A Time Series Proposal Model to Define the Speed of Carbon Steel Corrosion in an Extreme Acid Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Statistical Treatment
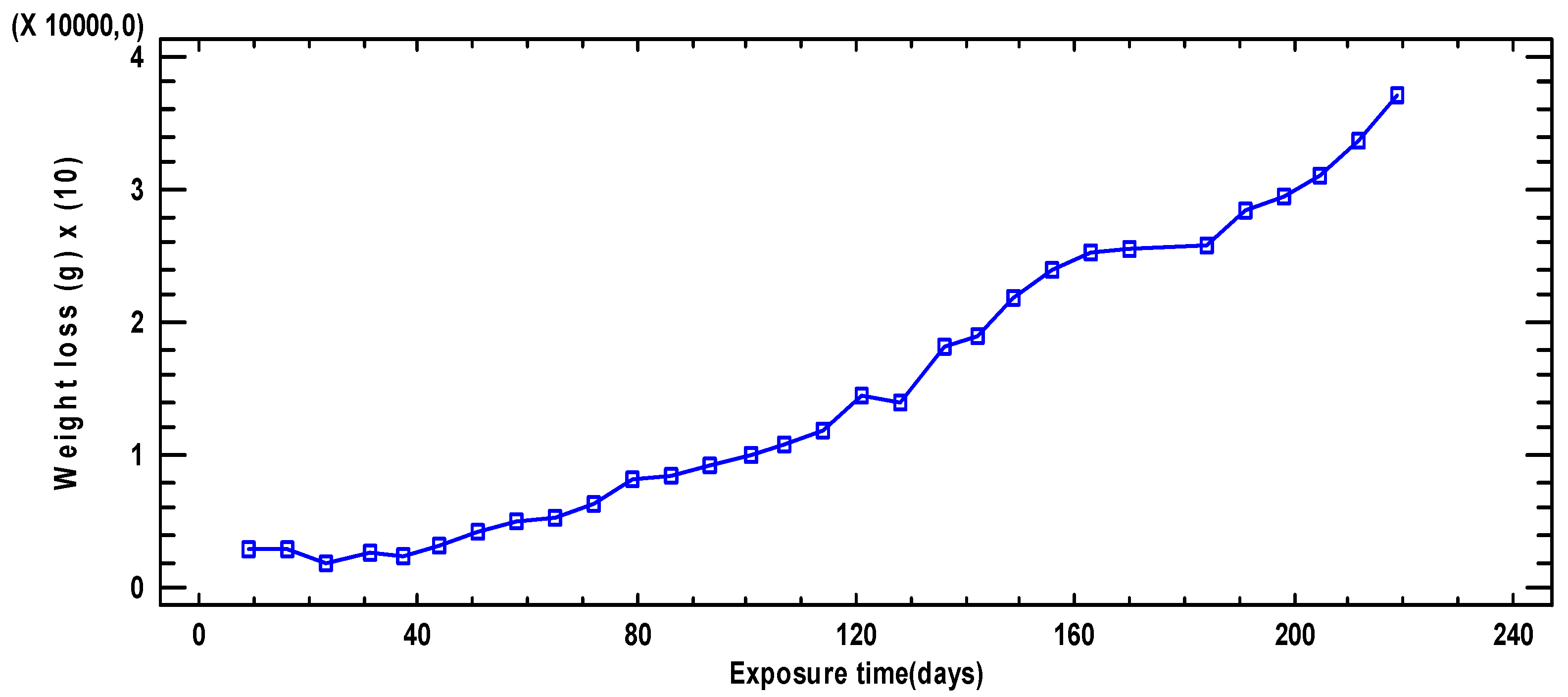
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Summary
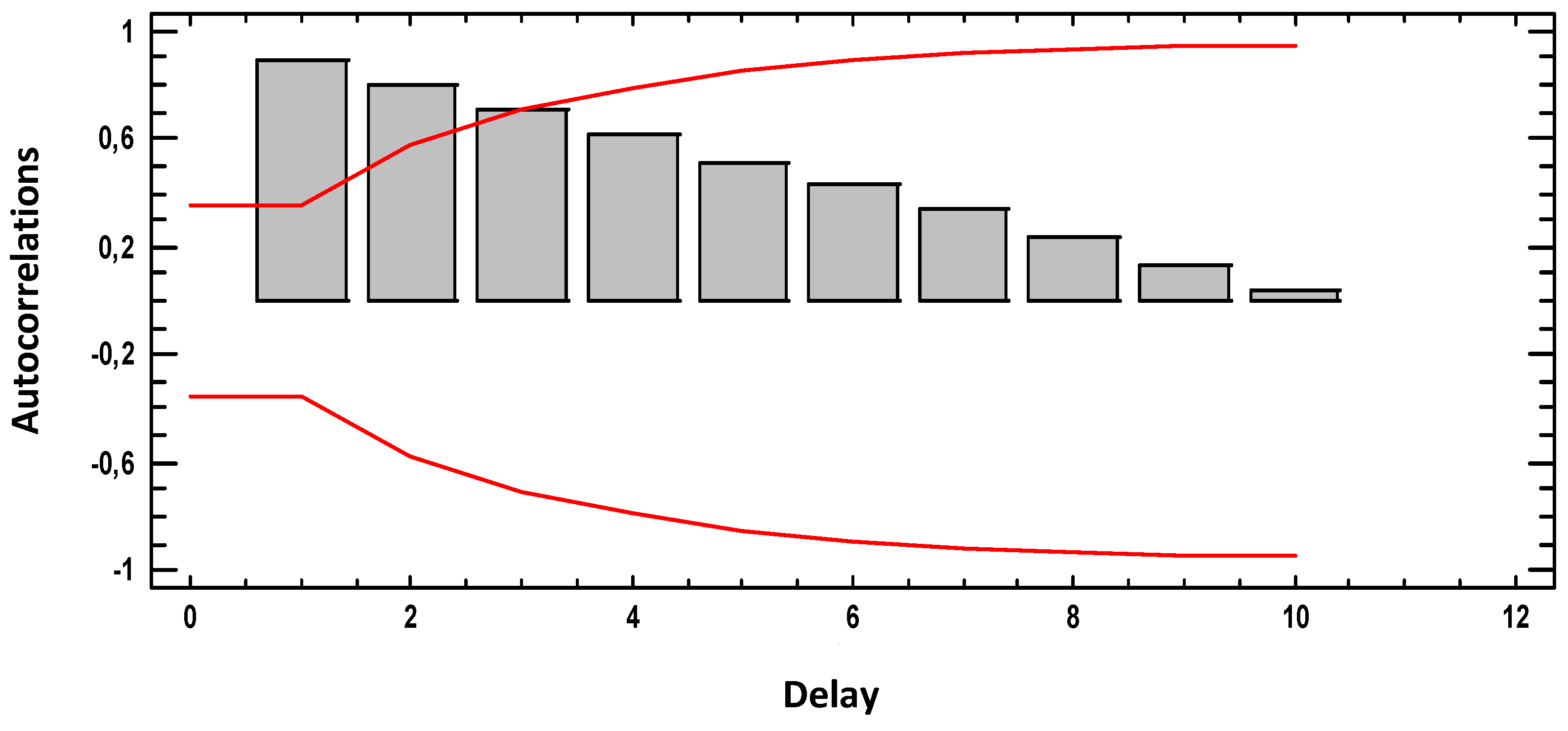
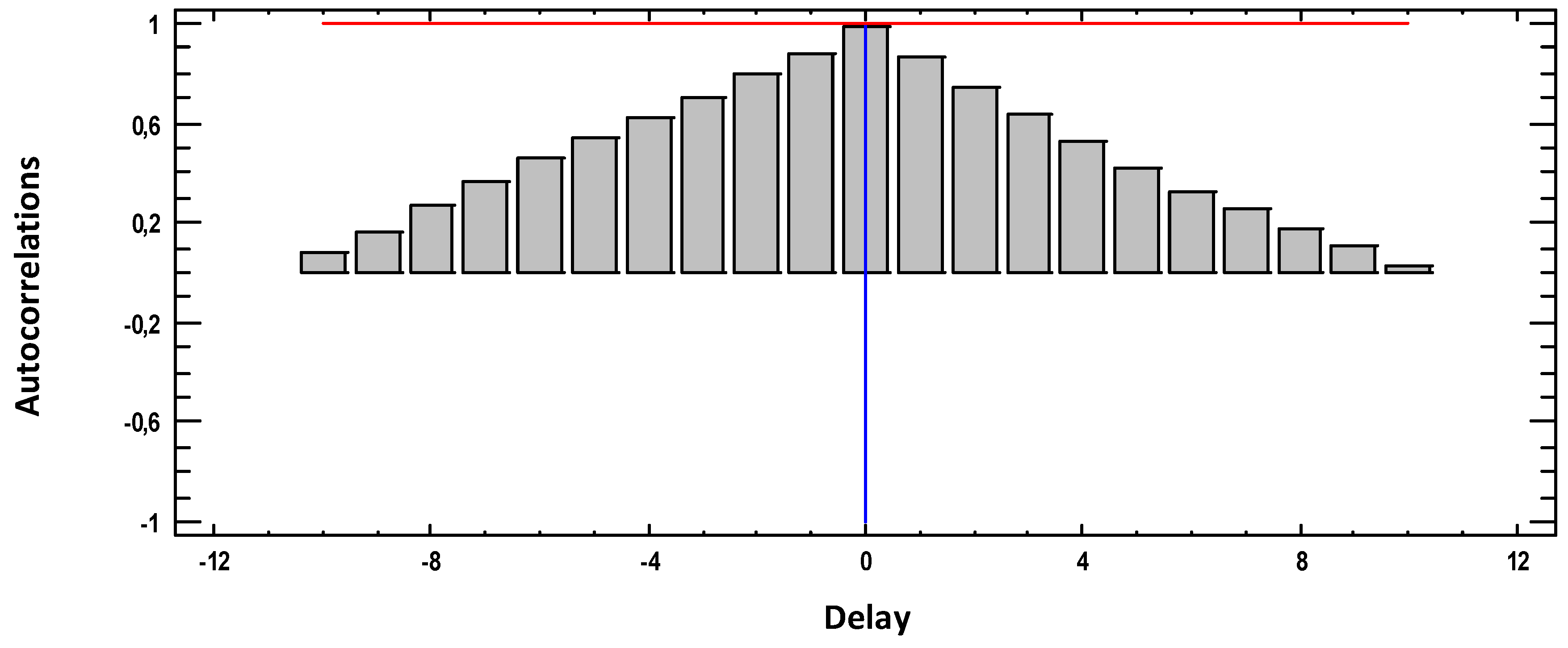
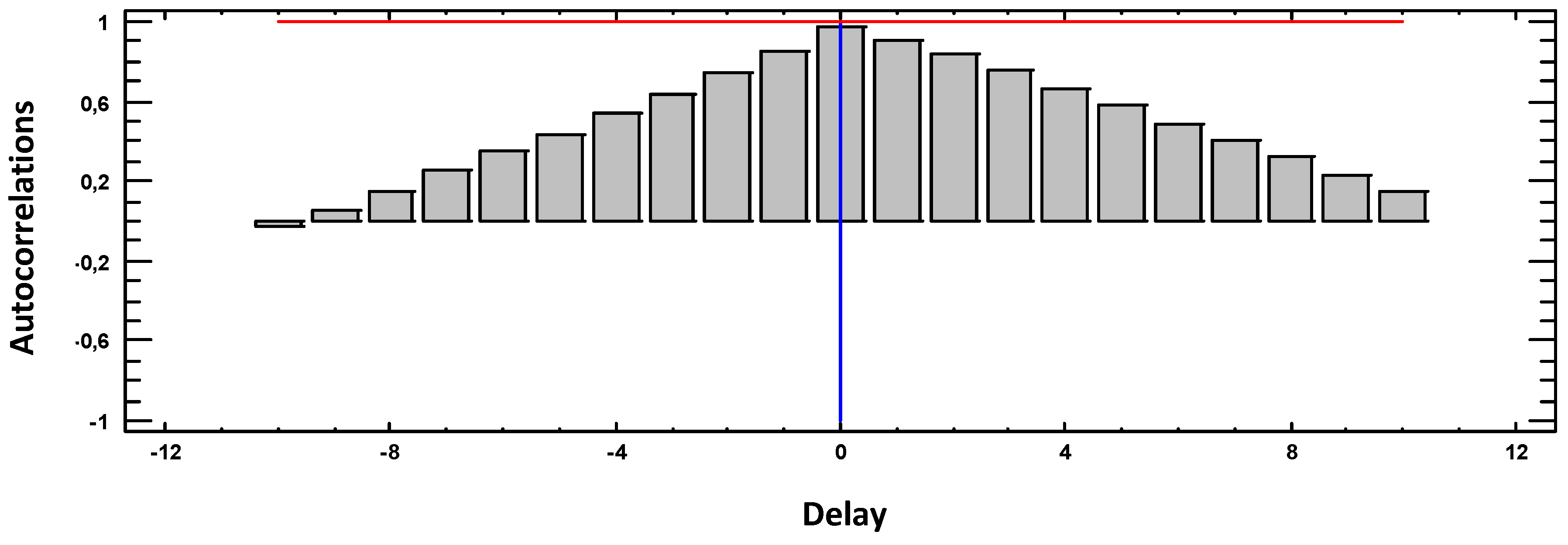
3.2. Autocorrelation Function (ACF)
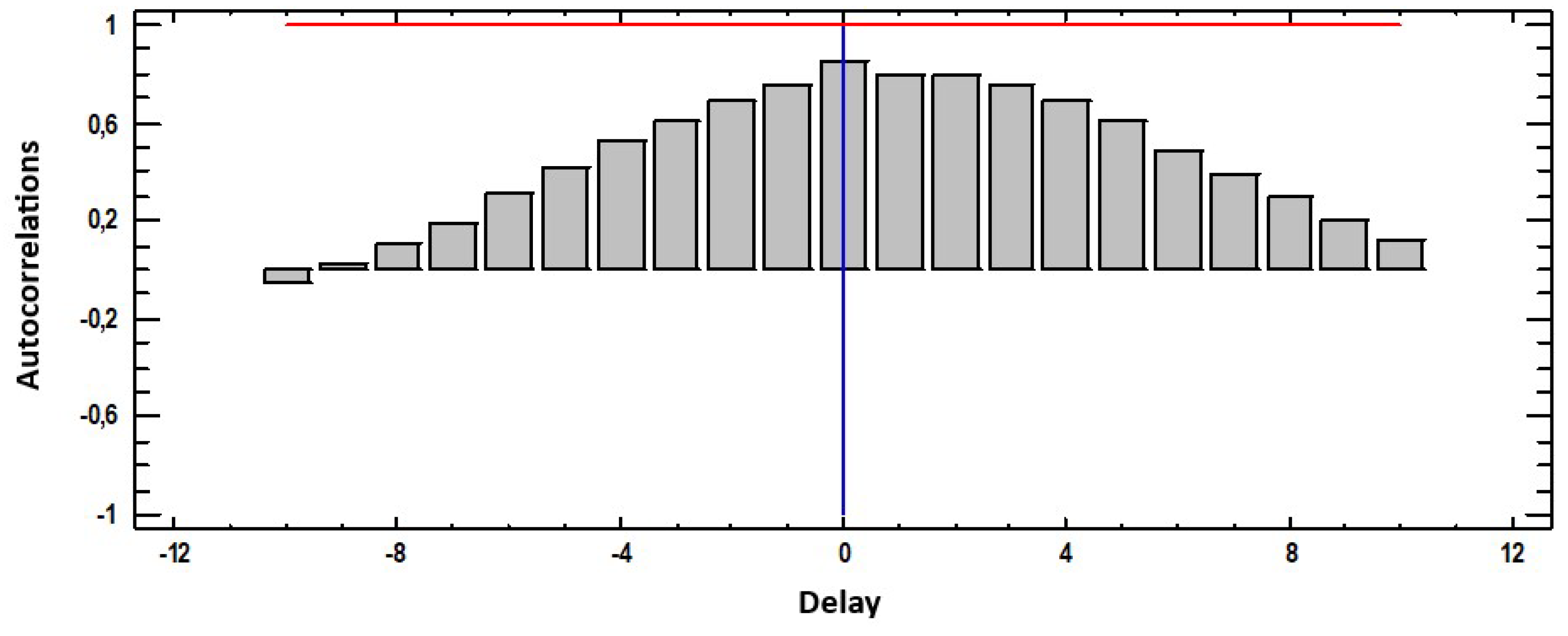
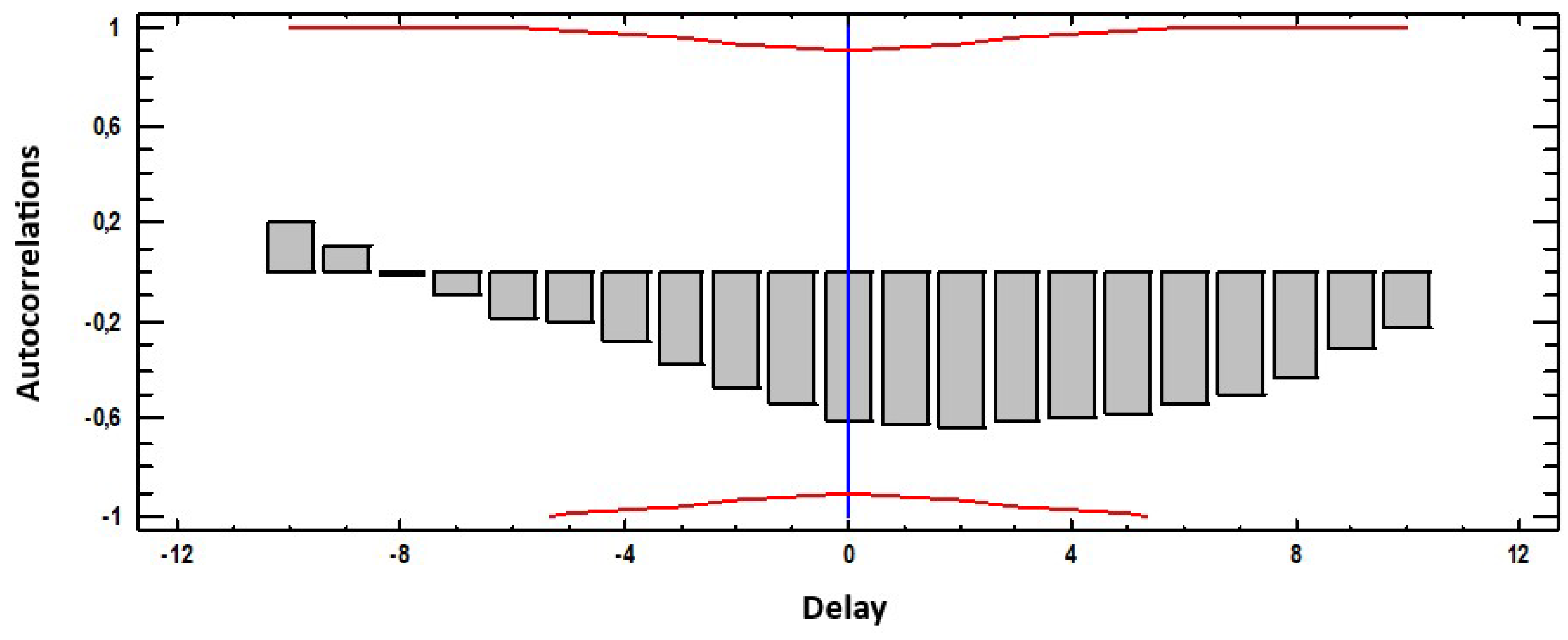
3.3. Cross-Correlations Function
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, P.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Ma, T. A review of acid mine drainage: Formation mechanism, treatment technology, typical engineering cases and resource utilization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 1240–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A., Jr.; Welty, A.T.; Borrego, J.; Morales, J.A.; Pendón, J.G.; Ryan, J.G. Rio Tinto estuary (Spain): 5000 years of pollution. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, J.C.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Luís, A.T.; Santisteban, M.; Dávila, J.M.; Córdoba, F.; Grande, J.A. Wasted Critical Raw Materials: A Polluted Environmental Scenario as potential source of economic interest elements in the Spanish part of the Iberian Pyrite Belt. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, S.; Igarashi, T.; Tabelin, C.B.; Tangviroon, P.; Ii, H. Acid mine drainage sources and hydrogeochemistry at the Yatani mine, Yamagata, Japan: A geochemical and isotopic study. