Effect of Fe Concentration and Superheating on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of High Mg 413.0-Type Alloys: Role of Sr, Be, P, and La
Abstract
1. Introduction
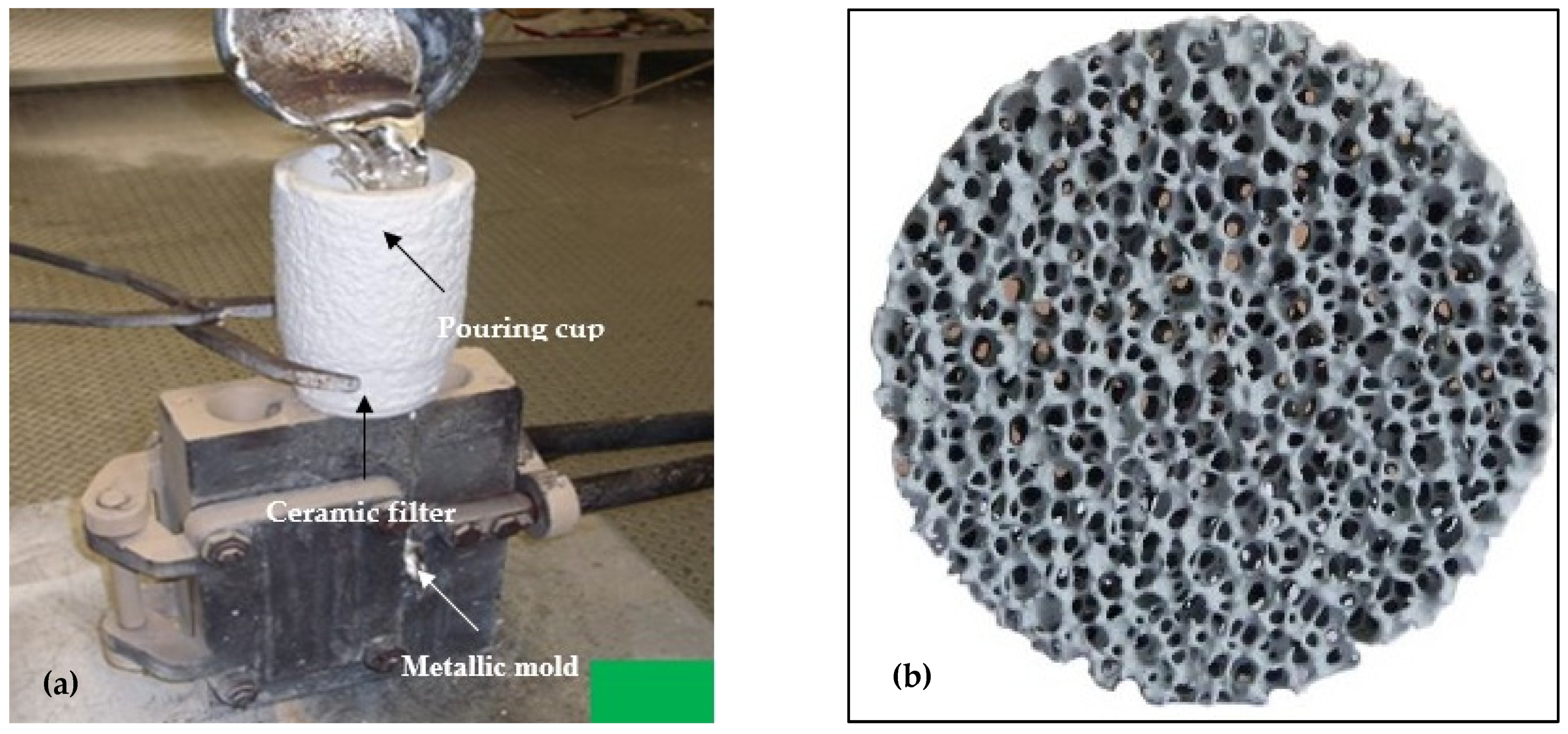
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
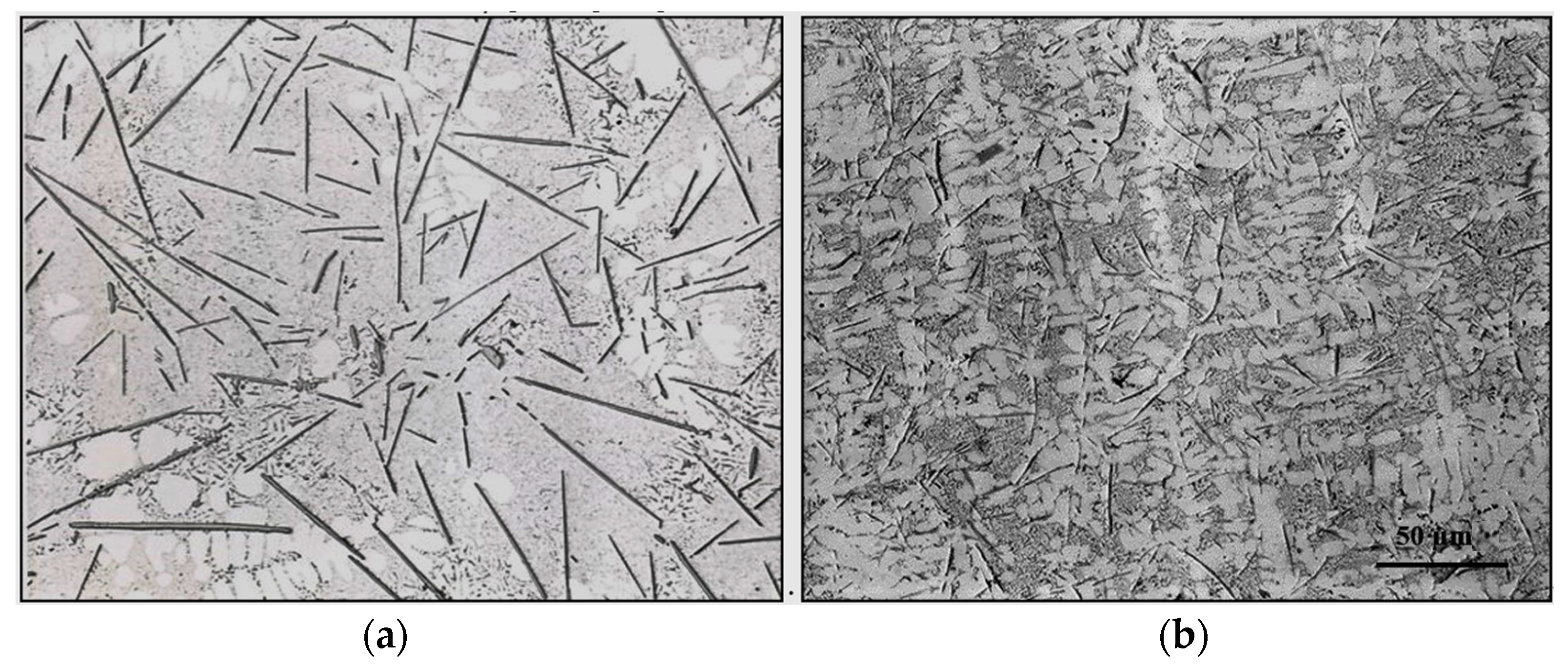
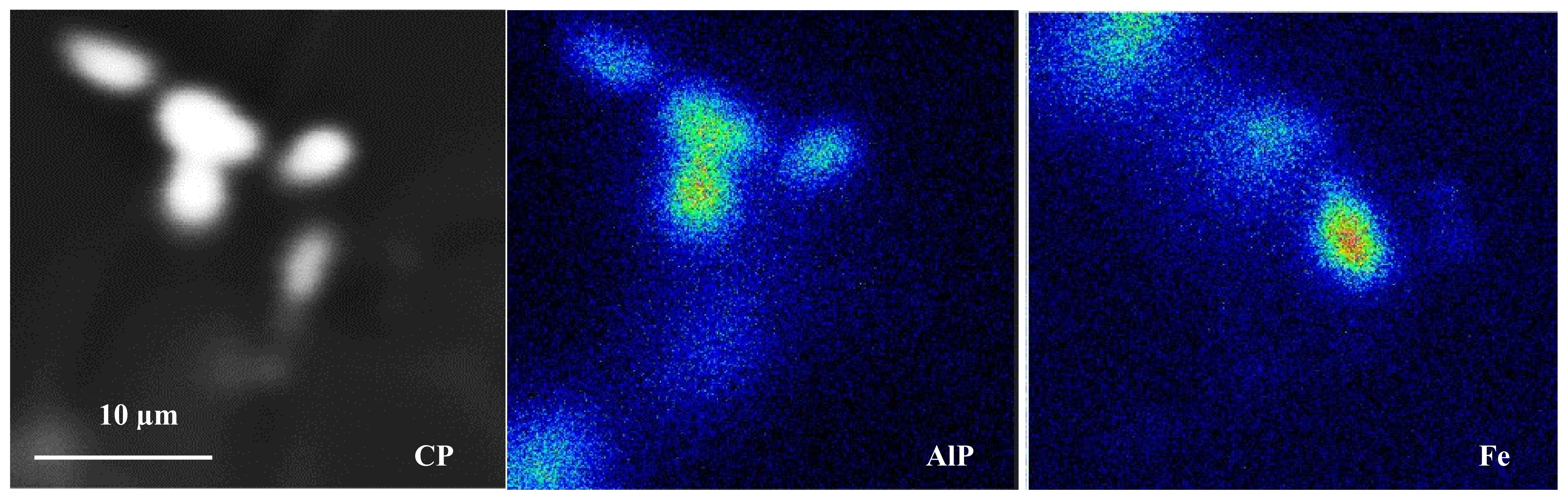
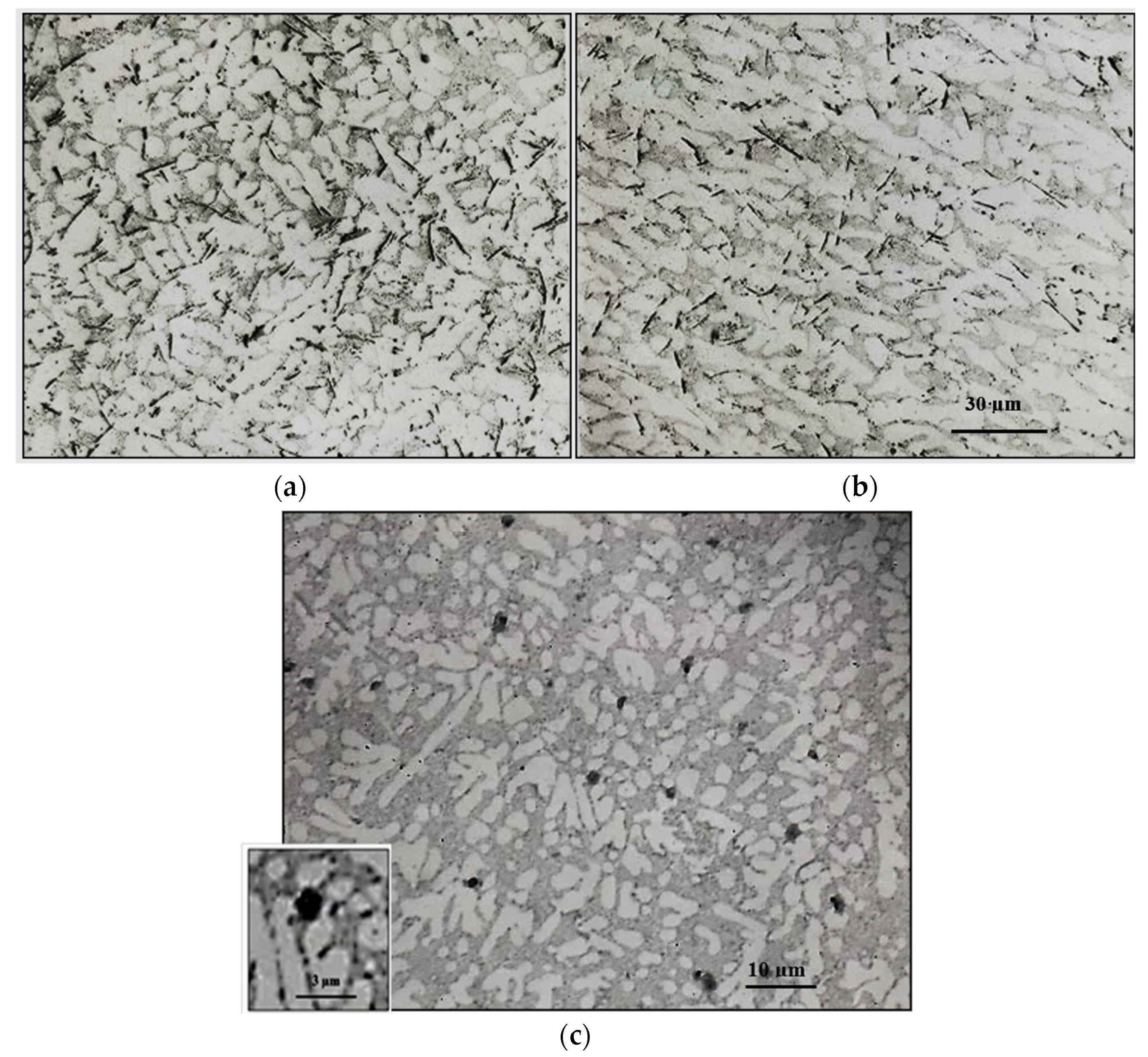
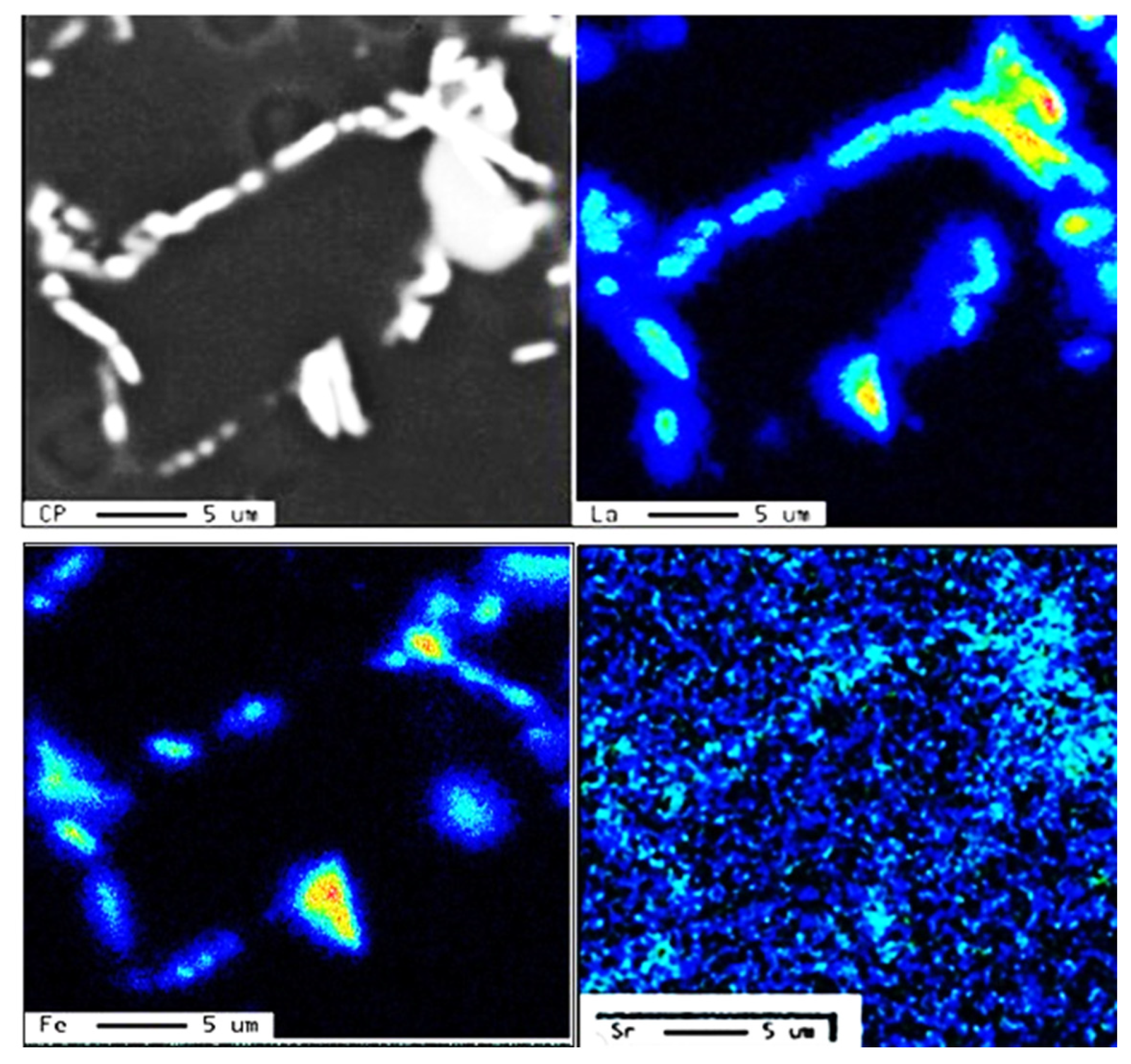
