Crystallisation and Microstructure of Sludge Particles in AlSi7Mg Secondary Alloys with Increased Iron Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aim and Scope of Research
- performing melts of the AlSi7Mg alloy with varying shares of iron, manganese, and chromium according to the experimental plan (Figure 1),
- analysis of phase transformations occurring during heating and cooling using Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and determination of the range of characteristic temperatures of these transformations,
- determination of the heat of reaction (enthalpy ΔH) for AlFeMn phases and sludge particles,
- metallographic examinations.
2.2. Method of Melting Alloys
- aluminium grade A00 (99.9 wt.% Al),
- technical silicon with a purity of 99.6 wt.% Si,
- AlMg10 alloy (approx. 10 wt.% Mg),
- AlFe25 master alloy (approx. 25 wt.% Fe),
- AlMn50 master alloy (approx. 50 wt.% Mn), as a manganese carrier,
- AlCr10 master alloy (approx. 10 wt.% Cr), as a chromium carrier (Mn and Cr additions were introduced to change the unfavourable morphology of the β-Fe phase).
2.3. Research on Structure, Phase Composition, and Phase Transformation Temperatures
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition Test Results
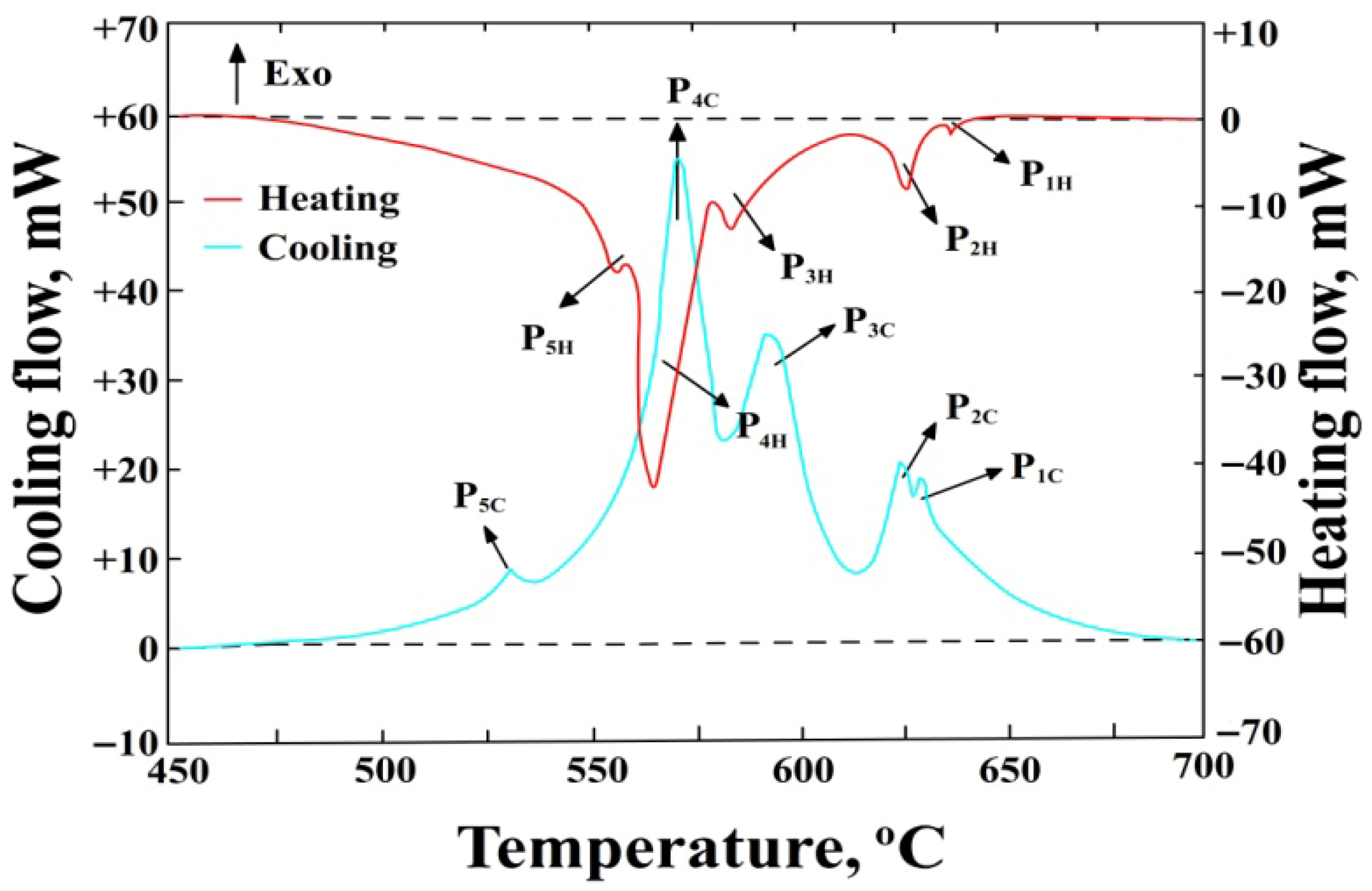
