Hydration and Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Binders Using CFBC Ash
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
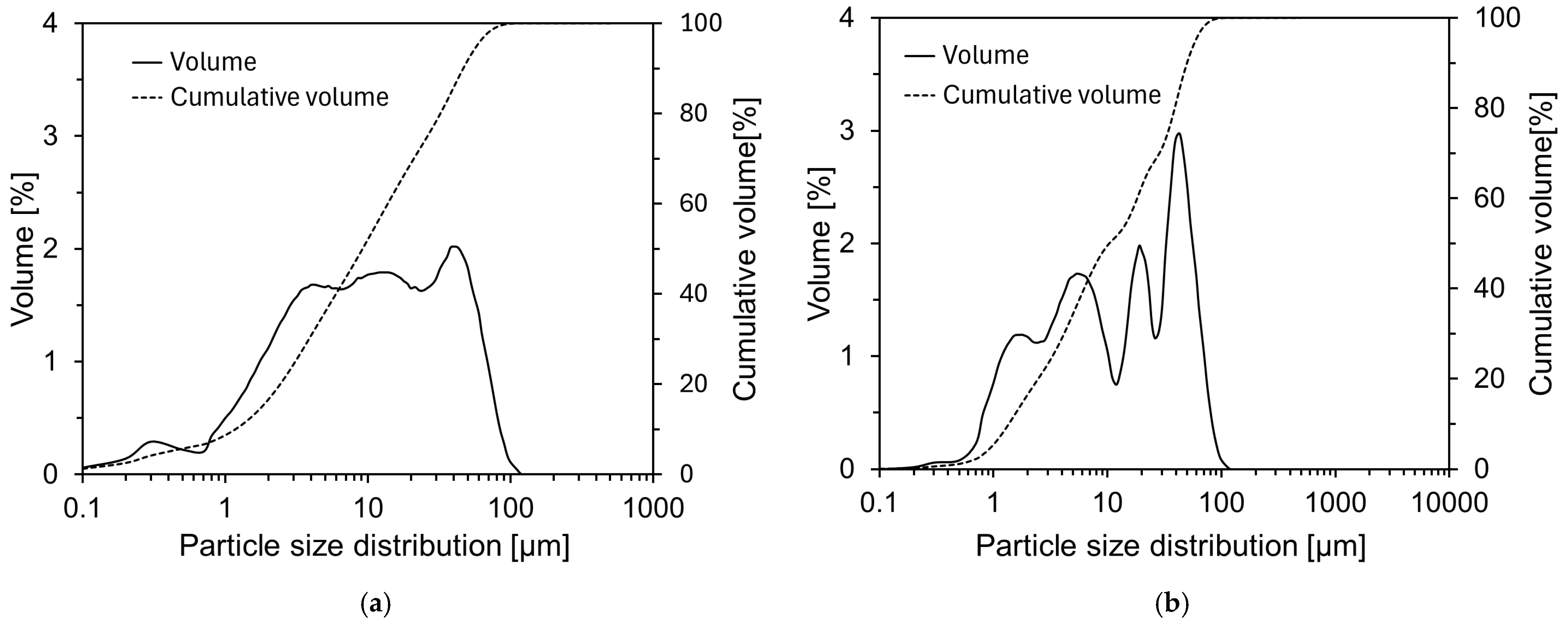
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Proportions and Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
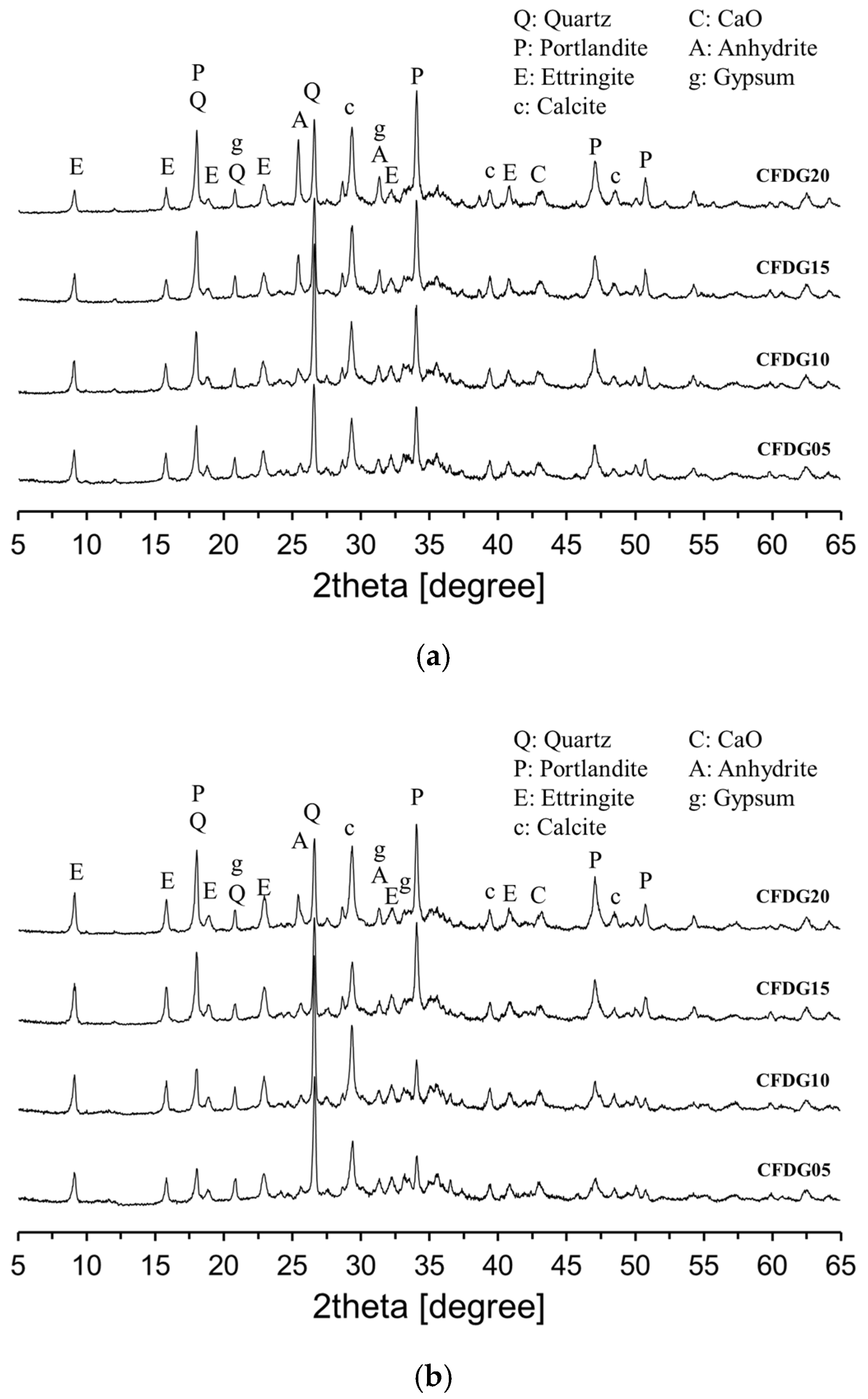
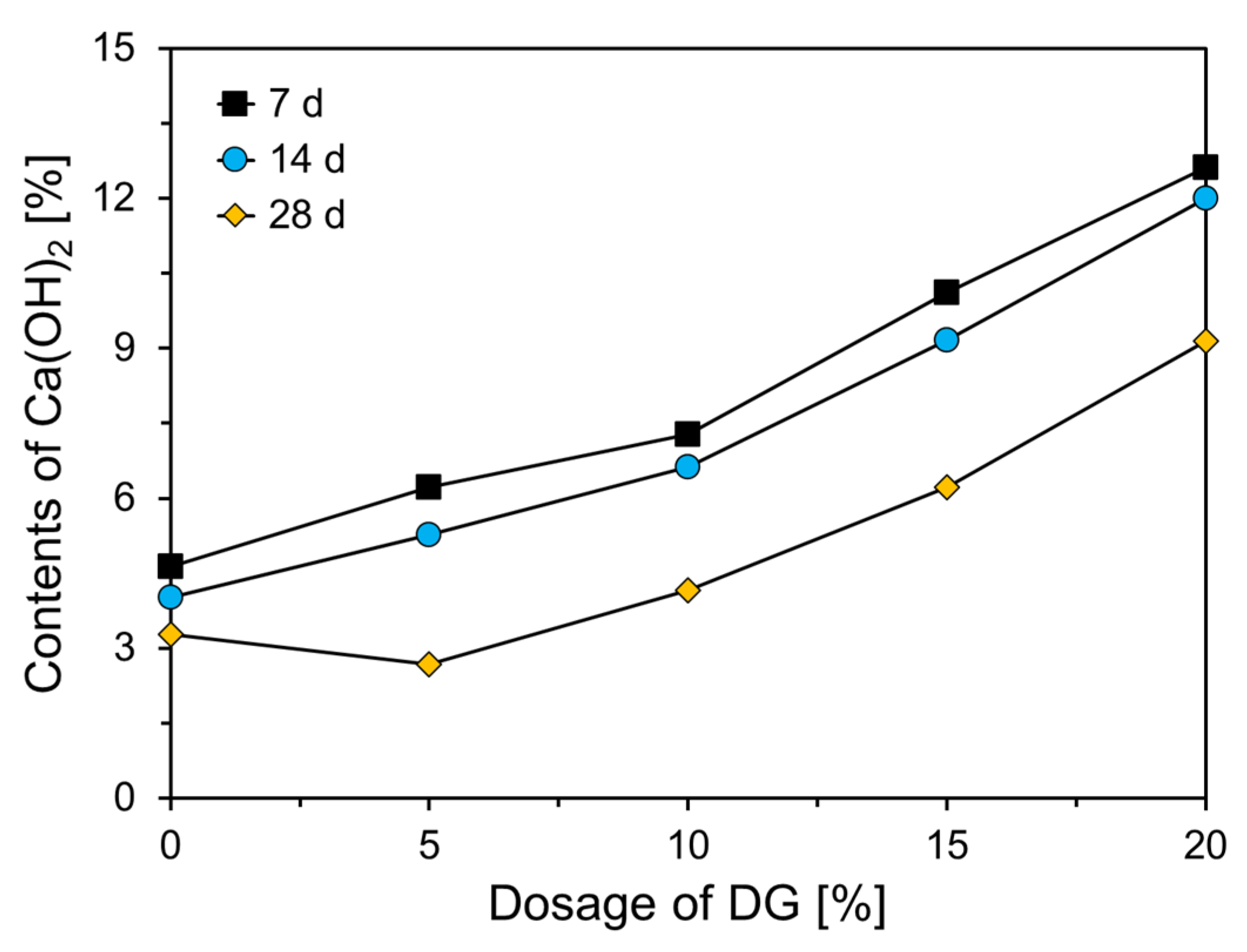
3.1. Hydration of CFBC Ash Containing DG
3.2. Setting Time and Compressive Strength
3.3. Microstructure of CFBC Ash Paste Containing DG
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havlica, J.; Brandstetr, J.; Odler, I. Possibilities of Utilizing Solid Residues from Pressured Fluidized Bed Coal Combustion (PSBC) for the Production of Blended Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J. Fluidized Bed Combustion of Alternative Solid Fuels; Status, Successes and Problems of the Technology. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1995, 21, 239–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Granatstein, D.L. Sulfation Phenomena in Fluidized Bed Combustion Systems. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2001, 27, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Jia, L.; Wu, Y. CFBC Ash Hydration Studies. Fuel 2005, 84, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Song, Y. Methods for the Control of Volume Stability of Sulfur Rich CFBC Ash Cementitious System. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Huang, R. Effect of Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Ash on the Properties of Roller Compacted Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Choi, Y.C. Development of Non-Sintered Zero-OPC Binders Using Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qian, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z. Self-Cementing Mechanism of CFBC Coal Ashes at Early Ages. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2008, 23, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illikainen, M.; Tanskanen, P.; Kinnunen, P.; Körkkö, M.; Peltosaari, O.; Wigren, V.; Österbacka, J.; Talling, B.; Niinimäki, J. Reactivity and Self-Hardening of Fly Ash from the Fluidized Bed Combustion of Wood and Peat. Fuel 2014, 135, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chi, M.; Huang, R. Characteristics of CFBC Fly Ash and Properties of Cement-Based Composites with CFBC Fly Ash and Coal Fired Fly Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.C.; Huang, R.; Wu, T.H.; Fou, T.C. Utilization of Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) Fly Ash and Coal-Fired Fly Ash in Portland Cement. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 629–630, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Shang, L. Mechanical Properties of High Performance Concrete Made with High Calcium High Sulfate Fly Ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Huang, K.; Ma, B.; Wu, B. Cementitious Properties and Hydration Mechanism of Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) Desulfurization Ashes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Li, Q.; Zhai, J. Investigation on the Hydration of CFBC Fly Ash. Fuel 2012, 98, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, P.; Chen, X.; Ge, X.; Wang, Y. Study on Hydration Characteristics of Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash (CFBCA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Li, Q.; Zhai, J.; Li, F. Self-Cementitious Properties of Fly Ashes from CFBC Boilers Co-Firing Coal and High Sulphur Petroleum Coke. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Zhai, J.; Li, Q.; Li, F. Utilization of Fly Ash Coming from a CFBC Boiler Co-Firing Coal and Petroleum Coke in Portland Cement. Fuel 2007, 86, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Y.; Huang, W.-H. Activation of Blast Furnace Slag with CFB Fly Ash as a Supplementary Binder Material: Hydration Products and Effects of Sulfate Attack. Crystals 2022, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Ma, S.; Feng, Y.; Xu, N.; Bai, S. Study on the Composite Gravel Preparation and the Synergistic Absorption of CO2 by Fly Ash of CFB Boiler. Fuel 2023, 342, 127843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Hao, X.; Lu, Y. Circulating Fluidized Bed Fly Ash Mixed Functional Cementitious Materials: Shrinkage Compensation of F-CaO, Autoclaved Hydration Characteristics and Environmental Performance. Materials 2021, 14, 6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazdič, D.; Fridrichová, M.; Kulísek, K.; Vehovská, L. The Potential Use of the FBC Ash for the Preparation of Blended Cements. Procedia Eng. 2017, 180, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F. A Review on the Application of Circulating Fluidized Bed Fly Ash in Building Materials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7099430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohenoja, K.; Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M. Utilization of Fly Ashes from Fluidized Bed Combustion: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, A.S.; Lee, B.Y.; Park, S.; Kim, H.K. Self-Healing of Portland and Slag Cement Binder Systems Incorporating Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Bottom Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, T.; Xu, Y.; Da, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, R. Properties of