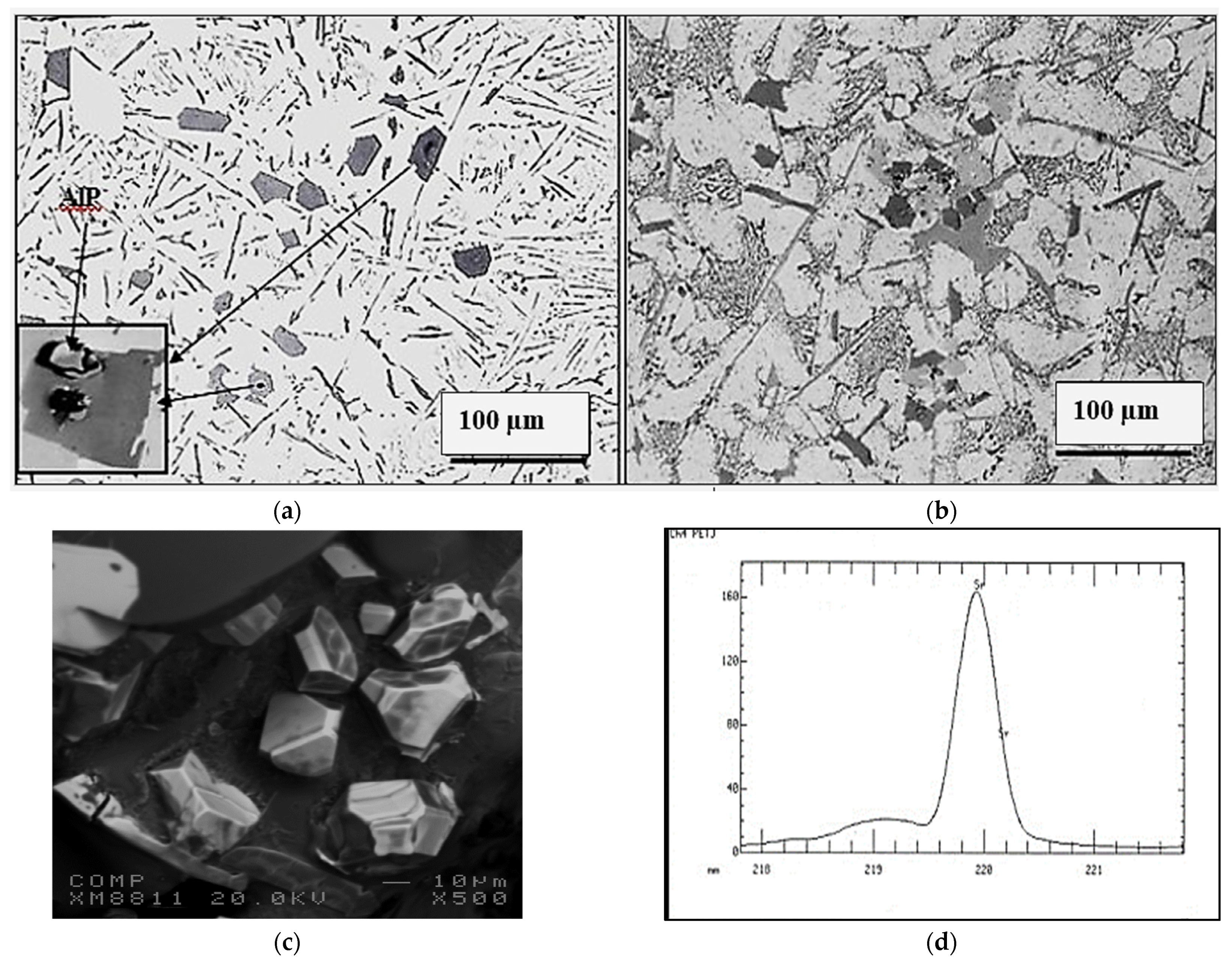
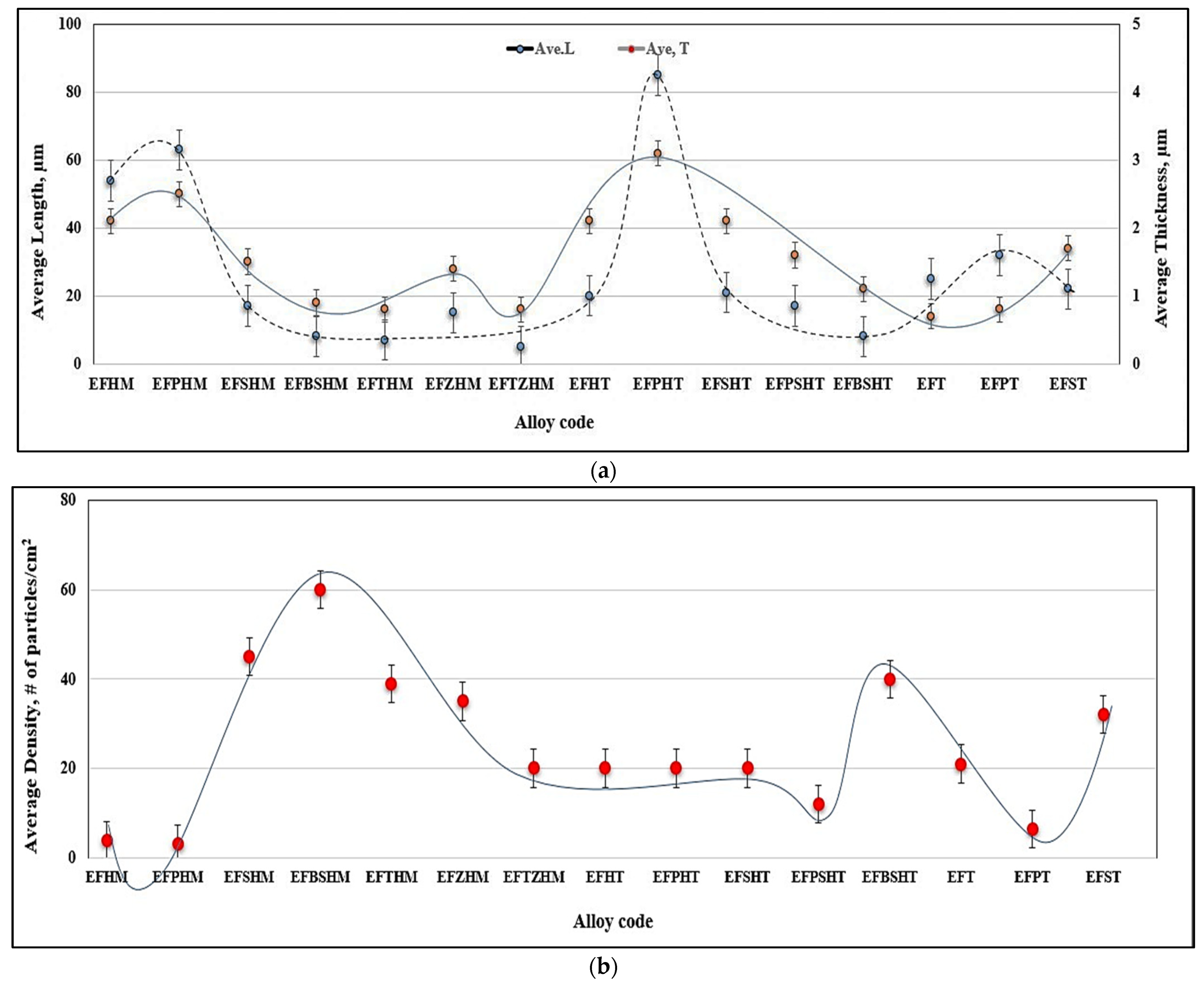
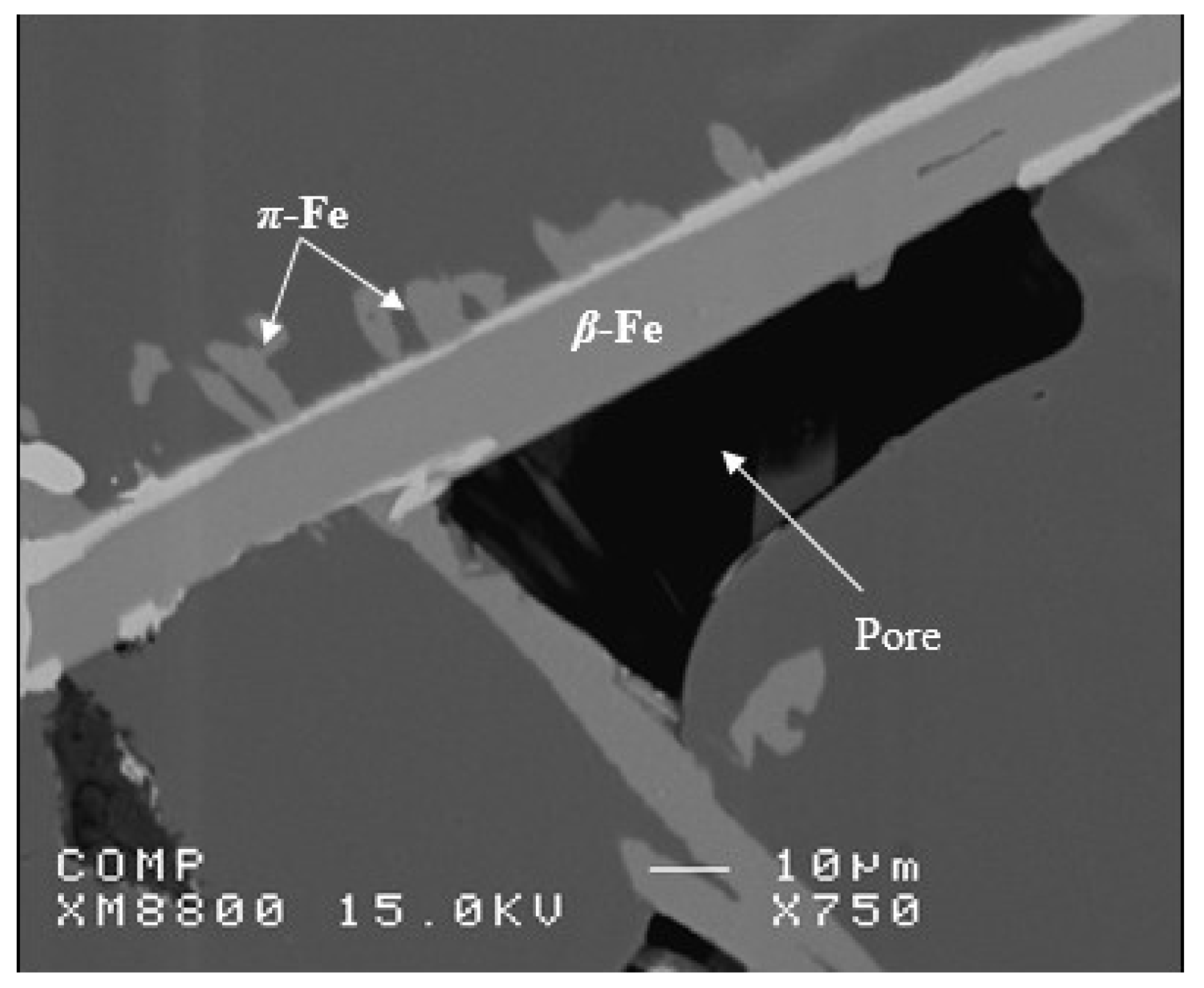
3.1. Characteristics of β-Al5FeSi Platelets
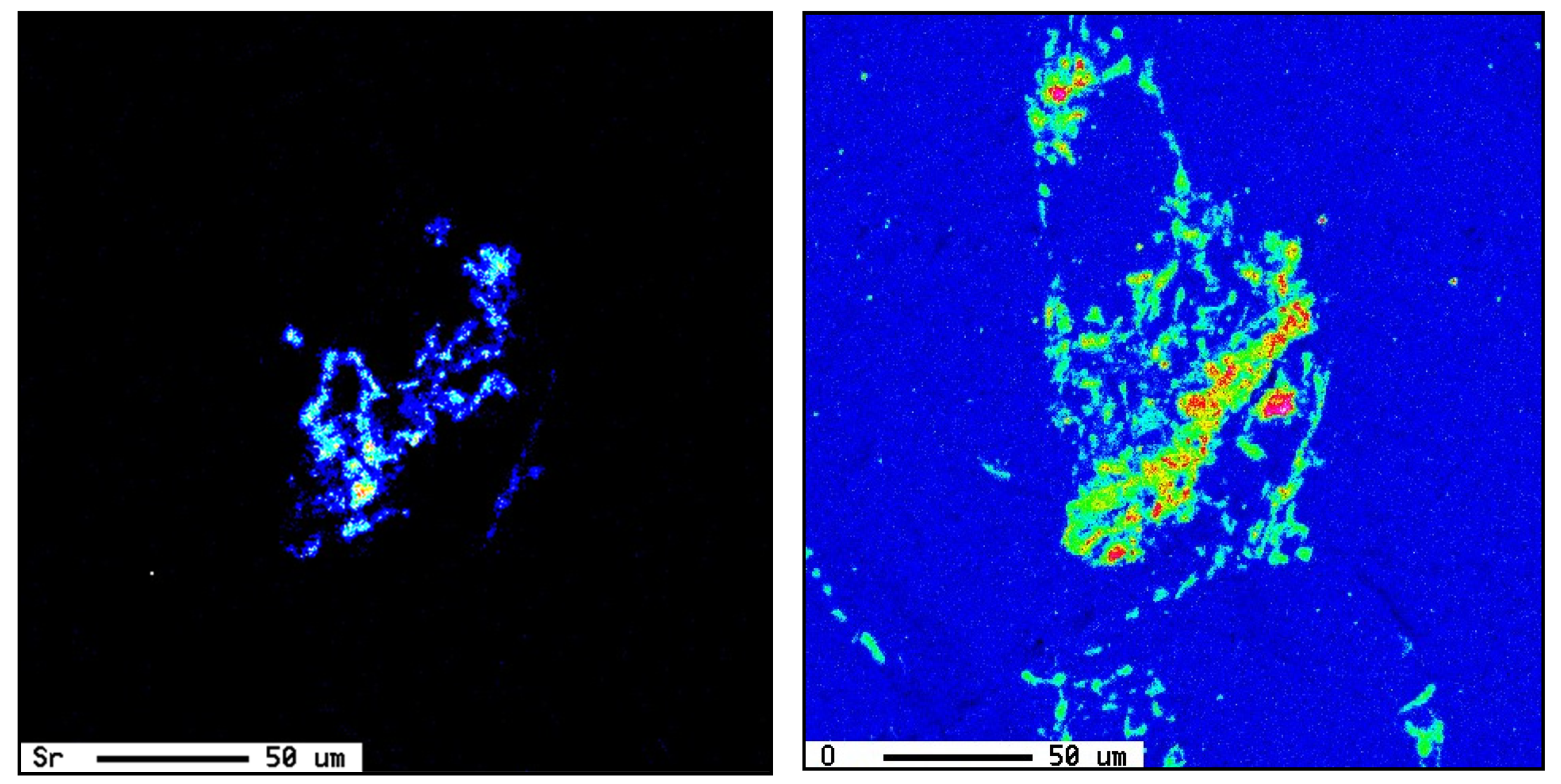
3.2. Microstuctural Characterization
3.3. Tensile Properties
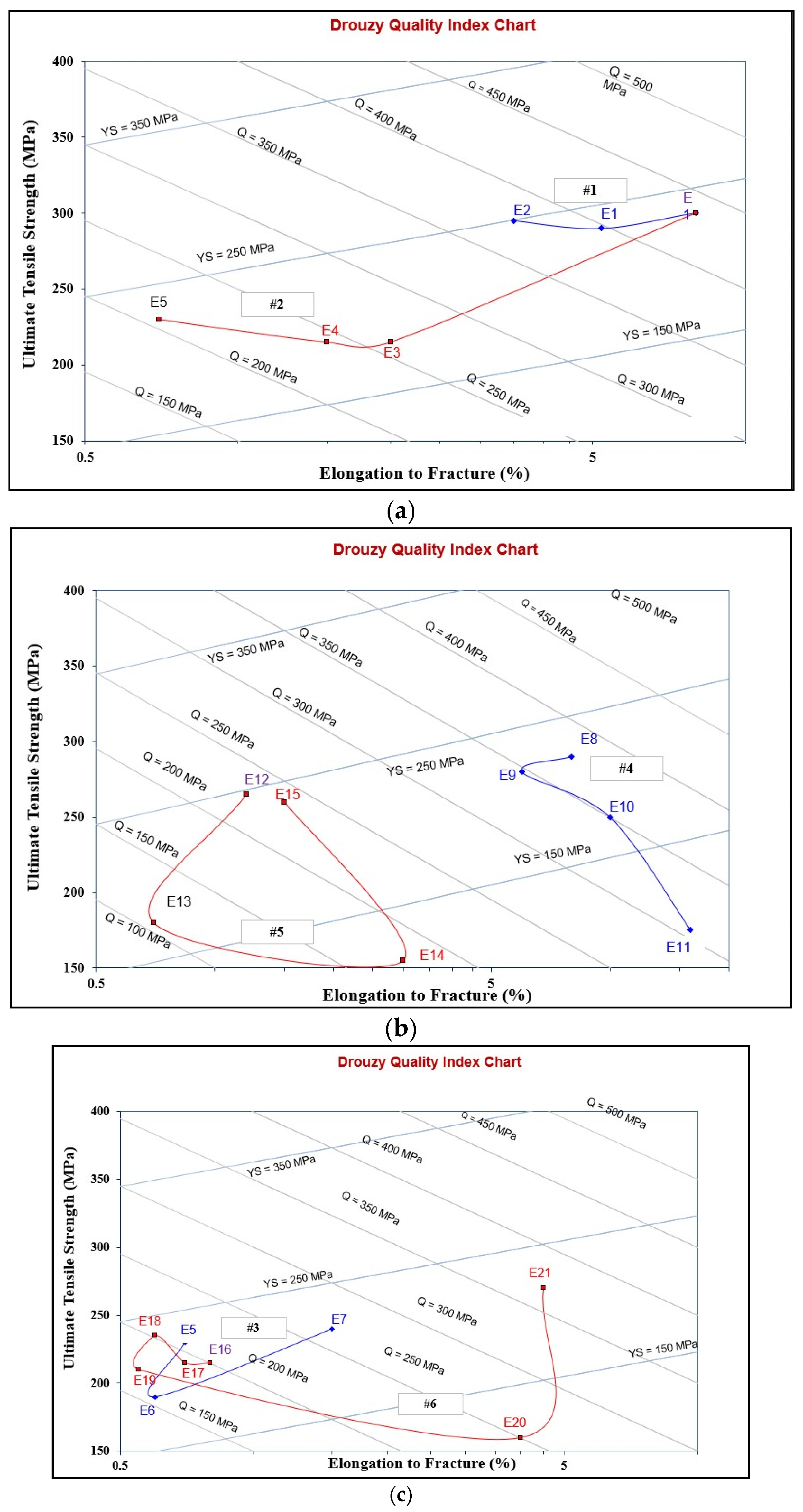
3.4. Alloy Quality: Interpretation of Tensile Properties Using the Quality Index
4. Conclusions
- Iron has a marked degradation impact on both the strength and the quality of the 413 based alloy castings due to the size and morphology of the β platelets. Tolerable Fe concentrations and methods of neutralization/fragmentations or dissolution have been discussed.
- The addition of Sr plays a significant role in improving the strength of these alloys. The combined addition of Sr and Be enhances the alloy performance due to destabilization of the β-Al5FeSi platelets, and their consequent fragmentation, in addition to a partial transformation of the Al5FeSi platelets to the new BeSiFe2Al8 phase, which has a polygonal shape or Chinese script form.
- Applying superheating at 950 °C would reduce the average β-platelet length by about 95%, which facilitates their dissolution thereafter during the solutionizing treatment. Also, over-modification with Sr results in the precipitation of Al2Si2Sr polygonal particles, causing reduction in the alloy strength.
- The addition of P has a strong tendency to deteriorate the alloy tensile properties and quality indices caused by accelerating the precipitation of Fe-containing intermetallic and primary Si and Al2Si2Sr phase particles, reducing the alloy ductility to about 0.6% from an initial value of 15% for the base alloy.
