Tribological Properties of Eutectic White Cast Iron with Directional and Non-Directional Microstructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Research Methodology
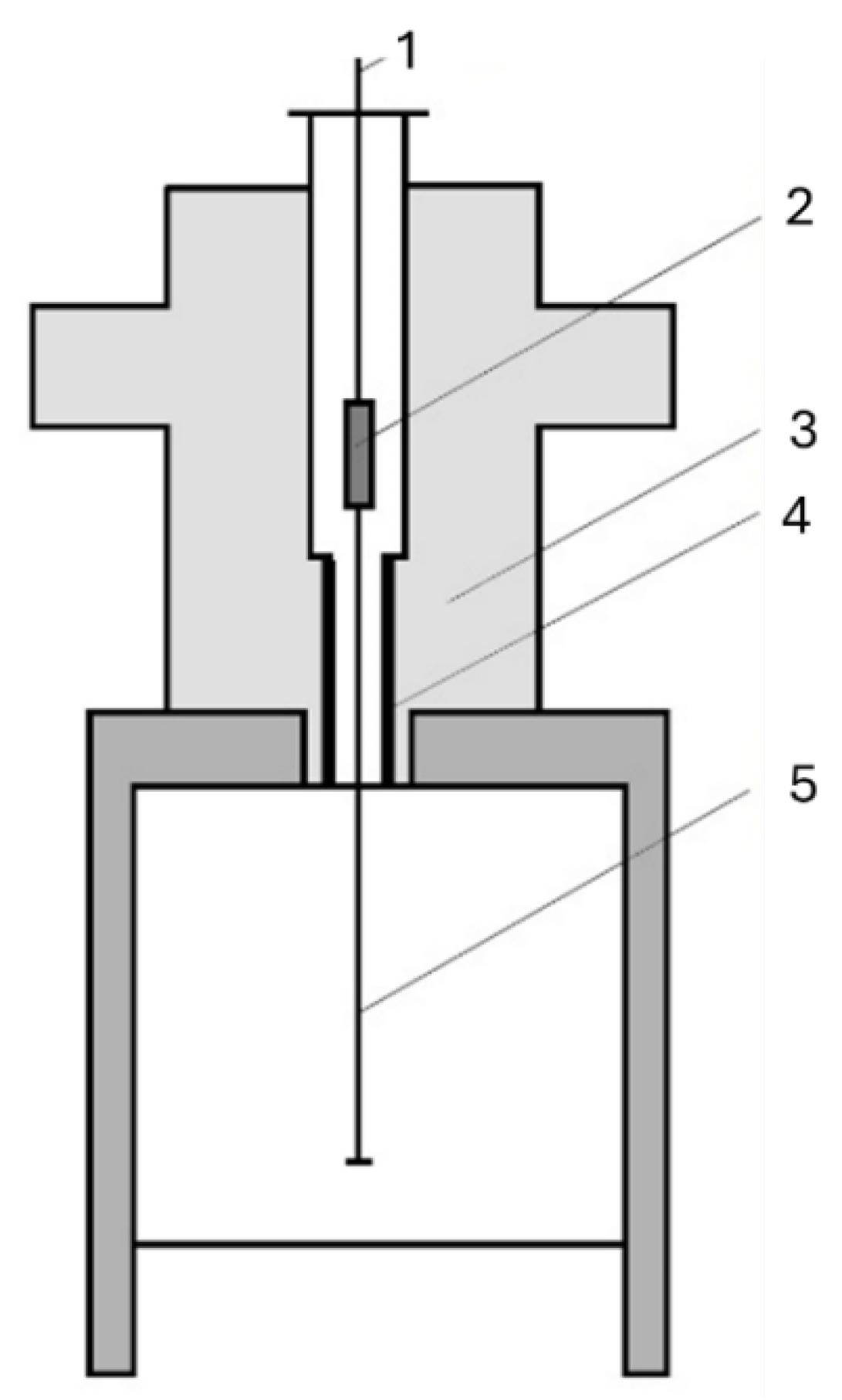
2.1. Directional Solidification of White Cast Iron
2.2. Tribological Investigations
- -
- measurement field 6 × 10 mm,
- -
- resolution 600 × 1000 measurement points,
- -
- data acquisition and processing—MARK III v3.8.21 for windows software (FRT GmbH, München, Germany).
