Effects of Ball Milling Time and Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Ti Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Mg-Al-Ti Alloys
2.2. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Ball Milling Time
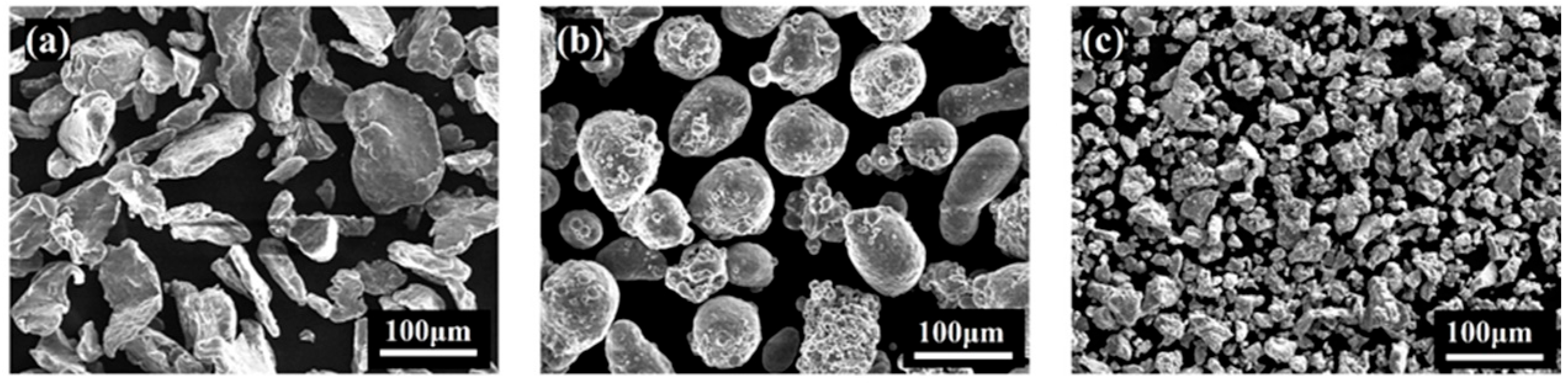
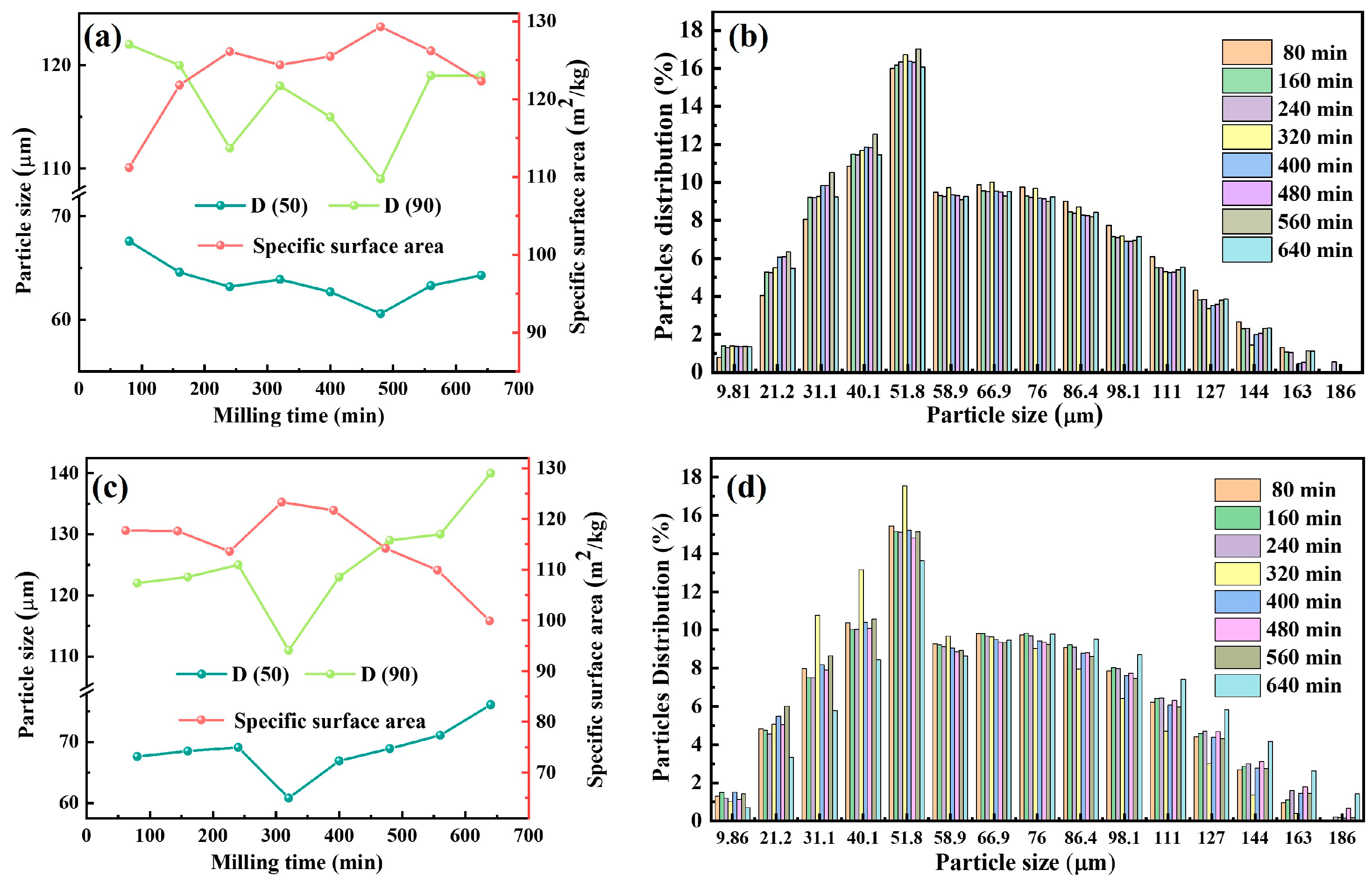
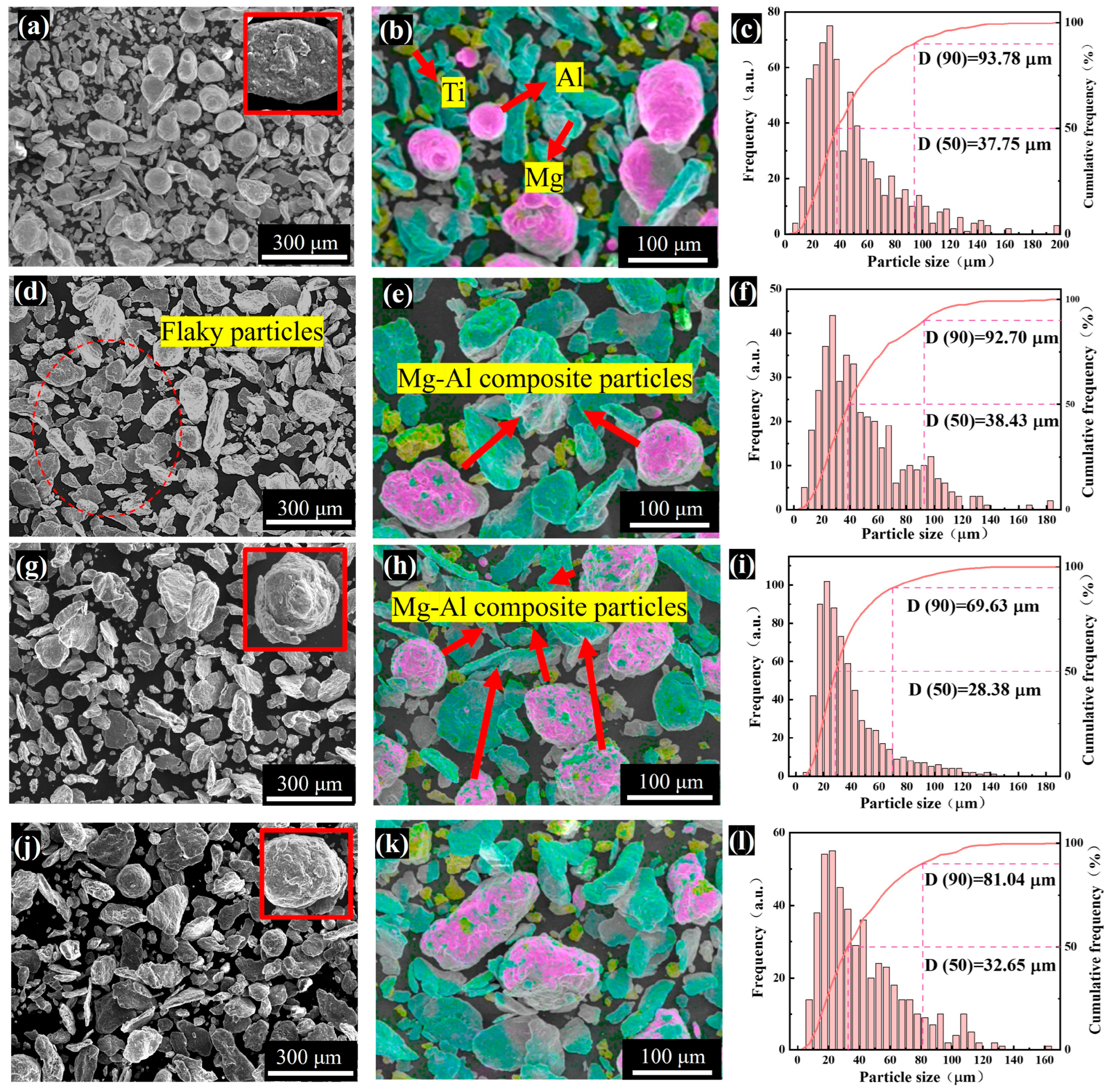
3.1.1. Particle Size and Distribution of Ball-Milled Powders
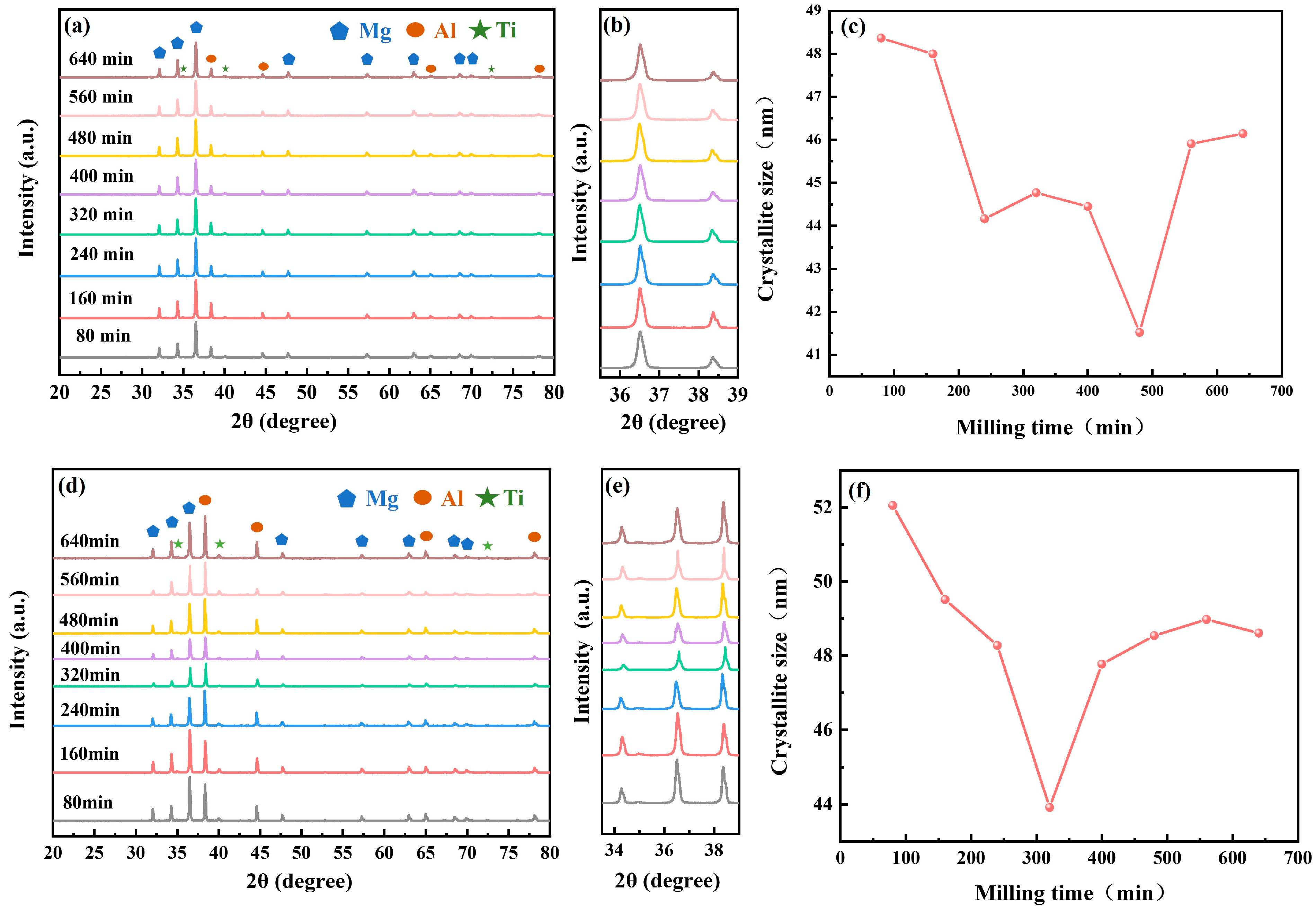
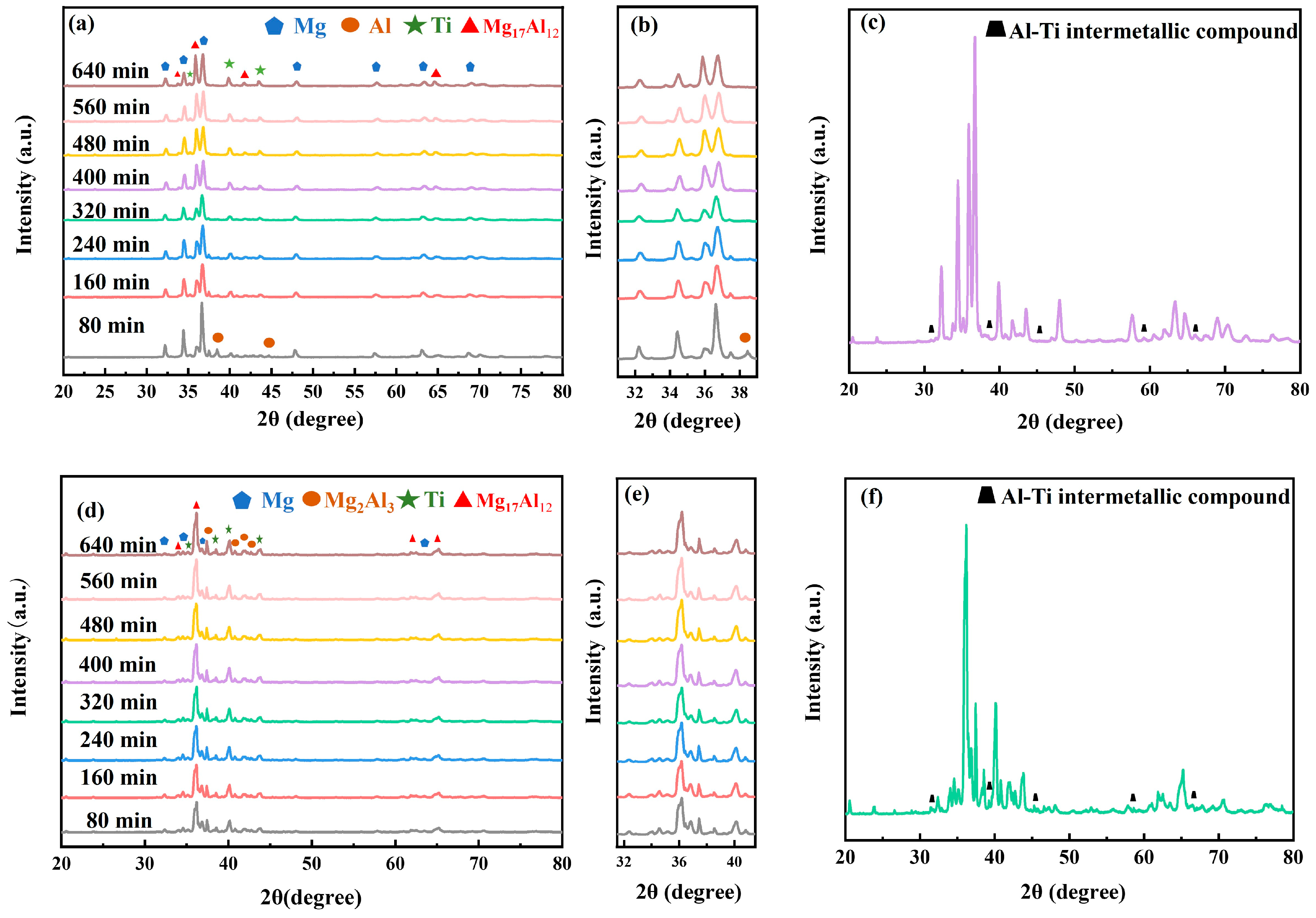
3.1.2. Phase Composition of Ball-Milled Powders
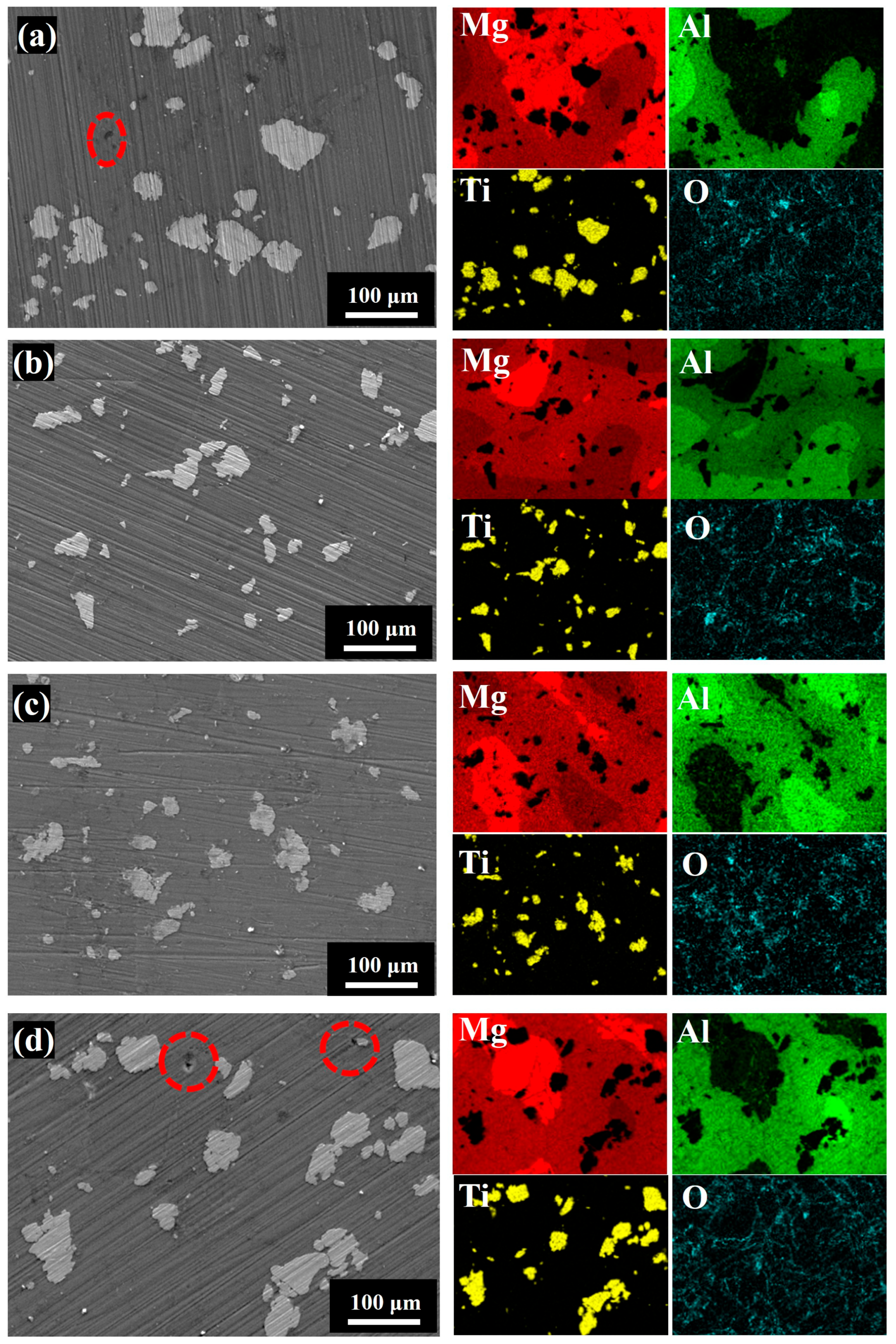
3.1.3. Phase Composition and Microstructure of Sintered Samples
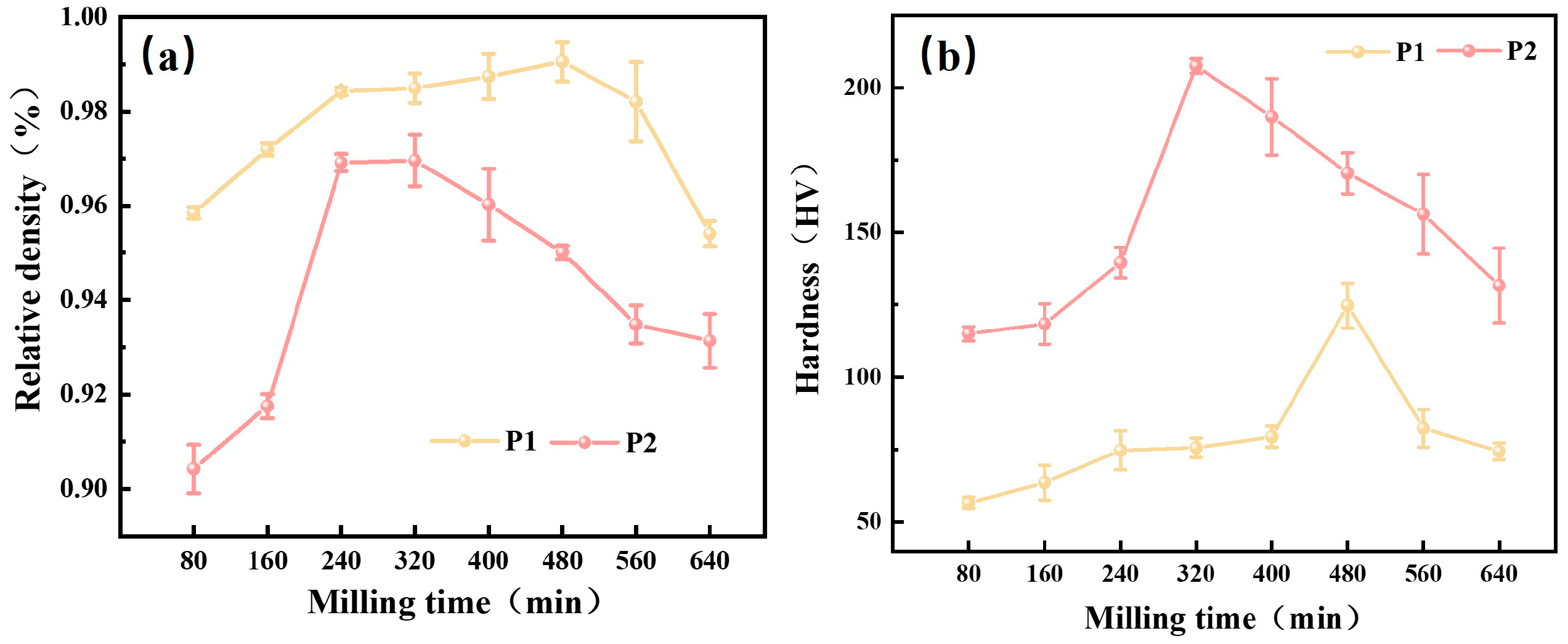
3.1.4. Densification and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Samples for Different Milling Times
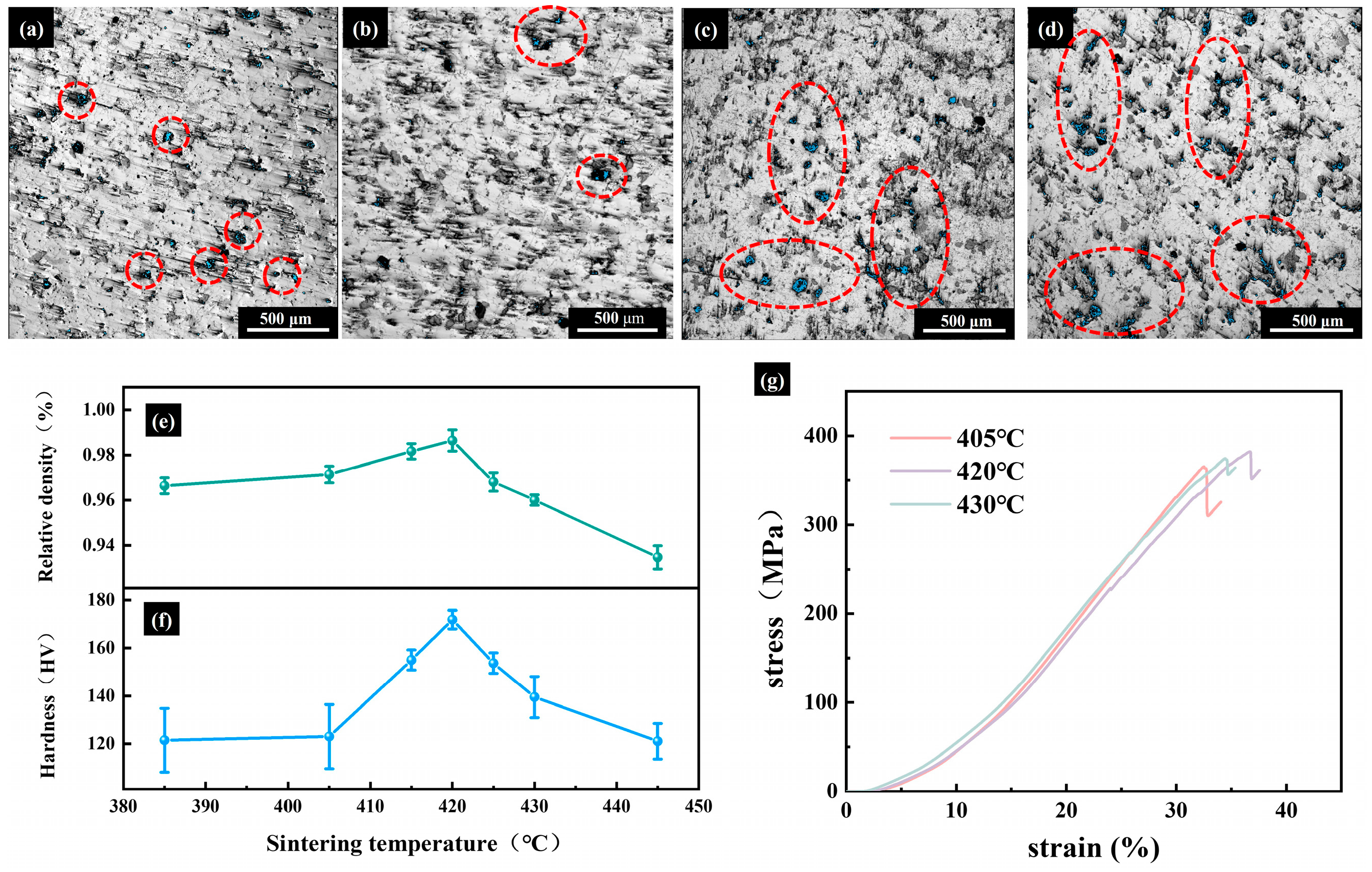
3.2. Effect of Sintering Parameters
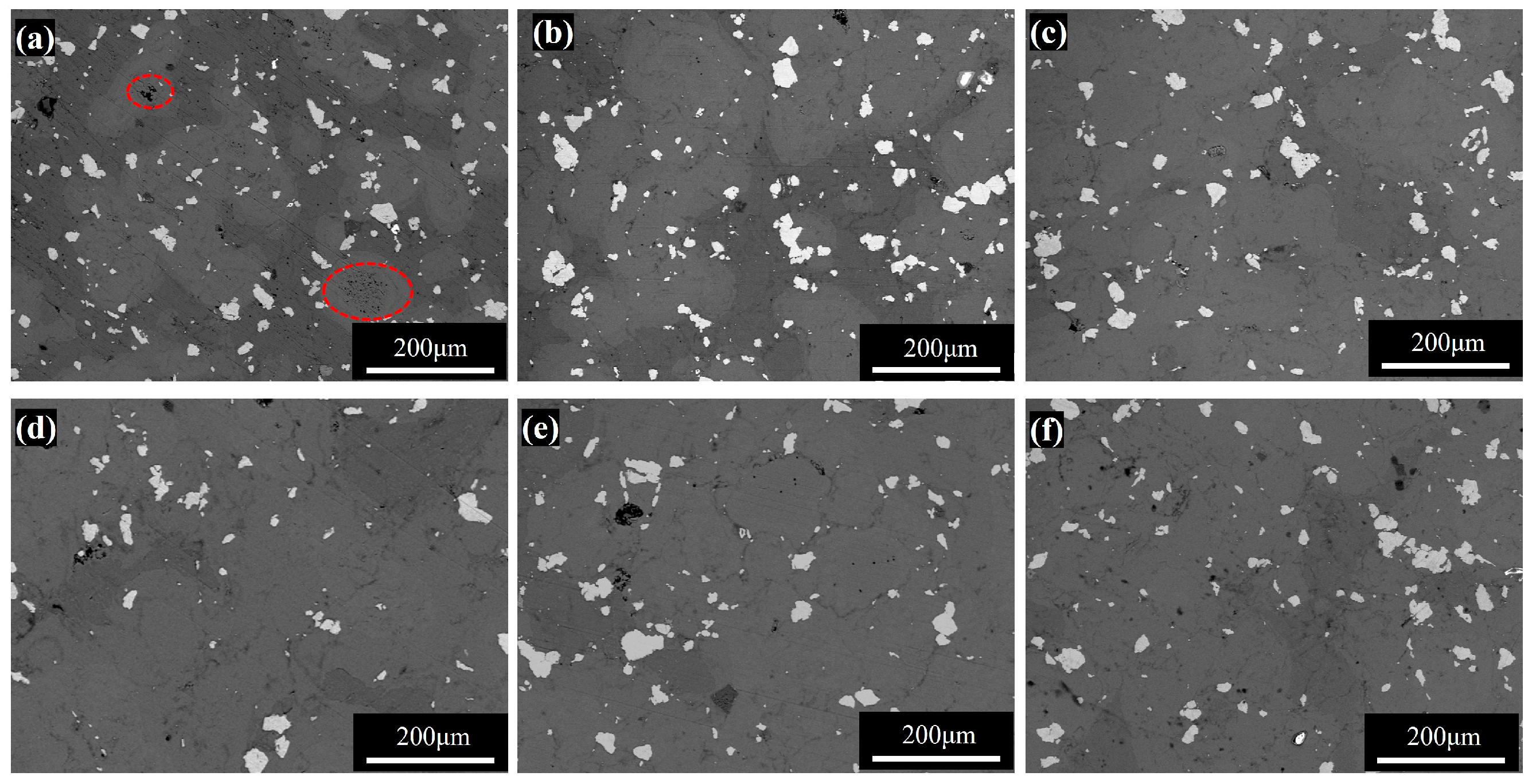
3.2.1. Microscopic Morphology and Phase Composition of Sintered Samples
3.2.2. Densification and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, S.; Chen, L.; Jing, J.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, H.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y. Role of Ca/Al ratio content on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Mg-Al-Ca alloy fabricated through squeeze casting. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1036, 181819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Lu, B.