- The addition of Ti or Zn has no effect on Fe-phase precipitation or dimensions.
- Increasing the solidification rate to about 50 °C/s would lead to complete dissolution of 1.8%Fe in the aluminum matrix.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Zykova, A.P.; Chumaevskiy, A.V. The Formation of Iron-Containing Intermetallic Phases in Al-12%Si Alloy by Using Tungsten Addition. Met. Microstruct. Anal. 2020, 9, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, L.B.; Soyama, J.; Zepon, G.; e Silva, A.C.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Bolfarini, C. Predicting the Formation of Intermetallic Phases in the Al-Si-Fe System with Mn Additions. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2017, 38, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chong, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Nagaumi, H. Exploring crystal structures, stability and mechanical properties of Fe, Mn-containing intermetallics in Al-Si Alloy by experiments and first-principles calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 160022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.; Timelli, G. Influence of sludge particles on the tensile properties of die-cast secondary aluminum alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Nagaumi, H. Understanding crystal structure and morphology evolution of Fe, Mn, Cr-containing phases in Al-Si cast alloy. Intermetallics 2021, 131, 107103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Hu, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X. Morphological evolution and strengthening behavior of α-Al(Fe,Mn)Si in Al–6Si–2Fe–xMn alloys. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, B.G.; Becker, H.; Smolka, M.; Keßler, A.; Leineweber, A.; Wolf, G. Intermetallic Sludge Formation in Fe Containing Secondary Al–Si Alloys Influenced by Cr and Mn as Preparative Tool for Metal Melt Filtration. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Thum, A.; Distl, B.; Kriegel, M.J.; Leineweber, A. Effect of melt conditioning on removal of Fe from secondary Al-Si alloys containing Mg, Mn, and Cr. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 6375–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Mendis, C.L. Heterogeneous nucleation and phase transformation of Fe-rich intermetallic compounds in Al-Mg-Si alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 836, 155515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjurenstedt, A.; Casari, D.; Seifeddine, S.; Mathiesen, R.H.; Dahle, A.K. In-situ study of morphology and growth of primary α-Al(FeMnCr)Si intermetallics in an Al-Si alloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 130, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Simensen, C.J.; Bjorneklett, A. A Model for α-Al(Mn, Fe)Si Crystals. In Light Metals 2017; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society; Springer International Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wanderka, N.; Rack, A.; Daudin, R.; Boller, E.; Markötter, H.; Manzoni, A.; Vogel, F.; Arlt, T.; Manke, I.; et al. Influence of impurities, strontium addition and cooling rate on microstructure evolution in Al-10Si-0.3Fe casting alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 766, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakitani, R.; Rodrigues, A.V.; Silva, C.; Garcia, A.; Cheung, N. The roles of solidification cooling rate and (Mn, Cr) alloying elements in the modification of β-AlFeSi and hardness evolvements in near-eutectic Al-Si alloys. J. Alloys Metall. Syst. 2023, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlock, J.G.; Mondolfo, L.F. Structure of Some Aluminium-Iron-Magnesium-Manganesesilicon Alloys. Z. Fur Met. 1975, 66, 605. [Google Scholar]
- Crepeau, P.N. Effect of iron in Al-Si casting alloys: A critical review. AFS Trans. 1995, 103, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, L.A.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Crystallization behavior of iron-containing intermetallic compounds in 319 aluminum alloy. Met. Mater. Trans. A 1994, 25, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, L.A.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Dissolution of iron intermetallics in Al-Si alloys through Nonequilibrium Heat Treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.S.; Chen, D. A Review on Processing–Microstructure–Property Relationships of Al-Si Alloys: Recent Advances in Deformation Behavior. Metals 2023, 13, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efzan, M.N.E.; Kong, H.; Kok, C. Review: Effect of Alloying Element on Al-Si Alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 845, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.R.; Moreau, C.; Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F.H.; Doty, H.W. Influences of alloying elements, solution treatment time and quenching media on quality indices of 413-type Al–Si casting alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 489, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Xing, S.; Sun, H.; Yan, G. Effect of Simultaneous Mg and Zn Addition on the Solidification and Microstructure of Multi-Element Hypoeutectic Al-Si Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Chang, G. Formation mechanism and conditions of fine primary silicon being uniformly distributed on single αAl matrix in Al-Si alloys. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Gao, T.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Y.; Qian, Z.; Liu, X. Generation and evolution of nanoscale AlP and Al13Fe4 particles in Al–Fe–P system. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, T.H.; Schaffer, P.L.; Arnberg, L. Influence of phosphorus on the nucleation of eutectic silicon in Al-Si alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 5796–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-K.; Mao, W.-M.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, D.; Yue, R. Refinement of primary Si grains in Al–20%Si alloy slurry through serpentine channel pouring process. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2016, 23, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Hu, Z.; Chen, A. Refinement of primary Si in Al– 20%Si alloy by MRB through phosphorus additions. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 225, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobel, A.; Kim, K.; Wolverton, C.; Walker, M.; Olson, G.B. Equilibrium composition variation of Q-phase precipitates in aluminum alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 138, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyaldin, L.; Abdelaziz, M.H.