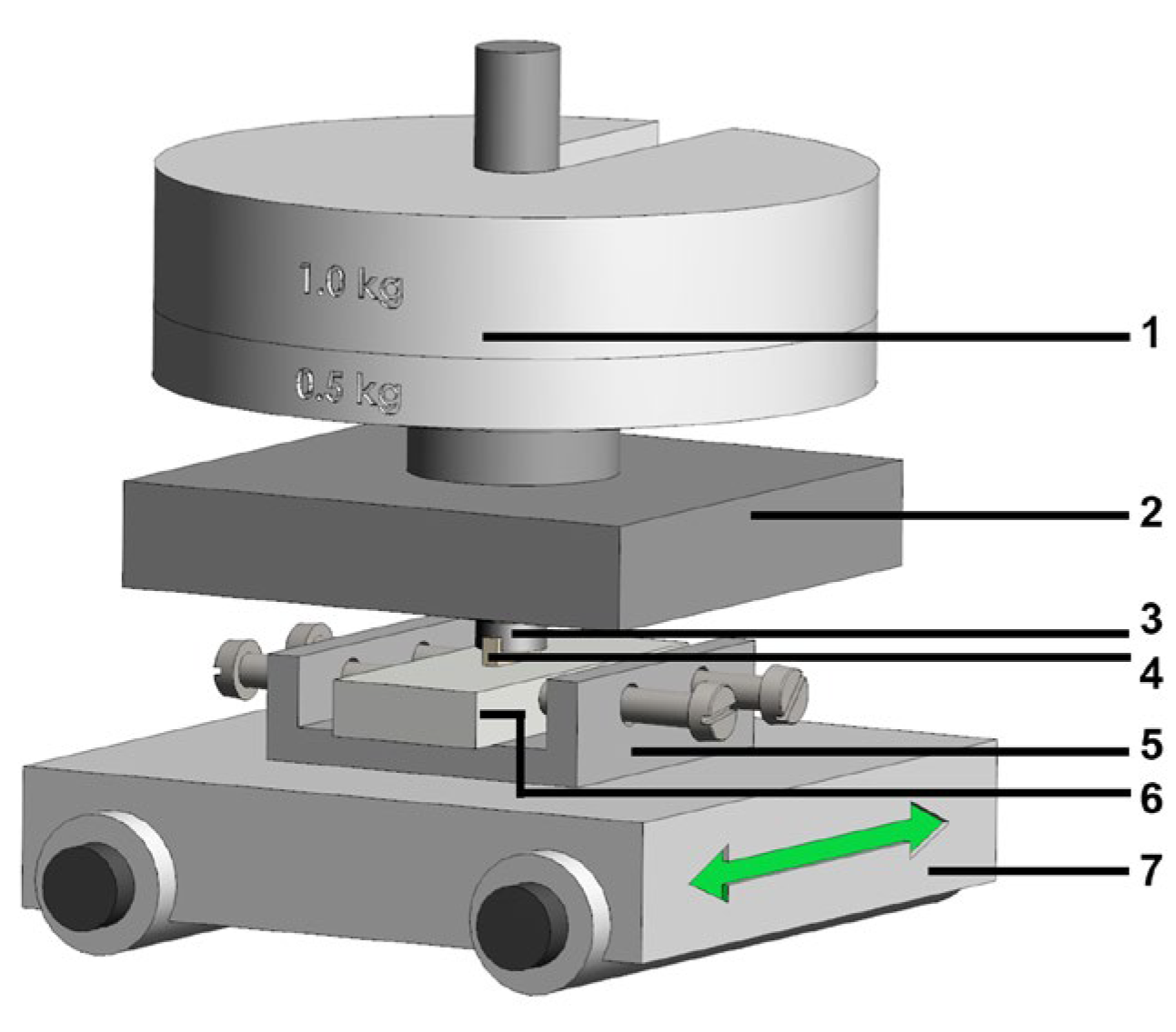
3. Results and Analysis
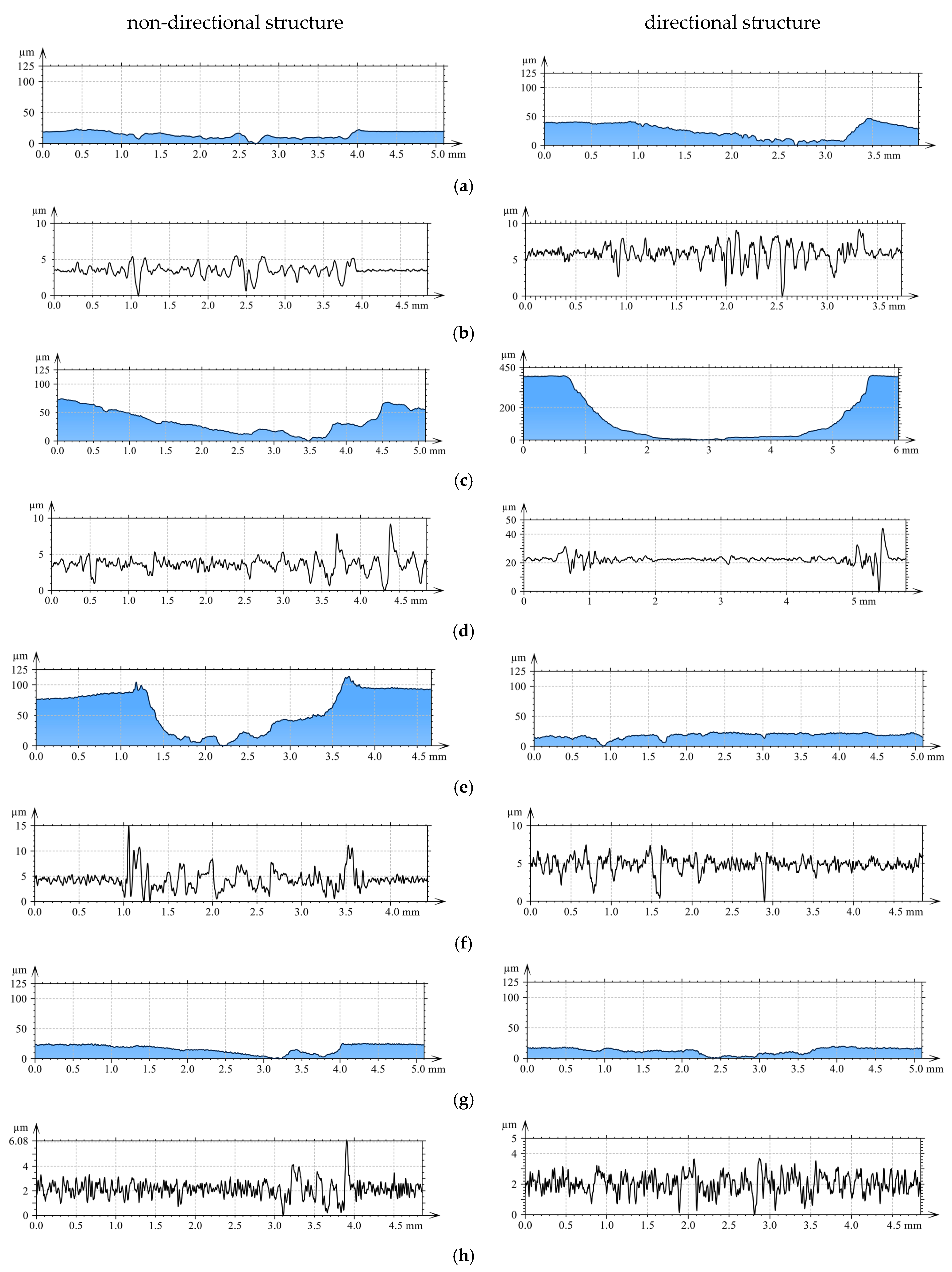
3.1. Profilometry of Wear Tracks
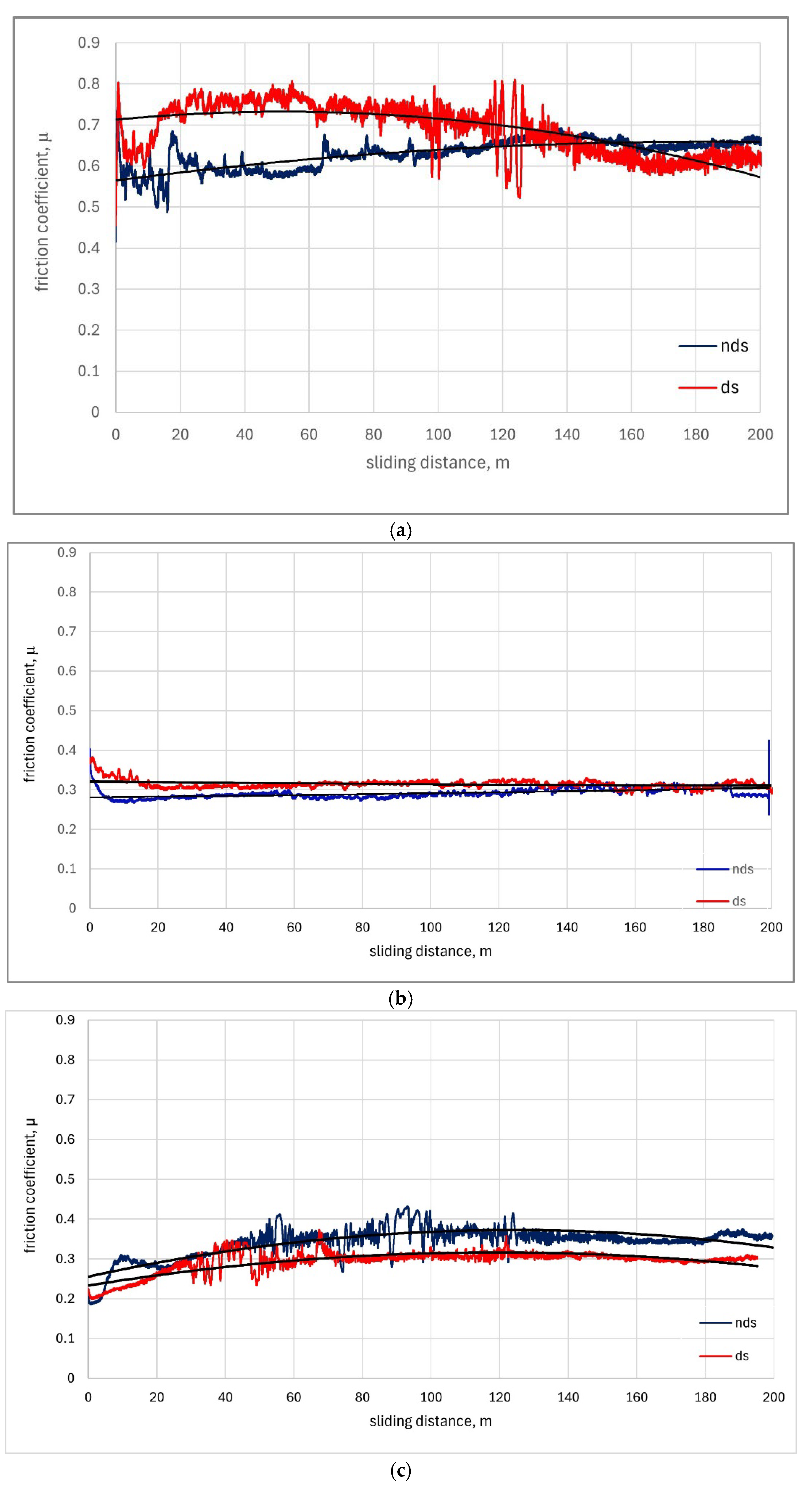
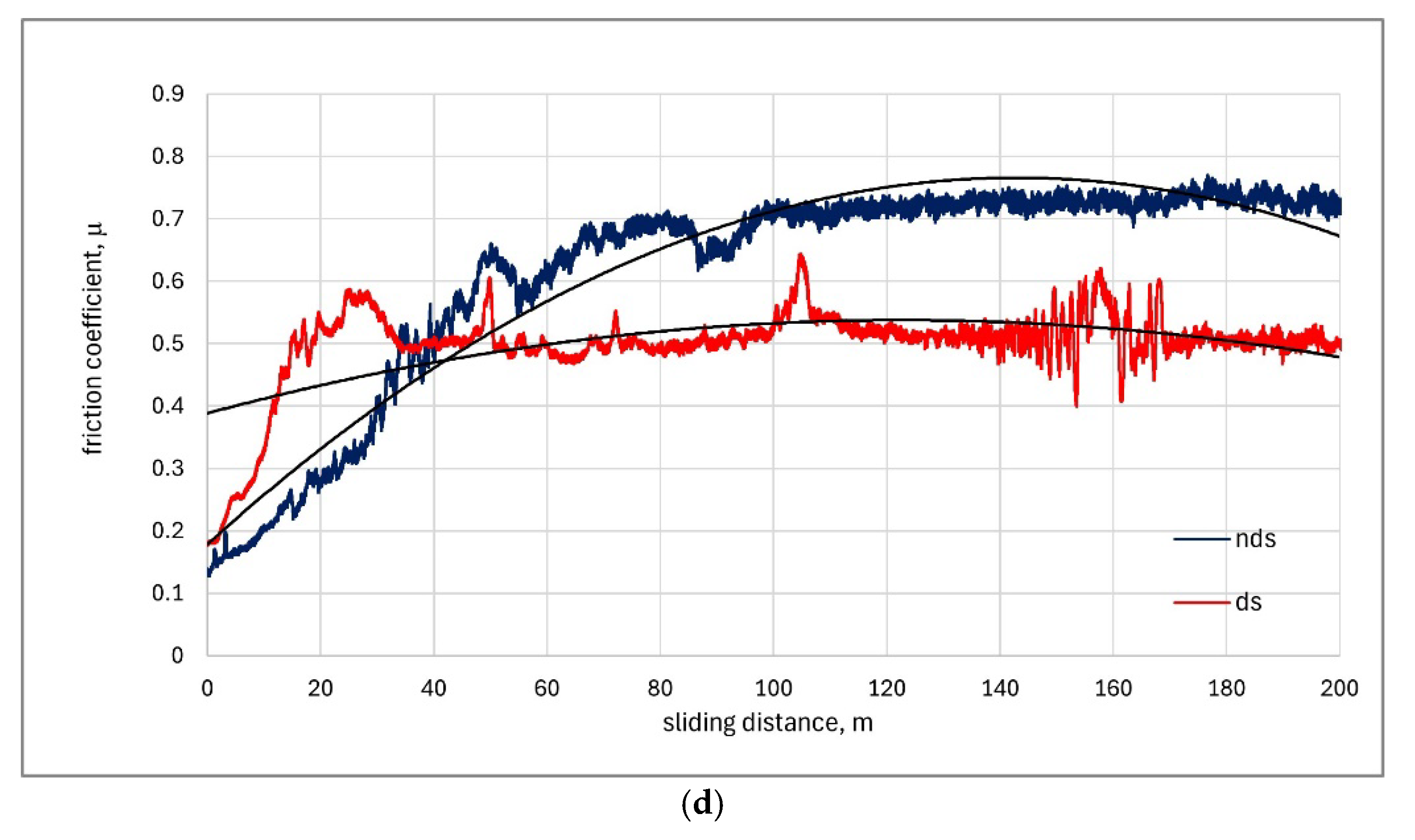
3.2. Coefficient of Friction
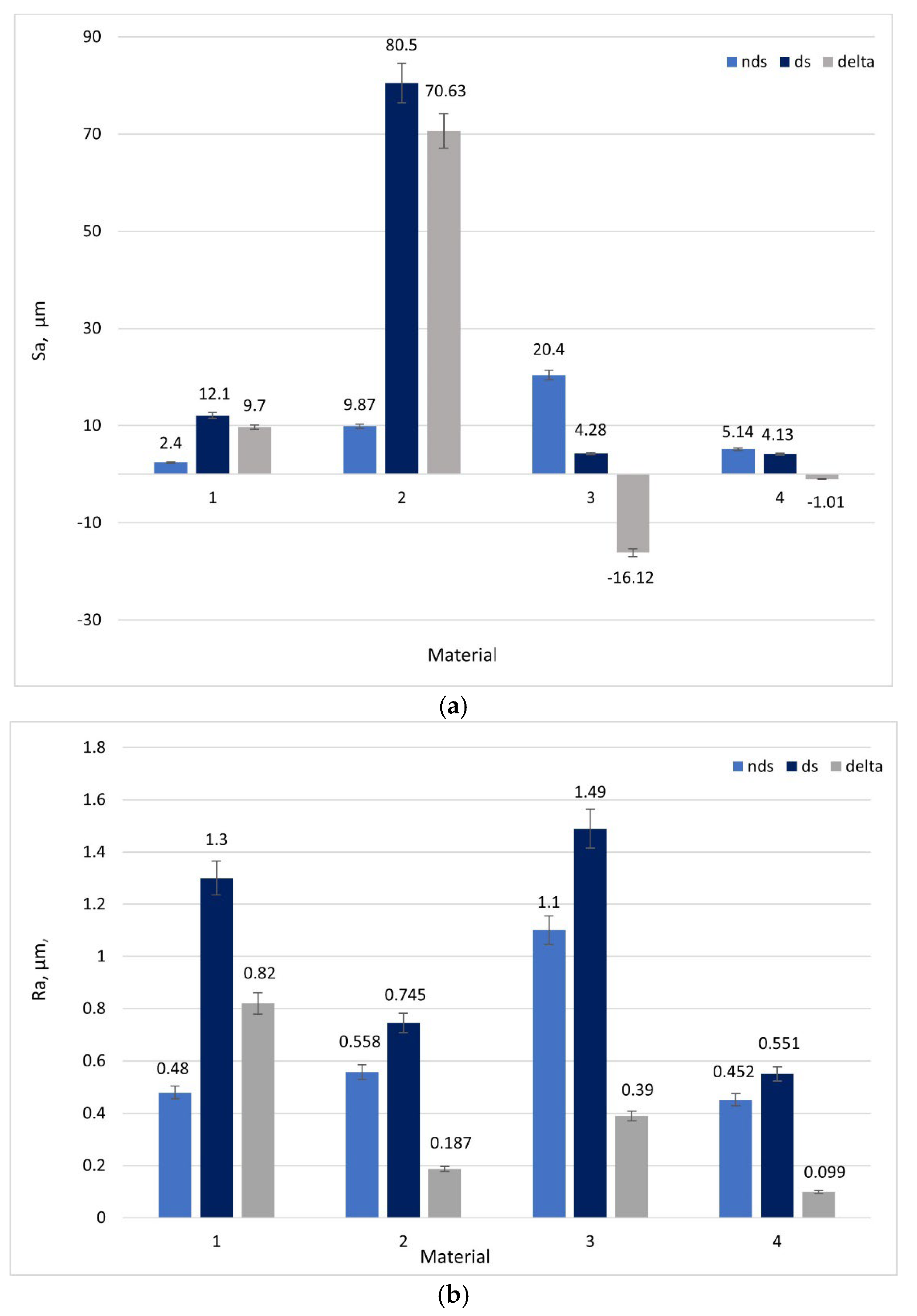
3.3. Roughness Parameters
4. Results Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Tribological Studies of White Cast Iron
4.2. Dependence of Wear Mechanisms on Microstructure
4.3. Analysis of Performance Specific to Material Pairs
4.4. Practical Implications and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laird, M.; Gundlach, J.; Roehring, K. Abrasion Resistant Cast Iron Handbook; American Foundry Society: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- David, J.R. Cast Irons. In ASM Specialty Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Azarhoushang, B.; Marinescu, I.D.; Rowe, W.B.; Dimitrov, B.; Ohmori, H. Tribology and Fundamentals of Abrasive Machining Processes, 3rd ed.; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach, R.B. White Iron and High-Alloyed Iron Castings. In Casting, ASM Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opapaiboon, J.; Inthidech, S.; Kaoru Yamamoto, K.; Matsubara, Y. Effect of Carbon Balance on Structural Properties and Wear Resistance of Multi-Component White Cast Iron; Inter Metalcast: Ochtrup, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, R.H.; Shimizu, K.; Kusumoto, K.; Gaqi, Y.; Huq, M.J. Tribological Characteristics of High-Chromium Based Multi-Component White Cast Irons. Crystals 2022, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, J. Microstructure and tribological properties of mottled cast iron with different chemical composition. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 51, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Fashu, S.; Trabadelo, V. Development and Performance of High Chromium White Cast Irons (HCWCIs) for Wear–Corrosive Environments: A Critical Review. Metals 2023, 13, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, R.H.; Shimizu, K.; Kusumoto, K.; Gaqi, Y.; Huq, M.J. A Study of the Three-Body Abrasive Wear Resistance of 5V/5Nb-5Cr-5Mo-5W-5Co-Fe Multicomponent Cast Alloys with Different Carbon Percentages. Materials 2023, 16, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pociño, A.; Asensio-Lozano, J.; Álvarez-Antolín, F.; García-Diez, A. Evaluation of hardness, sliding wear and strength of a hypoeutectic white iron with 25% Cr after heat treatments. Metals 2021, 11, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutçuoğlu, B.; Koç, F.G.; Erişir, E.; Karaarslan, G. The effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and wear behavior of tungsten and boron alloyed Ni-hard 4 white cast irons. Int. J. Met. 2024, 19, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokari-Sheshdeh, M.; Ali, Y.; Gallo, S.C.; Lin, W.; Gates, J.D. Comparing the abrasion performance of NiHard-4 and high-Cr-Mo white cast irons: The effects of chemical composition and microstructure. Wear 2022, 492, 204208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, A.N.; Markandeya, R.; Rao, B.