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 225, 103502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Li, X.; Seno, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Morley, N.H.; Cruzado, A.; Velasquez, Z.; Achterberg, E.P.; Braungardt, C.B. Trace metal and nutrient distribution in an extremely low pH (2.5) river-estuarine system, the Ria of Huelva (south-west Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 227, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, M.B.; Moncur, M.C.; Bain, J.G.; Jambor, J.L.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W. Geochemical and mineralogical aspects of sulfide mine tailings. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, J.A.; Loayza-Muro, R.; Alonso-Chaves, F.M.; Fortes, J.C.; Willems, B.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Santisteban, M.; Davila, J.M.; de la Torre, M.L.; Durães, N.; et al. The Negro River (Ancash-Peru): A unique case of water pollution, three environmental scenarios and an unresolved issue. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, P.C.; Stumm, W. Acid mine drainage: The rate-determining step. Science 1970, 167, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Du, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.; Su, P.; Jiao, Y.; Zhao, Y. A review: The formation, prevention, and remediation of acid mine drainage. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 111871–111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, J.A.; Santisteban, M.; De la Torre, M.L.; Fortes, J.C.; De Miguel, E.; Curiel, J.; Dávila, J.M.; Biosca, B. The paradigm of Circular Mining in the world: The Iberian Pyrite Belt as a potential scenario of interaction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento, A.M.; Grande, J.A.; Luís, A.T.; Dávila, J.M.; Fortes, J.C.; Santisteban, M.; Curiel, J.; de la Torre, M.L.; Ferreira, E. Negative pH values in an open-air radical environment affected by acid mine drainage. Characterization and proposal of a hydrogeochemical model. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.V. Iron-sulfide oxidation mechanism. In Chemical Weathering Rates of Silicate Minerals; White, A.F., Brantley, R.J., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 1994; Volume 31, pp. 173–225. [Google Scholar]