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. Effects of Alloying Elements and Testing Temperature on the Q-Index of Al–Si Based Alloys. Int. J. Met. 2018, 12, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, M.; Özyürek, D. The effects of Mg amount on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Si–Mg alloys. Mater. Des. 2013, 51, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yu, B.; Bian, J.; Chen, B.; Wu, H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Calculation Based on the Formation of Mg2Si and Its Effect on the Microstructure and Properties of Al–Si Alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ružbarský, J. Al-Si Alloys Casts by Die Casting; Springer Briefs in Applied Sciences and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM B-108; Standard Specification for Aluminum-Alloy Permanent Mold Castings. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Bolzoni, L.; Nowak, M.; Babu, N.H. Grain refinement of Al–Si alloys by Nb–B inoculation. Part II: Application to commercial alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.; Emamy, M.; Nemati, N. Effect of grain refinement on the microstructure and tensile properties of thin 319 Al castings. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, E.; Golbahar, B.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of grain refiner on the tensile and impact properties of Al–Si–Mg cast alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 468–479. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, E.; Tahiri, H.; Samuel, A.M.; Songmene, V.; Samuel, F.H. A Review on Fundamentals of Grain Refining of Al-Si Cast Alloys [Internet]. Recent Advancements in Aluminum Alloys. IntechOpen. 2024. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/88361 (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Sunitha, K.; Gurusami, K. Study of Al-Si alloys grain refinement by inoculation. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Nadendla, H.B.; Nowak, M.; Bolzoni, L. Grain Refiner for Al-Si Alloys. In Light Metals 2013; Sadler, B.A., Ed.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandersluis, E.; Emadi, P.; Andilab, B.; Ravindran, C. The Role of Silicon Morphology in the Electrical Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of As-Cast B319 Aluminum Alloy. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 1874–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, X.-S.; He, G.-Q.; Tian, D.-D.; Wang, Q.-G.; Lv, S.-Q. Quantitative microstructure and fatigue life of B319 casting alloys. Rare Met. 2017, 36, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.A.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Samuel, E.; Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F.H.; Doty, H.W. Assessment of the Effect of Mg Addition on the Solidification Behavior, Tensile and Impact Properties of Al–Si–Cu Cast Alloys. Int. J. Met. 2022, 17, 82–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, C.B.; Babu, N.H. Influence of Cu on modifying the beta phase and enhancing the mechanical properties of recycled Al-Si-Fe cast alloys. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Song, J.-W.; Zhou, X.-L.; Zha, M.; Wang, H.-Y. Fe-bearing phase formation, microstructure evolution, and mechanical properties of Al-Mg-Si-Fe alloy fabricated by the twin-roll casting process. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 886, 161202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epifano, E.; Monceau, D. Ellingham diagram: A new look at an old tool. Corros. Sci. 2023, 217, 111113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, K.; Zhao, G.; Zuo, L. Formation of Phases and Microstructures in Al-8Si Alloys with Different Mg Content. Materials 2021, 14, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisaabadi, B.G.; Davami, P.; Kim, S.K.; Varahram, N. Effects of hydrogen and oxides on tensile properties of Al–Si–Mg cast alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 552, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Eisaabadi, B.G.; Davami, P.; Kim, S.K.; Varahram, N.; Yoon, Y.O.; Yeom, G.Y. Effect of oxide films, inclusions and Fe on reproducibility of tensile properties in cast Al–Si–Mg alloys: Statistical and image analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.R.; Zhang, L.K.; Wang, Z.M.; Gao, A.J. Achievement of High Strength and Ductility in Al–Si–Cu–Mg Alloys by Intermediate Phase Optimization in As-Cast and Heat Treatment Conditions. Materials 2020, 13, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigezu, B.S.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Jha, P.K. Influence of Reinforcement Type on Microstructure, Hardness, and Tensile Properties of an Aluminum Alloy Metal Matrix Composite. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2013, 1, 33948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschi, S. Optimization of a354 Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy heat treatment: Effect on microstructure, hardness, and tensile properties of peak aged and overaged alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.P.; Zhi, W.L.; Zhu, J.Q.; Su, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.J.; Wang, J.H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–Si alloy modified with Al–3P. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.B.V.; Rao, C.S.P.; Selvaraj, N. Mechanical and Tribological Behaviour of Particulate Reinforced Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites—A Review. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2011, 10, 59–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, I.; Eker, A.A. Analysis of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Particle Reinforced AlSi7Mg2 Matrix Composite Materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2011, 20, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Tiryakioğlu, M. Review of effect of P and Sr on modification and porosity development in Al–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giovanni, M.; Kaduk, J.A.; Srirangam, P. Modification of Al-Si Alloys by Ce or Ce with Sr. JOM 2019, 71, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Hu, J.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Su, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. On the formation of Al2Si2Sr phase and its behavior in Al–Si–Sr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 985, 174023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrirero, J.; Li, J.; Engstler, M.; Ghafoor, N.; Schumacher, P.; Odén, M.; Mücklich, F. Cluster formation at the Si/liquid interface in Sr and Na modified Al–Si alloys. Scr. Mater. 2016, 117, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouzy, M.; Jacob, S.; Richard, M. Interpretation of Tensile Results by Means of Quality Index and Probable Yield Strength. AFS Int. Cast Met. J. 1980, 5, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, S. Quality Index in Predicting of Properties of Aluminum Castings-A Review. AFS Trans. 2000, 108, 811–818. [Google Scholar]






