The Impact of Operating Ratio on the Static and Fatigue Life of Forward-Acting Rupture Discs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Rupture Disc Parameters
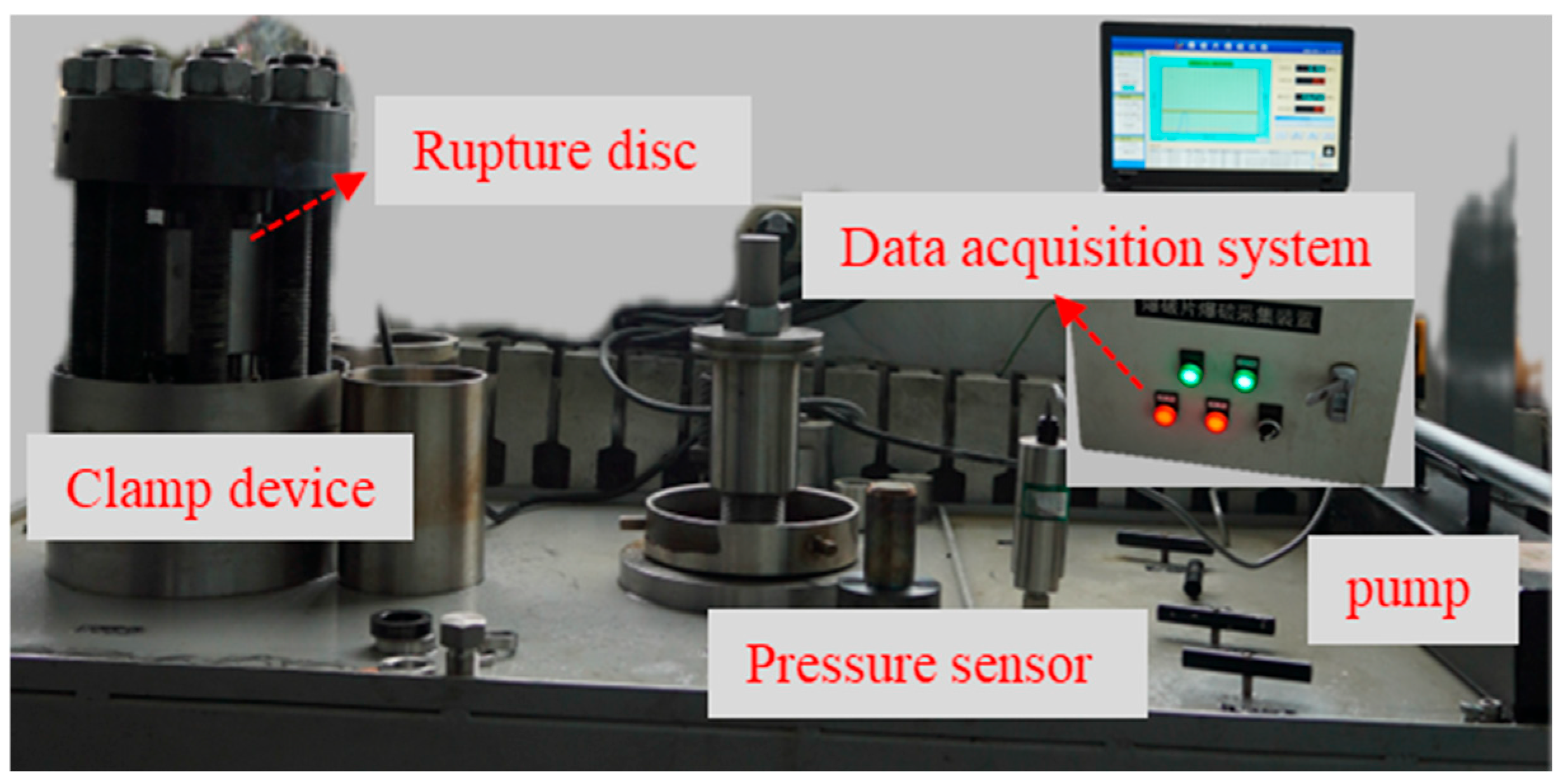
2.2. Testing Platforms
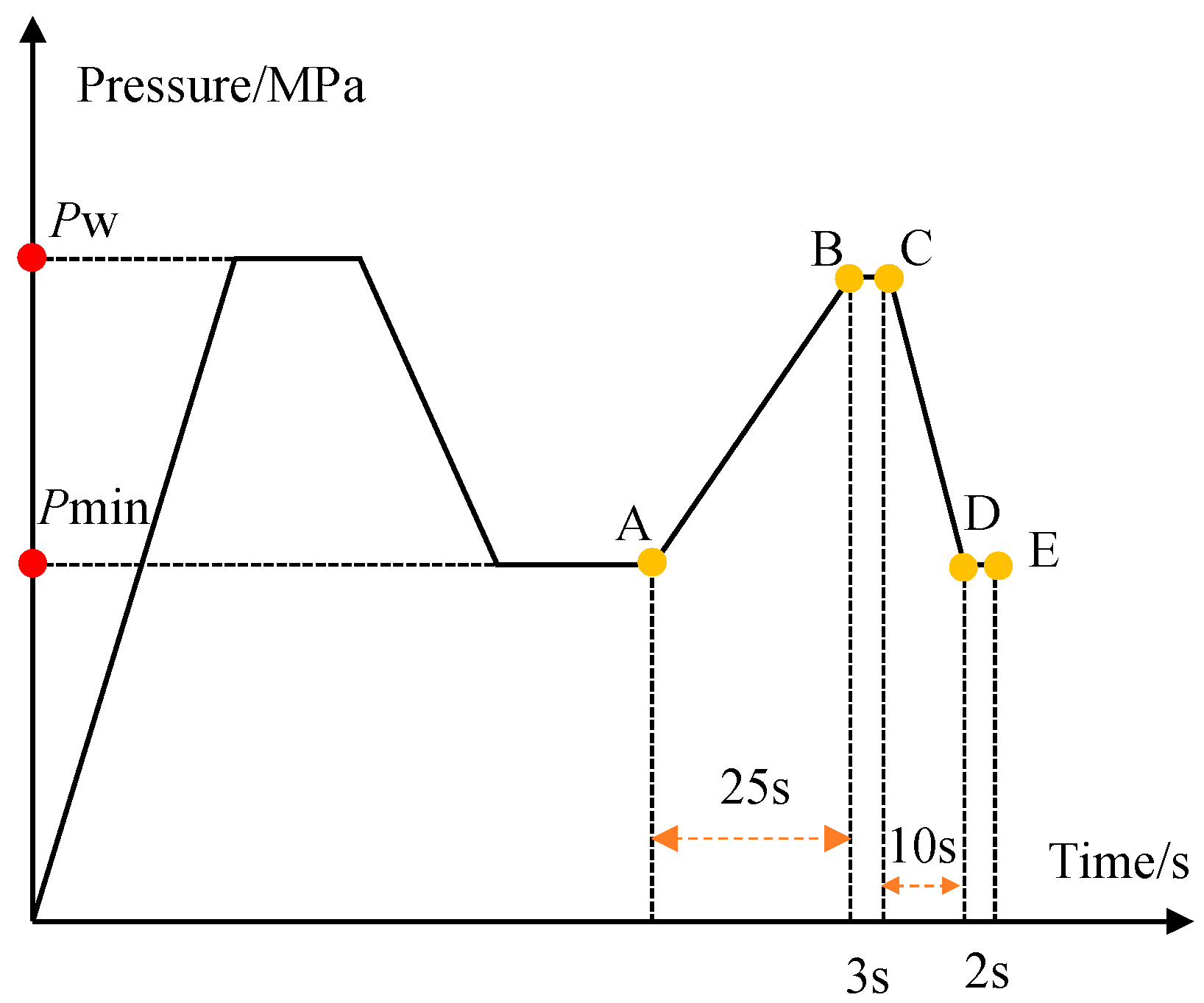
2.3. Testing Procedure
2.3.1. Static Load Testing
2.3.2. Fatigue Load Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Verification of Experimental Platform Reliability
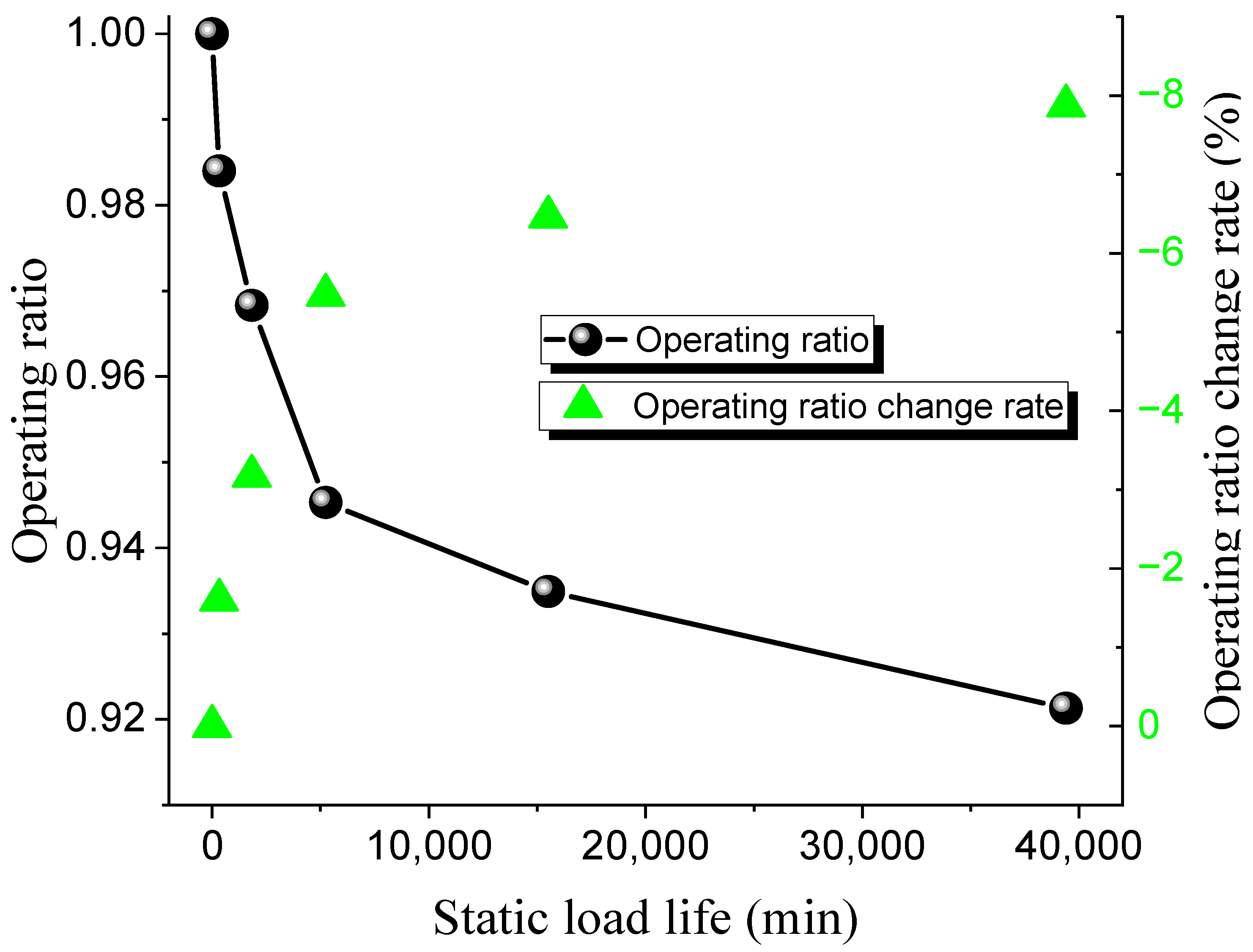
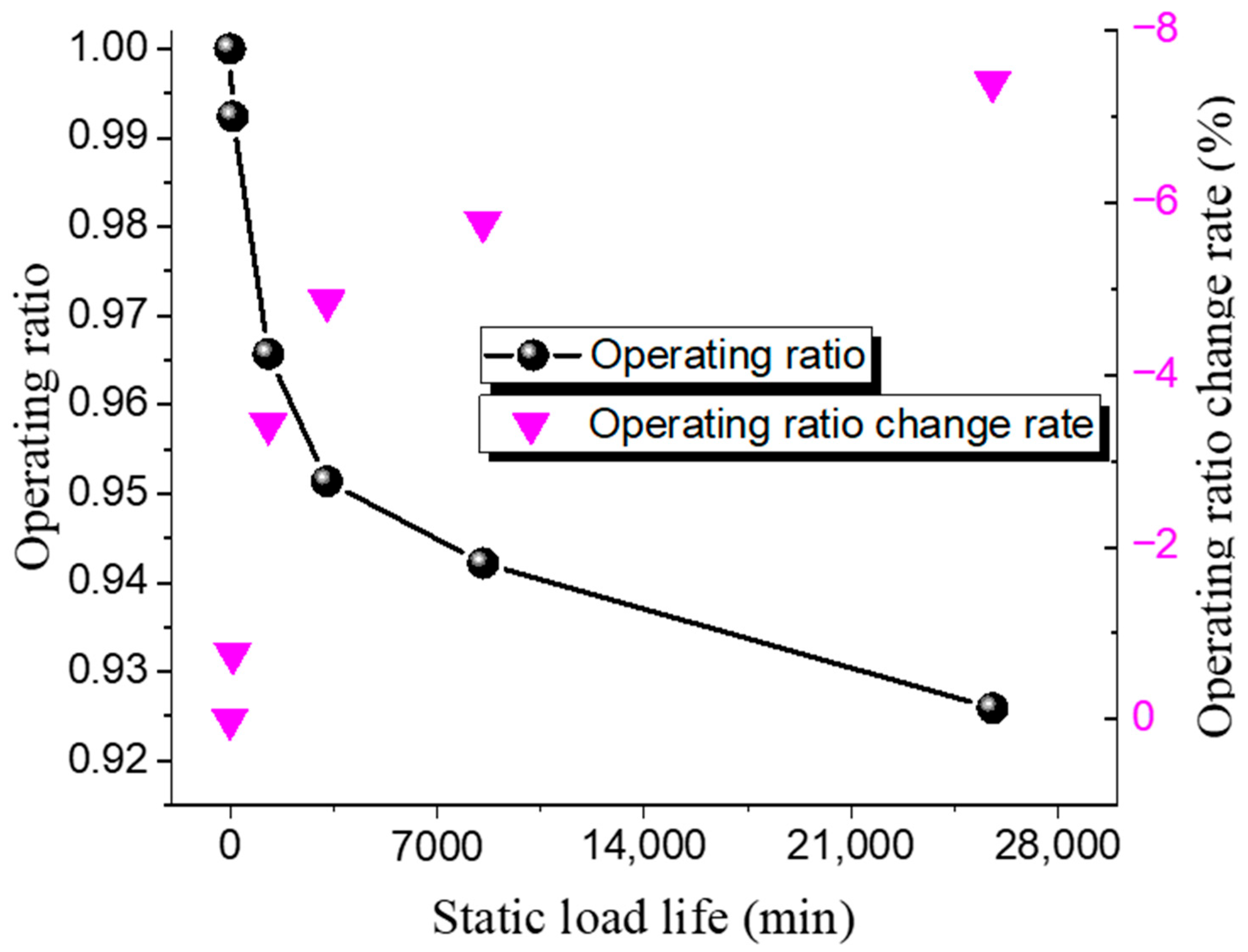
3.2. Static Load Life
3.3. Fatigue Life
4. Life Prediction
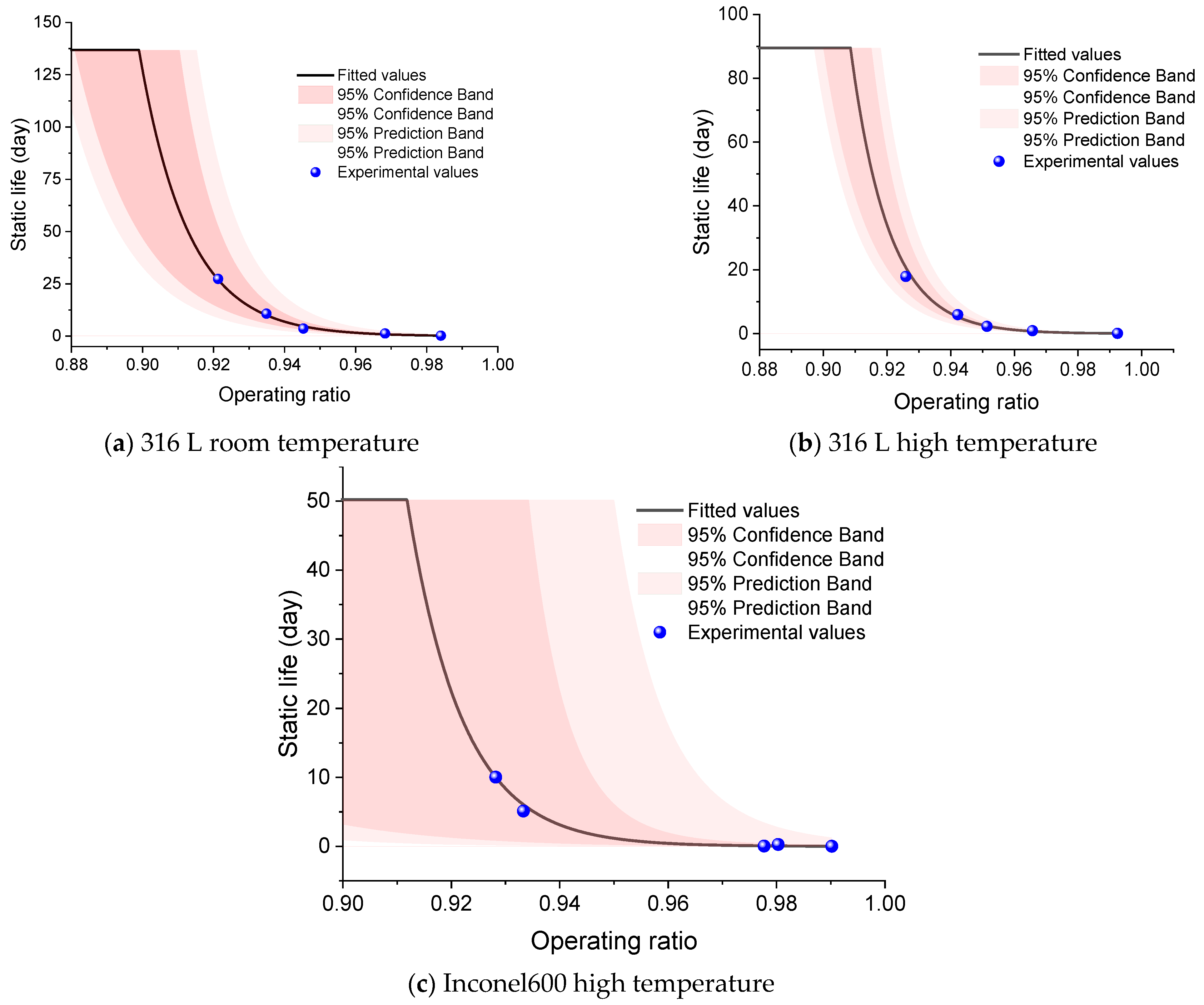
4.1. Static Load Life Prediction
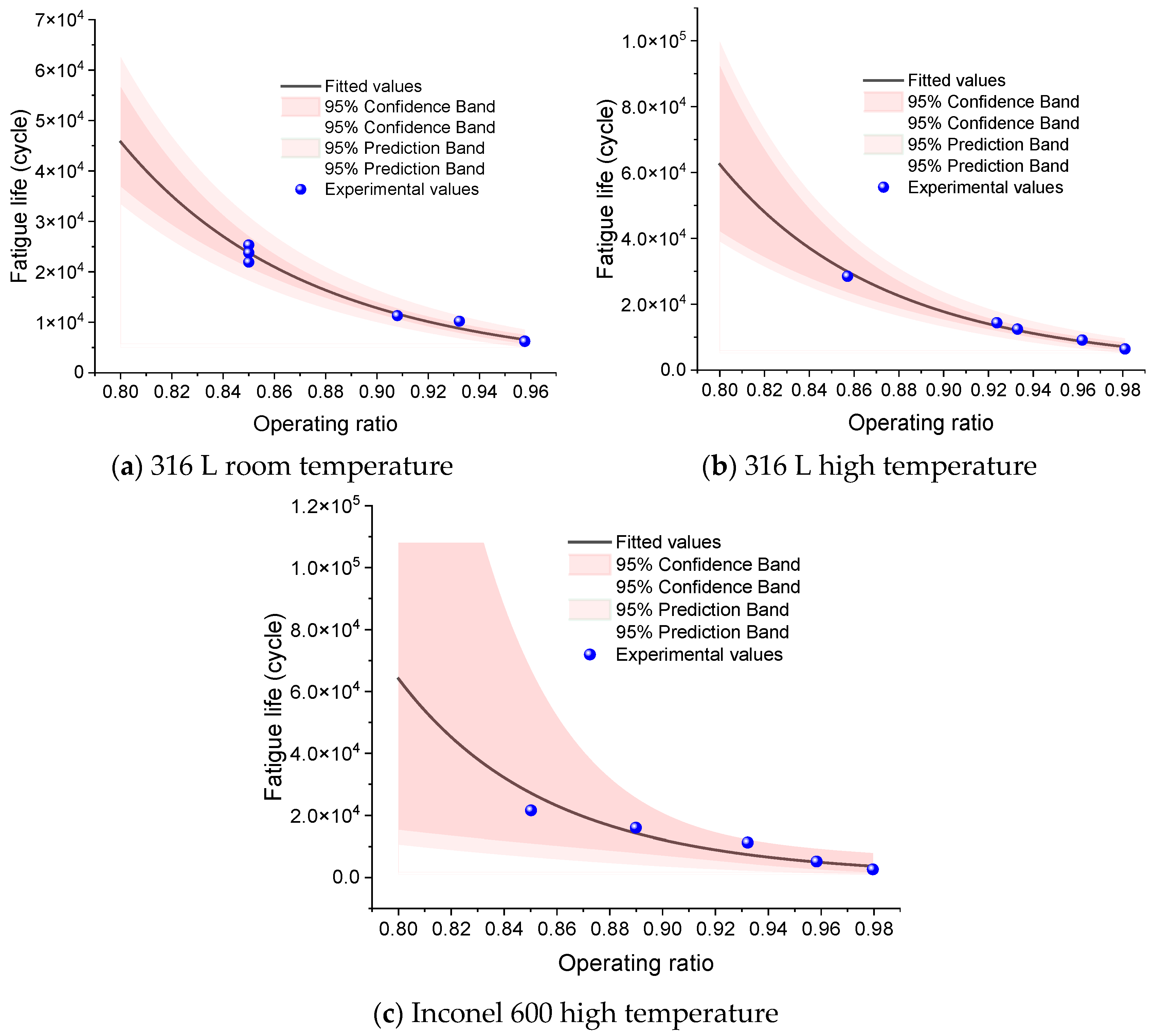
4.2. Fatigue Life Prediction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedel, L. Two phase pressure drop in a rupture disc/safety valve unit. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 1988, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbal, R. Transient flow phenomena and reaction forces during blowdown of gas at high pressures through relief lines behind rupture discs. Process Saf. Prog. 1993, 12, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutegi, M.K.; Schmidt, J.; Denecke, J. Sizing rupture disk vent line systems for high-velocity gas flows. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 62, 103950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannak, B. Experimental and theoretical investigation of gas–liquid flow pressure drop across rupture discs. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2010, 240, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Hui, H.; Gong, J. Design Research of the Double Rupture Disc Safety Relief Device Used on the Long Tube Trailer. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 394, 032052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xu, X.; Xuan, H.; Guo, B.; Huo, L.; Yu, J. Rupture Disc Monitoring Using Electro-mechanical Impedance (EMI): A Feasibility Study. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2023, 42, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, M.; Saburi, T.; Ando, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Miyasaka, T.; Kubota, S. Self-ignited flame behavior of high-pressure hydrogen release by rupture disk through a long tube. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 13484–13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Jin, K.; Zheng, X.; Han, Y.; Yao, Y.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Effect of Al-made burst disk on the shock wave and the spontaneous ignition of high-pressure hydrogen during its sudden discharge. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Yeom, S.; Choi, W.; Kim, T.G.; Hong, S.C.; Ryu, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.B. A study on the grooving process of a cross-scored rupture disc. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 13, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Z. A multi-scale damage model for fatigue accumulation due to short cracks nucleation and growth. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2014, 127, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santecchia, E.; Hamouda, A.M.S.; Musharavati, F.; Zalnezhad, E.; Cabibbo, M.; El Mehtedi, M.; Spigarelli, S. A Review on Fatigue Life Prediction Methods for Metals. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 9573524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Q.; Geng, L.Y.; Gong, J.M. Analysis on Bursting of Rupture Disc Made by Inconel 600 Alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 795, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Ellingwood, B. Continuum damage mechanics analysis of fatigue crack initiation. Int. J. Fatigue 1998, 20, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.J. The behaviour of short fatigue cracks and their initiation part I—A review of two recent books. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 1987, 10, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.R.; Jacob, M.S.D.; Salit, M.S.; Ahmed, E.M.; Saleem, M.; Edi, P. Experimental evaluation of fretting fatigue test apparatus. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoodeh, K. The Design of Pressure Safety and Relief Valves for Overpressure Protection: Essential considerations. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2023, 8, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doelp, L.C.; Brian, P.L.T. Reliability of pressure protective systems. A Markov analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1982, 21, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hui, H.; Huang, S. Theoretical and experimental study on sealing performance of a novel ultra-high pressure bursting disc. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 2020, 235, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüsenberg, S.; Vonnahme, G. Failure Analysis of High Pressure Rupture Discs and Effective Counter Measures. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–21 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ralls, A.M.; Menezes, P.L. Revealing the fretting corrosion mechanisms of laser shock peened cold spray 316 L stainless steel. Tribol. Int. 2024, 192, 109227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.K.; Shrivastava, A. Improvement in strength and ductility of rotary friction welded Inconel 600 and stainless steel 316 L with Cu interlayer. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Li, X.; Ni, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Shen, J. Theoretical design and experimental validation of rupture discs for water heat pipe blackbody source. Measurement 2025, 241, 115661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, D.; Xu, H.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J.; Yan, X. Experimental and numerical investigation of burst characteristics of ultra-high pressure rupture discs. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2025, 215, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, P.; Zhai, X.; Liu, Y. Numerical study on the influence mechanism of different types of burst disc on high pressure hydrogen spontaneous combustion in tube. J. Energy Storage 2023, 67, 107626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yuan, C.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Liu, X. Influence of Moulding Pressure on the Burst Pressure of Reverse-Acting Rupture Discs. Processes 2021, 9, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, W.; Luo, Z.; Zheng, H. Finite Element Analysis on the Temperature- Dependent Burst Behavior of Domed 316 L Austenitic Stainless Steel Rupture Disc. Metals 2020, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedel, F.; Chamberlain Pravia, Z.M.; Mezzomo, G.P. Methodology for assessment of statistical planning effects on the S-N curve determination using Monte Carlo simulations. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2019, 42, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Lili, L.; Wei, L.; Beibei, L.; Mingxing, L. Effects of fatigue and deformation on bursting pressure of conventional slotted blasting disc. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2024, 87, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
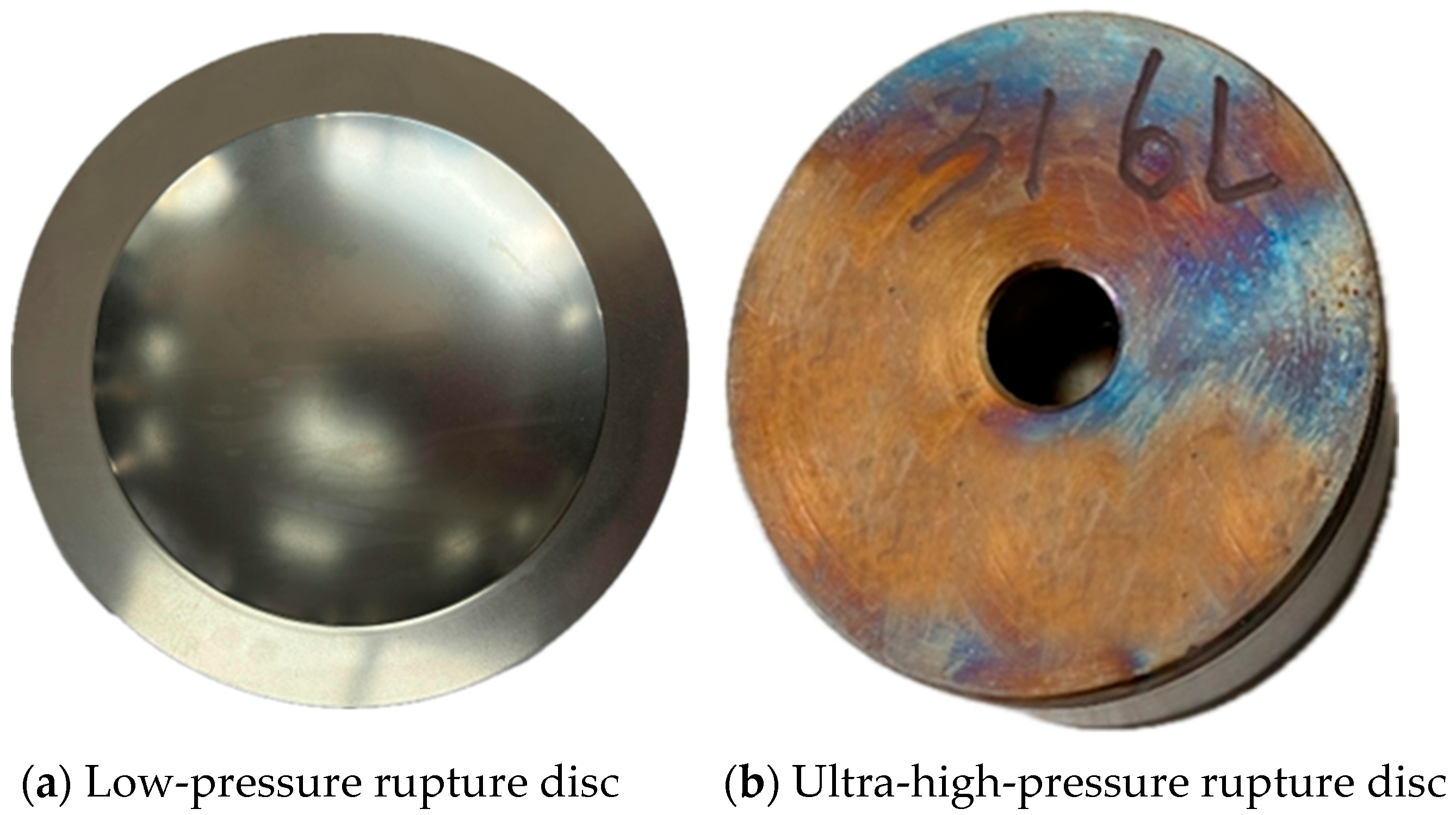
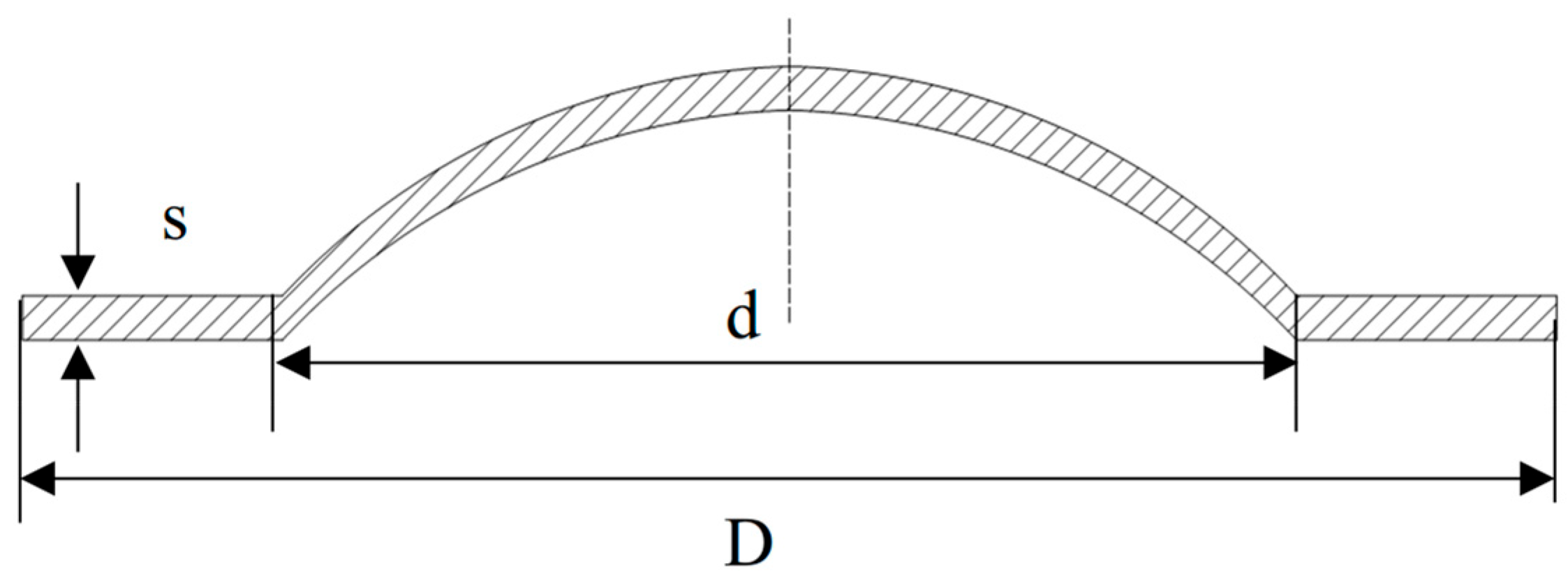
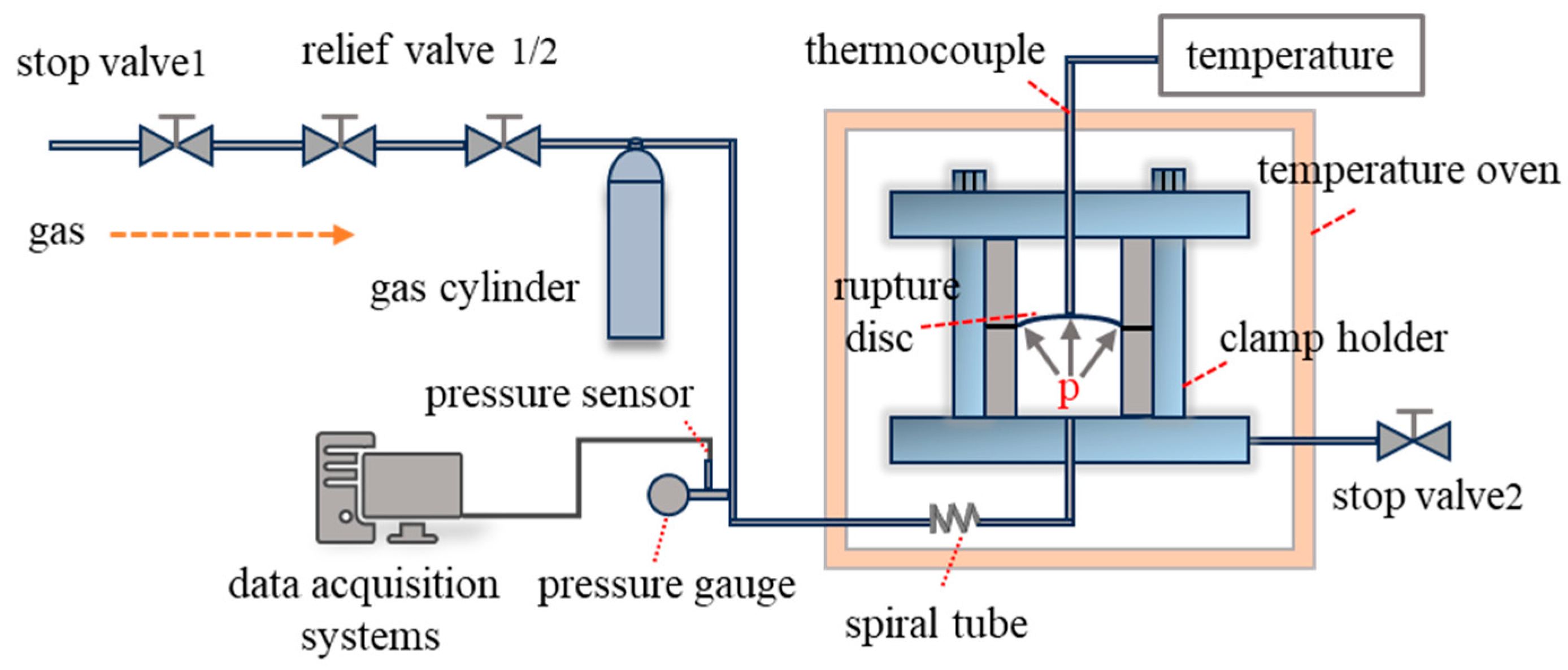
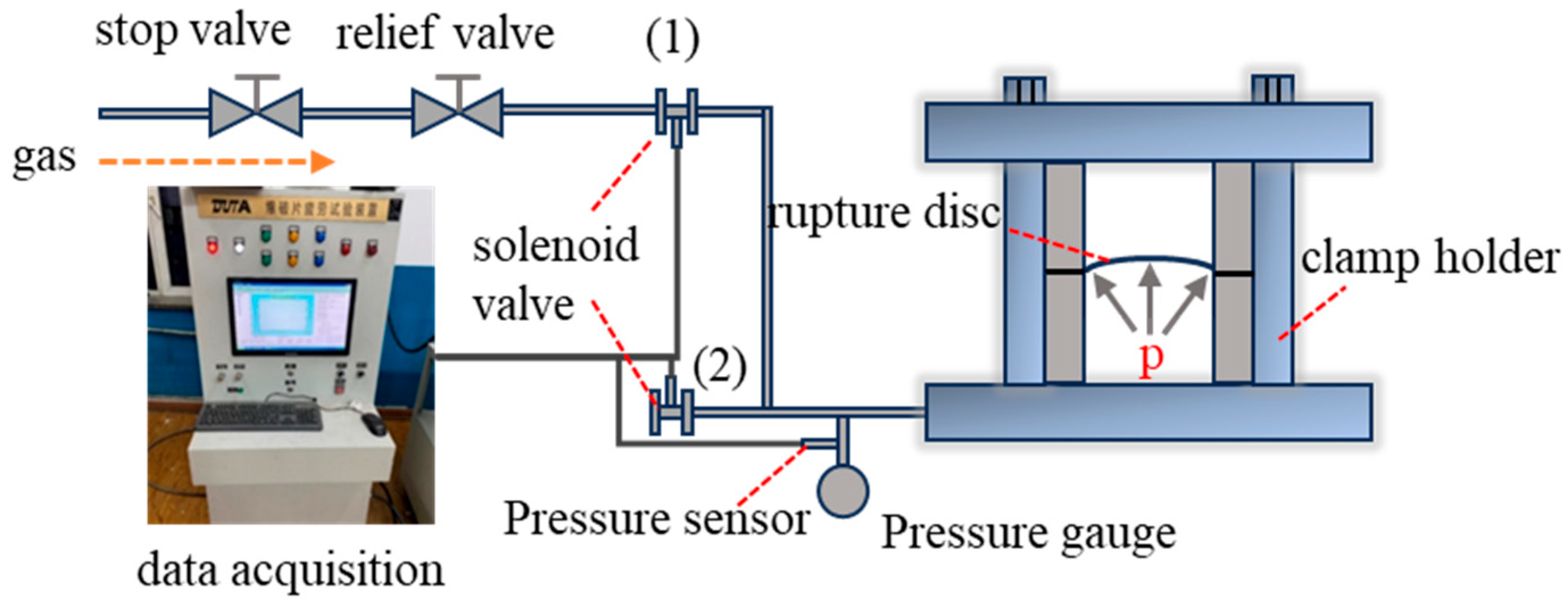
| Parameters | 316 L | Inconel 600 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Pressure | Ultra-High Pressure | Low Pressure | Ultra-High Pressure | |
| Design Burst Pressure/MPa | 1.0 | 140 | 1.0 | 160 |
| Burst Pressure Tolerance | ±3 | ±4 | ±3 | ±4 |
| Test Burst Pressure (Room Temperature 20 °C)/MPa | 1.24 | 142 | 1.08 | 159 |
| Test Burst Pressure (High Temperature 150 °C)/MPa | 1.06 | 121 | 1.02 | 146 |
| Material | Pressure Level | Membrane Thickness/mm | Burst Diameter/mm | Outer Diameter/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 L | Low pressure | 0.05 | 91 | 115 |
| 316 L | Ultra-high pressure | 0.5 | 10 | 42 |
| Inconel 600 | Low pressure | 0.05 | 91 | 115 |
| Inconel 600 | Ultra-high pressure | 0.8 | 15 | 42 |
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0162 | 0.0618 | 0.1354 | 0.0283 | 0.0014 | 16.52 | 10.05 | 2.03 | 0.0106 |
| C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.009 | 0.0002 | 0.19 | 15.81 | 74.80 | 0.03 | 8.26 |
| Material | Yield Strength/MPa | Ultimate Strength/MPa | Elongation/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316 L | 263 | 615 | 58 |
| Inconel 600 | 351 | 703 | 38 |
| Test Type | Low Pressure Conditions | Ultra High-Pressure Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Temperature/°C | Material | Temperature/°C | |
| Static Life | 316 L | 20 | 316 L | 150 |
| 150 | Inconel 600 | 150 | ||
| Inconel 600 | 20 | —— | ||
| 150 | ||||
| Fatigue Life | 316 L | 20 | —— | |
| 150 | ||||
| Inconel 600 | 20 | |||
| Number | Material | Burst Pressure/MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Value | Factory Calibration Value | ||