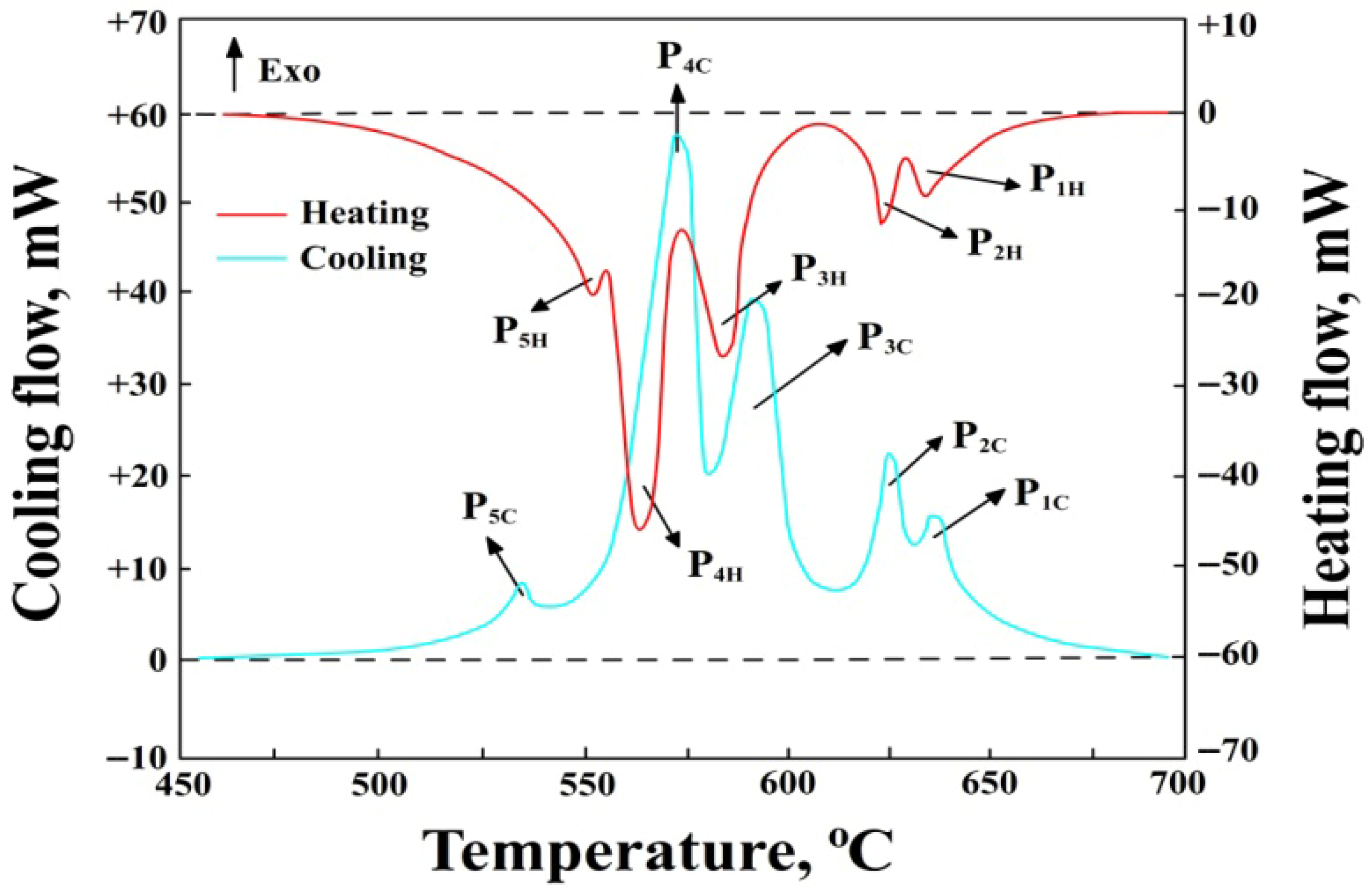
3.2. DSC Test Results
- P1H—thermal effect from the precipitation of sludge particles during heating, P1C—during cooling, mW,
- P2H—thermal effect from the precipitation of α(Al) solid solution dendrites during heating, P2C—during cooling, mW,
- P3H—thermal effect from the precipitation of AlFeMn-type phases during heating, P3C—during cooling, mW,
- P4H—thermal effect from the precipitation of the double eutectic α(Al)+β(Si) during heating, P4C—during cooling, mW,
- P5H—thermal effect from the precipitation of the eutectic containing the Mg2Si phase during heating, P5C—during cooling, mW,