| Alloy | Elements (wt.%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Ti | Be | Sr | Al | |
| E0–1 | 10.47 | 0.3801 | 0.4734 | 0.2374 | 0.0410 | 0.0302 | 0.0431 | 0.0006 | 0.000 | 87.8 |
| E0–2 | 10.69 | 0.3561 | 0.4968 | 0.2462 | 0.0487 | 0.0291 | 0.0645 | 0.0002 | <0.0000 | 87.8 |
| E0–3 | 10.87 | 0.3593 | 0.4972 | 0.2424 | 0.0477 | 0.0295 | 0.0648 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 87.7 |
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| EFHG EFPHG EFSHG EFBSHG | EF * alloy, super heating, graphite mold EF alloy + 30 ppm P, super heat, graphite mold EF alloy + 195 ppm Sr, super heat, graphite mold EF alloy + 195 ppm Sr + 500 ppm Be, super heat, graphite mold |
| EFHM EFPHM EFSHM EFBSHM EFTHM EFZHM EFTZHM EFSLHM | EF * alloy, super heating, metallic mold EF alloy + 30 ppm P, super heat, metallic mold EF alloy + 195 ppm Sr, super heat, metallic mold EF alloy + 195 ppm Sr + 500 ppm Be, super heat, metallic mold EF alloy + 0.2%Ti, super heat, metallic mold EF alloy + 1%Zn, super heat, metallic mold EF alloy + 1%Zn + 0.2%Ti, super heat, metallic mold EF alloy + 195 ppm Sr + 0.5%La, super heat, metallic mold |
| EFHC EFPHC EFSHC EFBSHC | EF * alloy, super heating, water quenching EF alloy + 30 ppm P, super heat, water quenching EF alloy + 195 ppm Sr, super heat, water quenching EF alloy + 195 ppm Sr + 500 ppm Be, super heat, water quenching |
| Alloy Codes | Composition |
|---|---|
| E | E0 + 0.35% Mg |
| E1 | E + 0.5%Be |
| E2 | E + 0.0030%P |
| E3 | E, 0.8%Fe total |
| E4 | E, 1.2%Fe total |
| E5 | E, 1.52%Fe total |
| E6 | E5 + 30 ppm P |
| E7 | E5 + 0.05%Be |
| E8 | E + 195 ppm Sr |
| E9 | E + 380 ppm Sr |
| E10 | E + 195 ppm Sr + 30ppm P |
| E11 | E + 380 ppm Sr + 30ppm P |
| E12 | E5 + 195ppm Sr |
| E13 | E5 + 195 ppm Sr + 30ppm P |
| E14 | E5 + 380 ppm Sr + 30ppm P |
| E15 | E5 + 380 ppm Sr + 0.05%Be |
| E16 | E5-superheated |
| E17 | E12-superheated |
| E18 | E14-superheated |
| E19 | E6-superheated |
| E20 | E13-superheated |
| E21 | E15-superheated |
| Mold Type/DAS * | Alloy Code | Av. Length (µm) | Av. Thickness (µm) | Density (#/cm2) | Av. Surface Area (µm2/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite mold DAS 80–90 µm | EFHG EFPHG EFSHG EFBSHG | 389 ± 6 174 ± 3 124 ± 4 52 ± 3 | 12.3 10.4 3.4 3.0 | 1.1 × 103 5.2 × 103 6.2 × 103 2.9 × 104 | 1.1 × 107 6.0 × 107 8.7 × 106 9.4 × 106 |
| Metallic mold DAS 15–20 µm | EFHM EFPHM EFSHM EFBSHM EFTHM EFZHM EFTZHM | 54 ± 2 63 ± 3 17 ± 7 8 ± 5 7 ± 3 13 ± 4 5 ± 2 | 2.1 2.4 1.5 0.9 0.8 1.4 0.8 | 3.9 × 104 3.1 × 104 4.5 × 105 5.9 × 104 3.9 × 105 3.6 × 105 2.7 × 105 | 3.6 × 106 5.7 × 106 2.5 × 106 7.5 × 105 3.5 × 105 1.1 × 105 2.8 × 105 |
| Water quench (solid droplet) DAS = 3–5 µm | EFHC EFPHC EFSHC EFBSHC | 7 ±3 9 ± 5 Nil Nil | 0.2 0.2 Nil Nil | 4.5 × 103 1.2 × 104 Nil Nil | 6.3 × 103 2.2 × 104 Nil Nil |
| Superheating Temperature, (°C) | Alloy Code | Av. Length (µm) | Av. Thickness (µm) | Density (#/cm2) | Av. Total Surface Area (µm/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 950 °C | EFHM | 54 ± 18 | 2.1 | 3.9 × 104 | 3.6 × 106 |
| 950 °C | EFHT EFPHT EFSHT EFPSHT EFBSHT | 20 ± 1 91 ± 7 20 ± 2 17 ± 9 8 ± 2 | 1.5 2.1 1.6 1.1 0.7 | 2.0 × 105 2.1 × 104 2.1 × 105 2.0 × 105 4.6 × 105 | 6.0 × 106 4.0 × 106 7.0 × 106 3.7 × 106 3.3 × 106 |
| 750 °C | EFT EFPT EFST EFPST EFBST | 25 ± 5 32 ± 2 22 ± 1 22 ± 1 12 ± 8 | 0.8 1.7 0.8 1.1 0.7 | 2.0 × 105 6.3 × 104 2.1 × 105 1.2 × 105 2.4 × 105 | 4.0 × 106 3.4 × 106 3.7 × 106 4.0 × 106 1.1 × 106 |
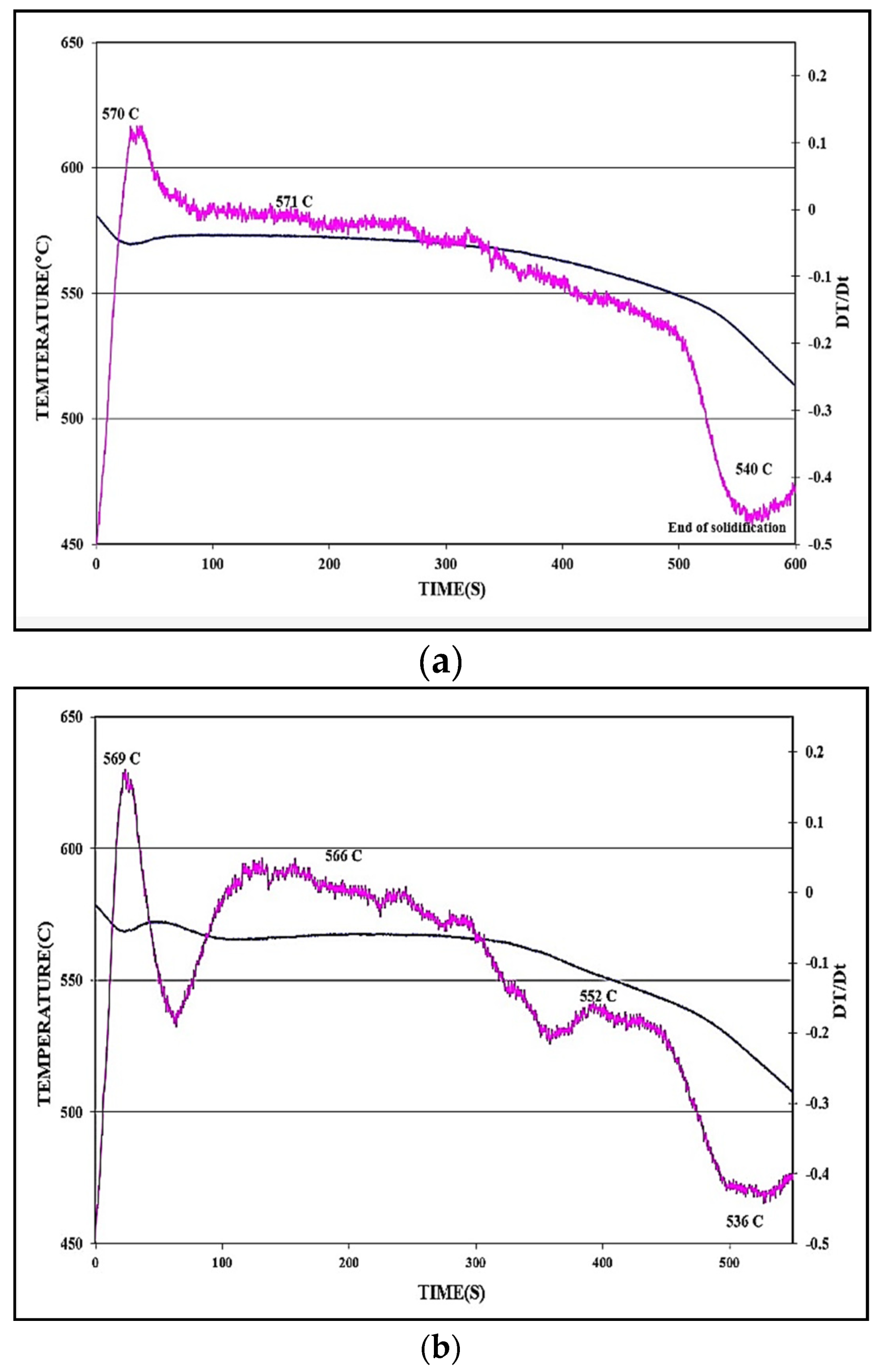
| Alloy | Undercooling Parameters Related to the Al-Si Eutectic Reaction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Te1 (°C) | Te2 (°C) | ΔTe (°C) | te1 (s) | te2 (s) | Δte (s) | |
| 413 (Figure 4a) | 570.1 | 571.3 | 1.4 | 124.4 | 233.6 | 132.2 |
| 431 + Sr (Figure 4b) | 565.6 | 568.3 | 2.7 | 104.4 | 213.2 | 88.8 |
| Alloy | ΔP−UTS (MPa) | ΔP−YS (MPa) | ΔP−%EL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Series #1 | |||
| E | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E1 | −10 | −5 | −2.5 |
| E2 | −5 | 10 | −4.5 |
| Series #2 | |||
| E | −10 | 0 | 0 |
| E3 | −85 | −40 | −6 |
| E4 | −80 | −35 | −6.5 |
| E5 | −70 | 5 | −7.3 |
| Series #3 | |||
| E5 | −70 | 5 | −7.3 |
| E6 | −110 | −35 | −7.7 |
| E7 | −60 | −10 | −6.8 |
| Series #4 | |||
| E8 | −10 | −10 | 0 |
| E9 | −20 | 10 | −2 |
| E10 | −50 | −50 | 3 |
| E11 | −125 | −125 | 8 |
| Series #5 | |||
| E12 | −35 | 65 | −7 |
| E13 | −110 | −35 | −7.5 |
| E14 | −145 | −115 | −5 |
| E15 | −40 | 5 | −6.5 |
| Series #6 | |||
| E16 | −85 | −10 | −7.3 |
| E17 | −85 | −5 | −7.4 |
| E18 | −65 | 11 | −7.5 |
| E19 | −90 | −15 | −7.7 |
| E20 | −150 | −105 | −4 |
| E21 | −30 | −15 | −3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doty, H.W.; Samuel, E.; Samuel, A.M.; Elsharkawi, E.; Songmene, V.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of Fe Concentration and Superheating on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of High Mg 413.0-Type Alloys: Role of Sr, Be, P, and La. Materials 2025, 18, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020249
Doty HW, Samuel E, Samuel AM, Elsharkawi E, Songmene V, Samuel FH. Effect of Fe Concentration and Superheating on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of High Mg 413.0-Type Alloys: Role of Sr, Be, P, and La. Materials. 2025; 18(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoty, Herbert W., Ehab Samuel, Agnes M. Samuel, Ehab Elsharkawi, Victor Songmene, and Fawzy H. Samuel. 2025. "Effect of Fe Concentration and Superheating on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of High Mg 413.0-Type Alloys: Role of Sr, Be, P, and La" Materials 18, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020249
APA StyleDoty, H. W., Samuel, E., Samuel, A. M., Elsharkawi, E., Songmene, V., & Samuel, F. H. (2025). Effect of Fe Concentration and Superheating on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of High Mg 413.0-Type Alloys: Role of Sr, Be, P, and La. Materials, 18(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020249