- Younger, P.L.; Banwart, S.A.; Hedin, R.S. Mine Water: Hydrology, Pollution, Remediation; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Alper, C.N. Negative pH, efflorescent mineralogy, and consequences for environmental restoration at the Iron Mountain Superfund site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefeni, K.; Msagati, A.M.; Mamba, B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, A.T.; Grande, J.A.; Durães, N.; Dávila, J.M.; Santisteban, M.; Salomé, F.P.; Sarmiento, A.M.; de la Torre, M.L.; Fortes, J.C.; Ferreira, E. Biogeochemical characterization of surface waters in the Aljustrel mining area (South Portugal). Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1909–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, F.; Luís, A.T.; Leiva, M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Santisteban, M.; Fortes, J.C.; Dávila, J.M.; Álvarez-Bajo, O.; Grande, J.A. Biogeochemical indicators (waters/diatoms) of acid mine drainage pollution in the Odiel river (Iberian Pyritic Belt, SW Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 31749–31760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, A. Eukaryotic organisms in extreme acidic environments. Life 2013, 3, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, M.; Bryka, K.; Romero, S.; Santisteban, M.; Dávila, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Fortes, J.C.; Luís, A.T.; Grande, J.A.; Córdoba, F. Diatoms of the Odiel river basin: Distribution according to the degree of pollution by Acid Mine Drainage. Comun. Geológicas 2020, 107, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; Xu, R.; Young, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Kong, T.; Xiao, E.; Wang, Q. Bacterial response to sharp geochemical gradients caused by acid mine drainage intrusion in a terrace: Relevance of C, N, and S cycling and metal resistance. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Etre, A.Y.; Abdallah, M. Natural honey as corrosion inhibitor for metals and alloys. II. C-steel in high saline water. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekolu, S.O.; Diop, S.; Azene, F.; Mkhize, N. Disintegration of concrete construction induced by acid mine drainage attack. J. South Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2016, 58, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, X. Design of a Multilayered Oxygen-Evolution Electrode with High Catalytic Activity and Corrosion Resistance for Saline Water Splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Fu, H.; Li, J. The effect of corrosion evolution on the stress corrosion cracking behavior of mooring chain steel. Corros. Sci. 2022, 203, 110316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biloshytskyi, M.; Tatarchenko, H.; Biloshytska, N.; Uvarov, P. Operational lifetime increase of the pumping equipment when pumping-out contaminated groundwater. Min. Miner. Depos. 2021, 15, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupnik, L.; Yelemessov, K.; Beisenov, B.; Baskanbayeva, D. Substantiation and process design to manufacture polymer-concrete transfer cases for mining machines. Min. Miner. Depos. 2020, 14, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Fortes, J.C.; Santisteban, M.; Leiva, M.; Cordoba, F.; Cabello, J.E.; Grande, J.A. Determination of the extreme reduction of concrete strength due to acid mine drainage by laboratory tests on specimens located in a real environment. Constr. Build. Materi. 