- Endo—endothermic reactions,
- Exo—exothermic reactions,
- --------—baseline determining the area under the peak for calculating the enthalpy ΔH value.
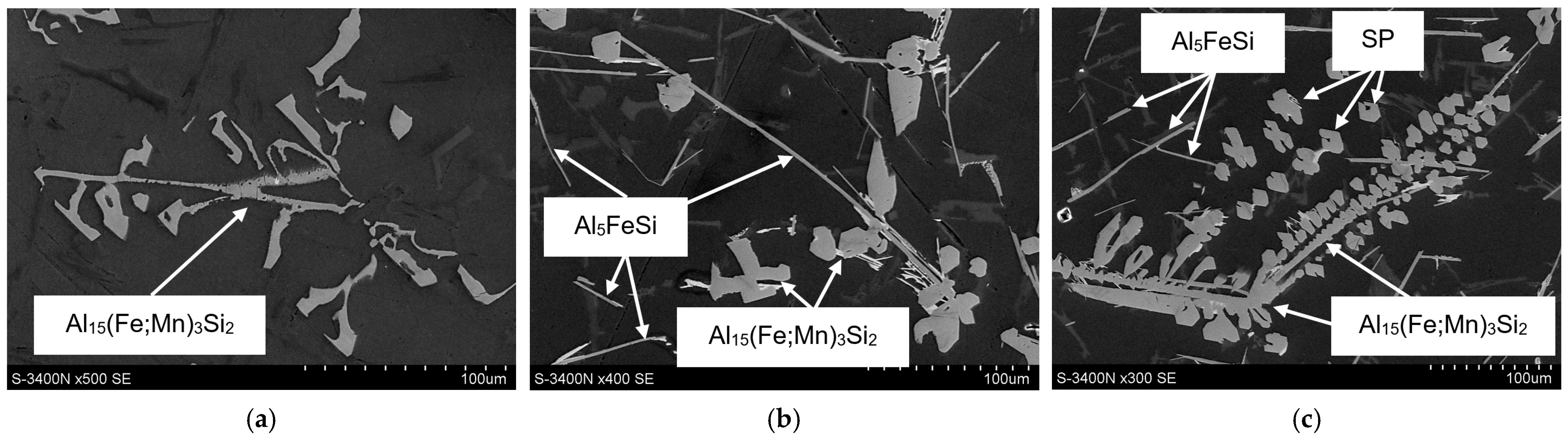
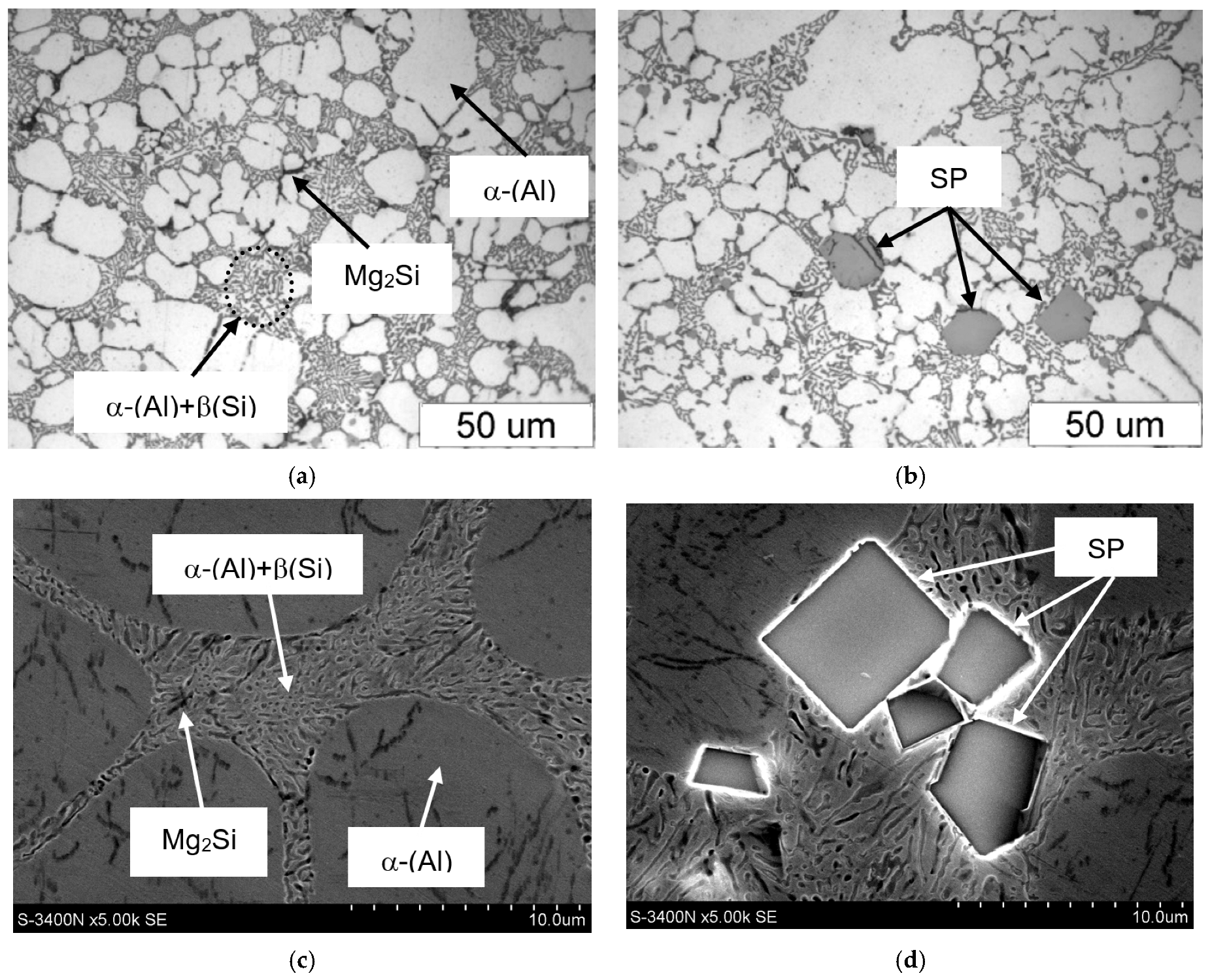
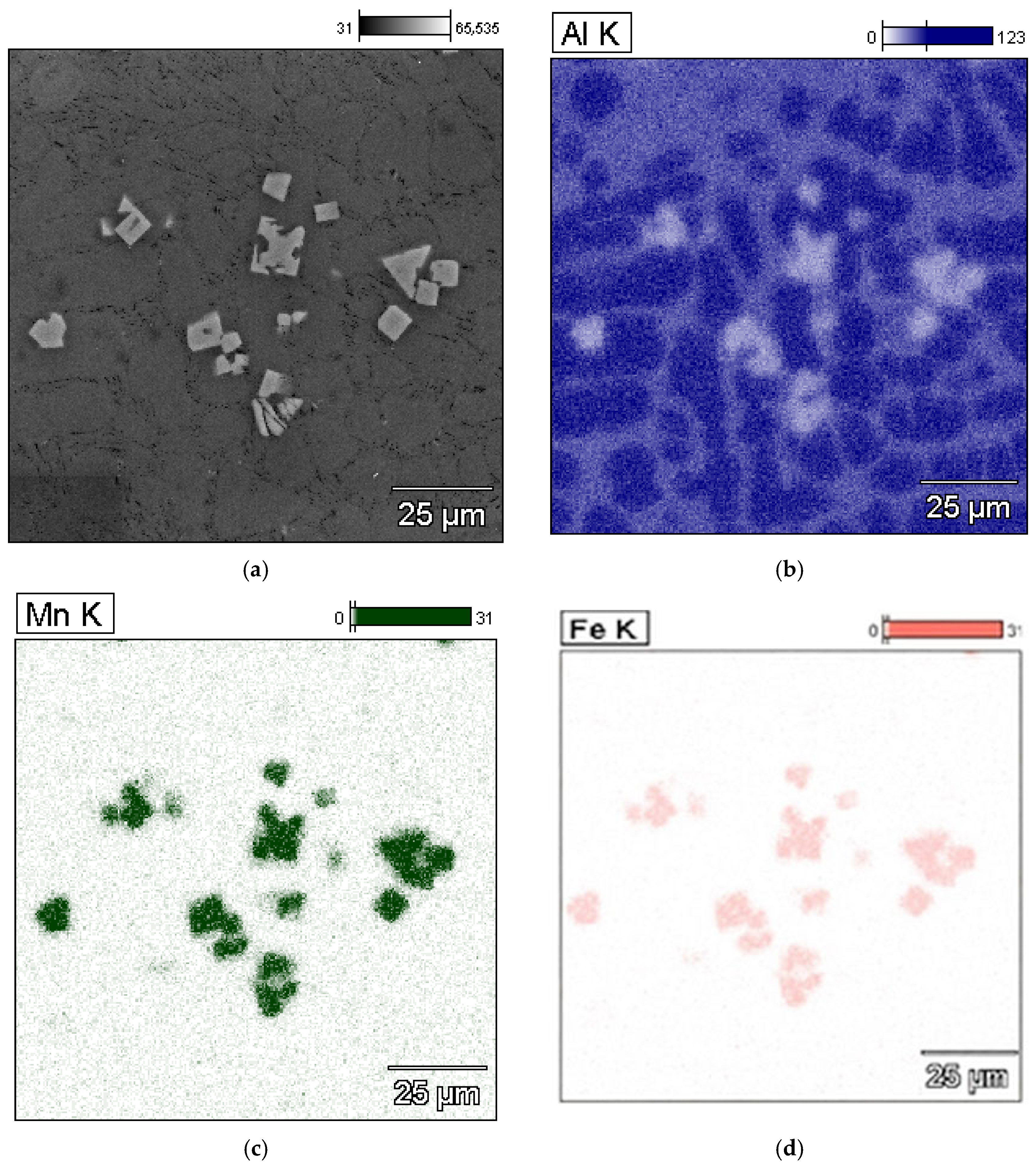
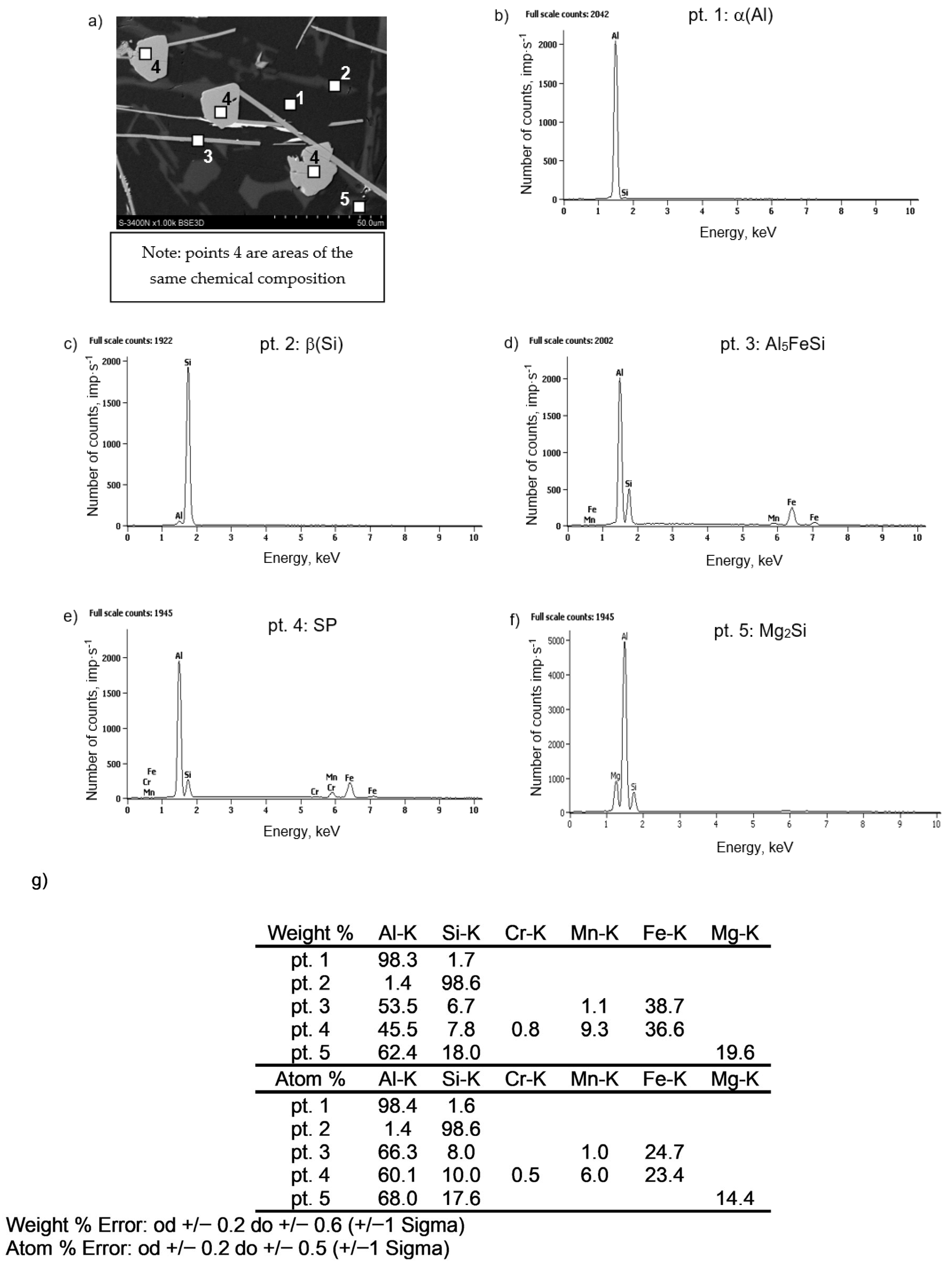
3.3. Microstructure Test Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- DSC tests revealed the primary crystallisation of sludge particles (SP), which, due to their weight, settle at the bottom of the crucible (ladle), reducing the casting process yield and are essential in controlling the microstructure of the AlSi7Mg(Fe) alloy.