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, Q.; Tang, W.; Mo, N.; Xu, Y.; Qin, G. Effect of Al addition on microstructure and mechanical property of Mg-Mn-Ca-Ce based alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 175975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, X.; Deng, L.; Zhu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Pan, F. Effect of La content on mechanical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of Mg-Zn-Y-La-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1008, 176611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.E.; Kennedy, J.R.; Lunt, D.; Guo, J.; Strong, D.; Robson, J.D. Preageing of magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 809, 141002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Y.; Peng, X.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Research advances of magnesium and magnesium alloys globally in 2023. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 3441–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahedi, M.; McWilliams, B.A.; Moy, P.; Knezevic, M. Deformation twinning in rolled WE43-T5 rare earth magnesium alloy: Influence on strain hardening and texture evolution. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Qin, G.; Huang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Sha, X.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, H.; et al. Development of low-alloyed and rare-earth-free magnesium alloys having ultra-high strength. Acta Mater. 2018, 149, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Chen, D.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Q.; Huang, G.; Pan, F. Strategies for enhancing the room-temperature stretch formability of magnesium alloy sheets: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 12965–12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Blawert, C.; Yang, H.; Wiese, B.; Feyerabend, F.; Bohlen, J.; Mei, D.; Deng, M.; Campos, M.S.; Scharnagl, N.; et al. Microstructure-corrosion behaviour relationship of micro-alloyed Mg-0.5Zn alloy with the addition of Ca, Sr, Ag, In and Cu. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 108980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Shan, L.; Jiang, B.; Yang, H.; He, C.; Hao, W.; He, J.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, M.; Pan, F. Ameliorating mechanical properties and reducing anisotropy of as-extruded Mg-1.0Sn-0.5Ca alloy via Al addition. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2021, 31, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Q.; Yang, H.; Yuan, M.; Huang, G.; Zhang, D.; Pan, F. Influence of Ce content on the microstructures and tensile properties of Mg-1Gd-0.5Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 823, 141675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, M.; Gupta, M. Magnesium nanocomposites: An overview on time-dependent plastic (creep) deformation. Def. Technol. 2019, 15, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Cheng, W.