2021, 269, 121817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskanbayeva, D.D.; Krupnik, L.A.; Yelemessov, K.K.; Bortebayev, S.A.; Igbayeva, A.E. Justification of rational parameters for manufacturing pump housings made of fibroconcrete. Nauk. Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetu 2020, 5, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoganandh, J.; Natarajan, S.; Kumaresh Babu, S. Erosive wear behavior of high-alloy cast iron and duplex stainless steel under mining conditions. J. Mater. Perform. 2015, 24, 3588–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, U.R. Metallic corrosion, passivity and protection. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 1937, 56, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, S.H.; Dierks, H.A.; Felegy, E.W.; Huston, K.M.; Kennedy, D.O.; Miller, P.S.; Rosella, J.J. Corrosive and Erosive Effects of Acid Mine Waters on Metals and Alloys for Mine Pumping Equipment and Drainage Facilities; Bulletin 555; US Bureau of Mines, Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1955.
- Aziz, N.I.; Craig, P.; Nemcik, J.A.; Hai, F.I. Rock bolt corrosion—An experimental study. Min. Technol. 2014, 123, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaherdashti, R.; Nikraz, H. On the role of deterioration of structures in their performance; with a focus on mining industry equipment and structures. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe, K.; Li, S.M.; Liu, J.H.; Yu, M. Corrosion Behavior of 10CrNiCu Steel Influenced by Thiobacillus Ferrooxidans. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 233–235, 2633–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, J.C.; Dávila, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Luis, A.T.; Santisteban, M.; Díaz-Curiel, J.; Córdoba, F.; Grande, J.A. Corrosion of Metallic and Structural Elements Exposed to Acid Mine Drainage (AMD). Mine Water Environ. 