Mapping of Lapping-Induced Subsurface Damage in Planar Fused Silica Glass Based on Polarized Laser Scattering Method
Highlights
- A polarized laser scattering detection system for subsurface damage mapping of glass is built;
- Polarized laser scattering detection signals increases with subsurface damage depths;
- Relation between detection signals and subsurface damage depths is developed;
- Subsurface damage mapping to show damage location and degree is achieved.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lapping Experiment Materials and Process
3. Detection Platform for SSD of Fused Silica Glass
3.1. PLS Detection Method
3.2. PLS Detection System
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Detection Results
4.2. Validation and Error Analysis
4.3. Fused Silica Glass SSD Mapping
5. Conclusions
- Because deeper SSD enhances the depolarization of incident P-polarized light, generating stronger S-polarized signals that carry SSD information means that the PLS detection signal increases with increasing SSD depth, indicating a direct correlation between the PLS signal and SSD depth;
- As the grit size increases to 20 μm, the SSD depth increases to approximately 2.74 μm. The relationship between the PLS detection signal and the SSD depth obtained through experiments was expressed as D = 5.78 × 10−6 S6.16 + 0.86, with an R2 value of 0.95;
- Established system and fitting results can effectively detect SSD in fused silica glass with an error within 5%, and the SSD mapping diagram established based on the fitting result clearly visualized the SSD location, SSD depth, and lapping quality (e.g., lapping uniformity and edge integrity);
- Future research will focus on realizing inline SSD detection during the processing of fused silica glass.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stebbins, J.F. Short-Range Structure and Order in Oxide Glasses. In Encyclopedia of Glass Science, Technology, History, and Culture; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Y. Resource, Characteristic, Purification and Application of Quartz: A Review. Miner. Eng. 2022, 183, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, F.; Quick, A.S.; Risch, P.; Martin, T.; Hoose, T.; Thiel, M.; Helmer, D.; Rapp, B.E. Two-Photon Polymerization of Nanocomposites for the Fabrication of Transparent Fused Silica Glass Microstructures. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guo, X.; Zhai, R.; Luo, X.; Kang, R.; Jin, Z.; Guo, D. Study on the Subsurface Damage Mechanism of Optical Quartz Glass during Single Grain Scratching. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 7683–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; Ma, B.; Chen, W.; Cheng, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, L.; Li, M.; et al. An Investigation of Al2O3 Coating on Quartz Fiber Fabric in Aqueous Solution near Room Temperature. Surf. Innov. 2022, 11, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toombs, J.T.; Luitz, M.; Cook, C.C.; Jenne, S.; Li, C.C.; Rapp, B.E.; Kotz-Helmer, F.; Taylor, H.K. Volumetric Additive Manufacturing of Silica Glass with Microscale Computed Axial Lithography. Science 2022, 376, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, C.; Xu, W.; Chen, D.; Feng, H. High- and Low-Temperature Properties and Thermal Stability of Silica Fume/SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt Mortar. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1317436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Wang, T.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y. Experimental Study of the Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Abrasive Waterjet Micromachining the Quartz Glass. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8904234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Guo, M.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, H.; Wu, Y. Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Grinding of Quartz Glass Micro-Hole. Precis. Eng. 2024, 91, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, X.; Mu, D.; Lawn, B.R. Science and Art of Ductile Grinding of Brittle Solids. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 161, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Kang, R.K.; Dong, Z.G. Surface Layer Damage of Quartz Glass Induced by Ultra-Precision Grinding with Different Grit Size. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2017, 872, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Bai, Q.; Haitjema, H.; Zhang, B. Depolarization of Surface Scattering in Polarized Laser Scattering Detection for Machined Silicon Wafers. Precis. Eng. 2022, 73, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Cheng, X.; Huang, B.; Liu, S.; Shao, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, M. Quantitative Evaluation of Subsurface Damage by Improved Total Internal Reflection Microscopy. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xiao, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Cheung, C.F. Image-Processing-Based Model for the Characterization of Surface Roughness and Subsurface Damage of Silicon Wafer in Diamond Wire Sawing. Precis. Eng. 2022, 77, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zuo, Y.; Sun, R.; Zhou, L. Solar Cells Produced by Diamond Wire Sawn Multicrystalline Silicon Wafer by Using Additive-Assisted Acidic Texturization. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7869901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Pan, Y.; An, Z.; Huang, S.; Dong, M. Review on Surface Polishing Methods of Optical Parts. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2002, 8723269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; He, W. A Review of Subsurface Damage Detection Methods for Optical Components. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 060702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Cui, J.; Bian, X. Overview of Subsurface Damage Detection Technologies for Ultra-Smooth Quartz Components. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 15th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Nanjing, China, 29–31 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xiao, H.; Shi, F. Experimental Study on Surface Integrity and Subsurface Damage of Fused Silica in Ultra-Precision Grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 115, 4021–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, W.; Ji, J.; Ren, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, C. Prediction and