Optimization of Recycled a-FePO4/rGO Composites via Thermal Reduction for Enhanced-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Recycled FePO4
2.2. Synthesis of GO Dispersion Solution
2.3. Synthesis of a-FePO4
2.4. Synthesis of a-FePO4-GO and Its Derivatives
2.5. Battery Assembly and Material Characterization
2.6. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
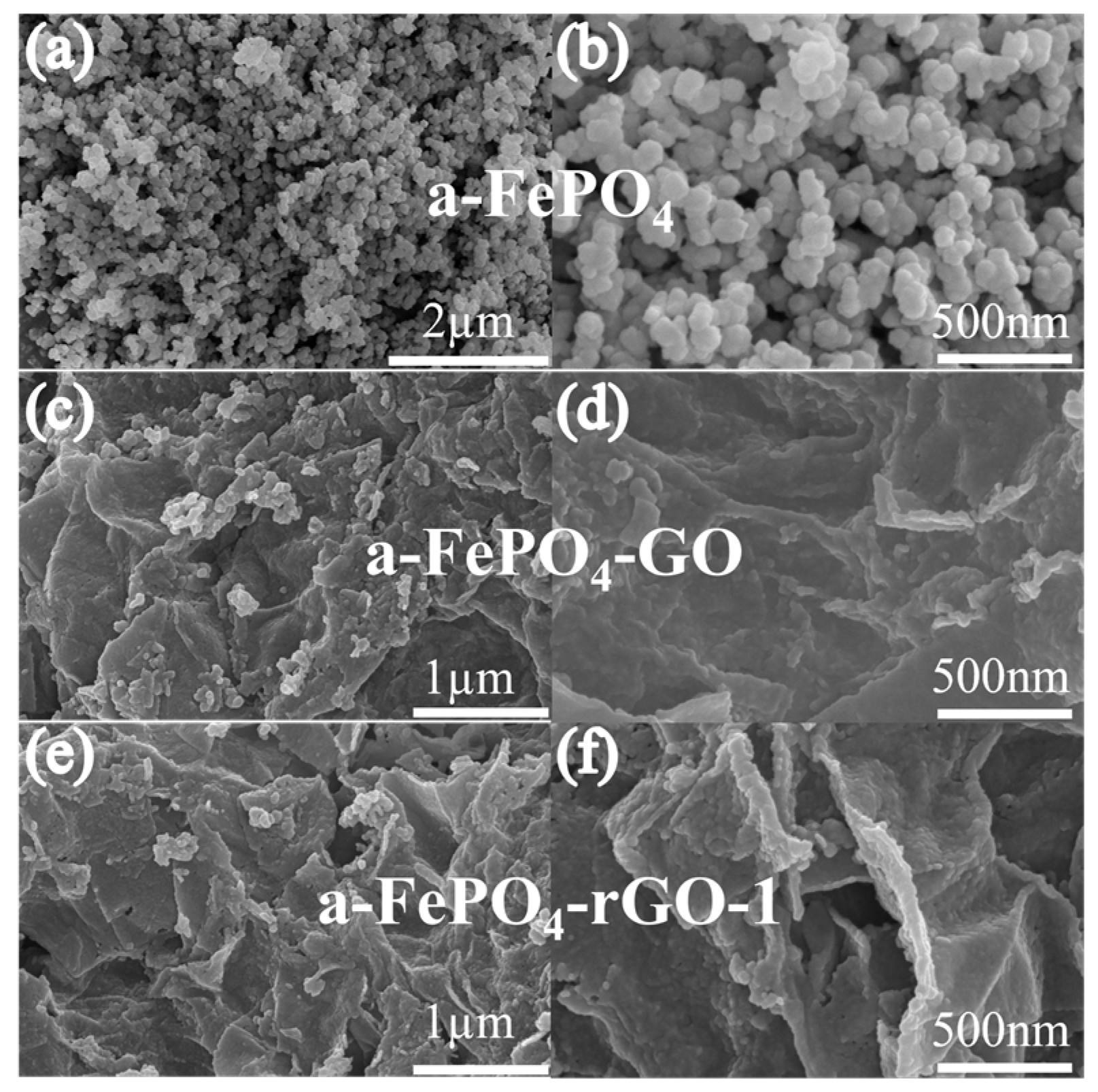
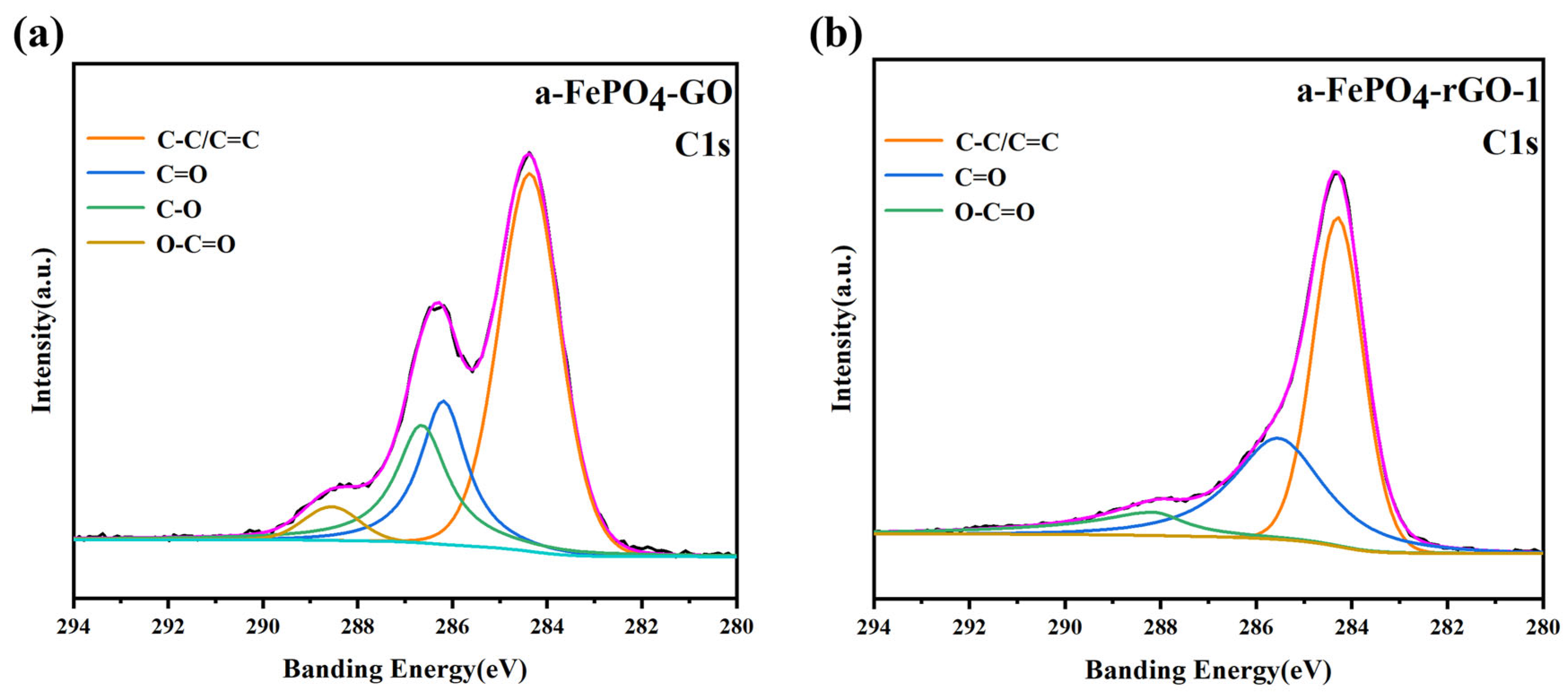
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization of the Materials
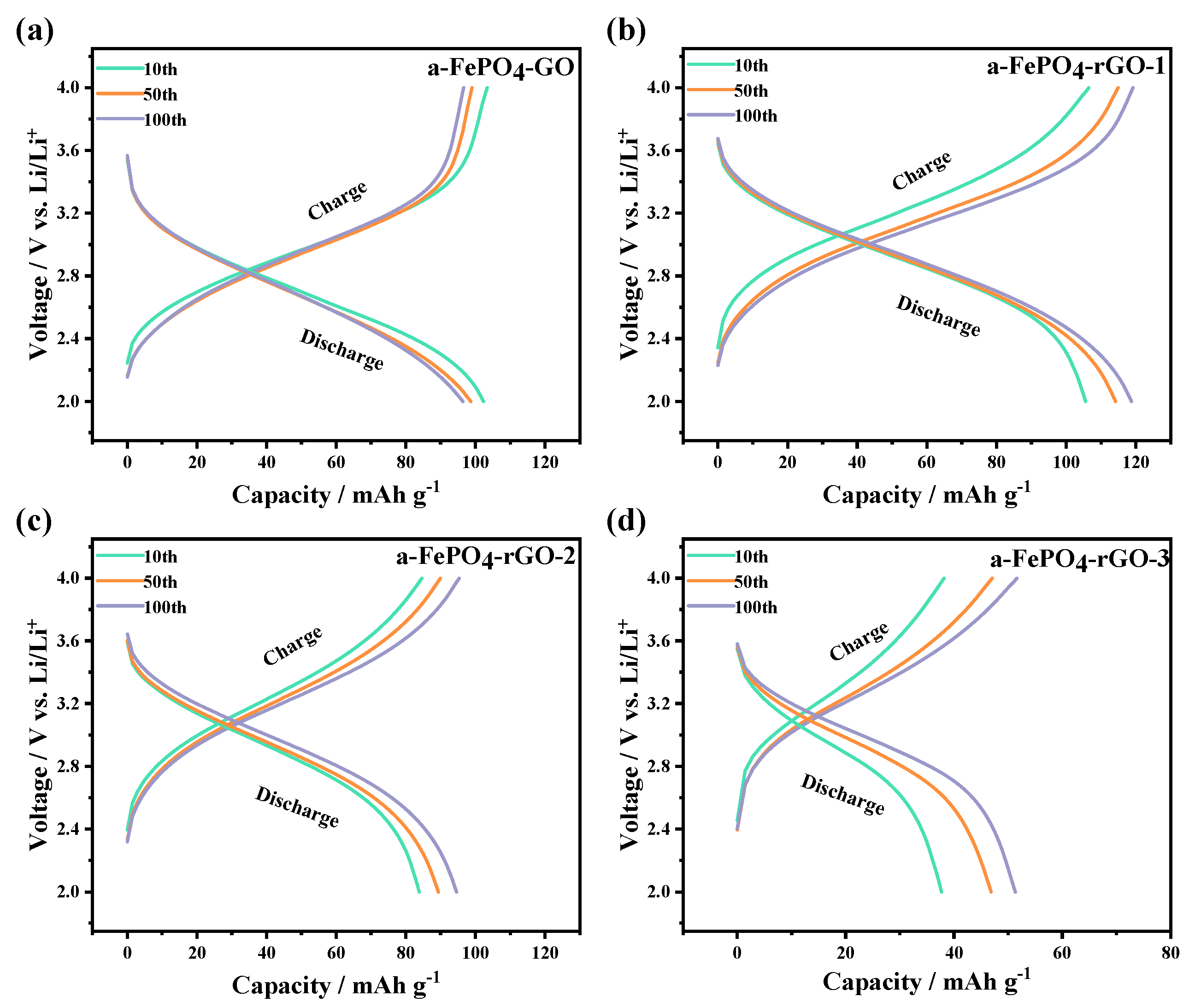
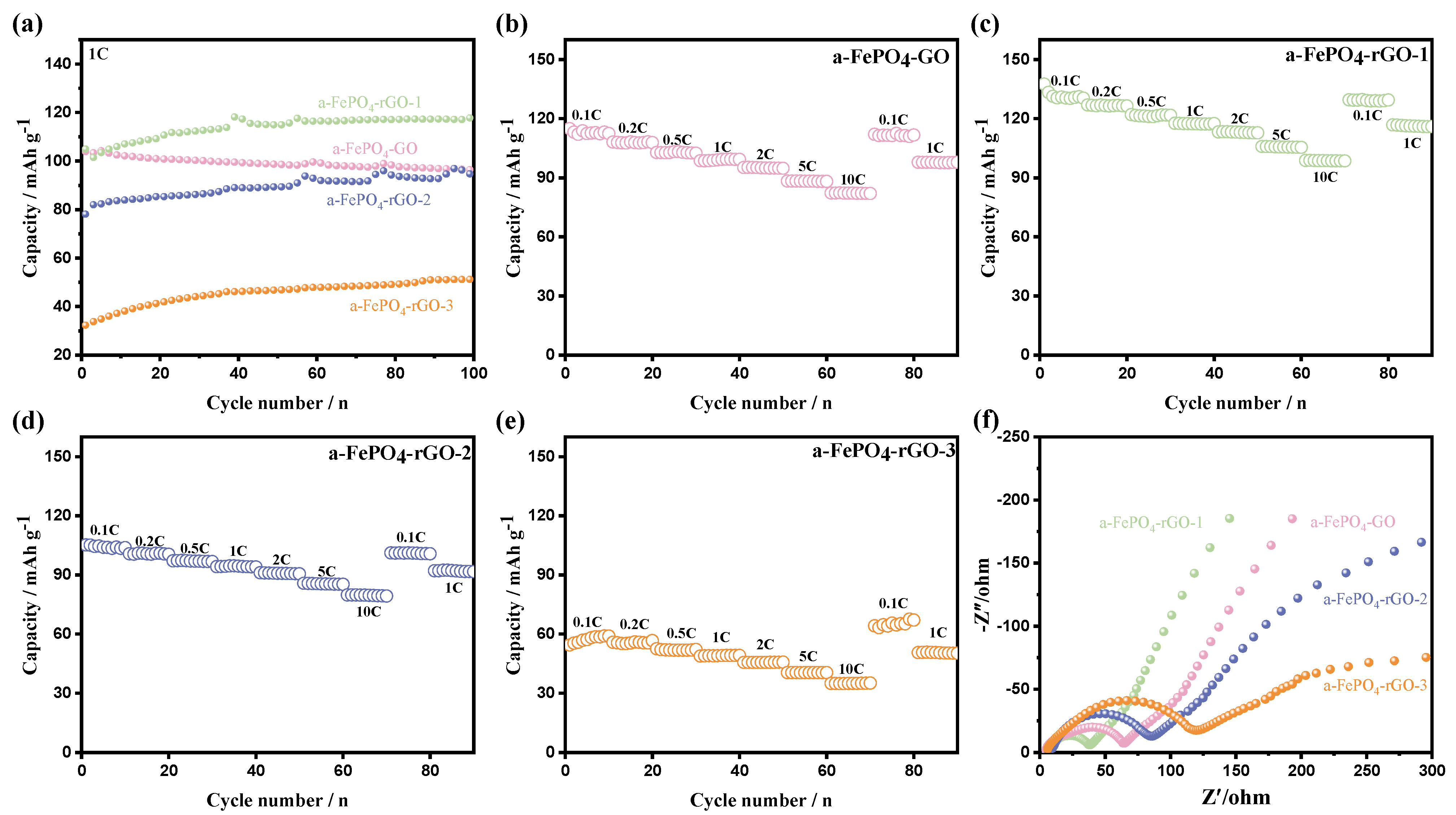
3.2. Electrochemical Performance of the a-FePO4 and Its Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| XPS | X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| LFP | LiFePO4 |
| LIBs | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
| FePO4 | Amorphous FePO4 |
| GO | Graphene Oxide |
| rGO | Reduced Graphene Oxide |
References
- Harper, G.; Sommerville, R.; Kendrick, E.; Driscoll, L.; Slater, P.; Stolkin, R.; Walton, A.; Christensen, P.; Heidrich, O.; Lambert, S.; et al. Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles. Nature 2019, 575, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive Technology for Recycling and Regenerating Materials from Spent Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3609–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangaja, B.; Nair, S.; Santhanagopalan, D. Reuse, Recycle, and Regeneration of LiFePO4 Cathode from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Rechargeable Lithium- and Sodium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4711–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. A Critical Review and Analysis on the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, M. Recycling spent lithium-ion battery cathode: An overview. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 7656–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Zhang, J.; Kong, J.; Zhou, T. Sustainable Recovery of Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Green Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3104–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, X.; Cao, H.; Lin, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Selective recovery of lithium from spent lithium iron phosphate batteries: A sustainable process. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3121–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentu, H.; Xiang, B.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Dong, T.; Gao, J.; Xia, Y. A fast and efficient method for selective extraction of lithium from spent lithium iron phosphate battery. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101569–101578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hua, D.; Gu, H.; Wang, N. Theoretical-molar Fe3+ recovering lithium from spent LiFePO4 batteries: An acid-free, efficient, and selective process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122707–122716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Qian, J.; Ai, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y. Mesoporous amorphous FePO4 nanospheres as high-performance cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 3539–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, S. Crystal orientation tuning of LiFePO4 nanoplates for high rate lithium battery cathode materials. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5632–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, Y. Facile Construction of High-Performance Amorphous FePO4/Carbon Nanomaterials as Cathodes of Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 13225–13233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhu, A.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Rao, D.; Yang, Y.; et al. Graphene-Enhanced FePO4 Composites with Superior Electrochemical Performance for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials 2025, 18, 3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. A cylindrical FePO4/MWCNTs composite with a 3D conductive network structure used as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Song, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Sandwich-like SnS2/Graphene/SnS2 with Expanded Interlayer Distance as High-Rate Lithium/Sodium-Ion Battery Anode Materials. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9100–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tang, S.; Shi, H.; Hu, H. Synthesis of FePO4·xH2O for fabricating submicrometer structured LiFePO4/C by a co-precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Luo, M.; Peng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Wang, B.; Zhu, C.; Yan, X.; Shi, K. Low-Temperature Synthesis of Amorphous FePO4@rGO Composites for Cost-Effective Sodium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 57442–57450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Xu, Q.; Jin, H.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Y.; Lai, W.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Qian, Q. A green strategy towards fabricating FePO4-graphene oxide for high-performance cathode of lithium/sodium-ion batteries recovered from spent batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 913, 116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yao, J.