2020, 39, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-España, F.J.; Lopez, E.; Santofimia, E.; Aduvire, O.; Reyes, J.; Barettino, D. Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Odiel river watershed, Huelva, SW Spain): Geochemistry, mineralogy and environmental implications. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1320–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braungardt, C.B.; Achterberg, E.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Morley, N.H. Metal geochemistry in a mine-polluted estuarine system in Spain. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caliani, J.C.; Barba-Brioso, C. Metal immobilization in hazardous contaminated minesoils after marble slurry waste application. A field assessment at the Tharsis mining district (Spain). J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, J.M.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Olías, M.; Cánovas, C.; Riba, I.; Kalman, J.; Delvalls, T.A. Acid mine drainage pollution in the Tinto and Odiel rivers (Iberian Pyrite Belt, SW Spain) and bioavailability of the transported metals to the Huelva estuary. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MathWorks Inc. Fuzzy Logic Toolbox Software. 2023. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/fuzzy/type-2-fuzzy-inference-systems.html (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Bisquerra, R. Introducción Conceptual al Análisis Multivariable; Promociones y Publicaciones Universitarias S.A.: Barcelona, Spain, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Harman, H.H. Análisis Factorial Modern; Saltés: Madrid, Spain, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy Sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, A.T.; Grande, J.A.; Dávila, J.M.; Aroba, J.; Duraes, N.; Almeida, S.F.P.; de la Torre, M.L.; Sarmiento, A.M.; Fortes, J.C.