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Kaushik, D. Effect of alloying elements on the dry sliding wear behavior of high chromium white cast iron and Ni-hard iron. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, M.J.; Shimizu, K.; Kusumoto, K. Abrasive Wear Characteristics of High-Cr Multicomponent White Cast Irons at Elevated Temperatures. Crystals 2025, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.S.; Ko, S.J.; Kim, J.G. Effect of chromium on microstructure and corrosion behavior of High-Cr white cast irons used in coal-fired power plant desulfurization facilities. Int. J. Met. 2024, 18, 1664–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedolla-Jacuinde, A.; Guerra, F.V.; Guerrero-Pastran, A.J.; Sierra-Cetina, M.A.; Valdez-Medina, S. Microstructural effect and wear performance of high chromium white cast iron modified with high boron contents. Wear 2021, 476, 203675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, R.H.; Shimizu, K.; Kusumoto, K.; Gaqi, Y.; Todaka, T. Effect of boron addition on three-body abrasive wear characteristics of high chromium based multi-component white cast iron. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 275, 125232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, W.M.; Polkowski, W.; Dudziak, T.; dos Santos, C.A.; de Barcellos, V.K. Microstructure Formation and Dry Reciprocating Sliding Wear Response of High-Entropy Hypereutectic White Cast Irons. Metals 2025, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortini, A.; Suman, A.; Vulpio, A.; Merlin, M.; Pinelli, M. Microstructural and Erosive Wear Characteristics of a High Chromium Cast Iron. Coatings 2021, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.-S.; Chang, H.; Tang, X.; Hinckley, B.; Zhang, M.-X. Refinement of primary carbides in hypereutectic high-chromium cast irons: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 999–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doǧan, Ö.N.; Laird, G., II; Hawk, J.A. Abrasion resistance of the columnar zone in high Cr white cast irons. Wear 1995, 181–183, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Zhou, R.; Li, L.; Lv, H.; Li, Y.; Bai, D.; Jiang, Y. Change in primary (Cr, Fe)7C3 carbides induced by electric current pulse modification of hypereutectic high chromium cast iron melt. Materials 2019, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doǧan, Ö.N.; Hawk, J.A. Effect of carbide orientation on abrasion of high Cr white cast iron. Wear 1995, 189, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, J.J. Effect of (Fe,Cr)7C3 carbide orientation on abrasion wear resistance and fracture toughness. Wear 2011, 270, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, M.; Ohtsuka, H. Mechanical Properties of Cementite. ISIJ Int. 2022, 62, 1313–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Huang, Z.; Xing, J.; Wang, Y.; Jian, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Fan, X. Three-Body Abrasive Behavior of Cementite-Iron Composite with Different Cementite Volume Fractions. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 62, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fras, T.; Koenig, B.; Meyer, P.P.; Diop, I. Microstructural characteristics of a high-chromium cast iron hard-facing alloy. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci.-Tech. Sci. 2025, 73, 151957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Xing, X.; Li, J.; Qi, X.; Yang, Q. Study of the wear resistance of Hypereutectic Fe-Cr-C Hardfacing Alloy reinforced with carbide particles. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, S.; Luo, Z.; Ning, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, T.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Z. Microstructure and wear resistance of WC and high chromium cast iron hardfacing layers. Coatings 2020, 10, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepczyńska-Łent, M.; Boroński, D.; Maćkowiak, P. Mechanical properties and microstructure of directionally solidified Fe-4.25%C eutectic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 822, 141644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepczyńska-Łent, M.; Seyda, J. Characteristics of ledeburite in EDS analyses of directionally solidified eutectic white cast iron. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2021, 22, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepczyńska-Łent, M. Characteristics of the growth of the directionally solidified Fe—4.25% C eutectic alloy. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2021, 66, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepczyńska-Łent, M.; Piątkowski, J. Study of directionally solidified Fe—4.25%C eutectic alloy using electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) technique. Metalurgija 2020, 59, 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Standard EN 1652:2000; Copper and Copper Alloys—Plate, Sheet, Strip and Circles for General Purposes. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000.
- Standard EN 1676:2020; Aluminium and Aluminium Alloys—Alloyed Ingots for Remelting—Specifications. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020.
- Standard ISO 683-17:2023; Heat-Treated Steels, Alloy Steels and Free-Cutting Steels—Part 17: Ball and Roller Bearing Steels. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Dolata, A.J.; Wieczorek, J.; Dyzia, M.; Starczewski, M. Assessment of the Tribological Properties of Aluminum Matrix Composites Intended for Cooperation with Piston Rings in Combustion Engines. Materials 2022, 15, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | Cu |
| 4.25 | 0.058 | 0.64 | 0.0079 | 0.021 | 0.033 | 0.0093 | <0.0020 | 0.011 | 0.032 |
| Co | Ti | Nb | V | W | Pb | Mg | B | Sn | Zn |
| 0.0024 | <0.001 | <0.0040 | 0.0022 | <0.010 | <0.0030 | <0.0010 | 0.0009 | 0.0061 | <0.002 |
| As | Bi | Ca | Ce | Zr | La | Fe | |||
| 0.0069 | <0.002 | 0.0005 | <0.0030 | 0.0043 | 0.0013 | 94.9 |