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xiao, S.; Li, Y. Amorphous porous FePO4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite cathode material prepared from the leaching solution of jarosite residue with excellent lithium/sodium storage performance. J. Power Sources 2025, 632, 236401–236412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, Y. Direct growth of FePO4/reduced graphene oxide nanosheet composites for the sodium-ion battery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5501–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Guo, S.; Zhou, H. Advanced cobalt-free cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 13189–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Cao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yin, Q. Controllable synthesis of spherical FePO4•2H2O: Insights into crystal-face interactions and amorphous-to-crystalline transition. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2026, 320, 122400–122410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, G.G.; Versace, C. Electrical and Optical Characterization of Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Thin Films. Crystals 2022, 12, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, H.; Nikookhesal, A.; Murugan, D.; Scholz, S.; Frentzen, M.; Cao, Y.; Nickl, P.; Radnik, J.; Stockmann, J.M.; Vu, X.-T.; et al. High precision correlative analysis of dielectric behavior evolution and anisotropy in graphene oxide thin film as a function of thermal annealing parameters. Nano Trends 2025, 11, 100130–100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Shen, C.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Gionet, P.; et al. Closed Loop Recycling of Electric Vehicle Batteries to Enable Ultra-high Quality Cathode Powder. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Y. Magnetic chitosan/graphene oxide composite loaded with novel photosensitizer for enhanced photodynamic therapy. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 10376–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Q.; Liang, X.; Gu, P.; Hu, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, Z.; Huang, J.; Wu, G.; et al. Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhu, Z. Impact of ultrasonic treatment duration on the microstructure and electrochemical performance of NiZnCo2O4 electrode materials for supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26262–26279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, F.; Jin, J. Interface chemistry engineering for stable cycling of reduced GO/SnO2 nanocomposites for lithium ion battery. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, F.; Guo, M.; Zhu, A.; Liu, Y. Optimization of Recycled a-FePO4/rGO Composites via Thermal Reduction for Enhanced-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials 2025, 18, 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214850
Hu S, Yu J, Chen H, Lin Z, Zhang F, Guo M, Zhu A, Liu Y. Optimization of Recycled a-FePO4/rGO Composites via Thermal Reduction for Enhanced-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials. 2025; 18(21):4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214850
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shuchun, Jinde Yu, Hua Chen, Zengbin Lin, Fengchun Zhang, Meiling Guo, Aipeng Zhu, and Yin Liu. 2025. "Optimization of Recycled a-FePO4/rGO Composites via Thermal Reduction for Enhanced-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries" Materials 18, no. 21: 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214850
APA StyleHu, S., Yu, J., Chen, H., Lin, Z., Zhang, F., Guo, M., Zhu, A., & Liu, Y. (2025). Optimization of Recycled a-FePO4/rGO Composites via Thermal Reduction for Enhanced-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries. Materials, 18(21), 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18214850