| 1 | 316 L | 1.24 | 1.21 |
| 2 | 1.23 | 1.21 | |
| 3 | 1.24 | 1.21 | |
| Average Value | Deviation from Factory Calibration Value/% | ||
| 1.24 | 2.2 | ||
| 4 | Inconel 600 | 1.08 | 1.04 |
| 5 | 1.08 | 1.04 | |
| 6 | 1.07 | 1.04 | |
| Average Value | Deviation from Factory Calibration Value/% | ||
| 1.08 | 3.5 | ||
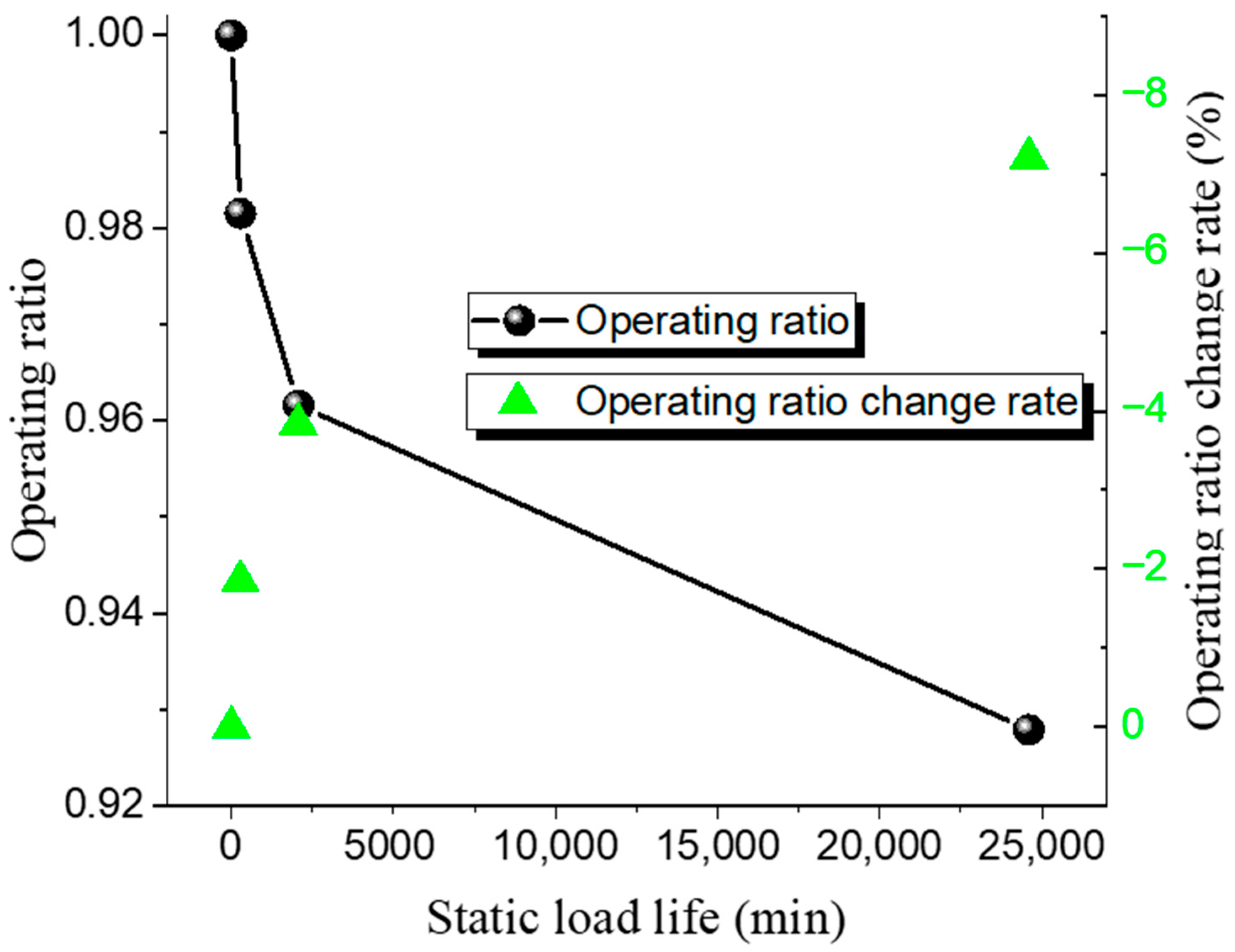
| Test | Temperature /°C | Static Load Pressure /MPa | Operating Ratio | Operating Ratio Change Rate /% | Hold Time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 1.22 | 0.984 | −1.6 | 335 |
| 2 | 20 | 1.20 | 0.9683 | −3.17 | 1840 |
| 3 | 20 | 1.17 | 0.9453 | −5.47 | 5248 |
| 4 | 20 | 1.16 | 0.9349 | −6.46 | 15,510 |
| 5 | 20 | 1.14 | 0.9213 | −7.87 | 39,400 |
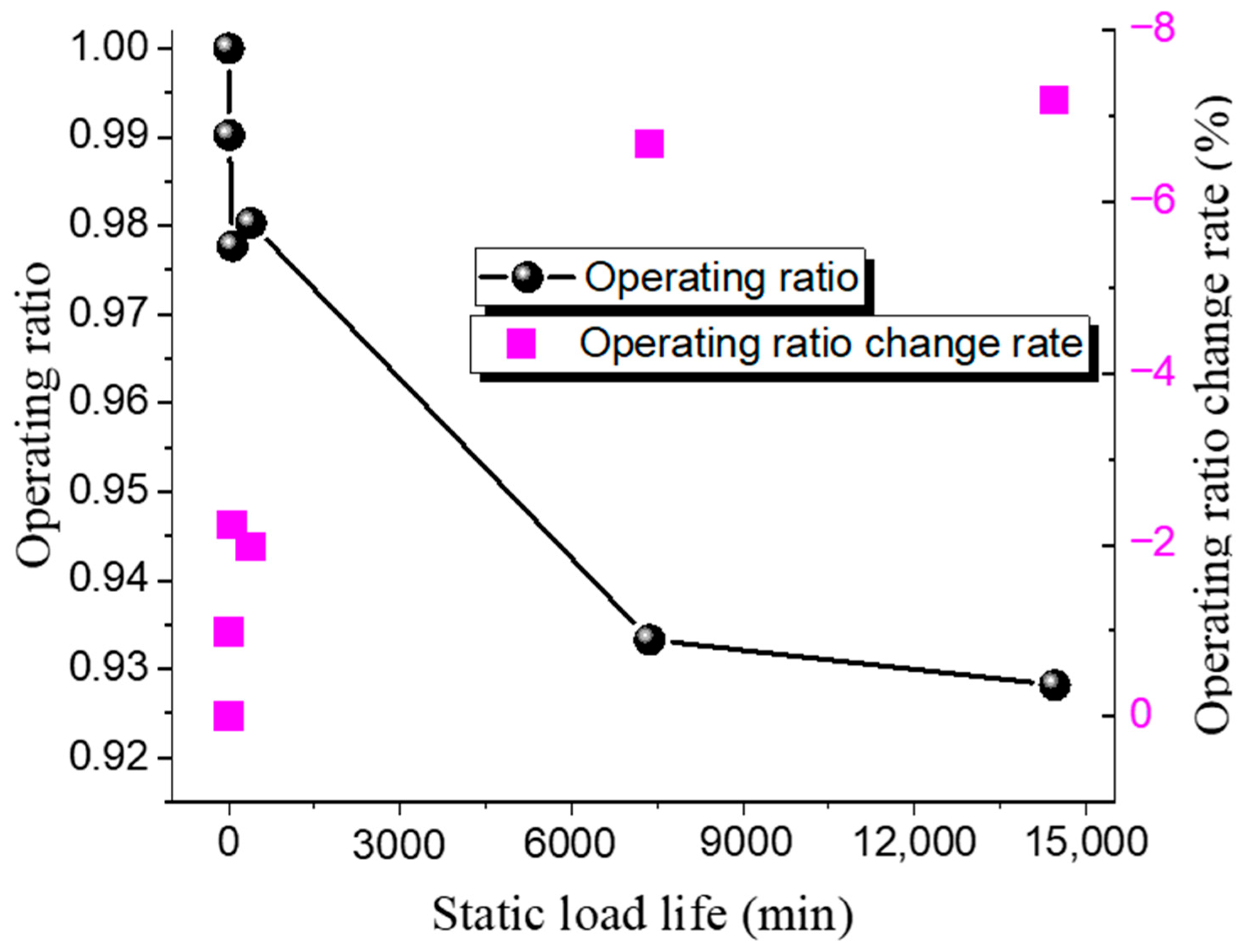
| Test | Temperature /°C | Static Load Pressure /MPa | Operating Ratio | Operating Ratio Change Rate /% | Hold Time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 151 | 1.052 | 0.9924 | −0.76 | 96 |
| 2 | 151 | 1.024 | 0.9657 | −3.43 | 1301 |
| 3 | 151 | 1.008 | 0.9514 | −4.86 | 3284 |
| 4 | 152 | 0.9987 | 0.9422 | −5.78 | 8559 |
| 5 | 151 | 0.9815 | 0.9259 | −7.41 | 25,780 |
| Test | Temperature /°C | Static Load Pressure /MPa | Operating Ratio | Operating Ratio Change Rate /% | Hold Time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 1.08 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 20 | 1.06 | 0.9815 | −1.85 | 280 |
| 3 | 20 | 1.05 | 0.9616 | −3.84 | 2075 |
| 4 | 20 | 1.00 | 0.9279 | −7.21 | 24,600 |
| Test | Temperature /°C | Static Load Pressure /MPa | Operating Ratio | Operating Ratio Change Rate /% | Hold Time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 151 | 1.01 | 0.9902 | −0.98 | 13 |
| 2 | 151 | 0.997 | 0.9777 | −2.23 | 69 |