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; et al. Application of fuzzy logic tools for the biogeochemical characterisation of (un)contaminated waters from Aljustrel mining area (South Portugal). Chemosphere 2018, 211, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.K.; Liu, D.; Song, K.; Mohamed, M.A.A.; Aldaw, E.; Elubid, B.A. Hydrochemical Analysis and Fuzzy Logic Method for Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in the North Chengdu Plain, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrones-Saeta, J.M.; Fortes, J.C.; Luís, A.T.; Aroba, J.; Díaz-Curiel, J.; Romero, E.; Grande, J.A. Fuzzy Logic Tools Application to the Characterization of Stress–Strain Processes in Waste Construction Dam Geopolymers: A New Circular Mining. Materials 2022, 15, 8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, J.C.; Castilla-Gutierrrez, J.; Sarmiento, A.; Grande, J.A. Corrosion of Carbon Steel in Extreme Environments by Acid Mine Water: Experimental Study of the Process Using a Factorial Analysis Tool. Minerals 2022, 12, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Dongare, P.A.; Garg, R.; Harsoor, S.S. Describing and Displaying Numerical and Categorical Data. Airway 2019, 2, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu Babu, U.; Kondraivendhan, B. Application of Statistics to the Analysis of Corrosion Data for Rebar in Metakaolin Concrete. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering (ICETE), Hyderabad, India, 22–23 March 2019; Learning and Analytics in Intelligent Systems. Satapathy, S., Raju, K., Molugaram, K., Krishnaiah, A., Tsihrintzis, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Swizterland, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, J.C.; Terrones-Saeta, J.M.; Luis, A.T.; Santisteban, M.; Grande, J.A. Corrosion