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y. The creep behavior of Mg–9Al–1Si–1SiC composite at elevated temperature. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.N.; Przełożyńska, E. The influence of Ti particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-5Al-5RE matrix alloy composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, G.; Song, J.; She, J.; Tan, J.; Zheng, K.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Microstructures and mechanical properties of titanium-reinforced magnesium matrix composites: Review and perspective. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 2311–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, R.; Ortgies, S.; Tamayol, A.; Bobaru, F.; Sealy, M.P. Additive manufacturing of magnesium alloys. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Dong, Q.; Tan, J.; Lv, H.; Wang, F.; Wu, G.; Yu, P.; Jiang, B.; Tang, A.; Pan, F. Synergistic enhancement of thermal conductivity and mechanical properties in cast Mg-Zn-Zr-Sr alloys via grain refinement and solute redistribution. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1036, 182094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Research advances in magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2020. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 705–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ni, J.; Song, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, K.; Zhou, S.; Hu, C.; Xu, Y.; Luo, L. Effect of post-sinter annealing on structure and coercivity of (Zr, Ti)-doped Nd-Ce-Fe-B magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 990, 174479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashif, I.; Abdelghany, A.; El-said, R. Effect of sintering and milling time on lead magnesium niobate nanocrystallite phase. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, J.; Das, S.; Das, K. Evaluating the influence of milling time, and sintering temperature and time on the microstructural changes and mechanical properties of Al-Y2W3O12-AlN hybrid composites. Powder Technol. 2021, 377, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, V.V.; Chak, S.K. The effect of process parameters in aluminum metal matrix composites with powder metallurgy. Manuf. Rev. 2018, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ding, W.; Ji, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, C. The influence and optimization of milling process parameters on corrosion resistance and surface quality of AZ31B magnesium alloy frame parts. J. Mater. Eng Perform. 2025, 34, 21980–21997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, D.; Sengupta, P.; Panigrahi, A.; Bajpai, S.; Gupta, S.; Debata, M. Effect of high-energy ball-milling duration on densification, microstructure, and mechanical properties of Cr2AlC-dispersed 90W-6Ni-2Fe-2Co heavy alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 27, 2400852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sreenivas, K. Influence