| 3 | 150 | 1.0 | 0.9803 | −1.97 | 390 |
| 4 | 152 | 0.952 | 0.9333 | −6.67 | 7362 |
| 5 | 150 | 0.9468 | 0.9282 | −7.18 | 14,450 |
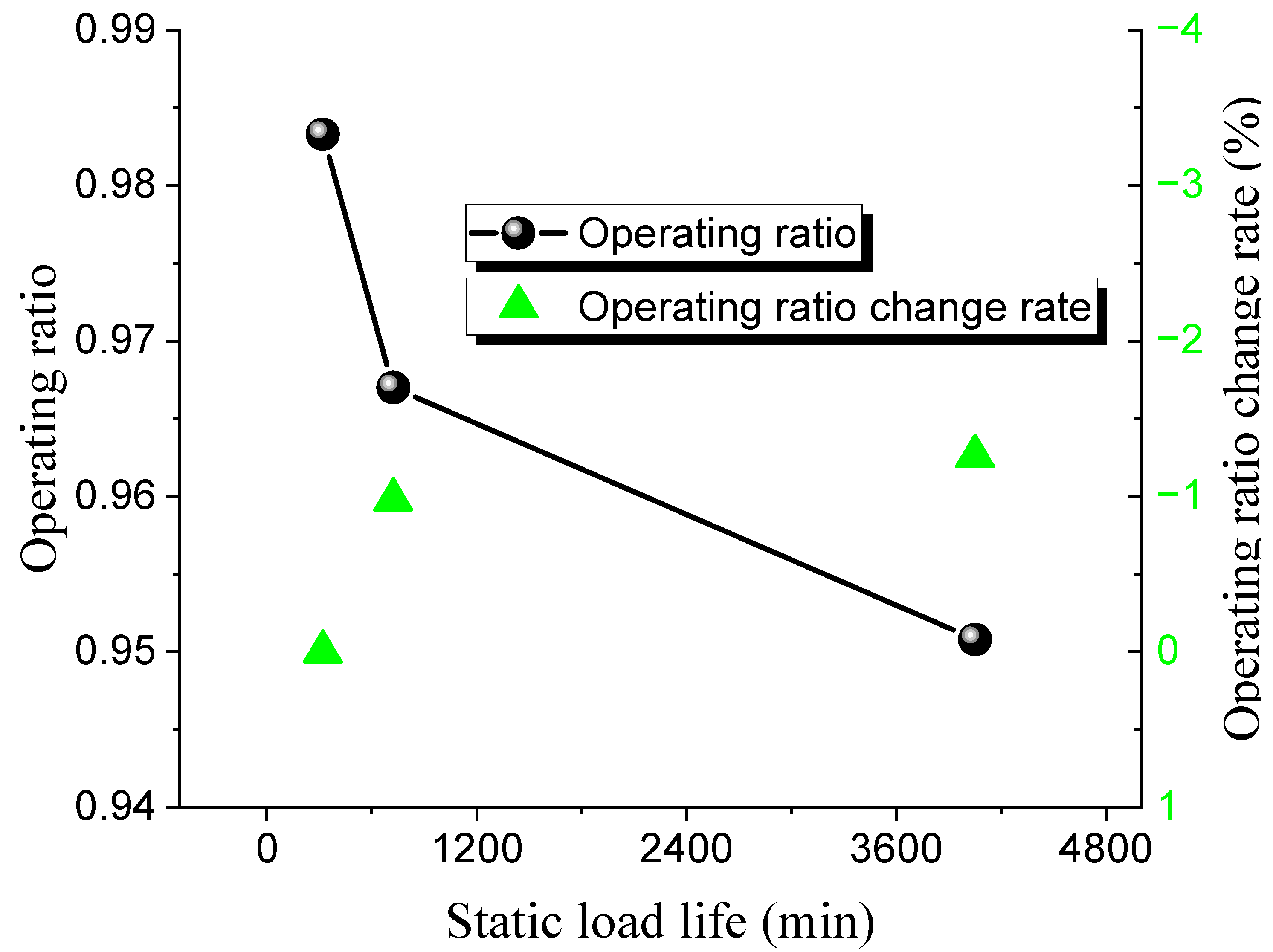
| Test | Temperature /°C | Static Load Pressure /MPa | Operating Ratio | Operating Ratio Change Rate /% | Hold Time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 152 | 119 | 0.9833 | 0 | 320 |
| 2 | 152 | 117 | 0.967 | −0.98 | 723 |
| 3 | 152 | 115 | 0.9508 | −1.26 | 4050 |
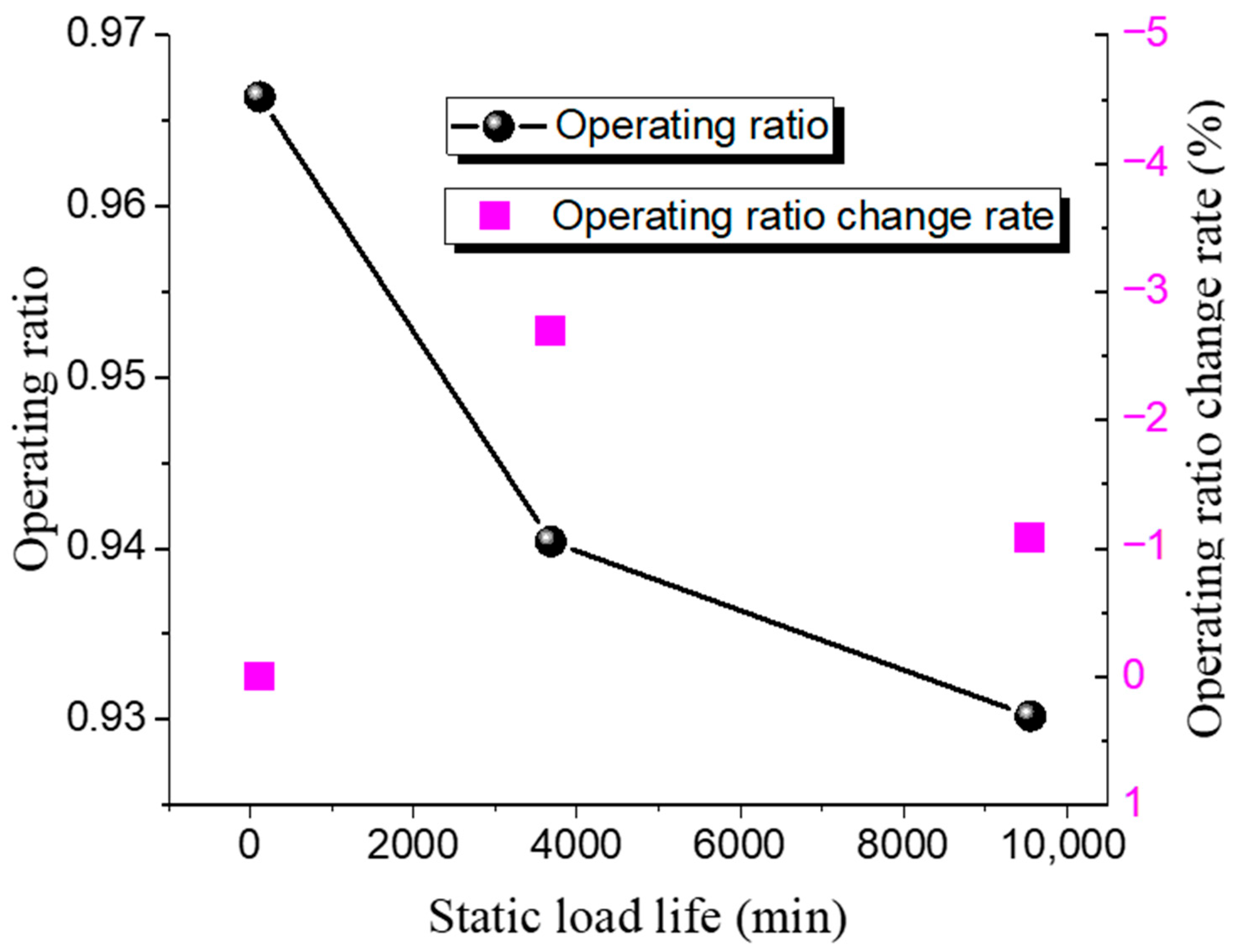
| Test | Temperature /°C | Static Load Pressure /MPa | Operating Ratio | Operating Ratio Change Rate /% | Hold Time /min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 151 | 141 | 0.9664 | 0 | 117 |
| 2 | 151 | 137.3 | 0.9404 | −2.69 | 3683 |
| 3 | 151 | 135.8 | 0.9302 | −1.08 | 9552 |
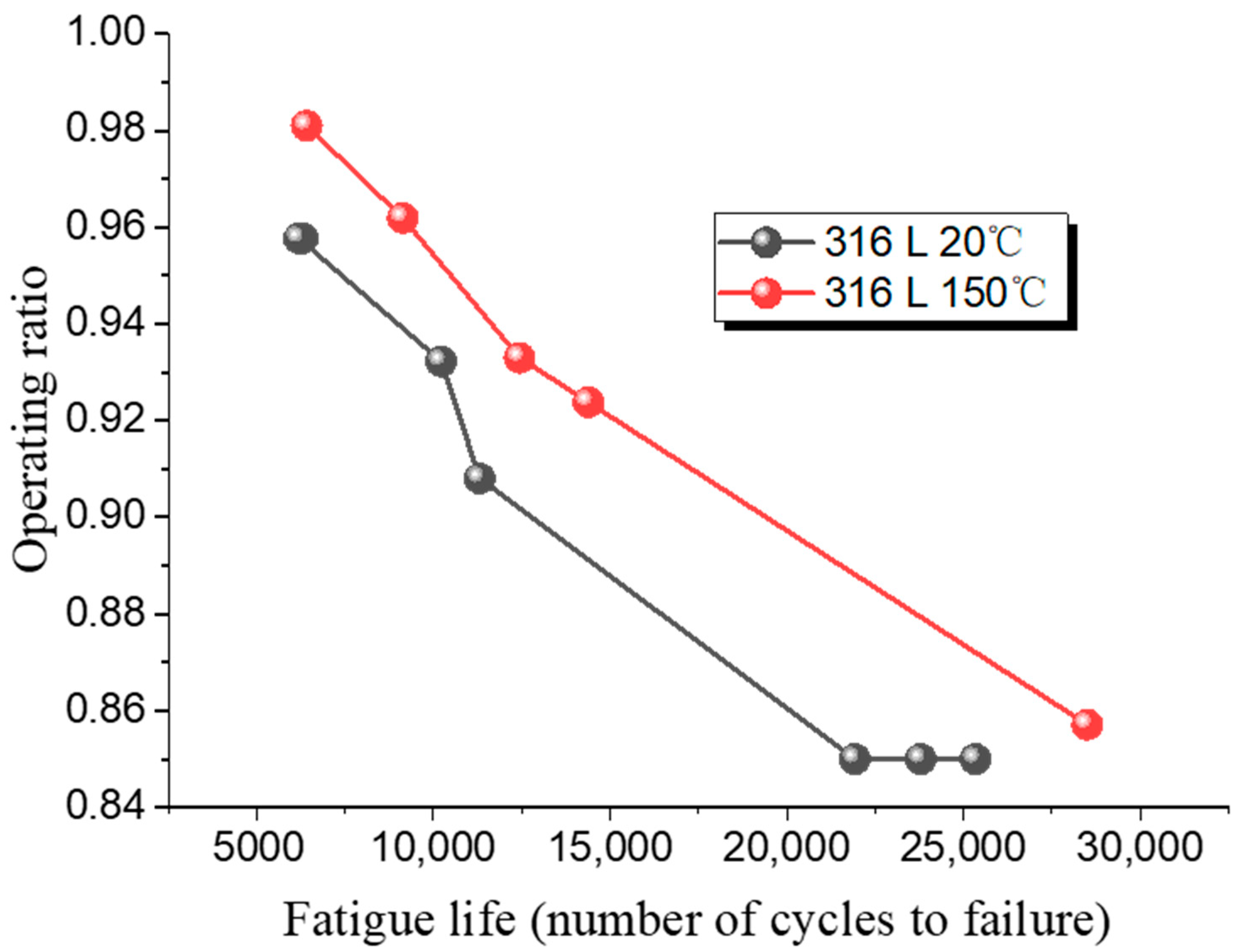
| Test | Temperature/°C | Valley Pressure/MPa | Peak Pressure/MPa | Operating Ratio | Fatigue Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.19 | 0.9577 | 6306 |
| 2 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.19 | 0.9577 | 6201 |
| 3 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.16 | 0.9322 | 10,221 |
| 4 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.126 | 0.908 | 11,316 |
| 5 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.05 | 0.85 | 21,930 |
| 6 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.05 | 0.85 | 25,341 |
| 7 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.05 | 0.85 | 23,795 |
| 8 | 153 | 0.2 | 1.03 | 0.981 | 6417 |
| 9 | 152 | 0.2 | 1.01 | 0.9619 | 9139 |
| 10 | 152 | 0.2 | 0.98 | 0.933 | 12,446 |
| 11 | 150 | 0.2 | 0.97 | 0.9238 | 14,385 |
| 12 | 150 | 0.2 | 0.90 | 0.8571 | 28,500 |
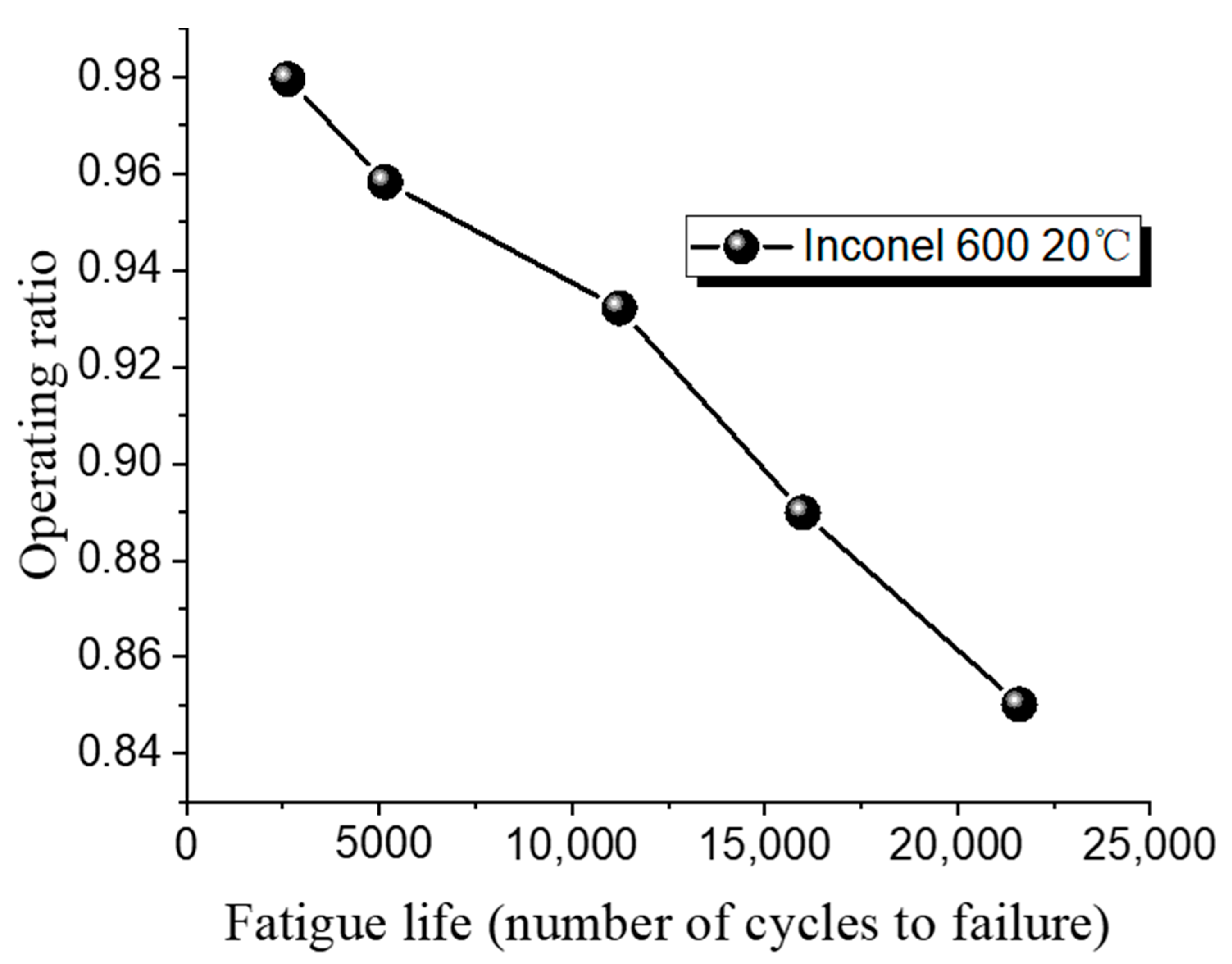