- The increase in the crystallisation temperature of SP, rich mainly in iron, manganese, and chromium, is directly proportional to the increase in the value of the sludge factor (SF) and ranges from 620 °C (for SF~1.3%) to approx. 645 °C (for SF~3.1%).
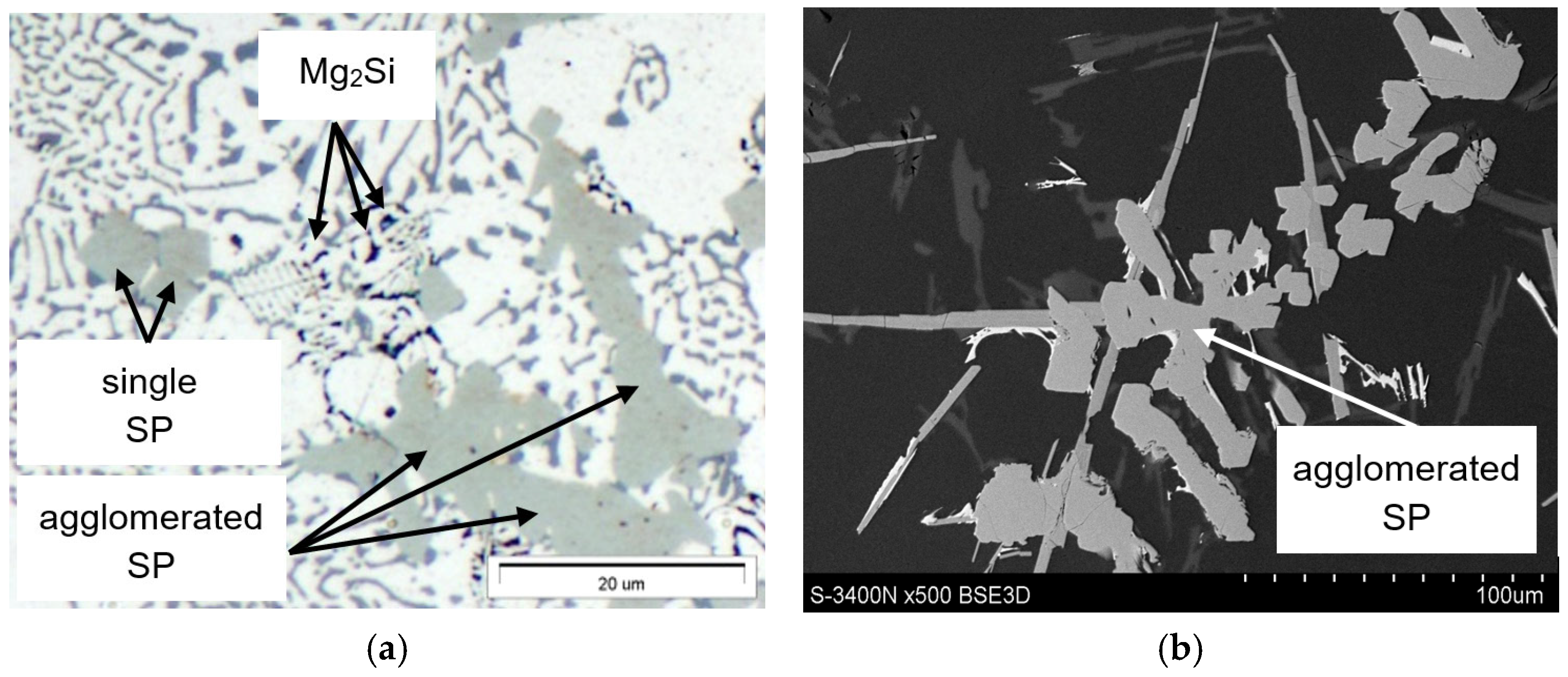
- The combined increase in iron and manganese content influences not only the increase in the precipitation temperature of SP but also the change in their morphology from individual polyhedra (appearing as polygons on the polished surface) to compact “cluster-like” structures.
- To avoid the formation of sludge particles with an unfavourable structure in high-pressure die-castings made of AlSi7Mg alloy, the SF should not exceed 2.0%.