of sintering temperature on structural, electrical, dielectric, and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4) ceramics prepared using powder derived via sol-gel auto-combustion. J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 2024, 111, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, J.; Das, S.; Das, K. The effect of milling time, and sintering temperature and time on the microstructure-property relationship of aluminium-matrix hybrid composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkova, A.I.; Cherniavsky, V.V.; Bolbut, V.; Krüger, M.; Bogomol, I. Structure formation and mechanical properties of the high-entropy AlCuNiFeCr alloy prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 786, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avar, B.; Simsek, T.; Ozcan, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.K.; Kalkan, B. Structural stability of mechanically alloyed amorphous (FeCoNi)70Ti10B20 under high-temperature and high-pressure. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 860, 158528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, U.; Gibson, N. The scherrer equation versus the “debye-scherrer equation”. Nat. Nanotech. 2011, 6, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Guo, X.-P. Mechanical alloying behaviors of Mo–Si–B-based alloy from elemental powders under different milling conditions. Rare Met. 2019, 38, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanalizadeh, H.; Emamy, M.; Shokouhimehr, M. A novel aluminum based nanocomposite with high strength and good ductility. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debata, M.; Acharya, T.S.; Sengupta, P.; Acharya, P.P.; Bajpai, S.; Jayasankar, K. Effect of high energy ball milling on structure and properties of 95W-3.5Ni-1.5Fe heavy alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 69, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogagnolo, J.B.; Robert, M.H.; Torralba, J.M. Mechanically alloyed AlN particle-reinforced Al-6061 matrix composites: Powder processing, consolidation and mechanical strength and hardness of the as-extruded materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 426, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, R.; Peng, C. The influence of ball milling conditions on the powder characteristics and sintering densification of MoCu alloy. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2024, 125, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lv, F.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Effects of milling time and sintering temperature on the mechanical properties of 8 wt% WC/AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 high entropy alloy matrix composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 173203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Alloy | Mg (wt%) | Al (wt%) | Ti (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 75 | 20 | 5 |
| P2 | 50 | 40 | 10 |
| Milling Time (min) | Sintering Temperature (°C) | Sintering Time (h) | Heating Rate (°C/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80 160 240 320 400 480 560 640 | 385 405 415 420 425 430 445 | 1 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, D.; Shen, Y.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, B.; Bai, W.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Effects of Ball Milling Time and Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Ti Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214936
Qian D, Shen Y, Geng Z, Zhao B, Bai W, Sun S, Li X, Zeng J, Zhang S, Wang Y, et al. Effects of Ball Milling Time and Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Ti Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214936
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Dan, Yue Shen, Zhanli Geng, Binyu Zhao, Wandong Bai, Shiping Sun, Xiang Li, Jinbo Zeng, Shengdi Zhang, Yumin Wang, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Ball Milling Time and Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Ti Alloy" Materials 18, no. 21: 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214936
APA StyleQian, D., Shen, Y., Geng, Z., Zhao, B., Bai, W., Sun, S., Li, X., Zeng, J., Zhang, S., Wang, Y., & Ren, X. (2025). Effects of Ball Milling Time and Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Al-Ti Alloy. Materials, 18(21), 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214936