| Test | Temperature/°C | Valley Pressure/MPa | Peak Pressure/MPa | Operating Ratio | Fatigue Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.06 | 0.9796 | 2630 |
| 2 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.035 | 0.9583 | 5157 |
| 3 | 20 | 0.2 | 1.007 | 0.9322 | 11,233 |
| 4 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.96 | 0.8899 | 15,987 |
| 5 | 20 | 0.2 | 0.98 | 0.8502 | 21,607 |
| 316 L Room Temperature | 316 L High Temperature | Inconel 600 High Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 77.61 | 88.26 | 101.05 |
| b | −72.77 | −84.20 | −98.55 |
| 316 L Room Temperature | 316 L High Temperature | Inconel 600 High Temperature | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 8.32 | 8.66 | 7.91 |
| b | −10.79 | −10.68 | −14.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Xuan, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, J. The Impact of Operating Ratio on the Static and Fatigue Life of Forward-Acting Rupture Discs. Materials 2025, 18, 4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214983
Wang H, Liu Z, Xuan H, Zhang H, Xu H, Chen S, Yu J. The Impact of Operating Ratio on the Static and Fatigue Life of Forward-Acting Rupture Discs. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214983
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haitao, Zhenxi Liu, Honglie Xuan, Hongxin Zhang, Hui Xu, Shan Chen, and Jianliang Yu. 2025. "The Impact of Operating Ratio on the Static and Fatigue Life of Forward-Acting Rupture Discs" Materials 18, no. 21: 4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214983
APA StyleWang, H., Liu, Z., Xuan, H., Zhang, H., Xu, H., Chen, S., & Yu, J. (2025). The Impact of Operating Ratio on the Static and Fatigue Life of Forward-Acting Rupture Discs. Materials, 18(21), 4983. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214983