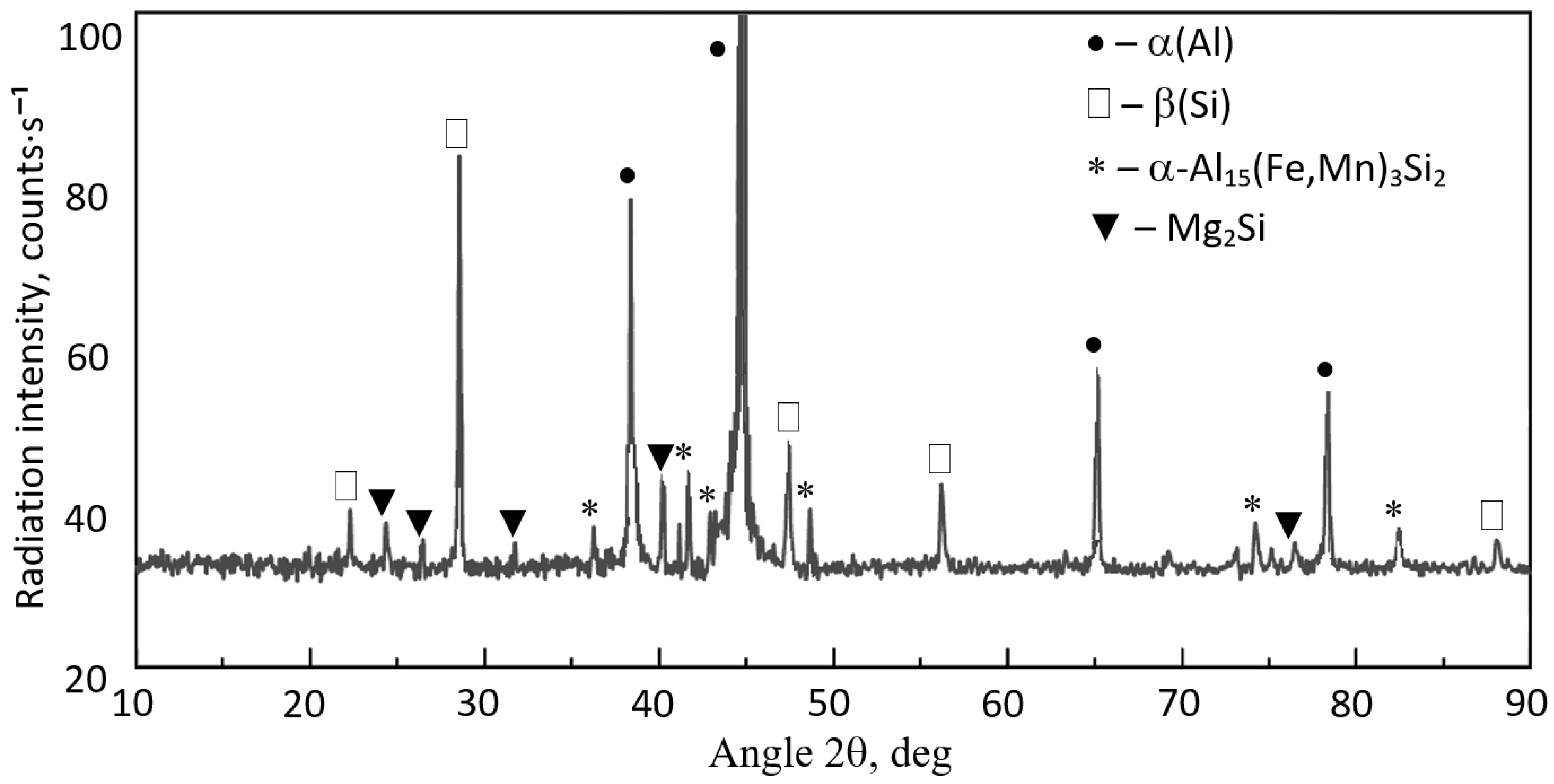
- DSC tests revealed the pre-eutectic crystallisation of the α-Al15(Fe;Mn)3Si2 phase, whose morphology depends on the combined content of iron, manganese, and chromium. For SF < 1.5%, the microstructure of the AlSi7Mg alloy with an elevated share of iron and manganese contains the α-Al15(Fe;Mn)3Si2 phase with a typical dendritic structure. A higher SF value leads to a significant thickening of the arms of the α phase.
- The Mg2Si phase identified in the AlSi7Mg alloy (crystallising last) is not a constituent of sludge particles and does not influence their morphology.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kammer, C. Aluminium Handbook. Vol. 1: Fundamentals and Materials; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- King, F. Aluminum and its Alloys; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mbuya, T.O.; Odera, B.; Ng’ang’a, S. Influence of Iron on Castability and Properties of Al-Si Alloys: Literature Review. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2003, 16, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R. Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys ASM Specialty Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.A. Iron-Containing Intermetallic Phases in Al-Si Based Casting Alloys. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2012, 1, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.; Fabrizi, A.; Timelli, G. Evolution of sludge particles in secondary die-cast aluminium alloys as function of Fe, Mn and Cr contents. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 153, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifedine, S.; Svensson, I.L. The influence of Fe and Mn content and cooling rate on the microstructure and mechanical properties of A380-die casting alloys. Metall. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Belov, N.A.; Aksenov, A.A.; Eskin, D.G. Iron in Aluminum Alloys. Impurity and Alloying Element; Taylor & Francis Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebhota, W.S.; Tien-Chien, J. Intermetallics Formation and Their Effect on Mechanical Properties of Al-Si-X Alloys; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestari, S.G. The effect of iron and manganese on the formation of intermetallic compounds in Al-Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 383, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.A. Effect of iron content on the formation of β-Al5FeSi and porosity in Al-Si eutectic alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gong, M.; Xie, D.; Wang, J. Structures and mechanical properties of Al-Al2Cu interfaces. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2019, 71, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Gaffar, M.A.; Mostafa, M.S.; Essam, A.Z. Precipitation kinetics of Al–1.12Mg2Si–0.35 Si and Al–1.07 Mg2Si–0.33Cu alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 429, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Campbell, J. Morphology of β-Al5FeSi phase in Al-Si cast alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahta, M.; Emamy, M.; Cao, X.; Campbell, J. Overview of β-Al5FeSi phase in Al-Si cast alloys. In Materials Science Research Trends; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cais, J.; Weiss, V.; Svobodova, J. Relation Between Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Al-Si Alloys Produced by Low-Pressure Casting; Archives of Foundry Engineering: Krakow, Poland, 2014; Volume 14, pp. 97–102. Available online: https://yadda.icm.edu.pl/baztech/element/bwmeta1.element.baztech-e333b27c-9532-4dc4-ab73-64260703c143 (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Lu, L.; Dahle, A.K. Iron-Rich Intermetallic Phases and Their Role in Casting Defect Formation in Hypoeutectic Al-Si Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2005, 36, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnis, C.M.; Taylor, J.A.; Dahle, A.K. Porosity Formation and Eutectic Growth in Al-Si-Cu-Mg Alloys Containing Iron and Manganese. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys 2004, Queensland, Australia, 2-5 August 2004; Nie, J.F., Morton, A.J., Muddle, B.C., Eds.; The University of Queensland: Queensland, Australia, 2004; Available online: http://www.icaa-conference.net/ICAA9/data/papers/GP%20149.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Campbell, J. Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design. In Complete Casting Handbook, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.M. Behaviours of Bifilms in A356 Alloy During Solidification: Developing Observation Techniques with 3-D Micro X-Ray Tomography; School of Metallurgy and Materials College of Engineering, The University of Birmingham: Birmingham, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Piątkowski, J.; Roskosz, S.; Stach, S. The Influence of Selected High–Pressure Die Casting Parameters on the Porosity of EN AB-46000 Alloy Castings. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2024, 18, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes de Mores, H.; Roberto de Oliveira, J.; Crocce Espinosa, D.; Tenario, J. Removal of iron from molten recycled aluminum through intermediate phase filtration. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, Y.; Takamori, S.; Kimura, T.; Minagawa, K.; Kakisawa, H. Morphology of intermetallic compounds in Al-Si-Fe alloy and its control by ultrasonic vibration. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.S.; Xiangfa, L. Refinement performance and mechanism of an Al-50Si alloy. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestari, S.G.; Gruzleski, J.E. Gravity segregation of complex intermetallic compounds in liquid Al-Si alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, G.C.; Bâckerud, L. Factors affecting modification of Al-Si alloys by addition of strontium-containing master alloys. AFS Trans. 1992, 100, 847–854. [Google Scholar]
