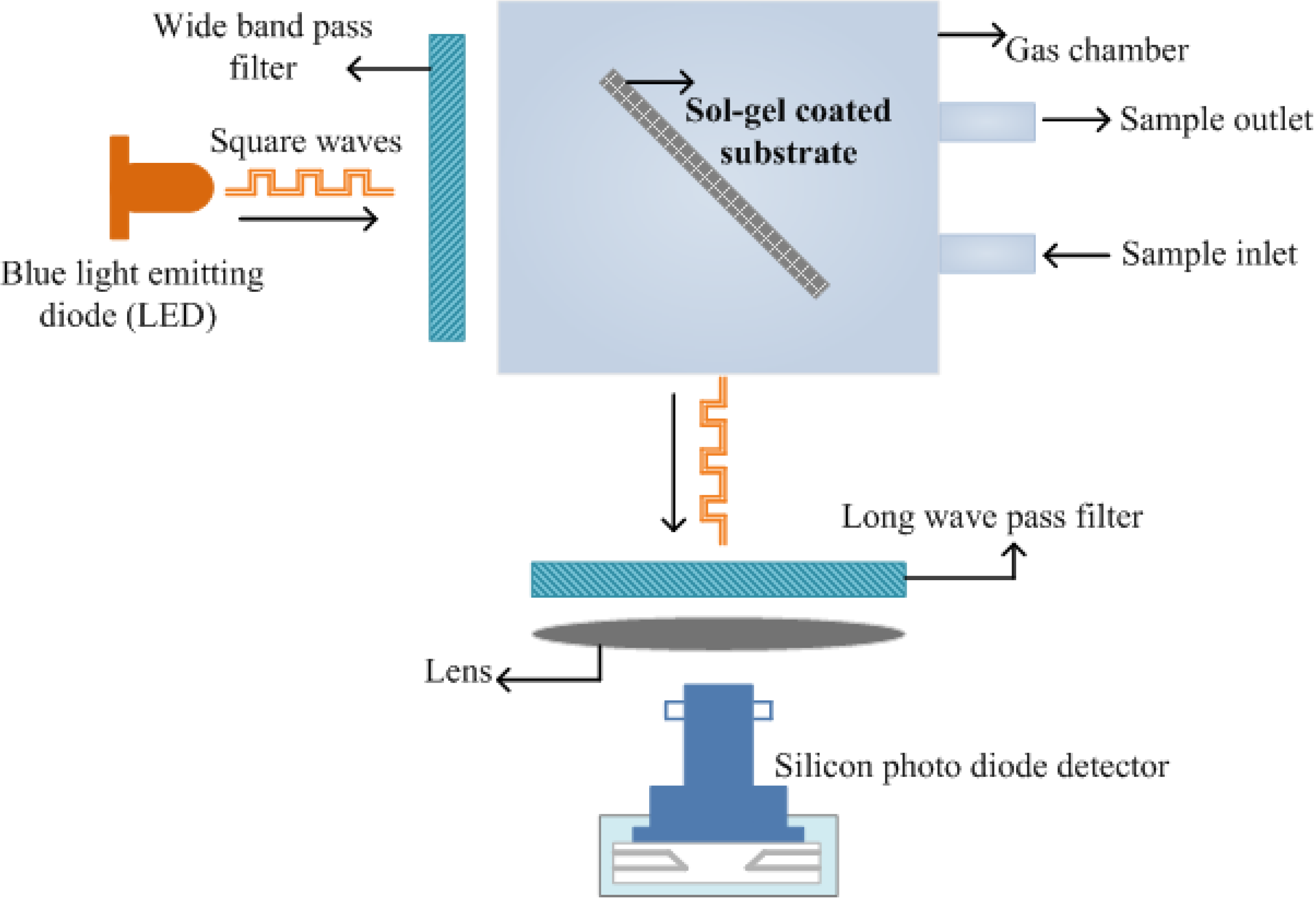
3.4. Biological Sensors
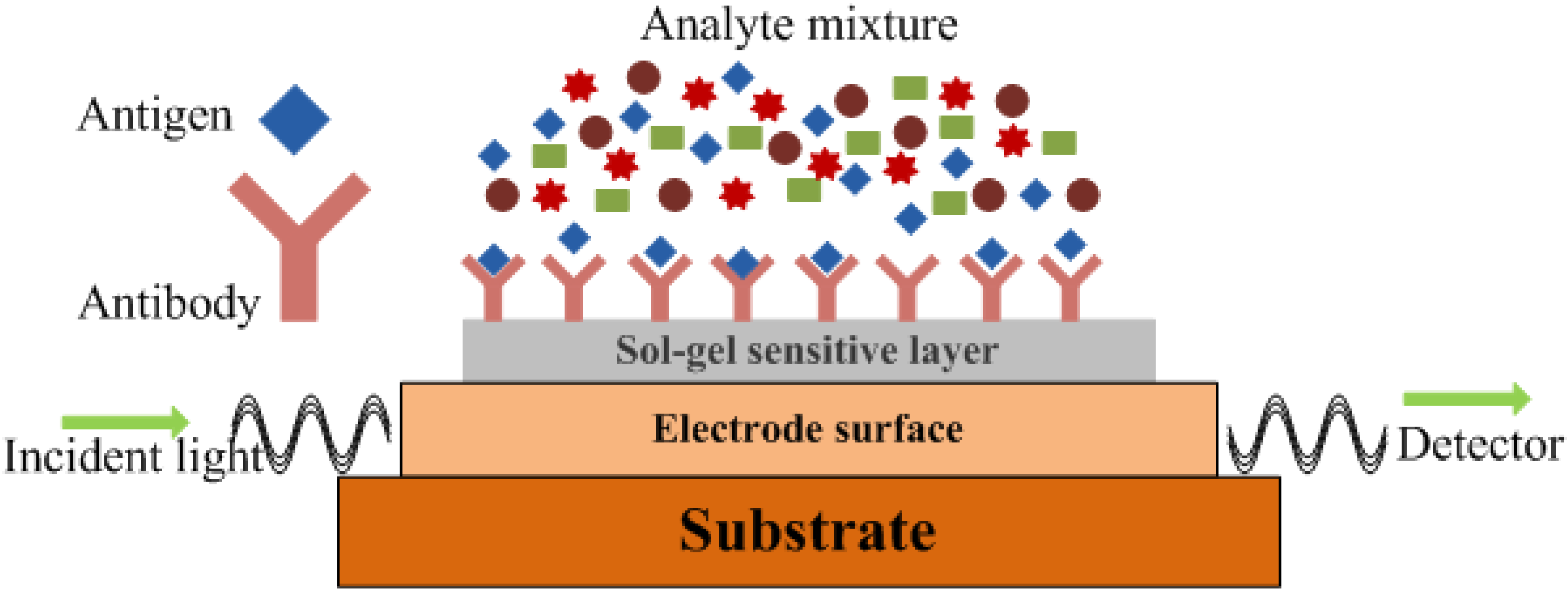
4. Molecular Imprinted Sol-Gel Materials as an Innovative Sensing Tool
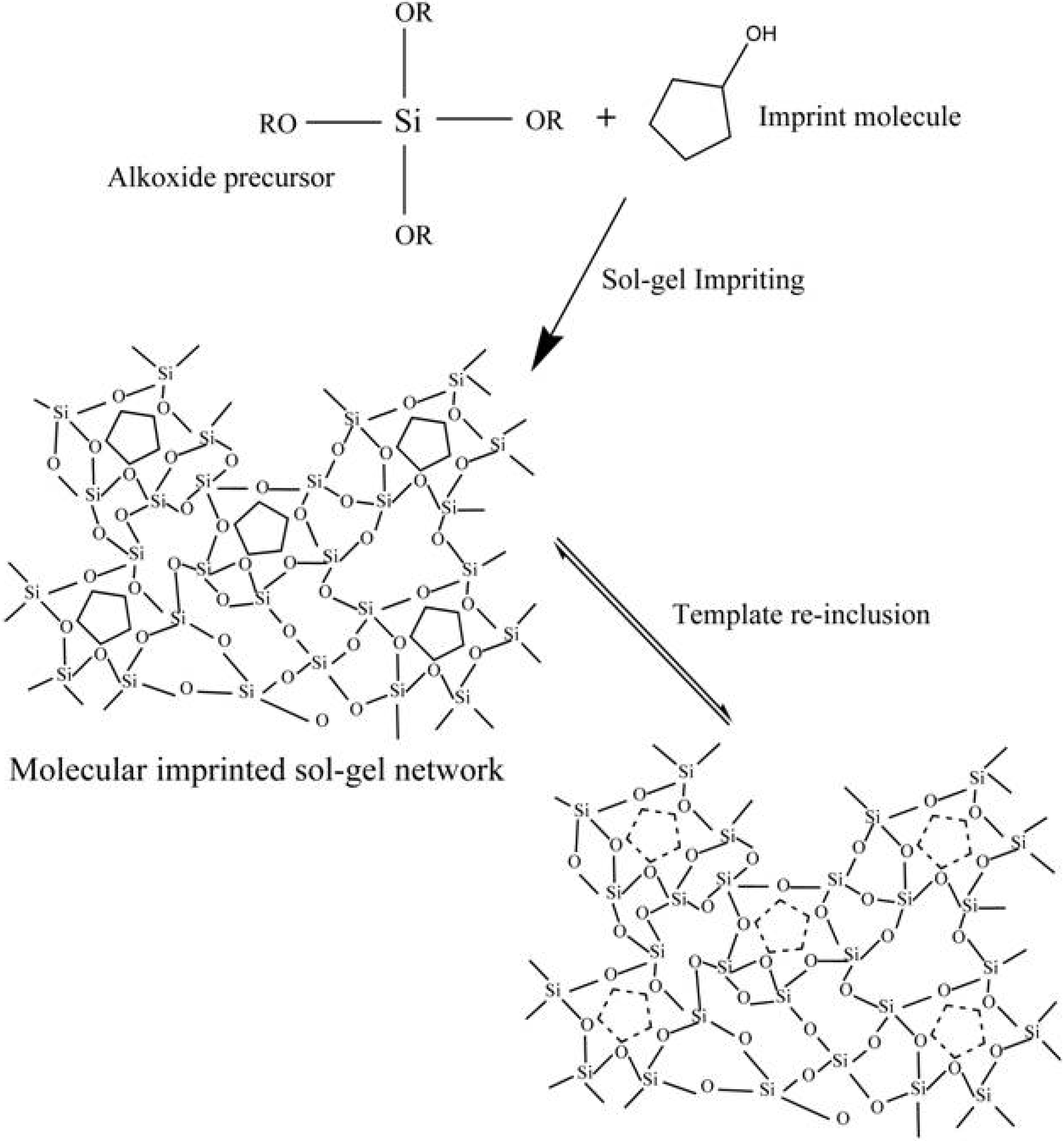

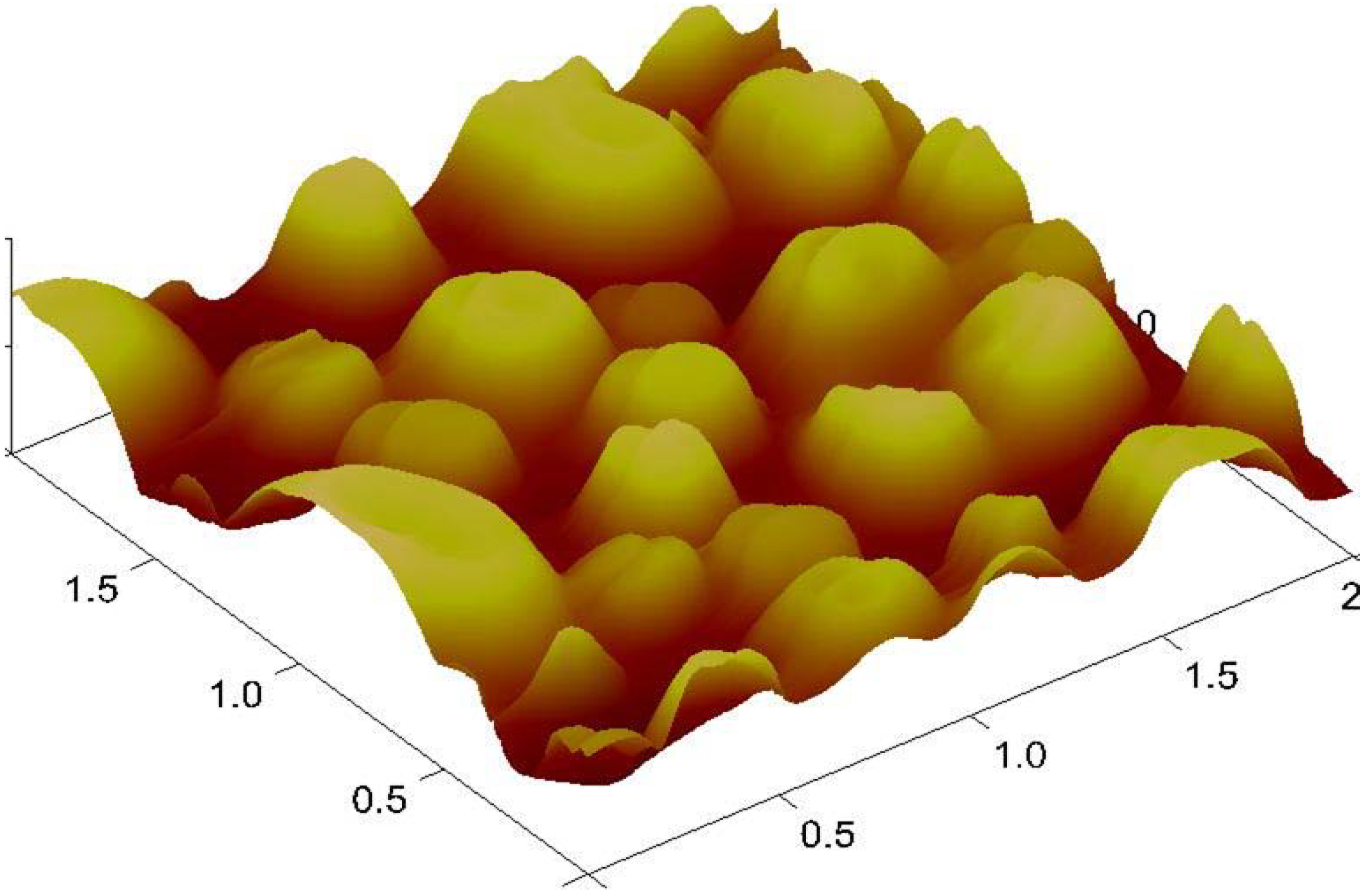
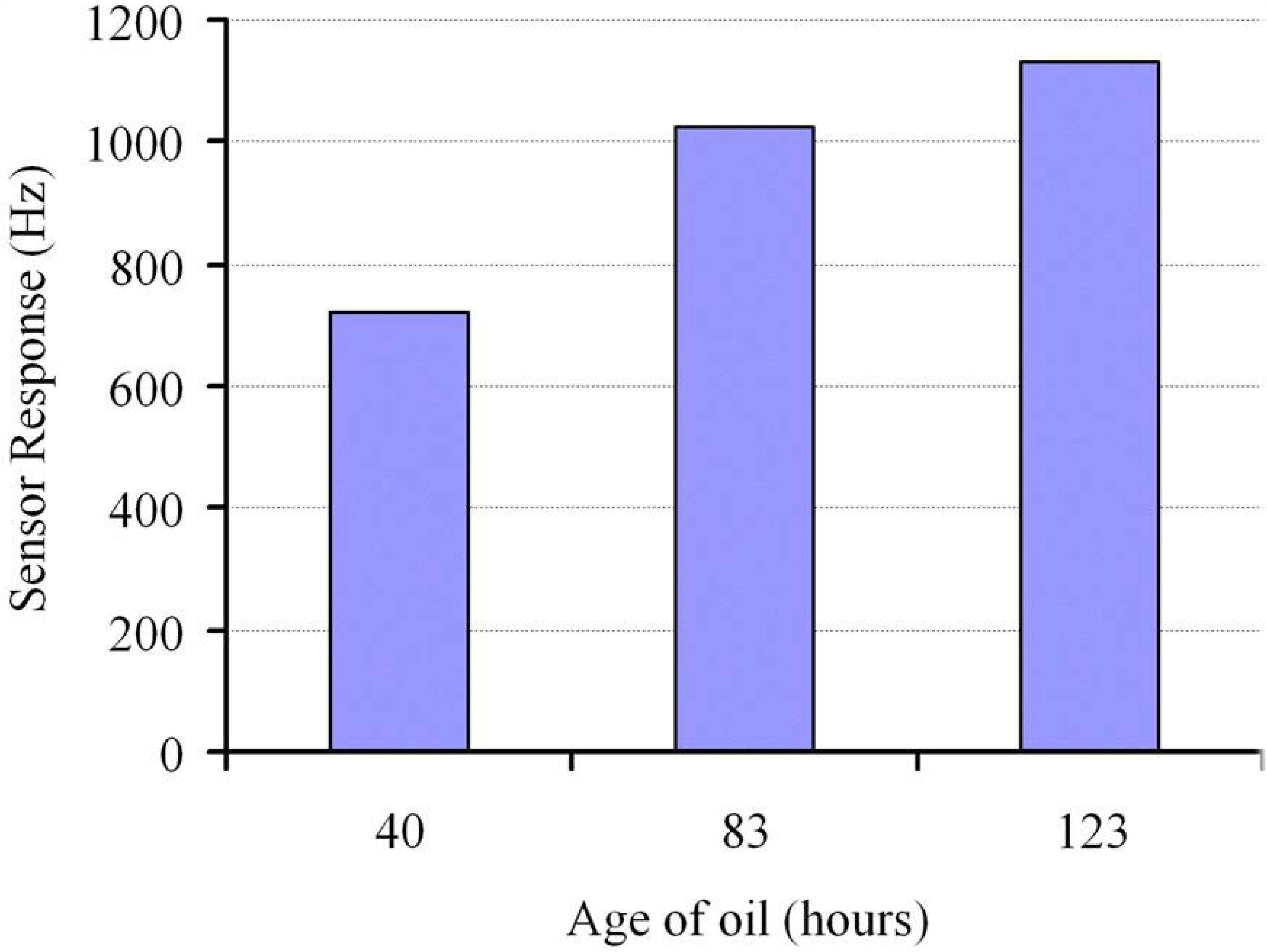
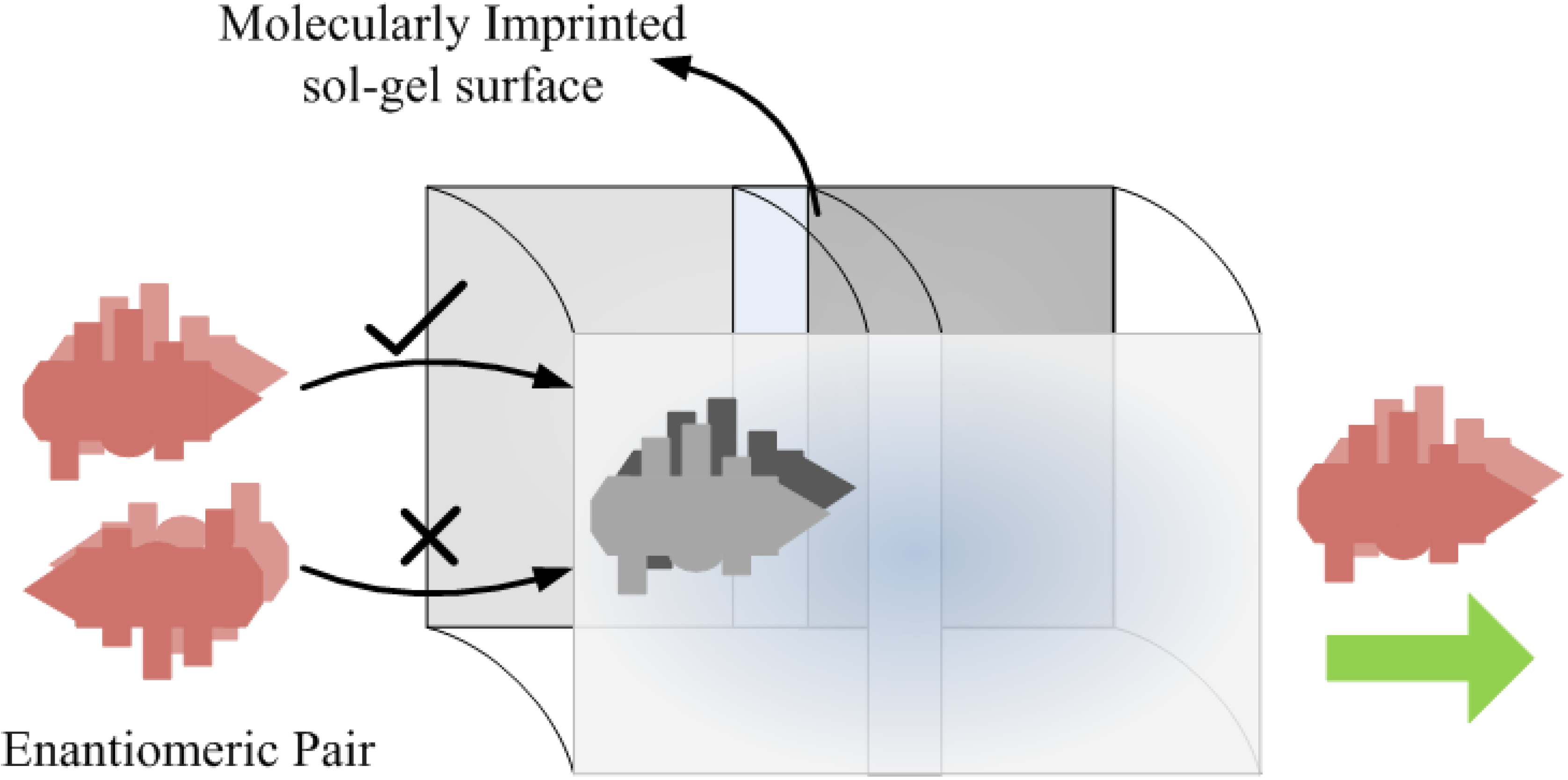
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Hench, L.L.; West, J.K. The sol-gel process. Chem. Rev. 1990, 90, 33–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCraith, B.D.; McDonagh, C.; Mcevoy, A.K.; Butler, T.; O’Keeffe, G.; Murphy, V. Optical chemical sensors based on sol-gel materials: Recent advances and critical issues. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukowiak, A.; Strek, W. Sensing abilities of materials prepared by sol–gel technology. J Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2009, 50, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, P.CA.; Araujo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.; Conceicao, B.S.M. Optical sensors and biosensors based on sol–gel films. Talanta 2007, 72, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, B.; Zink, J.I. Optical properties of sol–gel glasses doped with organic molecules. J. Mater. Chem. 1991, 1, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, O. Diagnostic applications of organically-doped sol–gel porous glass. Analusis 1992, 20, 543–553. [Google Scholar]
- Rodman, D.L.; Pan, H.; Clavier, C.W.; Feng, X.; Xue, Z. Optical metal ion sensor based on diffusion followed by an immobilizing reaction. Quantitative analysis by a mesoporous monolith containing functional groups. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3231–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrington, N.A.; Thomas, G.H.; Rodman, D.L.; Beach, D.B.; Xue, Z. Optical determination of Cr(VI) using regenerable, functionalized sol–gel monoliths. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 581, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zevin, M.; Reisfeld, R.; Oehme, I.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Sol–gel derived optical coatings for determination of chromate. Sens. Actuators B 1997, B39, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allain, L.R.; Sorasaenee, K.; Xue, Z. Doped thin-film sensors via a sol–gel process for high-acidity determination. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 3076–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allain, L.R.; Xue, Z. Optical sensors for the determination of concentrated hydroxide. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allain, L.R.; Xue, Z. Hysteresis in optical sensing and its impact on the analytical error of a calibration-free acid sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 433, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCraith, B.D.; Ruddy, V.; Potter, C.; O’Kelly, B.; McGilp, J.F. Optical waveguide sensor using evanescent wave excitation of fluorescent dye in sol–gel glass. Electron. Lett. 1991, 27, 1247–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobnik, A.; Oehme, I.; Murkovic, I.; Wolfbeis, O.S. pH Optical sensors based on sol–gels. Chemical doping versus covalent immobilization. Anal. Chim. Acta 1998, 367, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojtaba, S.; Gholamhassan, A. High-acidity optical sensors based on sol–gel derived thin films. Anal. Lett. 2001, 34, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Chow, K.F.; Wang, W.; Wong, C.; Yee, C.; Persad, A.; Mann, J.; Bocarsly, A. Optical sensing of HCl with phenol red doped sol–gels. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 534, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, F.L.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Imprinted polymers in chemical recognition for mass-sensitive devices. In Springer Series on Chemical Sensors and Biosensors; Wolfbeis, O.S., Ed.; Springer-Verlag Berlin: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 5, pp. 173–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ebelmen, M. Sur les combinaisons des acides borique et silicique avee les ethers. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1846, 16, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, T. On the properties of silicic acid and other analogous colloidal substances. J. Chem. Soc. 1864, 17, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.S.; Kandimalla, V.B.; Ju, H. Preparation of ormosils and its applications in the immobilizing biomolecules. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 1071–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, L.; Badia, R.; Diaz-Garcia, M.E. Molecular imprinted ormosils for nafcillin recognition by room temperature phosphorescence optosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suah, F.B.M.; Ahmad, M.; Taib, M.N. Applications of artificial neural network on signal processing of optical fiber pH sensor based on bromophenol blue doped with sol–gel film. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 90, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, S.; Uttamchandani, D. Development of micro-optrodes using sol-gel immobilization. IEEE Proc. Sci. Meas. Technol. 