Experimental Investigation of Depth of Subsurface Damage in Semi-Consolidated Abrasive Grinding of Cleavable Gallium Oxide Crystals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omiya, N.; Aida, H.; Takeda, H.; Kanda, M.; Doi, T. Analysis of Subsurface Damage Structures of Gallium Nitride Substrates Induced by Mechanical Polishing with Diamond Abrasives. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 2024, 261, 2400031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, A.; Li, M.; Gao, L.; Ling, H.; Hang, T. Sub-Surface Damage of Ultra-Thin Monocrystalline Silicon Wafer Induced by Dry Polishing. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2020, 16, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q. Investigation on the Surface Topography and Surface/Subsurface Damage Mechanisms of Polycrystalline Yttrium Aluminum Garnet Ceramics in Ultra-Precision Grinding. Mater. Charact. 2025, 220, 114688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.; Vo, T.H.; Vu, D.D.; Choi, J.; Park, S.; Mondal, S.; Lee, B.-I.; Oh, J. Development of Fast Scanning Module with a Novel Bubble Solution Applied to Scanning Acoustic Microscopy System for Industrial Nondestructive Inspection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 228, 120273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K.; Jhang, K.Y. Crack Detection in Single-Crystalline Silicon Wafer using Laser Generated Lamb Wave. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 950791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Du, F.; Xie, L.; Hu, Q.; Jin, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. Application of Laser Ultrasonic Testing Technology in the Characterization of Material Properties: A Review. Measurement 2024, 234, 114855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertussi, B.; Cormont, P.; Palmier, S.; Legros, P.; Rullier, J.-L. Initiation of laser-induced damage sites in fused silica optical components. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 11469–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, M.; Li Voti, R. A note on the history of photoacoustic, thermal lensing, and photothermal deflection techniques. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 230901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandison, D.R.; Williams, R.M.; Wells, K.S.; Strickler, J.; Webb, W.W. Quantitative fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). In Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, B.; Liang, X.; Du, A. Quantifying the subsurface damage and residual stress in ground silicon wafer using laser ultrasonic technology: A Bayesian approach. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 173, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordal, P.E.; Kanstad, S.O. Photothermal radiometry. Phys. Scr. 1979, 20, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q. Residual stress and subsurface damage in sapphire ultra-precision grinding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 328, 118418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Bai, Q.; Zhang, B. Detection of subsurface microcracks after grinding of single crystal silicon wafer by polarized laser scattering. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2020, 40, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Bai, Q.; Haitjema, H.; Zhang, B. Two-Dimensional Detection of Subsurface Damage in Silicon Wafers with Polarized Laser Scattering. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 284, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Ma, H.; Yin, J. Polarized Laser Confocal Technique for Subsurface Damage of Lapped Quartz Glass. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2021, 29, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Qiao, G.; Lv, Q.; Bai, Q. Polarized laser scattering detection of subsurface damage of quartz glass induced by grinding. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1167271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.P.; Hashimura, M.; Dornfeld, D.A. An investigation of material removal mechanisms in lapping with grain size transition. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2000, 122, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.X.; Shi, F.Y.; Bai, Q.