Effect in Carbon Steel: Process Modeling Using Fuzzy Logic Tools. Processes 2023, 11, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| T (Celsius) | pH | EC (mS/cm) | TDS (mg/L) | Eh (mV) | Exposure Time (Days) | Surface (cm2) | Volume (cm3) | Weight Loss (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Mean | 18.37 | 2.63 | 18.07 | 7564.35 | 258.32 | 112 | 71.08 | 16.58 | 14.79 |
| Coefficient of variation (%) | 22.7 | 15.6 | 63.1 | 56.9 | 21.2 | 56.8 | 2.62 | 7.30 | 73.7 |
| Minimum | 10.5 | 2.05 | 5.40 | 2600 | 190 | 9 | 66.9 | 14.1 | 1.98 |
| Maximum | 24.5 | 3.60 | 45.646 | 17,100 | 392 | 219 | 74.0 | 17.9 | 37.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fortes, J.C.; Luís, A.T.; Santisteban, M.; Grande, J.A. A Time Series Proposal Model to Define the Speed of Carbon Steel Corrosion in an Extreme Acid Environment. Materials 2025, 18, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010027
Fortes JC, Luís AT, Santisteban M, Grande JA. A Time Series Proposal Model to Define the Speed of Carbon Steel Corrosion in an Extreme Acid Environment. Materials. 2025; 18(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010027
Chicago/Turabian StyleFortes, Juan Carlos, Ana Teresa Luís, María Santisteban, and José Antonio Grande. 2025. "A Time Series Proposal Model to Define the Speed of Carbon Steel Corrosion in an Extreme Acid Environment" Materials 18, no. 1: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010027
APA StyleFortes, J. C., Luís, A. T., Santisteban, M., & Grande, J. A. (2025). A Time Series Proposal Model to Define the Speed of Carbon Steel Corrosion in an Extreme Acid Environment. Materials, 18(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010027