1997, 144, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.Y.; Shahriari, M.R.; Jun, S.G.H. Fibre optic pH sensors prepared by sol-gel immobilization technique. Electron. Lett. 1991, 27, 1560–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.D.; Sharma, S. A long-range fiber optic pH sensor prepared by dye doped sol-gel immobilization technique. Opt. Commun. 1998, 154, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.S.; Aneeshkumar, B.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Vallabhan, C.P.G.; Nampoori, V.P.N. A microbent fiber optic pH sensor. Opt. Commun. 2002, 205, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, D. An optical pH sensor with a linear response over a broad range. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 408, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Saavedra, S.S. Chemical sensing using sol-gel derived planner waveguides and indicator phases. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallington, S.; Labayen, T.; Poppe, A.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Wright, D.J. Sol-gel entrapped materials for optical sensing of solvents and metal ions. Sens. Actuators B 1997, 38, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, P.C.A.; Araujo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.; Conceicao, B.S.M.; Satinsky, D.; Solich, P. Colorimetric bismuth determination in pharmaceuticals using a xylenol orange sol–gel sensor coupled to a multicommutated flow system. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisfeld, R.; Shamrakov, D. Reversible optical sensor for in situ determination of heavy metal impurities in the environment. Sens. Mater. 1996, 8, 439–443. [Google Scholar]
- Jeronimo, P.C.A.; Araujo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.; Conceicao, B.S.M.; Pasquini, C.; Raimundo, I., Jr. Direct determination of copper in urine using a sol–gel optical sensor coupled to a multi commutated flow system. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 380, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plaschke, M.; Czolk, R.; Ache, H.J. Fluorimetric determination of mercury with a water-soluble porphyrin and porphyrin-doped sol-gel films. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 304, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panusa, A.; Flamini, A.; Poli, N. Sol-Gel hybrid silica thin films doped with 2-(5-amino-3,4-dicyano-2H-pyrrol-2-ylidene)-1,1,2-tricyanoethanide as optical chemical sensors. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, P.C.A.; Araujo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.; Conceicao, B.S.M. Development of a sol–gel optical sensor for analysis of zinc in pharmaceuticals. Sens. Actuators B 2004, 103, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunuwila, D.D.; Torgerson, A.B.; Chang, K.C.; Berglund, A.K. Sol-gel derived titanium carboxylate thin films for optical detection of analytes. Anal.Chem. 1994, 66, 2739–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwan, J.L.H.; Soumillion, J.P. A halogen anion sensor based on the hydrophobic entrapment of a fluorescent probe in silica sol-gel thin films. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1997, 220, 316. [Google Scholar]
- Martucci, A.; Bassiri, N.; Guglielmi, M.; Armelao, L.; Gross, S.; Pivin, J.C. NiO-SiO2 Sol-Gel nanocomposite films for optical gas sensor. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2003, 26, 993–996. [Google Scholar]
- Cantalini, C.; Post, M.; Buso, D.; Guglielmi, M.; Martucci, A. Gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline NiO and Co3O4 in porous silica sol–gel films. Sens. Actuators B 2005, 108, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultzingslowen, C.V.; McEvoy, A.K.; McDonagh, C.; MacCraith, B.D.; Klimant, I.; Krause, C.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Sol–gel based optical carbon dioxide sensor employing dual luminophore referencing for application in food packaging technology. Analyst 2002, 127, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, H.; Ohnishi, E.; Arai, Y.; Yoshida, K. Sensitivity of fiber-optic carbon dioxide sensors utilizing indicator dye. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 94, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malins, C.; MacCraith, B.D. Dye-doped organically modified silica glass for fluorescence based carbon dioxide gas detection. Analyst 1998, 123, 2373–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, C.; MacCraith, B.D. Tailoring of sol-gel films for optical sensing of oxygen in gas and aqueous phase. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Worsfold, O.; Dooling, C.M.; Richardson, T.H.; Vysotsky, M.O.; Tregonning, R.; Hunterb, C.A.; Malins, C. Nitrogen dioxide sensing characteristics at elevated temperature of sol-gel glass thin films containing substituted porphyrin dyes. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.A.; Satcher, J.H., Jr.; Bettencourt, K. Development of sol–gel-based fiber optic nitrogen dioxide gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2000, 69, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechery, S.J.; Singh, J.P. Fiber optic based gas sensor with nanoporous structure for the selective detection of NO2 in air samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 557, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyth, D.J.; Aylott, J.W.; Richardson, D.J.; Russell, D.A. Sol-gel encapsulation of metalloproteins for the development of optical biosensors for nitrogen monoxide and carbon monoxide. Analyst 1995, 120, 2725–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylott, J.W.; Richardson, D.J.; Russell, D.A. Optical biosensing of gaseous nitric oxide using spin-coated sol-gel thin films. Chem. Mater. 1997, 9, 2261–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doong, R.; Tsai, H. Immobilization and characterization of sol–gel encapsulated acetyl cholinesterase fiber-optic biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 434, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xiao, L.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L.; Cui, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Novel BOD optical fiber biosensor based on co-immobilized microorganisms in ormosils matrix. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, N.Y.; Dong, S.; Lo, W.; Wong, K. An optical biosensor for multi-sample determination of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Sens. Actuators B 2005, 110, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, P.C.A.; Araujo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.; Conceicao, B.S.M.; Satinsky, D.; Solich, P. Flow through sol–gel optical biosensor for the colorimetric determination of Acetazolamide. Analyst 2005, 130, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Malhotra, R.; Malhotra, B.D.; Grover, S.K. Co-immobilization of cholesterol oxidase and horseradish peroxidase in a sol–gel film. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 414, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, V.G.; Clonis, Y.D. A portable fiber-optic pesticide biosensor based on immobilized cholinesterase and sol-gel entrapped bromocresol purple for in-field use. Bios. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreniak, A.; Maruszewski, K.; Rybka, J.; Gamian, A.; Czyzewski, J. A luminescence endotoxin biosensor prepared by the sol-gel method. Opt. Mat. 2004, 26, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, L. Theory of the structure and process of formation of antibodies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1940, 62, 2643–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, H.C.; Congdon, W.I.; Scarpa, I.S.; Klotz, I.M. Catalytic accelerations of 1012-fold by anenzyme-like synthetic polymer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A. The use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for the resolution of racemates. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1972, 11, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Wulff, G. Molecular imprinting in crosslinked materials with the aid of molecular templates—way towards artificial antibodies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 1812–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbach, K. Molecular imprinting. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994, 19, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosbach, K.; Ramstrom, O. The emerging technique of molecular imprinting and its future impact on biotechnology. Biotechnology 1996, 14, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O. Bio imprinting of polymers and sol-gel phases. Selective detection of yeasts with imprinted polymers. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S. Road tests of oil condition sensor and sensing technique. Sens. Actuators B 2001, 73, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberzeit, P.A.; Glanznig, G.; Leidl, A.; Voigt, G.; Dickert, F.L. Nano structured polymers for detecting chemical changes during engine oil degradation. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberzeit, P.A.; Glanznig, G.; Leidl, A.; Dickert, F.L. Ceramic materials for mass-sensitive sensors detection of VOCs and monitoring oil degradation. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2006, 45, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Dickert, F.L.; Greibl, W.; Rohrer, A.; Voigt, G. Sol-gel coated quartz crystal microbalances for monitoring automotive oil degradation. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberzeit, P.A.; Afzal, A.; Glanzing, G.; Dickert, F.L. Molecularly imprinted sol–gel nanoparticles for mass-sensitive engine oil degradation sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 2007, 389, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Palfinger, C.; Pickert, D.; Wolff, U.; Scholl, G. Borderline applications of QCM-devices: Synthetic antibodies for analytes in both nm- and m-dimensions. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 95, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Garcia, M.E.; Laıno, R.B. Molecular imprinting in sol-gel materials: Recent developments and applications. Microchim. Acta 2005, 149, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, A. Molecular imprinting in sol–gel matrix. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holthoff, E.L.; Bright, F.V. Molecularly imprinted xerogels as platforms for sensing. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, N.R.; Linman, M.J.; Timmers, M.M.; Dean, S.L.; Burkett, C.M.; Lloyd, J.A.; Keelor, J.D.; Baughman, B.M.; Edmiston, P.L. Selective detection of gas-phase TNT by integrated optical waveguide spectrometry using molecularly imprinted sol–gel sensing films. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 593, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A.L.; Carlson, C.A.; Edmiston, P.L. Development and characterization of molecularly imprinted sol-gel materials for the selective detection of DDT. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, S.; Zaltsman, A.; Turyan, I.; Mandler, D. Parathion sensor based on molecularly imprinted sol-gel films. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.A.; Lloyd, J.A.; Dean, S.L.; Walker, N.R.; Edmiston, P.L. Sensor for fluorene based on the incorporation of an environmentally sensitive fluorophore proximal to a molecularly imprinted binding site. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3537–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Laino, R.B.; Diaz-Garcia, M.E.; Guardia, L.; Viale, A. Assessment of molecularly imprinted sol–gel materials for selective room temperature phosphorescence recognition of nafcillin. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 804, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, L.; Badiaa, R.; Diaaz-Garciaa, M.E. Molecularly imprinted sol-gels for nafcillin determination in milk-based products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Tehan, E.C.; Bukowski, R.M.; Tang, Y.; Shughart, E.L.; Holthoff, W.G.; Cartwright, A.N.; Titus, A.H.; Bright, F.V. Templated xerogels as platforms for biomolecule-less biomolecule sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 564, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Haiping, L.; Li, H.; Nie, L.; Yao, S. Stereoselective histidine sensor based on molecularly imprinted sol-gel films. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 336, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Nie, L.; Yao, S. Electrodeposited sol–gel-imprinted sensing film for cytidine recognition on Au-electrode surface. Talanta 2006, 69, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, M.; Nishiyama, M.; Yamamura, I.; Ohtsuki, S.; Nomura, R. A sol-gel method using acetic anhydride in the presence of cholesterol in organic solution media: Preparation of silicas that recognize steroid hormones. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 2374–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.W.; Yang, M.C. Enhancement of the imprinting effect in cholesterol-imprinted microporous silica. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 4037–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olwill, A.; Hughes, H.; Riordain, M.O.; McLoughlin, P. The use of molecularly imprinted sol–gels in pharmaceutical separations. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.K.P.; Chow, C.F.; Lam, M.H.W. A sol–gel derived molecular imprinted luminescent PET sensing material for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2985–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fireman-Shoresh, S.; Avnir, D.; Marx, S. General method for chiral imprinting of sol–gel thin films exhibiting enantioselectivity. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3607–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fireman-Shoresh, S.; Popov, I.; Avnir, D.; Marx, S. Enantioselective, chirally template sol–gel thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2650–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fireman-Shoresh, S.; Turyan, I.; Mandler, D.; Avnir, D.; Marx, S. Chiral electrochemical recognition by very thin molecularly imprinted sol–gel films. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7842–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Fernandez, S.; Lobo-Castann, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tunon-Blanco, P.; Carriedo, G.A.; Garcia-Alonso, F.J.; Fidalgo, J.I. Molecularly imprinted polyphosphazene films as recognition element in a voltammetric rifamycin SV sensor. Electroanalysis 2001, 13, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shustak, G.; Marx, S.; Turyan, I.; Mandler, D. Application of sol–gel technology for electroanalytical sensing. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 398–408. [Google Scholar]
- Marx, S.; Zaltsman, A.; Turyan, I.; Mandler, D. Parathion sensor based on molecularly imprinted sol–gel films. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mujahid, A.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Dickert, F.L. Chemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Sol-Gel Materials. Materials 2010, 3, 2196-2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042196
Mujahid A, Lieberzeit PA, Dickert FL. Chemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Sol-Gel Materials. Materials. 2010; 3(4):2196-2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042196
Chicago/Turabian StyleMujahid, Adnan, Peter A. Lieberzeit, and Franz L. Dickert. 2010. "Chemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Sol-Gel Materials" Materials 3, no. 4: 2196-2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042196
APA StyleMujahid, A., Lieberzeit, P. A., & Dickert, F. L. (2010). Chemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Sol-Gel Materials. Materials, 3(4), 2196-2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3042196