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, L. Polarized Laser Scattering Detection Method for Subsurface Microcracks in Quartz Glass. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2023, 31, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Li, B.; Cui, H.; Wang, J. Sensitive measurement of stress birefringence of fused silica substrates with cavity ring-down technique. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, M.; Chu, H.O.M. Laser wavelength selection in Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2025, 150, 1986–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y. Relationship between Subsurface Damage and Surface Roughness of Optical Materials in Grinding and Lapping Processes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 205, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

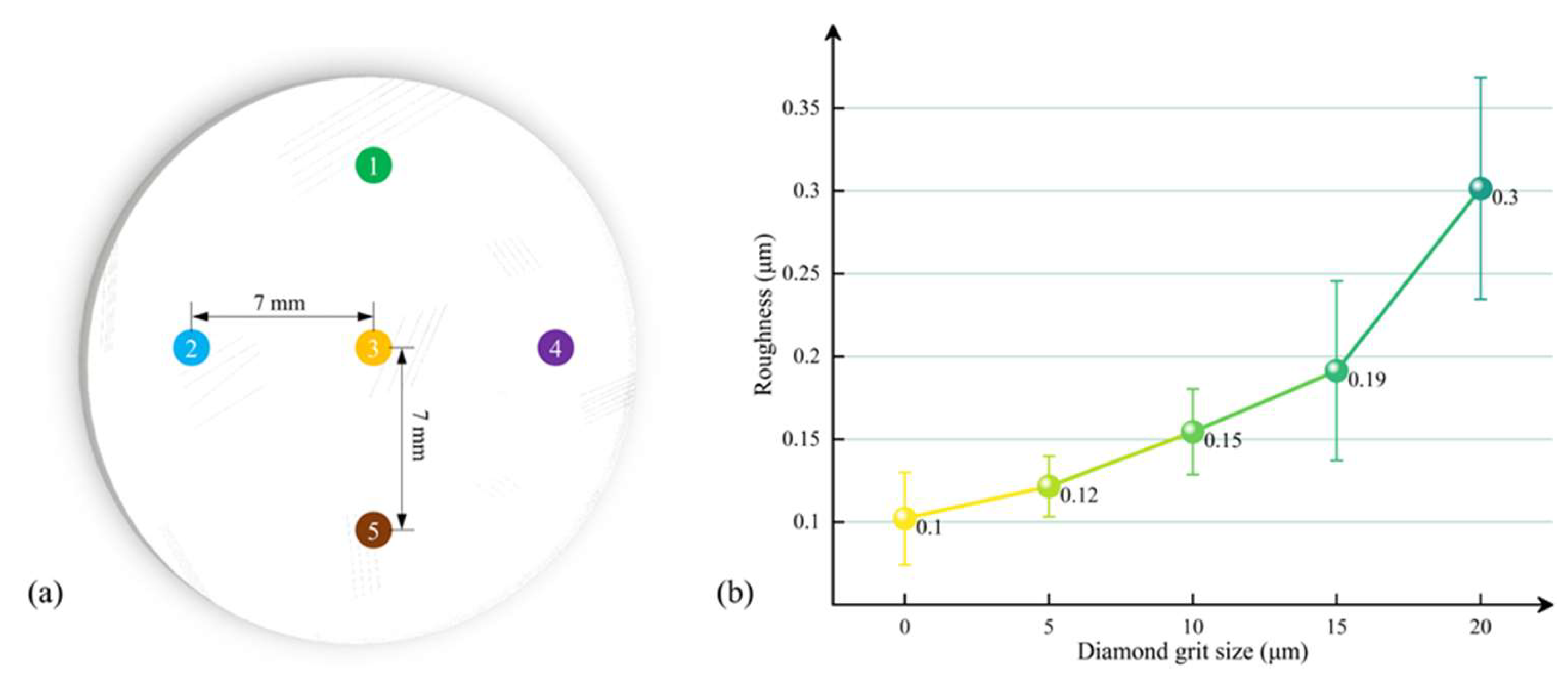
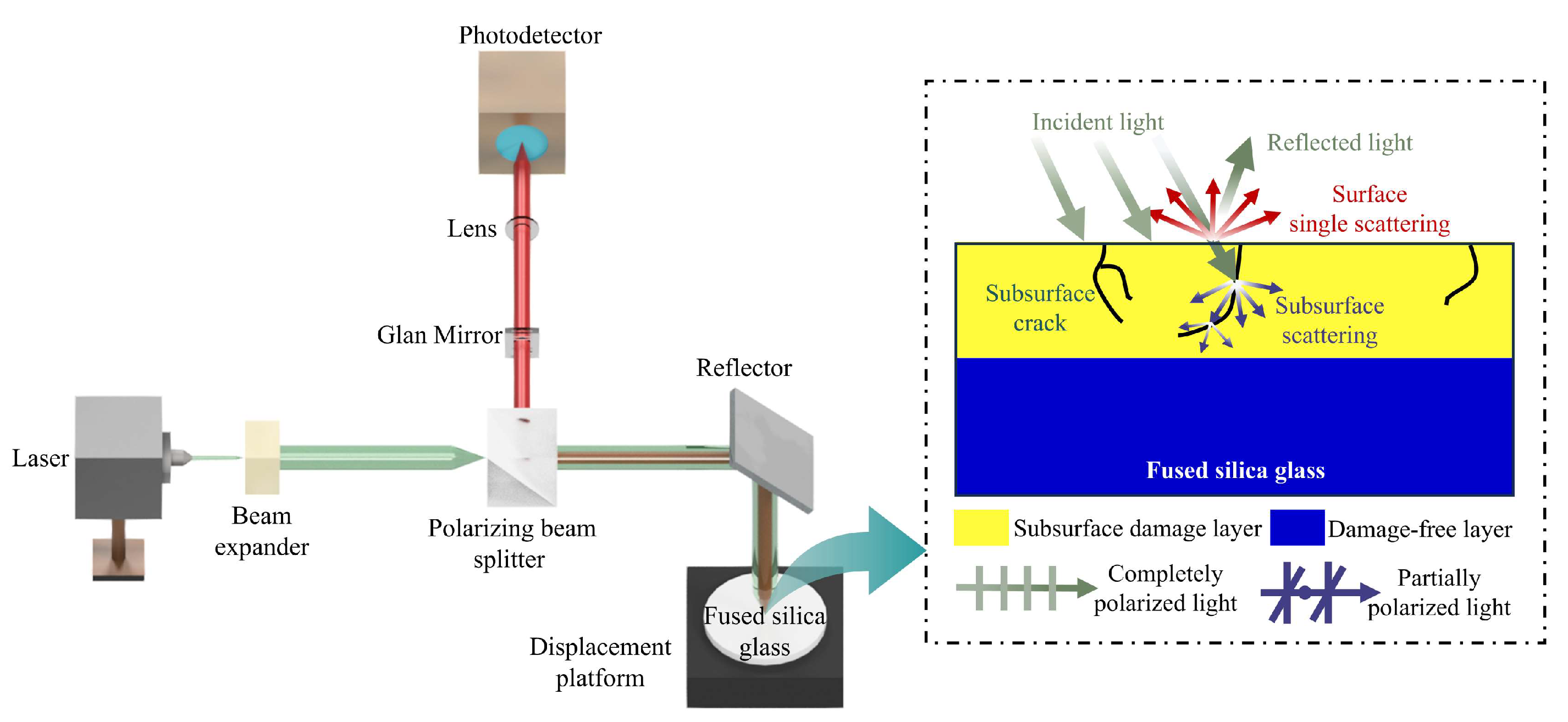



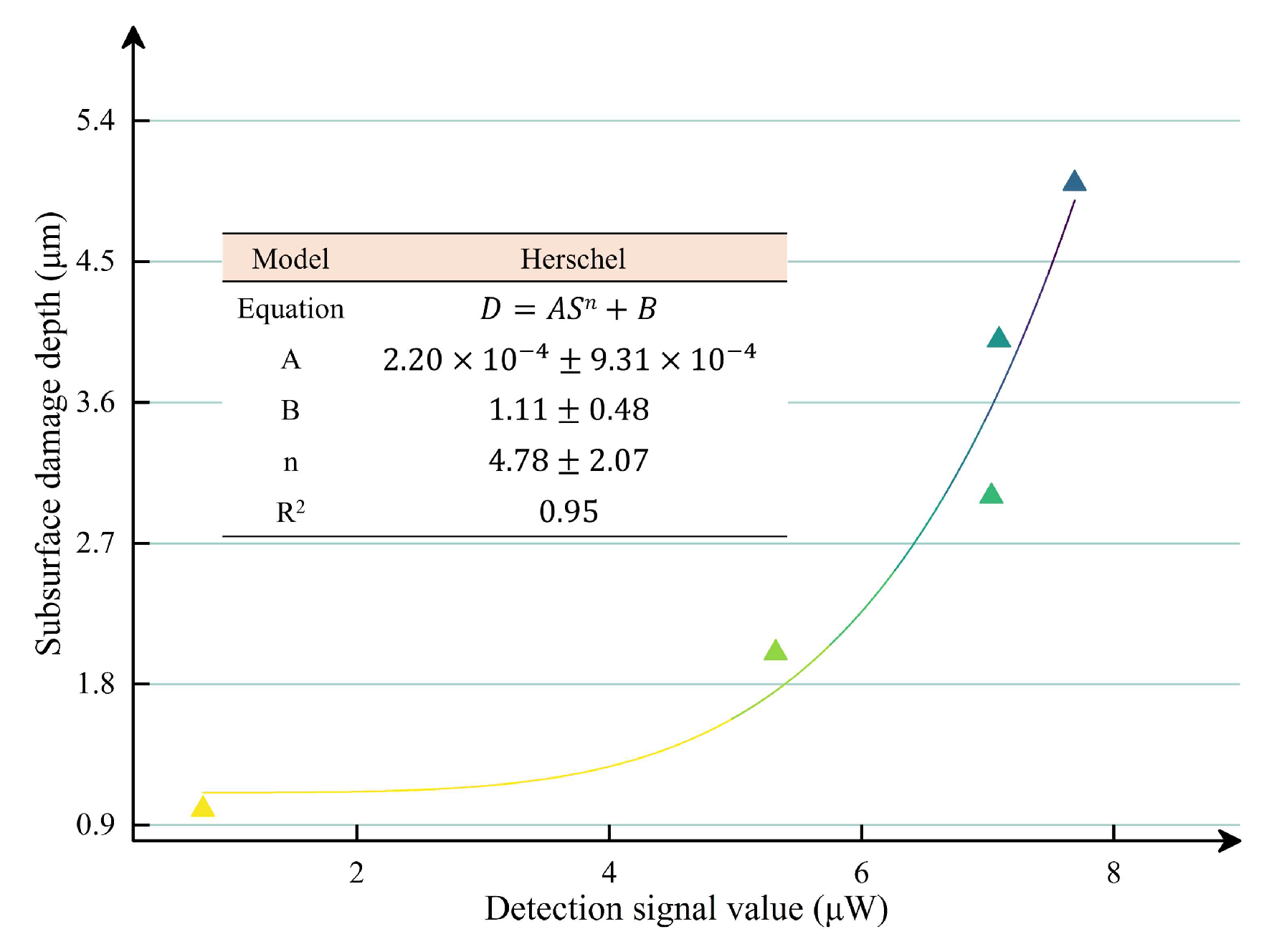
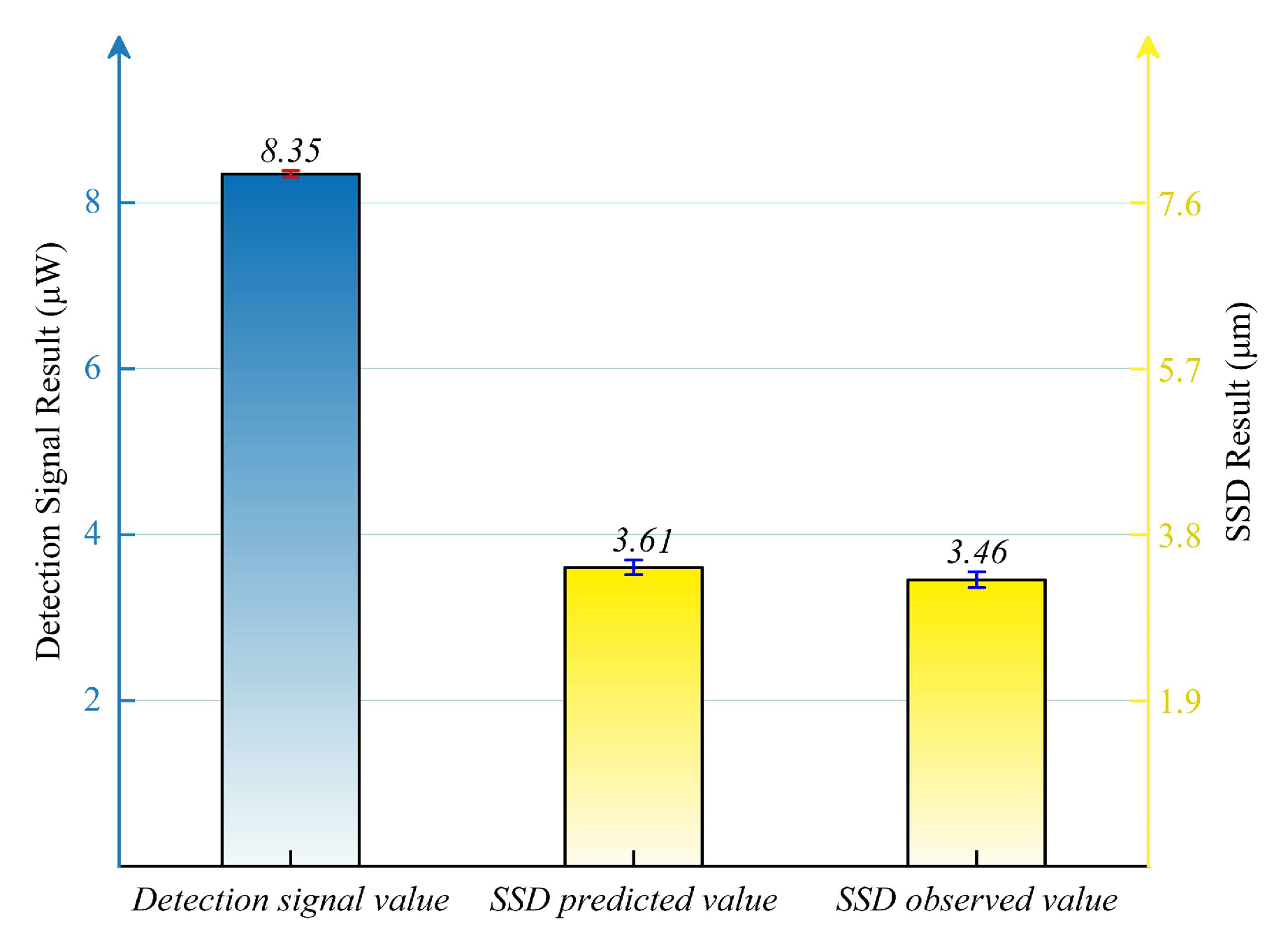

| Lapping Pressure | Plate Rotation Speed | Flow Rate of Slurry | Lapping Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 kPa | 50 rpm | 25 mL/min | 50 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; He, C.; Bai, Q. Mapping of Lapping-Induced Subsurface Damage in Planar Fused Silica Glass Based on Polarized Laser Scattering Method. Materials 2025, 18, 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112417
Gao M, Guo Y, Liu C, He C, Bai Q. Mapping of Lapping-Induced Subsurface Damage in Planar Fused Silica Glass Based on Polarized Laser Scattering Method. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112417
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Mingchuan, Yi Guo, Chenxi Liu, Chuanxin He, and Qian Bai. 2025. "Mapping of Lapping-Induced Subsurface Damage in Planar Fused Silica Glass Based on Polarized Laser Scattering Method" Materials 18, no. 11: 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112417
APA StyleGao, M., Guo, Y., Liu, C., He, C., & Bai, Q. (2025). Mapping of Lapping-Induced Subsurface Damage in Planar Fused Silica Glass Based on Polarized Laser Scattering Method. Materials, 18(11), 2417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112417