| C | Si | Cu | Mg | Ni | Mn | Ti | O | SiC | Al | Cr | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-ETP | - | ≥99.9 | - | - | - | - | ≤0.04 | - | - | - | - | |
| AlSi12CuNiMg | 12 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.05 | - | - | bal. | - | - | |
| AlSi12CuNiMg + SiC | 11.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.05 | - | 15.0 | bal. | - | - | |
| 1.3505 | 0.95 | 0.15 | - | - | 0.3 | 0.35 | - | - | - | - | 1.65 | bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trepczyńska-Łent, M.; Wieczorek, J. Tribological Properties of Eutectic White Cast Iron with Directional and Non-Directional Microstructure. Materials 2025, 18, 4516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194516
Trepczyńska-Łent M, Wieczorek J. Tribological Properties of Eutectic White Cast Iron with Directional and Non-Directional Microstructure. Materials. 2025; 18(19):4516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194516
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrepczyńska-Łent, Małgorzata, and Jakub Wieczorek. 2025. "Tribological Properties of Eutectic White Cast Iron with Directional and Non-Directional Microstructure" Materials 18, no. 19: 4516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194516
APA StyleTrepczyńska-Łent, M., & Wieczorek, J. (2025). Tribological Properties of Eutectic White Cast Iron with Directional and Non-Directional Microstructure. Materials, 18(19), 4516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18194516