Composite Sintered Modified Fluidized Bed Incineration Fly Ash as Cement Admixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 378, 131210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, T. Effects of High CaO Fly Ash and Sulfate Activator as a Finer Binder for Cementless Grouting Material. Materials 2019, 12, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Mortars with Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-T.; Weng, T.-L.; Cheng, A.; Chao, S.-J.; Hsu, H.-M. Properties of Controlled Low Strength Material with Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Ash and Recycled Aggregates. Materials 2018, 11, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.A.; Chang, T.P.; Shih, J.Y.; Chen, C.T.; Nguyen, T.D. Influence of Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) Fly Ash on Properties of Modified High Volume Low Calcium Fly Ash (HVFA) Cement Paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Wang, D.; Li, D.; Ren, C.; Tang, W. Study of High Volume Circulating Fluidized Bed Fly Ash on Rheological Properties of the Resulting Cement Paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Z. Investigations of Anhydrite in CFBC Fly Ash as Cement Retarders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, J. Low Reactive Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) Fly Ashes as Source Material for Geopolymer Synthesis. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Thaiwitcharoen, S.; Kaewpirom, S.; Rattanasak, U. Controlling Ettringite Formation in FBC Fly Ash Geopolymer Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 41, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Shao, N.; Hu, T.; Han, L.; Wang, D. Geopolymerization Enhanced Hydrothermal Synthesis of Analcime from Steel Slag and CFBC Fly Ash and Heavy Metal Adsorption on Analcime. Environ. Technol. 2018, 41, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Moreno, N.; Navia, R.; Querol, X. Study of a Chilean Petroleum Coke Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash and Its Potential Application in Copper, Lead and Hexavalent Chromium Removal. Fuel 2010, 89, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J.; Berry, E.E.; Blondin, J.; Bulewicz, E.M.; Burwell, S. Advanced Ash Management Technologies for CFBC Ash. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Duan, L.; Wang, J. Utilization of Composite Supplementary Cementitious Material Containing Circulating Fluidized Bed Ash in Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 479, 141486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, D.; Morrison, M.; Lawrence, M.; Lynsdale, C. Development of Low-Energy Cement Products Using Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion Ash and FGD Gypsum. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javellana, M.P.; Jawed, I. Extraction of Free Lime in Portland Cement and Clinker by Ethylene Glycol. Cem. Concr. Res. 1982, 12, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9597:2020; Cement—Test Methods—Determination of Setting Time and Soundness. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Pane, I.; Hansen, W. Investigation of Blended Cement Hydration by Isothermal Calorimetry and Thermal Analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo, S.M.; Moragues, A.; Gálvez, J.C.; Casati, M.J.; Reyes, E. The Degree of Hydration Assessment of Blended Cement Pastes by Differential Thermal and Thermogravimetric Analysis: Morphological Evolution of the Solid Phases. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 592, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Julnipitawong, P.; Krammart, P.; Tangtermsirikul, S. Effect and Limitation of Free Lime Content in Cement–Fly-Ash Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 102, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtarfi, N.H.; Rais, Z.; Taleb, M. Effect of Clinker Free Lime and Cement Fineness on the Cement Physicochemical Properties. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar]










| Chemical Oxide Composition (wt%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | SO3 | LOI | |
| CFBC ash | 27.1 | 11.3 | 11.1 | 35.5 | 4.6 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 5.6 | 1.9 |
| DG | 4.9 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 62.5 | 1.7 | 0.2 | - | 22.8 | 7.0 |
| Specimen | W/B (−) | CFBC Ash (g) | DG (g) | Sand (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | 0.5 | 100 | - | 300 |
| CFDG05 | 95 | 5 | ||
| CFDG10 | 90 | 10 | ||
| CFDG15 | 85 | 15 | ||
| CFDG20 | 80 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.-C. Hydration and Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Binders Using CFBC Ash. Materials 2025, 18, 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122731
Choi Y-C. Hydration and Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Binders Using CFBC Ash. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122731
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Young-Cheol. 2025. "Hydration and Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Binders Using CFBC Ash" Materials 18, no. 12: 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122731
APA StyleChoi, Y.-C. (2025). Hydration and Mechanical Properties of Low-Carbon Binders Using CFBC Ash. Materials, 18(12), 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122731