- Pennors, A.; Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F.H.; Doty, H.W. Precipitation of β-Al5FeSi iron intermetallic in Al-6%Si-3.5%Cu (319) type alloys: Role of Sr and P. AFS Trans. 1998, 106, 251–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F.H.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S. A study of tensile properties in Al-Si-Cu and Al-Si-Mg alloys: Effect of β-iron intermetallics and porosity. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 490, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestari, S.G.; Keshavarz, M.; Hejazi, M.M. Effect of strontium on the kinetics of formation and segregation of intermetallic compounds in A380 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 477, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, G.; Thorvaldsson, T.; Dunlop, G.L. The influence of Fe and Cr on the microstructure of cast Al-Si-Mg alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1986, 17, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timelli, G.; Bonollo, F. The influence of Cr content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi9Cu3(Fe) die-casting alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 528, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Robinson, K. The crystal structure of the ternary alloy α(AlMnSi). Acta Crystallogr. 1996, 20, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.T.L.; Greer, A.L. Solid state intermetallic phase transformations in 3XXX aluminium alloys. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 2571–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaja, S.S.T.; Gangadasari, P.R.; Ayyagari, K.P.R. Extending the Tolerance of Iron in Cast Al-Si Alloy. JOM 2021, 73, 2652–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifeddine, S.; Johansson, S.; Svensson, I.L. The influence of cooling rate and manganese content on the Al5FeSi phase formation and mechanical properties of Al-Si-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2008, 490, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timelli, G.; Capuzzi, S.; Fabrizi, A. Precipitation of primary Fe-rich compound in secondary AlSi9Cu3(Fe) alloys. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Makhlouf, M.M.; Apelian, D. Aluminium die casting alloys: Alloy composition, microstructure, and properties-performance relationships. Int. Mater. Rev. 1995, 40, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.; Sukiennik, M.; Castillejos, A.H.; Acosta, F.A.J.; Escobedo, C. A kinetic study on the nucleation and growth of the Al8FeMnSi2 intermetallic compound for aluminum scrap purification. Intermetallics 1998, 6, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metal Recycling Factsheet. Europe Aluminum Market Overview 2024–2028. Available online: https://circulareconomy.europa.eu/platform/sites/default/files/euric_metal_recycling_factsheet.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Passarini, F.; Ciacci, L.; Nuss, P.; Manfredi, S. Material Flow Analysis of Aluminium, Copper and Iron in the EU-28. JRC Technical Reports 2018 European Commission. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC111643/jrc111643_mfa_final_report_june2018.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Bösch, D.; Pogatscher, S.; Hummel, M.; Fragner, W.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Göken, M.; Höppel, H.W. Secondary Al-Si-Mg high-pressure die casting alloys with enhanced ductility. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2014, 46, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1706-2010; Aluminium and Aluminium Alloys–Castings–Chemical composition and Mechanical Properties. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2020.
- Piątkowski, J. Crystallization of Casting Aluminum Alloys; Publishing Archives of Foundry Engineering: Katowice-Gliwice, Poland, 2021; ISBN 978-83-63605-49-0. [Google Scholar]
- Piątkowski, J.; Chowaniec, L.; Matuła, T. Application of thermal-derivative analysis to study phase transformation in AlSi7Mg alloy with different iron content. Mach. Technol. Mater. 2025, 19, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Piątkowski, J.; Chowaniec, L.; Matuła, T.; Reyna, M.; Sanchez, G. Effect of chromium on the microstructure of AlSi7Mg alloy with increased iron content. Non-Equilibrium Phase Transformations. Mater. Sci. 2025, 11, 3–33. [Google Scholar]
- Schoß, J.P.; Schramm, E.; Schönherr, P.; Mrówka, N.M.; Schumann, H.; Becker, H.; Keßler, A.; Szucki, M.; Wolf, G. Investigation of the Formation of Iron-Rich Intermetallic Phases in Al–Si Alloys via Thermal Analysis Cooling Curves, Including a Real-Time Detection for Filtration Process. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, K.M.; Gonda, V.; Réger, M. Differential scanning calorimetry of aluminium EN AB-42000 alloy rheocasting semi-solid in different stage heating rates. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2023, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warmuzek, M. Analysis of the chemical composition of AlMnFe and AlFeMnSi intermetallic phases in the interdendritic eutectics in the Al-alloys. Trans. Foundry Res. Inst. 2014, 54, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Elgallad, E.; Breton, F.; Chen, X.-G. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Fingerprints of Various Heat-Treatment Tempers of Different Aluminum Alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Alloy No. | Element Content, wt.% 1; 2 | Quotient Mn/Fe | Quotient Cr/Fe | SF | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Fe | Cu | Mg | Ni | Mn | Zn | Ti | Cr | Sr | ||||
| 1. | 6.91 | 1.01 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.048 | 0.014 | 0.109 | 0.048 | 1.374 |
| 2. | 7.11 | 0.91 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.048 | 0.014 | 0.341 | 0.053 | 1.674 |
| 3. | 6.87 | 1.00 | 0.02 | 0.57 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.048 | 0.013 | 0.480 | 0.048 | 2.104 |
| 4. | 6.94 | 0.96 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.047 | 0.014 | 0.719 | 0.049 | 2.481 |
| 5. | 7.06 | 1.21 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.050 | 0.013 | 0.074 | 0.041 | 1.540 |
| 6. | 7.07 | 1.22 | 0.07 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.049 | 0.015 | 0.254 | 0.040 | 1.987 |
| 7. | 6.94 | 1.20 | 0.01 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.050 | 0.014 | 0.425 | 0.042 | 2.370 |
| 8. | 7.01 | 1.19 | 0.01 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.050 | 0.013 | 0.597 | 0.042 | 2.760 |
| 9. | 6.95 | 1.39 | 0.06 | 0.63 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.051 | 0.014 | 0.079 | 0.037 | 1.763 |
| 10. | 6.87 | 1.39 | 0.08 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.051 | 0.011 | 0.216 | 0.037 | 2.143 |
| 11. | 7.06 | 1.41 | 0.02 | 0.61 | 0.03 | 0.56 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.047 | 0.012 | 0.397 | 0.033 | 2.671 |
| 12. | 6.88 | 1.40 | 0.04 | 0.59 | 0.02 | 0.69 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.050 | 0.014 | 0.493 | 0.036 | 2.930 |
| 13. | 6.90 | 1.59 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.049 | 0.014 | 0.063 | 0.031 | 1.937 |
| 14. | 7.02 | 1.59 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.049 | 0.015 | 0.195 | 0.031 | 2.357 |
| 15. | 6.98 | 1.61 | 0.06 | 0.59 | 0.02 | 0.49 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.050 | 0.013 | 0.304 | 0.031 | 2.740 |
| 16. | 7.03 | 1.60 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0.01 | 0.71 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.049 | 0.014 | 0.444 | 0.031 | 3.167 |
| Alloy No. | Heating | Cooling | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T, °C | E(Mg) | α+β | AlFeMn | α(Al) | SP | SP | α(Al) | AlFeMn | α+β | E(Mg) | |
| 1. | Tstart | 542 | 559 | 572 | 618 | 621 | 620 | 620 | 572 | 561 | 548 |
| Tend | 553 | 568 | 596 | 628 | 631 | 630 | 625 | 592 | 568 | 552 | |
| 4. | Tstart | 540 | 560 | 574 | 617 | 621 | 620 | 619 | 575 | 560 | 541 |
| Tend | 552 | 565 | 597 | 627 | 635 | 633 | 622 | 595 | 568 | 554 | |
| 5. | Tstart | 541 | 559 | 577 | 619 | 625 | 622 | 618 | 577 | 559 | 540 |
| Tend | 554 | 562 | 597 | 625 | 634 | 635 | 624 | 599 | 567 | 550 | |
| 8. | Tstart | 540 | 561 | 577 | 618 | 626 | 626 | 620 | 577 | 560 | 547 |
| Tend | 552 | 565 | 600 | 624 | 637 | 638 | 623 | 600 | 565 | 549 | |
| 9. | Tstart | 539 | 558 | 577 | 618 | 625 | 626 | 619 | 577 | 561 | 541 |
| Tend | 550 | 564 | 602 | 626 | 640 | 640 | 626 | 602 | 564 | 554 | |
| 12. | Tstart | 543 | 560 | 578 | 619 | 623 | 626 | 621 | 577 | 560 | 547 |
| Tend | 554 | 568 | 604 | 626 | 641 | 641 | 626 | 605 | 565 | 552 | |
| 13. | Tstart | 544 | 561 | 580 | 619 | 626 | 626 | 620 | 580 | 559 | 541 |
| Tend | 552 | 567 | 606 | 624 | 643 | 643 | 625 | 608 | 564 | 554 | |
| 16. | Tstart | 540 | 563 | 580 | 618 | 627 | 626 | 618 | 580 | 560 | 546 |
| Tend | 550 | 566 | 607 | 625 | 645 | 645 | 624 | 610 | 566 | 550 | |
| Alloy No. | Component | ΔH, J·g−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating | Cooling | ||
| 1. | SP | +5 | −6 |
| AlMnFe | +19 | −18 | |
| 4. | SP | +6 | −6 |
| AlMnFe | +22 | −20 | |
| 5. | SP | +7 | −6 |
| AlMnFe | +24 | −23 | |
| 8. | SP | +8 | −7 |
| AlMnFe | +27 | −27 | |
| 9. | SP | +8 | −7 |
| AlMnFe | +29 | −28 | |
| 12. | SP | +9 | −9 |
| AlMnFe | +29 | −30 | |
| 13. | SP | +10 | −10 |
| AlMnFe | +30 | −30 | |
| 16. | SP | +12 | −12 |
| AlMnFe | +30 | −30 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piątkowski, J.; Roskosz, S.; Stach, S.; Górny, M. Crystallisation and Microstructure of Sludge Particles in AlSi7Mg Secondary Alloys with Increased Iron Content. Materials 2025, 18, 4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214921
Piątkowski J, Roskosz S, Stach S, Górny M. Crystallisation and Microstructure of Sludge Particles in AlSi7Mg Secondary Alloys with Increased Iron Content. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214921
Chicago/Turabian StylePiątkowski, Jarosław, Stanisław Roskosz, Sebastian Stach, and Marcin Górny. 2025. "Crystallisation and Microstructure of Sludge Particles in AlSi7Mg Secondary Alloys with Increased Iron Content" Materials 18, no. 21: 4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214921
APA StylePiątkowski, J., Roskosz, S., Stach, S., & Górny, M. (2025). Crystallisation and Microstructure of Sludge Particles in AlSi7Mg Secondary Alloys with Increased Iron Content. Materials, 18(21), 4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214921









